CpG Methylation Altered the Stability and Structure of the i-Motifs Located in the CpG Islands
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Oligonucleotide Preparation
4.2. Circular Dichroism Spectrum Measurement and Melting Temperature (Tm)
4.3. Data Analysis
4.4. DNA Native-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (Native-PAGE)
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cutter, A.R.; Hayes, J.J. A brief review of nucleosome structure. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 2914–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bannister, A.J.; Kouzarides, T. Regulation of chromatin by histone modifications. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razin, A.; Cedar, H. DNA Methylation and Gene Expression. Microbiol. Rev. 1991, 55, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.Z.; Pettersson, U.; Beard, C.; Jackson-grusby, L.; Jaenisch, R. DNA hypomethylation leads to elevated mutation rates. Nature 1998, 395, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deaton, A.M.; Bird, A. CpG islands and the regulation of transcription. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 1010–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, I.V.; Schwartz, D.A. Epigenetic Control of Gene Expression in the Lung. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burge, S.; Parkinson, G.N.; Hazel, P.; Todd, A.K.; Neidle, S. Quadruplex DNA: Sequence, topology, and structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 5402–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iida, K.; Nakamura, T.; Yoshida, W.; Tera, M.; Nakabayashi, K.; Hata, K.; Ikebukuro, K.; Nagasawa, K. Fluorescent-Ligand-Mediated Screening of G-Quadruplex Structures Using a DNA Microarray. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 12052–12055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilbaud, G.; Murat, P.; Recolin, B.; Campbell, B.C.; Maiter, A.; Sale, S.; Balasubramanian, J.E. Local epigenetic reprogramming induced by G-quadruplex ligands. Nat. Chem. 2017, 9, 1110–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brooks, T.A.; Kendrick, S.; Hurley, L. Making sense of G-quadruplex and i-motif functions in oncogene promoters. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 3459–3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gilmour, J.; Assi, S.A.; Jaegle, U.; Kulu, D.; Werken, H.; Clarke, D.; Westhead, D.R.; Philipsen, S.; Bonifer, C. A crucial role for the ubiquitously expressed transcription factor Sp1 at early stages of hematopoietic specification. Development 2014, 141, 2391–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raiber, E.A.; Kranaster, R.; Lam, E.; Nikan, M.; Balasubramanian, S. A non-canonical DNA structure is a binding motif for the transcription factor SP1 in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 1499–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoshida, W.; Saito, T.; Yokoyama, T.; Ferri, S.; Ikebukuro, K. Aptamer Selection Based on G4-Forming Promoter Region. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, J.; Hou, J.Q.; Xiang, H.D.; Yan, Y.Y.; Gu, Y.C.; Tan, J.H.; Li, D.; Gu, L.Q.; Ou, T.M.; Huang, Z.S. Stabilization of G-quadruplex DNA by C-5-methyl-cytosine in bcl-2 promoter: Implications for epigenetic regulation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 433, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogoi, S.; Shchekotikhin, E.A.; Xodo, E.L. HRAS is silenced by two neighboring G-quadruplexes and activated by MAZ, a zinc-finger transcription factor with DNA unfolding property. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 8379–8388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Membrino, A.; Cogoi, S.; Pedersen, E.B.; Xodo, L.E. G4-DNA Formation in the HRAS Promoter and Rational Design of Decoy Oligonucleotides for Cancer Therapy. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsukakoshi, K.; Saito, S.; Yoshida, W.; Goto, S.; Ikebukuro, K. CpG Methylation Changes G-Quadruplex Structures Derived from Gene Promoters and Interaction with VEGF and SP1. Molecules 2018, 23, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harrington, M.A.; Jones, P.A.; Imagawa, M.; Karin, M. Cytosine methylation does not affect binding of transcription factor Sp1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 2066–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manzini, G.; Yathindra, N.; Xodo, L.E. Evidence for intramolecularly folded i-DNA structures in biologically relevant CCC-repeat sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4634–4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Day, H.A.; Pavlou, P.; Waller, Z.A.E. i-Motif DNA: Structure, stability and targeting with ligands. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 4407–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, A.; Nakano, S.I.; Sugimoto, N. Molecular crowding of the cosolutes induces an intramolecular i-motif structure of triplet repeat DNA oligomers at neutral pH. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 1299–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhamid, M.A.S.; Fábián, L.; Macdonald, C.J.; Cheesman, M.R.; Gates, A.J.; Waller, Z.A.E. Redox-dependent control of i-Motif DNA structure using copper cations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 5886–5893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, E.P.; Huppert, J.L.; Waller, Z.A.E. Identification of multiple genomic DNA sequences which form i-motif structures at neutral pH. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 2951–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeraati, M.; Langley, D.B.; Schofield, P.; Moye, A.L.; Rouet, R.; Hughes, W.E.; Bryan, T.M.; Dinger, M.E.; Christ, D. I-motif DNA structures are formed in the nuclei of human cells. Nat. Chem. 2018, 10, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzatko, S.; Krafcikova, M.; Hänsel-Hertsch, R.; Fessl, T.; Fiala, R.; Loja, T.; Krafcik, D.; Mergny, J.L.; Foldynova-Trantirkova, S.; Trantirek, L. Evaluation of the Stability of DNA i-Motifs in the Nuclei of Living Mammalian Cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 2165–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wright, E.P.; Abdelhamid, M.A.S.; Ehiabor, M.O.; Grigg, M.C.; Irving, K.; Smith, N.M.; Waller, Z.A.E. Epigenetic modification of cytosines fine tunes the stability of i-motif DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, K.; Oshikawa, D.; Ikebukuro, K.; Yoshida, W. Stabilization of VEGF i-motif structure by CpG methylation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 594, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozmogova, G.; Isaakova, E.; Varizhuk, A. Cpg Methylation in G-Quadruplex and IMotif DNA Structures. Significances Bioeng. Biosci. 2018, 1, 4–10. [Google Scholar]
