Dietary Long-Chain n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Supplementation Alters Electrophysiological Properties in the Nucleus Accumbens and Emotional Behavior in Naïve and Chronically Stressed Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
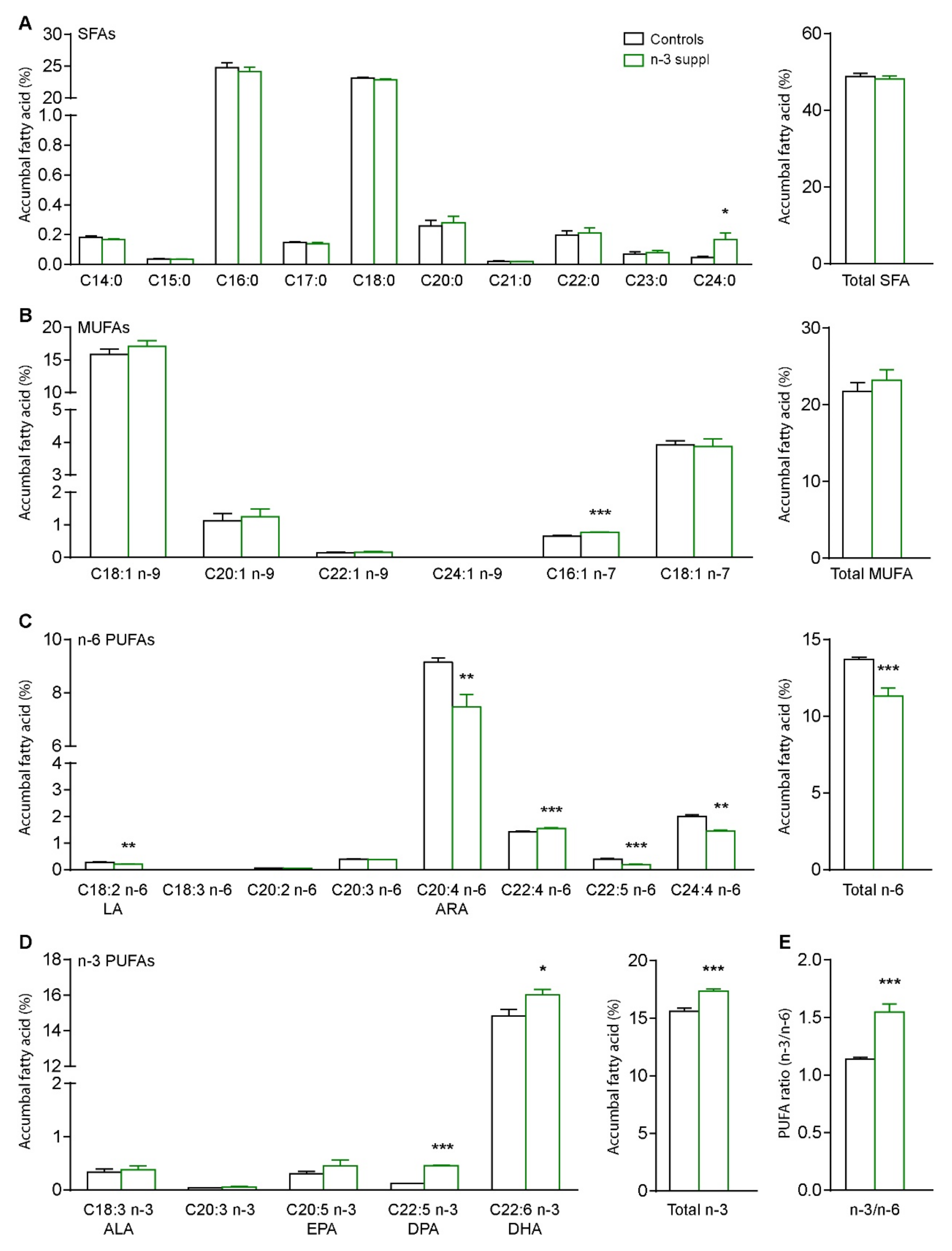
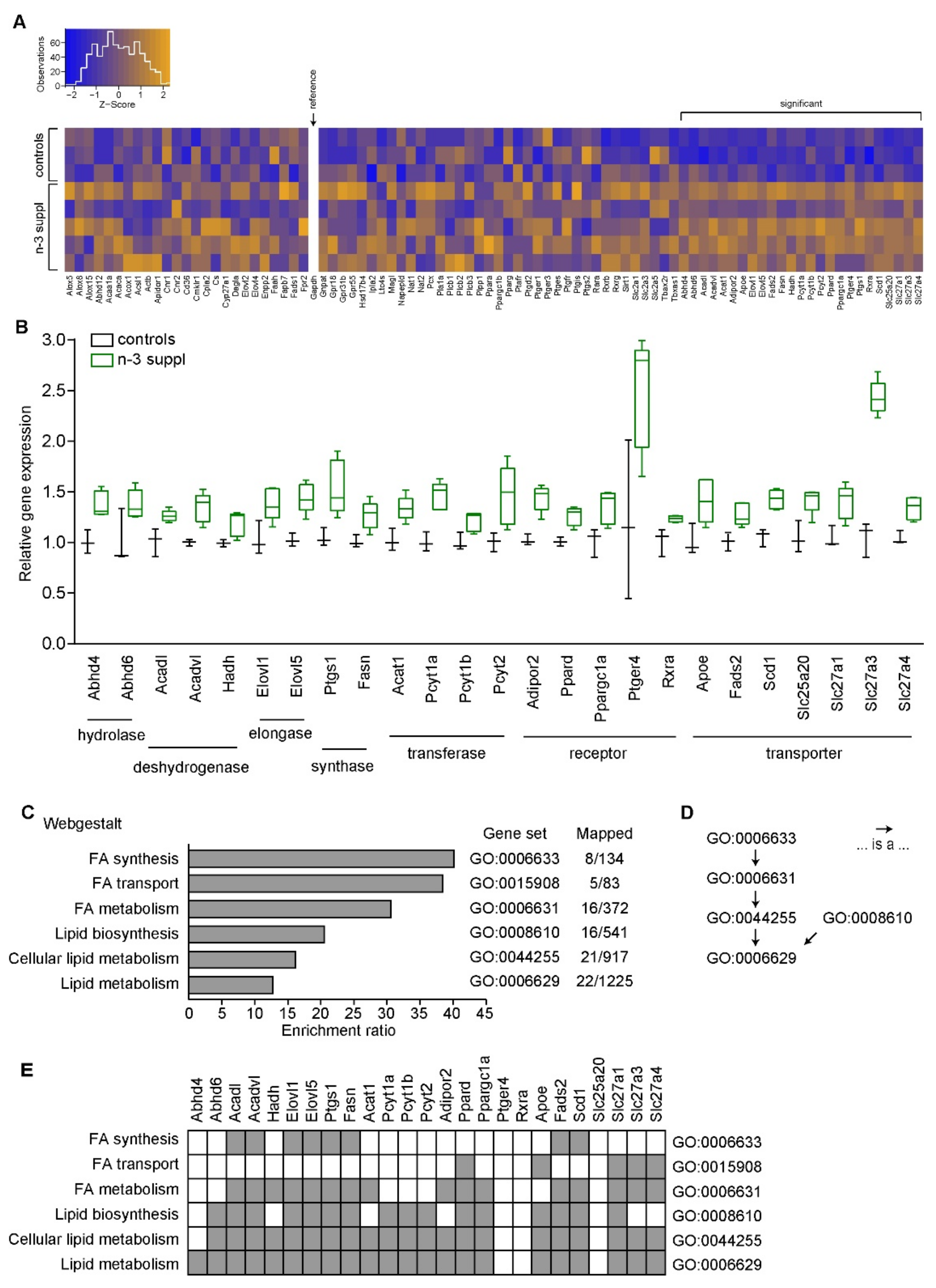
2.1. Fatty Acids and Molecular Signature of LC n-3 PUFA Dietary Supplementation
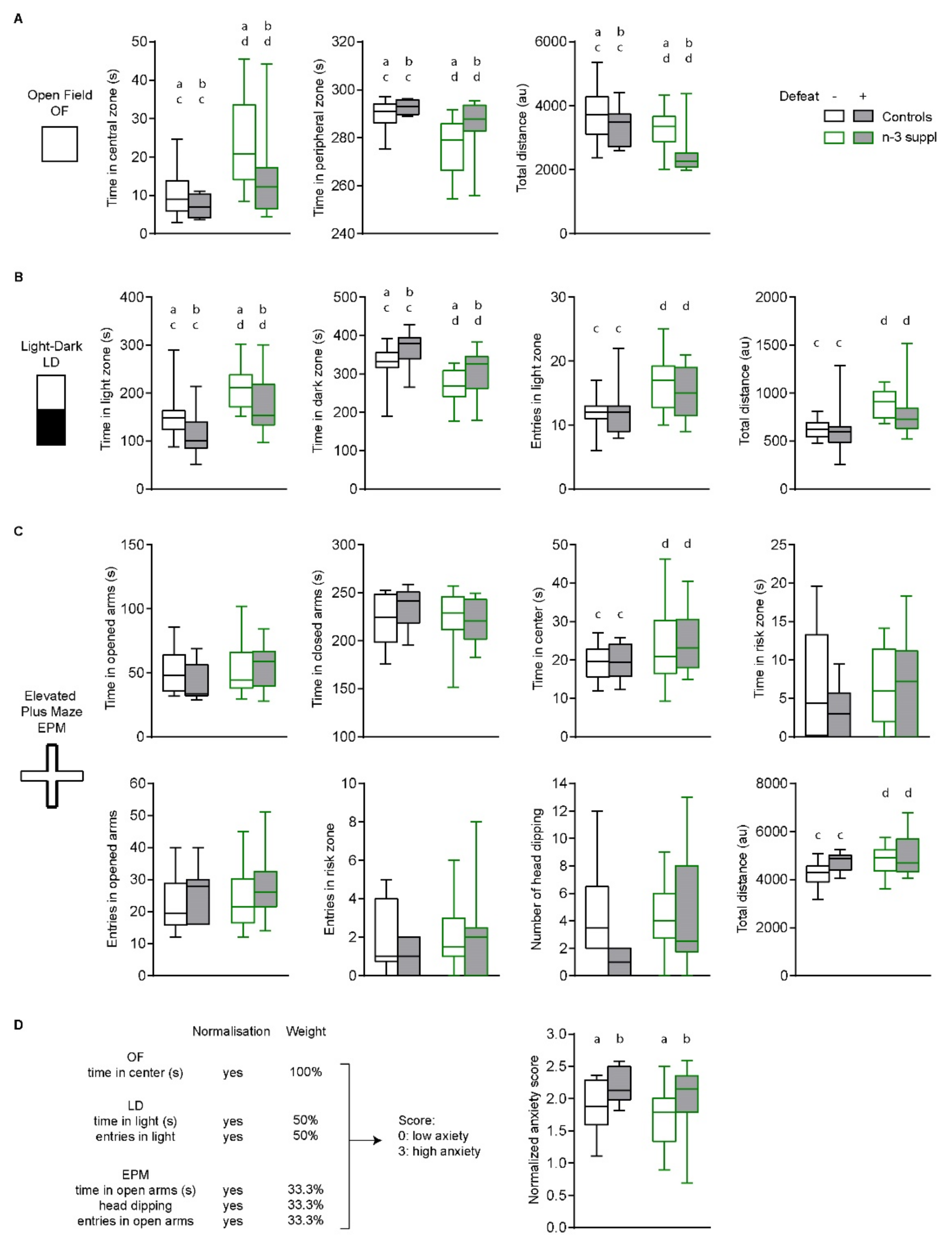
2.2. Anxiolytic-like Effect of LC n-3 PUFA Dietary Supplementation
2.3. Reversal of CSDS-Induced Social Interaction Deficits by LC n-3 PUFA Dietary Supplementation
2.4. Alteration of Electrophysiological Properties of Accumbal Medium Spiny Neurons by LC n-3 PUFA Dietary Supplementation
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Ethical Approval
4.2. Animals
4.3. Diets
4.4. Chronic Social Defeat Stress (CSDS)
4.5. Behavioral Assessments
4.6. Gene Expression Analysis
4.7. Endogenous Fatty Acid Determination by Gas Chromatography-Flame Ion Detection
4.8. Ex Vivo Whole-Cell Patch-Clamp Electrophysiology
4.9. Resampling
4.10. Data Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krishnan, V.; Nestler, E.J. The Molecular Neurobiology of Depression. Nature 2008, 455, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLachlan, G. Treatment Resistant Depression: What Are the Options? BMJ 2018, 363, k5354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazinet, R.P.; Layé, S. Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Their Metabolites in Brain Function and Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 15, 771–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Xie, B.; Zhang, H.; He, Q.; Guo, L.; Subramanieapillai, M.; Fan, B.; Lu, C.; McIntyre, R.S. Efficacy of Omega-3 PUFAs in Depression: A Meta-Analysis. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bazinet, R.P.; Metherel, A.H.; Chen, C.T.; Shaikh, S.R.; Nadjar, A.; Joffre, C.; Layé, S. Brain Eicosapentaenoic Acid Metabolism as a Lead for Novel Therapeutics in Major Depression. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 85, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larrieu, T.; Layé, S. Food for Mood: Relevance of Nutritional Omega-3 Fatty Acids for Depression and Anxiety. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mocking, R.J.T.; Harmsen, I.; Assies, J.; Koeter, M.W.J.; Ruhé, H.G.; Schene, A.H. Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Supplementation for Major Depressive Disorder. Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 6, e756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.-D.; Feng, J.-S.; Yang, Z.; Huang, Q.-T.; Lin, J.; Yang, B.; Su, K.-P.; Pan, J.-Y. High-Dose Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Supplementation Might Be More Superior than Low-Dose for Major Depressive Disorder in Early Therapy Period: A Network Meta-Analysis. BMC Psychiatry 2020, 20, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNamara, R.K.; Rider, T.; Jandacek, R.; Tso, P. Abnormal Fatty Acid Pattern in the Superior Temporal Gyrus Distinguishes Bipolar Disorder from Major Depression and Schizophrenia and Resembles Multiple Sclerosis. Psychiatry Res. 2014, 215, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McNamara, R.K.; Strimpfel, J.; Jandacek, R.; Rider, T.; Tso, P.; Welge, J.A.; Strawn, J.R.; Delbello, M.P. Detection and Treatment of Long-Chain Omega-3 Fatty Acid Deficiency in Adolescents with SSRI-Resistant Major Depressive Disorder. PharmaNutrition 