Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Promising Treatment Option for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer?
Abstract
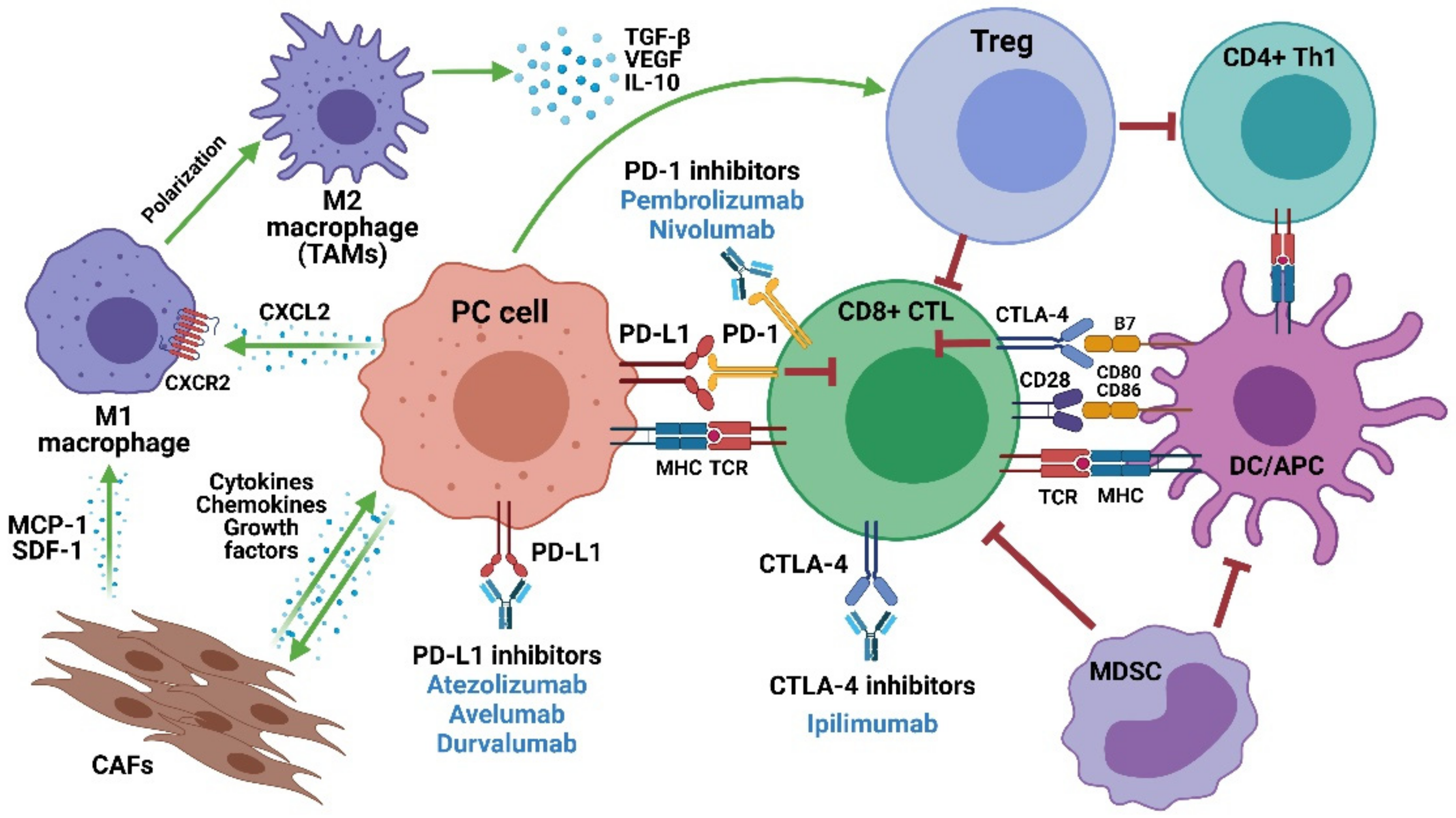
:1. Current Treatment Options for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer (mCRPC)
2. ICIs in mCRPC: An Overview
3. PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors in mCRPC
4. CTLA-4 Inhibitors in mCRPC
5. Mechanisms of Resistance and Potential Predictive Biomarkers of ICI Response
6. Conclusions and Future Challenges
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davies, A.; Conteduca, V.; Zoubeidi, A.; Beltran, H. Biological Evolution of Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. Focus 2019, 5, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartor, O.; de Bono, J.S. Metastatic Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, P.A.; Arora, V.K.; Sawyers, C.L. Emerging mechanisms of resistance to androgen receptor inhibitors in prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ryan, C.J.; Smith, M.R.; de Bono, J.S.; Molina, A.; Logothetis, C.J.; de Souza, P.; Fizazi, K.; Mainwaring, P.; Piulats, J.M.; Ng, S.; et al. Abiraterone in metastatic prostate cancer without previous chemotherapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Bono, J.S.; Logothetis, C.J.; Molina, A.; Fizazi, K.; North, S.; Chu, L.; Chi, K.N.; Jones, R.J.; Goodman, O.B., Jr.; Saad, F.; et al. Abiraterone and increased survival in metastatic prostate cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1995–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, T.M.; Armstrong, A.J.; Rathkopf, D.E.; Loriot, Y.; Sternberg, C.N.; Higano, C.S.; Iversen, P.; Bhattacharya, S.; Carles, J.; Chowdhury, S.; et al. Enzalutamide in metastatic prostate cancer before chemotherapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scher, H.I.; Fizazi, K.; Saad, F.; Taplin, M.E.; Sternberg, C.N.; Miller, K.; de Wit, R.; Mulders, P.; Chi, K.N.; Shore, N.D.; et al. Increased survival with enzalutamide in prostate cancer after chemotherapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1187–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, M.R.; Saad, F.; Chowdhury, S.; Oudard, S.; Hadaschik, B.A.; Graff, J.N.; Olmos, D.; Mainwaring, P.N.; Lee, J.Y.; Uemura, H.; et al. Apalutamide Treatment and Metastasis-free Survival in Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1408–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Fizazi, K.; Saad, F.; Rathenborg, P.; Shore, N.; Ferreira, U.; Ivashchenko, P.; Demirhan, E.; Modelska, K.; Phung, B.S.; et al. Enzalutamide in Men with Nonmetastatic, Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 2465–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fizazi, K.; Shore, N.; Tammela, T.L.; Ulys, A.; Vjaters, E.; Polyakov, S.; Jievaltas, M.; Luz, M.; Alekseev, B.; Kuss, I.; et al. Darolutamide in Nonmetastatic, Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1235–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthold, D.R.; Pond, G.R.; Soban, F.; de Wit, R.; Eisenberger, M.; Tannock, I.F. Docetaxel plus prednisone or mitoxantrone plus prednisone for advanced prostate cancer: Updated survival in the TAX 327 study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrylak, D.P.; Tangen, C.M.; Hussain, M.H.; Lara, P.N., Jr.; Jones, J.A.; Taplin, M.E.; Burch, P.A.; Berry, D.; Moinpour, C.; Kohli, M.; et al. Docetaxel and estramustine compared with mitoxantrone and prednisone for advanced refractory prostate cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tannock, I.F.; de Wit, R.; Berry, W.R.; Horti, J.; Pluzanska, A.; Chi, K.N.; Oudard, S.; Theodore, C.; James, N.D.; Turesson, I.; et al. Docetaxel plus prednisone or mitoxantrone plus prednisone for advanced prostate cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1502–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- James, N.D.; Sydes, M.R.; Clarke, N.W.; Mason, M.D.; Dearnaley, D.P.; Spears, M.R.; Ritchie, A.W.; Parker, C.C.; Russell, J.M.; Attard, G.; et al. Addition of docetaxel, zoledronic acid, or both to first-line long-term hormone therapy in prostate cancer (STAMPEDE): Survival results from an adaptive, multiarm, multistage, platform randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 1163–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sweeney, C.J.; Chen, Y.H.; Carducci, M.; Liu, G.; Jarrard, D.F.; Eisenberger, M.; Wong, Y.N.; Hahn, N.; Kohli, M.; Cooney, M.M.; et al. Chemohormonal Therapy in Metastatic Hormone-Sensitive Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrignaud, P.; Semiond, D.; Lejeune, P.; Bouchard, H.; Calvet, L.; Combeau, C.; Riou, J.F.; Commercon, A.; Lavelle, F.; Bissery, M.C. Preclinical antitumor activity of cabazitaxel, a semisynthetic taxane active in taxane-resistant tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2973–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Bono, J.S.; Oudard, S.; Ozguroglu, M.; Hansen, S.; Machiels, J.P.; Kocak, I.; Gravis, G.; Bodrogi, I.; Mackenzie, M.J.; Shen, L.; et al. Prednisone plus cabazitaxel or mitoxantrone for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer progressing after docetaxel treatment: A randomised open-label trial. Lancet 2010, 376, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Wit, R.; de Bono, J.; Sternberg, C.N.; Fizazi, K.; Tombal, B.; Wulfing, C.; Kramer, G.; Eymard, J.C.; Bamias, A.; Carles, J.; et al. Cabazitaxel versus Abiraterone or Enzalutamide in Metastatic Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2506–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hager, S.; Ackermann, C.J.; Joerger, M.; Gillessen, S.; Omlin, A. Anti-tumour activity of platinum compounds in advanced prostate cancer-a systematic literature review. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, F.; Garcia-Perdomo, H.A. Effectiveness of Platinum-Based Chemotherapy in Patients With Metastatic Prostate Cancer: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2019, 17, e627–e644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corn, P.G.; Heath, E.I.; Zurita, A.; Ramesh, N.; Xiao, L.; Sei, E.; Li-Ning-Tapia, E.; Tu, S.M.; Subudhi, S.K.; Wang, J.; et al. Cabazitaxel plus carboplatin for the treatment of men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancers: A randomised, open-label, phase 1–2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1432–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio, A.M.; Harzstark, A.L.; Corn, P.G.; Wen, S.; Araujo, J.C.; Tu, S.M.; Pagliaro, L.C.; Kim, J.; Millikan, R.E.; Ryan, C.; et al. Platinum-based chemotherapy for variant castrate-resistant prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 3621–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beltran, H.; Prandi, D.; Mosquera, J.M.; Benelli, M.; Puca, L.; Cyrta, J.; Marotz, C.; Giannopoulou, E.; Chakravarthi, B.V.; Varambally, S.; et al. Divergent clonal evolution of castration-resistant neuroendocrine prostate cancer. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aparicio, A.M.; Shen, L.; Tapia, E.L.; Lu, J.F.; Chen, H.C.; Zhang, J.; Wu, G.; Wang, X.; Troncoso, P.; Corn, P.; et al. Combined Tumor Suppressor Defects Characterize Clinically Defined Aggressive Variant Prostate Cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 1520–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruiz de Porras, V.; Wang, X.C.; Palomero, L.; Marin-Aguilera, M.; Sole-Blanch, C.; Indacochea, A.; Jimenez, N.; Bystrup, S.; Bakht, M.; Conteduca, V.; et al. Taxane-induced Attenuation of the CXCR2/BCL-2 Axis Sensitizes Prostate Cancer to Platinum-based Treatment. Eur. Urol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, R.; Castro, E.; Aragon, I.M.; Cendon, Y.; Cattrini, C.; Lopez-Casas, P.P.; Olmos, D. Genetic aberrations in DNA repair pathways: A cornerstone of precision oncology in prostate cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 552–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nombela, P.; Lozano, R.; Aytes, A.; Mateo, J.; Olmos, D.; Castro, E. BRCA2 and Other DDR Genes in Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nizialek, E.; Antonarakis, E.S. PARP Inhibitors in Metastatic Prostate Cancer: Evidence to Date. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 8105–8114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateo, J.; Carreira, S.; Sandhu, S.; Miranda, S.; Mossop, H.; Perez-Lopez, R.; Nava Rodrigues, D.; Robinson, D.; Omlin, A.; Tunariu, N.; et al. DNA-Repair Defects and Olaparib in Metastatic Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1697–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bono, J.; Mateo, J.; Fizazi, K.; Saad, F.; Shore, N.; Sandhu, S.; Chi, K.N.; Sartor, O.; Agarwal, N.; Olmos, D.; et al. Olaparib for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2091–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.C.; Duffy, C.R.; Allison, J.P. Fundamental Mechanisms of Immune Checkpoint Blockade Therapy. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 1069–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bilusic, M.; Madan, R.A.; Gulley, J.L. Immunotherapy of Prostate Cancer: Facts and Hopes. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 6764–6770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rizzo, A.; Mollica, V.; Cimadamore, A.; Santoni, M.; Scarpelli, M.; Giunchi, F.; Cheng, L.; Lopez-Beltran, A.; Fiorentino, M.; Montironi, R.; et al. Is There a Role for Immunotherapy in Prostate Cancer? Cells 2020, 9, 2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas, A. Releasing the Brakes on Cancer Immunotherapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1490–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolchok, J.D.; Kluger, H.; Callahan, M.K.; Postow, M.A.; Rizvi, N.A.; Lesokhin, A.M.; Segal, N.H.; Ariyan, C.E.; Gordon, R.A.; Reed, K.; et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robert, C.; Long, G.V.; Brady, B.; Dutriaux, C.; Maio, M.; Mortier, L.; Hassel, J.C.; Rutkowski, P.; McNeil, C.; Kalinka-Warzocha, E.; et al. Nivolumab in previously untreated melanoma without BRAF mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brahmer, J.; Reckamp, K.L.; Baas, P.; Crino, L.; Eberhardt, W.E.; Poddubskaya, E.; Antonia, S.; Pluzanski, A.; Vokes, E.E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in Advanced Squamous-Cell Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Motzer, R.J.; Escudier, B.; McDermott, D.F.; George, S.; Hammers, H.J.; Srinivas, S.; Tykodi, S.S.; Sosman, J.A.; Procopio, G.; Plimack, E.R.; et al. Nivolumab versus Everolimus in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1803–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Callahan, M.K.; Bono, P.; Kim, J.; Spiliopoulou, P.; Calvo, E.; Pillai, R.N.; Ott, P.A.; de Braud, F.; Morse, M.; et al. Nivolumab monotherapy in recurrent metastatic urothelial carcinoma (CheckMate 032): A multicentre, open-label, two-stage, multi-arm, phase 