Lifelong Exposure to a Low-Dose of the Glyphosate-Based Herbicide RoundUp® Causes Intestinal Damage, Gut Dysbiosis, and Behavioral Changes in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
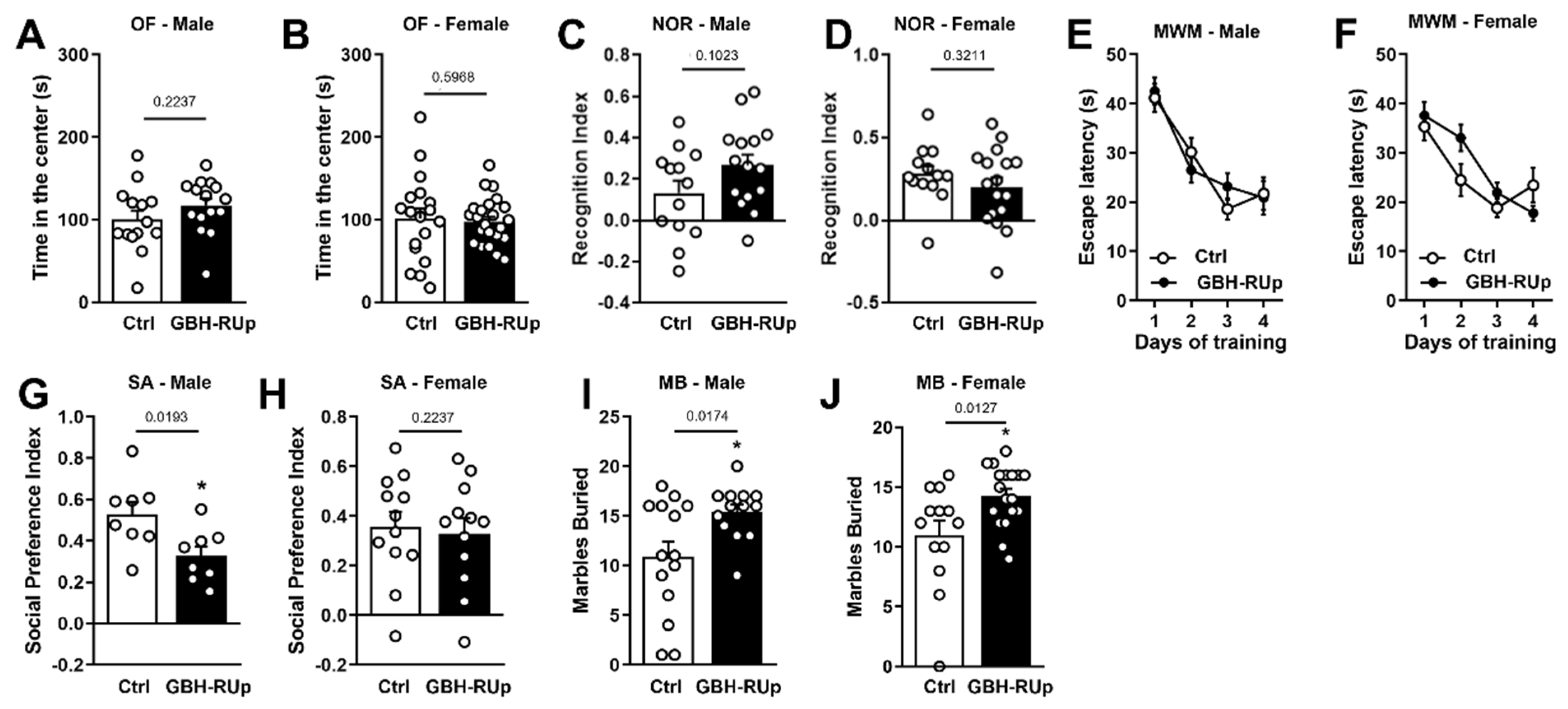
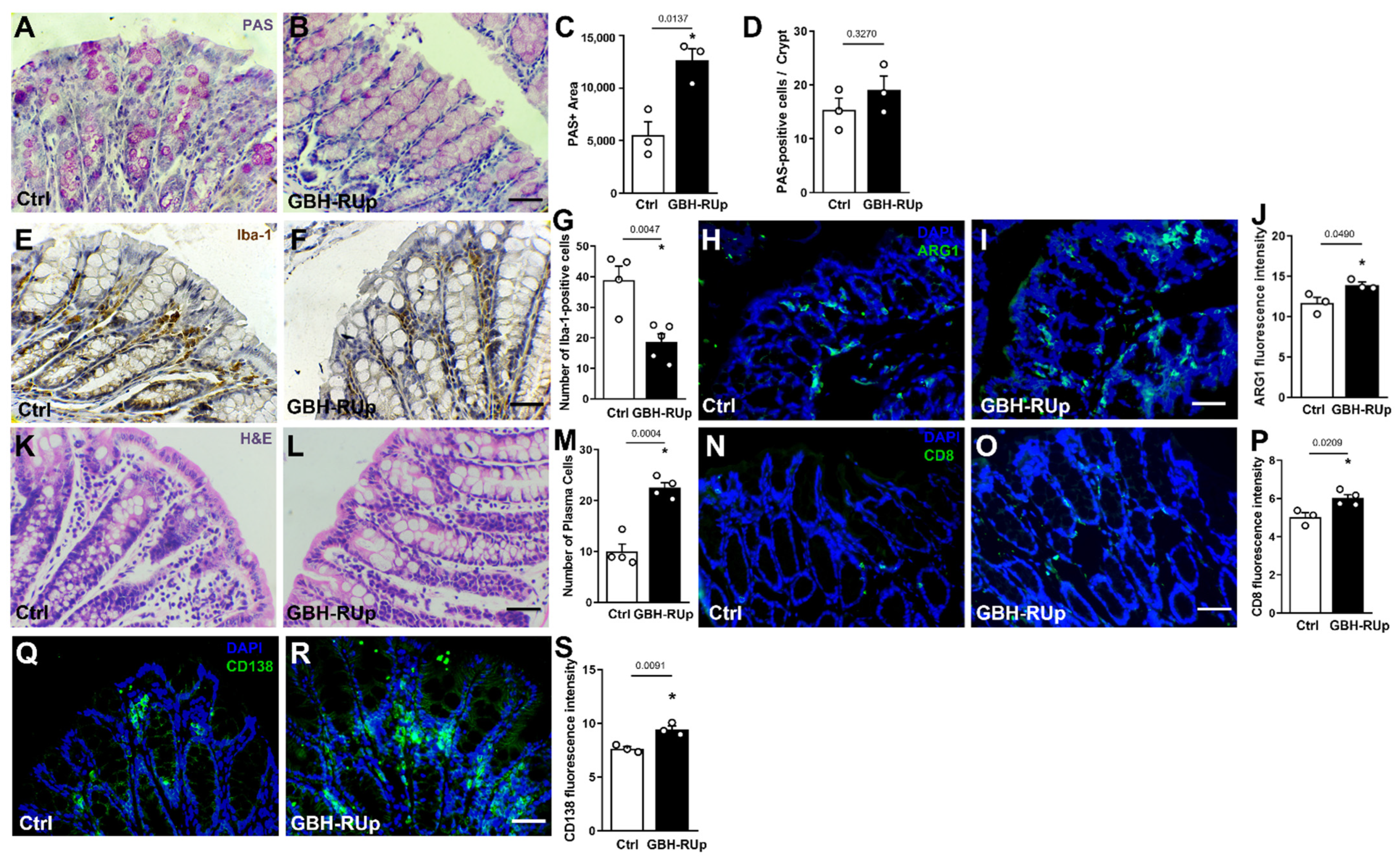
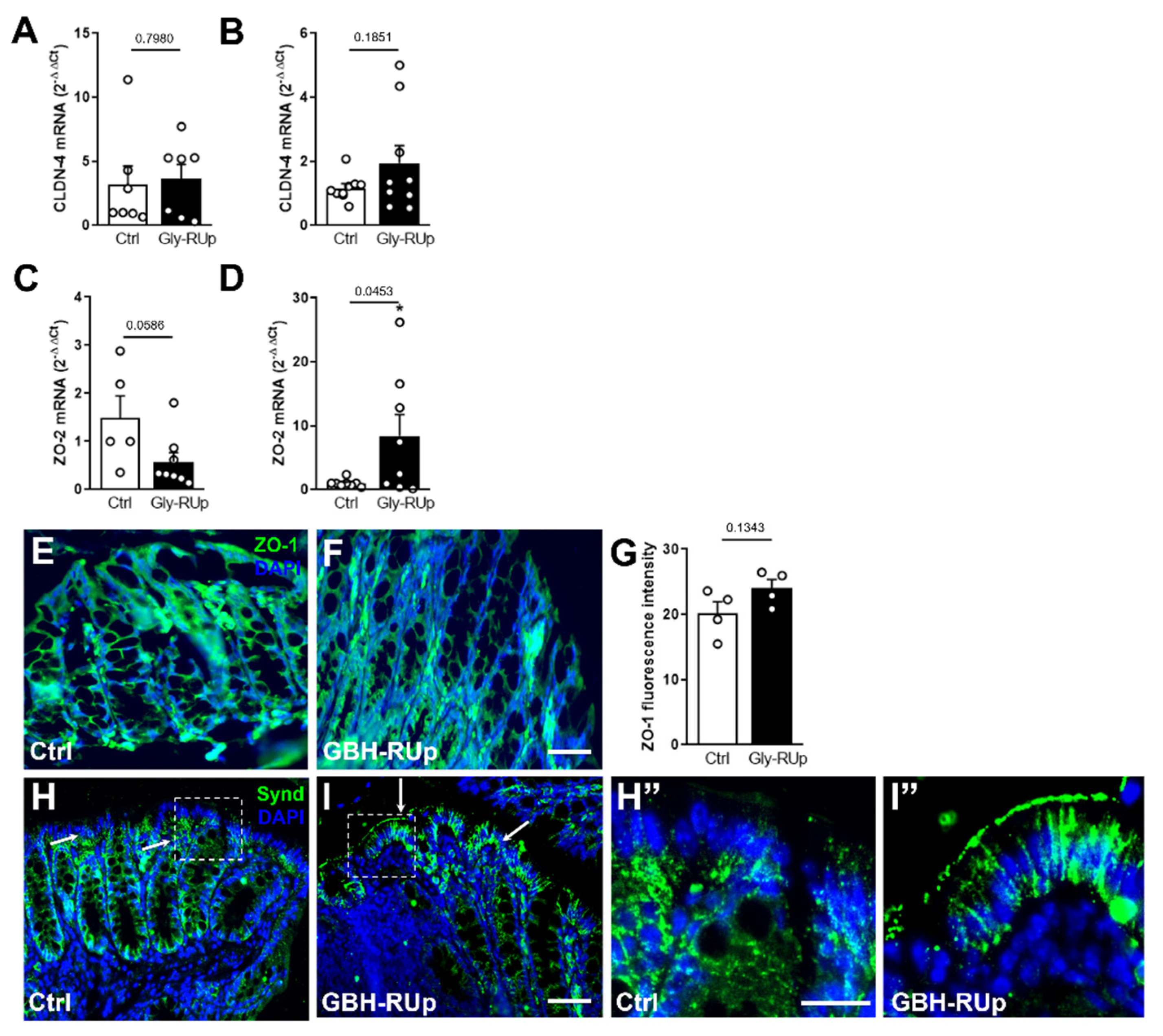
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elghareeb, T.A.; Ahmed, M.A.I.; Mohamed, I.A.; Saleh, S.M.M.; El-Din, H.A.E. Synergistic action of glyphosate on novel pesticides against Culex pipiens L. (Diptera: Culicidae) mosquitoes under laboratory conditions. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2018, 12, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meftaul, I.M.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Annamalai, P.; Parven, A.; Megharaj, M. Glyphosate use in urban landscape soils: Fate, distribution, and potential human and environmental health risks. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 292, 112786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brewster, D.W.; Warren, J.; Hopkins, W.E., 2nd. Metabolism of glyphosate in Sprague-Dawley rats: Tissue distribution, identification, and quantitation of glyphosate-derived materials following a single oral dose. Fundam. Appl. Toxicol. 1991, 17, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemann, L.; Sieke, C.; Pfeil, R.; Solecki, R. A critical review of glyphosate findings in human urine samples and comparison with the exposure of operators and consumers. J. Verbr. Lebensm. 2015, 10, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samsel, A.; Seneff, S. Glyphosate, pathways to modern diseases II: Celiac sprue and gluten intolerance. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2013, 6, 159–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samsel, A.; Seneff, S. Glyphosate, pathways to modern diseases III: Manganese, neurological diseases, and associated pathologies. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2015, 6, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesnage, R.; Antoniou, M.N. Facts and Fallacies in the Debate on Glyphosate Toxicity. Front. Public Health 2017, 5, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Negga, R.; Stuart, J.A.; Machen, M.L.; Salva, J.; Lizek, A.J.; Richardson, S.J.; Osborne, A.S.; Mirallas, O.; McVey, K.A.; Fitsanakis, V.A. Exposure to Glyphosate- and/or Mn/Zn-Ethylene-bis-Dithiocarbamate-Containing Pesticides Leads to Degeneration of γ-Aminobutyric Acid and Dopamine Neurons in Caenorhabditis elegans. Neurotox. Res. 2012, 21, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Modesto, K.A.; Martinez, C.B.R. Roundup® causes oxidative stress in liver and inhibits acetylcholinesterase in muscle and brain of the fish Prochilodus lineatus. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astiz, M.; de Alaniz, M.J.T.; Marra, C.A. Effect of pesticides on cell survival in liver and brain rat tissues. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2009, 72, 2025–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattani, D.; de Liz Oliveira Cavalli, V.L.; Heinz Rieg, C.E.; Domingues, J.T.; Dal-Cim, T.; Tasca, C.I.; Mena Barreto Silva, F.R.; Zamoner, A. Mechanisms underlying the neurotoxicity induced by glyphosate-based herbicide in immature rat hippocampus: Involvement of glutamate excitotoxicity. Toxicology 2014, 320, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gallegos, C.E.; Bartos, M.; Bras, C.; Gumilar, F.; Antonelli, M.C.; Minetti, A. Exposure to a glyphosate-based herbicide during pregnancy and lactation induces neurobehavioral alterations in rat offspring. NeuroToxicology 2016, 53, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Human Microbiome Project Consortium Structure, function and diversity of the healthy human microbiome. Nature 2012, 486, 207–214. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blaser, M.J.; Falkow, S. What are the consequences of the disappearing human microbiota? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuong, H.E.; Yano, J.M.; Fung, T.C.; Hsiao, E.Y. The Microbiome and Host Behavior. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 40, 21–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, H.E.; Hsiao, E.Y. Emerging Roles for the Gut Microbiome in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 81, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurenbach, B.; Marjoshi, D.; Amábile-Cuevas, C.F.; Ferguson, G.C.; Godsoe, W.; Gibson, P.; Heinemann, J.A. Sublethal Exposure to Commercial Formulations of the Herbicides Dicamba, 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid, and Glyphosate Cause Changes in Antibiotic Susceptibility in Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. mBio 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saleh, S.M.M.; Elghareeb, T.A.; Atia, M.M.; Ahmed, M.A.I. Impact of Glyphosate-Roundup® in the Ileal Structure of Male and Female Rats: A Morphological and Immunohistochemical Study. Microsc. Microanal. 2021, 27, 1547–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, C.; Koifman, S. Pesticides, depression and suicide: A systematic review of the epidemiological evidence. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2013, 216, 445–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kori, R.K.; Mandrah, K.; Hasan, W.; Patel, D.K.; Roy, S.K.; Yadav, R.S. Identification of markers of depression and neurotoxicity in pesticide exposed agriculture workers. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2020, 34, e22477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcelli, S.; Van Der Wee, N.; van der Werff, S.; Aghajani, M.; Glennon, J.C.; van Heukelum, S.; Mogavero, F.; Lobo, A.; Olivera, F.J.; Lobo, E.; et al. Social brain, social dysfunction and social withdrawal. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 97, 10–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takumi, T.; Tamada, K.; Hatanaka, F.; Nakai, N.; Bolton, P.F. Behavioral neuroscience of autism. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 110, 60–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangiola, F. Gut microbiota in autism and mood disorders. WJG 2016, 22, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, A.K.; Bockmann, J.; Steinestel, K.; Boeckers, T.M.; Grabrucker, A.M. Altered Intestinal Morphology and Microbiota Composition in the Autism Spectrum Disorders Associated SHANK3 Mouse Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhuang, Z.; Yang, R.; Wang, W.; Qi, L.; Huang, T. Associations between gut microbiota and Alzheimer’s disease, major depressive disorder, and schizophrenia. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Khan, W. Goblet Cells and Mucins: Role in Innate Defense in Enteric Infections. Pathogens 2013, 2, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Camilleri, M. Leaky gut: Mechanisms, measurement and clinical implications in humans. Gut 2019, 68, 1516–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruff, W.E.; Greiling, T.M.; Kriegel, M.A. Host–microbiota interactions in immune-mediated diseases. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 521–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, M.; von der Weid, P.-Y. Lipopolysaccharides modulate intestinal epithelial permeability and inflammation in a species-specific manner. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, R.; Tan, J.; Peng, L.; Wang, P.; Liu, J.; Xiong, H.; Jiang, B.; Chen, Y. Syndecan-1 Acts in Synergy with Tight Junction Through Stat3 Signaling to Maintain Intestinal Mucosal Barrier and Prevent Bacterial Translocation. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 1894–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantino, J.N.; Marrus, N. The Early Origins of Autism. Child Adolesc. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 26, 555–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, J.R.; Dawley, E.H.; Reigart, J.R. Children’s low-level pesticide exposure and associations with autism and ADHD: A review. Pediatr. Res. 2019, 85, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duke, S.O. The history and current status of glyphosate: History and current status of glyphosate. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, J.P.; Bleak, T.C.; Calaf, G.M. Glyphosate and the key characteristics of an endocrine disruptor: A review. Chemosphere 2021, 270, 128619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonio Carbonari, C.; Gomes, G.L.G.C.; Domingues Velini, E.; Fernandes Machado, R.; Simões, P.S.; de Castro Macedo, G. Glyphosate Effects on Sugarcane Metabolism and Growth. AJPS 2014, 05, 3585–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Rana, I.; Shaffer, R.M.; Taioli, E.; Sheppard, L. Exposure to glyphosate-based herbicides and risk for non-Hodgkin lymphoma: A meta-analysis and supporting evidence. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2019, 781, 186–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiyori, Y.; Nishida, M.; Shioda, K.; Suda, S.; Kato, S. Unilateral hippocampal infarction associated with an attempted suicide: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2014, 8, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yokoyama, S.; Sugisaki, T.; Ryota, Y.; Yoshiteru, S.; Okayasu, H.; Shioda, M.; Suzuki, K.; Yasui-Furukori, N.; Shimoda, K. Transient glyphosate encephalopathy due to a suicide attempt. Neuropsychopharm. Rep. 2021, 41, 444–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bali, Y.A.; Kaikai, N.; Ba-M’hamed, S.; Bennis, M. Learning and memory impairments associated to acetylcholinesterase inhibition and oxidative stress following glyphosate based-herbicide exposure in mice. Toxicology 2019, 415, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Rao, C.; Yuan, R.; Sun, D.; Guo, S.; Li, L.; Yang, S.; Qian, D.; Lu, R.; Cao, X. Long-term exposure to polyethylene microplastics and glyphosate interferes with the behavior, intestinal microbial homeostasis, and metabolites of the common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 152681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait Bali, Y.; Ba-Mhamed, S.; Bennis, M. Behavioral and Immunohistochemical Study of the Effects of Subchronic and Chronic Exposure to Glyphosate in Mice. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baier, C.J.; Gallegos, C.E.; Raisman-Vozari, R.; Minetti, A. Behavioral impairments following repeated intranasal glyphosate-based herbicide administration in mice. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2017, 64, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, Y.; Yang, J.; Chang, L.; Qu, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, K.