Adhesion Molecule Targeted Therapy for Non-Infectious Uveitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
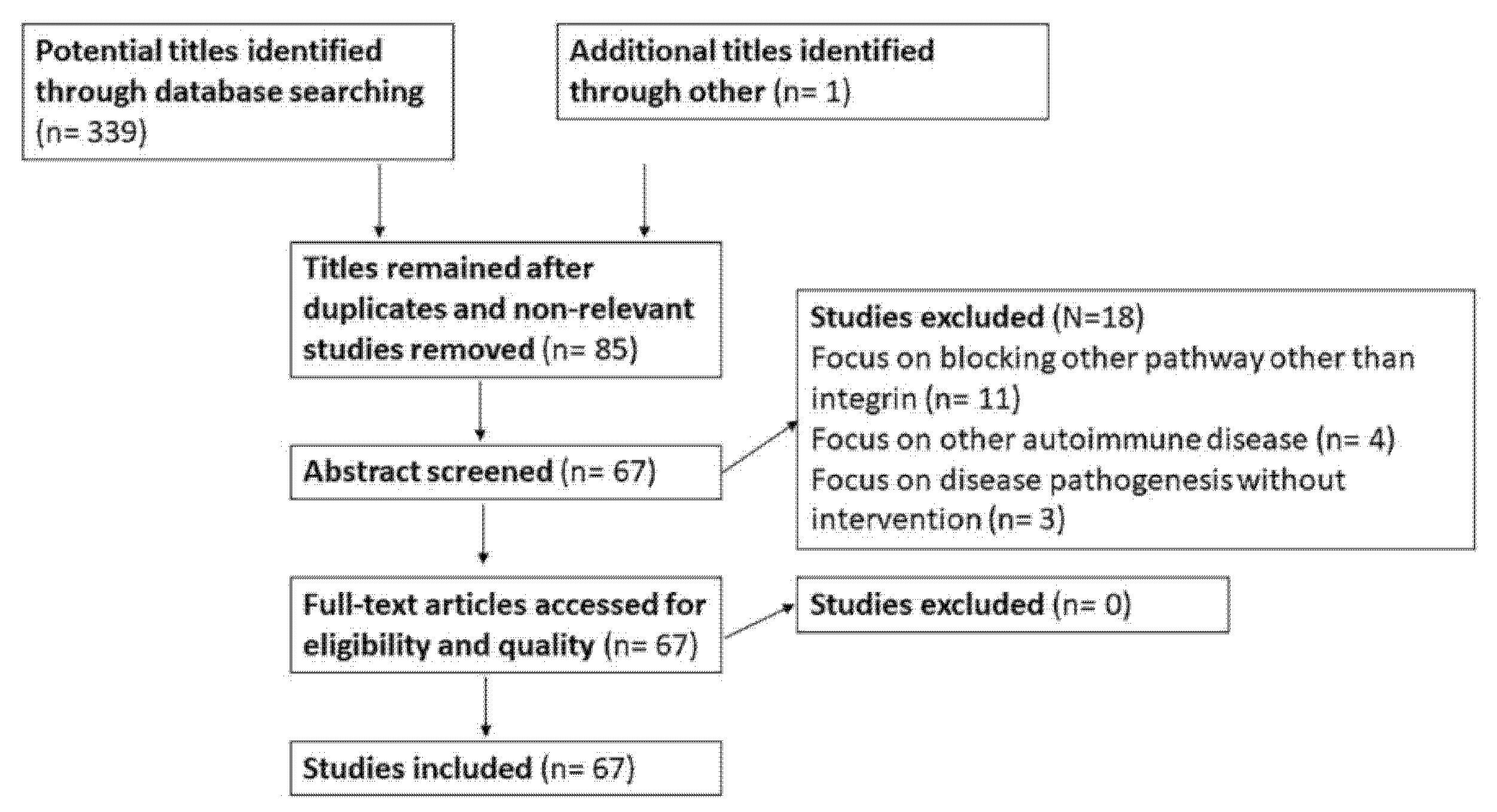
2. Material and Methods
3. Results
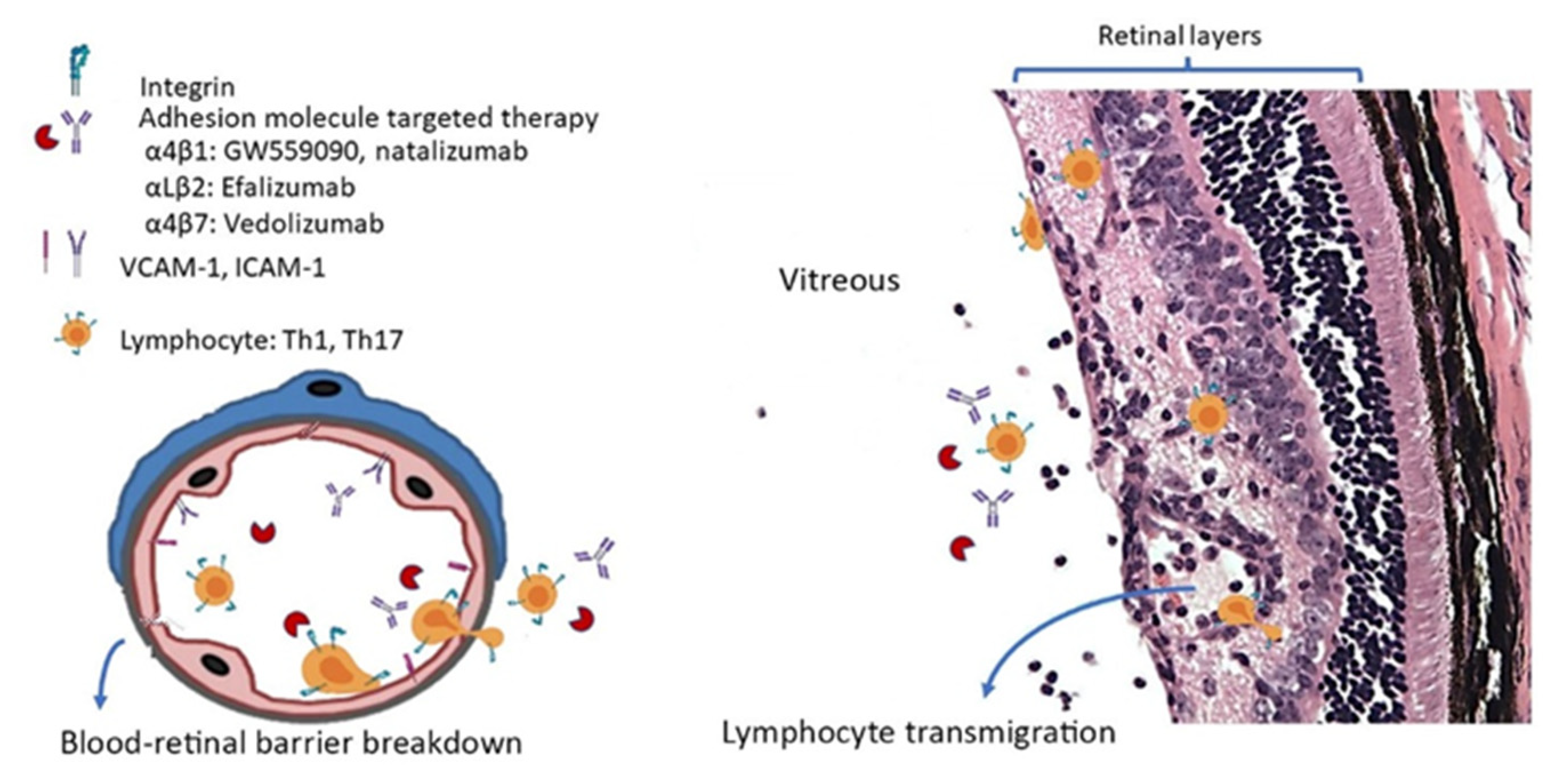
3.1. Role of Cell Adhesion Molecules in Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis
3.2. Role of Adhesion Molecules in NIU
3.3. Clinical Trials of Anti-Adhesion Molecule Therapy for NIU
3.4. Efficacy of Adhesion Molecule-Based Therapy in Other Retinal Disorders
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Caspi, R.R. A look at autoimmunity and inflammation in the eye. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 3073–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrester, J.V.; Kuffova, L.; Dick, A.D. Autoimmunity, Autoinflammation, and Infection in Uveitis. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 189, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, D.S.; Johnson, S.J.; Mallya, U.G.; Davis, M.R.; Sorg, R.A.; Duh, M.S. Healthcare costs and utilization for privately insured patients treated for non-infectious uveitis in the USA. J. Ophthalmic Inflamm. Infect. 2013, 3, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Aparicio, Á.; García de Yébenes, M.J.; Otón, T.; Muñoz-Fernández, S. Prevalence and Incidence of Uveitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2021, 28, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egwuagu, C.E.; Alhakeem, S.A.; Mbanefo, E.C. Uveitis: Molecular Pathogenesis and Emerging Therapies. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 623725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, Y.M.; Lefort, C.T.; Kim, M. Leukocyte integrins and their ligand interactions. Immunol. Res. 2009, 45, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, T.A.; Stanford, M.R.; Graham, E.M.; Dumonde, D.C.; Brown, K.A. A new method for studying the selective adherence of blood lymphocytes to the microvasculature of human retina. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1997, 38, 2608–2618. [Google Scholar]
- Harjunpää, H.; Llort Asens, M.; Guenther, C.; Fagerholm, S.C. Cell Adhesion Molecules and Their Roles and Regulation in the Immune and Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Forrester, J.V.; Liversidge, J.; Crane, I.J. Leukocyte trafficking in experimental autoimmune uveitis: Breakdown of blood-retinal barrier and upregulation of cellular adhesion molecules. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2003, 44, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dustin, M.L. Integrins and Their Role in Immune Cell Adhesion. Cell 2019, 177, 499–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butzkueven, H.; Kappos, L.; Wiendl, H.; Trojano, M.; Spelman, T.; Chang, I.; Kasliwal, R.; Jaitly, S.; Campbell, N.; Ho, P.R.; et al. Long-term safety and effectiveness of natalizumab treatment in clinical practice: 10 years of real-world data from the Tysabri Observational Program (TOP). J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2020, 91, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelhardt, B.; Laschinger, M.; Schulz, M.; Samulowitz, U.; Vestweber, D.; Hoch, G. The development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in the mouse requires alpha4-integrin but not alpha4beta7-integrin. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 102, 2096–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döring, A.; Pfeiffer, F.; Meier, M.; Dehouck, B.; Tauber, S.; Deutsch, U.; Engelhardt, B. TET inducible expression of the α4β7-integrin ligand MAdCAM-1 on the blood-brain barrier does not influence the immunopathogenesis of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2011, 41, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takatsu, N.; Hisabe, T.; Higashi, D.; Ueki, T.; Matsui, T. Vedolizumab in the Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis: An Evidence-Based Review of Safety, Efficacy, and Place of Therapy. Core Evid. 2020, 15, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luzentales-Simpson, M.; Pang, Y.C.F.; Zhang, A.; Sousa, J.A.; Sly, L.M. Vedolizumab: Potential Mechanisms of Action for Reducing Pathological Inflammation in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 612830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelcic, I.; Jelcic, I.; Faigle, W.; Sospedra, M.; Martin, R. Immunology of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J. Neurovirol. 2015, 21, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damle, N.K.; Klussman, K.; Linsley, P.S.; Aruffo, A. Differential costimulatory effects of adhesion molecules B7, ICAM-1, LFA-3, and VCAM-1 on resting and antigen-primed CD4+ T lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 1992, 148, 1985–1992. [Google Scholar]
- Wakefield, D.; McCluskey, P.; Palladinetti, P. Distribution of lymphocytes and cell adhesion molecules in iris biopsy specimens from patients with uveitis. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1992, 110, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitcup, S.M.; Chan, C.C.; Li, Q.; Nussenblatt, R.B. Expression of cell adhesion molecules in posterior uveitis. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1992, 110, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppner, M.C.; Liversidge, J.; McKillop-Smith, S.; Lumsden, L.; Forrester, J.V. Adhesion molecule expression in acute and fibrotic sympathetic ophthalmia. Curr. Eye Res. 1993, 12, 923–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasem, A.R.; Bucolo, C.; Baiula, M.; Spartà, A.; Govoni, P.; Bedini, A.; Fascì, D.; Spampinato, S. Contribution of alpha4beta1 integrin to the antiallergic effect of levocabastine. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 76, 751–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haber, S.L.; Benson, V.; Buckway, C.J.; Gonzales, J.M.; Romanet, D.; Scholes, B. Lifitegrast: A novel drug for patients with dry eye disease. Ther. Adv. Ophthalmol. 2019, 11, 70366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, D.E.; Zhao, Y.; Ogundele, A.; Fulcher, N.; Acs, A.; Moore-Schiltz, L.; Karpecki, P.M. Real-World Treatment Patterns of Cyclosporine Ophthalmic Emulsion And Lifitegrast Ophthalmic Solution Among Patients With Dry Eye. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2019, 13, 2285–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnaby-Price, A.; Stanford, M.R.; Biggerstaff, J.; Howe, L.; Whiston, R.A.; Marshall, J.; Wallace, G.R. Leukocyte trafficking in experimental autoimmune uveitis in vivo. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1998, 64, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devine, L.; Lightman, S.L.; Greenwood, J. Role of LFA-1, ICAM-1, VLA-4 and VCAM-1 in lymphocyte migration across retinal pigment epithelial monolayers in vitro. Immunology 1996, 88, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenwood, J.; Wang, Y.; Calder, V.L. Lymphocyte adhesion and transendothelial migration in the central nervous system: The role of LFA-1, ICAM-1, VLA-4 and VCAM-1. off. Immunology 1995, 86, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Platts, K.E.; Benson, M.T.; Rennie, I.G.; Sharrard, R.M.; Rees, R.C. Cytokine modulation of adhesion molecule expression on human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1995, 36, 2262–2269. [Google Scholar]
- Dewispelaere, R.; Lipski, D.; Foucart, V.; Bruyns, C.; Frère, A.; Caspers, L.; Willermain, F. ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 are differentially expressed on blood-retinal barrier cells during experimental autoimmune uveitis. Exp. Eye Res. 2015, 137, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitcup, S.M.; DeBarge, L.R.; Caspi, R.R.; Harning, R.; Nussenblatt, R.B.; Chan, C.C. Monoclonal antibodies against ICAM-1 (CD54) and LFA-1 (CD11a/CD18) inhibit experimental autoimmune uveitis. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1993, 67, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamatani, T.; Kitamura, F.; Kuida, K.; Shirao, M.; Mochizuki, M.; Suematsu, M.; Schmid-Schönbein, G.W.; Watanabe, K.; Tsurufuji, S.; Miyasaka, M. Characterization of rat LECAM-1 (L-selectin) by the use of monoclonal antibodies and evidence for the presence of soluble LECAM-1 in rat sera. Eur. J. Immunol. 1993, 23, 2181–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Sun, D.; Zhang, P.; Jiang, G.; Kaplan, H.J.; Shao, H. Suppression of established experimental autoimmune uveitis by anti-LFA-1alpha Ab. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2007, 48, 2667–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, A.S.; Schewitz-Bowers, L.P.; Wei, L.; Lee, R.W.; Smith, J.R. Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 mediates migration of Th1 and Th17 cells across human retinal vascular endothelium. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 6917–6925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, W.; Harada, Y.; Fukuda, K.; Taguchi, O.; Yagita, H.; Fukushima, A. Inhibition of very late antigen-4 and leukocyte function-associated antigen-1 in experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 153, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimaraes de Souza, R.; Yu, Z.; Stern, M.E.; Pflugfelder, S.C.; de Paiva, C.S. Suppression of Th1-Mediated Keratoconjunctivitis Sicca by Lifitegrast. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. Off. J. Assoc. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 34, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.H.; Eskandarpour, M.; Zhang, X.; Galatowicz, G.; Greenwood, J.; Lightman, S.; Calder, V. Small-molecule antagonist of VLA-4 (GW559090) attenuated neuro-inflammation by targeting Th17 cell trafficking across the blood-retinal barrier in experimental autoimmune uveitis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Jiang, S.; Manczak, M.; Sugden, B.; Adamus, G. Phenotypes of T cells infiltrating the eyes in autoimmune anterior uveitis associated with EAE. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2002, 43, 1499–1508. [Google Scholar]
- Chawla, R.; Nath, M.; Moksha, L.; Nag, T.C.; Velpandian, T. An experimental study to evaluate safety/toxicity of intravitreal natalizumab. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 66, 1441–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenbaum, J.T.; Boney, R.S. Efficacy of antibodies to adhesion molecules, CD11a or CD18, in rabbit models of uveitis. Curr. Eye Res. 1993, 12, 827–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchio, E.; Kijima, M.; Tanaka, S.; Ohno, S. Suppression of experimental uveitis with monoclonal antibodies to ICAM-1 and LFA-1. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1994, 35, 2626–2631. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, A.P.; de Moraes, L.V.; Tadokoro, C.E.; Commodaro, A.G.; Urrets-Zavalia, E.; Rabinovich, G.A.; Urrets-Zavalia, J.; Rizzo, L.V.; Serra, H.M. Administration of a peptide inhibitor of alpha4-integrin inhibits the development of experimental autoimmune uveitis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2005, 46, 2056–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.R.; O’Rourke, L.M.; Becker, M.D.; Cao, M.; Williams, K.A.; Planck, S.R.; Rosenbaum, J.T. Anti-rat ICAM-1 antibody does not influence the course of experimental melanin-induced uveitis. Curr. Eye Res. 2000, 21, 906–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Manivannan, A.; Jiang, H.R.; Liversidge, J.; Sharp, P.F.; Forrester, J.V.; Crane, I.J. Recruitment of IFN-gamma-producing (Th1-like) cells into the inflamed retina in vivo is preferentially regulated by P-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1:P/E-selectin interactions. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 3215–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitcup, S.M.; Kozhich, A.T.; Lobanoff, M.; Wolitzky, B.A.; Chan, C.C. Blocking both E-selectin and P-selectin inhibits endotoxin-induced leukocyte infiltration into the eye. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1997, 83, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, K.; Ogura, Y.; Hamada, M.; Nishiwaki, H.; Hiroshiba, N.; Tsujikawa, A.; Mandai, M.; Suzuma, K.; Tojo, S.J.; Honda, Y. In vivo neutralization of P-selectin inhibits leukocyte-endothelial interactions in retinal microcirculation during ocular inflammation. Microvasc. Res. 1998, 55, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuma, I.; Mandai, M.; Suzuma, K.; Ishida, K.; Tojo, S.J.; Honda, Y. Contribution of E-selectin to cellular infiltration during endotoxin-induced uveitis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1998, 39, 1620–1630. [Google Scholar]
