Recombinant Integrin β1 Signal Peptide Blocks Gliosis Induced by Aβ Oligomers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Integrin β1 Signal Peptide Specifically Binds to Aβ Oligomers
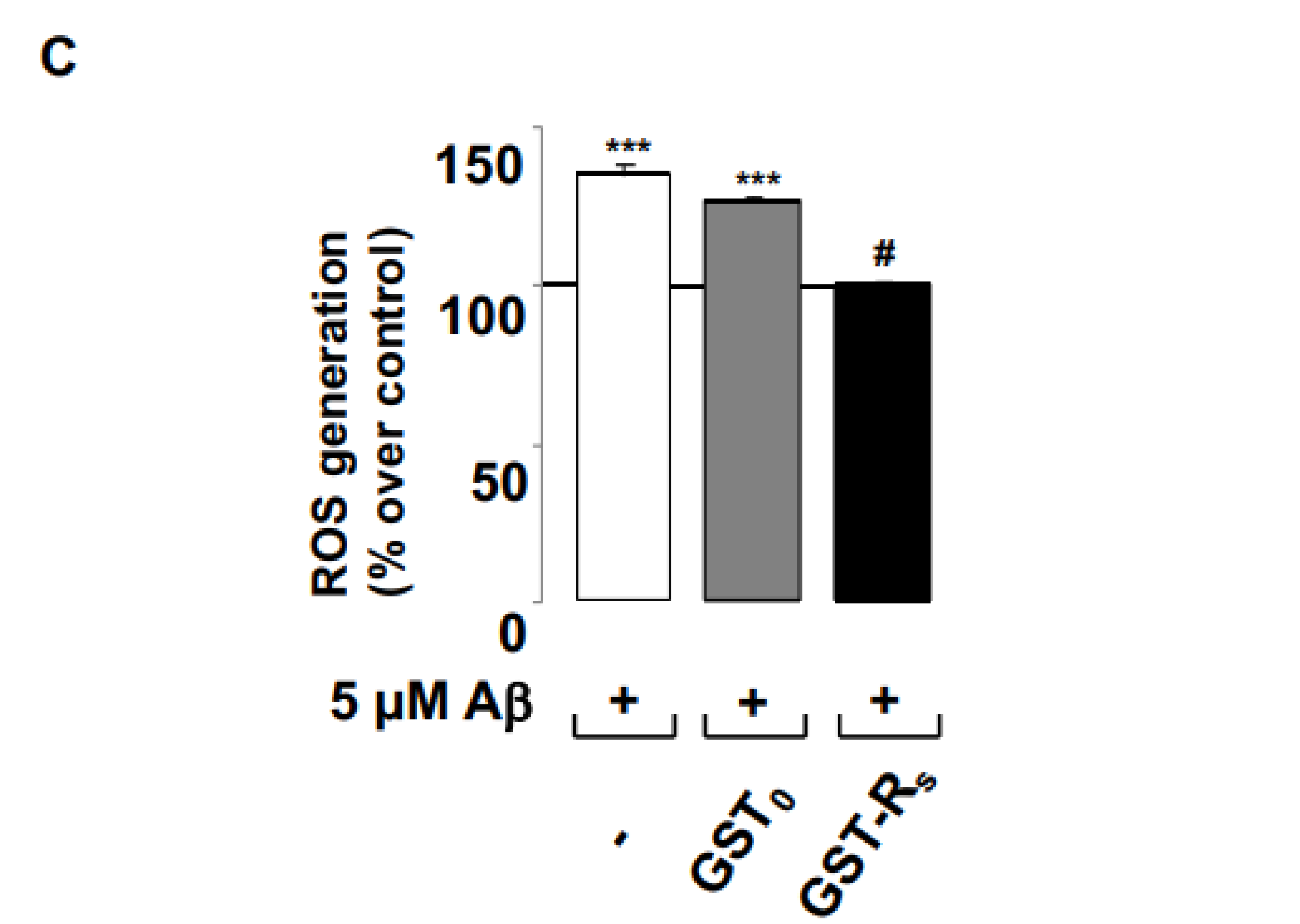
2.2. Rs Peptide Blocks Aβ Oligomer-Induced ROS Generation in Cultured Astrocytes
2.3. Aβ Oligomers Trigger Gliosis in Mouse Hippocampus In Vivo
2.4. Rs Peptide Prevents Glia Reactivity in the DG of Aβ Oligomer-Injected Mice Brain
2.5. Rs Peptide Reduces Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Astrocytes in DG of Aβ Oligomer-Injected Mice Brain
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Experimental Procedures
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Barker, W.W.; Luis, C.A.; Kashuba, A.; Luis, M.; Harwood, D.G.; Loewenstein, D.; Waters, C.; Jimison, P.; Shepherd, E.; Sevush, S.; et al. Relative frequencies of Alzheimer disease, Lewy body, vascular and frontotemporal dementia, and hippocampal sclerosis in the state of Florida brain Bank. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2002, 16, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzheimer, A.; Stelzmann, R.A.; Schnitzlein, H.N.; Murtagh, F.R. An English translation of Alzheimer’s 1907 paper, “Uber eine eigenartige Erkankung der Hirnrinde”. Clin. Anat. 1995, 8, 429–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, A.; Ekavali. A review on Alzheimer’s disease pathophysiology and its management: An update. Pharmacol. Rep. 2015, 67, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goedert, M. Oskar Fischer and the study of dementia. Brain 2009, 132, 1102–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thal, D.R.; Capetillo-Zarate, E.; Del Tredici, K.; Braak, H. The development of amyloid beta protein deposits in the aged brain. Sci. Aging Knowl. Environ. 2006, 2006, re1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeTure, M.A.; Dickson, D.W. The neuropathological diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2019, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braak, H.; Braak, E. Frequency of stages of Alzheimer-related lesions in different age categories. Neurobiol. Aging 1997, 18, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenner, G.G.; Wong, C.W. Alzheimer’s disease and Down’s syndrome: Sharing of a unique cerebrovascular amyloid fibril protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1984, 16, 1131–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, J.A.; Higgins, G.A. Alzheimer’s disease: The amyloid cascade hypothesis. Science 1992, 256, 184–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selkoe, D.J. The molecular pathology of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 1991, 6, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenner, G.G.; Wong, C.W. Alzheimer’s disease: Initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1984, 120, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, J.; Allsop, D. Amyloid deposition as the central event in the aetiology of Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1991, 12, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, J.; Selkoe, D.J. The Amyloid Hypothesis of Alzheimer’s Disease: Progress and Problems on the Road to Therapeutics. Science 2002, 297, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grangeon, L.; Cassinari, K.; Rousseau, S.; Croisile, B.; Formaglio, M.; Moreaud, O.; Boutonnat, J.; Le Meur, N.; Miné, M.; Coste, T.; et al. Early-Onset Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy and Alzheimer Disease Related to an APP Locus Triplication. Neurol. Genet. 