Overcoming Depression with 5-HT2A Receptor Ligands
Abstract
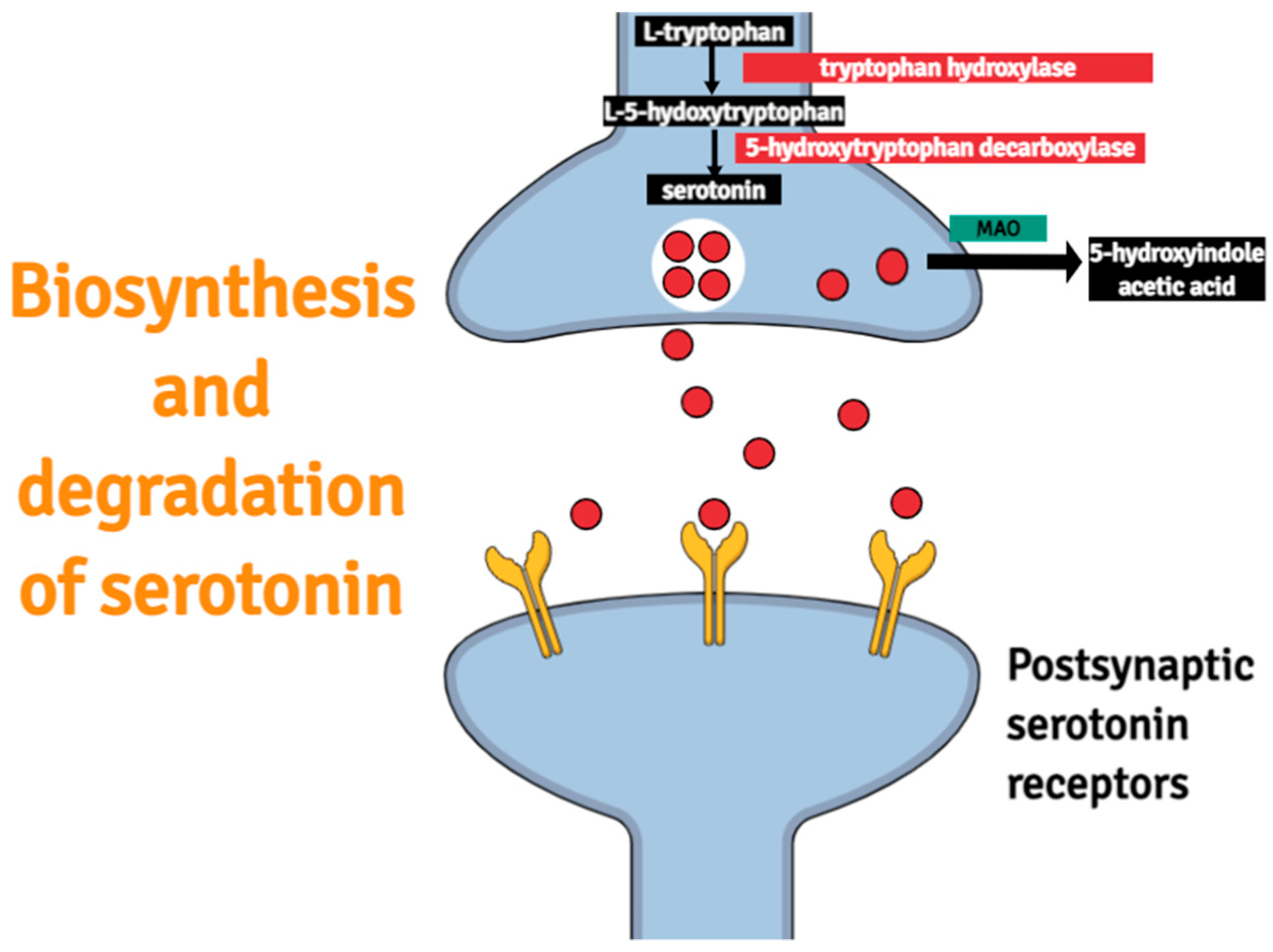
:1. Introduction
2. Studies on Structure of 5-HT2A Receptor
3. 5-HT2A Receptor Is It the Right Target?