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, J.; Tan, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Maternal glyphosate exposure causes autism-like behaviors in offspring through increased expression of soluble epoxide hydrolase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 11753–11759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilbo, S.D.; Block, C.L.; Bolton, J.L.; Hanamsagar, R.; Tran, P.K. Beyond infection—Maternal immune activation by environmental factors, microglial development, and relevance for autism spectrum disorders. Exp. Neurol. 2018, 299, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, P.S.; Barros-Aragão, F.; da Silva, R.T.; Venancio, A.; Matias, I.; Lyra e Silva, N.M.; Kincheski, G.C.; Pimentel-Coelho, P.M.; De Felice, F.G.; Gomes, F.C.A.; et al. Neonatal infection leads to increased susceptibility to Aβ oligomer-induced brain inflammation, synapse loss and cognitive impairment in mice. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saunders, J.M.; Moreno, J.L.; Ibi, D.; Sikaroodi, M.; Kang, D.J.; Muñoz-Moreno, R.; Dalmet, S.S.; García-Sastre, A.; Gillevet, P.M.; Dozmorov, M.G.; et al. Gut microbiota manipulation during the prepubertal period shapes behavioral abnormalities in a mouse neurodevelopmental disorder model. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelli, L.S.; Samsam, A.; Naser, S.A. Propionic Acid Induces Gliosis and Neuro-inflammation through Modulation of PTEN/AKT Pathway in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garcia, S.J.; Seidler, F.J.; Qiao, D.; Slotkin, T.A. Chlorpyrifos targets developing glia: Effects on glial fibrillary acidic protein. Dev. Brain Res. 2002, 133, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait-Bali, Y.; Ba-M’hamed, S.; Gambarotta, G.; Sassoè-Pognetto, M.; Giustetto, M.; Bennis, M. Pre- and postnatal exposure to glyphosate-based herbicide causes behavioral and cognitive impairments in adult mice: Evidence of cortical ad hippocampal dysfunction. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 1703–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.-H.; Jin, Z.; Yang, X.-X.; Lou, J.; Shan, W.-X.; Hu, Y.-X.; Du, Q.; Liao, Q.-S.; Xie, R.; Xu, J.-Y. Role of gut microbiota via the gut-liver-brain axis in digestive diseases. WJG 2020, 26, 6141–6162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesika, P.; Suganthy, N.; Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Chaiyasut, C. Role of gut-brain axis, gut microbial composition, and probiotic intervention in Alzheimer’s disease. Life Sci. 2021, 264, 118627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golubeva, A.V.; Joyce, S.A.; Moloney, G.; Burokas, A.; Sherwin, E.; Arboleya, S.; Flynn, I.; Khochanskiy, D.; Moya-Pérez, A.; Peterson, V.; et al. Microbiota-related Changes in Bile Acid & Tryptophan Metabolism are Associated with Gastrointestinal Dysfunction in a Mouse Model of Autism. eBioMedicine 2017, 24, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, S.