1/2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1590–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferris, R.L.; Blumenschein, G., Jr.; Fayette, J.; Guigay, J.; Colevas, A.D.; Licitra, L.; Harrington, K.; Kasper, S.; Vokes, E.E.; Even, C.; et al. Nivolumab for Recurrent Squamous-Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1856–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantoff, P.W.; Higano, C.S.; Shore, N.D.; Berger, E.R.; Small, E.J.; Penson, D.F.; Redfern, C.H.; Ferrari, A.C.; Dreicer, R.; Sims, R.B.; et al. Sipuleucel-T immunotherapy for castration-resistant prostate cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Small, E.J.; Schellhammer, P.F.; Higano, C.S.; Redfern, C.H.; Nemunaitis, J.J.; Valone, F.H.; Verjee, S.S.; Jones, L.A.; Hershberg, R.M. Placebo-controlled phase III trial of immunologic therapy with sipuleucel-T (APC8015) in patients with metastatic, asymptomatic hormone refractory prostate cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 3089–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Higano, C.S.; Schellhammer, P.F.; Small, E.J.; Burch, P.A.; Nemunaitis, J.; Yuh, L.; Provost, N.; Frohlich, M.W. Integrated data from 2 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trials of active cellular immunotherapy with sipuleucel-T in advanced prostate cancer. Cancer 2009, 115, 3670–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, D.T.; Durham, J.N.; Smith, K.N.; Wang, H.; Bartlett, B.R.; Aulakh, L.K.; Lu, S.; Kemberling, H.; Wilt, C.; Luber, B.S.; et al. Mismatch repair deficiency predicts response of solid tumors to PD-1 blockade. Science 2017, 357, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Antonarakis, E.S.; Shaukat, F.; Isaacsson Velho, P.; Kaur, H.; Shenderov, E.; Pardoll, D.M.; Lotan, T.L. Clinical Features and Therapeutic Outcomes in Men with Advanced Prostate Cancer and DNA Mismatch Repair Gene Mutations. Eur. Urol. 2019, 75, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abida, W.; Cheng, M.L.; Armenia, J.; Middha, S.; Autio, K.A.; Vargas, H.A.; Rathkopf, D.; Morris, M.J.; Danila, D.C.; Slovin, S.F.; et al. Analysis of the Prevalence of Microsatellite Instability in Prostate Cancer and Response to Immune Checkpoint Blockade. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, C.C.; Morrissey, C.; Kumar, A.; Zhang, X.; Smith, C.; Coleman, I.; Salipante, S.J.; Milbank, J.; Yu, M.; Grady, W.M.; et al. Complex MSH2 and MSH6 mutations in hypermutated microsatellite unstable advanced prostate cancer. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raymond, V.M.; Mukherjee, B.; Wang, F.; Huang, S.C.; Stoffel, E.M.; Kastrinos, F.; Syngal, S.; Cooney, K.A.; Gruber, S.B. Elevated risk of prostate cancer among men with Lynch syndrome. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 1713–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blankenstein, T.; Coulie, P.G.; Gilboa, E.; Jaffee, E.M. The determinants of tumour immunogenicity. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, D.; Van Allen, E.M. Genomic determinants of cancer immunotherapy. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2016, 41, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, N.A.; Hellmann, M.D.; Snyder, A.; Kvistborg, P.; Makarov, V.; Havel, J.J.; Lee, W.; Yuan, J.; Wong, P.; Ho, T.S.; et al. Cancer immunology. Mutational landscape determines sensitivity to PD-1 blockade in non-small cell lung cancer. Science 2015, 348, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yarchoan, M.; Hopkins, A.; Jaffee, E.M. Tumor Mutational Burden and Response Rate to PD-1 Inhibition. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2500–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maleki Vareki, S. High and low mutational burden tumors versus immunologically hot and cold tumors and response to immune checkpoint inhibitors. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, M.S.; Stojanov, P.; Polak, P.; Kryukov, G.V.; Cibulskis, K.; Sivachenko, A.; Carter, S.L.; Stewart, C.; Mermel, C.H.; Roberts, S.A.; et al. Mutational heterogeneity in cancer and the search for new cancer-associated genes. Nature 2013, 499, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardoll, D.M. The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Topalian, S.L.; Hodi, F.S.; Brahmer, J.R.; Gettinger, S.N.; Smith, D.C.; McDermott, D.F.; Powderly, J.D.; Carvajal, R.D.; Sosman, J.A.; Atkins, M.B.; et al. Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2443–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrylak, D.P.; Loriot, Y.; Shaffer, D.; Braiteh, F.; Powderly, J.; Harshman, L.C.; Conkling, P.; Delord, J.P.; Gordon, M.; Kim, J.W.; et al. Safety and Clinical Activity of Atezolizumab in Patients With Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: A Phase I Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonarakis, E.S.; Piulats, J.M.; Gross-Goupil, M.; Goh, J.; Ojamaa, K.; Hoimes, C.J.; Vaishampayan, U.; Berger, R.; Sezer, A.; Alanko, T.; et al. Pembrolizumab for Treatment-Refractory Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Multicohort, Open-Label Phase II KEYNOTE-199 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.M.; Nirschl, T.R.; Nirschl, C.J.; Francica, B.J.; Kochel, C.M.; van Bokhoven, A.; Meeker, A.K.; Lucia, M.S.; Anders, R.A.; DeMarzo, A.M.; et al. Paucity of PD-L1 expression in prostate cancer: Innate and adaptive immune resistance. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2015, 18, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baas, W.; Gershburg, S.; Dynda, D.; Delfino, K.; Robinson, K.; Nie, D.; Yearley, J.H.; Alanee, S. Immune Characterization of the Programmed Death Receptor Pathway in High Risk Prostate Cancer. Clin. Genitourin Cancer 2017, 15, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, A.R.; Massard, C.; Ott, P.A.; Haas, N.B.; Lopez, J.S.; Ejadi, S.; Wallmark, J.M.; Keam, B.; Delord, J.P.; Aggarwal, R.; et al. Pembrolizumab for advanced prostate adenocarcinoma: Findings of the KEYNOTE-028 study. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 1807–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, J.L.; Sio, A.; Angeles, A.; Roberts, M.E.; Azad, A.A.; Chi, K.N.; Zoubeidi, A. PD-L1 is highly expressed in Enzalutamide resistant prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Graff, J.N.; Beer, T.M.; Alumkal, J.J.; Slottke, R.E.; Redmond, W.L.; Thomas, G.V.; Thompson, R.F.; Wood, M.A.; Koguchi, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. A phase II single-arm study of pembrolizumab with enzalutamide in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer progressing on enzalutamide alone. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, W.R.; Fong, P.C.C.; Piulats, J.M.; Appleman, L.J.; Conter, H.J.; Feyerabend, S.; Shore, N.D.; Gravis, G.; Laguerre, B.; Gurney, H.; et al. KEYNOTE-365 cohort C updated results: Pembrolizumab (pembro) plus enzalutamide (enza) in abiraterone (abi)-pretreated patients (pts) with metastatic castrate-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, C.J.; Gillessen, S.; Rathkopf, D.; Matsubara, N.; Drake, C.; Fizazi, K.; Piulats, J.M.; Wysocki, P.J.; Buchschacher, G.L.; Doss, J.; et al. Abstract CT014: IMbassador250: A phase III trial comparing atezolizumab with enzalutamide vs enzalutamide alone in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). Cancer Res. 2020, 80, CT014. [Google Scholar]
- McNeel, D.G.; Eickhoff, J.C.; Wargowski, E.; Zahm, C.; Staab, M.J.; Straus, J.; Liu, G. Concurrent, but not sequential, PD-1 blockade with a DNA vaccine elicits anti-tumor responses in patients with metastatic, castration-resistant prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 25586–25596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez, J.S.; Biondo, A.; Tiu, C.; Scaranti, M.; Ameratunga, M.; Zachariou, A.; Turner, A.; Tunariu, N.; Prout, T.; Parmar, M.; et al. Abstract CT140: Proof-of-concept evidence of immune modulation by blockade of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-AKT signaling pathway in the phase I dose escalation study of Ipatasertib (Ipa) in combination with atezolizumab (A) in patients (pts) with advanced solid tumors (Ice-CAP). Cancer Res. 2020, 80, CT140. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, M.J.; Fong, L.; Petrylak, D.P.; Sartor, A.O.; Higano, C.S.; Pagliaro, L.C.; Alva, A.S.; Appleman, L.J.; Tan, W.; Vaishampayan, U.N.; et al. Safety and clinical activity of atezolizumab (atezo) + radium-223 dichloride (r-223) in 2L metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC): Results from a phase Ib clinical trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosser, C.J.; Hirasawa, Y.; Acoba, J.D.; Tamura, D.J.; Pal, S.K.; Huang, J.; Scholz, M.C.; Dorff, T.B. Phase Ib study assessing different sequencing regimens of atezolizumab (anti-PD-L1) and sipuleucel-T (SipT)in patients who have asymptomatic or minimally symptomatic metastatic castrate resistant prostate cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, e17564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, T.A.; Konstantinopoulos, P.; Telli, M.L.; Saraykar, S.; Beck, J.T.; Galsky, M.D.; Abraham, J.; Wise, D.R.; Khasraw, M.; Rubovszky, G.; et al. Abstract P1–19-03: JAVELIN PARP Medley, a phase 1b/2 study of avelumab plus talazoparib: Results from advanced breast cancer cohorts. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, P1-19-03. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.; Pachynski, R.K.; Narayan, V.; Flechon, A.; Gravis, G.; Galsky, M.D.; Mahammedi, H.; Patnaik, A.; Subudhi, S.K.; Ciprotti, M.; et al. Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Preliminary Analysis of Patients in the CheckMate 650 Trial. Cancer Cell. 2020, 38, 489–499.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenderov, E.; Boudadi, K.; Fu, W.; Wang, H.; Sullivan, R.; Jordan, A.; Dowling, D.; Harb, R.; Schonhoft, J.; Jendrisak, A.; et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab, with or without enzalutamide, in AR-V7-expressing metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: A phase-2 nonrandomized clinical trial. Prostate 2021, 81, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, E.D.; Drake, C.G.; Scher, H.I.; Fizazi, K.; Bossi, A.; van den Eertwegh, A.J.; Krainer, M.; Houede, N.; Santos, R.; Mahammedi, H.; et al. Ipilimumab versus placebo after radiotherapy in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer that had progressed after docetaxel chemotherapy (CA184–043): A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 700–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fizazi, K.; Drake, C.G.; Beer, T.M.; Kwon, E.D.; Scher, H.I.; Gerritsen, W.R.; Bossi, A.; den Eertwegh, A.; Krainer, M.; Houede, N.; et al. Final Analysis of the Ipilimumab Versus Placebo Following Radiotherapy Phase III Trial in Postdocetaxel Metastatic Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer Identifies an Excess of Long-term Survivors. Eur. Urol. 2020, 78, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, T.M.; Kwon, E.D.; Drake, C.G.; Fizazi, K.; Logothetis, C.; Gravis, G.; Ganju, V.; Polikoff, J.; Saad, F.; Humanski, P.; et al. Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase III Trial of Ipilimumab Versus Placebo in Asymptomatic or Minimally Symptomatic Patients With Metastatic Chemotherapy-Naive Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slovin, S.F.; Higano, C.S.; Hamid, O.; Tejwani, S.; Harzstark, A.; Alumkal, J.J.; Scher, H.I.; Chin, K.; Gagnier, P.; McHenry, M.B.; et al. Ipilimumab alone or in combination with radiotherapy in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: Results from an open-label, multicenter phase I/II study. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 1813–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholz, M.; Yep, S.; Chancey, M.; Kelly, C.; Chau, K.; Turner, J.; Lam, R.; Drake, C.G. Phase I clinical trial of sipuleucel-T combined with escalating doses of ipilimumab in progressive metastatic castrate-resistant prostate cancer. Immunotargets Ther. 2017, 6, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van den Eertwegh, A.J.; Versluis, J.; van den Berg, H.P.; Santegoets, S.J.; van Moorselaar, R.J.; van der Sluis, T.M.; Gall, H.E.; Harding, T.C.; Jooss, K.; Lowy, I.; et al. Combined immunotherapy with granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor-transduced allogeneic prostate cancer cells and ipilimumab in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: A phase 1 dose-escalation trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, E.Y.; Piulats, J.M.; Gravis, G.; Laguerre, B.; Arija, J.A.A.; Oudard, S.; Fong, P.C.C.; Kolinsky, M.P.; Augustin, M.; Feyerabend, S.; et al. KEYNOTE-365 cohort A updated results: Pembrolizumab (pembro) plus olaparib in docetaxel-pretreated patients (pts) with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Du, X.; Liu, M.; Zheng, P.; Liu, Y. Anti-CTLA-4 antibodies in cancer immunotherapy: Selective depletion of intratumoral regulatory T cells or checkpoint blockade? Cell Biosci. 2018, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Small, E.J.; Tchekmedyian, N.S.; Rini, B.I.; Fong, L.; Lowy, I.; Allison, J.P. A pilot trial of CTLA-4 blockade with human anti-CTLA-4 in patients with hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 1810–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tollefson, M.; Karnes, R.J.; Thompson, R.H.; Granberg, C.; Hillman, D.; Breau, R.; Allison, J.; Kwon, E.; Blute, M. 668 a randomized phase ii study of ipilimumab with androgen ablation compared with androgen ablation alone in patients with advanced prostate cancer. J. Urol. 2010, 183, e261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachynski, R.K. A “Tail” of Immunotherapy in Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2020, 78, 831–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graff, J.N.; Stein, M.N.; Surana, R.; Al Rabadi, L.; Liu, E.; Fong, L.; Bailey, S.; Latour, E.; Newby, T.A.; Moran, A.E.; et al. Phase II Study of Ipilimumab in Men With Metastatic Prostate Cancer With an Incomplete Response to Androgen Deprivation Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Ward, J.F.; Pettaway, C.A.; Shi, L.Z.; Subudhi, S.K.; Vence, L.M.; Zhao, H.; Chen, J.; Chen, H.; Efstathiou, E.; et al. VISTA is an inhibitory immune checkpoint that is increased after ipilimumab therapy in patients with prostate cancer. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, B.E.; Hansen, A.R. Dual Checkpoint Blockade in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Just a Gambit or Real CheckMate? Cancer Cell. 2020, 38, 438–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.N.S.; Sankey, P.; Josephs, D.H.; Jones, R.J.; Crabb, S.J.; Beare, S.; Duggan, M.; White, L.; Charlaftis, N.; Wheeler, G.; et al. Nivolumab and ipilimumab treatment in prostate cancer with an immunogenic signature (NEPTUNES). J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, TPS5090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlotta, A.R.; Egawa, S.; Pushkar, D.; Govorov, A.; Kimura, T.; Kido, M.; Takahashi, H.; Kuk, C.; Kovylina, M.; Aldaoud, N.; et al. Prevalence of prostate cancer on autopsy: Cross-sectional study on unscreened Caucasian and Asian men. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2013, 105, 1050–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pal, S.K.; Moreira, D.; Won, H.; White, S.W.; Duttagupta, P.; Lucia, M.; Jones, J.; Hsu, J.; Kortylewski, M. Reduced T-cell Numbers and Elevated Levels of Immunomodulatory Cytokines in Metastatic Prostate Cancer Patients De Novo Resistant to Abiraterone and/or Enzalutamide Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia-Lora, A.; Algarra, I.; Garrido, F. MHC class I antigens, immune surveillance, and tumor immune escape. J. Cell Physiol. 2003, 195, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bander, N.H.; Yao, D.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.T.; Steiner, M.; Zuccaro, W.; Moy, P. MHC class I and II expression in prostate carcinoma and modulation by interferon-alpha and -gamma. Prostate 1997, 33, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blery, M.; Vivier, E. NKG2D-MICA Interaction: A Paradigm Shift in Innate Recognition. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 2229–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivier, E.; Tomasello, E.; Paul, P. Lymphocyte activation via NKG2D: Towards a new paradigm in immune recognition? Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2002, 14, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.D.; Higgins, L.M.; Steinle, A.; Cosman, D.; Haugk, K.; Plymate, S.R. Prevalent expression of the immunostimulatory MHC class I chain-related molecule is counteracted by shedding in prostate cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundholm, M.; Schroder, M.; Nagaeva, O.; Baranov, V.; Widmark, A.; Mincheva-Nilsson, L.; Wikstrom, P. Prostate tumor-derived exosomes down-regulate NKG2D expression on natural killer cells and CD8+ T cells: Mechanism of immune evasion. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, H.R.; Rammensee, H.G.; Steinle, A. Cutting edge: Down-regulation of MICA on human tumors by proteolytic shedding. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 4098–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sakiyama, M.J.; Espinoza, I.; Reddy, A.; de Carlo, F.; Kumar, A.; Levenson, A.S.; Bae, S.; Zhou, X.; Claudio, P.P.; Lewin, J.; et al. Race-associated expression of MHC class I polypeptide-related sequence A (MICA) in prostate cancer. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2019, 108, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Soto, A.; Gonzalez, S.; Galluzzi, L. Soluble NKG2D ligands limit the efficacy of immune checkpoint blockade. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1346766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Larrocha, P.S.; Zhang, B.; Wainwright, D.; Dhar, P.; Wu, J.D. Antibody targeting tumor-derived soluble NKG2D ligand sMIC provides dual co-stimulation of CD8 T cells and enables sMIC(+) tumors respond to PD1/PD-L1 blockade therapy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonollo, F.; Thalmann, G.N.; Kruithof-de Julio, M.; Karkampouna, S. The Role of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Prostate Cancer Tumorigenesis. Cancers 2020, 12, 1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickman, R.E.; Broman, M.M.; Lanman, N.A.; Franco, O.E.; Sudyanti, P.A.G.; Ni, Y.; Ji, Y.; Helfand, B.T.; Petkewicz, J.; Paterakos, M.C.; et al. Heterogeneity of human prostate carcinoma-associated fibroblasts implicates a role for subpopulations in myeloid cell recruitment. Prostate 2020, 80, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gok Yavuz, B.; Gunaydin, G.; Gedik, M.E.; Kosemehmetoglu, K.; Karakoc, D.; Ozgur, F.; Guc, D. Cancer associated fibroblasts sculpt tumour microenvironment by recruiting monocytes and inducing immunosuppressive PD-1(+) TAMs. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, H.; Deep, G.; Kumar, S.; Jain, A.K.; Agarwal, C.; Agarwal, R. Beneficial effects of the naturally occurring flavonoid silibinin on the prostate cancer microenvironment: Role of monocyte chemotactic protein-1 and immune cell recruitment. Carcinogenesis 2016, 37, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kraman, M.; Bambrough, P.J.; Arnold, J.N.; Roberts, E.W.; Magiera, L.; Jones, J.O.; Gopinathan, A.; Tuveson, D.A.; Fearon, D.T. Suppression of antitumor immunity by stromal cells expressing fibroblast activation protein-alpha. Science 2010, 330, 827–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feig, C.; Jones, J.O.; Kraman, M.; Wells, R.J.; Deonarine, A.; Chan, D.S.; Connell, C.M.; Roberts, E.W.; Zhao, Q.; Caballero, O.L.; et al. Targeting CXCL12 from FAP-expressing carcinoma-associated fibroblasts synergizes with anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy in pancreatic cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 20212–20217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scott, A.M.; Wiseman, G.; Welt, S.; Adjei, A.; Lee, F.T.; Hopkins, W.; Divgi, C.R.; Hanson, L.H.; Mitchell, P.; Gansen, D.N.; et al. A Phase I dose-escalation study of sibrotuzumab in patients with advanced or metastatic fibroblast activation protein-positive cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 1639–1647. [Google Scholar]
- Fabre, M.; Ferrer, C.; Dominguez-Hormaetxe, S.; Bockorny, B.; Murias, L.; Seifert, O.; Eisler, S.A.; Kontermann, R.E.; Pfizenmaier, K.; Lee, S.Y.; et al. OMTX705, a Novel FAP-Targeting ADC Demonstrates Activity in Chemotherapy and Pembrolizumab-Resistant Solid Tumor Models. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 3420–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Idorn, M.; Kollgaard, T.; Kongsted, P.; Sengelov, L.; Thor Straten, P. Correlation between frequencies of blood monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells, regulatory T cells and negative prognostic markers in patients with castration-resistant metastatic prostate cancer. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2014, 63, 1177–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Bujanda, Z.; Drake, C.G. Myeloid-derived cells in prostate cancer progression: Phenotype and prospective therapies. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 102, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakaguchi, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Nomura, T.; Ono, M. Regulatory T cells and immune tolerance. Cell 2008, 133, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukumura, D.; Kloepper, J.; Amoozgar, Z.; Duda, D.G.; Jain, R.K. Enhancing cancer immunotherapy using antiangiogenics: Opportunities and challenges. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoos, A. Development of immuno-oncology drugs—from CTLA4 to PD1 to the next generations. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.; Subudhi, S.K.; Aparicio, A.; Ge, Z.; Guan, B.; Miura, Y.; Sharma, P. Differences in Tumor Microenvironment Dictate T Helper Lineage Polarization and Response to Immune Checkpoint Therapy. Cell 2019, 179, 1177–1190.