A Novel Human Neutralizing mAb Recognizes Delta, Gamma and Omicron Variants of SARS-CoV-2 and Can Be Used in Combination with Sotrovimab
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Epitope Mapping of D3 on Spike of SARS-CoV-2 by Testing Its Binding to Different Peptides Derived from the RBD Domain
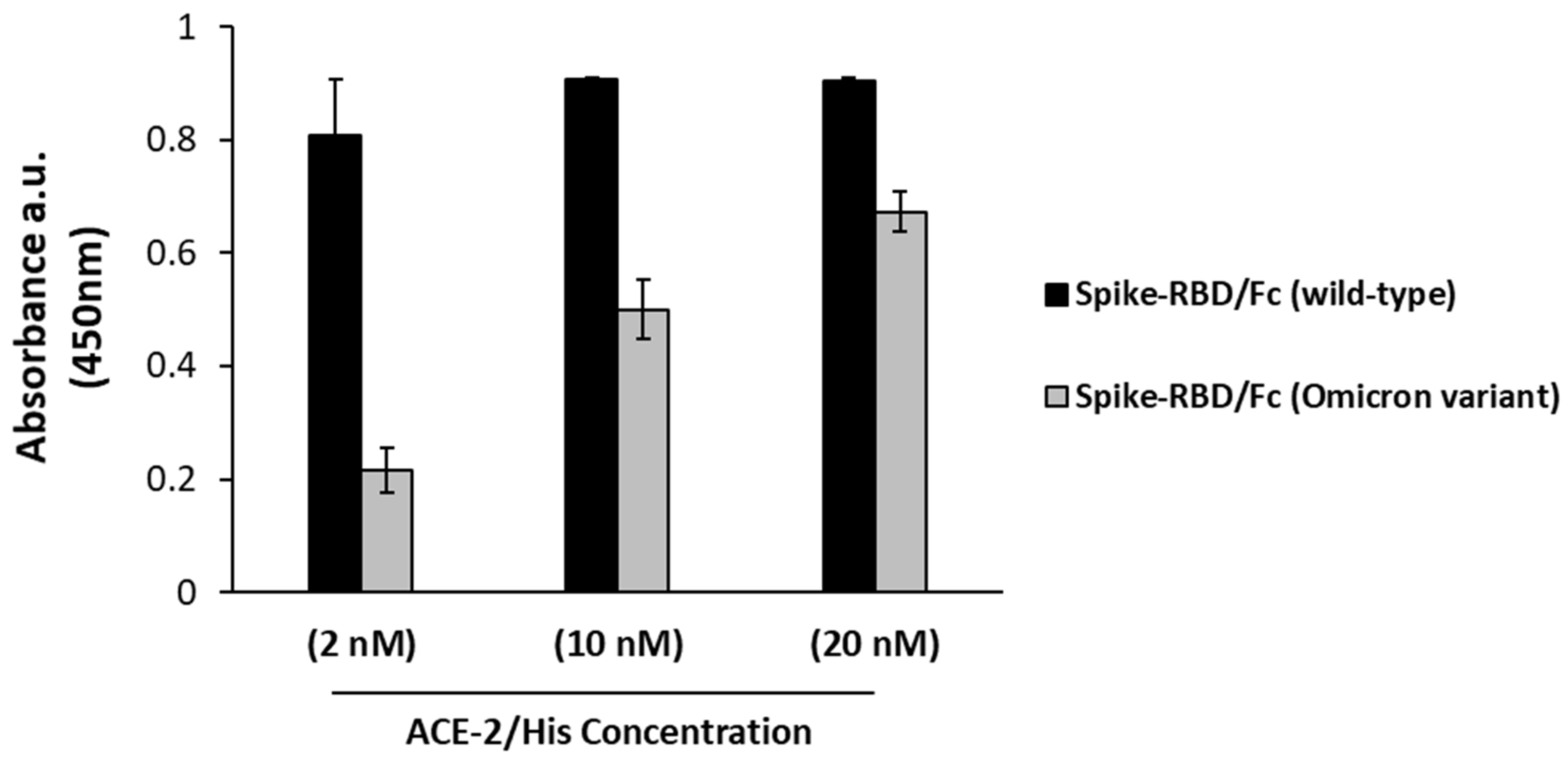
2.2. Binding of D3 to Recombinant RBD of Omicron Variant
2.3. Comparison of Binding to Omicron Variant of D3 and Other Therapeutic mAbs in Clinical Use
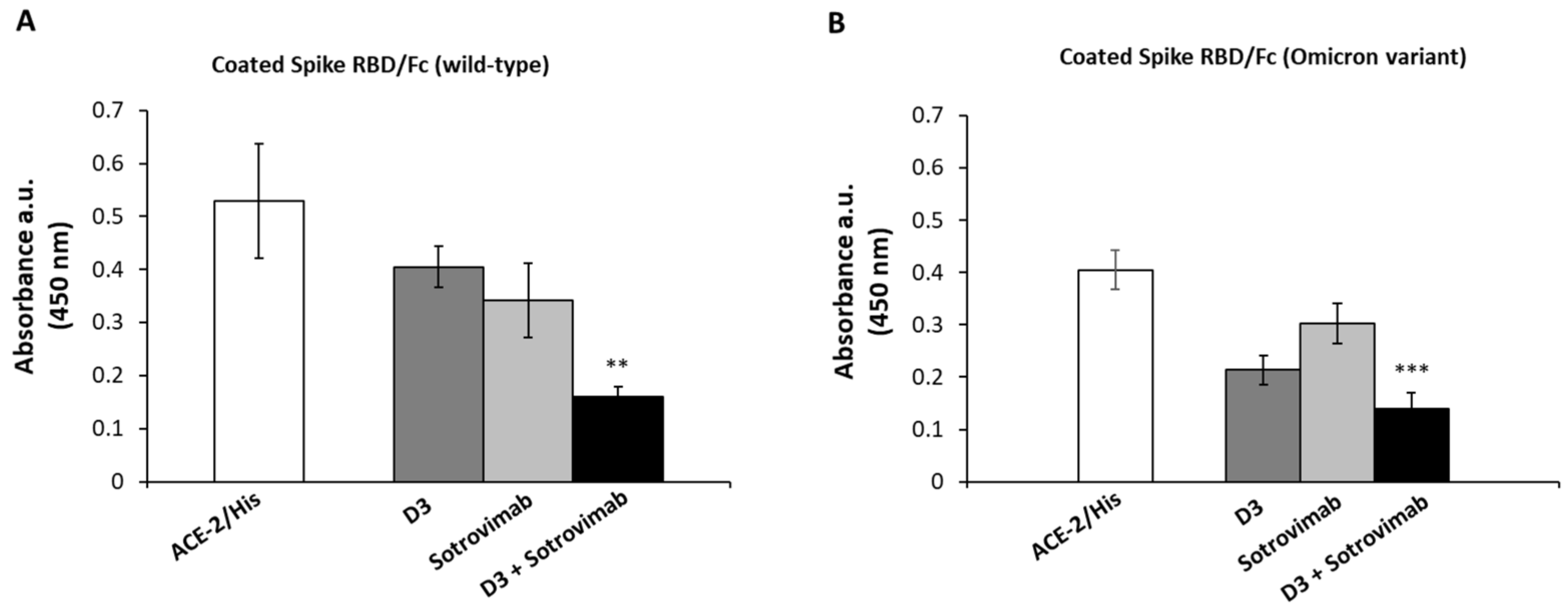
2.4. Competitive ELISA Assays to Verify Whether D3 and Sotrovimab mAbs Recognize Different Epitopes
2.5. SARS-CoV-2 Variants Neutralization by the Novel Human mAb D3
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Antibodies and Human Recombinant Proteins
4.2. ELISA Assays
4.2.1. Binding of D3 and ACE-2 to Spike-RBD Peptides
4.2.2. Binding of ACE-2 Receptor to Wild-Type or BA.1 Omicron Variant of Spike-RBD
4.2.3. Binding of mAbs to Spike-RBD from Wild-Type SARS-CoV-2 or Its BA.1 Omicron Variant
4.3. Competitive ELISA Assays of Biotinylated Sotrovimab
4.4. Interference Assays in Spike/ACE-2 Interaction
4.5. Cell Cultures
4.6. In Vitro Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Variants by D3 mAb
4.7. RNA Extraction and qPCR
- ○
- cDNA reactions: 25 °C for 5 min and 42 °C for 30 min;
- ○
- Heat-inactivation: 85 °C for 5 min;
- ○
- Hold stage: 4 °C.