-C.; Yang-Yen, H.-F.; Tsao, P.-N.; Weng, M.-T.; Tung, C.-C.; Yu, L.C.H.; Lai, L.-C.; Hsiao, J.-H.; Chuang, E.Y.; Shun, C.-T.; et al. SHANK3 Regulates Intestinal Barrier Function Through Modulating ZO-1 Expression Through the PKCε-dependent Pathway. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2017, 23, 1730–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ackermann, W.; Coenen, M.; Schrödl, W.; Shehata, A.A.; Krüger, M. The Influence of Glyphosate on the Microbiota and Production of Botulinum Neurotoxin During Ruminal Fermentation. Curr. Microbiol. 2015, 70, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitbali, Y.; Ba-M’hamed, S.; Elhidar, N.; Nafis, A.; Soraa, N.; Bennis, M. Glyphosate based-herbicide exposure affects gut microbiota, anxiety and depression-like behaviors in mice. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2018, 67, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueda-Ruzafa, L.; Cruz, F.; Roman, P.; Cardona, D. Gut microbiota and neurological effects of glyphosate. NeuroToxicology 2019, 75, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, E.Y.; McBride, S.W.; Hsien, S.; Sharon, G.; Hyde, E.R.; McCue, T.; Codelli, J.A.; Chow, J.; Reisman, S.E.; Petrosino, J.F.; et al. Microbiota Modulate Behavioral and Physiological Abnormalities Associated with Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Cell 2013, 155, 1451–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzales, J.; Marchix, J.; Aymeric, L.; Le Berre-Scoul, C.; Zoppi, J.; Bordron, P.; Burel, M.; Davidovic, L.; Richard, J.-R.; Gaman, A.; et al. Fecal Supernatant from Adult with Autism Spectrum Disorder Alters Digestive Functions, Intestinal Epithelial Barrier, and Enteric Nervous System. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, F.; Pira, E.; Ciocan, C.; Boffetta, P. Exposure to glyphosate and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma and multiple myeloma: An updated meta-analysis. Med. Lav. 2020, 111, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, C.; Elsabbagh, M.; Baird, G.; Veenstra-Vanderweele, J. Autism spectrum disorder. Lancet 2018, 392, 508–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peillex, C.; Pelletier, M. The impact and toxicity of glyphosate and glyphosate-based herbicides on health and immunity. J. Immunotoxicol. 2020, 17, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, K.R. Glyphosate in the general population and in applicators: A critical review of studies on exposures. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2016, 46, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seibenhener, M.L.; Wooten, M.C. Use of the Open Field Maze to Measure Locomotor and Anxiety-like Behavior in Mice. JoVE 2015, e52434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lueptow, L.M. Novel Object Recognition Test for the Investigation of Learning and Memory in Mice. JoVE 2017, e55718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverman, J.L.; Yang, M.; Lord, C.; Crawley, J.N. Behavioural phenotyping assays for mouse models of autism. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 11, 490–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nem de Oliveira Souza, I.; Frost, P.S.; França, J.V.; Nascimento-Viana, J.B.; Neris, R.L.S.; Freitas, L.; Pinheiro, D.J.L.L.; Nogueira, C.O.; Neves, G.; Chimelli, L.; et al. Acute and chronic neurological consequences of early-life Zika virus infection in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaar2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, Y.; Cole, T.B.; Costa, L.G. Behavioral Phenotyping for Autism Spectrum Disorders in Mice. Curr. Protoc. Toxicol. 2017, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossato, J.I.; Köhler, C.A.; Radiske, A.; Bevilaqua, L.R.M.; Cammarota, M. Inactivation of the dorsal hippocampus or the medial prefrontal cortex impairs retrieval but has differential effect on spatial memory reconsolidation. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2015, 125, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Platas, S.G.; Comeau, S.; Rachalski, A.; Bo, G.D.; Cruceanu, C.; Turecki, G.; Giros, B.; Mechawar, N. Morphometric characterization of microglial phenotypes in human cerebral cortex. J. Neuroinflamm. 2014, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wingett, S.W.; Andrews, S. FastQ Screen: A tool for multi-genome mapping and quality control. F1000Research 2018, 7, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. UNOISE2: Improved error-correction for Illumina 16S and ITS amplicon sequencing. bioRvix 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parks, D.H.; Chuvochina, M.; Chaumeil, P.-A.; Rinke, C.; Mussig, A.J.; Hugenholtz, P. A complete domain-to-species taxonomy for Bacteria and Archaea. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Lin, H.; Revanna, K.; Dong, Q. A Bayesian taxonomic classification method for 16S rRNA gene sequences with improved species-level accuracy. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McDonald, D.; Price, M.N.; Goodrich, J.; Nawrocki, E.P.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Probst, A.; Andersen, G.L.; Knight, R.; Hugenholtz, P. An improved Greengenes taxonomy with explicit ranks for ecological and evolutionary analyses of bacteria and archaea. ISME J. 2012, 6, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Primary Antibody | Distributor | Secondary |
|---|---|---|