4. Novel 5-HT2A Ligands as Antidepressant Agents–Agonists Emerge from the Shadows of Antagonists?
5. In Silico Methods Aiming to Identify Novel 5-HT2A Receptor Ligands
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 5-HT | Serotonin, 5-hydroxytryptamine |
| 5HT1BR | Serotonin 5-HT1B receptor |
| 5HT2BR | Serotonin 5-HT2B receptor |
| 5HT2CR | Serotonin 5-HT2C receptor |
| 25-CN-NBOH | 4-(2-((2-hydroxybenzyl)amino)ethyl)-2,5-dimethoxybenzonitrile |
| A2A | Alpha-2A adrenergic receptor |
| β1AR | Beta-1A adrenergic receptor |
| β2AR | Beta-2A adrenergic receptor |
| D3R | Dopamine D3 receptor |
| D4R | Dopamine D4 receptor |
| DOI | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodoamphetamine |
| H1R | Histamine H1 receptor |
| M1R | Muscarinic acetylcholine M1 receptor |
| M2R | Muscarinic acetylcholine M2 receptor |
| M3R | Muscarinic acetylcholine M3 receptor |
| M4R | Muscarinic acetylcholine M4 receptor |
| MD | Molecular dynamics |
| mGluR2 | Metabotropic glutamate receptor 2 |
| TCMNP | Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology database |
| QSAR | Quantitative-structure-activity relationship |
References
- Ervin, R.B. Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome Among Adults 20 Years of Age and Over, by Sex, Age, Race and Ethnicity, and Body Mass Index: United States, 2003–2006. Natl. Health Stat. Rep. 2009, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno-Agostino, D.; Wu, Y.-T.; Daskalopoulou, C.; Hasan, M.T.; Huisman, M.; Prina, M. Global Trends in the Prevalence and Incidence of Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 281, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, S.; Jain, A.; Gautam, M.; Vahia, V.N.; Grover, S. Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Depression. Indian J. Psychiatry 2017, 59, S34–S50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duval, F.; Lebowitz, B.D.; Macher, J.-P. Treatments in Depression. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2006, 8, 191–206. [Google Scholar]
- Celada, P.; Puig, M.V.; Amargós-Bosch, M.; Adell, A.; Artigas, F. The Therapeutic Role of 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A Receptors in Depression. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2004, 29, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sirek, A.; Sirek, O.V. Serotonin: A Review. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 1970, 102, 846–849. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rapport, M.M.; Green, A.A.; Page, I.H. Crystalline Serotonin. Science 1948, 108, 329–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, D.; Rudge, S. The Role of Serotonin in Depression and Anxiety. Int. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 1995, 9 (Suppl. S4), 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, C.L.; Anacker, A.M.J.; Veenstra-VanderWeele, J. The Serotonin System in Autism Spectrum Disorder: From Biomarker to Animal Models. Neuroscience 2016, 321, 24–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crowell, M.D. Role of Serotonin in the Pathophysiology of the Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 141, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleich, A.; Brown, S.L.; Kahn, R.; van Praag, H.M. The Role of Serotonin in Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 1988, 14, 297–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clark, C.T.; Weissbach, H.; Udenfriend, S. 5-Hydroxytryptophan Decarboxylase: Preparation and Properties. J. Biol. Chem. 1954, 210, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, P.; Cases, O.; Maroteaux, L. The Developmental Role of Serotonin: News from Mouse Molecular Genetics. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 1002–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad-Zadeh, L.F.; Moses, L.; Gwaltney-Brant, S.M. Serotonin: A Review. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 31, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, J.Z.; Crockett, M.J. How Serotonin Shapes Moral Judgment and Behavior. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2013, 1299, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jenkins, T.A.; Nguyen, J.C.D.; Polglaze, K.E.; Bertrand, P.P. Influence of Tryptophan and Serotonin on Mood and Cognition with a Possible Role of the Gut-Brain Axis. Nutrients 2016, 8, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Švob Štrac, D.; Pivac, N.; Mück-Šeler, D. The Serotonergic System and Cognitive Function. Transl. Neurosci. 2016, 7, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Curzon, G. Serotonin and Appetite. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1990, 600, 521–530, discussion 530–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.; Patrick, C.J.; Kennealy, P.J. Role of Serotonin and Dopamine System Interactions in the Neurobiology of Impulsive Aggression and Its Comorbidity with Other Clinical Disorders. Aggress. Violent Behav. 2008, 13, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kirby, L.; Zeeb, F.; Winstanley, C. Contributions of Serotonin in Addiction Vulnerability. Neuropharmacology 2011, 61, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morin, L.P. Serotonin and the Regulation of Mammalian Circadian Rhythmicity. Ann. Med. 1999, 31, 12–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.; Fairburn, C.; Cowen, P. Relapse of Depression after Rapid Depletion of Tryptophan. Lancet 1997, 349, 915–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhé, H.G.; Mason, N.S.; Schene, A.H. Mood Is Indirectly Related to Serotonin, Norepinephrine and Dopamine Levels in Humans: A Meta-Analysis of Monoamine Depletion Studies. Mol. Psychiatry 2007, 12, 331–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Tao, S.; Tian, S.; Shao, J.; Mo, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhao, P.; Chen, Z.; Yao, Z.; et al. Serotonin 2A Receptor Polymorphism Rs3803189 Mediated by Dynamics of Default Mode Network: A Potential Biomarker for Antidepressant Early Response. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 283, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirina, P.; Zinellu, E.; Paliogiannis, P.; Fois, A.G.; Marras, V.; Sotgia, S.; Carru, C.; Zinellu, A. Circulating Serotonin Levels in COPD Patients: A Pilot Study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2018, 18, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, E.C.C.; Sen, P.; Parks, W.T.; Langston, C.; Galambos, C. The Role of Serotonin Transporter in Human Lung Development and in Neonatal Lung Disorders. Can. Respir. J. 2017, 2017, 9064046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaur, G.; Krishan, P. Understanding Serotonin 5-HT2A Receptors-Regulated Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Chronic Kidney Diseases. Ren. Replace. Ther. 2020, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sole, M.J.; Madapallimattam, A.; Baines, A.D. An Active Pathway for Serotonin Synthesis by Renal Proximal Tubules. Kidney Int. 1986, 29, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berger, M.; Gray, J.A.; Roth, B.L. The Expanded Biology of Serotonin. Annu. Rev. Med. 2009, 60, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lv, J.; Liu, F. The Role of Serotonin beyond the Central Nervous System during Embryogenesis. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost, M.; Andersen, T.E.; Yadav, V.; Brixen, K.; Karsenty, G.; Kassem, M. Patients with High-Bone-Mass Phenotype Owing to Lrp5-T253I Mutation Have Low Plasma Levels of Serotonin. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2010, 25, 673–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCorvy, J.D.; Roth, B.L. Structure and Function of Serotonin G Protein-Coupled Receptors. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 150, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borroto-Escuela, D.O.; Ambrogini, P.; Chruścicka, B.; Lindskog, M.; Crespo-Ramirez, M.; Hernández-Mondragón, J.C.; Perez de la Mora, M.; Schellekens, H.; Fuxe, K. The Role of Central Serotonin Neurons and 5-HT Heteroreceptor Complexes in the Pathophysiology of Depression: A Historical Perspective and Future Prospects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Che, T.; Panova, O.; DiBerto, J.F.; Lyu, J.; Krumm, B.E.; Wacker, D.; Robertson, M.J.; Seven, A.B.; Nichols, D.E.; et al. Structure of a Hallucinogen-Activated Gq-Coupled 5-HT2A Serotonin Receptor. Cell 2020, 182, 1574–1588.