Regulator of G-Protein Signaling-4 Attenuates Cardiac Adverse Remodeling and Neuronal Norepinephrine Release-Promoting Free Fatty Acid Receptor FFAR3 Signaling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
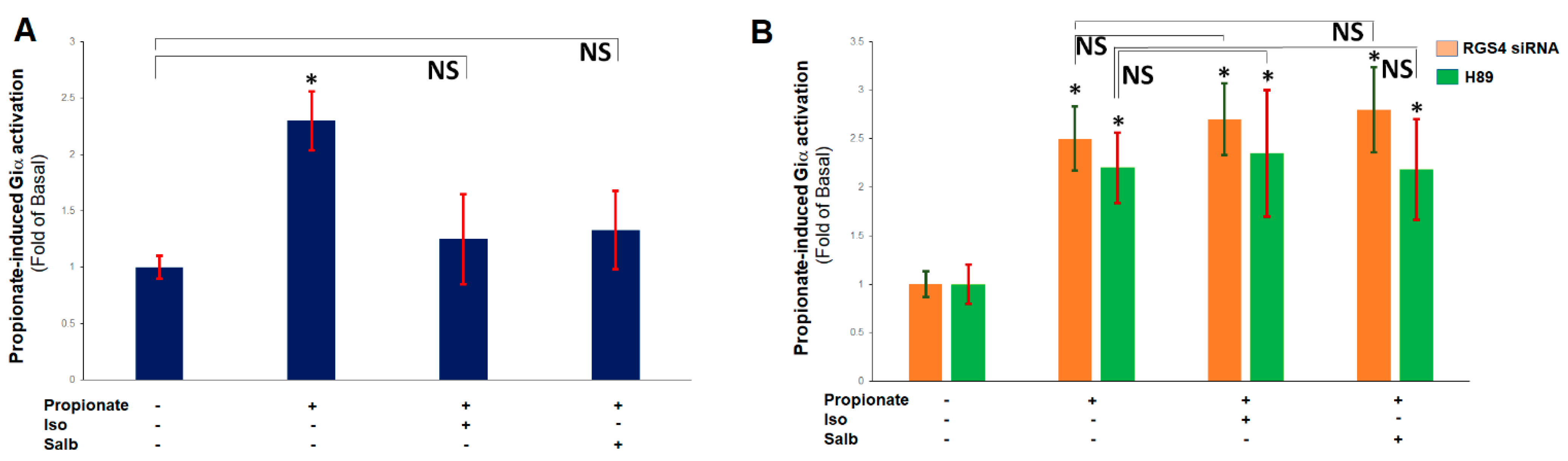
2.1. RGS4 Inactivates Cardiac FFAR3-Stimulated Gi/O Protein Signaling
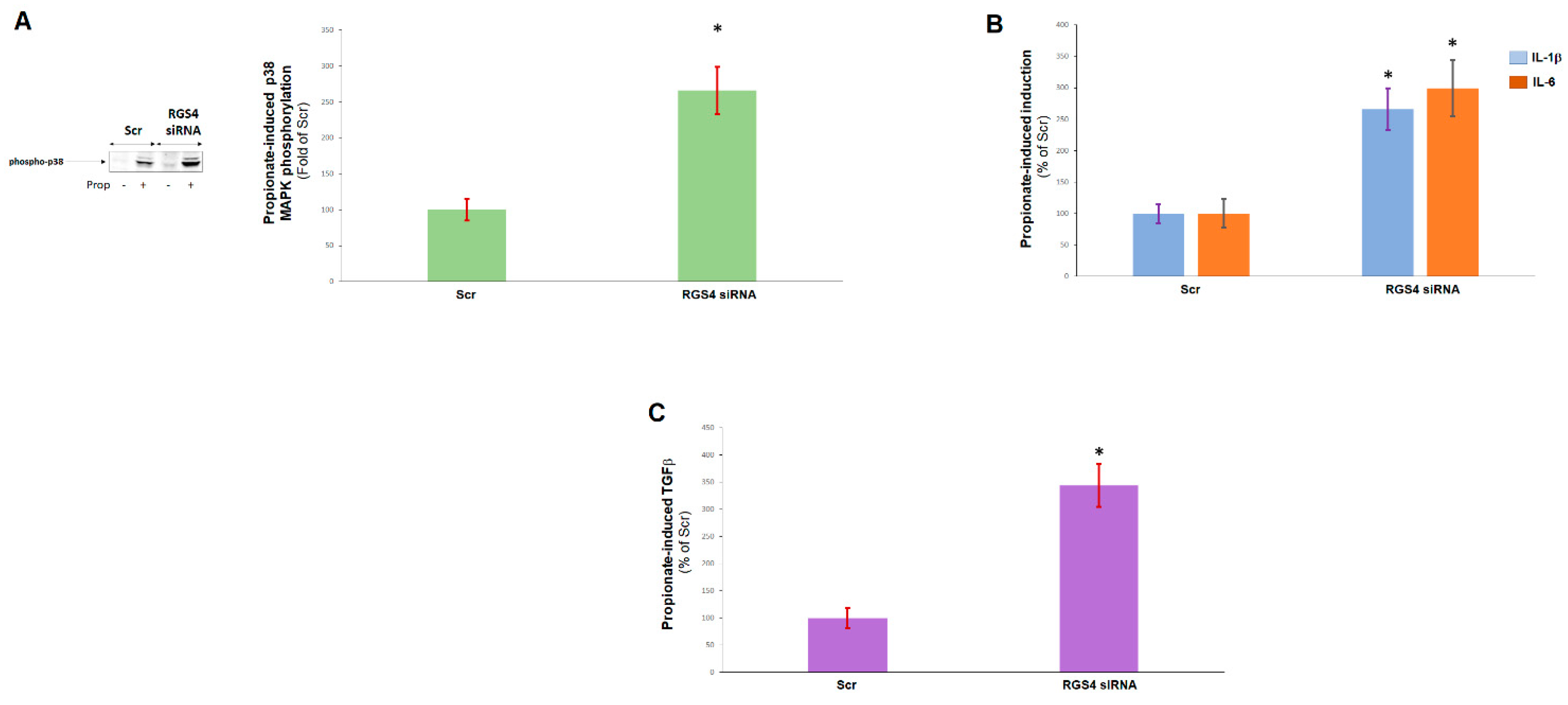
2.2. RGS4 Opposes Cardiac FFAR3 Pro-Inflammatory and Pro-Fibrotic Signaling
2.3. β ARs Reduce Cardiac FFAR3 Signaling via PKA-Dependent RGS4 Stimulation
2.4. RGS4 Inhibits FFAR3-Stimulated NE Release from Sympathetic Neurons
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cell Culture, Transfections, and Treatments
4.3. Giα Activity Assay and cAMP Accumulation Determination
4.4. ELISA and Western Blotting
4.5. βAR Density Measurements
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lymperopoulos, A.; Suster, M.S.; Borges, J.I. Short-Chain Fatty Acid Receptors and Cardiovascular Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, S.P.; Karunakar, P.; Taraphder, S.; Yadav, H. Free Fatty Acid Receptors 2 and 3 as Microbial Metabolite Sensors to Shape Host Health: Pharmacophysiological View. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, I.; Ichimura, A.; Ohue-Kitano, R.; Igarashi, M. Free Fatty Acid Receptors in Health and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2020, 100, 171–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, I.; Inoue, D.; Maeda, T.; Hara, T.; Ichimura, A.; Miyauchi, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Hirasawa, A.; Tsujimoto, G. Short-chain fatty acids and ketones directly regulate sympathetic nervous system via G protein-coupled receptor 41 (GPR41). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 8030–8035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, D.; Kimura, I.; Wakabayashi, M.; Tsumoto, H.; Ozawa, K.; Hara, T.; Takei, Y.; Hirasawa, A.; Ishihama, Y.; Tsujimoto, G. Short-chain fatty acid receptor GPR41-mediated activation of sympathetic neurons involves synapsin 2b phosphorylation. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 1547–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, G.; Druey, K.M.; Xie, Z. R4 RGS proteins: Regulation of G-protein signaling and beyond. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 116, 473–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.B.; Wilkinson, J.C.; Roman, D.L. Regulator of G-protein signaling (RGS) proteins as drug targets: Progress and future potentials. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 18571–18585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squires, K.E.; Montañez-Miranda, C.; Pandya, R.R.; Torres, M.P.; Hepler, J.R. Genetic Analysis of Rare Human Variants of Regulators of G Protein Signaling Proteins and Their Role in Human Physiology and Disease. Pharmacol Rev. 2018, 70, 446–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perschbacher, K.J.; Deng, G.; Fisher, R.A.; Gibson-Corley, K.N.; Santillan, M.K.; Grobe, J.L. Regulators of G protein signaling in cardiovascular function during pregnancy. Physiol. Genom. 