Cellular and Molecular Profiling of Tumor Microenvironment and Early-Stage Lung Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
Study Design
2. Results
2.1. Patients’ Characteristics
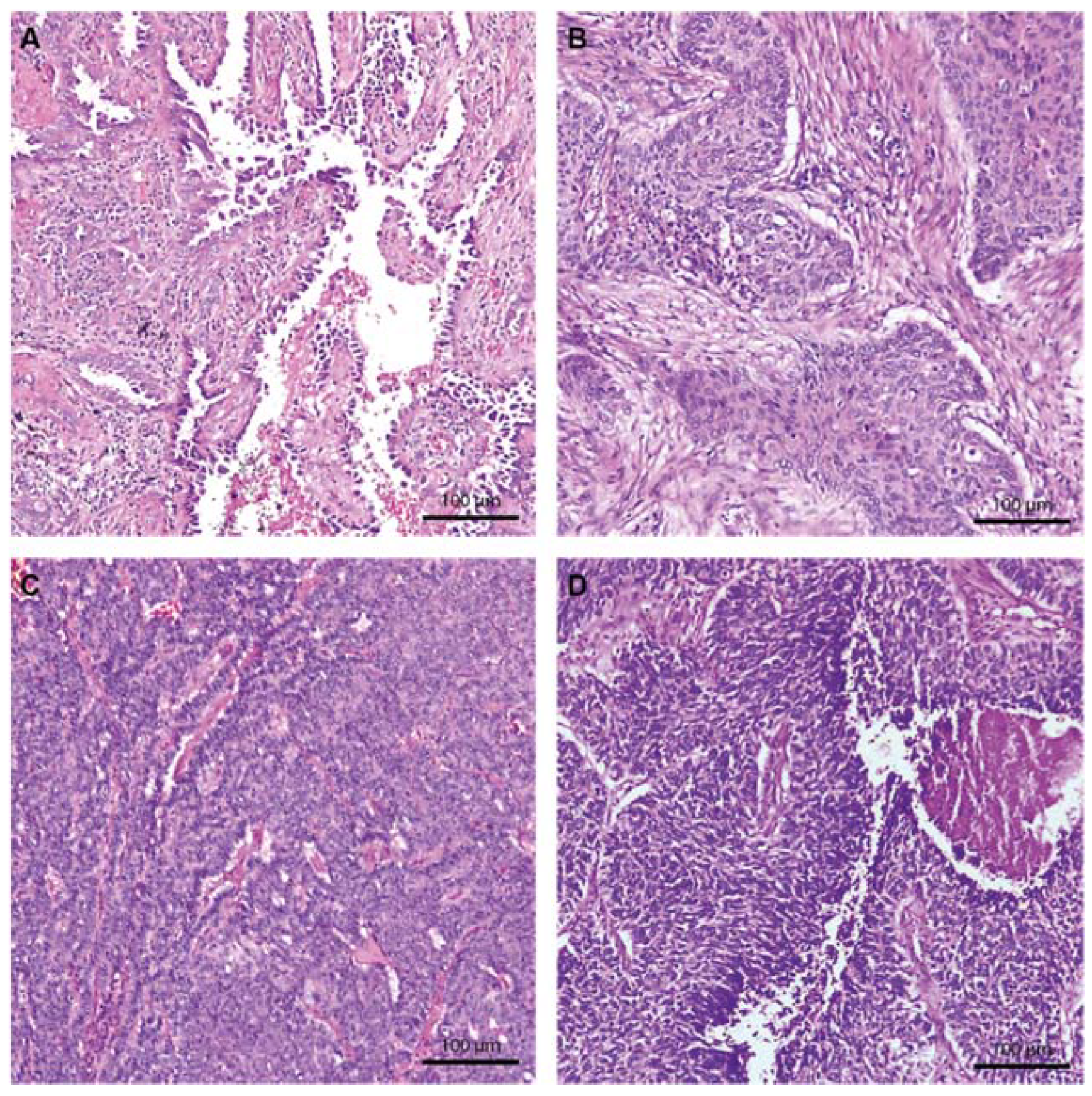
2.2. Morphologic Characteristics
2.3. Immunohistochemistry
2.4. Tumor Microenvironment
2.5. Bioinformatics Pipeline and In Silico Analysis
2.6. Validation of the Selected miRNA Panel on FFPE Tumor Tissue
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient Information
4.2. Baseline Data Collection
4.3. Morphological Characterization
4.4. Immunohistochemistry
4.5. Bioinformatics Analysis
4.6. RNA Extraction
4.7. cDNA and qRT-PCR
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schabath, M.B.; Cote, M.L. Cancer Progress and Priorities: Lung Cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Prev. Biomark. 2019, 28, 1563–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thandra, K.C.; Barsouk, A.; Saginala, K.; Aluru, J.S.; Barsouk, A. Epidemiology of Lung Cancer. Contemp. Oncol. 2021, 25, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.; Winslow, M.M.; Sage, J. Mechanisms of Small Cell Lung Cancer Metastasis. EMBO Mol. Med. 2021, 13, e13122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gierada, D.S.; Pinsky, P.F. Survival Following Detection of Stage I Lung Cancer by Screening in the National Lung Screening Trial. Chest 2021, 159, 862–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goebel, C.; Louden, C.L.; Mckenna, R.J.; Onugha, O.; Wachtel, A.; Long, T. Diagnosis of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer for Early Stage Asymptomatic Patients. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2019, 16, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, R.J.; Liu, B.; Krysan, K.; Dubinett, S.M. Lung Cancer and Immunity Markers. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. Publ. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. Cosponsored Am. Soc. Prev. Oncol. 