STABILON, a Novel Sequence Motif That Enhances the Expression and Accumulation of Intracellular and Secreted Proteins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Proteasome Subunit p54/Rpn10 Harbors a Conserved C-Terminal Stabilization Motif
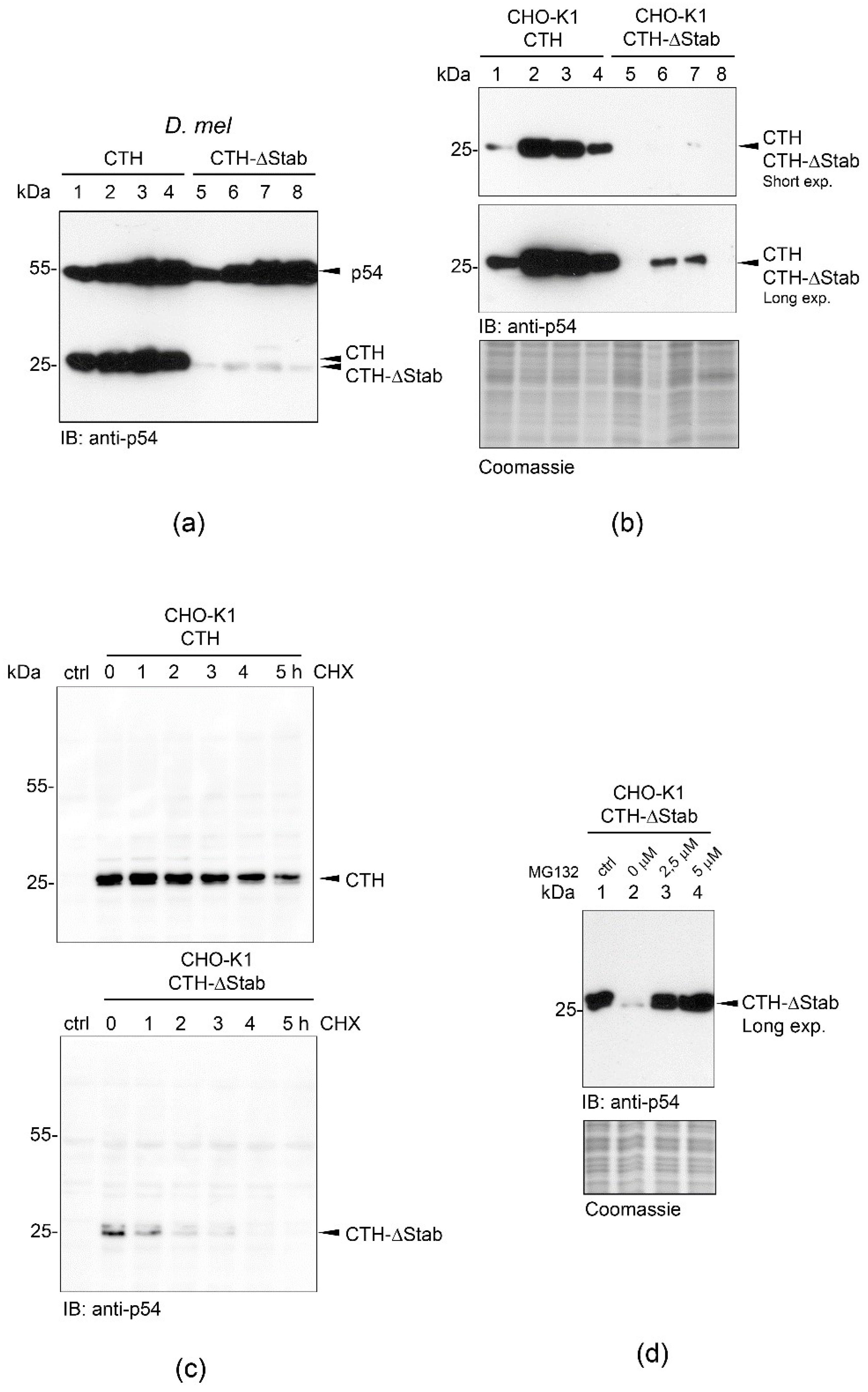
2.2. STABILON Is Required for the Extended Half-Life of p54-CTH
2.3. STABILON Is Not a Weak Initiation Sequence but a Genuine Cis-Acting Stabilization Motif
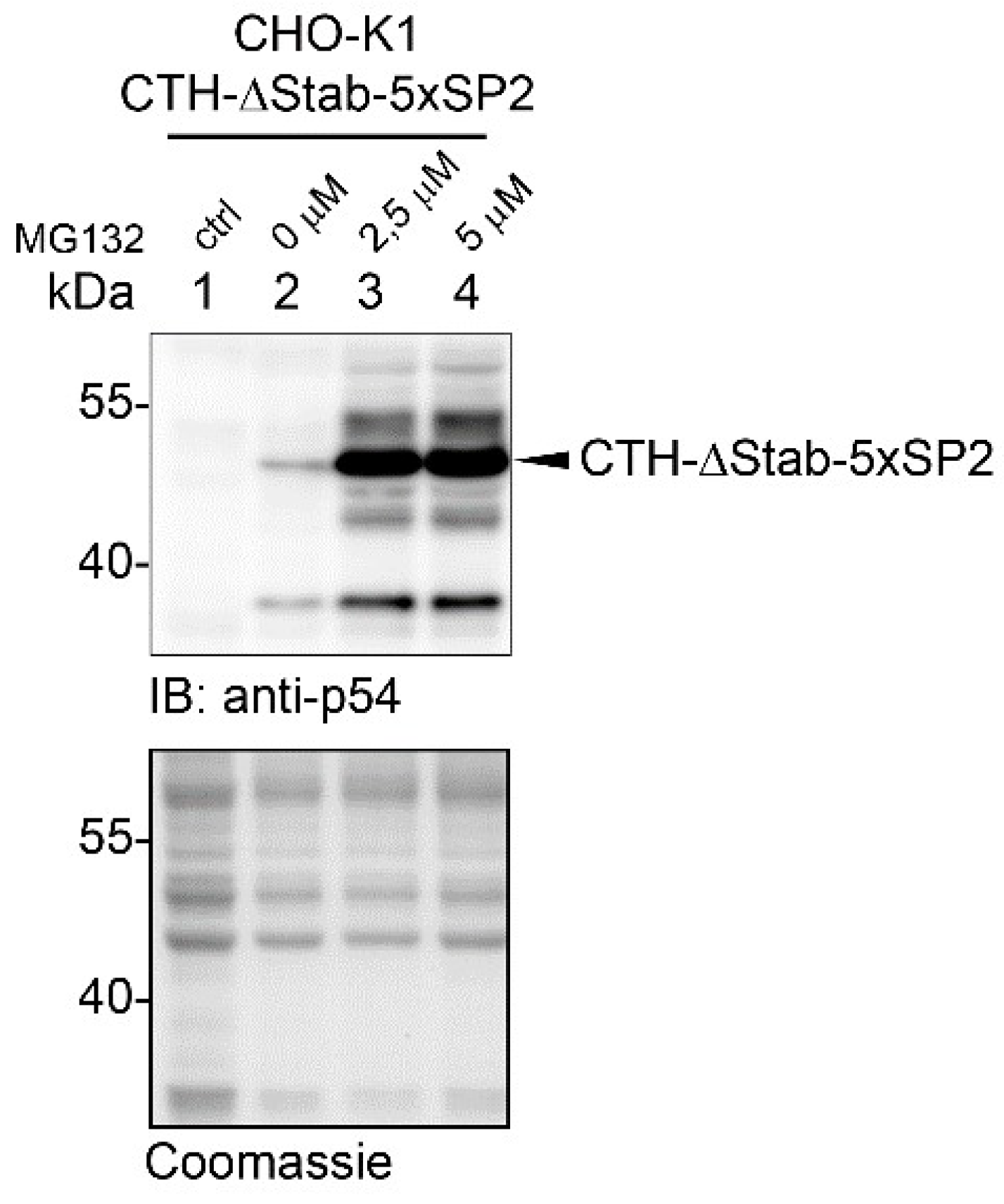
2.4. STABILON Prevents the Proteasomal Degradation of Short-Lived Proteins
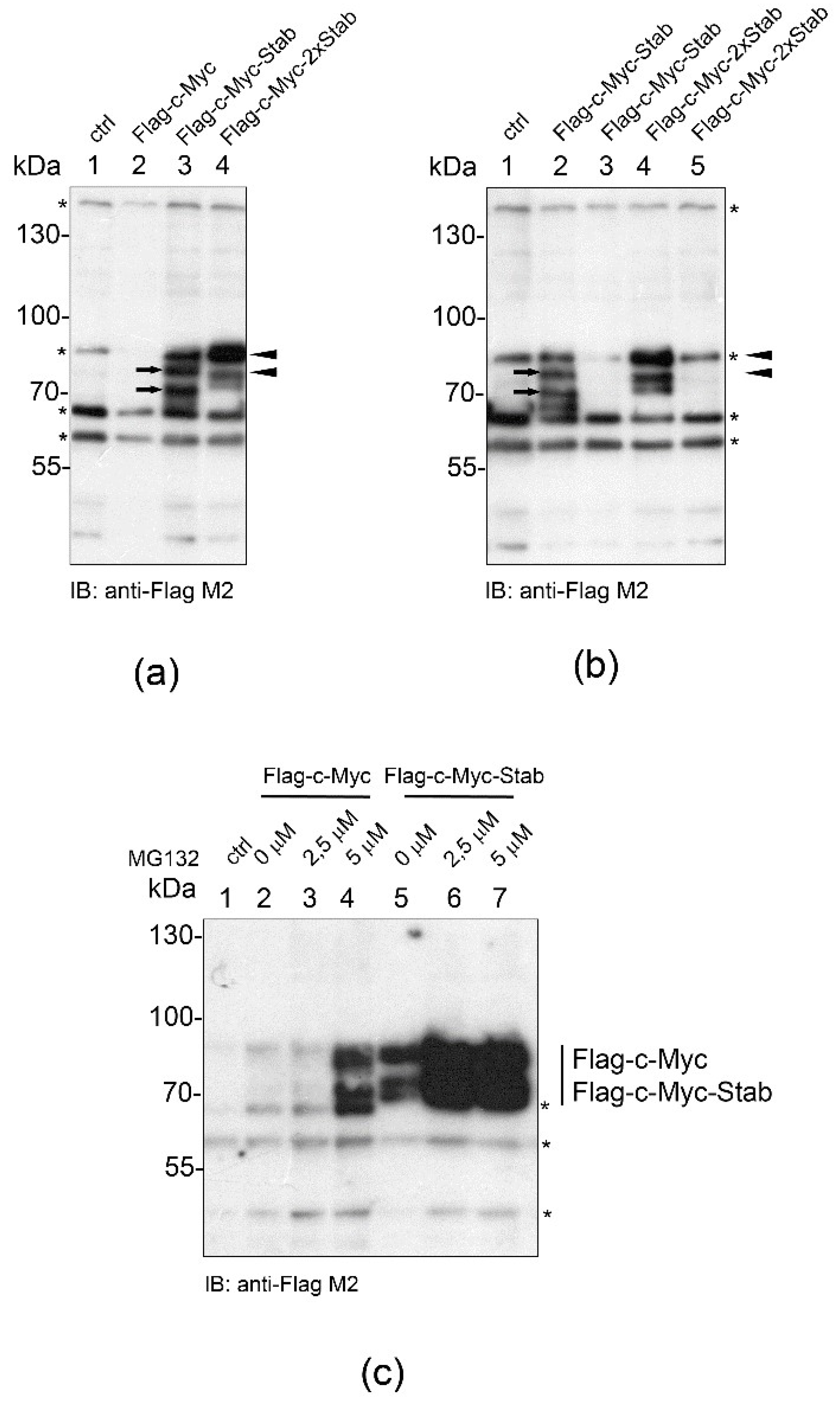
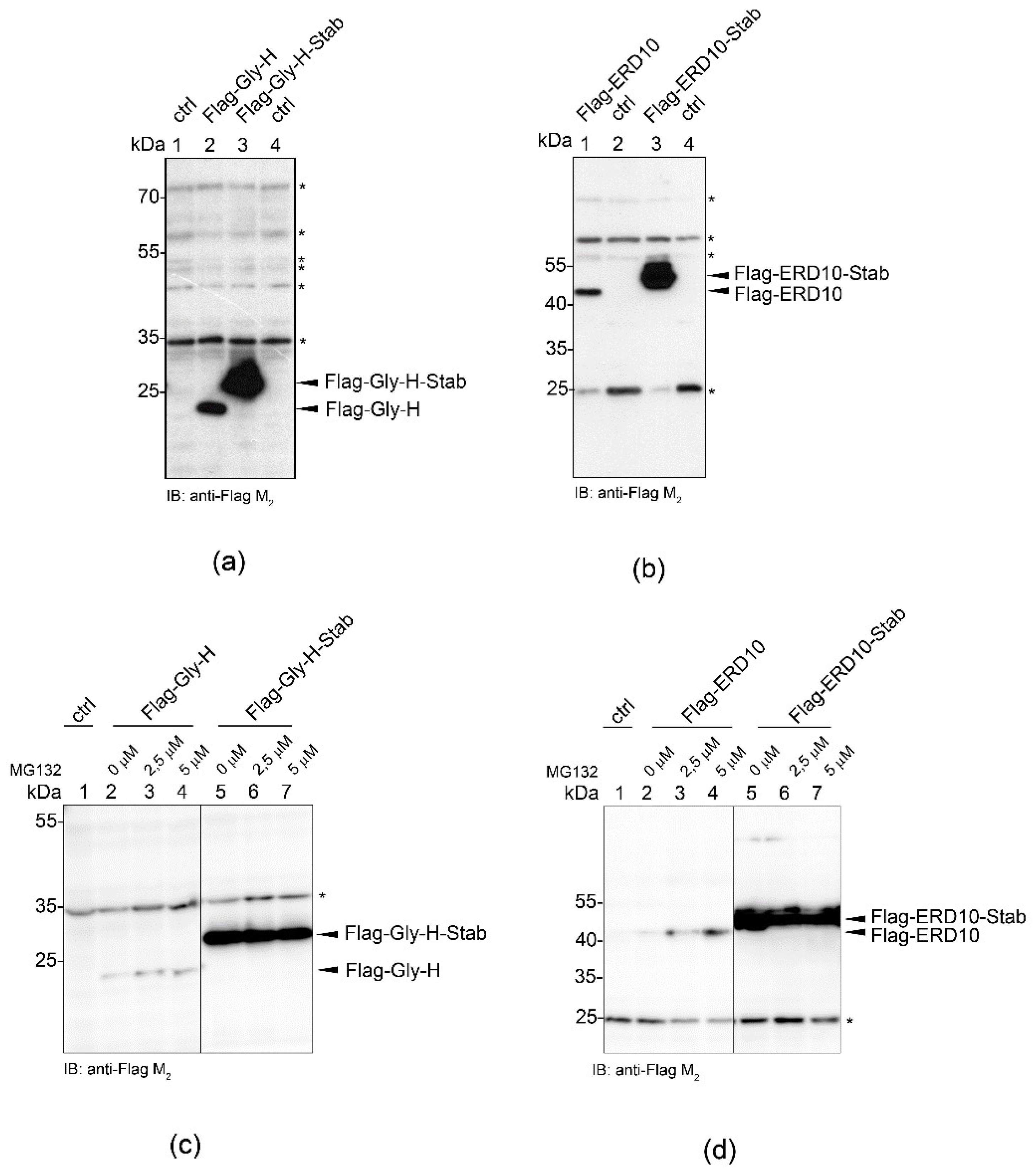
2.5. STABILON Enhances the Accumulation of Globular and Disordered Proteins
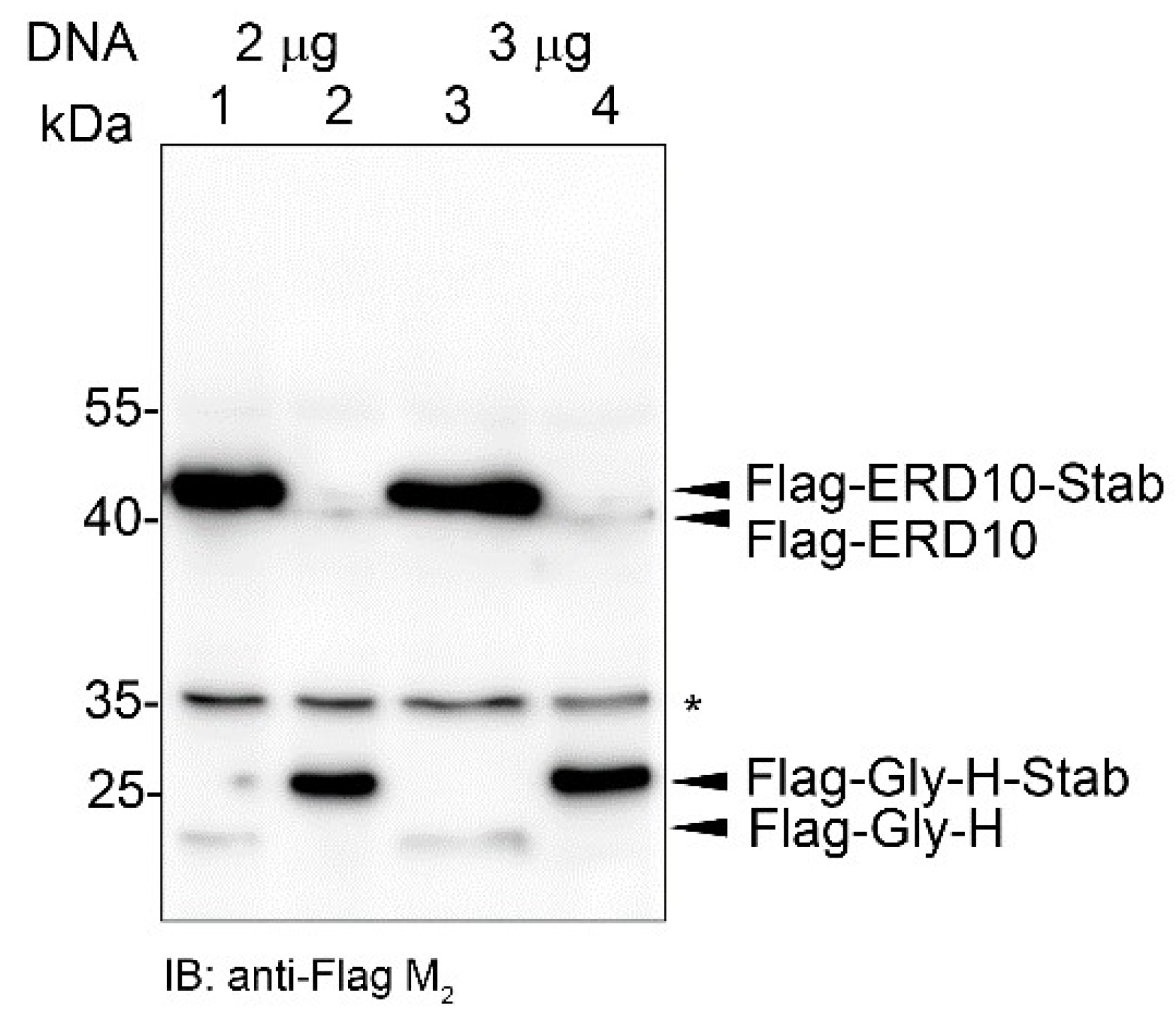
2.6. STABILON Boosts the Expression of Secreted Proteins
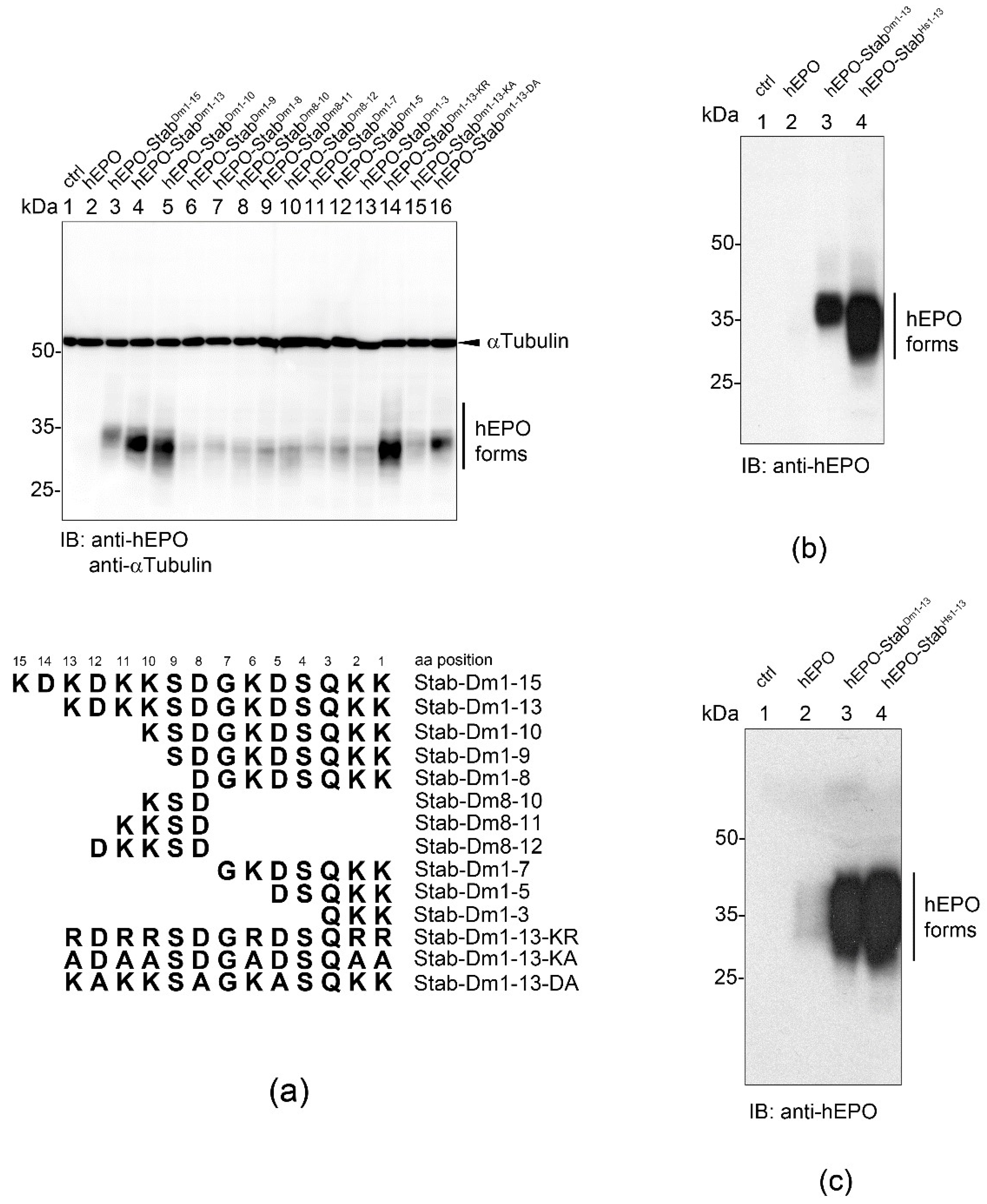
2.7. Mapping the Minimal STABILON
2.8. STABILON Affects the Transcript Levels of the Fusion Proteins
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. DNA Constructs
4.2. Drosophila Transgenic Lines
4.3. Generation of Stably Transfected Mammalian Cell Lines
4.4. Cycloheximide Chase Experiment
4.5. MG132 Treatment
4.6. Protein Preparation for SDS-PAGE and Mass Spectrometry
4.7. Mass Spectrometry