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundholm, M.; Hagglof, C.; Wikberg, M.L.; Stattin, P.; Egevad, L.; Bergh, A.; Wikstrom, P.; Palmqvist, R.; Edin, S. Secreted Factors from Colorectal and Prostate Cancer Cells Skew the Immune Response in Opposite Directions. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariathasan, S.; Turley, S.J.; Nickles, D.; Castiglioni, A.; Yuen, K.; Wang, Y.; Kadel, E.E., III; Koeppen, H.; Astarita, J.L.; Cubas, R.; et al. TGFbeta attenuates tumour response to PD-L1 blockade by contributing to exclusion of T cells. Nature 2018, 554, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Mitri, D.; Mirenda, M.; Vasilevska, J.; Calcinotto, A.; Delaleu, N.; Revandkar, A.; Gil, V.; Boysen, G.; Losa, M.; Mosole, S.; et al. Re-education of Tumor-Associated Macrophages by CXCR2 Blockade Drives Senescence and Tumor Inhibition in Advanced Prostate Cancer. Cell Rep. 2019, 28, 2156–2168.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wise, D.R.; Schneider, J.A.; Armenia, J.; Febles, V.A.; McLaughlin, B.; Brennan, R.; Thoren, K.L.; Abida, W.; Sfanos, K.S.; De Marzo, A.M.; et al. Dickkopf-1 Can Lead to Immune Evasion in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2020, 4, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitkin, N.; Nersesian, S.; Siemens, D.R.; Koti, M. The Tumor Immune Contexture of Prostate Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strickland, K.C.; Howitt, B.E.; Shukla, S.A.; Rodig, S.; Ritterhouse, L.L.; Liu, J.F.; Garber, J.E.; Chowdhury, D.; Wu, C.J.; D’Andrea, A.D.; et al. Association and prognostic significance of BRCA1/2-mutation status with neoantigen load, number of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and expression of PD-1/PD-L1 in high grade serous ovarian cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 13587–13598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.M.; Cieslik, M.; Lonigro, R.J.; Vats, P.; Reimers, M.A.; Cao, X.; Ning, Y.; Wang, L.; Kunju, L.P.; de Sarkar, N.; et al. Inactivation of CDK12 Delineates a Distinct Immunogenic Class of Advanced Prostate Cancer. Cell 2018, 173, 1770–1782.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antonarakis, E.S. Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 12, Immunity, and Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1087–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudadi, K.; Suzman, D.L.; Anagnostou, V.; Fu, W.; Luber, B.; Wang, H.; Niknafs, N.; White, J.R.; Silberstein, J.L.; Sullivan, R.; et al. Ipilimumab plus nivolumab and DNA-repair defects in AR-V7-expressing metastatic prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 28561–28571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Isaacsson Velho, P.; Antonarakis, E.S. PD-1/PD-L1 pathway inhibitors in advanced prostate cancer. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 11, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haffner, M.C.; Guner, G.; Taheri, D.; Netto, G.J.; Palsgrove, D.N.; Zheng, Q.; Guedes, L.B.; Kim, K.; Tsai, H.; Esopi, D.M.; et al. Comprehensive Evaluation of Programmed Death-Ligand 1 Expression in Primary and Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2018, 188, 1478–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chapoval, A.I.; Ni, J.; Lau, J.S.; Wilcox, R.A.; Flies, D.B.; Liu, D.; Dong, H.; Sica, G.L.; Zhu, G.; Tamada, K.; et al. B7-H3: A costimulatory molecule for T cell activation and IFN-gamma production. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benzon, B.; Zhao, S.G.; Haffner, M.C.; Takhar, M.; Erho, N.; Yousefi, K.; Hurley, P.; Bishop, J.L.; Tosoian, J.; Ghabili, K.; et al. Correlation of B7-H3 with androgen receptor, immune pathways and poor outcome in prostate cancer: An expression-based analysis. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2017, 20, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos, J.R.; Purvis, I.J.; Labak, C.M.; Guda, M.R.; Tsung, A.J.; Velpula, K.K.; Asuthkar, S. B7-H3 role in the immune landscape of cancer. Am. J. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2017, 6, 66–75. [Google Scholar]
- Picarda, E.; Ohaegbulam, K.C.; Zang, X. Molecular Pathways: Targeting B7-H3 (CD276) for Human Cancer Immunotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 3425–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shenderov, E.; Demarzo, A.; Boudadi, K.; Allaf, M.; Wang, H.; Chapman, C.; Pavlovich, C.; Bivalacqua, T.; O’Neal, T.S.; Harb, R.; et al. Phase II neoadjuvant and immunologic study of B7-H3 targeting with enoblituzumab in localized intermediate- and high-risk prostate cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosso, J.F.; Kelleher, C.C.; Harris, T.J.; Maris, C.H.; Hipkiss, E.L.; De Marzo, A.; Anders, R.; Netto, G.; Getnet, D.; Bruno, T.C.; et al. LAG-3 regulates CD8+ T cell accumulation and effector function in murine self- and tumor-tolerance systems. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 3383–3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Redmond, W.L.; Gough, M.J.; Charbonneau, B.; Ratliff, T.L.; Weinberg, A.D. Defects in the acquisition of CD8 T cell effector function after priming with tumor or soluble antigen can be overcome by the addition of an OX40 agonist. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 7244–7253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Youlin, K.; Li, Z.; Xiaodong, W.; Xiuheng, L.; Hengchen, Z. Combination immunotherapy with 4–1BBL and CTLA-4 blockade for the treatment of prostate cancer. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012, 439235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Trial ID | Treatment | Patients | Primary End Point | Patients | Trial Phase | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT02787005 (KEYNOTE-199) [59] | Pembrolizumab | Chemotherapy-resistant mCRPC | ORR | 370 | II | Substantial antitumor activity with an acceptable safety profile |