| Iba-1 | Wako | Rabbit, Biotinylated |
| Arginase-1 | Santa Cruz | Rabbit, Alexa Fluor-488 |
| ZO-1 | Invitrogen | Rabbit, Alexa Fluor-488 |
| Ki67 | Abcam | Rabbit, Alexa Fluor-488 |
| Syndecan-1/CD138 | BD Bioscience | Rat, Alexa Fluor-488 |
| CD8 | Abcam | Rabbit, Alexa Fluor-488 |
| B220 | BD Bioscience | Rat, Alexa Fluor-488 |
| Blimp-1 | BD Bioscience | Alexa Fluor-546 conjugated |
| GFAP | Invitrogen | Rabbit Alexa Fluor-488 |
| Target Gene | Primer Design | Product Size | |
|---|---|---|---|
| β-actin | Forward | GCC CTG AGG CTC TTT TCC AG | 51 |
| Reverse | TGC CAC AGG ATT CCA TAC CC | ||
| ZO-2 | Forward | GCC TGC AAG AAG GAG ACC AG | 132 |
| Reverse | CTC GGC TCT GAG CCA AAA TG | ||
| ZO-3 | Forward | GTG TCG TGA GCT TCC CCA AG | 156 |
| Reverse | ATG GCA TAC CAT TCA CCT GCA | ||
| CLDN-4 | Forward | TCG TGG GTG CTC TGG GGA T | 170 |
| Reverse | GCG GAT GAC GTT GTG AGC G | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Del Castilo, I.; Neumann, A.S.; Lemos, F.S.; De Bastiani, M.A.; Oliveira, F.L.; Zimmer, E.R.; Rêgo, A.M.; Hardoim, C.C.P.; Antunes, L.C.M.; Lara, F.A.; et al. Lifelong Exposure to a Low-Dose of the Glyphosate-Based Herbicide RoundUp® Causes Intestinal Damage, Gut Dysbiosis, and Behavioral Changes in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5583. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105583
Del Castilo I, Neumann AS, Lemos FS, De Bastiani MA, Oliveira FL, Zimmer ER, Rêgo AM, Hardoim CCP, Antunes LCM, Lara FA, et al. Lifelong Exposure to a Low-Dose of the Glyphosate-Based Herbicide RoundUp® Causes Intestinal Damage, Gut Dysbiosis, and Behavioral Changes in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(10):5583. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105583
Chicago/Turabian StyleDel Castilo, Ingrid, Arthur S. Neumann, Felipe S. Lemos, Marco A. De Bastiani, Felipe L. Oliveira, Eduardo R. Zimmer, Amanda M. Rêgo, Cristiane C. P. Hardoim, Luis Caetano M. Antunes, Flávio A. Lara, and et al. 2022. "Lifelong Exposure to a Low-Dose of the Glyphosate-Based Herbicide RoundUp® Causes Intestinal Damage, Gut Dysbiosis, and Behavioral Changes in Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 10: 5583. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105583
APA StyleDel Castilo, I., Neumann, A. S., Lemos, F. S., De Bastiani, M. A., Oliveira, F. L., Zimmer, E. R., Rêgo, A. M., Hardoim, C. C. P., Antunes, L. C. M., Lara, F. A., Figueiredo, C. P., & Clarke, J. R. (2022). Lifelong Exposure to a Low-Dose of the Glyphosate-Based Herbicide RoundUp® Causes Intestinal Damage, Gut Dysbiosis, and Behavioral Changes in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(10), 5583. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105583