2021, 7, e609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, H.; Vergallo, A.; Caraci, F.; Cuello, A.C.; Lemercier, P.; Vellas, B.; Virecoulon Giudici, K.; Baldacci, F.; Hanisch, B.; Haberkamp, M.; et al. Future avenues for Alzheimer’s disease detection and therapy: Liquid biopsy, intracellular signaling modulation, systems pharmacology drug discovery. Neuropharmacology 2021, 185, 108081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oddo, S.; Caccamo, A.; Shepherd, J.D.; Murphy, M.P.; Golde, T.E.; Kayed, R.; Metherate, R.; Mattson, M.P.; Akbari, Y.; LaFerla, F.M. 3xTg-AD model of Alzheimer’s disease with plaques and tangles intracellular Aβ and synaptic dysfunction. Neuron 2003, 39, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomiyama, T.; Matsuyama, S.; Iso, H.; Umeda, T.; Takuma, H.; Ohnishi, K.; Ishibashi, K.; Teraoka, R.; Sakama, N.; Yamashita, T.; et al. A Mouse Model of Amyloid Oligomers: Their Contribution to Synaptic Alteration, Abnormal Tau Phosphorylation, Glial Activation, and Neuronal Loss In Vivo. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 4845–4856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bao, F.; Wicklund, L.; Lacor, P.N.; Klein, W.L.; Nordberg, A.; Marutle, A. Different β-amyloid oligomer assemblies in Alzheimer brains correlate with age of disease onset and impaired cholinergic activity. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 825.e1–825.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.N.; Ewers, M.; Minthon, L.; Simm, A.; Silber, R.E.; Blennow, K.; Prvulovid, D.; Hansson, O.; Hampel, H. Amyloid-β oligomers in cerebrospinal fluid are associated with cognitive decline in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer Dis. 2012, 29, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberdi, E.; Sánchez-Gómez, M.V.; Cavaliere, F.; Peérez-Samartín, A.; Zugaza, J.L.; Trullas, R.; Domercq, M.; Matute, C. Amyloid β oligomers induce Ca2+ dysregulation and neuronal death through activation of ionotropic glutamate receptors. Cell Calcium 2010, 47, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lambert, M.P.; Barlow, A.K.; Chromy, B.A.; Edwards, C.; Freed, R.; Liosatos, M.; Morgan, T.E.; Rozovsky, I.; Trommer, B.; Viola, K.L.; et al. Diffusible, nonfibrillar ligands derived from Abeta1-42 are potent central nervous system neurotoxins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 6448–6453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Walsh, D.M.; Rowan, M.J.; Selkoe, D.J.; Anwyl, R. Block of Long- Term Potentiation by Naturally Secreted and Synthetic Amyloid—Peptide in Hippocampal Slices Is Mediated via Activation of the Kinases c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase, Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 5, and p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase as well as metabotropic glutamate receptor type 5. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 3370–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Demuro, A.; Mina, E.; Kayed, R.; Milton, S.C.; Parker, I.; Glabe, C.G. Calcium Dysregulation and Membrane Disruption as a Ubiquitous Neurotoxic Mechanism of Soluble Amyloid Oligomers. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 17294–17300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Viola, K.L.; Klein, W.L. Amyloid β oligomers in Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis, treatment, and diagnosis. Acta Neuropathol. 