2018, 50, 590–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Mende, U. Regulators of G-protein signaling in the heart and their potential as therapeutic targets. Circ. Res. 2011, 109, 320–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuho, I.; Balaji, S.; Muntean, B.S.; Skamangas, N.K.; Chavali, S.; Tesmer, J.J.G.; Babu, M.M.; Martemyanov, K.A. A Global Map of G Protein Signaling Regulation by RGS Proteins. Cell 2020, 183, 503–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowal, L.; Elliott, J.; Popov, S.; Wilkie, T.M.; Scarlata, S. Determination of the contact energies between a regulator of G protein signaling and G protein subunits and phospholipase C beta 1. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Zhou, H.; Mahavadi, S.; Sriwai, W.; Murthy, K.S. Inhibition of Galphaq-dependent PLC-beta1 activity by PKG and PKA is mediated by phosphorylation of RGS4 and GRK2. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2007, 292, C200-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifelli, C.; Rose, R.A.; Zhang, H.; Voigtlaender-Bolz, J.; Bolz, S.S.; Backx, P.H.; Heximer, S.P. RGS4 regulates parasympathetic signaling and heart rate control in the sinoatrial node. Circ. Res. 2008, 103, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, A.; Huang, J.; Fisher, R.A. RGS Proteins in Heart: Brakes on the Vagus. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, J.H.; Tamirisa, P.; Kovacs, A.; Weinheimer, C.; Courtois, M.; Blumer, K.J.; Kelly, D.P.; Muslin, A.J. RGS4 causes increased mortality and reduced cardiac hypertrophy in response to pressure overload. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 104, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tamirisa, P.; Blumer, K.J.; Muslin, A.J. RGS4 inhibits G-protein signaling in cardiomyocytes. Circulation 1999, 99, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, J.H.; Tsirka, A.; Kovacs, A.; Blumer, K.J.; Dorn, G.W., 2nd; Muslin, A.J. RGS4 reduces contractile dysfunction and hypertrophic gene induction in Galpha q overexpressing mice. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2001, 33, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Watson, N.; Zahner, J.; Rottman, J.N.; Blumer, K.J.; Muslin, A.J. RGS3 and RGS4 are GTPase activating proteins in the heart. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 1998, 30, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, V.J.; Burton, P.B.; Mullen, A.J.; Birks, E.J.; Barton, P.; Yacoub, M.H. Expression of RGS3, RGS4 and Gi alpha 2 in acutely failing donor hearts and end-stage heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2001, 22, 1015–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittmann, C.; Chung, C.H.; Höppner, G.; Michalek, C.; Nose, M.; Schüler, C.; Schuh, A.; Eschenhagen, T.; Weil, J.; Pieske, B.; et al. Expression of ten RGS proteins in human myocardium: Functional characterization of an upregulation of RGS4 in heart failure. Cardiovasc. Res. 2002, 55, 778–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mighiu, A.S.; Heximer, S.P. Controlling Parasympathetic Regulation of Heart Rate: A Gatekeeper Role for RGS Proteins in the Sinoatrial Node. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opel, A.; Nobles, M.; Montaigne, D.; Finlay, M.; Anderson, N.; Breckenridge, R.; Tinker, A. Absence of the Regulator of G-protein Signaling, RGS4, Predisposes to Atrial Fibrillation and Is Associated with Abnormal Calcium Handling. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 19233–19244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lymperopoulos, A.; Cora, N.; Maning, J.; Brill, A.R.; Sizova, A. Signaling and function of cardiac autonomic nervous system receptors: Insights from the GPCR signalling universe. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 2645–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lymperopoulos, A.; Borges, J.I.; Cora, N.; Sizova, A. Sympatholytic Mechanisms for the Beneficial Cardiovascular Effects of SGLT2 Inhibitors: A Research Hypothesis for Dapagliflozin’s Effects in the Adrenal Gland. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hua, Y.; Ren, J. Short-chain fatty acid propionate alleviates Akt2 knockout-induced myocardial contractile dysfunction. Exp. Diabetes Res. 2012, 2012, 851717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, C.M.; Desimine, V.L.; Wertz, S.L.; Perez, A.; Parker, B.M.; Maning, J.; McCrink, K.A.; Shehadeh, L.A.; Lymperopoulos, A. Deletion of Osteopontin Enhances β₂-Adrenergic Receptor-Dependent Anti-Fibrotic Signaling in Cardiomyocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capote, L.A.; Mendez Perez, R.; Lymperopoulos, A. GPCR signaling and cardiac function. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 763 Pt B, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maning, J.; McCrink, K.A.; Pollard, C.M.; Desimine, V.L.; Ghandour, J.; Perez, A.; Cora, N.; Ferraino, K.E.; Parker, B.M.; Brill, A.R.; et al. Antagonistic Roles of GRK2 and GRK5 in Cardiac Aldosterone Signaling Reveal GRK5-Mediated Cardioprotection via Mineralocorticoid Receptor Inhibition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, A.J.; Dowsell, R.S.; Gold, M.G. Assaying Protein Kinase A Activity Using a FRET-Based Sensor Purified from Mammalian Cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2483, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, R.G.; Sikorska, M.; Sandhu, J.K.; Lanthier, P.; Ribecco-Lutkiewicz, M.; Bani-Yaghoub, M. Differentiation of mouse Neuro 2A cells into dopamine neurons. J. Neurosci. Methods 2010, 186, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, N.C.; Vallejos, X.; Siryk, A.; Rengo, G.; Cannavo, A.; Liccardo, D.; De Lucia, C.; Gao, E.; Leosco, D.; Koch, W.J.; et al. GRK2 blockade with βARKct is essential for cardiac β2-adrenergic receptor signaling towards increased contractility. Cell Commun. Signal. 2013, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, G.