- Biffi, G.; Tannahill, D.; McCafferty, J.; Balasubramanian, S. Quantitative visualization of DNA G-quadruplex structures in human cells. Nat. Chem. 2013, 5, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, S.; Konik, Z.; Yu, R.; Cui, Y.; Koirala, D.; Mao, H. G-Quadruplex and i-Motif Are Mutually Exclusive in ILPR Double-Stranded DNA. Biophys. J. 2012, 102, 2575–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panczyk, T.; Wolski, P. Molecular dynamics analysis of stabilities of the telomeric Watson-Crick duplex and the associated i-motif as a function of pH and temperature. Biophys. Chem. 2018, 237, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


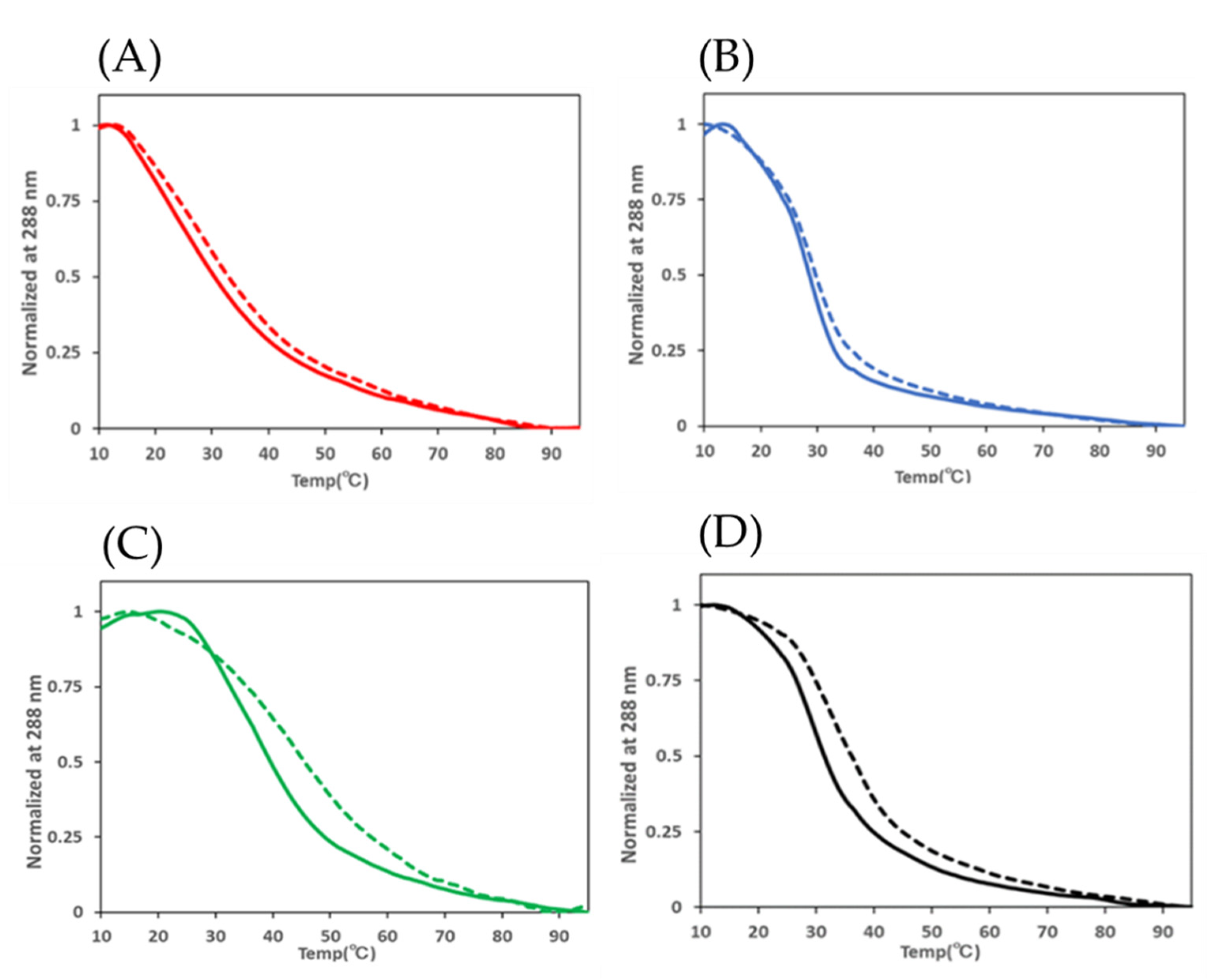
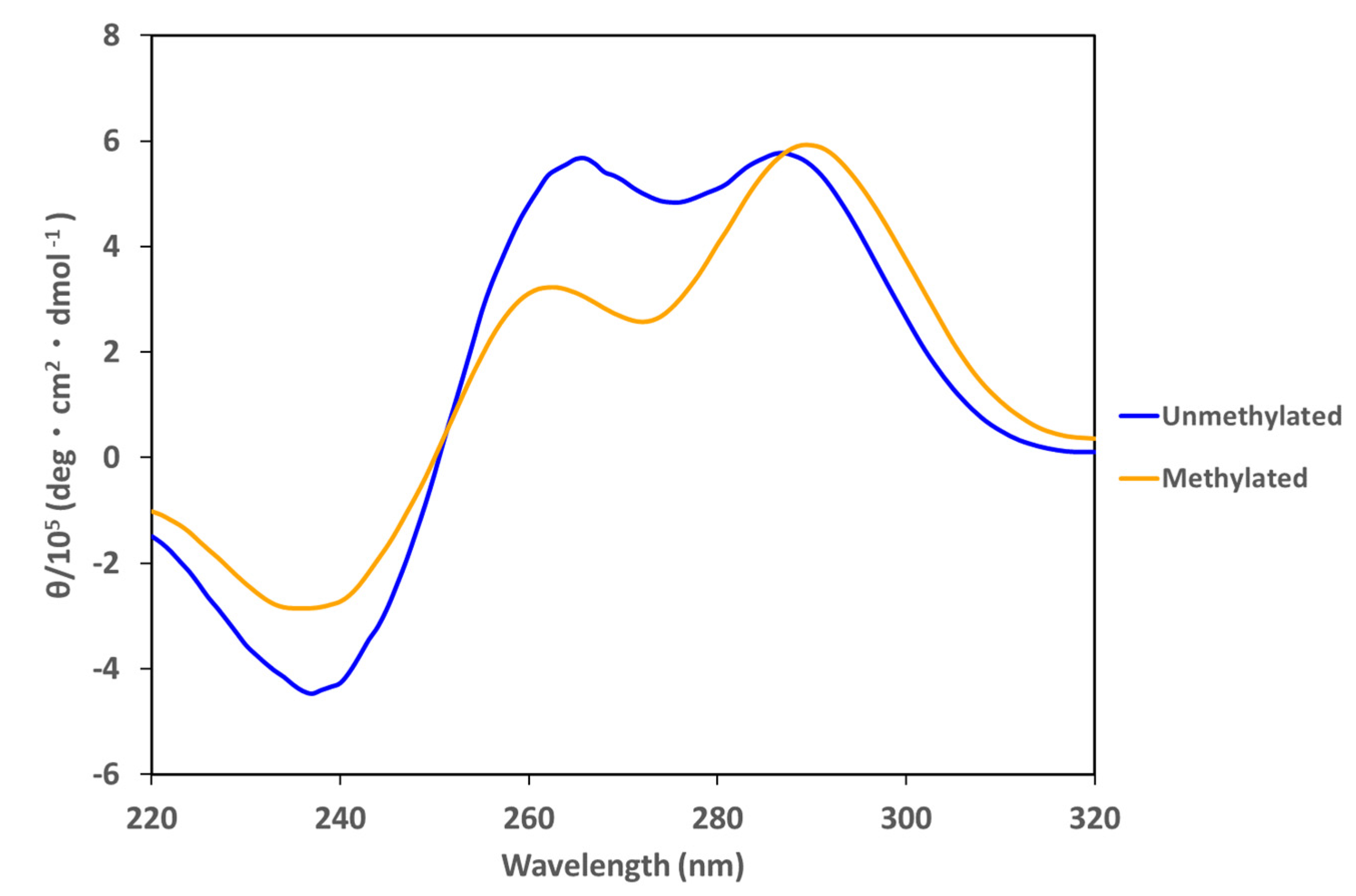
| i-Motif | Transitional pH Unmethylated | Transitional pH Methylated | ΔTransitional pH |
|---|---|---|---|
| VEGF | 6.47 | 6.50 | 0.03 |
| C-KIT | 6.02 | 6.18 | 0.16 |
| BCL2 | 6.81 | 6.82 | 0.01 |
| HRAS1 | 6.27 | 5.87 | −0.4 |
| HRAS2 | 6.80 | 6.95 | 0.15 |
| i-Motif | Transitional pH | Tm (°C) Unmethylated | Tm (°C) Methylated | ΔTm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VEGF | 6.4 | 29.6 | 32.7 | 2.9 |
| BCL2 | 6.8 | 28.1 | 30.0 | 1.9 |
| HRAS1 | 6.2 | 39.6 | 46.5 | 6.9 |
| HRAS2 | 6.8 | 31.5 | 36.0 | 4.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oshikawa, D.; Inaba, S.; Kitagawa, Y.; Tsukakoshi, K.; Ikebukuro, K. CpG Methylation Altered the Stability and Structure of the i-Motifs Located in the CpG Islands. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6467. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23126467
Oshikawa D, Inaba S, Kitagawa Y, Tsukakoshi K, Ikebukuro K. CpG Methylation Altered the Stability and Structure of the i-Motifs Located in the CpG Islands. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(12):6467. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23126467
Chicago/Turabian StyleOshikawa, Daiki, Shintaro Inaba, Yudai Kitagawa, Kaori Tsukakoshi, and Kazunori Ikebukuro. 2022. "CpG Methylation Altered the Stability and Structure of the i-Motifs Located in the CpG Islands" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 12: 6467. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23126467
APA StyleOshikawa, D., Inaba, S., Kitagawa, Y., Tsukakoshi, K., & Ikebukuro, K. (2022). CpG Methylation Altered the Stability and Structure of the i-Motifs Located in the CpG Islands. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(12), 6467. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23126467