2014, 2, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martins, J.G. EPA but Not DHA Appears to Be Responsible for the Efficacy of Omega-3 Long Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Supplementation in Depression: Evidence from a Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2009, 28, 525–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deane, K.; Jimoh, O.; O’Brien, A.; Hanson, S.; Abdelhamid, A.S.; Fox, C.; Hooper, L. Omega-3 and Polyunsaturated Fat for Prevention of Depression and Anxiety Symptoms: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. Br. J. Pshychiatry 2021, 218, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Zhang, X.Y.; Manku, M. Increased Phospholipase A2 Activity and Inflammatory Response but Decreased Nerve Growth Factor Expression in the Olfactory Bulbectomized Rat Model of Depression: Effects of Chronic Ethyl-Eicosapentaenoate Treatment. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, Z.; Zhang, C.; Yan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, J.; Song, C. EPA Is More Effective than DHA to Improve Depression-Like Behavior, Glia Cell Dysfunction and Hippcampal Apoptosis Signaling in a Chronic Stress-Induced Rat Model of Depression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, E1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pusceddu, M.M.; El Aidy, S.; Crispie, F.; O’Sullivan, O.; Cotter, P.; Stanton, C.; Kelly, P.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. N-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids (PUFAs) Reverse the Impact of Early-Life Stress on the Gut Microbiota. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrieu, T.; Hilal, M.L.; Hilal, L.M.; Fourrier, C.; De Smedt-Peyrusse, V.; Sans, N.N.S.; Capuron, L.; Layé, S. Nutritional Omega-3 Modulates Neuronal Morphology in the Prefrontal Cortex along with Depression-Related Behaviour through Corticosterone Secretion. Transl. Psychiatry 2014, 4, e437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Labrousse, V.F.; Nadjar, A.; Joffre, C.; Costes, L.; Aubert, A.; Grégoire, S.; Bretillon, L.; Layé, S. Short-Term Long Chain Omega3 Diet Protects from Neuroinflammatory Processes and Memory Impairment in Aged Mice. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.; Rani, B.; Bastiaanssen, T.F.S.; Bonfiglio, F.; Gunnigle, E.; Provensi, G.; Rossitto, M.; Boehme, M.; Strain, C.; Martínez, C.S.; et al. Diet Prevents Social Stress-Induced Maladaptive Neurobehavioural and Gut Microbiota Changes in a Histamine-Dependent Manner. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joffre, C.; Rey, C.; Layé, S. N-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and the Resolution of Neuroinflammation. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joffre, C.; Dinel, A.-L.; Chataigner, M.; Pallet, V.; Layé, S. N-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Their Derivates Reduce Neuroinflammation during Aging. Nutrients 2020, 12, E647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rapaport, M.H.; Nierenberg, A.A.; Schettler, P.J.; Kinkead, B.; Cardoos, A.; Walker, R.; Mischoulon, D. Inflammation as a Predictive Biomarker for Response to Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Major Depressive Disorder: A Proof-of-Concept Study. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mocking, R.J.T.; Ruhé, H.G.; Assies, J.; Lok, A.; Koeter, M.W.J.; Visser, I.; Bockting, C.L.H.; Schene, A.H. Relationship between the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal-Axis and Fatty Acid Metabolism in Recurrent Depression. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2013, 38, 1607–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rey, C.; Delpech, J.C.; Madore, C.; Nadjar, A.; Greenhalgh, A.D.; Amadieu, C.; Aubert, A.; Pallet, V.; Vaysse, C.; Layé, S.; et al. Dietary N-3 Long Chain PUFA Supplementation Promotes a pro-Resolving Oxylipin Profile in the Brain. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2019, 76, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Manku, M.S.; Horrobin, D.F. Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Modulate Interleukin-1beta-Induced Changes in Behavior, Monoaminergic Neurotransmitters, and Brain Inflammation in Rats. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borsini, A.; Di Benedetto, M.G.; Giacobbe, J.; Pariante, C.M. Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Interleukin (IL6) in Vitro: Relevance for Major Depression and for Human Hippocampal Neurogenesis. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020, 23, pyaa055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch-Bouju, C.; Layé, S. Dietary Omega-6/Omega-3 and Endocannabinoids: Implications for Brain Health and Diseases; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016; ISBN 978-953-51-2430-6. [Google Scholar]
- Di Miceli, M.; Bosch-Bouju, C.; Layé, S. PUFA and Their Derivatives in Neurotransmission and Synapses: A New Hallmark of Synaptopathies. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2020, 79, 388–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manduca, A.; Bara, A.; Larrieu, T.; Lassalle, O.; Joffre, C.; Layé, S.; Manzoni, O.J. Amplification of MGlu5-Endocannabinoid Signaling Rescues Behavioral and Synaptic Deficits in a Mouse Model of Adolescent and Adult Dietary Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Imbalance. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 6851–6868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lafourcade, M.; Larrieu, T.; Mato, S.; Duffaud, A.; Sepers, M.; Matias, I.; De Smedt-Peyrusse, V.; Labrousse, V.F.; Bretillon, L.; Matute, C.; et al. Nutritional Omega-3 Deficiency Abolishes Endocannabinoid-Mediated Neuronal Functions. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larrieu, T.; Madore, C.; Joffre, C.; Layé, S. Nutritional N-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Deficiency Alters Cannabinoid Receptor Signaling Pathway in the Brain and Associated Anxiety-like Behavior in Mice. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 68, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, S.J.; Nestler, E.J. The Brain Reward Circuitry in Mood Disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 609–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaouloff, F. Social Stress Models in Depression Research: What Do They Tell Us? Cell Tissue Res. 2013, 354, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bosch-Bouju, C.; Larrieu, T.; Linders, L.; Manzoni, O.J.; Layé, S. Endocannabinoid-Mediated Plasticity in Nucleus Accumbens Controls Vulnerability to Anxiety after Social Defeat Stress. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 1237–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene Ontology: Tool for the Unification of Biology. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Kirov, S.; Snoddy, J. WebGestalt: An Integrated System for Exploring Gene Sets in Various Biological Contexts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W741–W748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Wang, J.; Jaehnig, E.J.