- ○
- Hold stage: 50 °C for 2 min;
- ○
- Denaturation Step: 95 °C for 10 min;
- ○
- Denaturation and Annealing (×45 cycles): 95 °C for 15 s and 60 °C for 60 s;
- ○
- Melt curve stage: 95 °C for 15 s, 60 °C for 1 min and 95 °C for 15 s.
4.8. Docking Analyses
4.9. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, N.; Zhou, M.; Dong, X.; Qu, J.; Gong, F.; Han, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.; et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study. Lancet 2020, 395, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, D.D.; Sharma, A.; Lee, H.J.; Yadav, D.K. SARS-CoV-2: Recent Variants and Clinical Efficacy of Antibody-Based Therapy. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 839170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.J.; Nikolaienko, S.I.; Dibrova, V.A.; Dibrova, Y.V.; Vasylyk, V.M.; Novikov, M.Y.; Shults, N.V.; Gychka, S.G. SARS-CoV-2 spike protein-mediated cell signaling in lung vascular cells. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2021, 137, 106823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.D.; Han, I.; Choi, E.H.; Yadav, D.K. Recent Advances in Pathophysiology, Drug Development and Future Perspectives of SARS-CoV-2. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 580202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.D.; Han, I.; Choi, E.H.; Yadav, D.K. Immunopathology, host-virus genome interactions, and effective vaccine development in SARS-CoV-2. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 3774–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, S.; Li, K.; Shen, J.; Liu, S.; Liu, J.; Yang, L.; Hu, C.D.; Wan, J. GESS: A database of global evaluation of SARS-CoV-2/hCoV-19 sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D706–D714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Carballa, A.; Bello, X.; Pardo-Seco, J.; Martinón-Torres, F.; Salas, A. Mapping genome variation of SARS-CoV-2 worldwide highlights the impact of COVID-19 super-spreaders. Genome Res. 2020, 30, 1434–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyranoski, D. Alarming COVID variants show vital role of genomic surveillance. Nature 2021, 589, 337–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccia, A.; Tufano, R.; Ferrucci, V.; Sepe, L.; Bianchi, M.; Pascarella, S.; Zollo, M.; Paolella, G. SARS-CoV-2 pandemic tracing in Italy highlights lineages with mutational burden in growing subsets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Berger, N.A.; Kaelber, D.C.; Davis, P.B.; Volkow, N.D.; Xu, R. COVID infection rates, clinical outcomes, and racial/ethnic and gender disparities before and after Omicron emerged in the US. medRxiv, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasoba, D.; Kimura, I.; Nasser, H.; Morioka, Y.; Nao, N.; Ito, J.; Uriu, K.; Tsuda, M.; Zahradnik, J.; Shirakawa, K.; et al. Virological characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 BA.2 variant. bioRxiv, 2022; S0092-8674, 00533-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wei, G.W. Omicron BA.2 (B.1.1.529.2): High potential to becoming the next dominating variant. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 3840–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, R.; Gilby, N.B.; Wei, G.W. Omicron variant (B.1.1.529): Infectivity, vaccine breakthrough, and antibody resistance. J. Chem. Inf. Modeling 2022, 62, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, M.I.; MacGowan, S.A.; Kutuzov, M.A.; Dushek, O.; Barton, G.J.; van der Merwe, P.A. Effects of common mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD and its ligand, the human ACE2 receptor on binding affinity and kinetics. ELife 2021, 10, e70658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano, N.; Froechlich, G.; Lazarevic, D.; Passariello, M.; Nicosia, A.; De Lorenzo, C.; Morelli, M.J.; Sasso, E. High-Throughput Monoclonal Antibody Discovery from Phage Libraries: Challenging the Current Preclinical Pipeline to Keep the Pace with the Increasing mAb Demand. Cancers 2022, 14, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Cao, R.; Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Liu, J.; Xu, M.; Shi, Z.; Hu, Z.; Zhong, W.; Xiao, G. Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreano, E.; Nicastri, E.; Paciello, I.; Pileri, P.; Manganaro, N.; Piccini, G.; Manenti, A.; Pantano, E.; Kabanova, A.; Troisi, M.; et al. Extremely potent human monoclonal antibodies from COVID-19 convalescent patients. Cell 2021, 184, 1821–1835.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SARS-CoV-2 Variants & Therapeutics: Therapeutic Activity Explorer; National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2022. Available online: https://opendata.ncats.nih.gov/variant/activity/singlemutationvariant (accessed on 6 April 2022).
