Comprehensive Analysis of hsa-miR-654-5p’s Tumor-Suppressing Functions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
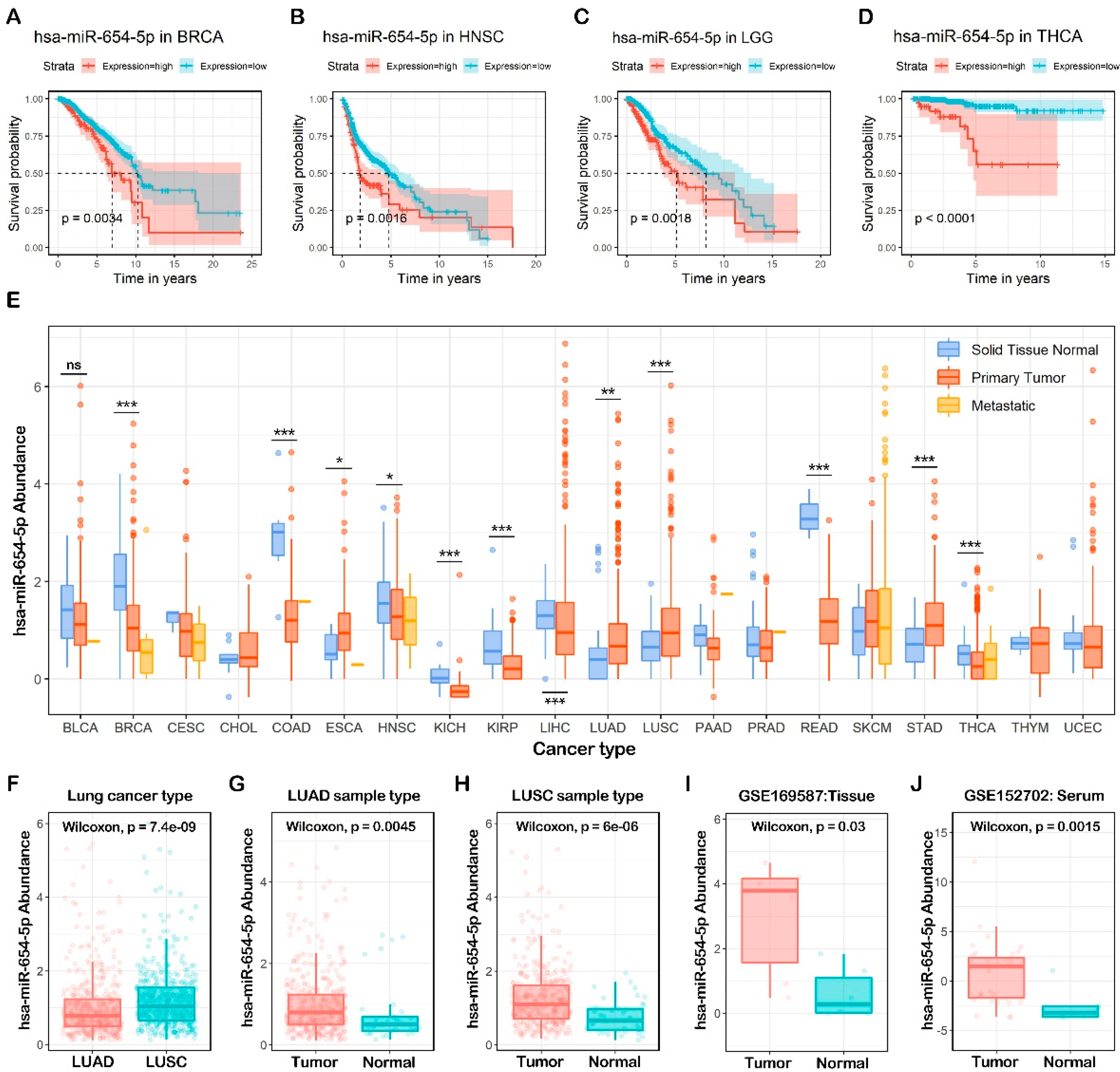
2.1. In Silico Prognostic Analysis of miR-654-5p in Cancers
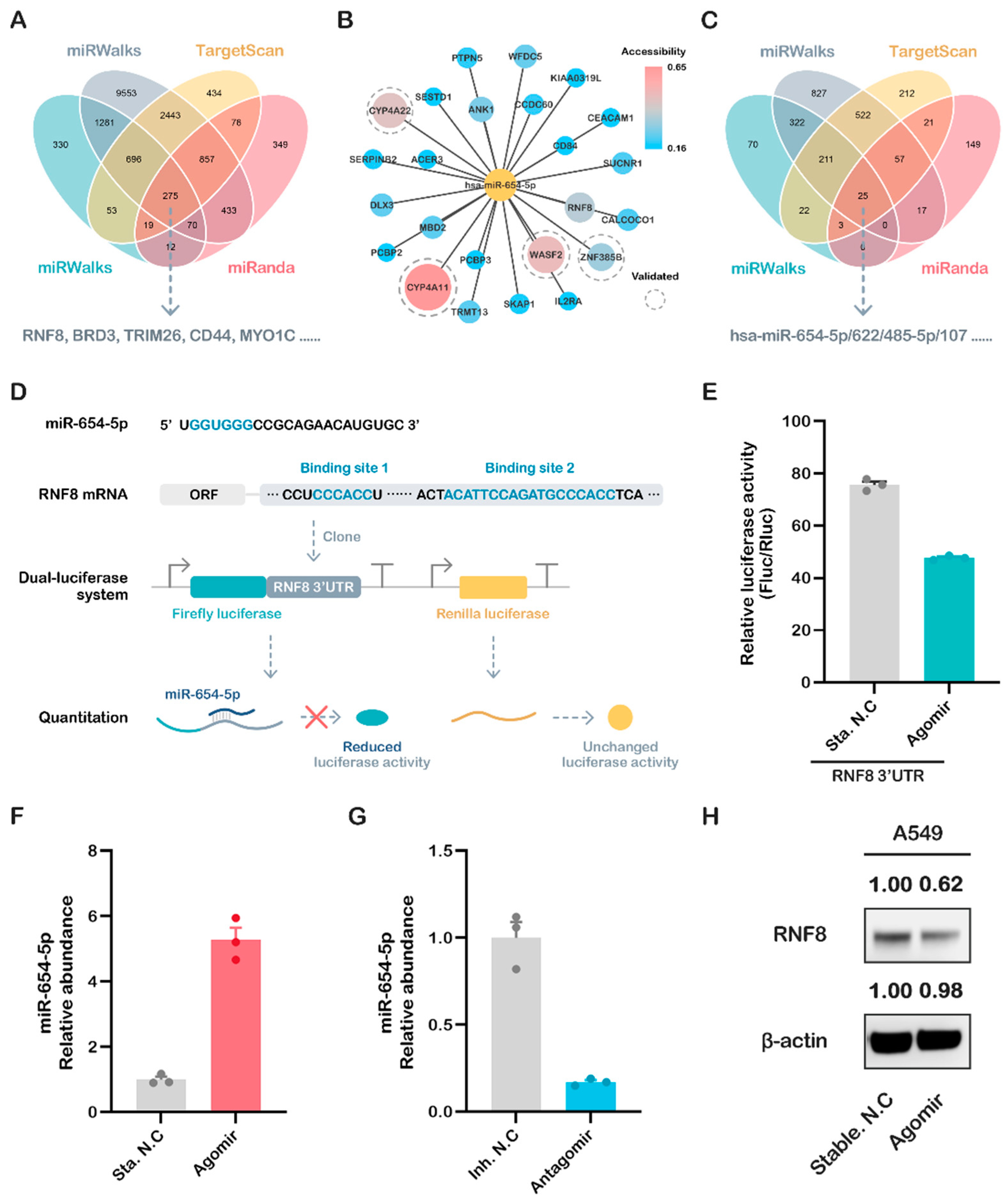
2.2. Integrated Targets Prediction of miR-654-5p
2.3. miR-654-5p/RNF8 Axis: A Case of In Vitro Validation of Predicted Targets
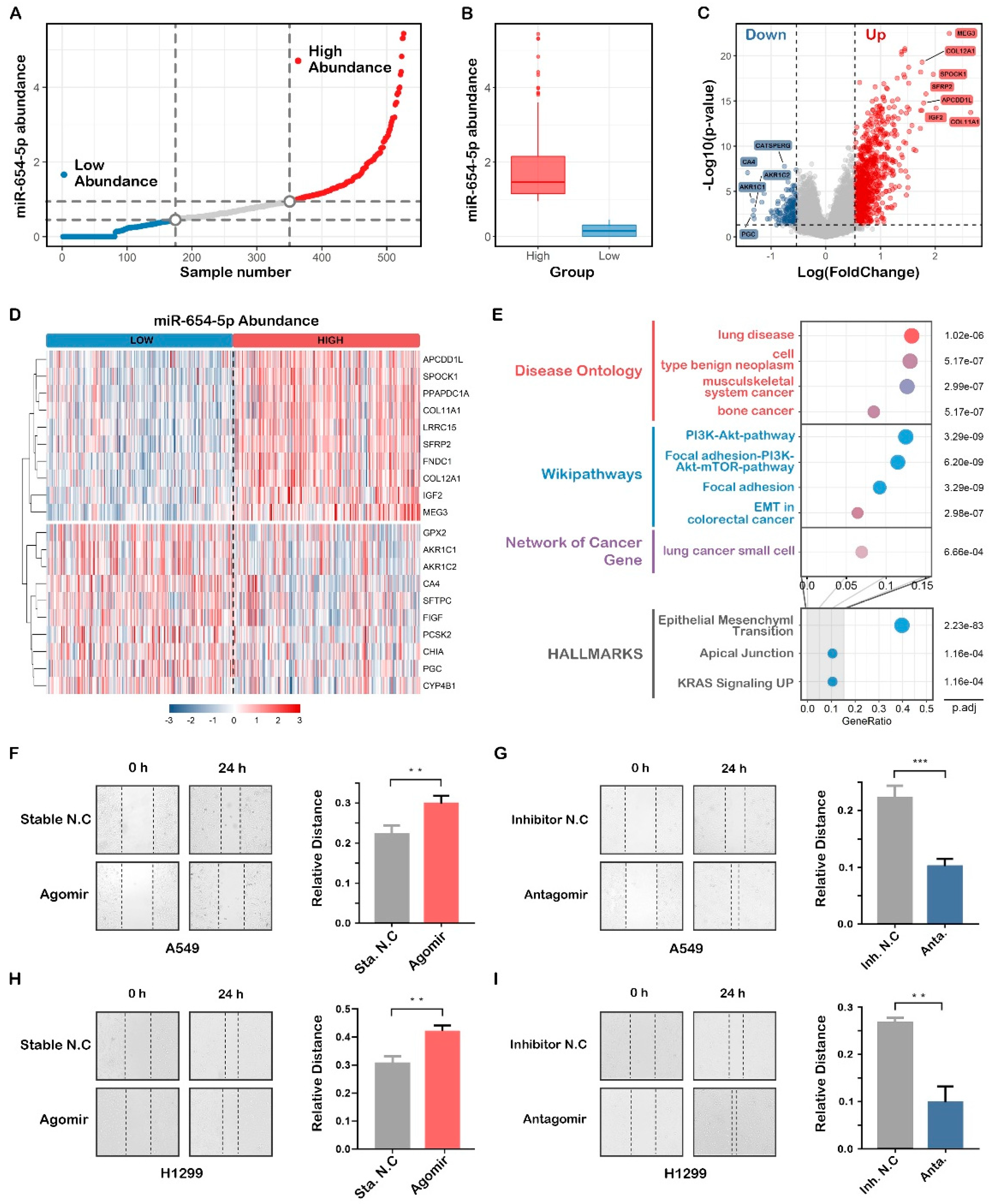
2.4. Comprehensive Analysis of the Predicted Target Genes and In Vitro Validation
2.4.1. Functional Enrichment Analyses Reveal the Inhibitory Roles of miR-654-5p on Lung Cancer Cell Proliferation
2.4.2. Abundance-Based Functional Analysis Shows That miR-654-5p Inhibits Lung Cancer Cell Migration
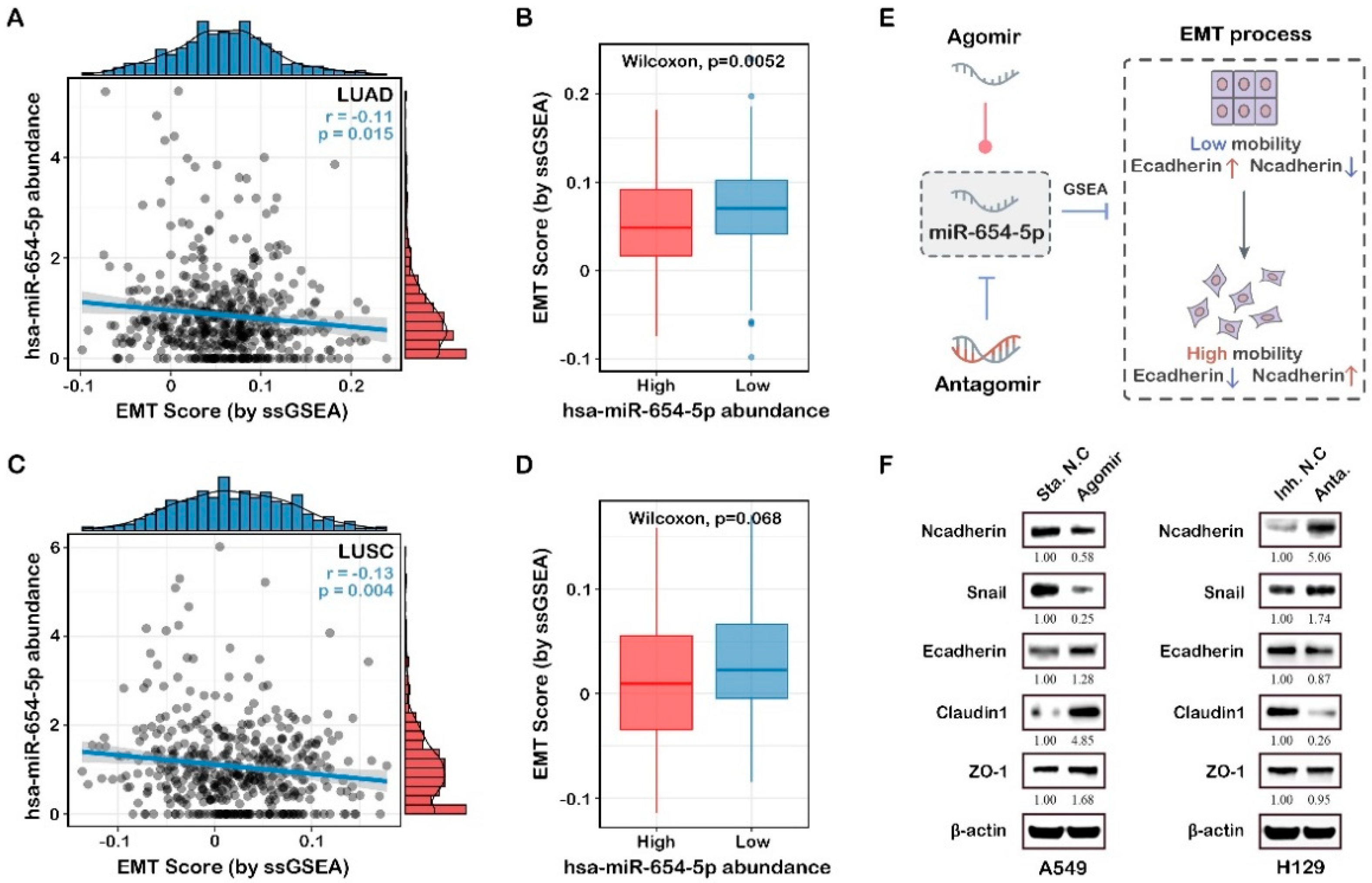
2.4.3. ssGSEA-Based Functional Analysis Shows That miR-654-5p Inhibits Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition
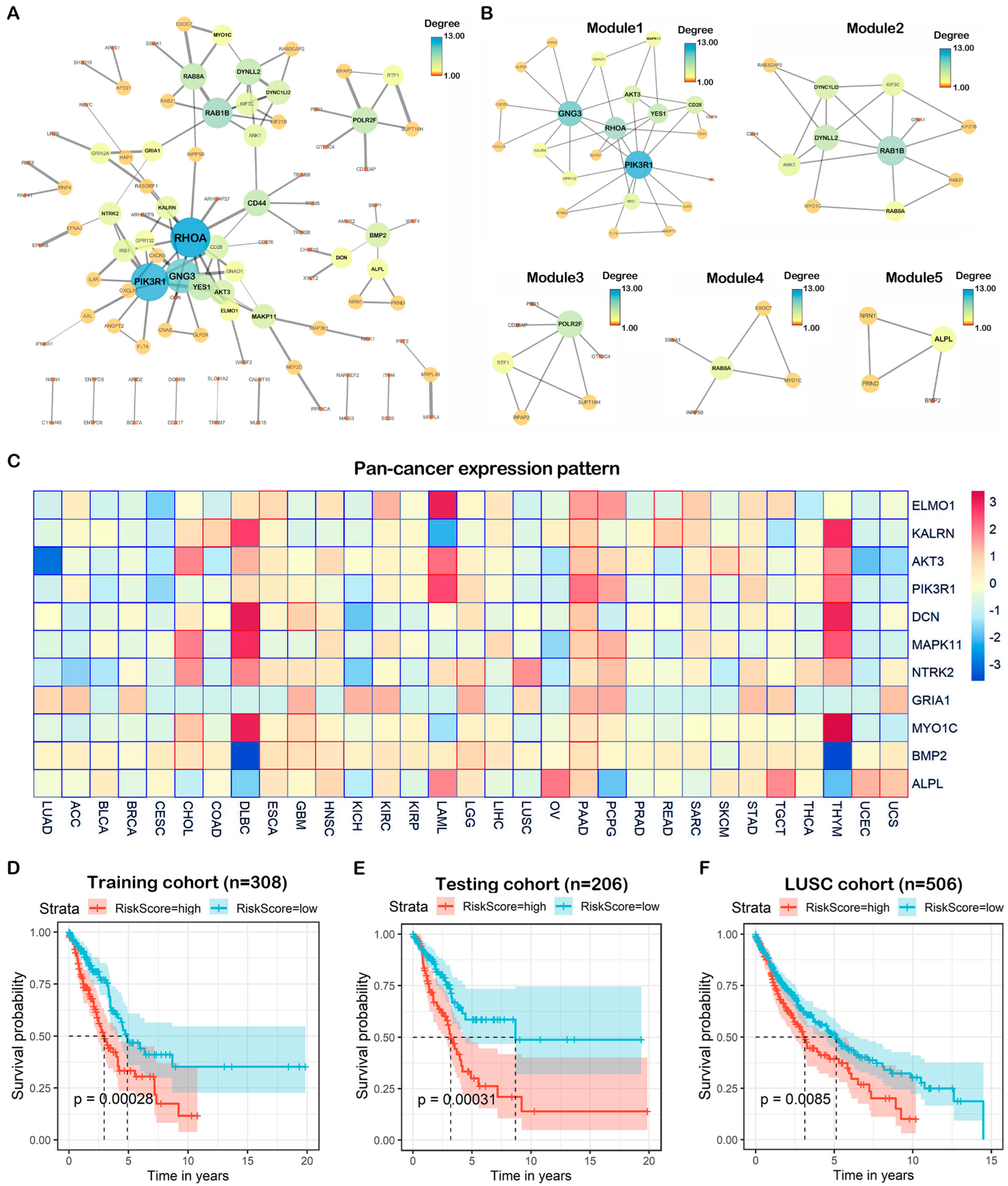
2.5. Construction of PPI Network and Identification of Hub Target Genes
2.6. Pan-Cancer Expression and Prognostic Value of Hub Genes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Pan-Cancer Analysis of hsa-miR-654-5p
4.2. Integrated Target Prediction of miR-654-5p Target Genes
4.3. Comprehensive Analysis of miR-654-5p Functions
4.3.1. Functional Analysis of hsa-miR-654-5p
4.3.2. Protein-Protein Interaction Analysis
4.3.3. Pan-Cancer Expression and Prognostic Value of Hub Genes
4.3.4. hsa-miR-654-5p Expression-Based Functional Analysis
4.3.5. Cox Model Construction and Validation
4.4. In Vitro Proof of Concept for Functional Analyses
4.4.1. Cell Culture
4.4.2. Overexpression or Knockdown of miRNA and RNF8