2020, 29, 2423–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Xu, Z.; Marignani, P.A. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing for the Identification of Early-Stage Lung Cancer Biomarkers from Circulating Blood. NPJ Genomic Med. 2021, 6, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammerman, P.S.; Lawrence, M.S.; Voet, D.; Jing, R.; Cibulskis, K.; Sivachenko, A.; Stojanov, P.; McKenna, A.; Lander, E.S.; Gabriel, S.; et al. Comprehensive Genomic Characterization of Squamous Cell Lung Cancers. Nature 2012, 489, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collisson, E.A.; Campbell, J.D.; Brooks, A.N.; Berger, A.H.; Lee, W.; Chmielecki, J.; Beer, D.G.; Cope, L.; Creighton, C.J.; Danilova, L.; et al. Comprehensive Molecular Profiling of Lung Adenocarcinoma. Nature 2014, 511, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.; Lim, J.S.; Jang, S.J.; Cun, Y.; Ozretić, L.; Kong, G.; Leenders, F.; Lu, X.; Fernández-Cuesta, L.; Bosco, G.; et al. Comprehensive Genomic Profiles of Small Cell Lung Cancer. Nature 2015, 524, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebuzzi, S.E.; Zullo, L.; Rossi, G.; Grassi, M.; Murianni, V.; Tagliamento, M.; Prelaj, A.; Coco, S.; Longo, L.; Dal Bello, M.G.; et al. Novel Emerging Molecular Targets in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirlog, R.; Piton, N.; Lamy, A.; Guisier, F.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Sabourin, J.-C.; Marguet, F. Morphological and Molecular Characterization of KRAS G12C-Mutated Lung Adenocarcinomas. Cancers 2022, 14, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NEJM. Crizotinib versus Chemotherapy in Advanced ALK-Positive Lung Cancer. Available online: https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/nejmoa1214886 (accessed on 10 October 2021).
- NEJM. Gefitinib or Chemotherapy for Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer with Mutated EGFR. Available online: https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/nejmoa0909530 (accessed on 10 October 2021).
