MYD88 Mutations: Transforming the Landscape of IgM Monoclonal Gammopathies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Signaling Pathway and Molecular Alterations
3. Clinical Applications
3.1. Diagnosis
3.2. Follow-Up
3.3. Prognosis
3.4. Treatment
3.5. Therapeutic Target
4. Current State-of-the-Art of MyD88
5. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Medzhitov, R.; Preston-Hurlburt, P.; Kopp, E.; Stadlen, A.; Chen, C.; Ghosh, S.; Janeway, C.A. MyD88 is an adaptor protein in the hToll/IL-1 receptor family signaling pathways. Mol. Cell 1998, 2, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, K.; Janssens, S.; Brissoni, B.; Olivos, N.; Beyaert, R.; Tschopp, J. Inhibition of interleukin 1 receptor/toll-like receptor signaling through the alternatively spliced, short form of MyD88 is due to its failure to recruit IRAK-4. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hardiman, G.; Jenkins, N.A.; Copeland, N.G.; Gilbert, D.J.; Garcia, D.K.; Naylor, S.L.; Kastelein, R.A.; Bazan, J.F. Genetic structure and chromosomal mapping of MyD88. Genomics 1997, 45, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzio, M.; Ni, J.; Feng, P.; Dixit, V.M. IRAK (Pelle) family member IRAK-2 and MyD88 as proximal mediators of IL-1 signaling. Science 1997, 278, 1612–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesche, H.; Henzel, W.J.; Shillinglaw, W.; Li, S.; Cao, Z. MyD88: An adapter that recruits IRAK to the IL-1 receptor complex. Immunity 1997, 7, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baeuerle, P.A.; Baltimore, D. Nf-κB: Ten years after. Cell 1996, 87, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grilli, M.; Chiu, J.J.S.; Lenardo, M.J. IMF-κB and Rel: Participants in a Multiform Transcriptional Regulatory System. Int. Rev. Cytol. 1993, 143, 1–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deguine, J.; Barton, G.M. MyD88: A central player in innate immune signaling. F1000Prime Rep. 2014, 6, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, P. The TLR and IL-1 signalling network at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127, 2383–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balka, K.R.; De Nardo, D. Understanding early TLR signaling through the Myddosome. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2019, 105, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treon, S.P.; Xu, L.; Yang, G.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Cao, Y.; Sheehy, P.; Manning, R.J.; Patterson, C.J.; Tripsas, C.; et al. MYD88 L265P somatic mutation in Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varettoni, M.; Arcaini, L.; Zibellini, S.; Boveri, E.; Rattotti, S.; Riboni, R.; Corso, A.; Orlandi, E.; Bonfichi, M.; Gotti, M.; et al. Prevalence and clinical significance of the MYD88 (L265P) somatic mutation in Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia and related lymphoid neoplasms. Blood 2013, 88, 2522–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, L.; Hunter, Z.R.; Yang, G.; Zhou, Y.; Cao, Y.; Liu, X.; Morra, E.; Trojani, A.; Greco, A.; Arcaini, L.; et al. MYD88 L265P in Waldenstrom’s Macroglobulinemia, IgM Monoclonal Gammopathy, and other B-cell Lymphoproliferative Disorders using Conventional and Quantitative Allele-Specific PCR. Blood 2013, 121, 2051–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulain, S.; Roumier, C.; Decambron, A.; Renneville, A.; Herbaux, C.; Bertrand, E.; Tricot, S.; Daudignon, A.; Galiègue-Zouitina, S.; Soenen, V.; et al. MYD88 L265P mutation in Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia. Blood 2013, 121, 4504–4511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, C.; Sebastián, E.; Chillón, M.C.; Giraldo, P.; Mariano Hernández, J.; Escalante, F.; González-López, T.J.; Aguilera, C.; García de Coca, A.; Murillo, I.; et al. MYD88 L265P is a marker highly characteristic of, but not restricted to, waldenström’s macroglobulinemia. Leukemia 2013, 27, 1722–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Castillo, J.J.; Advani, R.H.; Branagan, A.R.; Buske, C.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; D’Sa, S.; Kersten, M.J.; Leblond, V.; Minnema, M.C.; Owen, R.G.; et al. Consensus treatment recommendations from the tenth International Workshop for Waldenström Macroglobulinaemia. Lancet. Haematol. 2020, 7, e827–e837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Bernuth, H.; Picard, C.; Jin, Z.; Pankla, R.; Xiao, H.; Ku, C.L.; Chrabieh, M.; Ben Mustapha, I.; Ghandil, P.; Camcioglu, Y.; et al. Pyogenic bacterial infections in humans with MyD88 deficiency. Science 2008, 321, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loiarro, M.; Gallo, G.; Fantò, N.; De Santis, R.; Carminati, P.; Ruggiero, V.; Sette, C. Identification of critical residues of the MyD88 death domain involved in the recruitment of downstream kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 28093–28103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, S.C.; Lo, Y.C.; Wu, H. Helical assembly in the MyD88-IRAK4-IRAK2 complex in TLR/IL-1R signalling. Nature 2010, 465, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Owen, R.G.; Treon, S.P.; Al-Katib, A.; Fonseca, R.; Greipp, P.R.; McMaster, M.L.; Morra, E.; Pangalis, G.A.; San Miguel, J.F.; Branagan, A.R.; et al. Clinicopathological definition of Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia: Consensus panel recommendations from the Second International Workshop on Waldenstrom’s Macroglobulinemia. Semin. Oncol. 