4.4.3. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.4.4. Western Blotting
4.4.5. In Vitro Cell Proliferation and Wound Healing Assays
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, Z.M.; Wang, L.; Shen, H.; Jiang, C.F.; Ge, X.; Li, D.M.; Wen, Y.Y.; Sun, H.R.; Pan, M.H.; Li, W. Downregulation of miR-218 contributes to epithelial–mesenchymal transition and tumor metastasis in lung cancer by targeting Slug/ZEB2 signaling. Oncogene 2017, 36, 2577–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siegel, R.; Naishadham, D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2012, 62, 10–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Zheng, R.; Baade, P.D.; Zhang, S.; Zeng, H.; Bray, F.; Jemal, A.; Yu, X.Q.; He, J. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 5–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, J.R.; Yang, P.; Cassivi, S.D.; Schild, S.E.; Adjei, A.A. Non-small cell lung cancer: Epidemiology, risk factors, treatment, and survivorship. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, D.; Bu, J.; Ren, F.; Liu, B.; Zhang, S.; Xu, Z.; Pang, S.; Xu, S. miR-455-5p promotes cell growth and invasion by targeting SOCO3 in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 114956–114965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chatani, M. The state of the art: Radiation therapy for non-small cell lung cancer. Gan Kagaku Ryoho Cancer Chemother. 1997, 24 (Suppl. 3), 373–378. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Julie Li, Y.S.; Huang, H.D.; Shyy, J.Y.; Chien, S. microRNA: A master regulator of cellular processes for bioengineering systems. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, Z.; Xia, Y.; Pan, C.; Ma, T.; Liu, B.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y. Up-Regulation of MiR-452 Inhibits Metastasis of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer by Regulating BMI1. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 37, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Min, L.; Liu, C.; Kuang, J.; Wu, X.; Zhu, L. miR-214 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer cells via downregulation of RNF8. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2019, 51, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Croce, C.M. The role of MicroRNAs in human cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2016, 1, 15004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Shen, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, K.; Wang, S.; Ye, Y.; Wang, B. Downregulation of miR-654-3p in Colorectal Cancer Indicates Poor Prognosis and Promotes Cell Proliferation and Invasion by Targeting SRC. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 577948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, J.; Xing, S.; Dong, Z.; Niu, L.; Xu, Q.; Li, Y.; Liu, P.; Yang, P. miR-654-3p suppresses cell viability and promotes apoptosis by targeting RASAL2 in non-small-cell lung cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.Y.; Xu, X.Y.; Wang, J.F.; Zhang, C.W.; Zhang, S.C. MiR-654-5p attenuates breast cancer progression by targeting EPSTI1. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 6, 522. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.Z.; Song, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L. MiR-654-5p regulated cell progression and tumor growth through targeting SIRT6 in osteosarcoma. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 3517–3525. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, M.; Wang, C.; Chen, W.; Mao, C.; Wang, J. miR-654-5p Targets GRAP to Promote Proliferation, Metastasis, and Chemoresistance of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma through Ras/MAPK Signaling. DNA Cell Biol. 2018, 37, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, R. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0085131 is involved in cisplatin-resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer cells by regulating autophagy. Cell Biol. Int. 2020, 44, 1945–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, A.; Lanczky, A.; Menyhart, O.; Gyorffy, B. Validation of miRNA prognostic power in hepatocellular carcinoma using expression data of independent datasets. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowery, A.J.; Miller, N.; Mcneill, R.E.; Kerin, M.J. MicroRNAs as prognostic indicators and therapeutic targets: Potential effect on breast cancer management. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target Recognition and Regulatory Functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Xia, R.; Chen, H.; He, Y. TBtools, a Toolkit for Biologists integrating various HTS-data handling tools with a user-friendly interface. bioRxiv 2018, 289660, 289660. [Google Scholar]
