Promising Biomarkers in Head and Neck Cancer: The Most Clinically Important miRNAs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Role of the Most Common miRNAs in HNC
2.1. MiR-21
2.2. miR-375
2.3. miR-99
2.4. miR-34a
2.5. Let-7
2.6. MiR-200
2.7. MiR-31
2.8. MiR-125a/miR-125b
2.9. MiR-196a/miR-196b
2.10. MiR-9
2.11. MiR-181a
2.12. MiR-155
2.13. MiR-146a
2.14. MiR-23a
2.15. MiR-16
2.16. MiR-29
3. MiRNA Signatures of Diagnostic, Prognostic, and/or Predictive Value in HNC
3.1. MiRNA Ratios/miRNA Combined Expression
3.2. Multiple miRNA Signatures
3.2.1. HNSCC
3.2.2. OSCC
3.2.3. OPSCC
3.2.4. HSCC/NPC
4. Dynamic Correlation between miRNAs and HPV Status in HNSCC
5. Clinical Trials Assessing the Utility of miRNAs as Biomarkers for HNC Monitoring
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson, D.E.; Burtness, B.; Leemans, C.R.; Lui, V.W.Y.; Bauman, J.E.; Grandis, J.R. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltanova, B.; Raudenska, M.; Masarik, M. Effect of tumor microenvironment on pathogenesis of the head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, L.Q.M. Head and Neck Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falzone, L.; Salomone, S.; Libra, M. Evolution of Cancer Pharmacological Treatments at the Turn of the Third Millennium. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takes, R.P.; Rinaldo, A.; Silver, C.E.; Haigentz, M., Jr.; Woolgar, J.A.; Triantafyllou, A.; Mondin, V.; Paccagnella, D.; de Bree, R.; Shaha, A.R.; et al. Distant metastases from head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Part I. Basic aspects. Oral Oncol. 2012, 48, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulasinghe, A.; Schmidt, H.; Perry, C.; Whitfield, B.; Kenny, L.; Nelson, C.; Warkiani, M.E.; Punyadeera, C. A Collective Route to Head and Neck Cancer Metastasis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piotrowski, I.; Zhu, X.; Saccon, T.D.; Ashiqueali, S.; Schneider, A.; de Carvalho Nunes, A.D.; Noureddine, S.; Sobecka, A.; Barczak, W.; Szewczyk, M.; et al. miRNAs as Biomarkers for Diagnosing and Predicting Survival of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients. Cancers 2021, 13, 3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leemans, C.R.; Snijders, P.J.F.; Brakenhoff, R.H. The molecular landscape of head and neck cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumarasamy, C.; Madhav, M.R.; Sabarimurugan, S.; Krishnan, S.; Baxi, S.; Gupta, A.; Gothandam, K.M.; Jayaraj, R. Prognostic Value of miRNAs in Head and Neck Cancers: A Comprehensive Systematic and Meta-Analysis. Cells 2019, 8, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schoof, C.R.; Botelho, E.L.; Izzotti, A.; Vasques Ldos, R. MicroRNAs in cancer treatment and prognosis. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2012, 2, 414–433. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kabzinski, J.; Maczynska, M.; Majsterek, I. MicroRNA as a Novel Biomarker in the Diagnosis of Head and Neck Cancer. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabekkodu, S.P.; Shukla, V.; Varghese, V.K.; D’Souza, J.; Chakrabarty, S.; Satyamoorthy, K. Clustered miRNAs and their role in biological functions and diseases. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2018, 93, 1955–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Ma, X.; Chen, L.; Li, H.; Gu, L.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Fan, Y.; Chen, J.; et al. MicroRNAs with prognostic significance in bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.; Hayder, H.; Zayed, Y.; Peng, C. Overview of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Actions, and Circulation. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Macfarlane, L.A.; Murphy, P.R. MicroRNA: Biogenesis, Function and Role in Cancer. Curr. Genom. 2010, 11, 537–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gross, N.; Kropp, J.; Khatib, H. MicroRNA Signaling in Embryo Development. Biology 2017, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.H.; Liu, H.; Chiang, W.F.; Chen, T.W.; Chu, L.J.; Yu, J.S.; Chen, S.J.; Chen, H.C.; Tan, B.C. MiR-31-5p-ACOX1 Axis Enhances Tumorigenic Fitness in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Via the Promigratory Prostaglandin E2. Theranostics 2018, 8, 486–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoumpourlis, V.; Skourti, E.; Goulielmaki, M.; Vlahopoulos, S.; Christodoulou, I. The Ideological Frame of the Genetic Basis of Cancer: The Important Role of miRNAs. Crit. Rev. Oncog. 2017, 22, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabit, H.; Cevik, E.; Tombuloglu, H.; Abdel-Ghany, S.; Tombuloglu, G.; Esteller, M. Triple negative breast cancer in the era of miRNA. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2021, 157, 103196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.A.; Arora, S.; Prakasam, G.; Calin, G.A.; Syed, M.A. MicroRNA in lung cancer: Role, mechanisms, pathways and therapeutic relevance. Mol. Asp. Med. 2019, 70, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramovic, I.; Ulamec, M.; Katusic Bojanac, A.; Bulic-Jakus, F.; Jezek, D.; Sincic, N. miRNA in prostate cancer: Challenges toward translation. Epigenomics 2020, 12, 543–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Yu, S.; Ding, L.; Ma, L.; Chen, H.; Zhou, H.; Zou, Y.; Yu, M.; Lin, J.; Cui, Q. The Dual Role of Circular RNAs as miRNA Sponges in Breast Cancer and Colon Cancer. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, B.; Uddin, A.; Chakraborty, S. miRNAs and ovarian cancer: An overview. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 3846–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhong, L.; Wen, Y.; Ye, Q.; Cao, D.; Li, P.; Liu, Y. Construction of an 11-microRNA-based signature and a prognostic nomogram to predict the overall survival of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, X.; Niu, S.; Chen, H.; Li, C. A novel prognostic mRNA/miRNA signature for esophageal cancer and its immune landscape in cancer progression. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 1088–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitriana, M.; Hwang, W.L.; Chan, P.Y.; Hsueh, T.Y.; Liao, T.T. Roles of microRNAs in Regulating Cancer Stemness in Head and Neck Cancers. Cancers 2021, 13, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Mu, J.; Yang, D.; Gu, X.; Zhang, J. Exosomal miR-21-5p contributes to ovarian cancer progression by regulating CDK6. Hum. Cell 2021, 34, 1185–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, L.; Chen, F.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, D.; Qian, B.; Ji, H.; Long, F.; Cretoiu, D. miR-21 regulates growth and EMT in lung cancer cells via PTEN/Akt/GSK3β signaling. Front. Biosci. Landmark 2019, 24, 1426–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larki, P.; Ahadi, A.; Zare, A.; Tarighi, S.; Zaheri, M.; Souri, M.; Zali, M.R.; Ghaedi, H.; Omrani, M.D. Up-Regulation of miR-21, miR-25, miR-93, and miR-106b in Gastric Cancer. Iran. Biomed. J. 2018, 22, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Tan, Z.; Hu, H.; Liu, H.; Wu, T.; Zheng, C.; Wang, X.; Luo, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, S.; et al. microRNA-21 promotes breast cancer proliferation and metastasis by targeting LZTFL1. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, X.H.; Lu, S.; Wang, A.F. Expression and clinical significance of miR-4516 and miR-21-5p in serum of patients with colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drillis, G.; Goulielmaki, M.; Spandidos, D.A.; Aggelaki, S.; Zoumpourlis, V. Non-coding RNAs (miRNAs and lncRNAs) and their roles in lymphogenesis in all types of lymphomas and lymphoid malignancies. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 21, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ParvizHamidi, M.; Haddad, G.; Ostadrahimi, S.; Ostadrahimi, N.; Sadeghi, S.; Fayaz, S.; Fard-Esfahani, P. Circulating miR-26a and miR-21 as biomarkers for glioblastoma multiform. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2019, 66, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Deng, H.; Shen, Z.; Xiao, B.; Guo, J. miR-21, miR-106b and miR-375 as novel potential biomarkers for laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2014, 15, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Mao, M.; Liu, H. Droplet digital PCR and qRT-PCR to detect circulating miR-21 in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma and pre-malignant laryngeal lesions. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2016, 136, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, B.; Ishinaga, H.; Midorikawa, K.; Shah, S.A.; Nakamura, S.; Hiraku, Y.; Oikawa, S.; Murata, M.; Takeuchi, K. Circulating microRNAs as novel prognosis biomarkers for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2015, 16, 1042–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadhav, K.B.; Shah, V.; Chauhan, N.; Shah, N.; Parmar, G. Expression of microRNA-21 in saliva and tumor tissue of patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma: A predictor of cervical lymph node metastasis. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2022, 133, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, J.; Sun, Y.; Xiao, H.; Liu, M.; Tian, L. Combined detection of serum exosomal miR-21 and HOTAIR as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Xia, T.; Li, M.; Wang, T.; Liu, P.; Zhou, X.; Huang, Z.; Zhu, W. MicroRNA profiling in serum: Potential signatures for breast cancer diagnosis. Cancer Biomark. 2021, 30, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishinaga, H.; He, F.; Hou, B.; Shah, S.; Murata, M.; Takeuchi, K. A longitudinal study on circulating miR-21 as a therapeutic effect marker in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2019, 40, 1070–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.M.; Lin, P.M.; Wang, Y.M.; Chen, Z.J.; Lin, S.F.; Yang, M.Y. Circulating miRNA is a novel marker for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2012, 33, 1933–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Wang, X.; Venø, M.T.; Bakholdt, V.; Sørensen, J.A.; Krogdahl, A.; Sun, Z.; Gao, S.; Kjems, J. Circulating miRNAs as biomarkers for oral squamous cell carcinoma recurrence in operated patients. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 8206–8214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Luo, H.N.; Tian, W.D.; Lu, J.; Li, G.; Wang, L.; Zhang, B.; Liang, B.J.; Peng, X.H.; Lin, S.X.; et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of plasma microRNA deregulation in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2013, 14, 1133–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Qiang, C.; Gao, L.; Li, S.M.; Zhang, L.M.; Wang, X.L.; Dong, J.W.; Chen, C.; Liu, C.Y.; Zhi, K.Q. Circulating microRNA-21 (MIR-21) and phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) are promising novel biomarkers for detection of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Biomarkers 2014, 19, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darido, C.; Georgy, S.R.; Wilanowski, T.; Dworkin, S.; Auden, A.; Zhao, Q.; Rank, G.; Srivastava, S.; Finlay, M.J.; Papenfuss, A.T.; et al. Targeting of the tumor suppressor GRHL3 by a miR-21-dependent proto-oncogenic network results in PTEN loss and tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 2011, 20, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, Z.Y.; Luo, Z.Q.; Zhang, L.J.; Li, J.; Liu, J.Q. Integrated Analysis and MicroRNA Expression Profiling Identified Seven miRNAs Associated With Progression of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 232, 2178–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odar, K.; Boštjančič, E.; Gale, N.; Glavač, D.; Zidar, N. Differential expression of microRNAs miR-21, miR-31, miR-203, miR-125a-5p and miR-125b and proteins PTEN and p63 in verrucous carcinoma of the head and neck. Histopathology 2012, 61, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Li, S.; Kaufmann, A.M.; Albers, A.E. miR-21 increases the programmed cell death 4 gene-regulated cell proliferation in head and neck squamous carcinoma cell lines. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 32, 2283–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Chen, Z.; Cabay, R.J.; Zhang, L.; Luan, X.; Chen, D.; Yu, T.; Wang, A.; Zhou, X. microRNA-21 and microRNA-375 from oral cytology as biomarkers for oral tongue cancer detection. Oral Oncol. 2016, 57, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ajuyah, P.; Hill, M. MicroRNA (miRNA)-to-miRNA Regulation of Programmed Cell Death 4 (PDCD4). Mol. Cell. Biol. 2019, 39, e00086-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, J.; Zhu, D.; Liu, M.; Sun, Y.; Tian, L. Downregulation of miR-21 modulates Ras expression to promote apoptosis and suppress invasion of Laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2010, 46, 3409–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, E.H.; Tu, H.F.; Wu, C.H.; Yang, C.C.; Chang, K.W. MicroRNA-21 promotes perineural invasion and impacts survival in patients with oral carcinoma. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. JCMA 2017, 80, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Hoyle, R.G.; Xie, N.; Wang, W.; Cai, H.; Zhang, M.; Ma, Z.; Xiong, G.; Xu, X.; Huang, Z.; et al. A Super-Enhancer Driven by FOSL1 Controls miR-21-5p Expression in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 656628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menderico Junior, G.M.; Theodoro, T.R.; Pasini, F.S.; de Menezes Ishikawa, M.; Santos, N.S.S.; de Mello, E.S.; da Silva Pinhal, M.A.; Moyses, R.A.; Kulcsar, M.A.V. MicroRNA-mediated extracellular matrix remodeling in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity. Head Neck 2021, 43, 2364–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.; Huang, J.J.; Xu, W.H.; Jin, X.J.; Li, J.P.; Tang, Y.J.; Huang, X.F.; Cui, H.J.; Sun, G.B. miR-21 and miR-375 microRNAs as candidate diagnostic biomarkers in squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx: Association with patient survival. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2014, 6, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hedbäck, N.; Jensen, D.H.; Specht, L.; Fiehn, A.M.; Therkildsen, M.H.; Friis-Hansen, L.; Dabelsteen, E.; von Buchwald, C. MiR-21 expression in the tumor stroma of oral squamous cell carcinoma: An independent biomarker of disease free survival. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajan, C.; Roshan, V.G.D.; Khan, I.; Manasa, V.G.; Himal, I.; Kattoor, J.; Thomas, S.; Kondaiah, P.; Kannan, S. MiRNA expression profiling and emergence of new prognostic signature for oral squamous cell carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Huang, H.; Sun, L.; Yang, M.; Pan, C.; Chen, W.; Wu, D.; Lin, Z.; Zeng, C.; Yao, Y.; et al. MiR-21 indicates poor prognosis in tongue squamous cell carcinomas as an apoptosis inhibitor. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 3998–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, W.; Wang, X.; Gao, L.; Li, S.; Yan, X.; Zhang, J.; Huang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhi, K. MiR-21 modulates chemosensitivity of tongue squamous cell carcinoma cells to cisplatin by targeting PDCD4. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2014, 390, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia-yuan, X.; Wei, S.; Fang-fang, L.; Zhi-jian, D.; Long-he, C.; Sen, L. miR-375 Inhibits the Proliferation and Invasion of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells by Suppressing PDK1. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 9704245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Yuan, Y. miR-375 Inhibits the Proliferation, Migration and Invasion of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Targeting XPR1. Curr. Gene Ther. 2021, 21, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avissar, M.; Christensen, B.C.; Kelsey, K.T.; Marsit, C.J. MicroRNA expression ratio is predictive of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Curr. Gene Ther. 2009, 15, 2850–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiklund, E.D.; Gao, S.; Hulf, T.; Sibbritt, T.; Nair, S.; Costea, D.E.; Villadsen, S.B.; Bakholdt, V.; Bramsen, J.B.; Sørensen, J.A.; et al. MicroRNA alterations and associated aberrant DNA methylation patterns across multiple sample types in oral squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avilés-Jurado, F.X.; Muñoz, C.; Meler, C.; Flores, J.C.; Gumà, J.; Benaiges, E.; Mora, J.; Camacho, M.; León, X.; Vilaseca, I.; et al. Circulating microRNAs modulating glycolysis as non-invasive prognostic biomarkers of HNSCC. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 278, 1585–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, K.; Wei, Z.; Cao, H. miR-375-3p inhibits the progression of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting hepatocyte nuclear factor-1β. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Li, B.; Song, W.; Cao, L.; Zhu, C.; Lin, S. Tumor suppressor functions of miRNA-375 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through inhibition of ubiquitin-specific protease 1 expression. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2021, 141, 106092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudcova, K.; Raudenska, M.; Gumulec, J.; Binkova, H.; Horakova, Z.; Kostrica, R.; Babula, P.; Adam, V.; Masarik, M. Expression profiles of miR-29c, miR-200b and miR-375 in tumour and tumour-adjacent tissues of head and neck cancers. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 12627–12633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Xu, L.; Li, L.; Ren, S.; Tang, J.; Zhang, M.; Xu, M. The microRNA-375 as a potentially promising biomarker to predict the prognosis of patients with head and neck or esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2019, 276, 957–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.M.; Benarroch, Y.; Chan, E.K. Anti-cancer drugs reactivate tumor suppressor miR-375 expression in tongue cancer cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 116, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.X.; Yue, Z.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, Z.H.; Wang, P.Y.; Li, Y.J.; Pang, M.; Xie, S.Y. miR-99 inhibits cervical carcinoma cell proliferation by targeting TRIB2. Oncol. Lett. 2013, 6, 1025–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, D.; Lee, Y.S.; Malhotra, A.; Kim, H.K.; Matecic, M.; Evans, C.; Jensen, R.V.; Moskaluk, C.A.; Dutta, A. miR-99 family of MicroRNAs suppresses the expression of prostate-specific antigen and prostate cancer cell proliferation. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 1313–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Guo, Y.; Wu, J.; Chen, F.; Dai, Z.; Fan, S.; Li, P.; Song, T. Roles of microRNA-99 family in human glioma. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 3613–3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, X.; Yan, H. MicroRNA-99a-5p suppresses cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by targeting isoprenylcysteine carboxylmethyltransferase in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Int. Med. Res. 2021, 49, 300060520939031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.H.; Han, L.; Lu, B.C.; Wang, H.Y.; Zheng, C.P. MiR-99a inhibits cell proliferation of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by targeting mTOR and serves as a prognostic factor. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 2053–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moratin, J.; Hartmann, S.; Brands, R.C.; Horn, D.; Fuchs, A.; Mutzbauer, G.; Seher, A.; Scholz, C.; Müller-Richter, U.D.A.; Linz, C. MicroRNA expression correlates with disease recurrence and overall survival in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2019, 47, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moratin, J.; Hartmann, S.; Brands, R.; Brisam, M.; Mutzbauer, G.; Scholz, C.; Seher, A.; Müller-Richter, U.; Kübler, A.C.; Linz, C. Evaluation of miRNA-expression and clinical tumour parameters in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2016, 44, 876–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Jin, Y.; Yu, D.; Wang, A.; Mahjabeen, I.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Zhou, X. Down-regulation of the microRNA-99 family members in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2012, 48, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okada, R.; Koshizuka, K.; Yamada, Y.; Moriya, S.; Kikkawa, N.; Kinoshita, T.; Hanazawa, T.; Seki, N. Regulation of Oncogenic Targets by miR-99a-3p (Passenger Strand of miR-99a-Duplex) in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cells 2019, 8, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jakob, M.; Mattes, L.M.; Küffer, S.; Unger, K.; Hess, J.; Bertlich, M.; Haubner, F.; Ihler, F.; Canis, M.; Weiss, B.G. MicroRNA expression patterns in oral squamous cell carcinoma: Hsa-mir-99b-3p and hsa-mir-100-5p as novel prognostic markers for oral cancer. Head Neck 2019, 41, 3499–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manikandan, M.; Deva Magendhra Rao, A.K.; Arunkumar, G.; Rajkumar, K.S.; Rajaraman, R.; Munirajan, A.K. Down Regulation of miR-34a and miR-143 May Indirectly Inhibit p53 in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Pilot Study. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2015, 16, 7619–7625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.T.; Yao, J.N.; Qin, Y.T.; Hu, K.; Wu, F.; Fang, Y.Y. Biological role and clinical value of miR-99a-5p in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC): A bioinformatics-based study. FEBS Open Bio 2018, 8, 1280–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.G.; Guo, W.P.; Tang, Z.Y.; Li, S.H.; Wu, H.Y.; Zhang, L.C. Expression level and prospective mechanism of miRNA-99a-3p in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma based on miRNA-chip and miRNA-sequencing data in 1, 167 cases. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 963–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.-L.; Sheng, J.-F.; Huang, M.-L.; Zou, Y.; Wang, Y.-P.; Wang, F.; Zeng, F.; Hua, Q.-Q.; Chen, S.-M. Integrated analysis of deregulation microRNA expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Medicine 2021, 100, e24618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, S.; Li, K.; Qi, J.; Liu, C.; Zong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhai, X.; Li, J.; et al. Evaluation of microRNA expression profiling in highly metastatic laryngocarcinoma cells. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2018, 138, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, L.O.; Sobral, L.M.; Matsumoto, C.S.; Saggioro, F.P.; López, R.V.M.; Panepucci, R.A.; Curti, C.; Silva, W.A., Jr.; Greene, L.J.; Leopoldino, A.M. Lymph node or perineural invasion is associated with low miR-15a, miR-34c and miR-199b levels in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. BBA Clin. 2016, 6, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Figueroa-González, G.; Carrillo-Hernández, J.F.; Perez-Rodriguez, I.; De León, D.C.; Campos-Parra, A.D.; Martínez-Gutiérrez, A.D.; Coronel-Hernández, J.; García-Castillo, V.; López-Camarillo, C.; Peralta-Zaragoza, O.; et al. Negative Regulation of Serine Threonine Kinase 11 (STK11) through miR-100 in Head and Neck Cancer. Genes 2020, 11, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Hu, J.; Pan, L.; Yin, X.; Wang, Q.; Chen, H. Diagnostic and prognostic value of serum miR-99a expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Biomark. 2018, 23, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, F.; Ou, Y.; Luo, P.; Zhong, X. LncRNA NCK1-AS1 in plasma distinguishes oral ulcer from early-stage oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Biol. Res. 2020, 27, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yin, Z.; Zhao, Y.; He, M.; Dong, C.; Zhong, M. Identifying potential prognostic biomarkers in head and neck cancer based on the analysis of microRNA expression profiles in TCGA database. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 21, 1647–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Yadav, A.; Lang, J.; Teknos, T.N.; Kumar, P. Dysregulation of microRNA-34a expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma promotes tumor growth and tumor angiogenesis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Kaller, M.; Rokavec, M.; Kirchner, T.; Horst, D.; Hermeking, H. Characterization of a p53/miR-34a/CSF1R/STAT3 Feedback Loop in Colorectal Cancer. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 10, 391–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, H. miR-34a inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion of paediatric neuroblastoma cells via targeting HNF4α. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 3072–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Xu, G.C.; Liu, S.T.; Liu, T.; Geng, B. MiR-34a affects G2 arrest in prostate cancer PC3 cells via Wnt pathway and inhibits cell growth and migration. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 8349–8358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Deng, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, C.; Liang, Y. LncRNA XIST/miR-34a axis modulates the cell proliferation and tumor growth of thyroid cancer through MET-PI3K-AKT signaling. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.C.; Wentzel, E.A.; Kent, O.A.; Ramachandran, K.; Mullendore, M.; Lee, K.H.; Feldmann, G.; Yamakuchi, M.; Ferlito, M.; Lowenstein, C.J.; et al. Transactivation of miR-34a by p53 broadly influences gene expression and promotes apoptosis. Mol. Cell 2007, 26, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raver-Shapira, N.; Marciano, E.; Meiri, E.; Spector, Y.; Rosenfeld, N.; Moskovits, N.; Bentwich, Z.; Oren, M. Transcriptional activation of miR-34a contributes to p53-mediated apoptosis. Mol. Cell 2007, 26, 731–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; He, X.; Lim, L.P.; de Stanchina, E.; Xuan, Z.; Liang, Y.; Xue, W.; Zender, L.; Magnus, J.; Ridzon, D.; et al. A microRNA component of the p53 tumour suppressor network. Nature 2007, 447, 1130–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, X. miR-34a targets BCL-2 to suppress the migration and invasion of sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 6566–6572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Li, L.; Feng, P.; Wan, J.; Li, J. Downregulation of miR-34a contributes to the proliferation and migration of laryngeal carcinoma cells by targeting cyclin D1. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tazawa, H.; Tsuchiya, N.; Izumiya, M.; Nakagama, H. Tumor-suppressive miR-34a induces senescence-like growth arrest through modulation of the E2F pathway in human colon cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 15472–15477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Kelnar, K.; Liu, B.; Chen, X.; Calhoun-Davis, T.; Li, H.; Patrawala, L.; Yan, H.; Jeter, C.; Honorio, S.; et al. The microRNA miR-34a inhibits prostate cancer stem cells and metastasis by directly repressing CD44. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.H.; Weng, X.; Xiong, Q.Y.; Tu, J.H.; Xiao, A.; Qiu, W.; Gong, Y.; Hu, E.W.; Huang, S.; Cao, Y.L. miR-34a expression in human breast cancer is associated with drug resistance. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 106270–106282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, X.J.; Zheng, H.L.; Ke, X.Q.; Deng, M.; Ma, Z.Z.; Zhu, Y.; Cui, Y.Y. Hsa-miR-34a-5p reverses multidrug resistance in gastric cancer cells by targeting the 3′-UTR of SIRT1 and inhibiting its expression. Cell. Signal 2021, 84, 110016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, K.; Zhang, T.; Yang, Z.; Wang, R.; Chen, G.; Kang, M. A comprehensive investigation using meta-analysis and bioinformatics on miR-34a-5p expression and its potential role in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 2246–2263. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhao, S.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, J.; Liu, L.; Jiang, H. miR-34a-5p functions as a tumor suppressor in head and neck squamous cell cancer progression by targeting Flotillin-2. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 4327–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Jiang, F.; Sun, Y.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J. MiR-34a suppresses HNSCC growth through modulating cell cycle arrest and senescence. Neoplasma 2017, 64, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Cheng, Y.-S.L.; Matthen, M.; Yoon, A.; Schwartz, G.K.; Bala, S.; Taylor, A.M.; Momen-Heravi, F. Down-regulation of the tumor suppressor miR-34a contributes to head and neck cancer by up-regulating the MET oncogene and modulating tumor immune evasion. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Cheng, Z.; Jiang, T.; Xu, Y.; Wang, B. MicroRNA-34a inhibits cell invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition via targeting AXL/PI3K/AKT/Snail signaling in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Genes Genom. 2020, 42, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalfert, D.; Pesta, M.; Kulda, V.; Topolcan, O.; Ryska, A.; Celakovsky, P.; Laco, J.; Ludvikova, M. MicroRNA profile in site-specific head and neck squamous cell cancer. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 2455–2463. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Shi, C.; Zhang, Y. Expression of miR-34a and Ki67 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and the relationship with clinicopathological features and prognosis. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 1273–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogawa, T.; Saiki, Y.; Shiga, K.; Chen, N.; Fukushige, S.; Sunamura, M.; Nagase, H.; Hashimoto, S.; Matsuura, K.; Saijo, S.; et al. miR-34a is downregulated in cis-diamminedichloroplatinum treated sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma patients with poor prognosis. Cancer Sci. 2012, 103, 1737–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Childs, G.; Fazzari, M.; Kung, G.; Kawachi, N.; Brandwein-Gensler, M.; McLemore, M.; Chen, Q.; Burk, R.D.; Smith, R.V.; Prystowsky, M.B.; et al. Low-level expression of microRNAs let-7d and miR-205 are prognostic markers of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 174, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, C.C.; Chen, Y.W.; Chiou, G.Y.; Tsai, L.L.; Huang, P.I.; Chang, C.Y.; Tseng, L.M.; Chiou, S.H.; Yen, S.H.; Chou, M.Y.; et al. MicroRNA let-7a represses chemoresistance and tumourigenicity in head and neck cancer via stem-like properties ablation. Oral Oncol. 2011, 47, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.J.; Hsu, C.C.; Chang, C.H.; Tsai, L.L.; Chang, Y.C.; Lu, S.W.; Yu, C.H.; Huang, H.S.; Wang, J.J.; Tsai, C.H.; et al. Let-7d functions as novel regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and chemoresistant property in oral cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 26, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclellan, S.A.; Lawson, J.; Baik, J.; Guillaud, M.; Poh, C.F.-Y.; Garnis, C. Differential expression of miRNAs in the serum of patients with high-risk oral lesions. Cancer Med. 2012, 1, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, A.; Victoria, B.; Lopez, Y.N. Tissue and serum microRNA profile of oral squamous cell carcinoma patients. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fadhil, R.S.; Wei, M.Q.; Nikolarakos, D.; Good, D.; Nair, R.G. Salivary microRNA miR-let-7a-5p and miR-3928 could be used as potential diagnostic bio-markers for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0221779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, S.S.; Jiang, W.W.; Smith, I.; Poeta, L.M.; Begum, S.; Glazer, C.; Shan, S.; Westra, W.; Sidransky, D.; Califano, J.A. MicroRNA alterations in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 123, 2791–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Ruyck, K.; Duprez, F.; Ferdinande, L.; Mbah, C.; Rios-Velazquez, E.; Hoebers, F.; Praet, M.; Deron, P.; Bonte, K.; Speel, E.J.; et al. A let-7 microRNA polymorphism in the KRAS 3′-UTR is prognostic in oropharyngeal cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. 2014, 38, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.C.; Yang, Y.; Liu, J.X. Expression and significances of MiRNA Let-7 and HMGA2 in laryngeal carcinoma. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 20, 4452–4458. [Google Scholar]