4.8. Gel-Electrophoresis and Immunoblotting
4.9. Densitometry Band Quantification of Western Blot Experiments
4.10. cDNA Synthesis and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Varshavsky, A. N-degron and C-degron pathways of protein degradation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.C.; Yeh, C.W.; Chen, Y.F.; Lee, T.T.; Hsieh, P.Y.; Rusnac, D.V.; Lin, S.Y.; Elledge, S.J.; Zheng, N.; Yen, H.S. C-Terminal End-Directed Protein Elimination by CRL2 Ubiquitin Ligases. Mol. Cell 2018, 70, 602–613.e603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, I.; Timms, R.T.; Kula, T.; Xu, Q.; Li, M.Z.; Elledge, S.J. The Eukaryotic Proteome Is Shaped by E3 Ubiquitin Ligases Targeting C-Terminal Degrons. Cell 2018, 173, 1622–1635.e1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinszki, Z.; Kiss, P.; Pal, M.; Deak, P.; Szabo, A.; Hunyadi-Gulyas, E.; Klement, E.; Medzihradszky, K.F.; Udvardy, A. Developmental-stage-specific regulation of the polyubiquitin receptors in Drosophila melanogaster. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 3083–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lipinszki, Z.; Kovacs, L.; Deak, P.; Udvardy, A. Ubiquitylation of Drosophila p54/Rpn10/S5a regulates its interaction with the UBA-UBL polyubiquitin receptors. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 2461–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, I.; Glickman, M.H. Proteasome in action: Substrate degradation by the 26S proteasome. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2021, 49, 629–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Fonts, K.; Davis, C.; Tomita, T.; Elsasser, S.; Nager, A.R.; Shi, Y.; Finley, D.; Matouschek, A. The proteasome 19S cap and its ubiquitin receptors provide a versatile recognition platform for substrates. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szlanka, T.; Haracska, L.; Kiss, I.; Deak, P.; Kurucz, E.; Ando, I.; Viragh, E.; Udvardy, A. Deletion of proteasomal subunit S5a/Rpn10/p54 causes lethality, multiple mitotic defects and overexpression of proteasomal genes in Drosophila melanogaster. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 1023–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haracska, L.; Udvardy, A. Cloning and sequencing a non-ATPase subunit of the regulatory complex of the Drosophila 26S protease. Eur. J. Biochem. 1995, 231, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, J.B. GAL4 system in Drosophila: A fly geneticist’s Swiss army knife. Genesis 2002, 34, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, J.R.; Lee, A.M.; Wu, C.T. Site-specific transformation of Drosophila via phiC31 integrase-mediated cassette exchange. Genetics 2006, 173, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinszki, Z.; Klement, E.; Hunyadi-Gulyas, E.; Medzihradszky, K.F.; Markus, R.; Pal, M.; Deak, P.; Udvardy, A. A novel interplay between the ubiquitin-proteasome system and serine proteases during Drosophila development. Biochem. J. 2013, 454, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yu, H.; Singh Gautam, A.K.; Wilmington, S.R.; Wylie, D.; Martinez-Fonts, K.; Kago, G.; Warburton, M.; Chavali, S.; Inobe, T.; Finkelstein, I.J.; et al. Conserved Sequence Preferences Contribute to Substrate Recognition by the Proteasome. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 14526–14539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junttila, M.R.; Westermarck, J. Mechanisms of MYC stabilization in human malignancies. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sears, R.C. The life cycle of C-myc: From synthesis to degradation. Cell Cycle 2004, 3, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, A.S.; Sears, R.C. MYC