- Conway, J.R.; Lex, A.; Gehlenborg, N. UpSetR: An R package for the visualization of intersecting sets and their properties. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2938–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.; Li, C.; Ruan, D.; Powers, S.; Thompson, P.A.; Frohman, M.A.; Chan, C.H. The DNA Damage Transducer RNF8 Facilitates Cancer Chemoresistance and Progression through Twist Activation. Mol. Cell 2016, 63, 1021–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuang, J.; Li, L.; Guo, L.; Su, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X.; Meng, S.; Lei, L.; Xu, L. RNF8 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.; Ruan, D.; He, J.; Chan, C.H. Two-faced activity of RNF8: What “twists” it from a genome guardian to a cancer facilitator? Mol. Cell. Oncol. 2016, 3, e1242454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuang, J.; Min, L.; Liu, C.; Chen, S.; Gao, C.; Ma, J.; Wu, X.; Li, W.; Wu, L.; Zhu, L. RNF8 Promotes Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition in Lung Cancer Cells via Stabilization of Slug. Mol. Cancer Res. 2020, 18, 1638–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; Weinberg, R.A. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 119, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Shang, Y. Epigenetic control of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and cancer metastasis. Exp. Cell Res. 2013, 319, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiery, J.P.; Acloque, H.; Huang, R.Y.; Nieto, M.A. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell 2009, 139, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaffer, C.L.; Weinberg, R.A. A Perspective on Cancer Cell Metastasis. Science 2011, 331, 1559–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hausser, J.; Zavolan, M. Identification and consequences of miRNA–target interactions—beyond repression of gene expression. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Min, L.; Kuang, J.; Zhu, C.; Qiu, X.-Y.; Zhu, L. Bioinformatic Identification of miR-622 Key Target Genes and Experimental Validation of the miR-622-RNF8 Axis in Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorio, M.V.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA dysregulation in cancer: Diagnostics, monitoring and therapeutics. A comprehensive review. Embo Mol. Med. 2012, 4, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-C.; You, J.-Y.; Lung, J.; Huang, C.-E.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Leu, Y.-W.; Ho, H.-Y.; Li, C.-P.; Lu, C.-H.; Lee, K.-D. Aberrant let7a/HMGA2 signaling activity with unique clinical phenotype in JAK2 mutated myeloproliferative neoplasms. Haematologica 2017, 102, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, M.S.; Lu, J.; Mercer, K.L.; Golub, T.R.; Jacks, T. Impaired microRNA processing enhances cellular transformation and tumorigenesis. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majem, B.; Parrilla, A.; Jiménez, C.; Suárez-Cabrera, L.; Barber, M.; Marín, A.; Castellví, J.; Tamayo, G.; Moreno-Bueno, G.; Ponce, J.; et al. MicroRNA-654-5p suppresses ovarian cancer development impacting on MYC, WNT and AKT pathways. Oncogene 2019, 38, 6035–6050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Syed, S.N.; Brüne, B. Exosomal and Non-Exosomal MicroRNAs: New Kids on the Block for Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, N.L.; Marylin, L.; Mélanie, M.; Christelle, M.; Julien, F.; Karine, S.P.; Anne, P.; François, F.; Bruno, G.; Claire, R. Profiling