- Chien, C.S.; Wang, M.L.; Chu, P.Y.; Chang, Y.L.; Liu, W.H.; Yu, C.C.; Lan, Y.T.; Huang, P.I.; Lee, Y.Y.; Chen, Y.W.; et al. Lin28B/Let-7 Regulates Expression of Oct4 and Sox2 and Reprograms Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells to a Stem-like State. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 2553–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hilly, O.; Pillar, N.; Stern, S.; Strenov, Y.; Bachar, G.; Shomron, N.; Shpitzer, T. Distinctive pattern of let-7 family microRNAs in aggressive carcinoma of the oral tongue in young patients. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 1729–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lamperska, K.M.; Kolenda, T.; Teresiak, A.; Kowalik, A.; Kruszyna-Mochalska, M.; Jackowiak, W.; Bliźniak, R.; Przybyła, W.; Kapałczyńska, M.; Kozlowski, P. Different levels of let-7d expression modulate response of FaDu cells to irradiation and chemotherapeutics. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.Y.; Wang, T.Y.; Lee, S.S.; Hsieh, P.L.; Liao, Y.W.; Tsai, L.L.; Fang, C.Y.; Yu, C.C. Let-7c restores radiosensitivity and chemosensitivity and impairs stemness in oral cancer cells through inhibiting interleukin-8. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2018, 47, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Wang, Z.; Fillmore, R.; Xi, Y. MiR-200, a new star miRNA in human cancer. Cancer Lett. 2014, 344, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Díaz-Martín, J.; Díaz-López, A.; Moreno-Bueno, G.; Castilla, M.; Rosa-Rosa, J.M.; Cano, A.; Palacios, J. A core microRNA signature associated with inducers of the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. J. Pathol. 2014, 232, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skourti, E.; Logotheti, S.; Kontos, C.K.; Pavlopoulou, A.; Dimoragka, P.T.; Trougakos, I.P.; Gorgoulis, V.; Scorilas, A.; Michalopoulos, I.; Zoumpourlis, V. Progression of mouse skin carcinogenesis is associated with the orchestrated deregulation of mir-200 family members, mir-205 and their common targets. Mol. Carcinog. 2016, 55, 1229–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphries, B.; Yang, C. The microRNA-200 family: Small molecules with novel roles in cancer development, progression and therapy. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 6472–6498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koshizuka, K.; Hanazawa, T.; Arai, T.; Okato, A.; Kikkawa, N.; Seki, N. Involvement of aberrantly expressed microRNAs in the pathogenesis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2017, 36, 525–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappellesso, R.; Marioni, G.; Crescenzi, M.; Giacomelli, L.; Guzzardo, V.; Mussato, A.; Staffieri, A.; Martini, A.; Blandamura, S.; Fassina, A. The prognostic role of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers E-cadherin and Slug in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Histopathology 2015, 67, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, J.; Walter, V. Integrative Analysis of miRNAs Identifies Clinically Relevant Epithelial and Stromal Subtypes of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, W.L.; Yu, C.C.; Chiou, G.Y.; Chen, Y.W.; Huang, P.I.; Chien, C.S.; Tseng, L.M.; Chu, P.Y.; Lu, K.H.; Chang, K.W.; et al. MicroRNA-200c attenuates tumour growth and metastasis of presumptive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma stem cells. J. Pathol. 2011, 223, 482–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, N.J.; Zhou, H.; Elashoff, D.; Henson, B.S.; Kastratovic, D.A.; Abemayor, E.; Wong, D.T. Salivary microRNA: Discovery, characterization, and clinical utility for oral cancer detection. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 5473–5477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Greither, T.; Vorwerk, F.; Kappler, M.; Bache, M.; Taubert, H.; Kuhnt, T.; Hey, J.; Eckert, A.W. Salivary miR-93 and miR-200a as post-radiotherapy biomarkers in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 1268–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, E.J.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, S.; Lee, H.; Yoon, J.S.; Hong, J.H.; Chun, S.H.; Sun, S.; Won, H.S.; Hong, S.A.; et al. QKI, a miR-200 target gene, suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and tumor growth. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 1585–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamagawa, S.; Beder, L.B.; Hotomi, M.; Gunduz, M.; Yata, K.; Grenman, R.; Yamanaka, N. Role of miR-200c/miR-141 in the regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and migration in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 33, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, L.; Yang, T. miR-31 Modulates Liver Cancer HepG2 Cell Apoptosis and Invasion via ROCK1/F-Actin Pathways. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, P.-C.; Chiu, Y.-L.; Banerjee, S.; Park, K.; Mosquera, J.M.; Giannopoulou, E.; Alves, P.; Tewari, A.K.; Gerstein, M.B.; Beltran, H.; et al. Epigenetic repression of miR-31 disrupts androgen receptor homeostasis and contributes to prostate cancer progression. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 1232–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, L.J.; Yang, F.; Ding, J.J.; Yan, D.L.; Wang, D.D.; Yang, S.J.; Ding, L.; Li, J.; Chen, D.; Ma, R.; et al. MiR-31 inhibits migration and invasion by targeting SATB2 in triple negative breast cancer. Gene 2016, 594, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q. Significance of miR-27a and miR-31 in early diagnosis and prognosis of colorectal cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 3092–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Hu, X. miR-31 functions as an oncogene in cervical cancer. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2015, 292, 1083–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, J.F.; Wang, X.D.; Sun, P.D. Expression of miR-31 in rectal cancer patients and its effect on proliferation ability of rectal cancer cells SW837. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 8675–8681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, M.L.; Echols, J.B. miR-31 Displays Subtype Specificity in Lung Cancer. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 1942–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, S.Y.; Tsai, M.M.; Wu, C.H.; Chen, J.J.; Tseng, S.H.; Lin, S.C.; Chang, K.W. Co-targeting of multiple microRNAs on factor-Inhibiting hypoxia-Inducible factor gene for the pathogenesis of head and neck carcinomas. Head Neck 2016, 38, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajer, C.B.; Nielsen, F.C.; Friis-Hansen, L.; Norrild, B.; Borup, R.; Garnæs, E.; Rossing, M.; Specht, L.; Therkildsen, M.H.; Nauntofte, B.; et al. Different miRNA signatures of oral and pharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas: A prospective translational study. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 104, 830–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinpolat, O.; Unal, Z.N.; Ismi, O.; Gorur, A.; Unal, M. Comparison of microRNA profiles between benign and malignant salivary gland tumors in tissue, blood and saliva samples: A prospective, case-control study. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 83, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiang, H.; Zhan, X.; Wang, W.; Cheng, Z.; Ma, S.; Jiang, C. A Study on the Correlations of the miR-31 Expression with the Pathogenesis and Prognosis of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2019, 34, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.J.; Kao, S.Y.; Tu, H.F.; Tsai, M.M.; Chang, K.W.; Lin, S.C. Increase of microRNA miR-31 level in plasma could be a potential marker of oral cancer. Oral Dis. 2010, 16, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.J.; Tsai, M.M.; Hung, P.S.; Kao, S.Y.; Liu, T.Y.; Wu, K.J.; Chiou, S.H.; Lin, S.C.; Chang, K.W. miR-31 ablates expression of the HIF regulatory factor FIH to activate the HIF pathway in head and neck carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 1635–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oshima, S.; Asai, S.; Seki, N. Identification of Tumor Suppressive Genes Regulated by miR-31-5p and miR-31-3p in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.J.; Liu, P.; Chen, B.L.; Ou-Yang, L.; Xiong, W.M.; Su, J.P. Circulating miR-31-5p may be a potential diagnostic biomarker in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Neoplasma 2019, 66, 825–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, M.P.; Pasini, F.S.; Diao, L.; Garcia, F.O.T.; Takahashi, T.K.; Nakazato, D.; Martins, R.E.; Almeida, C.M.; Kulcsar, M.A.V.; Lamounier, V.A.; et al. Valproic acid combined with cisplatin-based chemoradiation in locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients and associated biomarkers. Ecancermedicalscience 2020, 14, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Wang, J. Long non-coding RNA LOC554202 promotes laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma progression through regulating miR-31. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 6953–6960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.J.; Lin, S.C.; Yang, C.C.; Cheng, H.W.; Chang, K.W. Exploiting salivary miR-31 as a clinical biomarker of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 2012, 34, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyurkchiyan, S.G.; Popov, T.M. A pilot study reveals the potential of miR-31-3p and miR-196a-5p as non-invasive biomarkers in advanced laryngeal cancer. Folia Medica 2021, 63, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Park, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Yin, J.; Liu, Q.; Wei, M. Progress on the relationship between miR-125 family and tumorigenesis. Exp. Cell Res. 2015, 339, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henson, B.J.; Bhattacharjee, S.; O’Dee, D.M.; Feingold, E.; Gollin, S.M. Decreased expression of miR-125b and miR-100 in oral cancer cells contributes to malignancy. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2009, 48, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hui, A.B.; Lenarduzzi, M.; Krushel, T.; Waldron, L.; Pintilie, M.; Shi, W.; Perez-Ordonez, B.; Jurisica, I.; O’Sullivan, B.; Waldron, J.; et al. Comprehensive MicroRNA profiling for head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 1129–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, P.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, F.; Wang, H.; Ma, D.; Tian, J. Comprehensive expression profiling of microRNAs in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 2013, 35, 720–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, M.; Deva Magendhra Rao, A.K.; Rajkumar, K.S.; Rajaraman, R.; Munirajan, A.K. Altered levels of miR-21, miR-125b-2*, miR-138, miR-155, miR-184, and miR-205 in oral squamous cell carcinoma and association with clinicopathological characteristics. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2015, 44, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.L.; Wang, W.J.; Qiu, Y.T.; Xie, X.F.; Bai, J.; Shi, Z.Z. miR-125b-5p functions as a tumor suppressor gene partially by regulating HMGA2 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troiano, G.; Mastrangelo, F.; Caponio, V.C.A.; Laino, L.; Cirillo, N.; Lo Muzio, L. Predictive Prognostic Value of Tissue-Based MicroRNA Expression in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Dent. Res. 2018, 97, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayaz, L.; Görür, A.; Yaroğlu, H.Y.; Ozcan, C.; Tamer, L. Differential expression of microRNAs in plasma of patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma: Potential early-detection markers for laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 139, 1499–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Arriagada, W.; Olivero, P.; Rodriguez, B.; Lozano, C.; Oliveira, C.; Coletta, R. Clinicopathological significance of miR-26, miR-107, miR-125b and miR-203 in head and neck carcinomas. Oral Dis. 2018, 24, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiiba, M.; Shinozuka, K.; Saito, K.; Fushimi, K.; Kasamatsu, A.; Ogawara, K.; Uzawa, K.; Ito, H.; Takiguchi, Y.; Tanzawa, H. MicroRNA-125b regulates proliferation and radioresistance of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 1817–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vo, D.T.; Karanam, N.K.; Ding, L.; Saha, D.; Yordy, J.S.; Giri, U.; Heymach, J.V.; Story, M.D. miR-125a-5p Functions as Tumor Suppressor microRNA And Is a Marker of Locoregional Recurrence And Poor prognosis in Head And Neck Cancer. Neoplasia 2019, 21, 849–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.-C.; Chang, J.T.; Chan, E.-C.; Chao, Y.-K.; Yeh, T.-S.; Chen, J.-S.; Cheng, A.-J. miR-196, an Emerging Cancer Biomarker for Digestive Tract Cancers. J. Cancer 2016, 7, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Álvarez-Teijeiro, S.; Menéndez, S.T.; Villaronga, M.; Rodrigo, J.P.; Manterola, L.; de Villalaín, L.; de Vicente, J.C.; Alonso-Durán, L.; Fernández, M.P.; Lawrie, C.H.; et al. Dysregulation of Mir-196b in Head and Neck Cancers Leads to Pleiotropic Effects in the Tumor Cells and Surrounding Stromal Fibroblasts. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Chen, L.; Wu, J.; Wu, K.; Du, J.; Xue, H.; Shen, B. Molecular mechanisms and prognostic markers in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A bioinformatic analysis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2020, 13, 371–381. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.J.; Tsai, M.M.; Tu, H.F.; Lui, M.T.; Cheng, H.W.; Lin, S.C. miR-196a overexpression and miR-196a2 gene polymorphism are prognostic predictors of oral carcinomas. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 20 (Suppl. S3), S406–S414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.C.; Chang, J.T.; Huang, Y.C.; Huang, C.C.; Chen, W.H.; Lee, L.Y.; Huang, B.S.; Chen, Y.J.; Li, H.F.; Cheng, A.J. Combined determination of circulating miR-196a and miR-196b levels produces high sensitivity and specificity for early detection of oral cancer. Clin. Biochem. 2015, 48, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.; Warnakulasuriya, S. Blood-based circulating microRNAs as potential biomarkers for predicting the prognosis of head and neck cancer-a systematic review. Clin. Oral Investig. 2020, 24, 3833–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, Y.E.; Raulf, N.; Gäken, J.; Lawler, K.; Urbano, T.G.; Bullenkamp, J.; Gobeil, S.; Huot, J.; Odell, E.; Tavassoli, M. MicroRNA-196a promotes an oncogenic effect in head and neck cancer cells by suppressing annexin A1 and enhancing radioresistance. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 1021–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darda, L.; Hakami, F.; Morgan, R.; Murdoch, C.; Lambert, D.W.; Hunter, K.D. The role of HOXB9 and miR-196a in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, S.C.; Huang, S.F.; Chiang, J.H.; Chen, Y.F.; Huang, C.C.; Tsai, M.H.; Tsai, F.J.; Kao, M.C.; Yang, J.S. The differential regulation of microRNAs is associated with oral cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 1613–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, W.; Ji, W. miR-196b is a prognostic factor of human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma and promotes tumor progression by targeting SOCS2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 501, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Sun, G.; Sun, J.W. MiR-196b affects the progression and prognosis of human LSCC through targeting PCDH-17. Auris Nasus Larynx 2019, 46, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Álvarez-Teijeiro, S.; Menéndez, S.T.; Villaronga, M.; Pena-Alonso, E.; Rodrigo, J.P.; Morgan, R.O. Annexin A1 down-regulation in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma is mediated via transcriptional control with direct involvement of miR-196a/b. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maruyama, T.; Nishihara, K.; Umikawa, M.; Arasaki, A.; Nakasone, T.; Nimura, F.; Matayoshi, A.; Takei, K.; Nakachi, S.; Kariya, K.I.; et al. MicroRNA-196a-5p is a potential prognostic marker of delayed lymph node metastasis in early-stage tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 2349–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Inagaki, K.; Kamimoto, T.; Ito, Y.; Sugita, T.; Nakajo, S.; Hirasawa, A.; Iwamaru, A.; Ishikura, T.; Hanaoka, H.; et al. MicroRNA-196a is a putative diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target for laryngeal cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coolen, M.; Katz, S.; Bally-Cuif, L. miR-9: A versatile regulator of neurogenesis. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tang, K.D.; Blick, T.; Kenny, L.; Thompson, E.W.; Punyadeera, C. Overexpression of miRNA-9 enhances galectin-3 levels in oral cavity cancers. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 3979–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavakolian, S.; Goudarzi, H.; Faghihloo, E. Evaluating the expression level of miR-9-5p and miR-192-5p in gastrointestinal cancer: Introducing novel screening biomarkers for patients. BMC Res. Notes 2020, 13, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Milanesi, E.; Dobre, M.; Bucuroiu, A.I.; Herlea, V.; Manuc, T.E. miRNAs-Based Molecular Signature for KRAS Mutated and Wild Type Colorectal Cancer: An Explorative Study. J. Immunol. Res. 2020, 2020, 4927120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Yuan, B.; Zhang, X.; Yan, T.; Li, J.; Xu, W. Long non-coding RNA DUXAP8 promotes tumorigenesis by regulating IGF1R via miR-9-3p in hepatocellular carcinoma. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutkowska, A.; Szmyd, B.; Kaszkowiak, M.; Domańska-Senderowska, D.; Pastuszak-Lewandoska, D.; Brzeziańska-Lasota, E.; Kordiak, J.; Antczak, A. Expression of inflammatory interleukins and selected miRNAs in non-small cell lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tang, X.; Li, K.; Lu, L. Evaluation of Serum MicroRNAs (miR-9-5p, miR-17-5p, and miR-148a-3p) as Potential Biomarkers of Breast Cancer. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 9961412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzanehpour, M.; Mozhgani, S.H.; Jalilvand, S.; Faghihloo, E.; Akhavan, S.; Salimi, V.; Azad, T.M. Serum and tissue miRNAs: Potential biomarkers for the diagnosis of cervical cancer. Virol. J. 2019, 16, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kovaříková, J.; Baranová, I.; Laco, J.; Rozkošová, K.; Vošmíková, H.; Vošmík, M.; Dundr, P.; Němejcová, K.; Michálek, J.; Palička, V.; et al. Deregulation of Selected MicroRNAs in Sinonasal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Searching for Potential Prognostic Biomarkers. Folia Biol. 2019, 65, 142–151. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Y.; Vagenas, D.; Salazar, C.; Kenny, L.; Perry, C.; Calvopiña, D.; Punyadeera, C. Salivary miRNA panel to detect HPV-positive and HPV-negative head and neck cancer patients. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 99990–100001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salazar, C.; Nagadia, R.; Pandit, P.; Cooper-White, J.; Banerjee, N.; Dimitrova, N.; Coman, W.B.; Punyadeera, C. A novel saliva-based microRNA biomarker panel to detect head and neck cancers. Cell. Oncol. 2014, 37, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Luo, H.; Liu, X.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, L.; Xu, X.; Peng, X.; Li, G.; Tian, W.; et al. miR-9 targets CXCR4 and functions as a potential tumor suppressor in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, J.; Liu, Q.-H.; Wang, F.; Tan, J.-J.; Deng, Y.-Q.; Peng, X.-H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, B.; Xu, X.; Li, X.-P. Exosomal miR-9 inhibits angiogenesis by targeting MDK and regulating PDK/AKT pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, J.; Xu, X.; Liu, X.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, L.; Luo, H.; Peng, X.; Li, G.; Tian, W.; et al. Predictive value of miR-9 as a potential biomarker for nasopharyngeal carcinoma metastasis. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiao, C.; Wang, L.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, J. Curcumin inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma SCC-9 cells proliferation by regulating miR-9 expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 454, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Liu, K.; Wu, Y.; Fan, J.; Chen, J.; Li, C.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Z. MicroRNA-9 inhibits the proliferation of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells by suppressing expression of CXCR4 via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncogene 2014, 33, 5017–5027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, L.; Liu, L.; Fu, H.; Wang, Q.; Shi, Y. Association of Decreased Expression of Serum miR-9 with Poor Prognosis of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients. Med. Sci. Monit. 