- Hoffmann, M.; Krüger, N.; Schulz, S.; Cossmann, A.; Rocha, C.; Kempf, A.; Nehlmeier, I.; Graichen, L.; Moldenhauer, A.-S.; Winkler, M.S.; et al. The Omicron variant is highly resistant against antibody-mediated neutralization: Implications for control of the COVID-19 pandemic. Cell 2022, 185, 447–456.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mader, A.L.; Tydykov, L.; Glück, V.; Bertok, M.; Weidlich, T.; Gottwald, C.; Stefl, A.; Vogel, M.; Plentz, A.; Köstler, J.; et al. Omicron’s binding to sotrovimab, casirivimab, imdevimab, CR3022, and sera from previously infected or vaccinated individuals. IScience 2022, 25, 104076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaa, A.L.; Julia, L.M.; Manar, A.; Ginger, T.; Marco, C.; Emily, H.; Jerry, Z.; Mark, Z.; Emory, H.; Nate, M.; et al. BA.2 Lineage Report. Available online: https://outbreak.info/situation-reports?pango=BA.2&%3Bloc=USA&%3Bloc=USA_US%20CA&%3Bselected=Worldwide&%3Boverlay=false,%20Accessed%205%20April%202022%3B (accessed on 6 April 2022).
- Passariello, M.; Gentile, C.; Ferrucci, V.; Sasso, E.; Vetrei, C.; Fusco, G.; Viscardi, M.; Brandi, S.; Cerino, P.; Zambrano, N.; et al. Novel human neutralizing mAbs specific for Spike-RBD of SARS-CoV-2. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passariello, M.; Vetrei, C.; Amato, F.; De Lorenzo, C. Interactions of Spike-RBD of SARS-CoV-2 and Platelet Factor 4: New Insights in the Etiopathogenesis of Thrombosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavazzoni, P. Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA Limits Use of Certain Monoclonal Antibodies to Treat COVID-19 Due to the Omicron Variant. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-limits-use-certain-monoclonal-antibodies-treat-covid-19-due-omicron (accessed on 7 April 2022).
- Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Jian, F.; Xiao, T.; Song, W.; Yisimayi, A.; Huang, W.; Li, Q.; Wang, P.; An, R.; et al. Omicron escapes the majority of existing SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies. Nature 2022, 602, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colson, P.; Delerce, J.; Marion-Paris, E.; Lagier, J.C.; Levasseur, A.; Fournier, P.E.; La Scola, B.; Raoult, D. A 21L/BA.2-21K/BA.1 “MixOmicron” SARS-CoV-2 hybrid undetected by qPCR that screen for variant in routine diagnosis. medRxiv, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potential BA.1/BA.2 Recombinant Lineage with Likely Breakpoint at NSP5/NSP6 (267 Sequences in the UK and Ireland). Available online: https://github.com/cov-lineages/pango-designation/issues/454 (accessed on 7 April 2022).