2003, 30, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyle, R.A.; Benson, J.T.; Larson, D.R.; Therneau, T.M.; Dispenzieri, A.; Kumar, S.; Melton, L.J.; Rajkumar, S.V. Progression in smoldering Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia: Long-term results. Blood 2012, 119, 4462–4466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morel, P.; Duhamel, A.; Gobbi, P.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Dhodapkar, M.V.; McCoy, J.; Crowley, J.; Ocio, E.M.; Garcia-Sanz, R.; Treon, S.P.; et al. International prognostic scoring system for Waldenström macroglobulinemia. Blood 2009, 113, 4163–4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ngo, V.N.; Young, R.M.; Schmitz, R.; Jhavar, S.; Xiao, W.; Lim, K.H.; Kohlhammer, H.; Xu, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, H.; et al. Oncogenically active MYD88 mutations in human lymphoma. Nature 2011, 470, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Puente, X.S.; Pinyol, M.; Quesada, V.; Conde, L.; Ordóñez, G.R.; Villamor, N.; Escaramis, G.; Jares, P.; Beà, S.; González-Díaz, M.; et al. Whole-genome sequencing identifies recurrent mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nature 2011, 475, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rousseau, S.; Martel, G. Gain-of-function mutations in the toll-like receptor pathway: TPL2-mediated ERK1/ERK2 MAPK activation, a path to tumorigenesis in lymphoid neoplasms? Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 4, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, G.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, L.; Cao, Y.; Manning, R.J.; Patterson, C.J.; Buhrlage, S.J.; Gray, N.; Tai, Y.-T.; et al. A mutation in MYD88 (L265P) supports the survival of lymphoplasmacytic cells by activation of Bruton tyrosine kinase in Waldenström macroglobulinemia. Blood 2013, 122, 1222–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.Q.; Jeelall, Y.S.; Humburg, P.; Batchelor, E.L.; Kaya, S.M.; Yoo, H.M.; Goodnow, C.C.; Horikawa, K. Synergistic cooperation and crosstalk between MYD88L265P and mutations that dysregulate CD79B and surface IgM. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 2759–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, W.H.; Young, R.M.; Schmitz, R.; Yang, Y.; Pittaluga, S.; Wright, G.; Lih, C.-J.J.; Williams, P.M.; Shaffer, A.L.; Gerecitano, J.; et al. Targeting B cell receptor signaling with ibrutinib in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 922–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, C.; Prieto-Conde, M.I.; García-Álvarez, M.; Alcoceba, M.; Escalante, F.; Chillón, M.D.C.; García de Coca, A.; Balanzategui, A.; Cantalapiedra, A.; Aguilar, C.; et al. Unraveling the heterogeneity of IgM monoclonal gammopathies: A gene mutational and gene expression study. Ann. Hematol. 2018, 97, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelan, J.D.; Young, R.M.; Webster, D.E.; Roulland, S.; Wright, G.W.; Kasbekar, M.; Shaffer, A.L.; Ceribelli, M.; Wang, J.Q.; Schmitz, R.; et al. A multiprotein supercomplex controlling oncogenic signalling in lymphoma. Nature 2018, 560, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munshi, M.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.G.; Xu, L.; Tsakmaklis, N.; Demos, M.G.; Kofides, A.; Guerrera, M.L.; Jimenez, C.; Chan, G.G.; et al. SYK is activated by mutated MYD88 and drives pro-survival signaling in MYD88 driven B-cell lymphomas. Blood Cancer J. 2020, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Argyropoulos, K.; Vogel, R.; Ziegler, C.; Altan-Bonnet, G.; Velardi, E.; Calafiore, M.; Dogan, A.; Arcila, M.; Patel, M.; Knapp, K.; et al. Clonal B cells in Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia exhibit functional features of chronic active B-cell receptor signaling. Leukemia 2016, 30, 1116–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, G.; Buhrlage, S.; Tan, L.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Xu, L.; Tsakmaklis, N.; Chen, J.G.; Patterson, C.J.; Brown, J.R.; et al. HCK is a survival determinant transactivated by mutated MYD88, and a direct target of ibrutinib. Blood 2016, 127, 3237–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lam, L.T.; Wright, G.; Davis, R.E.; Lenz, G.; Farinha, P.; Dang, L.; Chan, J.W.; Rosenwald, A.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Staudt, L.M. Cooperative signaling through the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 and nuclear factor-kκB pathways in subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2008, 111, 3701–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fukumura, K.; Kawazu, M.; Kojima, S.; Ueno, T.; Sai, E.; Soda, M.; Ueda, H.; Yasuda, T.; Yamaguchi, H.; Lee, J.; et al. Genomic characterization of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraan, W.; Van Keimpema, M.; Horlings, H.M.; Schilder-Tol, E.J.M.; Oud, M.E.C.M.; Noorduyn, L.A.; Kluin, P.M.; Kersten, M.J.; Spaargaren, M.; Pals, S.T. High prevalence of oncogenic MYD88 and CD79B mutations in primary testicular diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 2014, 28, 719–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraan, W.; Horlings, H.M.; van Keimpema, M.; Schilder-Tol, E.J.M.M.; Oud, M.E.C.M.C.M.; Scheepstra, C.; Kluin, P.M.; Kersten, M.J.; Spaargaren, M.; Pals, S.T. High prevalence of oncogenic MYD88 and CD79B mutations in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas presenting at immune-privileged sites. Blood Cancer J. 2013, 3, e139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.H.; Jeong, H.; Choi, J.W.; Oh, H.E.; Kim, Y.S. Clinicopathologic significance of MYD88 L265P mutation in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmitz, R.; Wright, G.W.; Huang, D.W.; Johnson, C.A.; Phelan, J.D.; Wang, J.Q.; Roulland, S.; Kasbekar, M.; Young, R.M.; Shaffer, A.L.; et al. Genetics and Pathogenesis of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1396–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treon, S.P.; Cao, Y.; Xu, L.; Yang, G.; Liu, X.; Hunter, Z.R. Somatic mutations in MYD88 and CXCR4 are determinants of clinical presentation and overall survival in Waldenström macroglobulinemia. Blood 2014, 123, 2791–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treon, S.P.; Gustine, J.; Xu, L.; Manning, R.J.; Tsakmaklis, N.; Demos, M.; Meid, K.; Guerrera, M.L.; Munshi, M.; Chan, G.; et al. MYD88 wild-type Waldenstrom Macroglobulinaemia: Differential diagnosis, risk of histological transformation, and overall survival. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 180, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zanwar, S.; Abeykoon, J.P.; Durot, E.; King, R.; Perez Burbano, G.E.; Kumar, S.; Gertz, M.A.; Quinquenel, A.; Delmer, A.; Gonsalves, W.; et al. Impact of MYD88L265P mutation status on histological transformation of Waldenström Macroglobulinemia. Am. J. Hematol. 2020, 95, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, Z.R.; Xu, L.; Tsakmaklis, N.; Demos, M.G.; Kofides, A.; Jimenez, C.; Chan, G.G.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Munshi, M.; et al. Insights into the genomic landscape of MYD88 wild-type Waldenström macroglobulinemia. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 2937–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abeykoon, J.P.; Paludo, J.; King, R.L.; Ansell, S.M.; Gertz, M.A.; LaPlant, B.R.; Halvorson, A.E.; Gonsalves, W.I.; Dingli, D.; Fang, H.; et al. MYD88 mutation status does not impact overall survival in Waldenström macroglobulinemia. Am. J. Hematol. 2018, 93, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- García-Sanz, R. WM, MYD88, and CXCR4: Following the thread. Blood 2016, 128, 746–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landgren, O.; Staudt, L. MYD88 L265P Somatic Mutation in IgM MGUS. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 2255–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, R.; Braggio, E. The MYDas touch of next-gen sequencing. Blood 2013, 121, 2373–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knittel, G.; Liedgens, P.; Korovkina, D.; Seeger, J.M.; Al-Baldawi, Y.; Al-Maarri, M.; Fritz, C.; Vlantis, K.; Bezhanova, S.; Scheel, A.H.; et al. B-cell-specific conditional expression of Myd88p.L252P leads to the development of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in mice. Blood 2016, 127, 2732–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sewastianik, T.; Guerrera, M.L.; Adler, K.; Dennis, P.S.; Wright, K.; Shanmugam, V.; Huang, Y.; Tanton, H.; Jiang, M.; Kofides, A.; et al. Human MYD88L265P is insufficient by itself to drive neoplastic transformation in mature mouse B cells. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 3360–3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gachard, N.; Parrens, M.; Soubeyran, I.; Petit, B.; Marfak, A.; Rizzo, D.; Devesa, M.; Delage-Corre, M.; Coste, V.; Laforêt, M.P.; et al. IGHV gene features and MYD88 L265P mutation separate the three marginal zone lymphoma entities and Waldenström macroglobulinemia/lymphoplasmacytic lymphomas. Leukemia 2013, 27, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willenbacher, W.; Willenbacher, E.; Brunner, A.; Manzl, C. Improved accuracy of discrimination between IgM Multiple Myeloma and Waldenström Macroglobulinaemia by testing for MYD88 L265P mutations. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 161, 902–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argentou, N.; Vassilopoulos, G.; Ioannou, M.; Germenis, A.E.; Speletas, M. Rapid detection of MYD88-L265P mutation by PCR-RFLP in B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders. Leukemia 2014, 28, 447–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondrejka, S.L.; Lin, J.J.; Warden, D.W.; Durkin, L.; Cook, J.R.; Hsi, E.D. MYD88 L265P somatic mutation: Its usefulness in the differential diagnosis of bone marrow involvement by B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2013, 140, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martinez-Lopez, A.; Curiel-Olmo, S.; Mollejo, M.; Cereceda, L.; Martinez, N.; Montes-Moreno, S.; Almaraz, C.; Revert, J.B.; Piris, M.A. MYD88 (L265P) somatic mutation in marginal zone B-cell lymphoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2015, 39, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Je, E.M.; Yoo, N.J.; Lee, S.H. Absence of MYD88 gene mutation in acute leukemias and multiple myelomas. Eur. J. Haematol. 2012, 88, 273–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willenbacher, E.; Willenbacher, W.; Wolf, D.G.; Zelger, B.; Peschel, I.; Manzl, C.; Haun, M.; Brunner, A. Digital PCR in bone marrow trephine biopsies is highly sensitive for MYD88 L265P detection in lymphomas with plasmacytic/plasmacytoid differentiation. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 186, 189–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, L.; Hunter, Z.R.; Yang, G.; Cao, Y.; Liu, X.; Manning, R.; Tripsas, C.; Chen, J.; Patterson, C.J.; Kluk, M.; et al. Detection of MYD88 L265P in peripheral blood of patients with Waldenström’s Macroglobulinemia and IgM monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance. Leukemia 2014, 28, 1698–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante, M.; Furlan, D.; Zibellini, S.; Borriero, M.; Candido, C.; Sahnane, N.; Uccella, S.; Genuardi, E.; Alessandria, B.; Bianchi, B.; et al. MYD88 L265P detection in IgM monoclonal gammopathies: Methodological considerations for routine implementation. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, A.; Ohwada, C.; Takeuchi, M.; Takeda, Y.; Tsukamoto, S.; Mimura, N.; Nagisa, O.H.; Sugita, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Wakita, H.; et al. Detection of MYD88 L265P mutation by next-generation deep sequencing in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia and IgM monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagratuni, T.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I.; Gavriatopoulou, M.; Mavrianou-Koutsoukou, N.; Liacos, C.; Patseas, D.; Kanellias, N.; Migkou, M.; Ziogas, D.C.; Eleutherakis-Papaiakovou, E.; et al. Detection of MYD88 and CXCR4 mutations in cell-free DNA of patients with IgM monoclonal gammopathies. Leukemia 2018, 32, 2617–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I.; Bagratuni, T.; Gavriatopoulou, M.; Patseas, D.; Liacos, C.; Kanellias, N.; Fotiou, D.; Tsiligkeridou, E.; Andreatou, A.; Mavrianou-Koutsoukou, N.; et al. Cell-free DNA analysis for the detection of MYD88 and CXCR4 mutations in IgM monoclonal gammopathies; an update with clinicopathological correlations. Am. J. Hematol. 2020, 95, E148–E150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kiss, T.L.; Xu, W.M.; Jamal, N.; Messner, H.A. Comparative testing of peripheral blood and bone marrow for BCR-ABL transcripts in patients post allogeneic bone marrow transplantation and during interferon treatment for chronic myeloid leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 1999, 34, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passamonti, F. How I treat polycythemia vera. Blood 2012, 120, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tiacci, E.; Schiavoni, G.; Forconi, F.; Santi, A.; Trentin, L.; Ambrosetti, A.; Cecchini, D.; Sozzi, E.; Francia di Celle, P.; Di Bello, C.; et al. Simple genetic diagnosis of hairy cell leukemia by sensitive detection of the BRAF-V600E mutation. Blood 2012, 119, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, J.; Natsumeda, M.; Okada, M.; Kobayashi, D.; Kanemaru, Y.; Tsukamoto, Y.; Oishi, M.; Kakita, A.; Fujii, Y. High Detection Rate of MYD88 Mutations in Cerebrospinal Fluid From Patients with CNS Lymphomas. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2019, 3, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiemcke-Jiwa, L.S.; Minnema, M.C.; Radersma-van Loon, J.H.; Jiwa, N.M.; de Boer, M.; Leguit, R.J.; de Weger, R.A.; Huibers, M.M.H. The use of droplet digital PCR in liquid biopsies: A highly sensitive technique for MYD88 p.(L265P) detection in cerebrospinal fluid. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 36, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, K.; Sakata-Yanagimoto, M.; Okoshi, Y.; Goshima, Y.; Yanagimoto, S.; Nakamoto-Matsubara, R.; Sato, T.; Noguchi, M.; Takano, S.; Ishikawa, E.; et al. MYD88 (L265P) mutation is associated with an unfavourable outcome of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2017, 177, 492–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drandi, D.; Genuardi, E.; Dogliotti, I.; Ferrante, M.; Jiménez, C.; Guerrini, F.; Lo Schirico, M.; Mantoan, B.; Muccio, V.; Lia, G.; et al. Highly sensitive MYD88L265P mutation detection by droplet digital polymerase chain reaction in Waldenström macroglobulinemia. Haematologica 2018, 103, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dimopoulos, M.A.; Kastritis, E. How I treat Waldenström macroglobulinemia. Blood 2019, 134, 2022–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varettoni, M.; Zibellini, S.; Arcaini, L.; Boveri, E.; Rattotti, S.; Pascutto, C.; Mangiacavalli, S.; Gotti, M.; Pochintesta, L.; Paulli, M.; et al. MYD88 (L265P) mutation is an independent risk factor for progression in patients with IgM monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance. Blood 2013, 122, 2284–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varettoni, M.; Zibellini, S.; Boveri, E.; Klersy, C.; Candido, C.; Rattotti, S.; Ferretti, V.V.; Defrancesco, I.; Mangiacavalli, S.; Nizzoli, M.E.; et al. A risk-stratification model based on the initial concentration of the serum monoclonal protein and MYD88 mutation status identifies a subset of patients with IgM monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance at high risk of progression to Waldenström. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 187, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustoros, M.; Sklavenitis-Pistofidis, R.; Kapoor, P.; Liu, C.J.; Kastritis, E.; Zanwar, S.; Fell, G.; Abeykoon, J.P.; Hornburg, K.; Neuse, C.J.; et al. Progression risk stratification of asymptomatic Waldenström macroglobulinemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1403–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanwar, S.; Abeykoon, J.P.; Ansell, S.M.; Gertz, M.A.; Colby, C.; Larson, D.; Paludo, J.; He, R.; Warsame, R.; Greipp, P.T.; et al. Disease outcomes and biomarkers of progression in smouldering Waldenström macroglobulinaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 195, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Gali, V.L.