- La Heij, E.; Kuijpers, R.W.; Baarsma, S.G.; Kijlstra, A.; van der Weiden, M.; Mooy, C.M. Adhesion molecules in iris biopsy specimens from patients with uveitis. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1998, 82, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, A.G.; Edelsten, C.; Stanford, M.R.; Graham, E.M.; Ellis, B.A.; Direskeneli, H.; D’Cruz, D.P.; Hughes, G.R.; Dumonde, D.C.; Wallace, G.R. Soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1) as a marker of disease relapse in idiopathic uveoretinitis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1994, 95, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arocker-Mettinger, E.; Steurer-Georgiew, L.; Steurer, M.; Huber-Spitzy, V.; Hoelzl, E.; Grabner, G.; Kuchar, A. Circulating ICAM-1 levels in serum of uveitis patients. Curr. Eye Res. 1992, 11, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira-Neves, L.; Palma-Carlos, M.L.; Soares, I.; Pereira-Santos, M.C.; Ganhao, F.; Palma-Carlos, A.G. Soluble ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 serum levels in uveitis. Allerg. Immunol. 1996, 28, 302–306. [Google Scholar]
- Klok, A.M.; Luyendijk, L.; Zaal, M.J.; Rothova, A.; Kijlstra, A. Soluble ICAM-1 serum levels in patients with intermediate uveitis. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1999, 83, 847–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchio, E.; Matsumoto, T.; Tanaka, S.I.; Ohno, S. Soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), CD4, CD8 and interleukin-2 receptor in patients with Behçet’s disease and Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada’s disease. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 1999, 17, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martin, C.M.; Lacomba, M.S.; Molina, C.I.; Chamond, R.R.; Galera, J.M.; Estevez, E.C. Levels of soluble ICAM-1 and soluble IL-2R in the serum and aqueous humor of uveitis patients. Curr. Eye Res. 2000, 20, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verity, D.H.; Wallace, G.R.; Seed, P.T.; Kanawati, C.A.; Ayesh, I.; Holland-Gladwish, J.; Stanford, M.R. Soluble adhesion molecules in Behcet’s disease. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 1998, 6, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Lee, S.; Park, C.; Seo, J.S.; Kim, J.I.; Yu, H.G. Targeted resequencing of candidate genes reveals novel variants associated with severe Behçet’s uveitis. Exp. Mol. Med. 2013, 45, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Haznedaroglu, E.; Karaaslan, Y.; Büyükaşik, Y.; Koşar, A.; Ozcebe, O.; Haznedaroglu b, C.; Kirazli, E.; Dündar, S.V. Selectin adhesion molecules in Behçet’s disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2000, 59, 61–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.T.; Hooper, L.C.; Kump, L.; Hayashi, K.; Nussenblatt, R.; Hooks, J.J.; Detrick, B. Interferon-beta and adhesion molecules (E-selectin and s-intracellular adhesion molecule-1) are detected in sera from patients with retinal vasculitis and are induced in retinal vascular endothelial cells by Toll-like receptor 3 signalling. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2007, 147, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaku, H.; Mizukawa, H.; Kishi, I.; Yanagida, T.; Inaba, G. Peripheral leukocyte adhesion molecules in patients of Behçet’s disease associated with active ocular lesions. Ryumachi 1994, 34, 608–615. [Google Scholar]