2015, 129, 183–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdier, Y.; Zarándi, M.; Penke, B. Amyloid β-peptide interactions with neuronal and glial cell plasma membrane: Binding sites and implications for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Pept. Sci. 2004, 10, 229–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Klyubin, I.; Wright, S.; Griswold-Prenner, I.; Rowan, M.J.; Anwyl, R. αv Integrins mediate beta-Amyloid induced inhibition of long-term potentiation. Neurobiol. Aging 2008, 29, 1485–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Butler, J.P.; Ingber, D.E. Mechanotransduction across the cell surface and through the cytoskeleton. Science 1993, 21, 1124–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, T.L.; Cress, A.E.; Dalkin, B.L.; Nagle, R.B. Unique expression pattern of the alpha6beta4 integrin and laminin-5 in human prostate carcinoma. Prostate 2001, 46, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynes, R.O. Integrins: Versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell 1992, 3, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.A.; Hemler, M.E. Interaction of the integrin beta1 cytoplasmic domain with ICAP-1 protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheah, M.; Andrews, M.R. Integrin Activation: Implications for Axon Regeneration. Cells 2018, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Reddy, D.S. Integrins as receptor targets for neurological disorders. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 134, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shattil, S.J.; Kim, C.; Ginsberg, M.H. The final steps of integrin activation: The end game. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Legate, K.R.; Wickström, S.A.; Fässler, R. Genetic and cell biological analysis of integrin outside-in signaling. Genes Dev. 2009, 15, 397–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wright, S.; Malinin, N.L.; Powell, K.A.; Yednock, T.; Rydel, R.E.; Griswold-Prenner, I. α2β1 and αVβ1 Integrin Signaling Pathways Mediate Amyloid-β-Induced Neurotoxicity. Neurobiol. Aging 2007, 28, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, M.; Guccione, S.; Haddix, T.; Sims, L.; Cheshier, S.; Chu, P.; Vogel, H.; Harsh, G. alpha(v)beta(3) Integrin in central nervous system tumors. Hum. Pathol. 2005, 36, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matter, M.L.; Zhang, Z.; Nordstedt, C.; Ruoslahti, E. The alpha5beta1 integrin mediates elimination of amyloid-beta peptide and protects against apoptosis. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 18, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wyssenbach, A.; Quintela, T.; Llavero, F.; Zugaza, J.L.; Matute, C.; Alberdi, E. Amyloid β-induced astrogliosis is mediated by β1-integrin via NADPH oxidase 2 in Alzheimer’s disease. Aging Cell 2016, 15, 1140–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberdi, E.; Wyssenbach, A.; Alberdi, M.; Sánchez-Gómez, M.V.; Cavaliere, F.; Rodriguez, J.J.; Verkhratsky, A.; Matute, C. Ca2+-dependent endoplasmic reticulum stress correlates with astrogliosis in oligomeric amyloid β-treated astrocytes and in a model of Alzheimer’s disease. Aging Cell 2013, 12, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mroczko, B.; Groblewska, M.; Litman-Zawadzka, A.; Kornhuber, J.; Lewczuk, P. Cellular receptors of amyloid β oligomers (AβOs) in Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Texidó, L.; Martín-Satué, M.; Alberdi, E.; Solsona, C.; Matute, C. Amyloid β peptide oligomers directly activate NMDA receptors. Cell Calcium 2011, 49, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Sanz, C.; Gaminde-Blasco, A.; Valero, J.; Bakota, L.; Brandt, R.; Zugaza, J.L.; Matute, C.; Alberdi, E. Early Effects of Aβ Oligomers on Dendritic Spine Dynamics and Arborization in Hippocampal Neurons. Front. Synaptic Neurosci. 2020, 12, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donner, L.; Gremer, L.; Ziehm, T.; Gertzen, C.G.W.; Gohlke, H.; Willbold, D.; Elvers, M. Relevance of N-terminal residues for amyloid-β binding to platelet integrin αIIbβ3, integrin outside-in signaling and amyloid-β fibril formation. Cell. Signal. 