A Quantitative Systems Approach to Define Novel Effects of Tumour p53 Mutations on Binding Oncoprotein MDM2
Abstract
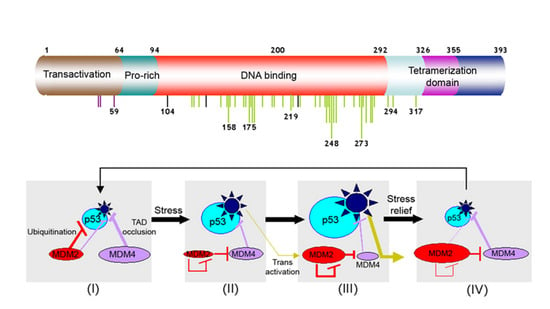
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
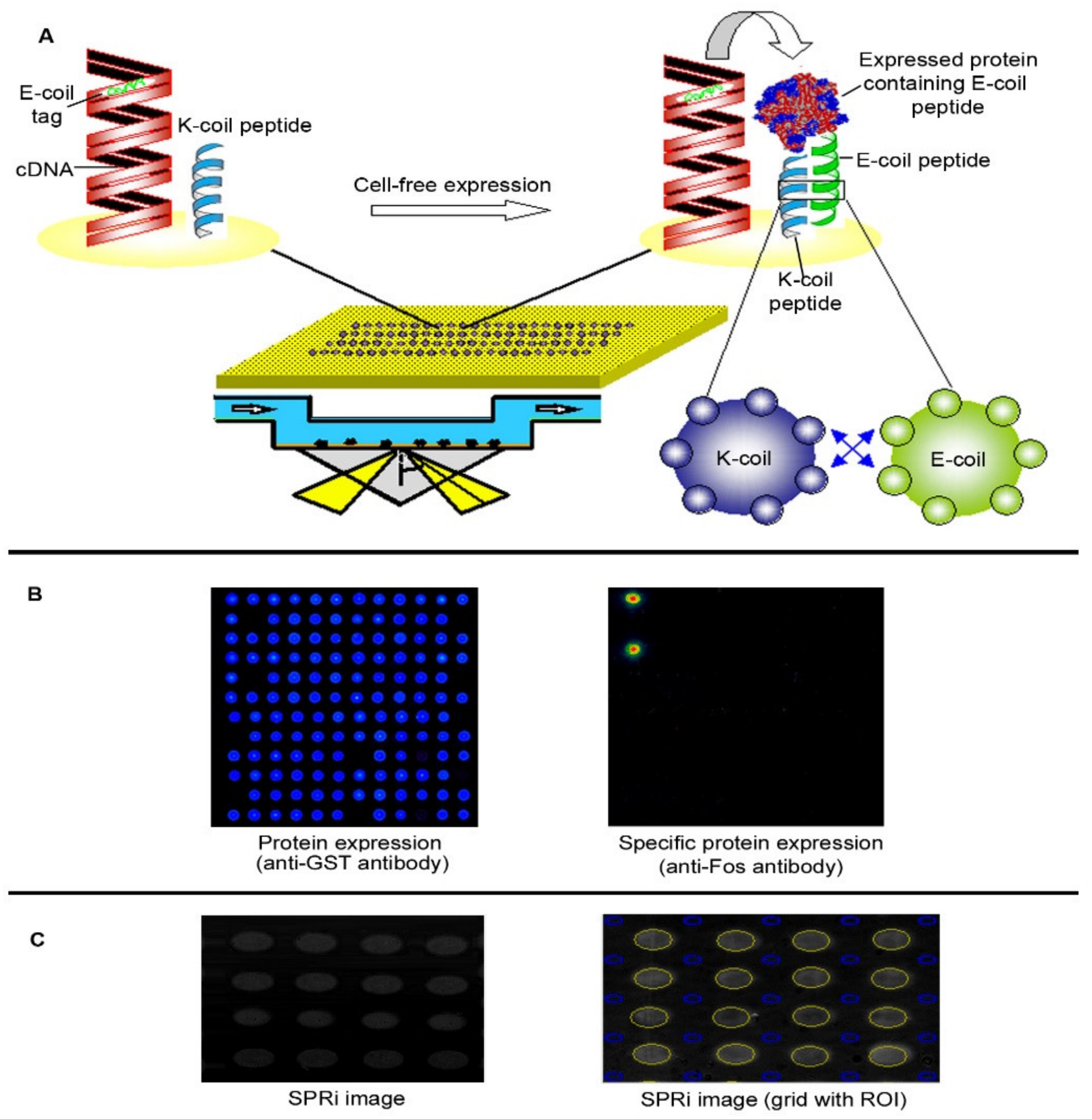
2.1. The NAPPA-SPRi Array
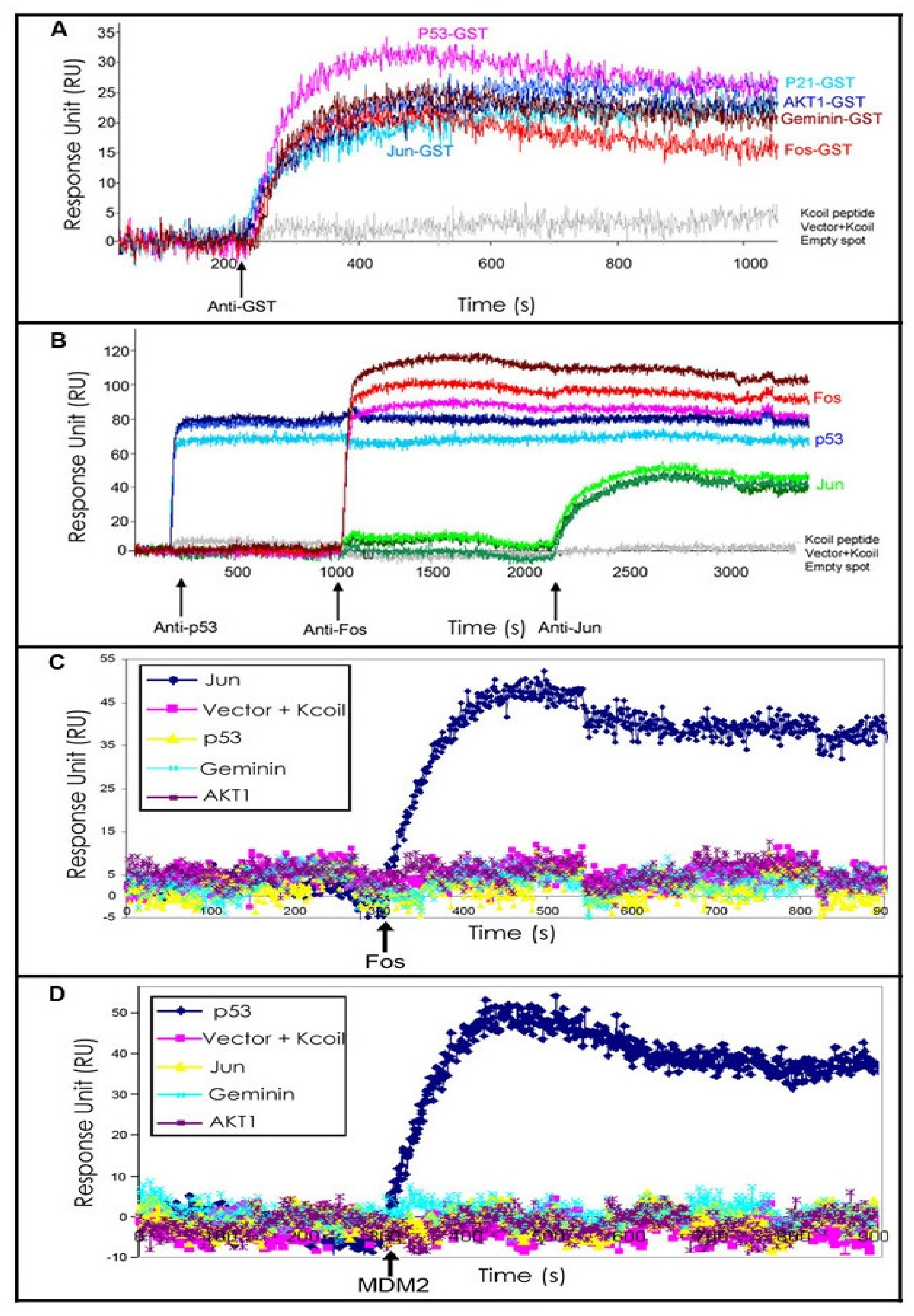
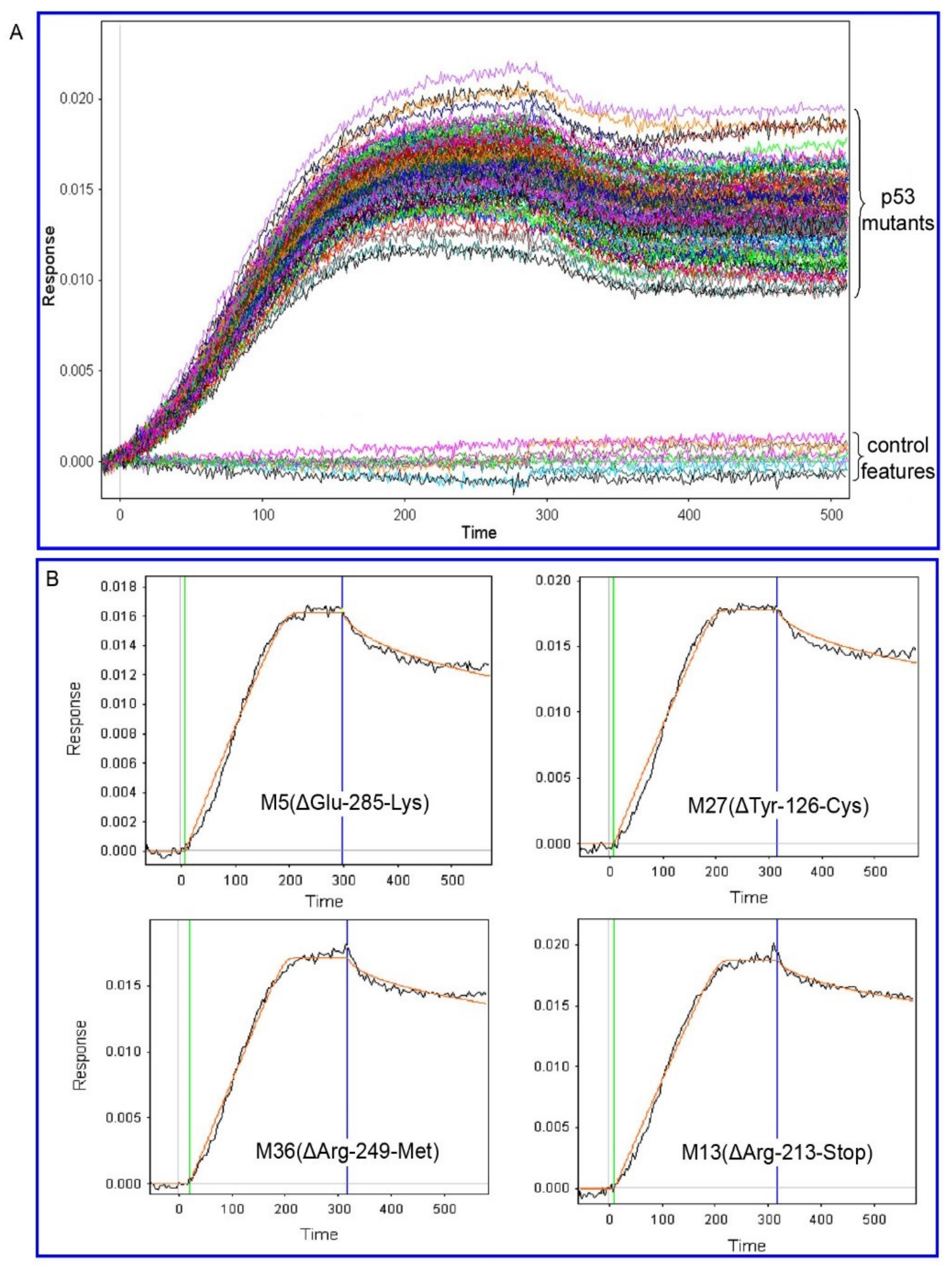
2.2. p53 Mutant—Mdm2 Interaction Studies
2.3. p53-Mdm2 Interaction Studies in the Presence of Nutlin-3
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. DNA Preparation and Substrate Functionalization
3.2. Sample Preparation and Array Printing
3.3. In Situ Protein Expression in NAPPA-SPRi Approach
3.4. Protein Display and Visualization
3.5. SPRi Instrument Set-Up
3.6. Detection of In Situ Expressed Protein by SPRi
3.7. Protein Interaction Studies by SPRi
3.8. Protein Interaction Studies in the Presence of Nutlin-3 Using SPRi
3.9. SPRi Data Processing
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mintseris, J.; Weng, Z. Structure, function, and evolution of transient and obligate protein-protein interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 10930–10935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nooren, I.M.A.; Thornton, J.M. Diversity of protein interactions. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 3486–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nooren, I.M.A.; Thornton, J.M. Structural characterization and functional significance of transient protein-protein interactions. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 325, 991–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, S. High-throughput two-hybrid analysis. The promise and the peril. EMBO J. 2005, 272, 5391–5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labaer, J.; Ramachandran, N. Protein Microarrays as a tool for Functional Proteomics. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2005, 9, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, N.; Hainsworth, E.; Bhullar, B.; Eisenstein, S.; Rosen, B.; Lau, A.Y.; Walter, J.C.; Labaer, J. Self-assembling protein microarrays. Science 2004, 305, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramachandran, N.; Raphael, J.V.; Hainsworth, E.; Demirkan, G.; Fuentes, M.; Rolfs, A.; Hu, Y.; Labaer, J. Next-generation high-density self-assembling functional protein arrays. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campbell, C.T.; Gibum, K. SPR microscopy and its applications to high-throughput analyses of molecular binding events and their kinetics. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 2380–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumaker-Parry, J.S.; Campbell, C.T. Quantitative methods for spatially resolved adsorption/desorption measurements in real time by surface Plasmon resonance microscopy. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 907–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lausted, C.; Hu, Z.; Hood, L. Quantitative serum proteomics from surface Plasmon resonance imaging. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2008, 7, 2464–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wassaf, D.; Kuang, G.; Kopacz, K.; Wu, Q.L.; Nguyen, Q.; Toews, M.; Cosic, J.; Jacques, J.; Wiltshire, S.; Lambert, J.; et al. High-throughput affinity ranking of antibodies using surface plasmon resonance microarrays. Anal. Biochem. 2006, 351, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, H.; Houston, M.E.; Grothe, S.; Kay, C.M.; O’Connor-McCourt, M.; Irvin, R.T.; Hodges, R.S. Kinetic study on the formation of a de novo designed heterodimeric coiled-coil: Use of surface Plasmon resonance to monitor the association and dissociation of polypeptides chains. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 12175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripet, B.; Yu, L.; Bautista, D.L.; Wong, W.Y.; Irvill, R.T.; Hodges, R.S. Engineering a de-novo designed coiled-coil heterodimerization domain for the rapid detection, purification and characterization of recombinantly expressed peptides and proteins. Protein Eng. 1996, 9, 1092–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turner, R.; Tjian, R. Leucine repeats and an adjacent DNA binding domain mediate the formation of functional cFos-cJun heterodimers. Science 1989, 243, 1689–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, Y.; Kazaz, A.; Oren, M. Mdm2 promotes the rapid degradation of p53. Nature 1997, 387, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, F.; Wahl, G.M. Mdm2 and Mdm4: p53 regulators as targets in anticancer therapy. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 1476–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Oliver, J.D.; Zhan, Q.; Fornance, A.J.; Vogelstein, B.; Kastan, M.B. Interactions between p53 and Mdm2 in a mammalian cell cycle checkpoint. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 2684–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, X.; Yuan, Z. Stochastic modelling and simulation of the p53-Mdm2/mdmx loop. J. Comput. Biol. 2009, 16, 917–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pazgier, M.; Liu, M.; Zou, G.; Yuan, W.; Li, C.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Monbo, J.; Zella, D.; Tarasov, S.G.; et al. Structural basis for high-affinity peptide inhibition of p53 interactions with Mdm2 and Mdmx. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 4665–4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, Y.; Gorina, S.; Jeffrey, P.D.; Pavletich, N.P. Crystal Structure of a p53 tumor suppressor-DNA complex: Understanding tumorigenic mutations. Science 1994, 265, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, F.; Wahl, G. Regulation the p53 pathway: In vitro hypothesis, in vivo veritas. Nat. Rev. 2006, 6, 909–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilev, L.T.; Vu, B.T.; Graves, B.; Carvajal, D.; Podlaski, F.; Filipovic, Z.; Kong, N.; Kammlott, U.; Lukacs, C.; Klein, C.; et al. In vivo activation of the p53 pathway by small-molecule antagonist of mdm2. Science 2004, 303, 844–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tovar, C.; Rosinski, J.; Filipovic, Z.; Higgins, B.; Kolinsky, K.; Hilton, H.; Zhao, X.; Vu, B.T.; Qing, W.; Packman, K.; et al. Small-molecule Mdm2 antagonists reveal aberrant p53 signaling in cancer: Implications for therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 1888–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roden, L.D.; Myzska, D.G. Global analysis of a macromolecular interaction measure on BIAcore. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 225, 1073–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffrey, P.D.; Gorina, S.; Pavletich, N.P. Crystal structure of the tetramerization domain of the p53 tumor suppressor at 1.7 angstroms. Science 1995, 267, 1498–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.Y.; Grinkevich, V.V.; Nikulenkov, F.; Bao, W.; Selivanova, G. Rescue of the apoptotic-inducing function of mutant p53 by small molecule RITA. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 1847–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grinkevich, V. p53 Reactivation by the Small Molecule RITA: Molecular Mechanisms; Karolinska Institutet: Stockholm, Sweden, 2011; ISBN 978-91-7457-289-6. [Google Scholar]
- Hjorstberg, L.; Rubio-Nevado, J.M.; Hamroun, D.; Claustre, M.; Beroud, C.; Soussi, T. The p53 Mutation Handbook. Available online: http://p53.free.fr/Database/p53_database.html (accessed on 5 May 2008).
- Carvajal, D.; Tovar, C.; Yang, H.; Vu, B.T.; Heimbrook, D.C.; Vassilev, L.T. Activation of p53 by MDM2 Antagonists Can Protect Proliferating Cells from Mitotic Inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 1918–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, B.; Gilkes, D.M.; Farooqi, B.; Sebti, S.; Chen, J. MDMX overexpression prevents p53 activation by the Mdm2 inhibitor Nutlin. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 33030–33035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michaelis, M.; Rothweiler, F.; Klassert, D.; Von Deimling, A.; Weber, K.; Feshe, B.; Kammerer, B.; Doerr, H.W.; Cinatl, J. Reversal of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance by the muring double minute 2 antagonist nutlin-3. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harris, C.C. Protein-protein interactions for cancer therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 1888–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wade, M.; Rodewald, L.W.; Espinosa, J.M.; Wahl, G.M. BH3 activation blocks Hdmx suppression of apoptosis and cooperates with Nutlin to induce cell death. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 1973–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.F.; Bodmer, Y. Analysis of p53 MUTAtions and their expression in 56 colorectal cancer cell lines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shangary, S.; Ding, K.; Qiu, S.; Nikoloska-Coleska, Z.; Bauer, J.; Liu, M. Reactivation of p53 by a specific MDM2 antagonist (MI-43) leads to p21-mediated cell cycle arrest and selective cell death in colon cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 1533–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Supiot, R.P.; Hill, R.G.; Bristow, R.G. Nutlin-3 radiosensitizes hypoxic prostate cancer cells independent of p53. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, B.; Vassilev, L.T. Reduced transcriptional activity in the p53 pathway of senescent cells revealed by the mdm2 antagonist nutlin-3. Aging 2009, 1, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ambrosini, G.; Sambol, E.B.; Carvajal, D.; Vassilev, L.T.; Singer, S.; Swartz, G.K. Mouse Double minute antagonist Nutlin-3a enhances chemotherapy induced apoptosis in cancer cells with MUTAnt p53 by activating E2F1. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3473–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tokalov, S.V.; Abolmaali, N.D. Protection of p53 wild-type cells from taxol by nutlin-3 in the combined lung cancer treatment. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, S.H.; Zheng, M.; Ding, K.; Wang, S.; Sun, Y. A small molecule that disrupts Mdm2-p53 binding activates p53, induces apoptosis and sensitizes lung cancer cells to chemotherapy. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2008, 7, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheok, C.F.; Dey, A.; Lane, D.P. Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors sensitize tumor cells to nutlin-induce apoptosis: A potent drug combination. Mol. Cancer Res. 2007, 5, 1133–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Secchiero, P.; Grazia de Iasio, M.; Gonelli, A.; Zauli, G. The MDM2 inhibitor Nutlins as an innovative therapeutic tool for the treatment of haematological malignancies. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 2100–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.C.; Liu, C.J.; Chiu, C.P.; Chang, S.M.; Lu, S.Y.; Chen, Y.J. Establishment of OC3 oral carcinoma cell line identification of NF-kappa B activation responses to areca nut extract. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2004, 33, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, Y.; Ogawa, I.; Kitagawa, M.; Kitajima, S.; Samadarani Siriwardena, B.S.; Aobara, N.; Matsuda, C.; Miyauchi, M.; Takata, T. Establishment and characterization of a spindle cell squamous carcinoma cell line. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2006, 35, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coll-Mulet, L.I.; Iglesias-Serret, D.; Santidrian, A.F.; Cosialls, A.M.; Frias, M.; Castaño, E.; Campas, C.; Barragan, M.; de Sevilla, A.F.; Domingo, A.; et al. MDM2 antagonist activate p53 and synergize with genotoxic drugs in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Neoplasia 2006, 107, 4109–4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sturm, I.; Bosanquet, A.G.; Hermann, S.; Guner, D.; Dorken, B.; Daniel, P.T. MUTAtion of p53 and consequtive selective drug resistance in B-CLL occurs as a consequence of prior DNA-damaging chemotherapy. Cell Death Differ. 2003, 10, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zauli, G.; di Iasio, M.G.; Seccherio, P.; Dal Bo, M.; Marconi, D.; Bomben, R.; Del Poeta, G.; Gattei, V. Exposure of B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) cells to Nutlin-3 induces a characteristic gene expression profile, which correlates with Nutlin-3-mediated cytotoxicity. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2009, 9, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurie, N.A.; Donovan, S.L.; Zhang, J.; Shih, C.S.; Fuller, C.E.; Teunisse, A.; Johnson, D.A.; Wilson, M.W.; Rodriguez-Galindo, C.; Quarto, M.; et al. Inactivation of the p53 pathway in retinoblastoma. Nature 2006, 444, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elison, J.R.; Cobrinik, D.; Claros, N.; Abramson, D.H.; Lee, T.C. Small molecule inhibition of HDM2 leads to p53-mediated cell death in retinoblastoma cells. Arch. Ophtalmol. 2006, 124, 1269–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, T.; Wang, J.; Song, X.; Meng, X.; Pan, S.; Jiang, H.; Liu, L. Nutlin-3 cooperates with doxorubicin to induce apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells through p53 or p73 signaling pathways. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 136, 1597–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Pabla, N.; Murhpy, R.F.; Yang, T.; Yin, X.M.; Degenhardt, K.; White, E.; Dong, Z. Nultin-3 protects kidney cells during cisplatine therapy by suppressing Bax/Bak activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 2635–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Maerken, T.; Ferdinande, L.; Taildeman, J.; Lambertz, I.; Yigit, N.; Vercruysse, L.; Rihani, A.; Michaelis, M., Jr.; Cinatl, J.; Cuvelier, C.A.; et al. Antitumor activity of the selective mdm2 antagonist nutlin-3 against chemoresistant neuroblastoma with wild-type p53. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2009, 101, 1562–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Gu, L.; Zhou, M. Inhibition of Akt/surviving pathway synergizes the anti-leukemia effect of nutlin-3 in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 1101–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gu, L.; Zhu, N.; Findley, H.W.; Zhou, M. Mdm2 antagonist nutlin-3 is a potent inducer of apoptosis in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells with wild-type p53 and over-expression of Mdm2. Leukemia 2008, 22, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drakos, E.; Thomaides, A.; Medeiros, L.J.; Leventaki, V.; Konopleva, M.; Andreeff, M.; Rassidakis, G.Z. Inhibition of p53-muring double minute 2 interaction by nutlin-3A stabilizes p53 and induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in Hodgkin lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 13, 3380–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tabe, Y.; Sebasigari, D.; Jin, J.; Rudelius, M.; Davies-Hil, T.; Miyake, K.; Milda, T.; Pittaluga, S.; Raffeld, M. Mdm2 antagonist nutlin-3 displays antiproliferative and proapoptotic activity in mantle cell lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gorina, S.; Pavletich, N.P. Structure of the p53 tumor suppressor bound to the ankyrin and SH3 domains of 53BP2. Science 1996, 274, 1001–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kussie, P.H.; Gorina, S.; Marechal, V.; Elenbaas, B.; Moreau, J.; Levine, A.J.; Pavletich, N.P. Structure of the Mdm2 oncoprotein bound to the p53 tumor suppressor transactivation domain. Science 1996, 274, 948–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, S.-W.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, D.-H.; Ahn, M.-J.; Kim, J.-S.; Woo, J.-Y.; Torizawa, T.; Kainosho, M.; Han, K.-H. Structural details on mdm2-p53 interaction. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 38795–38802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poyurosky, M.V.; Priest, C.; Kentsis, A.; Borden, K.L.; Pan, Z.Q.; Pavletich, N.; Prives, C. The Mdm2 ring domain C-terminus is required for supramolecular assembly and ubiquiting ligase activity. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wawrzynow, B.; Pettersson, S.; Zylicz, A.; Bramham, J.; Worrall, E.; Hupp, T.R.; Ball, K.L. A function for the RING finger domain in the allosteric control of MDM2 conformation and activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 11517–11530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grinkevich, V.V.; Nikulenkov, F.; Shi, Y.; Enge, M.; Bao, W.; Maljukova, A.; Gluch, A.; Kel, A.; Sangfelt, O.; Selivanova, G. Ablation of key oncogenic pathways by RITA-reactivated p53 is required for efficient apoptosis. Cancer Cell 2009, 15, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| KD | kon | koff | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spot | Mutant ID | Log(Ratio KD Nutlin3/Non-Nutlin3 | Log(Ratio kon Nutlin3/Non-Nutlin3) | Log(Ratio Nutlin3/Non-Nutlin3) | Nutlin Response |
| M29 | Val157Phe | −1.060 | 0.0949 | −0.962 | Resistant |
| M38 | His179Arg | −2.40 | 0.0714 | −1.69 | Resistant |
| M49 | Tyr234Cys | −1.89 | −1.18 | −3.07 | Resistant |
| Average | −1.78 | −0.123 | −1.91 | ||
| M51 | Asp281Asn | 3.30 | −3.74 | −0.435 | Intermediate |
| M2 | Gly245Asp | 1.44 | −2.75 | −1.31 | Intermediate |
| Average | 2.73 | −3.25 | −0.0873 | ||
| M1 | Gly245Ser | 6.26 | −5.49 | −0.770 | Sensitive |
| 53WT | p53-WT | 4.91 | −4.63 | −0.027 | Sensitive |
| M39 | His179Tyr | 4.90 | −4.17 | 0.740 | Sensitive |
| M22 | Arg280Thr | 6.80 | −4.33 | −2.480 | Sensitive |
| Average | 5.73 | −4.66 | −0.695 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fuentes, M.; Srivastava, S.; Gronenborn, A.M.; LaBaer, J. A Quantitative Systems Approach to Define Novel Effects of Tumour p53 Mutations on Binding Oncoprotein MDM2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010053
Fuentes M, Srivastava S, Gronenborn AM, LaBaer J. A Quantitative Systems Approach to Define Novel Effects of Tumour p53 Mutations on Binding Oncoprotein MDM2. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(1):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010053
Chicago/Turabian StyleFuentes, Manuel, Sanjeeva Srivastava, Angela M. Gronenborn, and Joshua LaBaer. 2022. "A Quantitative Systems Approach to Define Novel Effects of Tumour p53 Mutations on Binding Oncoprotein MDM2" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 1: 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010053
APA StyleFuentes, M., Srivastava, S., Gronenborn, A. M., & LaBaer, J. (2022). A Quantitative Systems Approach to Define Novel Effects of Tumour p53 Mutations on Binding Oncoprotein MDM2. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(1), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010053