olfactory stem cells from living patients identifies miRNAs relevant for autism pathophysiology. Mol. Autism 2016, 7, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.Q.; Chen, H.; Zheng, X.F.; Zhang, B.X.; Li, T.S. Hsa-miR-654-5p regulates osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by repressing bone morphogenetic protein 2. J. South. Med. Univ. 2012, 32, 291–295. [Google Scholar]
- Gyorffy, B.; Lanczky, A.; Eklund, A.C.; Denkert, C.; Budczies, J.; Li, Q.; Szallasi, Z. An online survival analysis tool to rapidly assess the effect of 22,277 genes on breast cancer prognosis using microarray data of 1809 patients. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 123, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koch, A.; De Meyer, T.; Jeschke, J.; Van Criekinge, W. MEXPRESS: Visualizing expression, DNA methylation and clinical TCGA data. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sticht, C.; De La Torre, C.; Parveen, A.; Gretz, N. miRWalk: An online resource for prediction of microRNA binding sites. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.Y. clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. Omics A J. Integr. Biol. 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, B.; Pache, L.; Chang, M.; Khodabakhshi, A.H.; Tanaseichuk, O.; Benner, C.; Chanda, S.K. Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Kang, B.; Li, C.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Z. GEPIA2: An enhanced web server for large-scale expression profiling and interactive analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W556–W560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, Z.C.; Li, T.T.; Gan, B.L.; Gao, X.; Gao, L.; Chen, G.; Hu, X.H. Investigation of miR-136-5p key target genes and pathways in lung squamous cell cancer based on TCGA database and bioinformatics analysis. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2018, 214, 644–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, X.; Turck, N.; Hainard, A.; Tiberti, N.; Lisacek, F.; Sanchez, J.C.; Müller, M. pROC: An open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Min, L.; Kuang, J.; Zhu, C.; Qiu, X.; Wu, X.; Zhang, T.; Xie, S.; Zhu, L. Comprehensive Analysis of hsa-miR-654-5p’s Tumor-Suppressing Functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6411. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23126411
Liu C, Min L, Kuang J, Zhu C, Qiu X, Wu X, Zhang T, Xie S, Zhu L. Comprehensive Analysis of hsa-miR-654-5p’s Tumor-Suppressing Functions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(12):6411. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23126411
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Chuanyang, Lu Min, Jingyu Kuang, Chushu Zhu, Xinyuan Qiu, Xiaomin Wu, Tianyi Zhang, Sisi Xie, and Lingyun Zhu. 2022. "Comprehensive Analysis of hsa-miR-654-5p’s Tumor-Suppressing Functions" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 12: 6411. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23126411
APA StyleLiu, C., Min, L., Kuang, J., Zhu, C., Qiu, X., Wu, X., Zhang, T., Xie, S., & Zhu, L. (2022). Comprehensive Analysis of hsa-miR-654-5p’s Tumor-Suppressing Functions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(12), 6411. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23126411






