Liposomal Formulations of a New Zinc(II) Complex Exhibiting High Therapeutic Potential in a Murine Colon Cancer Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and Apparatus
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Synthesis of HL
2.2.2. Synthesis of the Zinc(II) Complexes
2.2.3. Stability Assays under Aqueous Conditions
2.2.4. Interaction Studies with Biomolecules
Fluorescence Assays with Bovine Serum Albumin
Circular Dichroism Assays with Bovine Serum Albumin
Fluorescence Competition Assays with Ethidium Bromide and DNA
2.2.5. Cell Culture Conditions
Spheroids
2.2.6. Antiproliferative Activity
2D Setting
3D Setting
2.2.7. Cell Death Analysis
2.2.8. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.2.9. Liposomal Formulations
Preparation of Liposomal Formulations
Physicochemical Characterization of Liposomal Formulations
Assessment of pH-Sensitive Properties
Internalization Cell Studies
In Vitro Safety Assay by Hemolytic Activity
2.2.10. In Vivo Assays
Animals
Tumor Syngeneic Mouse Model
Hepatic Biochemical Parameters
Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Ligand Precursor
3.2. The Zn(II) Complexes
3.3. Interaction with Bovine Serum Albumin
3.4. Interaction Studies with DNA
3.5. In Vitro Screening of the Zinc Complexes: 2D and 3D Settings
3.6. Cell Death and Cell Cycle Analysis
3.7. Physicochemical Characterization of Liposomal Formulations
3.8. Assessment of pH-Sensitive Properties of the Liposomal Formulation
3.9. Antiproliferative Properties of Liposomal Formulation
3.10. Liposome Internalization Studies in Spheroids
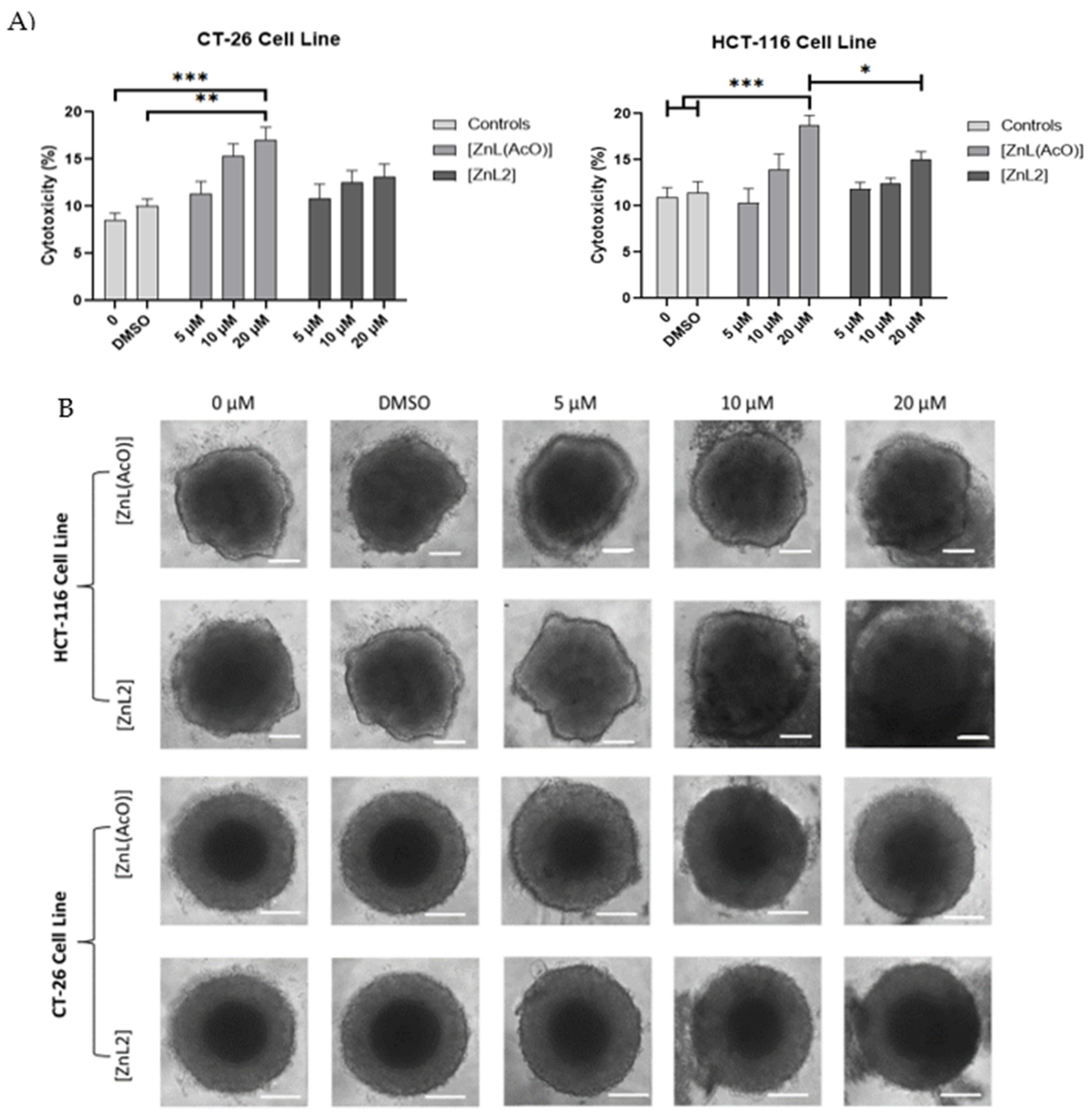
3.11. Antiproliferative Properties of [ZnL(AcO)] in a 3D Setting
3.12. In Vitro Safety Assay of [ZnL(AcO)]
3.13. In Vivo Efficacy of [ZnL(AcO)] in a Syngeneic Colon Cancer Mouse Model
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UICC. Available online: https://www.uicc.org/news/globocan-2020-new-global-cancer-data# (accessed on 10 April 2022).
- Ewing, I.; Hurley, J.J.; Josephides, E.; Millar, A. The molecular genetics of colorectal cancer. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2014, 5, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gustavsson, B.; Carlsson, G.; Machover, D.; Petrelli, N.; Roth, A.; Schmoll, H.-J.; Tveit, K.-M.; Gibson, F. A Review of the Evolution of Systemic Chemotherapy in the Management of Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Colorectal Cancer 2015, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Farinha, P.; Pinho, J.; Matias, M.; Gaspar, M. Nanomedicines in the treatment of colon cancer: A focus on metallodrugs. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2022, 12, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, F.; Cai, H.; Peng, F. Anti-prostate cancer activity of 8-hydroxyquinoline-2-carboxaldehyde-thiosemicarbazide copper complexes in vivo by bioluminescence imaging. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 23, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollingshead, R.G.W. Oxine and Its Derivatives; Butterworths Scientific Publications: London, UK, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Xu, H.; Chen, W.; Zhan, P.; Liu, X. 8-Hydroxyquinoline: A privileged structure with a broad-ranging pharmacological potential. MedChemComm 2015, 6, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prachayasittikul, V.; Prachayasittikul, S.; Ruchirawat, S. 8-Hydroxyquinolines: A review of their metal chelating properties and medicinal applications. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2013, 7, 1157–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, R.; Luxami, V.; Paul, K. Insights of 8-hydroxyquinolines: A novel target in medicinal chemistry. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 108, 104633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joaquim, A.R.; Gionbelli, M.P.; Gosmann, G.; Fuentefria, A.M.; Lopes, M.S.; Fernandes de Andrade, S. Novel Antimicrobial 8-Hydroxyquinoline-Based Agents: Current Development, Structure–Activity Relationships, and Perspectives. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 16349–16379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Santos, I.; Sanmartín, J.; García-Deibe, A.M.; Fondo, M.; Gómez, E. Structural and spectroscopic studies on some metal complexes of an 8-hydroxyquinoline derivative. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2010, 363, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maayan, G.; Dayagi, Y.; Arad-Yellin, R.; Shimon, L.J.W.; Shanzer, A. Stabilization of unique valencies of cobalt, nickel and copper by complexation with the tridentate ligand 2-(2′-pyridyl)-8-hydroxyquinoline. Polyhedron 2013, 64, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malecki, J.G.; Maron, A.; Gryca, I.; Serda, M. Characterization of a PdII complex with (E)-8-hydroxyquinoline-2-carbaldehyde O-benzyl oxime. Mendeleev Commun. 2014, 24, 26–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacopetta, D.; Ceramella, J.; Catalano, A.; Saturnino, C.; Bonomo, M.G.; Franchini, C.; Sinicropi, M.S. Schiff Bases: Interesting Scaffolds with Promising Antitumoral Properties. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridevi, G.; Arul Antony, S.; Angayarkani, R. Schiff Base Metal Complexes as Anticancer Agents. Asian J. Chem. 2019, 31, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weekes, A.A.; Westwell, A.D. 2-Arylbenzothiazole as a privileged scaffold in drug discovery. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 2430–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, K.; Shrivastava, N.; Pathak, A.; Prasad Dewangan, R.; Yahya, S.; Shahar Yar, M. Recent advances and SAR study of 2-substituted benzothiazole scaffold based potent chemotherapeutic agents. Results Chem. 2022, 4, 100258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjorgjieva, M.; Tomašič, T.; Barančokova, M.; Katsamakas, S.; Ilaš, J.; Tammela, P.; Peterlin Mašič, L.; Kikelj, D. Discovery of Benzothiazole Scaffold-Based DNA Gyrase B Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 8941–8954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, E.; de Brito, M.; Vasconcelos, T.; de Moraes, M.; Montenegro, R.; Yoneda, J.; Leal, K. Synthesis and anticancer activity of (E)-2-benzothiazole hydrazones. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 86, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, Z.S.; Ralph, A.C.L.; Calcagno, D.Q.; dos Santos Barbosa, G.; do Nascimento Pedrosa, T.; Antony, L.P.; de Arruda Cardoso Smith, M.; de Lucas Chazin, E.; Vasconcelos, T.R.A.; Montenegro, R.C.; et al. Anticancer potential of benzothiazolic derivative (E)-2-((2-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)hydrazono)methyl)-4-nitrophenol against melanoma cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2018, 50, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, R.; Foreman, D.; Lin, H.; Carney, B.; Fox, K.; Cassimeris, L.; Tanski, J.; Tyler, L. Synthesis, characterization, crystal structures and biological activity of set of Cu(II) benzothiazole complexes: Artificial nucleases with cytotoxic activities. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2014, 137, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehra, S.; Shavez Khan, M.; Ahmad, I.; Arjmand, F. New tailored substituted benzothiazole Schiff base Cu(II)/Zn(II) antitumor drug entities: Effect of substituents on DNA binding profile, antimicrobial and cytotoxic activity. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2019, 37, 1863–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellei, M.; Del Bello, F.; Porchia, M.; Santini, C. Zinc coordination complexes as anticancer agents. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 445, 214088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabra, M.; Babu, L.T.; Mondal, A.; Sun, H.; Paira, P. Amberlite IRA 402(OH) Mediated Green Synthesis of Novel Benzothiazole–quinoline Conjugates as Cancer Theranostics. ChemistrySelect 2017, 2, 2480–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hani, U.; Honnavalli, Y.K.; Begum, M.Y.; Yasmin, S.; Osmani, R.A.M.; Ansari, M.Y. Colorectal cancer: A comprehensive review based on the novel drug delivery systems approach and its management. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 63, 102532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.O.; Pinho, J.O.; Lopes, J.M.; Almeida, A.J.; Gaspar, M.M.; Reis, C. Current Trends in Cancer Nanotheranostics: Metallic, Polymeric, and Lipid-Based Systems. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.; Merlin, D. Lipid-Based Drug Delivery Nanoplatforms for Colorectal Cancer Therapy. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulbake, U.; Doppalapudi, S.; Kommineni, N.; Khan, W. Liposomal Formulations in Clinical Use: An Updated Review. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stathopoulos, G.P.; Boulikas, T. Lipoplatin formulation review article. J. Drug Deliv. 2012, 2012, 581363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stathopoulos, G.P.; Boulikas, T.; Kourvetaris, A.; Stathopoulos, J. Liposomal Oxaliplatin in the Treatment of Advanced Cancer: A Phase I Study. Anticancer. Res. 2006, 26, 1489. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda, H.; Wu, J.; Sawa, T.; Matsumura, Y.; Hori, K. Tumor vascular permeability and the EPR effect in macromolecular therapeutics: A review. J. Control. Release 2000, 65, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Din, F.U.; Aman, W.; Ullah, I.; Qureshi, O.S.; Mustapha, O.; Shafique, S.; Zeb, A. Effective use of nanocarriers as drug delivery systems for the treatment of selected tumors. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 7291–7309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Persi, E.; Duran-Frigola, M.; Damaghi, M.; Roush, W.R.; Aloy, P.; Cleveland, J.L.; Gillies, R.J.; Ruppin, E. Systems analysis of intracellular pH vulnerabilities for cancer therapy. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinho, J.O.; Amaral, J.D.; Castro, R.E.; Rodrigues, C.M.P.; Casini, A.; Soveral, G.; Gaspar, M.M. Copper complex nanoformulations featuring highly promising therapeutic potential in murine melanoma models. Nanomedicine 2019, 14, 835–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinho, J.O.; da Silva, I.V.; Amaral, J.D.; Rodrigues, C.M.P.; Casini, A.; Soveral, G.; Gaspar, M.M. Therapeutic potential of a copper complex loaded in pH-sensitive long circulating liposomes for colon cancer management. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 599, 120463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coutinho, A.; Prieto, M. Ribonuclease-t(1) and alcohol-dehydrogenase fluorescence quenching by acrylamide—A laboratory experiment for undergraduate students. J. Chem. Educ. 1993, 70, 425–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquês, J.T.; de Almeida, R.F.M. Application of Ratiometric Measurements and Microplate Fluorimetry to Protein Denaturation: An Experiment for Analytical and Biochemistry Students. J. Chem. Educ. 2013, 90, 1522–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nave, M.; Castro, R.E.; Rodrigues, C.M.P.; Casini, A.; Soveral, G.; Gaspar, M.M. Nanoformulations of a potent copper-based aquaporin inhibitor with cytotoxic effect against cancer cells. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 1817–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rouser, G.; Fleischer, S.; Yamamoto, A. Two dimensional thin layer chromatographic separation of polar lipids and determination of phospholipids by phosphorus analysis of spots. Lipids 1970, 5, 494–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, M.M.; Calado, S.; Pereira, J.; Ferronha, H.; Correia, I.; Castro, H.; Tomás, A.M.; Cruz, M.E.M. Targeted delivery of paromomycin in murine infectious diseases through association to nano lipid systems. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2015, 11, 1851–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levina, A.; Crans, D.; Lay, P. Speciation of metal drugs, supplements and toxins in media and bodily fluids controls in vitro activities. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 352, 473–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, C.P.; Yildizhan, Y.; Adiguzel, Z.; Pavan, F.R.; Campos, D.L.; Pessoa, J.C.; Ferreira, L.P.; Tomaz, A.I.; Correia, I.; Acilan, C. New ternary iron(iii) aminobisphenolate hydroxyquinoline complexes as potential therapeutic agents. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 8702–8716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, P.; Correia, I.; Marques, F.; Matos, A.P.; dos Santos, M.M.C.; Azevedo, C.G.; Capelo, J.-L.; Santos, H.M.; Gama, S.; Pinheiro, T.; et al. Copper Complexes with 1,10-Phenanthroline Derivatives: Underlying Factors Affecting Their Cytotoxicity. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 9116–9134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Arnaiz, C.; Leal, J.; Busto, N.; Carrión, M.C.; Rubio, A.R.; Ortiz, I.; Barone, G.; Díaz de Greñu, B.; Santolaya, J.; Leal, J.M.; et al. Role of Seroalbumin in the Cytotoxicity of cis-Dichloro Pt(II) Complexes with (N^N)-Donor Ligands Bearing Functionalized Tails. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 6124–6134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Phopin, K.; Ruankham, W.; Prachayasittikul, S.; Prachayasittikul, V.; Tantimongcolwat, T. Insight into the Molecular Interaction of Cloxyquin (5-chloro-8-hydroxyquinoline) with Bovine Serum Albumin: Biophysical Analysis and Computational Simulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sathyadevi, P.; Krishnamoorthy, P.; Jayanthi, E.; Butorac, R.R.; Cowley, A.H.; Dharmaraj, N. Studies on the effect of metal ions of hydrazone complexes on interaction with nucleic acids, bovine serum albumin and antioxidant properties. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2012, 384, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topală, T.; Bodoki, A.; Oprean, L.; Oprean, R. Bovine Serum Albumin Interactions with Metal Complexes. Clujul Med. (1957) 2014, 87, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nunes, A.S.; Barros, A.S.; Costa, E.C.; Moreira, A.F.; Correia, I.J. 3D tumor spheroids as in vitro models to mimic in vivo human solid tumors resistance to therapeutic drugs. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2019, 116, 206–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karlsson, H.; Fryknäs, M.; Larsson, R.; Nygren, P. Loss of cancer drug activity in colon cancer HCT-116 cells during spheroid formation in a new 3-D spheroid cell culture system. Exp. Cell Res. 2012, 318, 1577–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, N.T.; Yuan, F. A Review of Three-Dimensional In Vitro Tissue Models for Drug Discovery and Transport Studies. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekert, J.E.; Johnson, K.; Strake, B.; Pardinas, J.; Jarantow, S.; Perkinson, R.; Colter, D.C. Three-Dimensional Lung Tumor Microenvironment Modulates Therapeutic Compound Responsiveness In Vitro—Implication for Drug Development. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimlin, L.C.; Casagrande, G.; Virador, V.M. In vitro three-dimensional (3D) models in cancer research: An update. Mol. Carcinog. 2013, 52, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantino, L.; Mehta, R.T.; Cruz, M.E.; Lopez-berestein, G. Formulation and Toxicity of Liposomes Containing Rifampicin. J. Liposome Res. 1993, 3, 275–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Nakamura, H.; Fang, J. The EPR effect for macromolecular drug delivery to solid tumors: Improvement of tumor uptake, lowering of systemic toxicity, and distinct tumor imaging in vivo. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danaei, M.; Dehghankhold, M.; Ataei, S.; Hasanzadeh Davarani, F.; Javanmard, R.; Dokhani, A.; Khorasani, S.; Mozafari, M.R. Impact of Particle Size and Polydispersity Index on the Clinical Applications of Lipidic Nanocarrier Systems. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Draffehn, S.; Kumke, M.U. Monitoring the Collapse of pH-Sensitive Liposomal Nanocarriers and Environmental pH Simultaneously: A Fluorescence-Based Approach. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 1608–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshpande, P.P.; Biswas, S.; Torchilin, V.P. Current trends in the use of liposomes for tumor targeting. Nanomedicine 2013, 8, 1509–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Allen Theresa, M.; Cullis Pieter, R. Drug Delivery Systems: Entering the Mainstream. Science 2004, 303, 1818–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gabizon, A.; Shmeeda, H.; Barenholz, Y. Pharmacokinetics of Pegylated Liposomal Doxorubicin. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2003, 42, 419–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, T.M.; Cullis, P.R. Liposomal drug delivery systems: From concept to clinical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vodenkova, S.; Buchler, T.; Cervena, K.; Veskrnova, V.; Vodicka, P.; Vymetalkova, V. 5-fluorouracil and other fluoropyrimidines in colorectal cancer: Past, present and future. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 206, 107447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lainé, A.-L.; Passirani, C. Novel metal-based anticancer drugs: A new challenge in drug delivery. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2012, 12, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bayón-Cordero, L.; Alkorta, I.; Arana, L. Application of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles to Improve the Efficiency of Anticancer Drugs. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barenholz, Y. Doxil®—The first FDA-approved nano-drug: Lessons learned. J. Control. Release 2012, 160, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA. Guidance for Industry Nonclinical Studies for then Safety Evaluation of Pharmaceutical Excipients; Center for Drug Evaluation and Research: White Oak, MD, USA, 2005; pp. 1–9.