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John Jayakumar, J.A.K.; Panicker, M.M.; Basu, B. Serotonin 2A (5-HT2A) Receptor Affects Cell–Matrix Adhesion and the Formation and Maintenance of Stress Fibers in HEK293 Cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raote, I.; Bhattacharya, A.; Panicker, M.M. Serotonin 2A (5-HT2A) Receptor Function: Ligand-Dependent Mechanisms and Pathways. In Serotonin Receptors in Neurobiology; Chattopadhyay, A., Ed.; Frontiers in Neuroscience; CRC Press/Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-0-8493-3977-6. [Google Scholar]
- Höltje, H.D.; Jendretzki, U.K. Construction of a Detailed Serotoninergic 5-HT2a Receptor Model. Arch. Pharm. 1995, 328, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palczewski, K.; Kumasaka, T.; Hori, T.; Behnke, C.A.; Motoshima, H.; Fox, B.A.; Trong, I.L.; Teller, D.C.; Okada, T.; Stenkamp, R.E.; et al. Crystal Structure of Rhodopsin: A G Protein-Coupled Receptor. Science 2000, 289, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chambers, J.J.; Nichols, D.E. A Homology-Based Model of the Human 5-HT2A Receptor Derived from an in Silico Activated G-Protein Coupled Receptor. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2002, 16, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, F.; Lei, M. Molecular Modeling and Docking Study on Dopamine D2-like and Serotonin 5-HT2A Receptors. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2015, 57, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhimathi, A.; Sowdhamini, R. Molecular Modelling of Human 5-Hydroxytryptamine Receptor (5-HT2A) and Virtual Screening Studies towards the Identification of Agonist and Antagonist Molecules. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2016, 34, 952–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, B.K.; Buckle, M.J.C.; Doughty, S.W. Homology Modeling of the Human 5-HT1A, 5-HT2A, D1, and D2 Receptors: Model Refinement with Molecular Dynamics Simulations and Docking Evaluation. J. Mol. Model. 2012, 18, 3639–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiteh, M.; Rodríguez-Espigares, I.; Selent, J.; Carlsson, J. Performance of Virtual Screening against GPCR Homology Models: Impact of Template Selection and Treatment of Binding Site Plasticity. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2020, 16, e1007680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly Accurate Protein Structure Prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, K.T.; Asada, H.; Inoue, A.; Kadji, F.M.N.; Im, D.; Mori, C.; Arakawa, T.; Hirata, K.; Nomura, Y.; Nomura, N.; et al. Structures of the 5-HT2A Receptor in Complex with the Antipsychotics Risperidone and Zotepine. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2019, 26, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.S.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; Rajagopal, S. Biased Signalling: From Simple Switches to Allosteric Microprocessors. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Aguilar, J.M.; Shan, J.; LeVine, M.V.; Khelashvili, G.; Weinstein, H. A Functional Selectivity Mechanism at the Serotonin-2A GPCR Involves Ligand-Dependent Conformations of Intracellular Loop 2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 16044–16054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, J.; Cai, X.; Zhao, J.; Yan, Z. Serotonin Receptors Modulate GABA(A) Receptor Channels through Activation of Anchored Protein Kinase C in Prefrontal Cortical Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 6502–6511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kohen, D.P.; Mahowald, M.W.; Rosen, G.M. Sleep-Terror Disorder in Children: The Role of Self-Hypnosis in Management. Am. J. Clin. Hypn. 1992, 34, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amargós-Bosch, M.; Bortolozzi, A.; Puig, M.V.; Serrats, J.; Adell, A.; Celada, P.; Toth, M.; Mengod, G.; Artigas, F. Co-Expression and In Vivo Interaction of Serotonin1A and Serotonin2A Receptors in Pyramidal Neurons of Prefrontal Cortex. Cereb. Cortex 2004, 14, 281–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marek, G.J. Activation of Adenosine1 (A1) Receptors Suppresses Head Shakes Induced by a Serotonergic Hallucinogen in Rats. Neuropharmacology 2009, 56, 1082–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bohn, L.M.; Schmid, C.L. Serotonin Receptor Signaling and Regulation via β-Arrestins. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 45, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gelber, E.I.; Kroeze, W.K.; Willins, D.L.; Gray, J.A.; Sinar, C.A.; Hyde, E.G.; Gurevich, V.; Benovic, J.; Roth, B.L. Structure and Function of the Third Intracellular Loop of the 5-Hydroxytryptamine2A Receptor: The Third Intracellular Loop Is Alpha-Helical and Binds Purified Arrestins. J. Neurochem. 1999, 72, 2206–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guiard, B.P.; Giovanni, G.D. Central Serotonin-2A (5-HT2A) Receptor Dysfunction in Depression and Epilepsy: The Missing Link? Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abbas, A.; Roth, B.L. Arresting Serotonin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 831–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmid, C.L.; Raehal, K.M.; Bohn, L.M. Agonist-Directed Signaling of the Serotonin 2A Receptor Depends on Beta-Arrestin-2 Interactions In Vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 1079–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- González-Maeso, J.; Weisstaub, N.V.; Zhou, M.; Chan, P.; Ivic, L.; Ang, R.; Lira, A.; Bradley-Moore, M.; Ge, Y.; Zhou, Q.; et al. Hallucinogens Recruit Specific Cortical 5-HT(2A) Receptor-Mediated Signaling Pathways to Affect Behavior. Neuron 2007, 53, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moreno, J.L.; Holloway, T.; Albizu, L.; Sealfon, S.C.; González-Maeso, J. Metabotropic Glutamate MGlu2 Receptor Is Necessary for the Pharmacological and Behavioral Effects Induced by Hallucinogenic 5-HT2A Receptor Agonists. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 493, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borroto-Escuela, D.O.; Li, X.; Tarakanov, A.O.; Savelli, D.; Narváez, M.; Shumilov, K.; Andrade-Talavera, Y.; Jimenez-Beristain, A.; Pomierny, B.; Díaz-Cabiale, Z.; et al. Existence of Brain 5-HT1A-5-HT2A Isoreceptor Complexes with Antagonistic Allosteric Receptor-Receptor Interactions Regulating 5-HT1A Receptor Recognition. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 4779–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, S.; King, M.V.; Williams, S.; Edwards, A.; Ballard, T.M.; Steward, L.J.; Alberati, D.; Fone, K.C.F. Oxytocin Attenuates Phencyclidine Hyperactivity and Increases Social Interaction and Nucleus Accumben Dopamine Release in Rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019, 44, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefevre, A.; Richard, N.; Jazayeri, M.; Beuriat, P.-A.; Fieux, S.; Zimmer, L.; Duhamel, J.-R.; Sirigu, A. Oxytocin and Serotonin Brain Mechanisms in the Nonhuman Primate. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 6741–6750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Stackman, R.W.J. The Role of Serotonin 5-HT2A Receptors in Memory and Cognition. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pandey, G.N.; Dwivedi, Y.; Rizavi, H.S.; Ren, X.; Pandey, S.C.; Pesold, C.; Roberts, R.C.; Conley, R.R.; Tamminga, C.A. Higher Expression of Serotonin 5-HT2A Receptors in the Postmortem Brains of Teenage Suicide Victims. Am. J. Psychiatry 2002, 159, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marek, G.J.; Carpenter, L.L.; McDougle, C.J.; Price, L.H. Synergistic Action of 5-HT2A Antagonists and Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors in Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 2003, 28, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blier, P.; Szabo, S.T. Potential Mechanisms of Action of Atypical Antipsychotic Medications in Treatment-Resistant Depression and Anxiety. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2005, 66 (Suppl. S8), 30–40. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marek, G.J.; Martin-Ruiz, R.; Abo, A.; Artigas, F. The Selective 5-HT2A Receptor Antagonist M100907 Enhances Antidepressant-like Behavioral Effects of the SSRI Fluoxetine. Neuropsychopharmacology 2005, 30, 2205–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, S.