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Sano, D.; Thomas, S.K.; Weber, D.M.; Zhu, F.; Fang, X.; Deng, M.; Zhang, M.; et al. Molecular and genetic biomarkers implemented from next-generation sequencing provide treatment insights in clinical practice for Waldenström macroglobulinemia. Neoplasia 2021, 23, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, R.; Novak, A.J.; Ansell, S.M.; Muchtar, E.; Kapoor, P.; Hayman, S.R.; Dispenzieri, A.; Buadi, F.K.; Lacy, M.Q.; King, R.L.; et al. First report of MYD88 L265P somatic mutation in IgM-associated light-chain amyloidosis. Blood 2016, 127, 2936–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varettoni, M.; Zibellini, S.; Defrancesco, I.; Ferretti, V.V.; Rizzo, E.; Malcovati, L.; Gallì, A.; Giovanni, M.; Porta, D.; Boveri, E.; et al. Pattern of somatic mutations in patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia or IgM monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance. Haematologica 2017, 102, 2077–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lawrence, M.S.; Wan, Y.; Stojanov, P.; Sougnez, C.; Stevenson, K.; Werner, L.; Sivachenko, A.; DeLuca, D.S.; Zhang, L.; et al. SF3B1 and other novel cancer genes in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 2497–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Trillos, A.; Pinyol, M.; Navarro, A.; Aymerich, M.; Jares, P.; Juan, M.; Rozman, M.M.; Colomer, D.; Delgado, J.; Giné, E.; et al. Mutations in TLR/MYD88 pathway identify a subset of young chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients with favorable outcome. Blood 2014, 123, 3790–3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baliakas, P.; Hadzidimitriou, A.; Agathangelidis, A.; Rossi, D.; Sutton, L.A.; Kminkova, J.; Scarfo, L.; Pospisilova, S.; Gaidano, G.; Stamatopoulos, K.; et al. Prognostic relevance of MYD88 mutations in CLL: The jury is still out. Blood 2015, 126, 1043–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qin, S.C.; Xia, Y.; Miao, Y.; Zhu, H.Y.; Wu, J.Z.; Fan, L.; Qiao, C.; Xu, W.; Li, J.Y. MYD88 mutations predict unfavorable prognosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients with mutated IGHV gene. Blood Cancer J. 2017, 7, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernández-Rodríguez, C.; Bellosillo, B.; García-García, M.; Sánchez-González, B.; Gimeno, E.; Vela, M.C.; Serrano, S.; Besses, C.; Salar, A. MYD88 (L265P) mutation is an independent prognostic factor for outcome in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 2014, 28, 2104–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovira, J.; Karube, K.; Valera, A.; Colomer, D.; Enjuanes, A.; Colomo, L.; Martínez-Trillos, A.; Giné, E.; Dlouhy, I.; Magnano, L.; et al. MYD88 L265P mutations, but no other variants, identify a subpopulation of DLBCL patients of activated B-cell origin, extranodal involvement, and poor outcome. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 2755–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vermaat, J.S.; Somers, S.F.; De Wreede, L.C.; Kraan, W.; De Groen, R.A.L.; Schrader, A.M.R.; Kerver, E.D.; Scheepstra, C.G.; Berenschot, H.; Deenik, W.; et al. MYD88 mutations identify a molecular subgroup of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with an unfavorable prognosis. Haematologica 2020, 105, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Treon, S.P.; Xu, L.; Hunter, Z. MYD88 Mutations and Response to Ibrutinib in Waldenström’s Macroglobulinemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 584–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treon, S.P.; Meid, K.; Gustine, J.; Yang, G.; Xu, L.; Liu, X.; Patterson, C.J.; Hunter, Z.R.; Branagan, A.R.; Laubach, J.P.; et al. Long-Term Follow-Up of Ibrutinib Monotherapy in Symptomatic, Previously Treated Patients with Waldenström Macroglobulinemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treon, S.P.; Gustine, J.; Meid, K.; Yang, G.; Xu, L.; Liu, X.; Demos, M.; Kofides, A.; Tsakmaklis, N.; Chen, J.G.; et al. Ibrutinib Monotherapy in Symptomatic, Treatment-Naïve Patients with Waldenström Macroglobulinemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2755–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buske, C.; Tedeschi, A.; Trotman, J.; García-Sanz, R.; MacDonald, D.; Leblond, V.; Mahe, B.; Herbaux, C.; Matous, J.V.; Tam, C.S.; et al. Ibrutinib Plus Rituximab Versus Placebo Plus Rituximab for Waldenström’s Macroglobulinemia: Final Analysis from the Randomized Phase III iNNOVATE Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, M.; Sanz, R.G.; Lee, H.P.; Trneny, M.; Varettoni, M.; Opat, S.; D’Sa, S.; Owen, R.G.; Cull, G.; Mulligan, S.; et al. Zanubrutinib for the treatment of MYD88 wild-type Waldenström macroglobulinemia: A substudy of the phase 3 ASPEN trial. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 6009–6018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotman, J.; Opat, S.; Gottlieb, D.; Simpson, D.; Marlton, P.; Cull, G.; Munoz, J.; Tedeschi, A.; Roberts, A.W.; Seymour, J.F.; et al. Zanubrutinib for the treatment of patients with Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia: 3 years of follow-up. Blood 2020, 136, 2027–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, R.G.; McCarthy, H.; Rule, S.; D’Sa, S.; Thomas, S.K.; Tournilhac, O.; Forconi, F.; Kersten, M.J.; Zinzani, P.L.; Iyengar, S.; et al. Acalabrutinib monotherapy in patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia: A single-arm, multicentre, phase 2 study. Lancet Haematol. 