2018, 50, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fourel, L.; Valat, A.; Faurobert, E.; Guillot, R.; Bourrin-Reynard, I.; Ren, K.; Albiges-Rizo, C. β3 integrin-mediated spreading induced by matrix-bound BMP-2 controls Smad signaling in a stiffness-independent manner. J. Cell Biol. 2016, 212, 693–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogh, B.S.; Multhaupt, H.A.B.; Couchman, J.R. Protein Kinase C, focal adhesions and the regulation of cell migration. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2014, 62, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ortiz-Sanz, C.; Balantzategi, U.; Quintela-López, T.; Ruiz, A.; Luchena, C.; Zuazo-Ibarra, J.; Capetillo-Zarate, E.; Matute, C.; Zugaza, J.L.; Alberdi, E. Amyloid β/PKC-dependent alterations in NMDA receptor composition are detected in early stages of Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 19, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, U.C.; Deller, T.; Korte, M. Not just amyloid: Physiological functions of the amyloid precursor protein family. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlgren, K.N.; Manelli, A.M.; Stine, W.B.; Baker, L.K.; Krafft, G.A.; Ladu, M.J. Oligomeric and fibrillar species of amyloid-β peptides differentially affect neuronal viability. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 32046–32053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaldua, N.; Gastineau, M.; Hoshino, M.; Lezoualc’h, F.; Zugaza, J.L. Epac signaling pathway involves STEF, a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Rac, to regulate APP processing. FEBS Lett. 2007, 22, 5814–5818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zugaza, J.L.; Lopez, M.A.; Caloca, M.J.; Dosil, M.; Movilla, N.; Bustelo, X.R. Structural Determinants for the Biological Activity of Vav Proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 45377–45392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mccarthy, K.D. Preparation of separate astroglial and oligodendroglial cell cultures from rat cerebral tissue. J. Cell Biol. 1980, 85, 890–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ortiz-Sanz, C.; Llavero, F.; Zuazo-Ibarra, J.; Balantzategi, U.; Quintela-López, T.; Wyssenbach, A.; Capetillo-Zarate, E.; Matute, C.; Alberdi, E.; Zugaza, J.L. Recombinant Integrin β1 Signal Peptide Blocks Gliosis Induced by Aβ Oligomers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105747
Ortiz-Sanz C, Llavero F, Zuazo-Ibarra J, Balantzategi U, Quintela-López T, Wyssenbach A, Capetillo-Zarate E, Matute C, Alberdi E, Zugaza JL. Recombinant Integrin β1 Signal Peptide Blocks Gliosis Induced by Aβ Oligomers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(10):5747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105747
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrtiz-Sanz, Carolina, Francisco Llavero, Jone Zuazo-Ibarra, Uxue Balantzategi, Tania Quintela-López, Ane Wyssenbach, Estibaliz Capetillo-Zarate, Carlos Matute, Elena Alberdi, and José L. Zugaza. 2022. "Recombinant Integrin β1 Signal Peptide Blocks Gliosis Induced by Aβ Oligomers" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 10: 5747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105747
APA StyleOrtiz-Sanz, C., Llavero, F., Zuazo-Ibarra, J., Balantzategi, U., Quintela-López, T., Wyssenbach, A., Capetillo-Zarate, E., Matute, C., Alberdi, E., & Zugaza, J. L. (2022). Recombinant Integrin β1 Signal Peptide Blocks Gliosis Induced by Aβ Oligomers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(10), 5747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105747