-H.; Lee, L.-T.; Yang, Y.K. Serotonin and Mental Disorders: A Concise Review on Molecular Neuroimaging Evidence. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2014, 12, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ly, C.; Greb, A.C.; Cameron, L.P.; Wong, J.M.; Barragan, E.V.; Wilson, P.C.; Burbach, K.F.; Zarandi, S.S.; Sood, A.; Paddy, M.R.; et al. Psychedelics Promote Structural and Functional Neural Plasticity. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 3170–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grob, C.S.; Grigsby, J. (Eds.) Handbook of Medical Hallucinogens; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2021; ISBN 978-1-4625-4544-5. [Google Scholar]
- Hesselgrave, N.; Troppoli, T.A.; Wulff, A.B.; Cole, A.B.; Thompson, S.M. Harnessing Psilocybin: Antidepressant-like Behavioral and Synaptic Actions of Psilocybin Are Independent of 5-HT2R Activation in Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2022489118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raval, N.R.; Johansen, A.; Donovan, L.L.; Ros, N.F.; Ozenne, B.; Hansen, H.D.; Knudsen, G.M. A Single Dose of Psilocybin Increases Synaptic Density and Decreases 5-HT2A Receptor Density in the Pig Brain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, B.; Hermand, M.; Pétillion, A.; Karila, L.; Benyamina, A. Clinical and Biological Predictors of Psychedelic Response in the Treatment of Psychiatric and Addictive Disorders: A Systematic Review. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2021, 137, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, B.; Karila, L.; Martelli, C.; Benyamina, A. Efficacy of Psychedelic Treatments on Depressive Symptoms: A Meta-Analysis. J. Psychopharmacol. 2020, 34, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Cha, E.; Park, W.K.; Lee, H.Y.; Lim, S.M.; Kim, H.J.; Pae, A.N. Evaluation of Anti-Depressant Effects of Phthalazinone-Based Triple-Acting Small Molecules against 5-HT2A, 5-HT2C, and the Serotonin Transporter. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 126882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Wei, Y.; Guo, Q.; Zhao, S.; Liu, Z.; Xiao, T.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, G.; et al. Pharmacological Characterization of H05, a Novel Serotonin and Noradrenaline Reuptake Inhibitor with Moderate 5-HT2A Antagonist Activity for the Treatment of Depression. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2018, 365, 624–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evans, C.A.; Zuluaga, A.; Vasquez Matute, D.; Baradaran-Noviri, S.; Perez-Cervantes, N.; Siegler, M.A. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Thioadatanserin and Its Dialkylated Products as Partial 5-HTR1A Agonists and 5-HTR2A Antagonists for Potential Use in Depression and Anxiety Disorders. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 127358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, L.P.; Olson, D.E. Dark Classics in Chemical Neuroscience: N,N-Dimethyltryptamine (DMT). ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 2344–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, L.P.; Tombari, R.J.; Lu, J.; Pell, A.J.; Hurley, Z.Q.; Ehinger, Y.; Vargas, M.V.; McCarroll, M.N.; Taylor, J.C.; Myers-Turnbull, D.; et al. A Non-Hallucinogenic Psychedelic Analogue with Therapeutic Potential. Nature 2021, 589, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hough, L.B.; Pearl, S.M.; Glick, S.D. Tissue Distribution of Ibogaine after Intraperitoneal and Subcutaneous Administration. Life Sci. 1996, 58, PL119–PL122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, X.; Kovar, M.; Boehm, S.; Sandtner, W.; Hilber, K. Anti-Addiction Drug Ibogaine Inhibits HERG Channels: A Cardiac Arrhythmia Risk. Addict. Biol. 2014, 19, 237–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iyer, R.N.; Favela, D.; Zhang, G.; Olson, D.E. The Iboga Enigma: The Chemistry and Neuropharmacology of Iboga Alkaloids and Related Analogs. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2021, 38, 307–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zloh, M.; Kirton, S.B. The Benefits of in Silico Modeling to Identify Possible Small-Molecule Drugs and Their off-Target Interactions. Future Med. Chem. 2018, 10, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maia, E.H.B.; Assis, L.C.; de Oliveira, T.A.; da Silva, A.M.; Taranto, A.G. Structure-Based Virtual Screening: From Classical to Artificial Intelligence. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jegerschöld, C.; Pawelzik, S.-C.; Purhonen, P.; Bhakat, P.; Gheorghe, K.R.; Gyobu, N.; Mitsuoka, K.; Morgenstern, R.; Jakobsson, P.-J.; Hebert, H. Structural Basis for Induced Formation of the Inflammatory Mediator Prostaglandin E2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11110–11115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamza, A.; Wei, N.-N.; Zhan, C.-G. Ligand-Based Virtual Screening Approach Using a New Scoring Function. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 963–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stahura, F.L.; Bajorath, J. New Methodologies for Ligand-Based Virtual Screening. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2005, 11, 1189–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Q.; Meng, L.; Ren, Y. Design of Novel Dopamine D2 and Serotonin 5-HT2A Receptors Dual Antagonists toward Schizophrenia: An Integrated Study with QSAR, Molecular Docking, Virtual Screening and Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 38, 860–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Jade, D.; Gupta, D. A Novel Identification Approach for Discovery of 5-HydroxyTriptamine 2A Antagonists: Combination of 2D/3D Similarity Screening, Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2019, 37, 931–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leelananda, S.P.; Lindert, S. Computational Methods in Drug Discovery. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2016, 12, 2694–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Joseph, J.; Gao, Y.; Hu, B.; Geng, X.; Wu, D.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F. Revealing the Interaction Modes of 5-HT2A Receptor Antagonists and the Structure-Based Virtual Screening from FDA and TCMNP Database. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 3681–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staroń, J.; Kurczab, R.; Warszycki, D.; Satała, G.; Krawczyk, M.; Bugno, R.; Lenda, T.; Popik, P.; Hogendorf, A.S.; Hogendorf, A.; et al. Virtual Screening-Driven Discovery of Dual 5-HT6/5-HT2A Receptor Ligands with pro-Cognitive Properties. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 185, 111857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Group | Receptor Subtype | Pharmacological Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Gαi-coupled serotonin receptors; usually decrease the activity of adenylyl cyclase and lower the intracellular cAMP concentration [32] | 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B, 5-HT1D, 5-HT1E, 5-HT1F 5-HT5A, 5-HT5B |
|
| Gαq/11-coupled serotonin receptors; activate the phospholipase C, increase the concentration of inositol triphosphate, diacylglycerol, and intracellular calcium levels [32] | 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, 5-HT2C |
|
| Gαs-coupled serotonin receptors; couple to adenylyl cyclase, elevate cAMP levels, may also result in increased calcium [32] | 5-HT4, 5-HT6, 5-HT7 |
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zięba, A.; Stępnicki, P.; Matosiuk, D.; Kaczor, A.A. Overcoming Depression with 5-HT2A Receptor Ligands. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010010
Zięba A, Stępnicki P, Matosiuk D, Kaczor AA. Overcoming Depression with 5-HT2A Receptor Ligands. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleZięba, Agata, Piotr Stępnicki, Dariusz Matosiuk, and Agnieszka A. Kaczor. 2022. "Overcoming Depression with 5-HT2A Receptor Ligands" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010010
APA StyleZięba, A., Stępnicki, P., Matosiuk, D., & Kaczor, A. A. (2022). Overcoming Depression with 5-HT2A Receptor Ligands. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010010