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, B. WebGestalt 2019: Gene Set Analysis Toolkit with Revamped UIs and APIs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W199–W205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Golden, S.A.; Covington, H.E.; Berton, O.; Russo, S.J. A Standardized Protocol for Repeated Social Defeat Stress in Mice. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, V.; Han, M.-H.; Graham, D.L.; Berton, O.; Renthal, W.; Russo, S.J.; Laplant, Q.; Graham, A.; Lutter, M.; Lagace, D.C.; et al. Molecular Adaptations Underlying Susceptibility and Resistance to Social Defeat in Brain Reward Regions. Cell 2007, 131, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joffre, C.; Grégoire, S.; De Smedt, V.; Acar, N.; Bretillon, L.; Nadjar, A.; Layé, S. Modulation of Brain PUFA Content in Different Experimental Models of Mice. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 2016, 114, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delpech, J.-C.; Thomazeau, A.; Madore, C.; Bosch-Bouju, C.; Larrieu, T.; Lacabanne, C.; Remus-Borel, J.; Aubert, A.; Joffre, C.; Nadjar, A.; et al. Dietary N-3 PUFAs Deficiency Increases Vulnerability to Inflammation-Induced Spatial Memory Impairment. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015, 40, 2774–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kodas, E.; Vancassel, S.; Lejeune, B.; Guilloteau, D.; Chalon, S. Reversibility of N-3 Fatty Acid Deficiency-Induced Changes in Dopaminergic Neurotransmission in Rats: Critical Role of Developmental Stage. J. Lipid Res. 2002, 43, 1209–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alashmali, S.M.; Kitson, A.P.; Lin, L.; Lacombe, R.J.S.; Bazinet, R.P. Maternal Dietary N-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Deprivation Does Not Exacerbate Post-Weaning Reductions in Arachidonic Acid and Its Mediators in the Mouse Hippocampus. Nutr. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L.F.C.; Tocher, D.R.; Monroig, O. Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Biosynthesis in Chordates: Insights into the Evolution of Fads and Elovl Gene Repertoire. Prog. Lipid Res. 2016, 62, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbo, I.; Montarolo, F.; Boda, E.; Tempia, F.; Hoxha, E. Elovl5 Expression in the Central Nervous System of the Adult Mouse. Front. Neuroanat. 2021, 15, 669073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttenplan, K.A.; Weigel, M.K.; Prakash, P.; Wijewardhane, P.R.; Hasel, P.; Rufen-Blanchette, U.; Münch, A.E.; Blum, J.A.; Fine, J.; Neal, M.C.; et al. Neurotoxic Reactive Astrocytes Induce Cell Death via Saturated Lipids. Nature 2021, 599, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabernero, A.; Lavado, E.M.; Granda, B.; Velasco, A.; Medina, J.M. Neuronal Differentiation Is Triggered by Oleic Acid Synthesized and Released by Astrocytes. J. Neurochem. 2001, 79, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dziedzic, B.; Bewicz-Binkowska, D.; Zgorzynska, E.; Stulczewski, D.; Wieteska, L.; Kaza, B.; Walczewska, A. DHA Upregulates FADS2 Expression in Primary Cortical Astrocytes Exposed to Vitamin, A. Physiol. Res. 2018, 67, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cribb, L.; Murphy, J.; Froud, A.; Oliver, G.; Bousman, C.A.; Ng, C.H.; Sarris, J. Erythrocyte Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Composition Is Associated with Depression and FADS Genotype in Caucasians. Nutr. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNamara, R.K.; Liu, Y. Reduced Expression of Fatty Acid Biosynthesis Genes in the Prefrontal Cortex of Patients with Major Depressive Disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2011, 129, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bewicz-Binkowska, D.; Zgorzynska, E.; Dziedzic, B.; Walczewska, A. Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) Inhibits FADS2 Expression in Astrocytes but Increases Survival of Neurons Co-Cultured with DHA-Enriched Astrocytes. Int. J. Mol. Cell. Med. 2019, 8, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maekawa, M.; Iwayama, Y.; Ohnishi, T.; Toyoshima, M.; Shimamoto, C.; Hisano, Y.; Toyota, T.; Balan, S.; Matsuzaki, H.; Iwata, Y.; et al. Investigation of the Fatty Acid Transporter-Encoding Genes SLC27A3 and SLC27A4 in Autism. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iacobazzi, V.; Invernizzi, F.; Baratta, S.; Pons, R.; Chung, W.; Garavaglia, B.; Dionisi-Vici, C.; Ribes, A.; Parini, R.; Huertas, M.D.; et al. Molecular and Functional Analysis of SLC25A20 Mutations Causing Carnitine-Acylcarnitine Translocase Deficiency. Hum. Mutat. 2004, 24, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giudetti, A.M.; Stanca, E.; Siculella, L.; Gnoni, G.V.; Damiano, F. Nutritional and Hormonal Regulation of Citrate and Carnitine/Acylcarnitine Transporters: Two Mitochondrial Carriers Involved in Fatty Acid Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, E817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huizing, M.; Iacobazzi, V.; Ijlst, L.; Savelkoul, P.; Ruitenbeek, W.; van den Heuvel, L.; Indiveri, C.; Smeitink, J.; Trijbels, F.; Wanders, R.; et al. Cloning of the Human Carnitine-Acylcarnitine Carrier CDNA and Identification of the Molecular Defect in a Patient. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1997, 61, 1239–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woodling, N.S.; Wang, Q.; Priyam, P.G.; Larkin, P.; Shi, J.; Johansson, J.U.; Zagol-Ikapitte, I.; Boutaud, O.; Andreasson, K.I. Suppression of Alzheimer-Associated Inflammation by Microglial Prostaglandin-E2 EP4 Receptor Signaling. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 5882–5894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeMars, K.M.; McCrea, A.O.; Siwarski, D.M.; Sanz, B.D.; Yang, C.; Candelario-Jalil, E. Protective Effects of L-902,688, a Prostanoid EP4 Receptor Agonist, against Acute Blood-Brain Barrier Damage in Experimental Ischemic Stroke. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Rivest, S. A Functional Analysis of EP4 Receptor-Expressing Neurons in Mediating the Action of Prostaglandin E2 within Specific Nuclei of the Brain in Response to Circulating Interleukin-1beta. J. Neurochem. 2000, 74, 2134–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.S.; Ahmad, M.; de Brum-Fernandes, A.J.; Doré, S. Prostaglandin EP4 Receptor Agonist Protects against Acute Neurotoxicity. Brain Res. 2005, 1066, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujikawa, R.; Higuchi, S.; Ikedo, T.; Nagata, M.; Hayashi, K.; Yang, T.; Miyata, T.; Yokode, M.; Minami, M. Behavioral Abnormalities and Reduced Norepinephrine in EP4 Receptor-Associated Protein (EPRAP)-Deficient Mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 486, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Serafin, E.; Baccei, M.L. Prostaglandin Signaling Governs Spike Timing-Dependent Plasticity at Sensory Synapses onto Mouse Spinal Projection Neurons. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 6628–6639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, T.C.; Chandra, R.; Friend, D.M.; Finkel, E.; Dayrit, G.; Miranda, J.; Brooks, J.M.; Iñiguez, S.D.; O’Donnell, P.; Kravitz, A.; et al. Nucleus Accumbens Medium Spiny Neuron Subtypes Mediate Depression-Related Outcomes to Social Defeat Stress. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 77, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grossman, Y.S.; Fillinger, C.; Manganaro, A.; Voren, G.; Waldman, R.; Zou, T.; Janssen, W.G.; Kenny, P.J.; Dumitriu, D. Structure and Function Differences in the Prelimbic Cortex to Basolateral Amygdala Circuit Mediate Trait Vulnerability in a Novel Model of Acute Social Defeat Stress in Male Mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2022, 47, 788–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-X.; Zheng, H.-L.; Luo, Y.; He, J.-G.; Wang, W.; Han, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Ni, L.; Zhou, H.-Y.; et al. Gene Deficiency and Pharmacological Inhibition of Caspase-1 Confers Resilience to Chronic Social Defeat Stress via Regulating the Stability of Surface AMPARs. Mol. Psychiatry 2018, 23, 556–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murra, D.; Hilde, K.L.; Fitzpatrick, A.; Maras, P.M.; Watson, S.J.; Akil, H. Characterizing the Behavioral and Neuroendocrine Features of Susceptibility and Resilience to Social Stress. Neurobiol. Stress 2022, 17, 100437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fieberg, J.R.; Vitense, K.; Johnson, D.H. Resampling-Based Methods for Biologists. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, M.E.; Chandra, R.; Menken, M.S.; Larkin, E.J.; Nam, H.; Engeln, M.; Francis, T.C.; Lobo, M.K. Dendritic Remodeling of D1 Neurons by RhoA/Rho-Kinase Mediates Depression-like Behavior. Mol. Psychiatry 2020, 25, 1022–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomazeau, A.; Bosch-Bouju, C.; Manzoni, O.; Layé, S. Nutritional N-3 PUFA Deficiency Abolishes Endocannabinoid Gating of Hippocampal Long-Term Potentiation. Cereb. Cortex 2017, 27, 2571–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iñiguez, S.D.; Flores-Ramirez, F.J.; Riggs, L.M.; Alipio, J.B.; Garcia-Carachure, I.; Hernandez, M.A.; Sanchez, D.O.; Lobo, M.K.; Serrano, P.A.; Braren, S.H.; et al. Vicarious Social Defeat Stress Induces Depression-Related Outcomes in Female Mice. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 83, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, A.; Chung, J.-R.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, H.; Grossman, Y.; Aleyasin, H.; Flanigan, M.E.; Pfau, M.L.; Menard, C.; Dumitriu, D.; et al. Establishment of a Repeated Social Defeat Stress Model in Female Mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furman, O.; Tsoory, M.; Chen, A. Differential Chronic Social Stress Models in Male and Female Mice. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2022, 55, 2777–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A.Z.; Atsak, P.; Bretton, Z.H.; Holt, E.S.; Alam, R.; Morton, M.P.; Abbas, A.I.; Leonardo, E.D.; Bolkan, S.S.; Hen, R.; et al. A Novel Method for Chronic Social Defeat Stress in Female Mice. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018, 43, 1276–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, S.; Ikegaya, Y.; Nishikawa, M.; Nishiyama, N.; Matsuki, N. Docosahexaenoic Acid Improves Long-Term Potentiation Attenuated by Phospholipase A(2) Inhibitor in Rat Hippocampal Slices. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 132, 1417–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kavraal, S.; Oncu, S.K.; Bitiktas, S.; Artis, A.S.; Dolu, N.; Gunes, T.; Suer, C. Maternal Intake of Omega-3 Essential Fatty Acids Improves Long Term Potentiation in the Dentate Gyrus and Morris Water Maze Performance in Rats. Brain Res. 2012, 1482, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Ju, W.; Zhang, H.; Sun, L. Effect of Ketamine on LTP and NMDAR EPSC in Hippocampus of the Chronic Social Defeat Stress Mice Model of Depression. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kamal, A.; Van der Harst, J.E.; Kapteijn, C.M.; Baars, A.J.M.; Spruijt, B.M.; Ramakers, G.M.J. Announced Reward Counteracts the Effects of Chronic Social Stress on Anticipatory Behavior and Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity in Rats. Exp. Brain Res. 2010, 201, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Artola, A.; von Frijtag, J.C.; Fermont, P.C.J.; Gispen, W.H.; Schrama, L.H.; Kamal, A.; Spruijt, B.M. Long-Lasting Modulation of the Induction of LTD and LTP in Rat Hippocampal CA1 by Behavioural Stress and Environmental Enrichment. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006, 23, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manz, K.M.; Levine, W.A.; Seckler, J.C.; Iskander, A.N.; Reich, C.G. A Novel Adolescent Chronic Social Defeat Model: Reverse-Resident-Intruder Paradigm (RRIP) in Male Rats. Stress Amst. Neth. 2018, 21, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincel, M.; Aubert, P.; Chevalier, J.; Grohard, P.-A.; Basso, L.; Monchaux de Oliveira, C.; Helbling, J.C.; Lévy, É.; Chevalier, G.; Leboyer, M.; et al. Multi-Hit Early Life Adversity Affects Gut Microbiota, Brain and Behavior in a Sex-Dependent Manner. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2019, 80, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metherel, A.H.; Domenichiello, A.F.; Kitson, A.P.; Hopperton, K.E.; Bazinet, R.P. Whole-Body DHA Synthesis-Secretion Kinetics from Plasma Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Alpha-Linolenic Acid in the Free-Living Rat. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1861, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloane Stanley, G.H. A Simple Method for the Isolation and Purification of Total Lipides from Animal Tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fino, E.; Glowinski, J.; Venance, L. Effects of Acute Dopamine Depletion on the Electrophysiological Properties of Striatal Neurons. Neurosci. Res. 2007, 58, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilbao, A.; Neuhofer, D.; Sepers, M.; Wei, S.; Eisenhardt, M.; Hertle, S.; Lassalle, O.; Ramos-Uriarte, A.; Puente, N.; Lerner, R.; et al. Endocannabinoid LTD in Accumbal D1 Neurons Mediates Reward-Seeking Behavior. iScience 2020, 23, 100951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheyer, A.F.; Borsoi, M.; Pelissier-Alicot, A.-L.; Manzoni, O.J.J. Maternal Exposure to the Cannabinoid Agonist WIN 55,12,2 during Lactation Induces Lasting Behavioral and Synaptic Alterations in the Rat Adult Offspring of Both Sexes. eNeuro 2020, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheyer, A.F.; Borsoi, M.; Pelissier- Alicot, A.-L.; Manzoni, O.J.J. Perinatal THC Exposure via Lactation Induces Lasting Alterations to Social Behavior and Prefrontal Cortex Function in Rats at Adulthood. Neuropsychopharmacology 2020, 45, 1826–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deroche, M.A.; Lassalle, O.; Castell, L.; Valjent, E.; Manzoni, O.J. Cell-Type- and Endocannabinoid-Specific Synapse Connectivity in the Adult Nucleus Accumbens Core. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2020, 40, 1028–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Foundation for Statistical Computing. R Core Team R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, T.; Soh, Y.H.; Barnett, D.; Anastasiadis, S. INZightPlots: Graphical Tools for Exploring Data with “INZight”. Comprehensive R Archive Network. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/ (accessed on 1 May 2022).
- Wild, C.J.; Elliott, T.; Sporle, A. On Democratizing Data Science: Some INZights Into Empowering the Many. Harv. Data Sci. Rev. 2021, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Electrophysiological Parameter | Control | Control + CSDS | n-3 Suppl | n-3 Suppl + CSDS | Significant Variable |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AP threshold (mV) | −36.8 ± 1.9 | −37.6 ± 2.7 | −40.7 ± 0.9 | −39.2 ± 1.9 | - |
| AP amplitude (mV) | 61.0 ± 2.9 | 62.3 ± 3.1 | 72.0 ± 2.1 | 69.9 ± 3.8 | diet |
| AP duration (ms) | 5.6 ± 0.5 | 5.1 ± 0.4 | 6.5 ± 0.5 | 7.8 ± 0.5 | diet |
| Delay to first spike (ms) | 387.5 ± 44.2 | 427.8 ± 55.7 | 352.4 ± 40.4 | 253.2 ± 34.8 | diet |
| AP rise kinetics (mV/ms) | 34.8 ± 3.3 | 35.0 ± 3.9 | 31.5 ± 2.9 | 27.0 ± 4.3 | - |
| AP decay kinetics (mV/ms) | 18.3 ± 2.2 | 21.2 ± 3.0 | 19.4 ± 1.3 | 15.5 ± 1.5 | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Miceli, M.; Martinat, M.; Rossitto, M.; Aubert, A.; Alashmali, S.; Bosch-Bouju, C.; Fioramonti, X.; Joffre, C.; Bazinet, R.P.; Layé, S. Dietary Long-Chain n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Supplementation Alters Electrophysiological Properties in the Nucleus Accumbens and Emotional Behavior in Naïve and Chronically Stressed Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6650. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23126650
Di Miceli M, Martinat M, Rossitto M, Aubert A, Alashmali S, Bosch-Bouju C, Fioramonti X, Joffre C, Bazinet RP, Layé S. Dietary Long-Chain n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Supplementation Alters Electrophysiological Properties in the Nucleus Accumbens and Emotional Behavior in Naïve and Chronically Stressed Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(12):6650. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23126650
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Miceli, Mathieu, Maud Martinat, Moïra Rossitto, Agnès Aubert, Shoug Alashmali, Clémentine Bosch-Bouju, Xavier Fioramonti, Corinne Joffre, Richard P. Bazinet, and Sophie Layé. 2022. "Dietary Long-Chain n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Supplementation Alters Electrophysiological Properties in the Nucleus Accumbens and Emotional Behavior in Naïve and Chronically Stressed Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 12: 6650. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23126650
APA StyleDi Miceli, M., Martinat, M., Rossitto, M., Aubert, A., Alashmali, S., Bosch-Bouju, C., Fioramonti, X., Joffre, C., Bazinet, R. P., & Layé, S. (2022). Dietary Long-Chain n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Supplementation Alters Electrophysiological Properties in the Nucleus Accumbens and Emotional Behavior in Naïve and Chronically Stressed Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(12), 6650. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23126650






