Effects of Chronic LY341495 on Hippocampal mTORC1 Signaling in Mice with Chronic Unpredictable Stress-Induced Depression
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
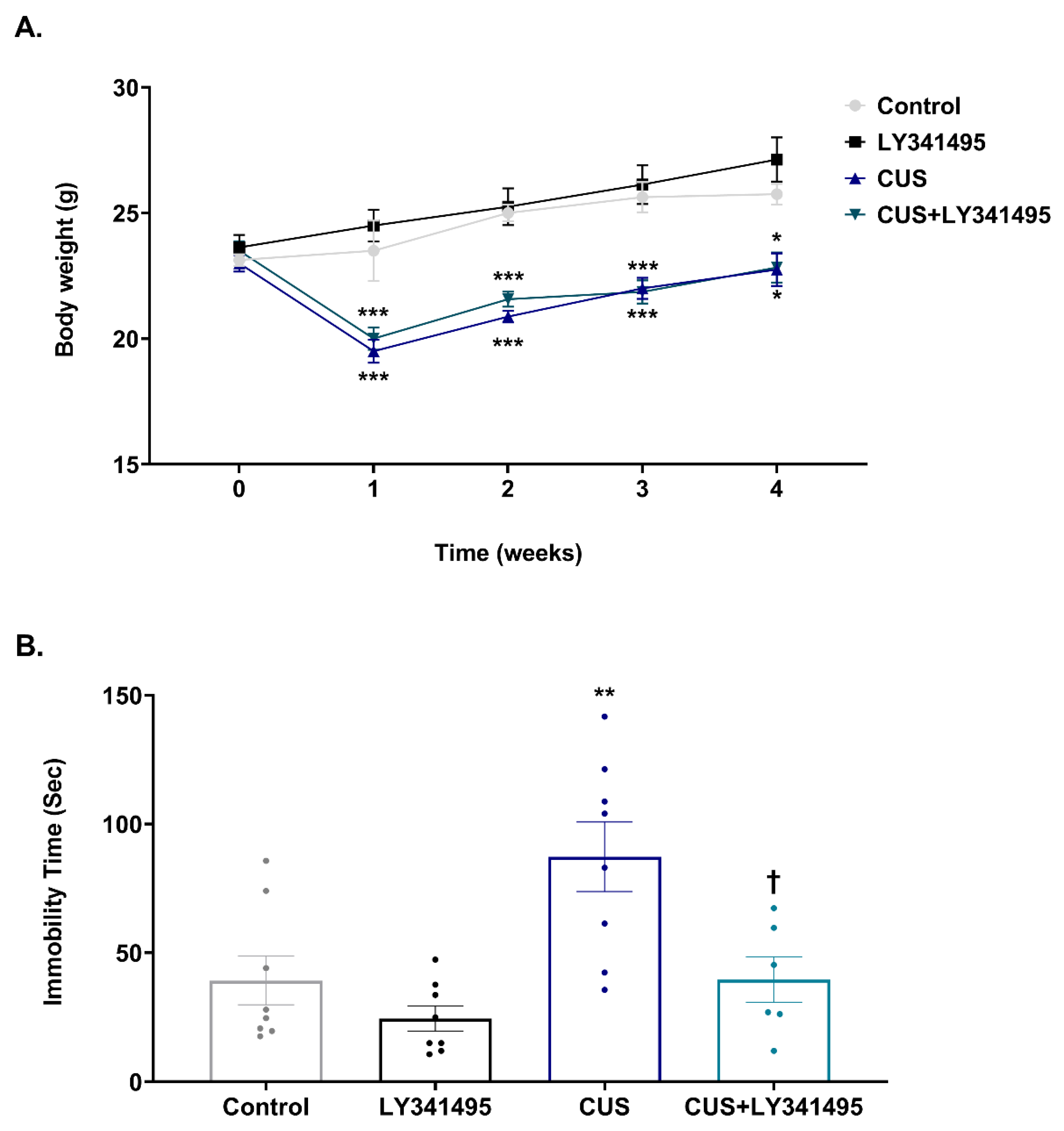
2.1. Behavioral Effect of Chronic LY341495 Administration in a Mouse Model of CUS-Induced Depression
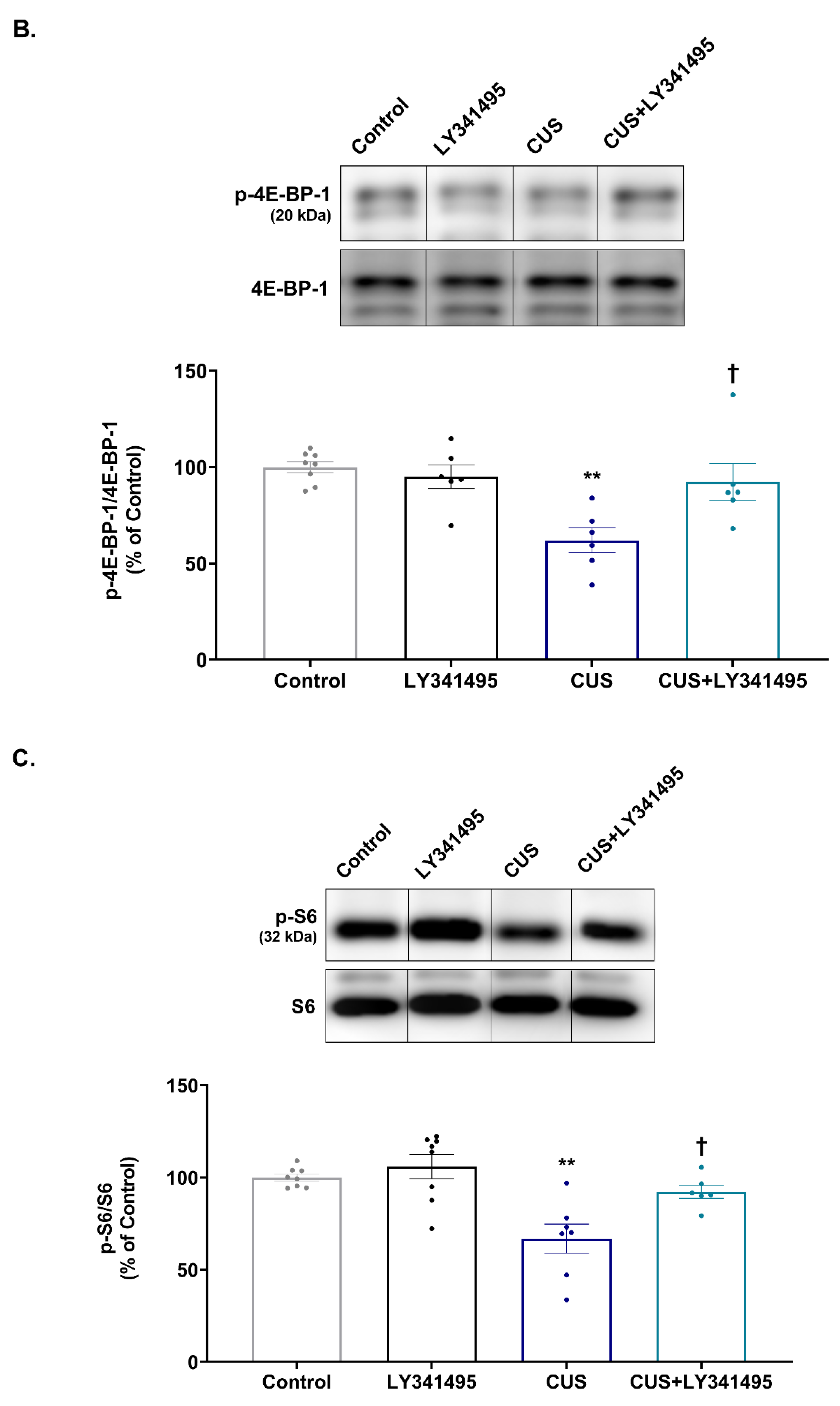
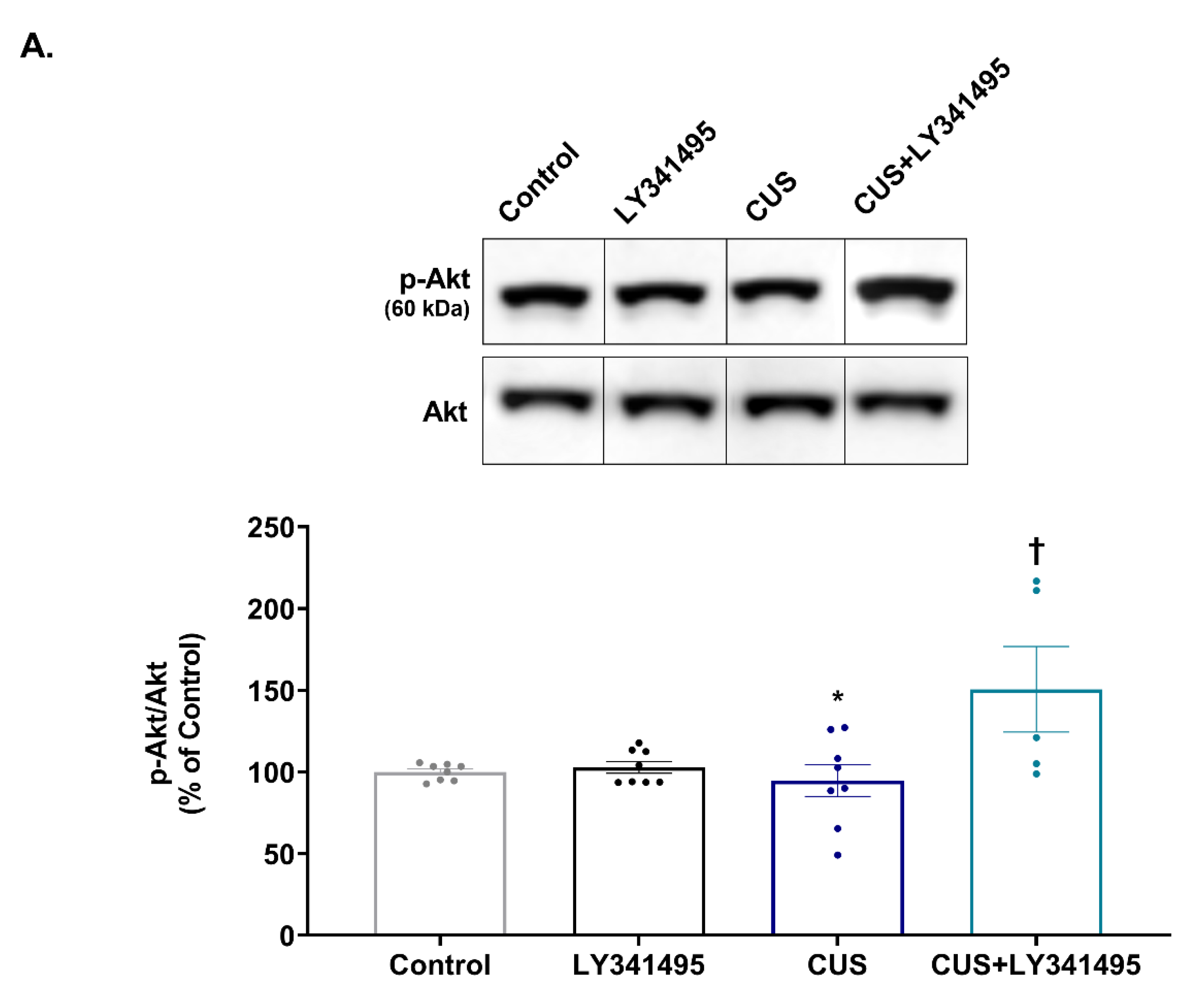
2.2. Effects of Chronic LY341495 Treatment on Hippocampal mTORC1 Signaling in CUS-Exposed Mice
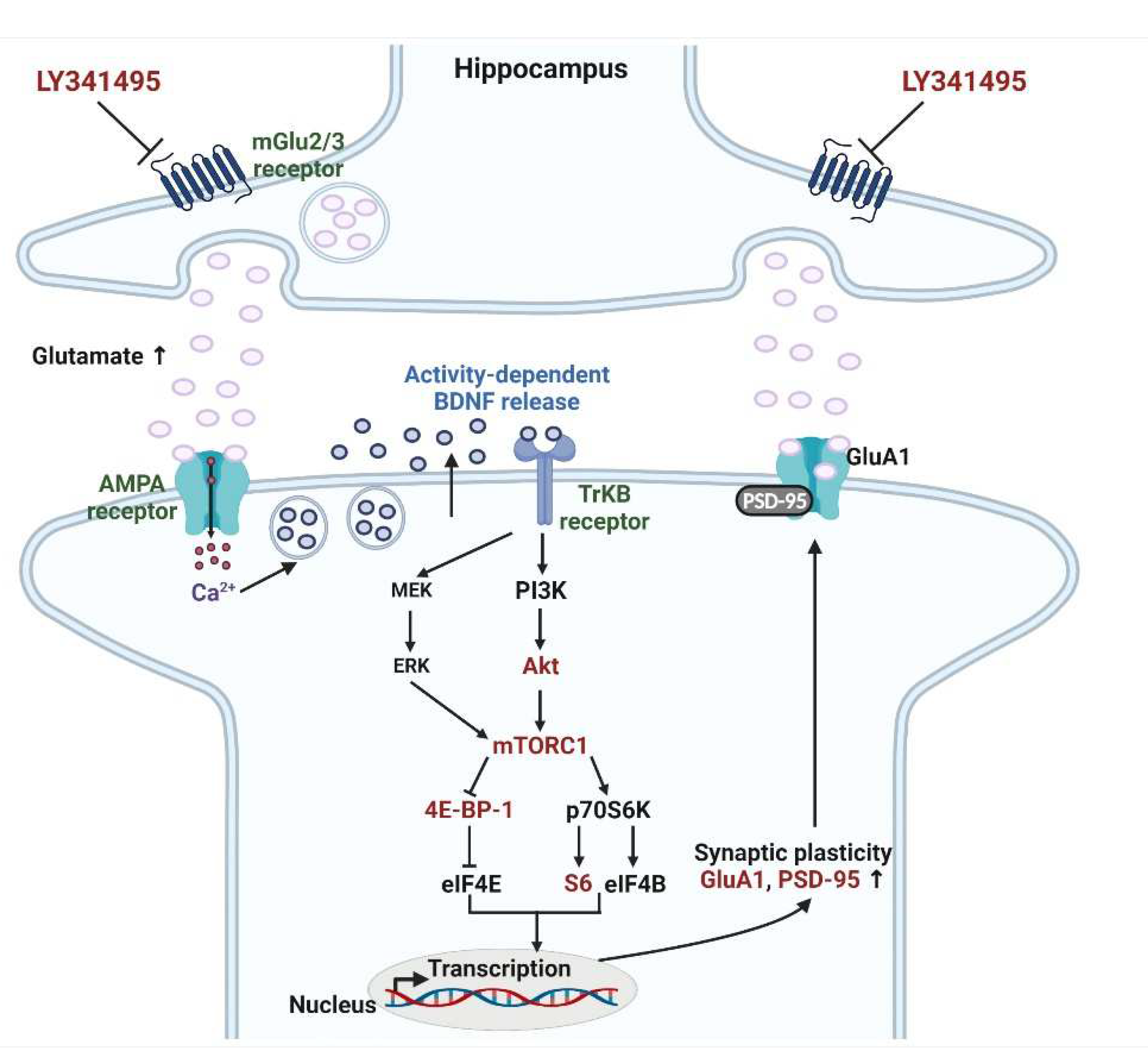
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Drug Administration and Experimental Groups
4.3. Chronic Unpredictable Stress (CUS) Induction
4.4. Forced Swimming Test (FST)
4.5. Western Blotting
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berman, R.M.; Cappiello, A.; Anand, A.; Oren, D.A.; Heninger, G.R.; Charney, D.S.; Krystal, J.H. Antidepressant effects of ketamine in depressed patients Biol Psychiatry. Biol. Psychiatry 2000, 47, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, L.; Diazgranados, N.; Luckenbaugh, D.A.; Machado-Vieira, R.; Baumann, J.; Mallinger, A.G.; Zarate, C.A., Jr. Rapid decrease in depressive symptoms with an N-methyl-d-aspartate antagonist in ECT-resistant major depression. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 35, 1155–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zarate, C.A., Jr.; Singh, J.B.; Carlson, P.J.; Brutsche, N.E.; Ameli, R.; Luckenbaugh, D.A.; Charney, D.S.; Manji, H.K. A randomized trial of an N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist in treatment-resistant major depression. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2006, 63, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duman, R.S.; Voleti, B. Signaling pathways underlying the pathophysiology and treatment of depression: Novel mechanisms for rapid-acting agents. Trends Neurosci. 