2016, 22, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citron, F.; Segatto, I.; Musco, L.; Pellarin, I.; Rampioni Vinciguerra, G.L.; Franchin, G.; Fanetti, G.; Miccichè, F.; Giacomarra, V.; Lupato, V.; et al. miR-9 modulates and predicts the response to radiotherapy and EGFR inhibition in HNSCC. EMBO Mol. Med. 2021, 13, e12872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.B.; Lu, Y.; Yue, S.; Giffard, R.G. miR-181 targets multiple Bcl-2 family members and influences apoptosis and mitochondrial function in astrocytes. Mitochondrion 2012, 12, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henao-Mejia, J.; Williams, A.; Goff, L.A.; Staron, M.; Licona-Limon, P.; Kaech, S.M.; Nakayama, M.; Rinn, J.L.; Flavell, R.A. The microRNA miR-181 is a critical cellular metabolic rheostat essential for NKT cell ontogenesis and lymphocyte development and homeostasis. Immunity 2013, 38, 984–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pop-Bica, C.; Pintea, S.; Cojocneanu-Petric, R.; Del Sal, G.; Piazza, S.; Wu, Z.H.; Alencar, A.J.; Lossos, I.S.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Calin, G.A. MiR-181 family-specific behavior in different cancers: A meta-analysis view. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2018, 37, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indrieri, A.; Carrella, S.; Carotenuto, P.; Banfi, S.; Franco, B. The Pervasive Role of the miR-181 Family in Development, Neurodegeneration, and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, W.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; You, C.; Lu, P.; Feng, H.; Kong, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Jiao, R.; et al. MicroRNA-181a promotes angiogenesis in colorectal cancer by targeting SRCIN1 to promote the SRC/VEGF signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Xu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Han, J. Expression and mechanism of microRNA-181A on incidence and survival in late liver metastases of colorectal cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 1403–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, Y.; Zhao, D.; Li, P.; Wang, L.; Qiao, B.; Qin, X.; Li, L.; Wang, Y. MicroRNA-181a-5p Impedes IL-17-Induced Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer Proliferation and Migration through Targeting VCAM-1. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 42, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, D.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, D.; Jiang, X.; Xu, L. LPS induced miR-181a promotes pancreatic cancer cell migration via targeting PTEN and MAP2K4. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2014, 59, 1452–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parikh, A.; Lee, C.; Joseph, P.; Marchini, S.; Baccarini, A.; Kolev, V.; Romualdi, C.; Fruscio, R.; Shah, H.; Wang, F.; et al. microRNA-181a has a critical role in ovarian cancer progression through the regulation of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhiping, C.; Shijun, T.; Linhui, W.; Yapei, W.; Lianxi, Q.; Qiang, D. MiR-181a promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition of prostate cancer cells by targeting TGIF2. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 4835–4843. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jamali, Z.; Asl Aminabadi, N.; Attaran, R.; Pournagiazar, F.; Ghertasi Oskouei, S.; Ahmadpour, F. MicroRNAs as prognostic molecular signatures in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oral Oncol. 2015, 51, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Zang, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Wan, B. miR-181a and miR-203 inhibit migration and invasion of laryngeal carcinoma cells by interacting with ATF2. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2019, 12, 133–141. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.C.; Hung, P.S.; Wang, P.W.; Liu, C.J.; Chu, T.H.; Cheng, H.W.; Lin, S.C. miR-181 as a putative biomarker for lymph-node metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2011, 40, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Lee, C.R.; Rigas, N.K.; Kim, R.H.; Kang, M.K.; Park, N.H.; Shin, K.H. Human papillomavirus 16 (HPV16) enhances tumor growth and cancer stemness of HPV-negative oral/oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma cells via miR-181 regulation. Papillomavirus Res. 2015, 1, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quabius, E.S.; Merz, I.; Gorogh, T.; Hedderich, J.; Haag, J.; Rocken, C.; Ambrosch, P.; Hoffmann, M. miRNA-expression in tonsillar squamous cell carcinomas in relation to HPV infection and expression of the antileukoproteinase SLPI. Papillomavirus Res. 2017, 4, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Chen, Y.; Lin, Y.; Lin, H.; Li, H.; Su, X.; Fang, Z.; Wang, J.; Wei, Q.; Teng, J.; et al. Potential miRNA biomarkers for the diagnosis and prognosis of esophageal cancer detected by a novel absolute quantitative RT-qPCR method. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; You, M.; Wang, F.; Wang, Z.; Gao, X.; Jing, C.; Liu, J.; Guo, M.; Li, J.; Luo, A.; et al. Multifunctional Graphdiyne-Cerium Oxide Nanozymes Facilitate MicroRNA Delivery and Attenuate Tumor Hypoxia for Highly Efficient Radiotherapy of Esophageal Cancer. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2100556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Z.; Dong, X.; Sun, Q.; Li, X.; Yan, B. Clinical significance of up-regulated miR-181a in prognosis and progression of esophageal cancer. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2014, 46, 1007–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, L.; Bai, Y.; Ma, H. The Value of MicroRNA-155 as a Prognostic Factor for Survival in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Zhou, X.; Li, Y.; Jiang, H.; Chen, A. Long Non-Coding RNA NORAD Inhibits Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation and Metastasis by Regulating miR-155-5p/SOCS1 Axis. J. Breast Cancer 2021, 24, 330–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, C.; Liang, F.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, S. MiRNA-155 promotes proliferation by targeting caudal-type homeobox 1 (CDX1) in glioma cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 95, 1759–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Gao, S.Q.; Huang, L.D.; Huang, Y.H.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Zhou, M.T.; Shi, H.Q.; Song, Q.T.; Shan, Y.F. MicroRNA-155 promotes the proliferation and invasion abilities of colon cancer cells by targeting quaking. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 2355–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Souza, W.; Kumar, A. microRNAs in oral cancer: Moving from bench to bed as next generation medicine. Oral Oncol. 2020, 111, 104916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, S.; Liu, H.; Gao, B.; Wei, W.; Yang, A.; Li, J.; Zhang, L. miR-155, miR-96 and miR-99a as potential diagnostic and prognostic tools for the clinical management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 3381–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arantes, L.; De Carvalho, A.C.; Melendez, M.E.; Lopes Carvalho, A. Serum, plasma and saliva biomarkers for head and neck cancer. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2018, 18, 85–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.J.; Liang, T.S.; Wang, J.; Zhao, J.Y.; Zhai, S.N.; Yang, D.K.; Wang, L.D. MicroRNA-155 acts as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2020, 48, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Duan, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhang, P.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, L.; Cheng, J.; Jiang, H. MiR-155-5p promotes oral cancer progression by targeting chromatin remodeling gene ARID2. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 122, 109696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, O.; Hasegawa, S.; Nagai, H.; Uchida, F.; Yamatoji, M.; Kanno, N.I.; Yamagata, K.; Sakai, S.; Yanagawa, T.; Bukawa, H. MicroRNA-155-5p is associated with oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis and poor prognosis. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2016, 45, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, L.J.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zhou, Z.T.; Ma, J.Y.; Liu, Y.; Bao, Z.X.; Jiang, W.W. MicroRNA-155 in oral squamous cell carcinoma: Overexpression, localization, and prognostic potential. Head Neck 2015, 37, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, A.K.; Muer, A.; Mairinger, F.D.; Weichert, W.; Stenzinger, A.; Hummel, M.; Budach, V.; Tinhofer, I. MiR-200b and miR-155 as predictive biomarkers for the efficacy of chemoradiation in locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 77, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rather, M.I.; Nagashri, M.N.; Swamy, S.S.; Gopinath, K.S.; Kumar, A. Oncogenic microRNA-155 down-regulates tumor suppressor CDC73 and promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma cell proliferation: Implications for cancer therapeutics. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lerner, C.; Wemmert, S.; Bochen, F.; Kulas, P.; Linxweiler, M.; Hasenfus, A.; Heinzelmann, J.; Leidinger, P.; Backes, C.; Meese, E.; et al. Characterization of miR-146a and miR-155 in blood, tissue and cell lines of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients and their impact on cell proliferation and migration. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 142, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bersani, C.; Mints, M.; Tertipis, N.; Haeggblom, L.; Näsman, A.; Romanitan, M.; Dalianis, T.; Ramqvist, T. MicroRNA-155, -185 and -193b as biomarkers in human papillomavirus positive and negative tonsillar and base of tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2018, 82, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahand, J.S.; Karimzadeh, M.R.; Nezamnia, M.; Fatemipour, M.; Khatami, A.; Jamshidi, S.; Moghoofei, M.; Taghizadieh, M.; Hajighadimi, S.; Shafiee, A.; et al. The role of miR-146a in viral infection. IUBMB Life 2020, 72, 343–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, J.A.; Majid, S.; Khan, A.; Arafah, A.; Ahmad, A.; Jan, B.L.; Shah, N.N.; Kazi, M.; Rehman, M.U. Clinico-Pathological Importance of miR-146a in Lung Cancer. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezfuli, N.K.; Alipoor, S.D.; Dalil Roofchayee, N.; Seyfi, S.; Salimi, B.; Adcock, I.M.; Mortaz, E. Evaluation Expression of miR-146a and miR-155 in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 715677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortis, S.P.; Vaxevanis, C.K.; Mahaira, L.G.; Sofopoulos, M.; Sotiriadou, N.N.; Dinou, A.; Arnogiannaki, N.; Stavropoulos-Giokas, C.; Thanos, D.; Baxevanis, C.N.; et al. Serum miRNA-based distinct clusters define three groups of breast cancer patients with different clinicopathological and immune characteristics. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2019, 68, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adami, B.; Tabatabaeian, H.; Ghaedi, K.; Talebi, A.; Azadeh, M.; Dehdashtian, E. miR-146a is deregulated in gastric cancer. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2019, 15, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Song, J.; Ding, B.; Cui, Y.; Liang, J.; Han, S. miR-146a promotes cervical cancer cell viability via targeting IRAK1 and TRAF6. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 3015–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Bo, X.; Hou, S.; Zhang, B.; Qiu, J.; Zheng, J. MiR-146a suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma by downregulating TRAF6. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2016, 6, 2502–2513. [Google Scholar]