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zong, L.; Sun, L.; Huang, X.; Huang, L.; Zhang, L.; Tian, X.L.; Zhou, Z.; et al. TGF-β signaling alters H4K20me3 status via miR-29 and contributes to cellular senescence and cardiac aging. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barcena, M.L.; Aslam, M.; Pozdniakova, S.; Norman, K.; Ladilov, Y. Cardiovascular Inflammaging: Mechanisms and Translational Aspects. Cells 2022, 11, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusifov, A.; Woulfe, K.C.; Bruns, D.R. Mechanisms and implications of sex differences in cardiac aging. J. Cardiovasc. Aging 2022, 2, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lymperopoulos, A.; Rengo, G.; Koch, W.J. Adrenergic nervous system in heart failure: Pathophysiology and therapy. Circ. Res. 2013, 113, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lymperopoulos, A.; Rengo, G.; Funakoshi, H.; Eckhart, A.D.; Koch, W.J. Adrenal GRK2 upregulation mediates sympathetic overdrive in heart failure. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lymperopoulos, A.; Rengo, G.; Gao, E.; Ebert, S.N.; Dorn, G.W., 2nd; Koch, W.J. Reduction of sympathetic activity via adrenal-targeted GRK2 gene deletion attenuates heart failure progression and improves cardiac function after myocardial infarction. J Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 16378–16386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, J.I.; Ferraino, K.E.; Cora, N.; Nagliya, D.; Suster, M.S.; Carbone, A.M.; Lymperopoulos, A. Adrenal G protein-coupled receptors and the failing heart: A long-distance, yet intimate affair. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Kaindl, J.; Clark, M.J.; Hübner, H.; Hirata, K.; Sunahara, R.K.; Gmeiner, P.; Kobilka, B.K.; Liu, X. Binding pathway determines norepinephrine selectivity for the human β1AR over β2AR. Cell Res. 2021, 31, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lymperopoulos, A.; Rengo, G.; Koch, W.J. Adrenal adrenoceptors in heart failure: Fine-tuning cardiac stimulation. Trends Mol. Med. 2007, 13, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafferjee, M.; Reyes Valero, T.; Marrero, C.; McCrink, K.A.; Brill, A.; Lymperopoulos, A. GRK2 Up-Regulation Creates a Positive Feedback Loop for Catecholamine Production in Chromaffin Cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 2016, 30, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anton, S.E.; Kayser, C.; Maiellaro, I.; Nemec, K.; Möller, J.; Koschinski, A.; Zaccolo, M.; Annibale, P.; Falcke, M.; Lohse, M.J.; et al. Receptor-associated independent cAMP nanodomains mediate spatiotemporal specificity of GPCR signaling. Cell 2022, 185, 1130–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, A.Y.; Xiao, R.P. β-Adrenergic receptor subtype signaling in heart: From bench to bedside. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2012, 33, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djoussé, L.; Benkeser, D.; Arnold, A.; Kizer, J.R.; Zieman, S.J.; Lemaitre, R.N.; Tracy, R.P.; Gottdiener, J.S.; Mozaffarian, D.; Siscovick, D.S.; et al. Plasma free fatty acids and risk of heart failure: The Cardiovascular Health Study. Circ Heart Fail. 2013, 6, 964–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Jin, C.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, S.; Meng, S.; Ma, H.; Wang, J.; Xiang, M. Serum Free Fatty Acids Independently Predict Adverse Outcomes in Acute Heart Failure Patients. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 761537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCrink, K.A.; Maning, J.; Vu, A.; Jafferjee, M.; Marrero, C.; Brill, A.; Bathgate-Siryk, A.; Dabul, S.; Koch, W.J.; Lymperopoulos, A. β-Arrestin2 Improves Post-Myocardial Infarction Heart Failure via Sarco(endo)plasmic Reticulum Ca2+-ATPase-Dependent Positive Inotropy in Cardiomyocytes. Hypertension 2017, 70, 972–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, C.W.; David, P.; Naidu, M.; Wong, K.H.; Sabaratnam, V. Neurite outgrowth stimulatory effects of culinary-medicinal mushrooms and their toxicity assessment using differentiating Neuro-2a and embryonic fibroblast BALB/3T3. BMC Complement Altern. Med. 2013, 13, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Xie, X. Tools for GPCR drug discovery. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2012, 33, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carbone, A.M.; Borges, J.I.; Suster, M.S.; Sizova, A.; Cora, N.; Desimine, V.L.; Lymperopoulos, A. Regulator of G-Protein Signaling-4 Attenuates Cardiac Adverse Remodeling and Neuronal Norepinephrine Release-Promoting Free Fatty Acid Receptor FFAR3 Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5803. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105803
Carbone AM, Borges JI, Suster MS, Sizova A, Cora N, Desimine VL, Lymperopoulos A. Regulator of G-Protein Signaling-4 Attenuates Cardiac Adverse Remodeling and Neuronal Norepinephrine Release-Promoting Free Fatty Acid Receptor FFAR3 Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(10):5803. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105803
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarbone, Alexandra M., Jordana I. Borges, Malka S. Suster, Anastasiya Sizova, Natalie Cora, Victoria L. Desimine, and Anastasios Lymperopoulos. 2022. "Regulator of G-Protein Signaling-4 Attenuates Cardiac Adverse Remodeling and Neuronal Norepinephrine Release-Promoting Free Fatty Acid Receptor FFAR3 Signaling" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 10: 5803. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105803
APA StyleCarbone, A. M., Borges, J. I., Suster, M. S., Sizova, A., Cora, N., Desimine, V. L., & Lymperopoulos, A. (2022). Regulator of G-Protein Signaling-4 Attenuates Cardiac Adverse Remodeling and Neuronal Norepinephrine Release-Promoting Free Fatty Acid Receptor FFAR3 Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(10), 5803. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105803