2020, 7, e112–e121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treon, S.P.; Xu, L.; Guerrera, M.L.; Jimenez, C.; Hunter, Z.R.; Liu, X.; Demos, M.; Gustine, J.; Chan, G.; Munshi, M.; et al. Genomic landscape of Waldenström macroglobulinemia and its impact on treatment strategies. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1198–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.Q.; Smith, S.M.; Zhang, S.Y.; Lynn Wang, Y. Mechanisms of ibrutinib resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2015, 170, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez, C.; Chan, G.G.; Xu, L.; Tsakmaklis, N.; Kofides, A.; Demos, M.G.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Munshi, M.; Yang, G.; et al. Genomic evolution of ibrutinib-resistant clones in Waldenström macroglobulinaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 189, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, B.; Chowdhury, S.M.; Hart, A.; Sircar, A.; Singh, S.K.; Nath, U.K.; Mamgain, M.; Singhal, N.K.; Sehgal, L.; Jain, N. Ibrutinib resistance mechanisms and treatment strategies for B-cell lymphomas. Cancers 2020, 12, 1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, P.N.; Romero, D.L.; Yang, Y.; Shaffer, A.L.; Chaudhary, D.; Robinson, S.; Miao, W.; Rui, L.; Westlin, W.F.; Kapeller, R.; et al. Selective interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 inhibitors for the treatment of autoimmune disorders and lymphoid malignancy. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 2189–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loiarro, M.; Sette, C.; Gallo, G.; Ciacci, A.; Fantó, N.; Mastroianni, D.; Carminati, P.; Ruggiero, V. Peptide-mediated interference of TIR domain dimerization in MyD88 inhibits interleukin-1-dependent activation of NF-κB. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 15809–15814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scott, J.S.; Degorce, S.L.; Anjum, R.; Culshaw, J.; Davies, R.D.M.; Davies, N.L.; Dillman, K.S.; Dowling, J.E.; Drew, L.; Ferguson, A.D.; et al. Discovery and Optimization of Pyrrolopyrimidine Inhibitors of Interleukin-1 Receptor Associated Kinase 4 (IRAK4) for the Treatment of Mutant MYD88 L265P Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 10071–10091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.Q.; Beutler, B.; Goodnow, C.C.; Horikawa, K. Inhibiting TLR9 and other UNC93B1-dependent TLRs paradoxically increases accumulation of MYD88L265P plasmablasts in vivo. Blood 2016, 128, 1604–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhagat, L.; Wang, D.; Jiang, W.; Agrawal, S. Abstract 2570: IMO-8400, a selective antagonist of TLRs 7, 8 and 9, inhibits MYD88 L265P mutation-driven signaling and cell survival: A potential novel approach for treatment of B-cell lymphomas harboring MYD88 L265P mutation. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, M.A.; Lee, M.S.; Kissner, T.L.; Alam, S.; Waugh, D.S.; Saikh, K.U. Discovery of small molecule inhibitors of MyD88-dependent signaling pathways using a computational screen. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ansell, S.M.; Hodge, L.S.; Secreto, F.J.; Manske, M.; Braggio, E.; Price-Troska, T.; Ziesmer, S.; Li, Y.; Johnson, S.H.; Hart, S.N.; et al. Activation of TAK1 by MYD88 L265P drives malignant B-cell Growth in non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood Cancer J. 2014, 4, e183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brenner, L.; Arbeit, R.D.; Sullivan, T. IMO-8400, an Antagonist of Toll-like Receptors 7, 8, and 9, in Development for Genetically Defined B-Cell Lymphomas: Safety and Activity in Phase 1 and Phase 2 Clinical Trials. Blood 2014, 124, 3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.K.; Harb, W.A.; Beck, J.T.; Nashat, G.; Palomba, M.L.; Ansell, S.M.; Eradat, H.; Libby, E.N.; Advani, R.H.; Hajdenberg, J.; et al. Preliminary Results from a Phase 1/2, Open-Label, Dose-Escalation Clinical Trial of IMO-8400 in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Waldenstrom’s Macroglobulinemia. Blood 2015, 126, 1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Bai, G.; Ning, Y.; Cai, S.; Zhang, T.; Song, P.; Zhou, J.; Duan, W.; Ding, J.; Xie, H.; et al. Design and synthesis of Imidazo[1,2-b]pyridazine IRAK4 inhibitors for the treatment of mutant MYD88 L265P diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 190, 112092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delvecchio, V.S.; Sana, I.; Mantione, M.E.; Vilia, M.G.; Ranghetti, P.; Rovida, A.; Angelillo, P.; Scarfò, L.; Ghia, P.; Muzio, M. Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 inhibitor interrupts toll-like receptor signalling and sensitizes chronic lymphocytic leukaemia cells to apoptosis. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 189, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadashian, E.L.; McAuley, E.M.; Liu, D.; Shaffer, A.L.; Young, R.M.; Iyer, J.R.; Kruhlak, M.J.; Staudt, L.M.; Wiestner, A.; Herman, S.E.M. TLR signaling is activated in lymph node–resident CLL cells and is only partially inhibited by ibrutinib. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giménez, N.; Schulz, R.; Higashi, M.; Aymerich, M.; Villamor, N.; Delgado, J.; Juan, M.; López-Guerra, M.; Campo, E.; Rosich, L.; et al. Targeting IRAK4 disrupts inflammatory pathways and delays tumor development in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2020, 34, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ni, H.; Shirazi, F.; Baladandayuthapani, V.; Lin, H.; Kuiatse, I.; Wang, H.; Jones, R.J.; Berkova, Z.; Hitoshi, Y.; Ansell, S.M.; et al. Targeting myddosome signaling in Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia with the interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1/4 inhibitor R191. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 6408–6420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Hunter, Z.R.; Xu, L.; Chen, J.G.J.; Chen, J.G.J.; Tsakmaklis, N.; Patterson, C.J.; Castillo, J.J.; Buhrlage, S.; Gray, N.; et al. Targeting Myddosome Assembly in Waldenstrom Macroglobulinaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2017, 177, 808–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Tan, Y.; Huang, Z.; Huang, N.; Gao, M.; Zhou, F.; Hu, J.; Feng, W. Disrupting myddosome assembly in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells using the MYD88 dimerization inhibitor ST2825. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 42, 1755–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiratori, E.; Itoh, M.; Tohda, S. MYD88 inhibitor ST2825 suppresses the growth of lymphoma and leukaemia cells. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 6203–6209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avbelj, M.; Wolz, O.O.; Fekonja, O.; Benčina, M.; Repič, M.; Mavri, J.; Krüger, J.; Schärfe, C.; Garcia, M.D.; Panter, G.; et al. Activation of lymphoma-associated myd88 mutations via allostery-induced tir-domain oligomerization. Blood 2014, 124, 3896–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, G.; Wang, J.; Tan, L.; Munshi, M.; Liu, X.; Kofides, A.; Chen, J.G.; Tsakmaklis, N.; Demos, M.G.; Guerrera, M.L.; et al. The HCK/BTK inhibitor KIN-8194 is active in MYD88-driven lymphomas and overcomes mutated BTKCys481 ibrutinib resistance. Blood 2021, 138, 1966–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munshi, M.; Liu, X.; Kofides, A.; Tsakmaklis, N.; Gustine, J.; Sarosiek, S.; Flynn, C.A.; Meid, K.; White, T.P.; Leventoff, C.; et al. Pirtobrutinib (LOXO-305) Is Active and Overcomes ERK Related Pro-Survival Signaling in Ibrutinib Resistant, BTK Cys481 Mutant Expressing WM and ABC DLBCL Lymphoma Cells Driven By Activating MYD88 Mutations. Blood 2021, 138, 2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, A.R.; Shah, N.N.; Jurczak, W.; Cheah, C.Y.; Pagel, J.M.; Woyach, J.A.; Fakhri, B.; Eyre, T.A.; Lamanna, N.; Patel, M.R.; et al. Pirtobrutinib in relapsed or refractory B-cell malignancies (BRUIN): A phase 1/2 study. Lancet 2021, 397, 892–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelde, A.; Walz, J.S.; Kowalewski, D.J.; Schuster, H.; Wolz, O.O.; Peper, J.K.; Cardona Gloria, Y.; Langerak, A.W.; Muggen, A.F.; Claus, R.; et al. HLA class I-restricted MYD88 L265P-derived peptides as specific targets for lymphoma immunotherapy. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1219825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nielsen, J.S.; Chang, A.R.; Wick, D.A.; Sedgwick, C.G.; Zong, Z.; Mungall, A.J.; Martin, S.D.; Kinloch, N.N.; Ott-Langer, S.; Brumme, Z.L.; et al. Mapping the human T cell repertoire to recurrent driver mutations in MYD88 and EZH2 in lymphoma. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1321184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaushal, A.; Nooka, A.K.; Carr, A.R.; Pendleton, K.E.; Barwick, B.G.; Manalo, J.; McCachren, S.S.; Gupta, V.A.; Joseph, N.S.; Hofmeister, C.C.; et al. Aberrant Extrafollicular B Cells, Immune Dysfunction, Myeloid Inflammation, and MyD88-Mutant Progenitors Precede Waldenstrom Macroglobulinemia. Blood Cancer Discov. 2021, 2, 600–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çlnar, Ö.; Brzezicha, B.; Grunert, C.; Kloetzel, P.M.; Beier, C.; Peuker, C.A.; Keller, U.; Pezzutto, A.; Busse, A. High-affinity T-cell receptor specific for MyD88 L265P mutation for adoptive T-cell therapy of B-cell malignancies. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Weng, J.; Wei, X.; Qin, L.; Lai, P.; Zhao, R.; Jiang, Z.; Li, B.; Lin, S.; Wang, S.; et al. Toll-like receptor 2 costimulation potentiates the antitumor efficacy of CAR T Cells. Leukemia 2018, 32, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, P.; Dasyam, N.; Giunti, G.; Mester, B.; Bauer, E.; Andrews, B.; Perera, T.; Ostapowicz, T.; Frampton, C.; Li, P.; et al. Third-generation anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T-cells incorporating a TLR2 domain for relapsed or refractory B-cell lymphoma: A phase i clinical trial protocol (ENABLE). BMJ Open 2020, 10, e034629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Collinson-Pautz, M.R.; Chang, W.C.; Lu, A.; Khalil, M.; Crisostomo, J.W.; Lin, P.Y.; Mahendravada, A.; Shinners, N.P.; Brandt, M.E.; Zhang, M.; et al. Constitutively active MyD88/CD40 costimulation enhances expansion and efficacy of chimeric antigen receptor T cells targeting hematological malignancies. Leukemia 2019, 33, 2195–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weng, J.; Lai, P.; Qin, L.; Lai, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Luo, C.; Huang, X.; Wu, S.; Shao, D.; Deng, C.; et al. A novel generation 1928zT2 CAR T cells induce remission in extramedullary relapse of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, E.L.; Palomba, M.L.; Park, J.H.; Brentjens, R.J. A Systemic Xenograft Model of Waldenström’s Macroglobulinemia Demonstrates the Potent Anti-Tumor Effect of Second Generation CD19 Directed Chimeric Antigen Receptor Modified T Cells in This Disease. Blood 2014, 124, 4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata, M.; Gerken, C.; Nguyen, P.; Krenciute, G.; Spencer, D.M.; Gottschalk, S. Inducible activation of myD88 and CD40 in CAR T cells results in controllable and potent antitumor activity in preclinical solid tumor models. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 1306–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaczanowska, S.; Joseph, A.M.; Guo, J.; Tsai, A.K.; Lasola, J.J.; Younger, K.; Zhang, Y.; Gonzales, C.V.; Davila, E. A synthetic CD8α: MyD88 coreceptor enhances CD8+ T-cell responses to weakly immunogenic and lowly expressed tumor antigens. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 7049–7058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez, S.; Celay, J.; Goicoechea, I.; Jimenez, C.; Botta, C.; Garcia-Barchino, M.-J.; Garces, J.-J.; Larrayoz, M.; Santos, S.; Alignani, D.; et al. Preneoplastic somatic mutations including MYD88L265P in lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabl4644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, Z.R.; Xu, L.; Yang, G.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Cao, Y.; Manning, R.J.; Tripsas, C.; Patterson, C.J.; Sheehy, P.; et al. The genomic landscape of Waldenström macroglobulinemia is characterized by highly recurring MYD88 and WHIM-like CXCR4 mutations, and small somatic deletions associated with B-cell lymphomagenesis. Blood 2014, 123, 1637–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.Q.; Jeelall, Y.S.; Beutler, B.; Horikawa, K.; Goodnow, C.C. Consequences of the recurrent MYD88L265P somatic mutation for B cell tolerance. J. Exp. Med. 2014, 211, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, K.H.; Staudt, L.M. Toll-Like receptor signaling. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a011247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Theunissen, P.; Mejstrikova, E.; Sedek, L.; Van Der Sluijs-Gelling, A.J.; Gaipa, G.; Bartels, M.; Sobral da Costa, E.; Kotrová, M.; Novakova, M.; Sonneveld, E.; et al. Standardized flow cytometry for highly sensitive MRD measurements in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2017, 129, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Montero, J.; Sanoja-Flores, L.; Paiva, B.; Puig, N.; García-Sánchez, O.; Böttcher, S.; Van Der Velden, V.H.J.; Pérez-Morán, J.J.; Vidriales, M.B.; García-Sanz, R.; et al. Next Generation Flow for highly sensitive and standardized detection of minimal residual disease in multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2017, 31, 2094–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barakat, F.H.; Medeiros, L.J.; Wei, E.X.; Konoplev, S.; Lin, P.; Jorgensen, J.L. Residual monotypic plasma cells in patients with waldenström macroglobulinemia after therapy. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2011, 135, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
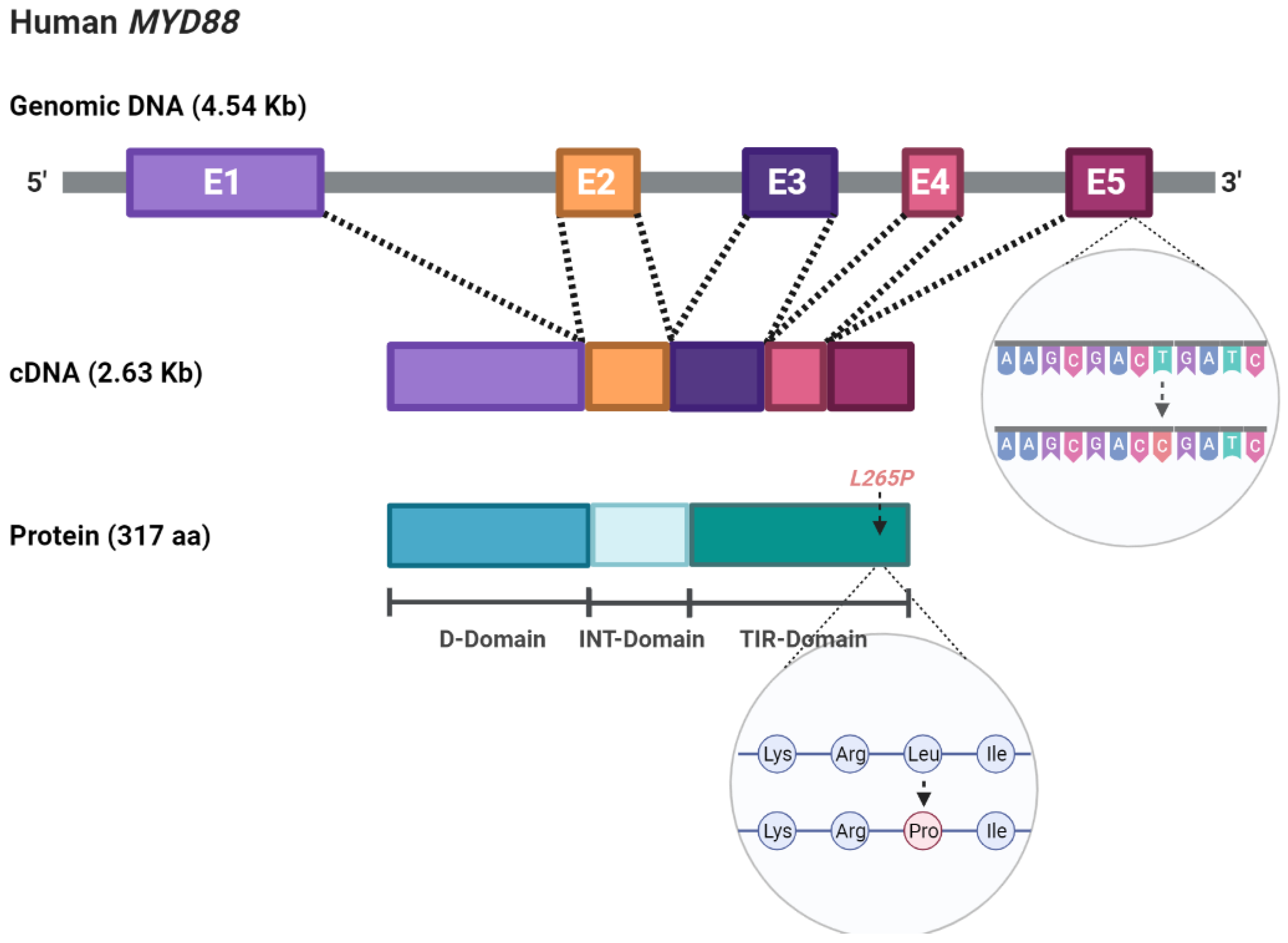
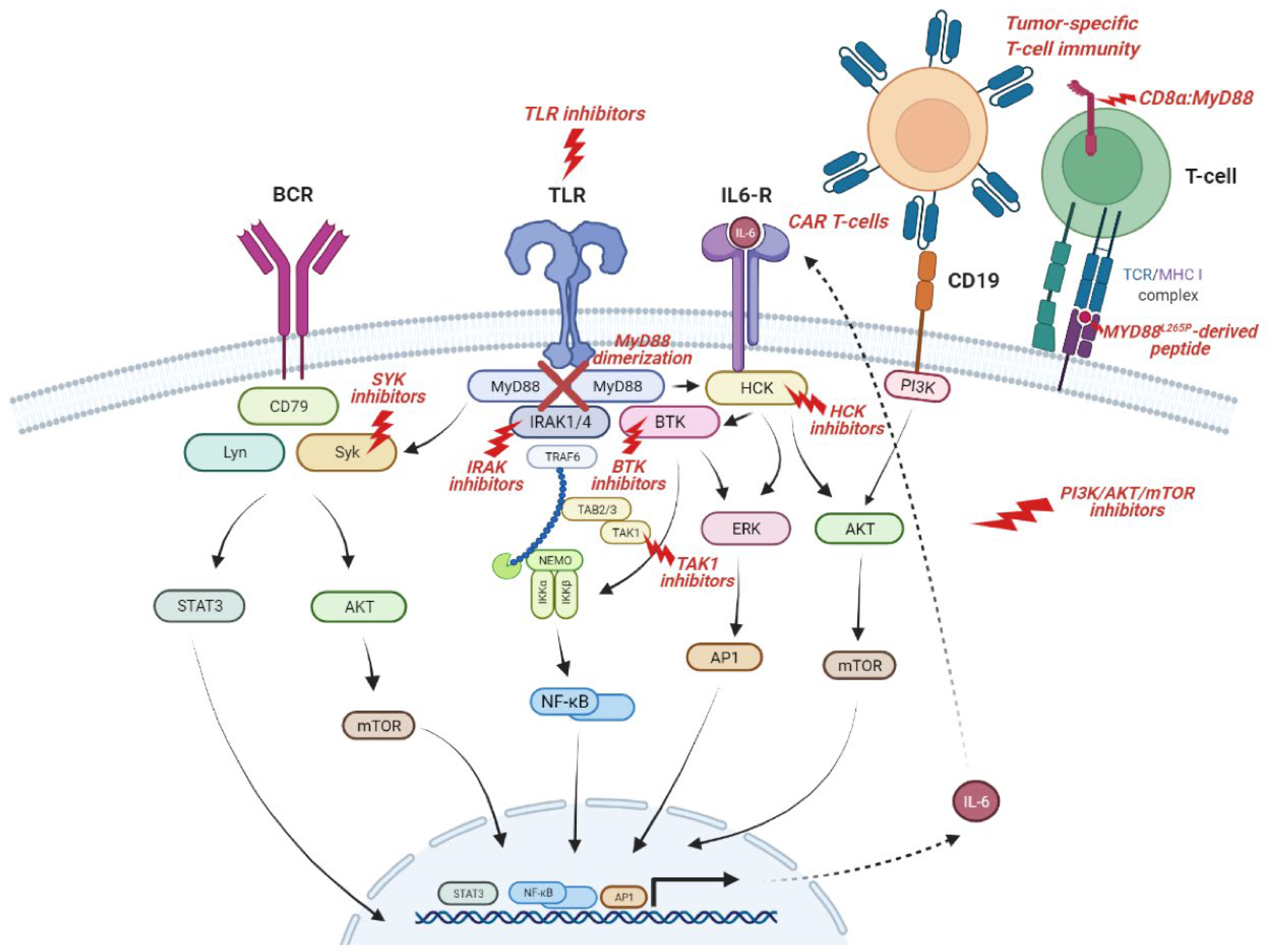
| Entity | N | MYD88L265P Range | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia | 470 | 67–100% | [11,12,13,14,15,50,51,52,56] |
| IgM-MGUS | 164 | 10–87% | [11,12,13,14,15,46] |
| MALT lymphoma | 105 | 0–9% | [23,50,54] |
| MZL | 325 | 0–21% | [11,12,13,14,15,50,53,54] |
| Multiple myeloma (including IgM) | 188 | 0% | [11,13,14,15,51,53,55,56] |
| Chronic lymphocytic leukemia | 412 | 0–43% 1 | [13,14,15,24,52,53,56] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alcoceba, M.; García-Álvarez, M.; Medina, A.; Maldonado, R.; González-Calle, V.; Chillón, M.C.; Sarasquete, M.E.; González, M.; García-Sanz, R.; Jiménez, C. MYD88 Mutations: Transforming the Landscape of IgM Monoclonal Gammopathies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5570. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105570
Alcoceba M, García-Álvarez M, Medina A, Maldonado R, González-Calle V, Chillón MC, Sarasquete ME, González M, García-Sanz R, Jiménez C. MYD88 Mutations: Transforming the Landscape of IgM Monoclonal Gammopathies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(10):5570. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105570
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlcoceba, Miguel, María García-Álvarez, Alejandro Medina, Rebeca Maldonado, Verónica González-Calle, María Carmen Chillón, María Eugenia Sarasquete, Marcos González, Ramón García-Sanz, and Cristina Jiménez. 2022. "MYD88 Mutations: Transforming the Landscape of IgM Monoclonal Gammopathies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 10: 5570. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105570
APA StyleAlcoceba, M., García-Álvarez, M., Medina, A., Maldonado, R., González-Calle, V., Chillón, M. C., Sarasquete, M. E., González, M., García-Sanz, R., & Jiménez, C. (2022). MYD88 Mutations: Transforming the Landscape of IgM Monoclonal Gammopathies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(10), 5570. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105570