| NCT02054806 (KEYNOTE-028) [62] | Pembrolizumab | mCRPC with PD-L1 expression in >1% of tumor or stromal cells | ORR | 23 | Ib | ORR: 13% |
| NCT02312557 [64] | Pembrolizumab + Enzalutamide | Enzalutamide resistant mCRPC | PSA response | 20 | II | PSA response: 30% |
| NCT02499835 [67] | Pembrolizumab + pTVG-HP(DNA vaccine) | Hormone-resistant mCRPC | AE | 32 | I/II | Acceptable safety profile |
| PFS | ||||||
| RP | ||||||
| ORR | ||||||
| PSA response | ||||||
| NCT00730639 (MDX-1106)[57] | Nivolumab | mCRPC | AE | 395 | Ib | No favorable ORR |
| NCT02985957 (CheckMate-650) [72] | Nivolumab + Ipilimumab | mCRPC | ORRr PFS | 497 | II | Superior ORR (26%) in chemotherapy-naïve patients |
| NCT02601014 (STARVE-PC)[73] | Nivolumab + Ipilimumab | mCRPC with detectable AR-V7 | PSA Response Safety | 15 | II | Favorable outcomes in patients with AR-V7 + PC with DDR |
| NCT00861614 (CA184-043) [74,75] | Ipilimumab | mCRPC following docetaxel therapy | OS | 988 | III | No significant improvement in OS Increased PFS and PSA response Long-term analysis: OS improvement in Ipilimumab arm |
| NCT01057810 (CA184-095) [76] | Ipilimumab | Chemotherapy-naïve mCRPC | OS | 837 | III | No significant improvement in OS Increased PFS and PSA response |
| NCT00323882 [77] | Ipilimumab + Radiotherapy | mCRPC | AE PSA response Tumor response | 75 | I/II | Manageable AEs and PSA responses suggestive of clinical activity |
| NCT01832870 (SIPIPI) [78] | Ipilimumab + Sipuleucel T | Progressive mCRPC | Antigen-specific memory T-cell response | 9 | I | Acceptable safety profile |
| NCT01510288 [79] | Ipilimumab + GVAX | mCRPC | AE | 28 | I | Acceptable safety profile |
| NCT03016312 (IMbassador250) [66] | Atezolizumab + Enzalutamide vs. Enzalutamide | mCRPC | OS | 730 | III | Atezolizumab + enzalutamide do not show improvement in OS over enzalutamide alone |
| Trial ID | Treatment | Indication | Primary End Point | Patients | Trial Phase | Preliminary Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT02861573 (KEYNOTE-365) [65,80] | Pembrolizumab + Coh. A: Olaparib Coh. B: Docteaxel Coh. C: Enzalutamide | Abiraterone resistant mCRPC | ORR PSA Response Safety | 210 | Ib/II | Cohort A: |
| ORR: 8% | ||||||
| PSA Resp: 9% | ||||||
| Cohort B: | ||||||
| ORR: 23% | ||||||
| PSA Resp: 34% | ||||||
| Cohort C: | ||||||
| ORR: 12% | ||||||
| PSA Resp: 22% | ||||||
| NCT03834493 (KEYNOTE-641) | Pembrolizumab + Enzalutamide | mCRPC | OS rPFS | 1200 | III | N/A |
| NCT03093428 | Pembrolizumab + Radium-223 | mCRPC | Extent Of Immune Cell Infiltration | 45 | II | N/A |
| NCT03473925 | Pembrolizumab + Navarixin | mCRPC | ORR | 120 | II | N/A |
| NCT03040791 (ImmunoProst) | Nivolumab | mCRPC with DNA repair defects | PSA Response | 45 | II | N/A |
| NCT03572478 | Nivolumab + Rucaparib (PARPi) | mCRPC | DLT T Cell Inflammation | 12 | I/II | N/A |
| NCT03061539 (NEPTUNES) | Nivolumab + Ipilimumab | mCRPC with specific immunogenic signatures | RR PSA response CTCs | 175 | II | N/A |
| NCT03098160 | Ipilimumab + Evofosfamide | Metastatic PC | MTD | 69 | I | N/A |
| NCT03024216 [70] | Atezolizumab + Sipuleucel-T | Asymptomatic or minimally symptomatic mCRPC | AE | 37 | Ib | Manageable safety profile |
| NCT03673787 [68] | Atezolizumab + Ipatasertib | mCRPC with PTEN loss |
MTD AE | 51 | I/II | Well-tolerated |
| NCT02814669 [69] | Atezolizumab + Radium-223 | ARPI-resistant mCRPC | Safety ORR | 45 | I | No dose-limiting toxicities, safety signals, or changes in serum biomarkers |
| NCT03330405 (JAVELIN PARP Medley) [71] | Avelumab + Talazoparib | mCRPC | DLT ORR | 216 | Ib/II | Preliminary antitumor activity and manageable safety profile |
| NCT03204812 | Durvalumab + Tremelimumab | Chemotherapy naïve CRPC | AE | 27 | II | N/A |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruiz de Porras, V.; Pardo, J.C.; Notario, L.; Etxaniz, O.; Font, A. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Promising Treatment Option for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4712. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094712
Ruiz de Porras V, Pardo JC, Notario L, Etxaniz O, Font A. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Promising Treatment Option for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer? International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(9):4712. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094712
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuiz de Porras, Vicenç, Juan Carlos Pardo, Lucia Notario, Olatz Etxaniz, and Albert Font. 2021. "Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Promising Treatment Option for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer?" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 9: 4712. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094712
APA StyleRuiz de Porras, V., Pardo, J. C., Notario, L., Etxaniz, O., & Font, A. (2021). Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Promising Treatment Option for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer? International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(9), 4712. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094712