- Amin, K.; Dannenfelser, R.-M. In vitro hemolysis: Guidance for the pharmaceutical scientist. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 95, 1173–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellers, R.S.; Mortan, D.; Michael, B.; Roome, N.; Johnson, J.K.; Yano, B.L.; Perry, R.; Schafer, K. Society of Toxicologic Pathology Position Paper: Organ Weight Recommendations for Toxicology Studies. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Shi, H.; Ruth, M.; Yu, H.; Lazar, L.; Zou, B.; Yang, C.; Wu, A.; Zhao, J. Acute Toxicity of Intravenously Administered Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles in Mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kew, M.C. Serum aminotransferase concentration as evidence of hepatocellular damage. Lancet 2000, 355, 591–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ware, W.R. Oxygen Quenching of Fluorescence in Solution: An Experimental Study of the Diffusion Process. J. Phys. Chem. 1962, 66, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scatchard, G. The Attractions of Proteins for Small Molecules and Ions. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 1949, 51, 660–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macii, F.; Biver, T. Spectrofluorimetric analysis of the binding of a target molecule to serum albumin: Tricky aspects and tips. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2021, 216, 111305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tedesco, D.; Bertucci, C. Induced circular dichroism as a tool to investigate the binding of drugs to carrier proteins: Classic approaches and new trends. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 113, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pessoa, J.C.; Correia, I.; Gonçalves, G.; Tomaz, I. Circular dichroism in coordination compounds. J. Argent. Chem. Soc. 2009, 97, 151–165. [Google Scholar]
- Allenmark, S. Induced circular dichroism by chiral molecular interaction. Chirality 2003, 15, 409–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Metal-Based Complex | IC50 (µM) ± SD | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy Cells | Tumor Cells | ||
| HaCaT | HCT-116 | CT-26 | |
| [ZnL(AcO)] | 17.5 ± 1.5 | 11.7 ± 1.0 | 11.0 ± 0.7 |
| [ZnL2] | 17.9 ± 0.5 | 8.7 ± 0.2 | 21.5 ± 0.6 |
| Formulation | Lipid Composition (Molar Ratio) | (ZnL(AcO)/Lip)i (µg/µmol) | (ZnL(AcO)/Lip)f (µg/µmol) | I.E. (%) | Ø (nm) (PdI) | ζ Pot. (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 * | DOPE:CHEMS:DMPC:DSPE-PEG (37.5:20:37.5:5) | 13 ± 0 | 7 ± 1 | 52 ± 4 | 151 ± 1 (<0.2) | −6 ± 1 |
| F2 * | DOPE:CHEMS:DOPC:DSPE-PEG (37.5:20:37.5:5) | 11 ± 0 | 6 ± 1 | 56 ± 3 | 141 ± 1 (<0.2) | −3 ± 1 |
| F3 * | DOPE:CHEMS:DOPC:DSPE-PEG (42.5:10:42.5:5) | 10 ± 2 | 7 ± 0 | 63 ± 2 | 135± 2 (<0.2) | −4 ± 1 |
| F4 ** | DOPE:CHEMS:DOPC:DSPE-PEG (42.5:10:42.5:5) | 31 ± 2 | 23 ± 1 | 76 ± 2 | 119 ± 7 (≤0.1) | −5 ± 1 |
| Formulations | IC50 (µM) | |
|---|---|---|
| Cell Line | ||
| HCT-116 | CT-26 | |
| [ZnL(AcO)] in free form | 11.7 ± 1.0 | 11.0 ± 0.7 |
| [ZnL(AcO)] in liposomal form (F4) | 11.8 ± 0.3 | 14.3 ± 0.8 |
| 5-FU | 43.7 ± 2.8 | 2.4 ± 0.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ribeiro, N.; Albino, M.; Ferreira, A.; Escrevente, C.; Barral, D.C.; Pessoa, J.C.; Reis, C.P.; Gaspar, M.M.; Correia, I. Liposomal Formulations of a New Zinc(II) Complex Exhibiting High Therapeutic Potential in a Murine Colon Cancer Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6728. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23126728
Ribeiro N, Albino M, Ferreira A, Escrevente C, Barral DC, Pessoa JC, Reis CP, Gaspar MM, Correia I. Liposomal Formulations of a New Zinc(II) Complex Exhibiting High Therapeutic Potential in a Murine Colon Cancer Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(12):6728. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23126728
Chicago/Turabian StyleRibeiro, Nádia, Melissa Albino, Andreia Ferreira, Cristina Escrevente, Duarte C. Barral, João Costa Pessoa, Catarina Pinto Reis, Maria Manuela Gaspar, and Isabel Correia. 2022. "Liposomal Formulations of a New Zinc(II) Complex Exhibiting High Therapeutic Potential in a Murine Colon Cancer Model" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 12: 6728. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23126728
APA StyleRibeiro, N., Albino, M., Ferreira, A., Escrevente, C., Barral, D. C., Pessoa, J. C., Reis, C. P., Gaspar, M. M., & Correia, I. (2022). Liposomal Formulations of a New Zinc(II) Complex Exhibiting High Therapeutic Potential in a Murine Colon Cancer Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(12), 6728. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23126728