2012, 35, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, N.; Lee, B.; Liu, R.J.; Banasr, M.; Dwyer, J.M.; Iwata, M.; Li, X.Y.; Aghajanian, G.; Duman, R.S. mTOR-dependent synapse formation underlies the rapid antidepressant effects of NMDA antagonists. Science 2010, 329, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Witkin, J.M.; Marek, G.J.; Johnson, B.G.; Schoepp, D.D. Metabotropic glutamate receptors in the control of mood disorders. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2007, 6, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaki, S.; Yoshikawa, R.; Hirota, S.; Shimazaki, T.; Maeda, M.; Kawashima, N.; Yoshimizu, T.; Yasuhara, A.; Sakagami, K.; Okuyama, S.; et al. Share MGS0039: A potent and selective group II metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonist with antidepressant-like activity. Neuropharmacology 2004, 46, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, H.; Chaki, S. Requirement of AMPA receptor stimulation for the sustained antidepressant activity of ketamine and LY341495 during the forced swim test in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 271, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pałucha-Poniewiera, A.; Wierońska, J.M.; Brański, P.; Stachowicz, K.; Chaki, S.; Pilc, A. On the mechanism of the antidepressant-like action of group II mGlu receptor antagonist, MGS0039. Psychopharmacology 2010, 212, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dwyer, J.M.; Lepack, A.E.; Duman, R.S. mTOR activation is required for the antidepressant effects of mGluR2/3 blockade. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2012, 15, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koike, H.; Iijima, M.; Chaki, S. Involvement of the mammalian target of rapamycin signaling in the antidepressant-like effect of group II metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonists. Neuropharmacology 2011, 61, 1419–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, M.K.; Hien, L.T.; Park, M.K.; Choi, A.J.; Seog, D.H.; Kim, S.H.; Park, S.W.; Lee, J.G. AMPA receptor-mTORC1 signaling activation is required for neuroplastic effects of LY341495 in rat hippocampal neurons. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwyer, J.M.; Lepack, A.E.; Duman, R.S. mGluR2/3 blockade produces rapid and long-lasting reversal of anhedonia caused by chronic stress exposure. J. Mol. Psychiatry 2013, 1, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pałucha-Poniewiera, A.; Podkowa, K.; Rafało-Ulińska, A. The group II mGlu receptor antagonist LY341495 induces a rapid antidepressant-like effect and enhances the effect of ketamine in the chronic unpredictable mild stress model of depression in C57BL/6J mice. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 109, 110239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Zhang, J.C.; Yao, W.; Ren, Q.; Ma, M.; Yang, C.; Chaki, S.; Hashimoto, K. Rapid and Sustained Antidepressant Action of the mGlu2/3 Receptor Antagonist MGS0039 in the Social Defeat Stress Model: Comparison with Ketamine. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017, 20, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, R.; Li, Y.; Du, A.; Yu, H.; He, B.; Shen, R.; Zhou, J.; Li, L.; Cui, W.; Zhang, G.; et al. Changes in hippocampal AMPA receptors and cognitive impairments in chronic ketamine addiction models: Another understanding of ketamine CNS toxicity. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caffino, L.; Piva, A.; Giannotti, G.; Di Chio, M.; Mottarlini, F.; Venniro, M.; Yew, D.T.; Chiamulera, C.; Fumagalli, F. Ketamine Self-Administration Reduces the Homeostasis of the Glutamate Synapse in the Rat Brain. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 7186–7193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, M.; He, H.; Fan, N. Chronic administration of ketamine induces cognitive deterioration by restraining synaptic signaling. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 4702–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, S.; Roque, S.; de Sá-Calçada, D.; Sousa, N.; Correia-Neves, M.; Cerqueira, J.J. An efficient chronic unpredictable stress protocol to induce stress-related responses in C57BL/6 mice. Front. Psychiatry 2015, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, N.; Liu, R.J.; Dwyer, J.M.; Banasr, M.; Lee, B.; Son, H.; Li, X.Y.; Aghajanian, G.; Duman, R.S. Glutamate N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists rapidly reverse behavioral and synaptic deficits caused by chronic stress exposure. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 69, 754–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.L.; Luo, L.; Mu, R.H.; Liu, B.B.; Geng, D.; Liu, Q.; Yi, L.T. Fluoxetine regulates mTOR signalling in a region-dependent manner in depression-like mice. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Sun, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Bao, G.; Wang, F.; Cui, Z.; Jiang, B. Hippocampal mTOR signaling is required for the antidepressant effects of paroxetine. Neuropharmacology 2018, 128, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandran, A.; Iyo, A.H.; Jernigan, C.S.; Legutko, B.; Austin, M.C.; Karolewicz, B. Reduced phosphorylation of the mTOR signaling pathway components in the amygdala of rats exposed to chronic stress. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 40, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oh, D.R.; Yoo, J.S.; Kim, Y.; Kang, H.; Lee, H.; Lm, S.J.; Choi, E.J.; Jung, M.A.; Bae, D.; Oh, K.N.; et al. Vaccinium bracteatum Leaf Extract Reverses Chronic Restraint Stress-Induced Depression-Like Behavior in Mice: Regulation of Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis, Serotonin Turnover Systems, and ERK/Akt Phosphorylation. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, L.; Wang, G.; Wu, Z.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, L.; Xiao, L.; Wang, H. Swimming exercise reduces the vulnerability to stress and contributes to the AKT/GSK3β/CRMP2 pathway and microtubule dynamics mediated protective effects on neuroplasticity in male C57BL/6 mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2021, 211, 173285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe-Higuchi, N.; Uchida, S.; Yamagata, H.; Higuchi, F.; Hobara, T.; Hara, K.; Kobayashi, A.; Watanabe, Y. Hippocampal Sirtuin 1 Signaling Mediates Depression-like Behavior. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 80, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Witkin, J.M.; Mitchell, S.N.; Wafford, K.A.; Carter, G.; Gilmour, G.; Li, J.; Eastwood, B.J.; Overshiner, C.; Li, X.; Rorick-Kehn, L.; et al. Comparative Effects of LY3020371, a Potent and Selective Metabotropic Glutamate (mGlu) 2/3 Receptor Antagonist, and Ketamine, a Noncompetitive N-Methyl-d-Aspartate Receptor Antagonist in Rodents: Evidence Supporting the Use of mGlu2/3 Antagonists, for the Treatment of Depression. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2017, 361, 68–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lepack, A.E.; Bang, E.; Lee, B.; Dwyer, J.M.; Duman, R.S. Fast-acting antidepressants rapidly stimulate ERK signaling and BDNF release in primary neuronal cultures. Neuropharmacology 2016, 111, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Autry, A.E.; Adachi, M.; Nosyreva, E.; Na, E.S.; Los, M.F.; Cheng, P.F.; Kavalali, E.T.; Monteggia, L.M. NMDA receptor blockade at rest triggers rapid behavioural antidepressant responses. Nature 2011, 475, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.; Hu, Y.M.; Zhou, Z.Q.; Zhang, G.F.; Yang, J.J. Acute administration of ketamine in rats increases hippocampal BDNF and mTOR levels during forced swimming test. Ups. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 118, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, W.; Wang, N.; Yang, C.; Li, X.M.; Zhou, Z.Q.; Yang, J.J. Ketamine-induced antidepressant effects are associated with AMPA receptors-mediated upregulation of mTOR and BDNF in rat hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. Eur. Psychiatry 2014, 29, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, S.; Macqueen, G. The role of the hippocampus in the pathophysiology of major depression. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2004, 29, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nestler, E.J.; Barrot, M.; DiLeone, R.J.; Eisch, A.J.; Gold, S.J.; Monteggia, L.M. Neurobiology of depression. Neuron 2002, 34, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaki, S.; Fukumoto, K. Role of Serotonergic System in the Antidepressant Actions of mGlu2/3 Receptor Antagonists: Similarity to Ketamine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawashima, N.; Karasawa, J.; Shimazaki, T.; Chaki, S.; Okuyama, S.; Yasuhara, A.; Nakazato, A. Neuropharmacological profiles of antagonists of group II metabotropic glutamate receptors. Neurosci. Lett. 2005, 378, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasawa, J.; Shimazaki, T.; Kawashima, N.; Chaki, S. AMPA receptor stimulation mediates the antidepressant-like effect of a group II metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonist. Brain Res. 2005, 1042, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.H.; Defaix, C.; Xu, X.; Deng, S.X.; Fabresse, N.; Alvarez, J.C.; Landry, D.W.; Brachman, R.A.; Denny, C.A.; Gardier, A.M. Common Neurotransmission Recruited in (R,S)-Ketamine and (2R,6R)-Hydroxynorketamine-Induced Sustained Antidepressant-like Effects. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 84, e3–e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumoto, K.; Iijima, M.; Chaki, S. Serotonin-1A receptor stimulation mediates effects of a metabotropic glutamate 2/3 receptor antagonist, 2S-2-amino-2-(1S,2S-2-carboxycycloprop-1-yl)-3-(xanth-9-yl)propanoic acid (LY341495), and an N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist, ketamine, in the novelty-suppressed feeding test. Psychopharmacology 2014, 231, 2291–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumoto, K.; Iijima, M.; Chaki, S. The Antidepressant Effects of an mGlu2/3 Receptor Antagonist and Ketamine Require AMPA Receptor Stimulation in the mPFC and Subsequent Activation of the 5-HT Neurons in the DRN. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 1046–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigliucci, V.; O’Dowd, G.; Casey, S.; Egan, D.; Gibney, S.; Harkin, A. Ketamine elicits sustained antidepressant-like activity via a serotonin-dependent mechanism. Psychopharmacology 2013, 228, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumoto, K.; Iijima, M.; Funakoshi, T.; Chaki, S. 5-HT1A receptor stimulation in the medial prefrontal cortex mediates the antidepressant effects of mGlu2/3 receptor antagonist in mice. Neuropharmacology 2018, 137, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.; Shui, L.; Wang, S.; Song, Z.; Tai, F. Bilobalide alleviates depression-like behavior and cognitive deficit induced by chronic unpredictable mild stress in mice. Behav. Pharmacol. 2016, 27, 596–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Can, A.; Dao, D.T.; Arad, M.; Terrillion, C.E.; Piantadosi, S.C.; Gould, T.D. The mouse forced swim test. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 59, e3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seo, M.K.; Lee, J.A.; Jeong, S.; Seog, D.-H.; Lee, J.G.; Park, S.W. Effects of Chronic LY341495 on Hippocampal mTORC1 Signaling in Mice with Chronic Unpredictable Stress-Induced Depression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23126416
Seo MK, Lee JA, Jeong S, Seog D-H, Lee JG, Park SW. Effects of Chronic LY341495 on Hippocampal mTORC1 Signaling in Mice with Chronic Unpredictable Stress-Induced Depression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(12):6416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23126416
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeo, Mi Kyoung, Jung An Lee, Sehoon Jeong, Dae-Hyun Seog, Jung Goo Lee, and Sung Woo Park. 2022. "Effects of Chronic LY341495 on Hippocampal mTORC1 Signaling in Mice with Chronic Unpredictable Stress-Induced Depression" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 12: 6416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23126416
APA StyleSeo, M. K., Lee, J. A., Jeong, S., Seog, D.-H., Lee, J. G., & Park, S. W. (2022). Effects of Chronic LY341495 on Hippocampal mTORC1 Signaling in Mice with Chronic Unpredictable Stress-Induced Depression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(12), 6416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23126416