- Roemer, S.; Bissig, A.; Rocca, A.; Du Pasquier, R.; Guex-Crosier, Y. Efficacy of Natalizumab in Intermediate Uveitis Related to Multiple Sclerosis: A Case Report. Klin. Monbl. Augenheilkd. 2018, 235, 476–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleisher, M.; Marsal, J.; Lee, S.D.; Frado, L.E.; Parian, A.; Korelitz, B.I.; Feagan, B.G. Effects of Vedolizumab Therapy on Extraintestinal Manifestations in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2018, 63, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faia, L.J.; Sen, H.N.; Li, Z.; Yeh, S.; Wroblewski, K.J.; Nussenblatt, R.B. Treatment of inflammatory macular edema with humanized anti-CD11a antibody therapy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 6919–6924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, V.; Kuppermann, B.D.; Bhaskar, V.; Wales, P.; Hagemann, L.F.; Marques, L.; Carvalho, R.P.d.; Wong, C.G.; Murray, R. F200, a Fab Derivative of M200 (Volociximab; Anti–A5ß1), Is a Potent Inhibitor of Angiogenesis in a Rabbit Model of Choroidal Neovascularization. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2005, 46, 465. [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa, M.; Jin, D.; Sawada, Y.; Abe, S.; Yoshitomi, T. Future therapies of wet age-related macular degeneration. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 2015, 138070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, A.C.; Regillo, C.D. The future of neovascular age-related macular degeneration. In Age-Related Macular Degeneration Diagnosis and Treatment, 1st ed.; Ho, A.C., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 135–153. [Google Scholar]
- Boyer, D.S.; Gonzalez, V.H.; Kunimoto, D.Y.; Maturi, R.K.; Roe, R.H.; Singer, M.A.; Xavier, S.; Kornfield, J.A.; Kuppermann, B.D.; Quiroz-Mercado, H.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Intravitreal Risuteganib for Non-Exudative AMD: A Multicenter, Phase 2a, Randomized, Clinical Trial. Ophthalmic Surg. Lasers Imaging Retin. 2021, 52, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.T.; Vanhove, M.; Porcu, M.; Van Hove, I.; Van Bergen, T.; Jonckx, B.; Barbeaux, P.; Vermassen, E.; Feyen, J.H.M. The potent small molecule integrin antagonist THR-687 is a promising next-generation therapy for retinal vascular disorders. Exp. Eye Res. 2019, 180, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanani, A.M.; Patel, S.S.; Gonzalez, V.H.; Moon, S.J.; Jaffe, G.J.; Wells, J.A.; Kozma, P.; Dugel, P.U.; Maturi, R.K. Phase 1 Study of THR-687, a Novel, Highly Potent Integrin Antagonist for the Treatment of Diabetic Macular Edema. Ophthalmol. Sci. 2021, 1, 100040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, D.; Boyer, D.S.; Kaiser, P.K.; Heier, J.S.; Askew, B. First-in human study of SF0166 Topical Ophthalmic Solution in patients with diabetic macular edema. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Takada, Y.; Ye, X.; Simon, S. The integrins. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Salinas, R.; Hernandez-Zimbron, L.F.; Gulias-Canizo, R.; Sanchez-Vela, M.A.; Ochoa-De La Paz, L.; Zamora, R.; Quiroz-Mercado, H. Current Anti-Integrin Therapy for Ocular Disease. Semin. Ophthalmol. 2018, 33, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Studies | Molecule and Animal Model | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Rosenbaum et al. [38] | Ab to LFA-1 (CD11a/CD18) and ICAM-1 (iv) in rabbit model of uveitis. | Anti-CD18 Ab effectively reduced cellular infiltration if injected after 24 h of induction. Anti-CD11a Ab was effective only in the IL-1-induced model. Anti-ICAM-1 Ab was ineffective. |
| Uchio et al. [39] | Anti-ICAM-1 Ab or anti-LFA-1 α chain Ab (iv) consecutively after EAU induction in rat. | The development of EAU could be completely prevented by anti-ICAM-1 Ab but partially by anti-LFA-1 α chain Ab. |
| Martin et al. [40] | α4 active peptide inhibitor (ip) was administered to classical and adoptive transferred B10.RIII EAU mice serially at afferent and efferent phase of disease. | Treatment at afferent and efferent phase has a similar extent of disease downregulation, however; it did not ablate the disease fully. Repeated injections can reduce the disease scores further. |
| Smith et al. [41] | Anti-ICAM-1 Ab (ip) sequentially after induction of EMIU. | Failed to suppress leukocyte infiltration. |
| Clinical Trial | Receptor and Mechanism | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| An open-label, prospective, noncomparative phase I/II clinical trial (ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT00280826.) [60] | Weekly subcutaneous Efalizumab (a humanized form of a murine IgG1 antibody to CD11a, the α subunit of LFA-1, Raptiva; Genentech Inc., San Francisco, CA, USA) treatment for 16 weeks for patients with macular edema secondary to NIU. | Improvement in uveitis severity and macular edema. Upregulation of CD56bright regulatory NK cell population in the peripheral blood. Side effects: neutropenia (17%) and headache (50%), resolved without sequelae. Efalizumab was taken off the market due to side effect of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML). |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.-H.; Lightman, S.; Eskandarpour, M.; Calder, V.L. Adhesion Molecule Targeted Therapy for Non-Infectious Uveitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010503
Chen Y-H, Lightman S, Eskandarpour M, Calder VL. Adhesion Molecule Targeted Therapy for Non-Infectious Uveitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(1):503. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010503
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yi-Hsing, Sue Lightman, Malihe Eskandarpour, and Virginia L. Calder. 2022. "Adhesion Molecule Targeted Therapy for Non-Infectious Uveitis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 1: 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010503
APA StyleChen, Y.-H., Lightman, S., Eskandarpour, M., & Calder, V. L. (2022). Adhesion Molecule Targeted Therapy for Non-Infectious Uveitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(1), 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010503