- Hong, D.S.; Fakih, M.G.; Strickler, J.H.; Desai, J.; Durm, G.A.; Shapiro, G.I.; Falchook, G.S.; Price, T.J.; Sacher, A.; Denlinger, C.S.; et al. KRASG12C Inhibition with Sotorasib in Advanced Solid Tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1207–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Z.; Xue, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, C.; Song, Y.; Qi, Y. The Role of Tumor Inflammatory Microenvironment in Lung Cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mlika, M.; Saidi, A.; Mejri, N.; Abdennadher, M.; Haddouchi, C.; Labidi, S.; Khiari, H.; Boussen, H.; Hsairi, M.; Mezni, F. Prognostic Impact of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinomas. Asian Cardiovasc. Thorac. Ann. 2021, 30, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushio, R.; Murakami, S.; Saito, H. Predictive Markers for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejarano, L.; Jordāo, M.J.C.; Joyce, J.A. Therapeutic Targeting of the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 933–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Antin, P.; Berx, G.; Blanpain, C.; Brabletz, T.; Bronner, M.; Campbell, K.; Cano, A.; Casanova, J.; Christofori, G.; et al. Guidelines and Definitions for Research on Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribatti, D.; Tamma, R.; Annese, T. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Cancer: A Historical Overview. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 13, 100773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsubara, T.; Tagawa, T.; Takada, K.; Toyokawa, G.; Shimokawa, M.; Kozuma, Y.; Akamine, T.; Haro, A.; Osoegawa, A.; Mori, M. Clinical and Prognostic Significance of the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Stage IA Lung Adenocarcinoma: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis. Clin. Lung Cancer 2019, 20, e504–e513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, G.-C.; Zhang, X.-P.; Wang, H.-E.; Wang, Z.-K.; Zhang, H.; Yu, L.; Xue, W.-F.; Xin, Z.-F.; Hu, Z.-H.; Zhao, Q.-T. Circulating Tumor Cells as a Screening and Diagnostic Marker for Early-Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 1931–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ancel, J.; Dewolf, M.; Deslée, G.; Nawrocky-Raby, B.; Dalstein, V.; Gilles, C.; Polette, M. Clinical Impact of the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Lung Cancer as a Biomarker Assisting in Therapeutic Decisions. Cells Tissues Organs 2022, 211, 91–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, H.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Shen, Y. Comprehensive Analysis of a Nine-Gene Signature Related to Tumor Microenvironment in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 700607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Peng, S.; Hu, H.; Wang, Y.; Shao, M.; Feng, G.; Liu, Y.; Bai, Y. Single-Cell Analysis Reveals Spatial Heterogeneity of Immune Cells in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 638374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Shao, Y.; He, W.; Hu, W.; Xu, Y.; Chen, J.; Wu, C.; Jiang, J. Prognostic Role of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 37, 1560–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Golpon, H.; Zardo, P.; Borlak, J. MiRNAs in Lung Cancer. A Systematic Review Identifies Predictive and Prognostic MiRNA Candidates for Precision Medicine in Lung Cancer. Transl. Res. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 2021, 230, 164–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliminejad, K.; Khorram Khorshid, H.R.; Soleymani Fard, S.; Ghaffari, S.H. An Overview of MicroRNAs: Biology, Functions, Therapeutics, and Analysis Methods. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 5451–5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.-L.; Tsai, Y.-M.; Lien, C.-T.; Kuo, P.-L.; Hung, A.J.-Y. The Roles of MicroRNA in Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Croce, C.M. The Role of MicroRNAs in Human Cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2016, 1, 15004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacFarlane, L.-A.; Murphy, P.R. MicroRNA: Biogenesis, Function and Role in Cancer. Curr. Genom. 2010, 11, 537–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Lin, X.; Ding, F. Role of MiRNA in Lung Cancer-Potential Biomarkers and Therapies. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 23, 5997–6010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Hu, N.; Cong, D.; Chen, K.; Li, J. MicroRNA-25-3p Promotes Cisplatin Resistance in Non-Small-Cell Lung Carcinoma (NSCLC) through Adjusting PTEN/PI3K/AKT Route. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 3219–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, T.; Liu, C.; Hou, J.; Shan, F. Hsa_circ_0043265 Suppresses Proliferation, Metastasis, EMT and Promotes Apoptosis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Through MiR-25-3p/FOXP2 Pathway. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 3867–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Du, Y.; Li, R.; Shen, A.; Liu, X.; Li, C.; Hu, B. MiR-29b-3p Increases Radiosensitivity in Stemness Cancer Cells via Modulating Oncogenes Axis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 741074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Wang, C. MiR-29b-3p Reverses Cisplatin Resistance by Targeting COL1A1 in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer A549/DDP Cells. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 2559–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, P.; Duan, P.; Shen, Y. MiR-29b Inhibits Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Progression by Targeting STRN4. Hum. Cell 2020, 33, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braicu, C.; Gulei, D.; Cojocneanu, R.; Raduly, L.; Jurj, A.; Knutsen, E.; Calin, G.A.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. MiR-181a/b Therapy in Lung Cancer: Reality or Myth? Mol. Oncol. 2019, 13, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop-Bica, C.; Pintea, S.; Cojocneanu-Petric, R.; Del Sal, G.; Piazza, S.; Wu, Z.-H.; Alencar, A.J.; Lossos, I.S.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Calin, G.A. MiR-181 Family-Specific Behavior in Different Cancers: A Meta-Analysis View. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2018, 37, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Ye, N.; Chen, Q.; Zheng, X.; Fang, M. MiR-181a Inhibits Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Proliferation by Targeting CDK1. Cancer Biomark. Sect. Dis. Markers 2017, 20, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulei, D.; Magdo, L.; Jurj, A.; Raduly, L.; Cojocneanu-Petric, R.; Moldovan, A.; Moldovan, C.; Florea, A.; Pasca, S.; Pop, L.-A.; et al. The Silent Healer: MiR-205-5p up-Regulation Inhibits Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Colon Cancer Cells by Indirectly up-Regulating E-Cadherin Expression. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.-L.; Zhang, J.-X.; Yang, J.-J.; Wei, Y.-B.; Peng, J.-F.; Fu, C.-J.; Huang, M.-H.; Wang, R.; Wang, P.-Y.; Sun, G.-B.; et al. MiR-205-5p Promotes Lung Cancer Progression and Is Valuable for the Diagnosis of Lung Cancer. Thorac. Cancer 2022, 13, 832–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, W.-X.; Zhang, M.-Y.; Li, R.; Liu, X.; Yin, Y.-H.; Qu, Y.-Q. Serum MiR-1228-3p and MiR-181a-5p as Noninvasive Biomarkers for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis. BioMed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, e9601876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulivi, P.; Petracci, E.; Marisi, G.; Baglivo, S.; Chiari, R.; Billi, M.; Canale, M.; Pasini, L.; Racanicchi, S.; Vagheggini, A.; et al. Prognostic Role of Circulating MiRNAs in Early-Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, D.; Chen, W.; Xin, Z.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xi, K.; Wang, G.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, D.; et al. Early Detection of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer by Using a 12-MicroRNA Panel and a Nomogram for Assistant Diagnosis. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-H.; Sun, S.-S.; Li, N.; Lv, P.; Xie, S.-Y.; Wang, P.-Y. MiR-205 as a Promising Biomarker in the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Lung Cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 91938–91949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Sun, L.; Zhou, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; She, M.; Chen, J. Diagnostic Value of MicroRNA-25 in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in Chinese Population. Medicine 2020, 99, e23425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Sharawat, S.K.; Ali, A.; Gaur, V.; Malik, P.S.; Kumar, S.; Mohan, A.; Guleria, R. Identification of Differentially Expressed Circulating Serum MicroRNA for the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Indian Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2020, 44, 100540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, L.; Lu, S. LncRNA H19 Promotes Viability and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells by Targeting MiR-29b-3p and Modifying STAT3. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 54, 929–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Li, H. MiRNAs as Biomarkers and for the Early Detection of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, 3119–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gkogkou, P.; Peponi, E.; Ntaskagiannis, D.; Murray, S.; Demou, A.; Sainis, I.; Ioakeim, E.; Briasoulis, E.; Tsekeris, P. E-Cadherin and Syndecan-1 Expression in Patients With Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treated With Chemoradiotherapy. In Vivo 2020, 34, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, Y.K.; Chang, S.; Ko, T.; Anker, J.; Agte, S.; Iams, W.; Choi, W.M.; Lee, K.; Cruz, M. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) Signature Is Inversely Associated with T-Cell Infiltration in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Liu, T.; Wang, Z. Analysis of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Microenvironment Indicates Preponderance of T Cell Exhaustion Marker Expression. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 360, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Rao, X.; Lin, W. Immune Landscape and a Promising Immune Prognostic Model Associated with TP53 in Early-Stage Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 806–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintanal-Villalonga, Á.; Mediano, M.; Ferrer, I.; Meléndez, R.; Carranza-Carranza, A.; Suárez, R.; Carnero, A.; Molina-Pinelo, S.; Paz-Ares, L. Histology-Dependent Prognostic Role of PERK and P53 Protein Levels in Early-Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 19945–19960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iggo, R.; Bartek, J.; Lane, D.; Gatter, K.; Harris, A.L.; Bartek, J. Increased Expression of Mutant Forms of P53 Oncogene in Primary Lung Cancer. Lancet 1990, 335, 675–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.-H.; Lee, H.S.; Park, J.-H.; Choi, J.-H.; Jang, S.-H.; Park, Y.-B.; Lee, M.G.; Hyun, I.G.; Kim, K.I.; Kim, H.S.; et al. Prognostic Role of P53 and Ki-67 Immunohistochemical Expression in Patients with Surgically Resected Lung Adenocarcinoma: A Retrospective Study. J. Thorac. Dis. 2015, 7, 822–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venhuizen, J.-H.; Jacobs, F.J.C.; Span, P.N.; Zegers, M.M. P120 and E-Cadherin: Double-Edged Swords in Tumor Metastasis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 60, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubrey, B.J.; Kelly, G.L.; Janic, A.; Herold, M.J.; Strasser, A. How Does P53 Induce Apoptosis and How Does This Relate to P53-Mediated Tumour Suppression? Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saifi, M.; Maran, A.; Raynaud, P.; Picot, M.C.; Quittet, P.; Cartron, G.; Rossi, J.F.; Costes, V. High Ratio of Interfollicular CD8/FOXP3-Positive Regulatory T Cells Is Associated with a High FLIPI Index and Poor Overall Survival in Follicular Lymphoma. Exp. Ther. Med. 2010, 1, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Meng, X.; Gao, Y.; Yang, L.; Jing, H.; Teng, F.; Huang, Z.; Xing, L. Immune Microenvironment Differences Between Squamous and Non-Squamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Their Influence on the Prognosis. Clin. Lung Cancer 2019, 20, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Qi, C.; Qin, B.; Kang, X.; Hu, Y.; Han, W. Immune-Stromal Score Signature: Novel Prognostic Tool of the Tumor Microenvironment in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Tian, S.; Sun, J.; Zhang, J.; Lin, L.; Hu, C. The Presence of Tumour-Infiltrating Lymphocytes (TILs) and the Ratios between Different Subsets Serve as Prognostic Factors in Advanced Hypopharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veatch, J.R.; Simon, S.; Riddell, S.R. Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes Make Inroads in Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1339–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynders, K.; De Ruysscher, D. Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Lung Cancer: A New Prognostic Parameter. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, E833–E835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Li, H.; Liu, C.; Xiang, X.; Wang, S.; Wu, A.; Shen, Y.; Li, G. Prognostic Value of the Common Tumour-Infiltrating Lymphocyte Subtypes for Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, S.M.; Klampatsa, A.; Thompson, J.C.; Martinez, M.C.; Hwang, W.-T.; Rao, A.S.; Standalick, J.E.; Kim, S.; Cantu, E.; Litzky, L.A.; et al. Function of Human Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Early-Stage Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 896–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.S.; Cheah, Y.K. The Interplay between MicroRNAs and Cellular Components of Tumour Microenvironment (TME) on Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Progression. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, e3046379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogiya, R.; Niikura, N.; Kumaki, N.; Bianchini, G.; Kitano, S.; Iwamoto, T.; Hayashi, N.; Yokoyama, K.; Oshitanai, R.; Terao, M.; et al. Comparison of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes between Primary and Metastatic Tumors in Breast Cancer Patients. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 1730–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germain, C.; Gnjatic, S.; Tamzalit, F.; Knockaert, S.; Remark, R.; Goc, J.; Lepelley, A.; Becht, E.; Katsahian, S.; Bizouard, G.; et al. Presence of B Cells in Tertiary Lymphoid Structures Is Associated with a Protective Immunity in Patients with Lung Cancer. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 189, 832–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barmpoutis, P.; Capite, M.D.; Kayhanian, H.; Waddingham, W.; Alexander, D.C.; Jansen, M.; Kwong, F.N.K. Tertiary Lymphoid Structures (TLS) Identification and Density Assessment on H&E-Stained Digital Slides of Lung Cancer. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquelot, N.; Tellier, J.; Nutt, S.I.; Belz, G.T. Tertiary Lymphoid Structures and B Lymphocytes in Cancer Prognosis and Response to Immunotherapies. Oncoimmunology 2021, 10, 1900508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goc, J.; Germain, C.; Vo-Bourgais, T.K.D.; Lupo, A.; Klein, C.; Knockaert, S.; de Chaisemartin, L.; Ouakrim, H.; Becht, E.; Alifano, M.; et al. Dendritic Cells in Tumor-Associated Tertiary Lymphoid Structures Signal a Th1 Cytotoxic Immune Contexture and License the Positive Prognostic Value of Infiltrating CD8+ T Cells. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz-Erazo, L.; Rhodes, J.L.; Marion, V.C.; Kemp, R.A. Tertiary Lymphoid Structures in Cancer—Considerations for Patient Prognosis. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuminello, S.; Veluswamy, R.; Lieberman-Cribbin, W.; Gnjatic, S.; Petralia, F.; Wang, P.; Flores, R.; Taioli, E. Prognostic Value of Immune Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment of Early-Stage Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 7142–7155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Wang, H.; Yao, X.; Zhang, D.; Xie, Y.; Cui, R.; Zhang, X. Circulating MicroRNAs in Cancer: Potential and Challenge. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerukala Sathipati, S.; Ho, S.-Y. Identifying the MiRNA Signature Associated with Survival Time in Patients with Lung Adenocarcinoma Using MiRNA Expression Profiles. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, G.; Wu, J.-H.; Jiang, C.-P. Diverse Roles of MiR-29 in Cancer (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 1509–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Vescovo, V.; Grasso, M.; Barbareschi, M.; Denti, M.A. MicroRNAs as Lung Cancer Biomarkers. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 5, 604–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Fei, S.; Chen, D.; Cai, X.; Liu, L.; Lin, B.; Su, H.; Zhao, L.; et al. Evaluation of Tumor-Derived Exosomal MiRNA as Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers for Early-Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Using Next-Generation Sequencing. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 5311–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Ding, M.; Duan, X.; Feng, X.; Wang, P.; Jiang, Q.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yu, S.; Yao, W.; et al. Diagnostic Value of Plasma MicroRNAs for Lung Cancer Using Support Vector Machine Model. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 5090–5098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, Q.; Fan, T.; Zhang, B.; Wang, W.; Xu, Y.; Hu, H. Five MicroRNAs in Plasma as Novel Biomarkers for Screening of Early-Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Respir. Res. 2014, 15, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azimi, S.A.; Sadegh Nia, H.R.; Mosavi Jarrahi, A.; Jamaati, H.R.; Kazempour Dizaji, M.; Dargahi, H.; Bahrami, N.; Pasdar, A.; Khosravi, A.; Bahrami, N.; et al. Ectopic Expression of MiRNA-21 and MiRNA-205 in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Cancer Manag. 2019, 12, e85456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Guo, Q.; Fu, F.-J.; Wang, Z.; Yin, Z.; Wei, Y.-B.; Yang, J.-R. The Role of MiR-29b in Cancer: Regulation, Function, and Signaling. OncoTargets Ther. 2015, 8, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, A.H.; Jacobson, K.A.; Rose, J.; Zeller, R. Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining of Tissue and Cell Sections. CSH Protoc. 2008, 2008, pdb.prot4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travis, W.D.; Brambilla, E.; Burke, A.P.; Marx, A.; Nicholson, A.G. WHO Classification of Tumours of the Lung, Pleura, Thymus and Heart; Organisation Mondiale de la Santé, Centre International de Recherche sur le Cancer, Eds.; World Health Organization Classification of Tumours; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2015; ISBN 978-92-832-2436-5. [Google Scholar]
- Konukiewitz, B.; Schlitter, A.M.; Jesinghaus, M.; Pfister, D.; Steiger, K.; Segler, A.; Agaimy, A.; Sipos, B.; Zamboni, G.; Weichert, W.; et al. Somatostatin Receptor Expression Related to TP53 and RB1 Alterations in Pancreatic and Extrapancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms with a Ki67-Index above 20%. Mod. Pathol. 2017, 30, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Siklenka, K.; Arora, S.K.; Ribeiro, P.; Kimmins, S.; Xia, J. MiRNet—Dissecting MiRNA-Target Interactions and Functional Associations through Network-Based Visual Analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W135–W141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachos, I.S.; Zagganas, K.; Paraskevopoulou, M.D.; Georgakilas, G.; Karagkouni, D.; Vergoulis, T.; Dalamagas, T.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.G. DIANA-MiRPath v3.0: Deciphering MicroRNA Function with Experimental Support. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W460–W466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-H.; Liu, S.; Zhou, H.; Qu, L.-H.; Yang, J.-H. StarBase v2.0: Decoding MiRNA-CeRNA, MiRNA-NcRNA and Protein-RNA Interaction Networks from Large-Scale CLIP-Seq Data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D92–D97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Chiorean, R.; Braicu, C.; Florian, I.S.; Leucuta, D.; Crisan, D.; Cocis, A.; Balacescu, O.; Irimie, A. Quantitative MRNA Expression of Genes Involved in Angiogenesis, Coagulation and Inflammation in Multiforme Glioblastoma Tumoral Tissue versus Peritumoral Brain Tissue: Lack of Correlation with Clinical Data. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2012, 23, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Parameter | LUAD | LUSC | NE LC | Total | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 22) | (n = 21) | (n = 8) | |||
| Sex | 0.0615 | ||||
| F | 6 (27.3%) | 2 (9.5%) | 4 (50%) | 12 (23.5%) | |
| M | 16 (72.7%) | 19 (90.5%) | 4 (50%) | 39 (76.5%) | |
| 5-year survival | 0.7485 | ||||
| Deceased | 8 (36.4%) | 6 (28.6%) | 2 (25%) | 16 (31.4%) | |
| Alive | 14 (63.6%) | 15 (71.4%) | 6 (75%) | 35 (68.6%) | |
| Pathological stage | 0.9821 | ||||
| IA | 11 (50%) | 9 (42.9% | 4 (50%) | 24 (47%) | |
| IB | 8 (36.4%) | 8 (38.1%) | 3 (37.5%) | 19 (37.3%) | |
| IIA | 3 (13.6%) | 4 (19%) | 1 (12.5%) | 8 (15.7%) | |
| pT stage | 0.9831 | ||||
| pT1a | 6 (27.3%) | 6 (28.6%) | 3 (37.5%) | 15 (29.4%) | |
| pT1b | 5 (22.7%) | 3 (14.3%) | 1 (12.5%) | 9 (17.6%) | |
| pT2a | 8 (36.4%) | 8 (38.1%) | 3 (37.5%) | 19 (37.3%) | |
| pT2b | 3 (13.6%) | 4 (19%) | 1 (12.5%) | 8 (15.7%) | |
| Differentiation grade | <0.0001 **** | ||||
| Well-differentiated (G1) | 4 (18.2%) | 0 (0%) | 5 (62.5%) | 9 (17.6%) | |
| Moderately differentiated (G2) | 9 (40.9%) | 10 (47.6%) | 0 (0%) | 19 (37.3%) | |
| Poorly differentiated (G3) | 9 (40.9%) | 11 (52.4%) | 1 (12.5%) | 21 (41.2%) | |
| Undifferentiated (G4) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (25%) | 2 (3.9%) | |
| Intratumor necrosis | 0.003 ** | ||||
| Absent | 8 (36.4%) | 0 (0%) | 4 (50%) | 12 (36.4%) | |
| Present | 14 (63.6%) | 21 (100%) | 4 (50%) | 39 (63.6%) | |