degradation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014, 4, a014365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csizmok, V.; Szollosi, E.; Friedrich, P.; Tompa, P. A novel two-dimensional electrophoresis technique for the identification of intrinsically unstructured proteins. Mol. Cell. Proteom. MCP 2006, 5, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uversky, V.N.; Redwan, E.M. Erythropoietin and co.: Intrinsic structure and functional disorder. Mol. Biosyst. 2016, 13, 56–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loew, R.; Heinz, N.; Hampf, M.; Bujard, H.; Gossen, M. Improved Tet-responsive promoters with minimized background expression. BMC Biotechnol. 2010, 10, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Ezzeddine, N.; Shyu, A.B. Messenger RNA half-life measurements in mammalian cells. Methods Enzymol. 2008, 448, 335–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, W.L.; Yu, D.; Ouyang, Q.; Lu, Y.; Mao, Y. Structural mechanism for nucleotide-driven remodeling of the AAA-ATPase unfoldase in the activated human 26S proteasome. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, W.L.; Zhu, Y.; Stoilova-McPhie, S.; Lu, Y.; Finley, D.; Mao, Y. Cryo-EM structures and dynamics of substrate-engaged human 26S proteasome. Nature 2018, 565, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Pena, A.H.; Goodall, E.A.; Gates, S.N.; Lander, G.C.; Martin, A. Substrate-engaged 26S proteasome structures reveal mechanisms for ATP-hydrolysis-driven translocation. Science 2018, 362, eaav0725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazzini, A.A.; Del Viso, F.; Moreno-Mateos, M.A.; Johnstone, T.G.; Vejnar, C.E.; Qin, Y.; Yao, J.; Khokha, M.K.; Giraldez, A.J. Codon identity regulates mRNA stability and translation efficiency during the maternal-to-zygotic transition. EMBO J. 2016, 35, 2087–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puetz, J.; Wurm, F.M. Recombinant Proteins for Industrial versus Pharmaceutical Purposes: A Review of Process and Pricing. Processes 2019, 7, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jesus, M.; Wurm, F.M. Manufacturing recombinant proteins in kg-ton quantities using animal cells in bioreactors. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. Off. J. Arb. Fur. Pharm. Verfahr. E.V. 2011, 78, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariko, K.; Muramatsu, H.; Keller, J.M.; Weissman, D. Increased erythropoiesis in mice injected with submicrogram quantities of pseudouridine-containing mRNA