- Sasso, E.; D’Avino, C.; Passariello, M.; D’Alise, A.M.; Siciliano, D.; Esposito, M.L.; Froechlich, G.; Cortese, R.; Scarselli, E.; Zambrano, N.; et al. Massive parallel screening of phage libraries for the generation of repertoires of human immunomodulatory monoclonal antibodies. MAbs 2018, 10, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passariello, M.; Camorani, S.; Vetrei, C.; Cerchia, L.; De Lorenzo, C. Novel Human Bispecific Aptamer—Antibody Conjugates for Efficient Cancer Cell Killing. Cancers 2019, 11, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vetrei, C.; Passariello, M.; Froechlich, G.; Rapuano Lembo, R.; Zambrano, N.; De Lorenzo, C. Immunomodulatory mAbs as Tools to Investigate on Cis-Interaction of PD-1/PD-L1 on Tumor Cells and to Set Up Methods for Early Screening of Safe and Potent Combinatorial Treatments. Cancers 2021, 13, 2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borriello, M.; Laccetti, P.; Terrazzano, G.; D’Alessio, G.; De Lorenzo, C. A novel fully human antitumour immunoRNase targeting ErbB2-positive tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 104, 1716–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gelardi, T.; Damiano, V.; Rosa, R.; Bianco, R.; Cozzolino, R.; Tortora, G.; Laccetti, P.; D’Alessio, G.; De Lorenzo, C. Two novel human anti-ErbB2 immunoagents are active on trastuzumab-resistant tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferrucci, V.; Kong, D.Y.; Asadzadeh, F.; Marrone, L.; Boccia, A.; Siciliano, R.; Criscuolo, G.; Anastasio, C.; Quarantelli, F.; Comegna, M.; et al. Long-chain polyphosphates impair SARS-CoV-2 infection and replication. Sci. Signal. 2021, 14, eabe5040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrucci, V.; de Antonellis, P.; Quarantelli, F.; Asadzadeh, F.; Bibbò, F.; Siciliano, R.; Sorice, C.; Pisano, I.; Izzo, B.; Di Domenico, C.; et al. Loss of Detection of sgN Precedes Viral Abridged Replication in COVID-19-Affected Patients-A Target for SARS-CoV-2 Propagation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zollo, M.; Ferrucci, V.; Izzo, B.; Quarantelli, F.; Domenico, C.D.; Comegna, M.; Paolillo, C.; Amato, F.; Siciliano, R.; Castaldo, G.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Subgenomic N (sgN) Transcripts in Oro-Nasopharyngeal Swabs Correlate with the Highest Viral Load, as Evaluated by Five Different Molecular Methods. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Passariello, M.; Ferrucci, V.; Sasso, E.; Manna, L.; Lembo, R.R.; Pascarella, S.; Fusco, G.; Zambrano, N.; Zollo, M.; De Lorenzo, C. A Novel Human Neutralizing mAb Recognizes Delta, Gamma and Omicron Variants of SARS-CoV-2 and Can Be Used in Combination with Sotrovimab. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5556. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105556
Passariello M, Ferrucci V, Sasso E, Manna L, Lembo RR, Pascarella S, Fusco G, Zambrano N, Zollo M, De Lorenzo C. A Novel Human Neutralizing mAb Recognizes Delta, Gamma and Omicron Variants of SARS-CoV-2 and Can Be Used in Combination with Sotrovimab. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(10):5556. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105556
Chicago/Turabian StylePassariello, Margherita, Veronica Ferrucci, Emanuele Sasso, Lorenzo Manna, Rosa Rapuano Lembo, Stefano Pascarella, Giovanna Fusco, Nicola Zambrano, Massimo Zollo, and Claudia De Lorenzo. 2022. "A Novel Human Neutralizing mAb Recognizes Delta, Gamma and Omicron Variants of SARS-CoV-2 and Can Be Used in Combination with Sotrovimab" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 10: 5556. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105556
APA StylePassariello, M., Ferrucci, V., Sasso, E., Manna, L., Lembo, R. R., Pascarella, S., Fusco, G., Zambrano, N., Zollo, M., & De Lorenzo, C. (2022). A Novel Human Neutralizing mAb Recognizes Delta, Gamma and Omicron Variants of SARS-CoV-2 and Can Be Used in Combination with Sotrovimab. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(10), 5556. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105556