| Nuclear Atypia | 0.026 * | ||||
| Absent | 15 (68.2%) | 8 (38.1%) | 7 (87.5%) | 30 (58.8%) | |
| Present | 7 (31.8%) | 13 (61.9%) | 1 (12.5%) | 21 (41.2%) | |
| Stromal TILs | <0.0001 **** | ||||
| Low | 2 (9.1%) | 1 (4.8%) | 7 (87.5%) | 10 (19.6%) | |
| Moderate | 12 (54.5%) | 10 (47.6%) | 1 (12.5%) | 23 (45.1%) | |
| High | 8 (36.4%) | 10 (47.6%) | 0 (0%) | 18 (35.3%) | |
| Intratumor TILs | 0.021 * | ||||
| Absent | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (25%) | 2 (3.9%) | |
| Low | 19 (86.4%) | 17 (81%) | 5 (62.5%) | 41 (80.4%) | |
| Moderate | 3 (13.6%) | 4 (19%) | 1 (12.5%) | 8 (15.7%) | |
| Tertiary lymphoid structures | 0.2146 | ||||
| Absent | 5 (22.7%) | 4 (19%) | 4 (50%) | 13 (25.5%) | |
| Present | 17 (77.3%) | 17 (81%) | 4 (50%) | 38 (74.5%) | |
| Active germinative centers | 0.3231 | ||||
| Absent | 9 (52.9%) | 13 (76.5%) | 3 (75%) | 25 (65.8%) | |
| Present | 8 (47.1%) | 4 (23.5%) | 1 (25%) | 13 (34.2%) | |
| Stromal CD4 TILs | <0.0001 **** | ||||
| Low | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 4 (50%) | 4 (7.8%) | |
| Moderate | 0 (0%) | 2 (9.5%) | 2 (25%) | 4 (7.8%) | |
| High | 14 (63.6%) | 13 (61.9%) | 1 (12.5%) | 28 (54.9%) | |
| Very High | 8 (36.4%) | 6 (28.6%) | 1 (12.5%) | 15 (29.5%) | |
| Intratumor CD4 TILs | 0.1011 | ||||
| Absent | 12 (54.5%) | 8 (38.1%) | 7 (87.5%) | 27 (53%) | |
| Low | 8 (36.4%) | 11 (52.4%) | 1 (12.5%) | 20 (39.2%) | |
| Moderate | 0 (0%) | 2 (9.5%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (3.9%) | |
| High | 2 (9.1%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (3.9%) | |
| Stromal CD8 | 0.0615 | ||||
| Absent | 0 (0%) | 1 (4.8%) | 2 (25%) | 3 (5.9%) | |
| Low | 7 (31.8%) | 6 (28.6%) | 3 (37.5%) | 16 (31.4%) | |
| Moderate | 9 (40.9%) | 5 (23.8%) | 3 (37.5%) | 17 (33.3%) | |
| High | 6 (27.3%) | 9 (42.8%) | 0 (0%) | 15 (29.4%) | |
| Intratumor CD8 TILs | 0.2261 | ||||
| Absent | 12 (54.5%) | 6 (28.6%) | 6 (75%) | 24 (47%) | |
| Low | 7 (31.8%) | 12 (57.1%) | 1 (12.5%) | 20 (39.2%) | |
| Moderate | 2 (9.1%) | 3 (14.3%) | 1 (12.5%) | 6 (11.8%) | |
| High | 1 (4.5%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (2%) | |
| E-cadherin | 0.6692 | ||||
| Moderate intensity (2+) | 14 (63.6%) | 12 (57.1%) | 6 (75%) | 32 (62.7%) | |
| High Intensity (3+) | 8 (36.4%) | 9 (42.9%) | 2 (25%) | 19 (37.3%) | |
| p53 | 0.1401 | ||||
| Absent | 9 (40.9%) | 5 (23.8%) | 5 (62.5%) | 19 (37.3%) | |
| Positive | 13 (59.1%) | 16 (76.2%) | 3 (37.5%) | 32 (62.7%) |
| miRNA | Regulation Status TCGA | Roles in Cancer | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| hsa-miR-25-3p | ↑ LUSC, ↑ LUAD | OncomiR, EMT activation through PTEN & FOXP2. | [36,37] |
| hsa-miR-29b-3p | ↑ LUAD | Tumor suppressor miRNA, EMT pathway, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy resistance. | [38,39,40] |
| hsa-miR-181a-5p | ↓ LUSC, ↓ LUAD | Tumor suppressor miRNA, EMT pathway, angiogenesis, proliferation. | [41,42,43] |
| hsa-miR-205-5p | ↑ LUSC, ↑ LUAD | OncomiR, TP53IN1 targeting, EMT pathway, proliferation, metastasis, | [44,45] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pirlog, R.; Chiroi, P.; Rusu, I.; Jurj, A.M.; Budisan, L.; Pop-Bica, C.; Braicu, C.; Crisan, D.; Sabourin, J.-C.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. Cellular and Molecular Profiling of Tumor Microenvironment and Early-Stage Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105346
Pirlog R, Chiroi P, Rusu I, Jurj AM, Budisan L, Pop-Bica C, Braicu C, Crisan D, Sabourin J-C, Berindan-Neagoe I. Cellular and Molecular Profiling of Tumor Microenvironment and Early-Stage Lung Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(10):5346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105346
Chicago/Turabian StylePirlog, Radu, Paul Chiroi, Ioana Rusu, Ancuta Maria Jurj, Liviuta Budisan, Cecilia Pop-Bica, Cornelia Braicu, Doinita Crisan, Jean-Christophe Sabourin, and Ioana Berindan-Neagoe. 2022. "Cellular and Molecular Profiling of Tumor Microenvironment and Early-Stage Lung Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 10: 5346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105346
APA StylePirlog, R., Chiroi, P., Rusu, I., Jurj, A. M., Budisan, L., Pop-Bica, C., Braicu, C., Crisan, D., Sabourin, J.-C., & Berindan-Neagoe, I. (2022). Cellular and Molecular Profiling of Tumor Microenvironment and Early-Stage Lung Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(10), 5346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105346