encoding erythropoietin. Mol. Ther. 2012, 20, 948–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spradling, A.C. Drosophila: A Practical Approach; IRL Press: Oxford, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, S.; Price, J.C.; Prusiner, S.B.; Ghaemmaghami, S.; Burlingame, A.L. A data processing pipeline for mammalian proteome dynamics studies using stable isotope metabolic labeling. Mol. Cell. Proteom. MCP 2011, 10, M111.010728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo-Oller, G.; Ordoñez, R.; Dotor, J. A new background subtraction method for Western blot densitometry band quantification through image analysis software. J. Immunol. Methods 2018, 457, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crooks, G.E.; Hon, G.; Chandonia, J.M.; Brenner, S.E. WebLogo: A sequence logo generator. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1188–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rethi-Nagy, Z.; Abraham, E.; Udvardy, K.; Klement, E.; Darula, Z.; Pal, M.; Katona, R.L.; Tubak, V.; Pali, T.; Kota, Z.; et al. STABILON, a Novel Sequence Motif That Enhances the Expression and Accumulation of Intracellular and Secreted Proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8168. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158168
Rethi-Nagy Z, Abraham E, Udvardy K, Klement E, Darula Z, Pal M, Katona RL, Tubak V, Pali T, Kota Z, et al. STABILON, a Novel Sequence Motif That Enhances the Expression and Accumulation of Intracellular and Secreted Proteins. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(15):8168. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158168
Chicago/Turabian StyleRethi-Nagy, Zsuzsanna, Edit Abraham, Katalin Udvardy, Eva Klement, Zsuzsanna Darula, Margit Pal, Robert L. Katona, Vilmos Tubak, Tibor Pali, Zoltan Kota, and et al. 2022. "STABILON, a Novel Sequence Motif That Enhances the Expression and Accumulation of Intracellular and Secreted Proteins" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 15: 8168. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158168
APA StyleRethi-Nagy, Z., Abraham, E., Udvardy, K., Klement, E., Darula, Z., Pal, M., Katona, R. L., Tubak, V., Pali, T., Kota, Z., Sinka, R., Udvardy, A., & Lipinszki, Z. (2022). STABILON, a Novel Sequence Motif That Enhances the Expression and Accumulation of Intracellular and Secreted Proteins. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(15), 8168. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158168