- Damodaran, M.; Paul, S.F.D.; Venkatesan, V. Genetic Polymorphisms in miR-146a, miR-196a2 and miR-125a Genes and its Association in Prostate Cancer. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2020, 26, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garo, L.P.; Ajay, A.K.; Fujiwara, M.; Gabriely, G.; Raheja, R.; Kuhn, C.; Kenyon, B.; Skillin, N.; Kadowaki-Saga, R.; Saxena, S.; et al. MicroRNA-146a limits tumorigenic inflammation in colorectal cancer. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.; Bachoo, R.; Zhang, C.L. MicroRNA-146a inhibits glioma development by targeting Notch1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2011, 31, 3584–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hung, P.S.; Liu, C.J.; Chou, C.S.; Kao, S.Y.; Yang, C.C.; Chang, K.W.; Chiu, T.H.; Lin, S.C. miR-146a enhances the oncogenicity of oral carcinoma by concomitant targeting of the IRAK1, TRAF6 and NUMB genes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Liu, F.; Zhang, J.; Guan, S.; Sun, Y.; Chen, P.; Wang, D.; et al. miR-146a-5p mediates epithelial-mesenchymal transition of oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma via targeting Notch2. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 115, 1548–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Guan, S.; Liu, F.; Chen, X.; Han, L.; Wang, D.; Nesa, E.U.; Wang, X.; Bao, C.; Wang, N.; et al. Prognostic and diagnostic potential of miR-146a in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 114, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emmett, S.E.; Stark, M.S.; Pandeya, N.; Panizza, B.; Whiteman, D.C.; Antonsson, A. MicroRNA expression is associated with human papillomavirus status and prognosis in mucosal head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Oral Oncol. 2021, 113, 105136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nariman-Saleh-Fam, Z.; Mansoori, Y.; Saadatian, Z.; Tavakkoly-Bazzaz, J.; Daraei, A.; Zununi Vahed, S.; Mahmoodzadeh, H.; Bastami, M. Dysregulated Expression of miR-146a and Its Associated Immune Effectors in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Esophageal Carcinoma Patients. Immunol Investig. 2022, 51, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Yao, X.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, D.; Cui, R.; Zhang, X. Interactive functions of microRNAs in the miR-23a-27a-24-2 cluster and the potential for targeted therapy in cancer. J. Cell Physiol. 2020, 235, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roufayel, R.; Kadry, S. Expression of miR-23a by apoptotic regulators in human cancer: A review. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2017, 18, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Itani, M.M.; Nassar, F.J.; Tfayli, A.H.; Talhouk, R.S.; Chamandi, G.K.; Itani, A.R.S.; Makoukji, J.; Boustany, R.N.; Hou, L.; Zgheib, N.K.; et al. A Signature of Four Circulating microRNAs as Potential Biomarkers for Diagnosing Early-Stage Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, K.; Chen, Y.T.; Chen, C.F.; Tang, Y.S.; Huang, T.T.; Lin, Y.C.; Yeh, T.S.; Huang, K.H.; Lee, H.C.; Hsu, M.T.; et al. MicroRNA-23a/27a/24-2 cluster promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation synergistically. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 2319–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bao, L.; Zhao, J.; Dai, X.; Wang, Y.; Ma, R.; Su, Y.; Cui, H.; Niu, J.; Bai, S.; Xiao, Z.; et al. Correlation between miR-23a and onset of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2014, 38, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Tao, S.; Li, Q.; Deng, B.; Tan, Q.Y.; Jin, H. The miR-23a/27a/24-2 cluster promotes postoperative progression of early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2022, 24, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piepoli, A.; Tavano, F.; Copetti, M.; Mazza, T.; Palumbo, O.; Panza, A.; di Mola, F.F.; Pazienza, V.; Mazzoccoli, G.; Biscaglia, G.; et al. Mirna expression profiles identify drivers in colorectal and pancreatic cancers. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, L.; Liu, M. Correlation analysis on the expression levels of microRNA-23a and microRNA-23b and the incidence and prognosis of ovarian cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hatzl, S.; Perfler, B.; Wurm, S.; Uhl, B.; Quehenberger, F.; Ebner, S.; Troppmair, J.; Reinisch, A.; Wolfler, A.; Sill, H.; et al. Increased Expression of Micro-RNA-23a Mediates Chemoresistance to Cytarabine in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancers 2020, 12, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Xue, W.; Ouyang, W.; Jiang, X.; Jiang, X. miR-23a-3p/SIX1 regulates glucose uptake and proliferation through GLUT3 in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 2529–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabra, R.; Adlakha, Y.K.; Hariharan, M.; Scaria, V.; Saini, N. Upregulation of miR-23a-27a-24-2 cluster induces caspase-dependent and -independent apoptosis in human embryonic kidney cells. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, N.; Zhu, M.; Tsao, S.W.; Man, K.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, Y. MiR-23a-mediated inhibition of topoisomerase 1 expression potentiates cell response to etoposide in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quan, J.; Pan, X.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Tao, L.; Li, Z.; Zhao, L.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Lai, Y.; et al. MiR-23a-3p acts as an oncogene and potential prognostic biomarker by targeting PNRC2 in RCC. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 110, 656–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.W.; Zhong, L.P.; Ji, T.; Zhang, P.; Chen, W.T.; Zhang, C.P. MicroRNAs contribute to the chemoresistance of cisplatin in tongue squamous cell carcinoma lines. Oral Oncol. 2010, 46, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Li, G.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Tang, Y. TMEM161B-AS1 suppresses proliferation, invasion and glycolysis by targeting miR-23a-3p/HIF1AN signal axis in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 6535–6549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.; Zha, W.J.; Li, X.M.; Li, H.; Gao, F.; Ye, T.; Du, W.Q.; Liu, Y.C. Circular RNA circ-Foxo3 inhibits esophageal squamous cell cancer progression via the miR-23a/PTEN axis. J. Cell. Biochem. 2020, 121, 2595–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niwa, Y.; Yamada, S.; Sonohara, F.; Kurimoto, K.; Hayashi, M.; Tashiro, M.; Iwata, N.; Kanda, M.; Tanaka, C.; Kobayashi, D.; et al. Identification of a serum-based miRNA signature for response of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, S.; Ichikawa, D.; Kawaguchi, T.; Takeshita, H.; Miyamae, M.; Ohashi, T.; Okajima, W.; Imamura, T.; Kiuchi, J.; Arita, T.; et al. Plasma microRNA profiles: Identification of miR-23a as a novel biomarker for chemoresistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 62034–62048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peng, F.; Zhang, H.; Du, Y.; Tan, P. miR-23a promotes cisplatin chemoresistance and protects against cisplatin-induced apoptosis in tongue squamous cell carcinoma cells through Twist. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Landgraf, P.; Rusu, M.; Sheridan, R.; Sewer, A.; Iovino, N.; Aravin, A.; Pfeffer, S.; Rice, A.; Kamphorst, A.O.; Landthaler, M.; et al. A mammalian microRNA expression atlas based on small RNA library sequencing. Cell 2007, 129, 1401–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, X.; Liang, H.; Deng, T.; Zhu, K.; Zhang, S.; Wang, N.; Jiang, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, R.; Zen, K.; et al. The identification of novel targets of miR-16 and characterization of their biological functions in cancer cells. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aird, J.; Baird, A.M.; Lim, M.C.J.; McDermott, R.; Finn, S.P.; Gray, S.G. Carcinogenesis in prostate cancer: The role of long non-coding RNAs. Noncoding RNA Res. 2018, 3, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pidikova, P.; Reis, R.; Herichova, I. miRNA Clusters with Down-Regulated Expression in Human Colorectal Cancer and Their Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Liu, P.; Han, G.; Xue, X.; Ma, D. Expression of Concern: CircRNA circPDSS1 promotes bladder cancer by downregulating miR-16. Biosci. Rep. 2021, 41, BSR20191961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredsoe, J.; Rasmussen, A.K.I.; Mouritzen, P.; Bjerre, M.T.; Ostergren, P.; Fode, M.; Borre, M.; Sorensen, K.D. Profiling of Circulating microRNAs in Prostate Cancer Reveals Diagnostic Biomarker Potential. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ke, Y.; Zhao, W.; Xiong, J.; Cao, R. Downregulation of miR-16 promotes growth and motility by targeting HDGF in non-small cell lung cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 3153–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, S.; Wang, H.; Yan, D.; Lu, W.; Gao, P.; Lou, W.; Kong, X. Loss of miR-16 contributes to tumor progression by activation of tousled-like kinase 1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Cycle 2018, 17, 2284–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manikandan, M.; Deva Magendhra Rao, A.K.; Arunkumar, G.; Manickavasagam, M.; Rajkumar, K.S.; Rajaraman, R.; Munirajan, A.K. Oral squamous cell carcinoma: microRNA expression profiling and integrative analyses for elucidation of tumourigenesis mechanism. Mol. Cancer 2016, 15, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Li, G.H. MicroRNA-16 functions as a tumor-suppressor gene in oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting AKT3 and BCL2L2. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 233, 9447–9457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koopaie, M.; Manifar, S.; Lahiji, S.S. Assessment of MicroRNA-15a and MicroRNA-16-1 Salivary Level in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients. Microrna 2021, 10, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Yu, Z.; Huang, S.; Zhao, Q.; Sun, Z.; Fletcher, C.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, D. Combined identification of three miRNAs in serum as effective diagnostic biomarkers for HNSCC. EBioMedicine 2019, 50, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.; Correa, A.M.; Hoque, A.; Guan, B.; Ye, F.; Huang, J.; Swisher, S.G.; Wu, T.T.; Ajani, J.A.; Xu, X.C. Prognostic significance of differentially expressed miRNAs in esophageal cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 128, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Niu, H.; Chen, Y. MiR-16 induced the suppression of cell apoptosis while promote proliferation in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 33, 1340–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, G.; Wu, J.H.; Jiang, C.P. Diverse roles of miR-29 in cancer (review). Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 1509–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, J.; Shim, H.G.; Hwang, T.; Kim, H.; Kang, S.H.; Dho, Y.S.; Park, S.H.; Kim, S.J.; Park, C.K. Restoration of miR-29b exerts anti-cancer effects on glioblastoma. Cancer Cell Int. 2017, 17, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hozaka, Y.; Seki, N.; Tanaka, T.; Asai, S.; Moriya, S.; Idichi, T.; Wada, M.; Tanoue, K.; Kawasaki, Y.; Mataki, Y.; et al. Molecular Pathogenesis and Regulation of the miR-29-3p-Family: Involvement of ITGA6 and ITGB1 in Intra-Hepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, R.; Goto, Y.; Kojima, S.; Enokida, H.; Chiyomaru, T.; Kinoshita, T.; Sakamoto, S.; Fuse, M.; Nakagawa, M.; Naya, Y.; et al. Tumor-suppressive microRNA-29s inhibit cancer cell migration and invasion via targeting LAMC1 in prostate cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, S.; Luo, S.; Ji, C.; Shi, J. miR-29c-3p regulates proliferation and migration in ovarian cancer by targeting KIF4A. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 18, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Shou, H.; Wang, Q.; Liu, S. Investigation of the potential theranostic role of KDM5B/miR-29c signaling axis in paclitaxel resistant endometrial carcinoma. Gene 2019, 694, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Gu, X.; Tang, L.; Feng, X. A regulatory circuitry comprising TP53, miR-29 family, and SETDB1 in non-small cell lung cancer. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Irani, S. miRNAs Signature in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Metastasis: A Literature Review. J. Dent. 2016, 17, 71–83. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.; Pavlasova, G.M.; Seda, V.; Cerna, K.A.; Vojackova, E.; Filip, D.; Ondrisova, L.; Sandova, V.; Kostalova, L.; Zeni, P.F.; et al. miR-29 modulates CD40 signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia by targeting TRAF4: An axis affected by BCR inhibitors. Blood 2021, 137, 2481–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhong, H.; Wang, L.; Dong, Y.; Jia, A.; Mo, Q.; Zhang, C. MiR-29 Induces K562 Cell Apoptosis by Down-Regulating FoxM1. Med. Sci. Monit. 2015, 21, 3115–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piasecka, D.; Braun, M.; Kordek, R.; Sadej, R.; Romanska, H. MicroRNAs in regulation of triple-negative breast cancer progression. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 144, 1401–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kinoshita, T.; Nohata, N.; Hanazawa, T.; Kikkawa, N.; Yamamoto, N.; Yoshino, H.; Itesako, T.; Enokida, H.; Nakagawa, M.; Okamoto, Y.; et al. Tumour-suppressive microRNA-29s inhibit cancer cell migration and invasion by targeting laminin-integrin signalling in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 2636–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koshizuka, K.; Kikkawa, N.; Hanazawa, T.; Yamada, Y.; Okato, A.; Arai, T.; Katada, K.; Okamoto, Y.; Seki, N. Inhibition of integrin beta1-mediated oncogenic signalling by the antitumor microRNA-29 family in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 3663–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, E.; Su, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y. CCL20/CCR6 promotes cell proliferation and metastasis in laryngeal cancer by activating p38 pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 85, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Tang, L.L.; Sun, Y.; Cui, R.X.; Wang, H.Y.; Huang, B.J.; He, Q.M.; Jiang, W.; Ma, J. MiR-29c suppresses invasion and metastasis by targeting TIAM1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2013, 329, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.F.; Huang, Y.P.; Zheng, Y.F.; Lyu, M.Y.; Wei, S.B.; Meng, Z.; Gan, Y.H. miR-29b suppresses proliferation, migration, and invasion of tongue squamous cell carcinoma through PTEN-AKT signaling pathway by targeting Sp1. Oral Oncol. 2014, 50, 1062–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Zhai, J.; Zhang, J.; Ni, C.; Zhou, H. Improved Radiotherapy Sensitivity of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells by miR-29-3p Targeting COL1A1 3′-UTR. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 3161–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Jin, J.; Liu, J.; Dong, X.; Li, D.; He, Y. MicroRNA-29b regulates the radiosensitivity of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by regulating the BTG2-mediated cell cycle. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2021, 197, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas Grzelczyk, W.; Szemraj, J.; Kwiatkowska, S.; Jozefowicz-Korczynska, M. Serum expression of selected miRNAs in patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC). Diagn. Pathol. 2019, 14, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Rawi, N.; Elmabrouk, N.; Abu Kou, R.; Mkadmi, S.; Rizvi, Z.; Hamdoon, Z. The role of differentially expressed salivary microRNA in oral squamous cell carcinoma. A systematic review. Arch. Oral Biol. 2021, 125, 105108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Xue, Y.; Dong, S.; Zhang, P. Plasma microRNA-9 as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Int. Med. Res. 2017, 45, 1310–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozinovic, K.; Sabol, I.; Dediol, E.; Milutin Gasperov, N.; Manojlovic, S.; Vojtechova, Z.; Tachezy, R.; Grce, M. Genome-wide miRNA profiling reinforces the importance of miR-9 in human papillomavirus associated oral and oropharyngeal head and neck cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Ding, Y.; Ma, Q.; Zhao, L.; Guo, X.; Shao, Y.; Niu, C.; He, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zheng, D.; et al. Identification of Novel Circulating miRNA Biomarkers for the Diagnosis of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Squamous Dysplasia. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2019, 28, 1212–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, W.; Chang, A.; Zhao, H.; Ye, H.; Li, D.; Zhuo, X. Identification of a novel microRNA profile including miR-106b, miR-17, miR-20b, miR-18a and miR-93 in the metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Biomark. 2020, 27, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.L.; Jiang, Y.H.; Feng, J.G.; Su, D.; Chen, P.C.; Mao, W.M. MicroRNA-17, microRNA-18a, and microRNA-19a are prognostic indicators in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2014, 97, 1037–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wen, W.; Zhu, J.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Qi, L.W.; Shan, X.; Wang, T.; Cheng, W.; et al. A six-microRNA signature in plasma was identified as a potential biomarker in diagnosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 34468–34480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hirajima, S.; Komatsu, S.; Ichikawa, D.; Takeshita, H.; Konishi, H.; Shiozaki, A.; Morimura, R.; Tsujiura, M.; Nagata, H.; Kawaguchi, T.; et al. Clinical impact of circulating miR-18a in plasma of patients with oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 1822–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, A.F.; Gupta, M.; Bansal, P. Micronome revealed miR-19a/b as key regulator of SOCS3 during cancer related inflammation of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Gene 2016, 594, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, K.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, X. miR-19a and miR-424 target TGFBR3 to promote epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and migration of tongue squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cell Adh. Migr. 2018, 12, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, Y.; Lin, H.; Fang, Z.; Luo, Q.; Fang, Y.; Su, Y.; Hu, Q.; Duan, H.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Z.Y. Plasma microRNA-19a as a potential biomarker for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma diagnosis and prognosis. Biomark. Med. 2017, 11, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, T.Y.; Zhang, T.H.; Qu, L.M.; Feng, J.P.; Tian, L.L.; Zhang, B.H.; Li, D.D.; Sun, Y.N.; Liu, M. MiR-19a is correlated with prognosis and apoptosis of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma by regulating TIMP-2 expression. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 56–63. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, W.; Chen, Y.; Lin, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z. The miR-19b-3p-MAP2K3-STAT3 feedback loop regulates cell proliferation and invasion in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 1566–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Julaiti, A.; Ran, W.; He, Y. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomal microRNA-19b-3p targets SOCS1 to facilitate progression of esophageal cancer. Life Sci. 2021, 278, 119491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Yin, L.; Wu, J.; Gu, J.J.; Wu, J.Z.; Chen, D.; Yu, H.L.; Ding, K.; Zhang, N.; Du, M.Y.; et al. MicroRNA-19b-3p regulates nasopharyngeal carcinoma radiosensitivity by targeting TNFAIP3/NF-kappaB axis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, L.H.; Duan, J.L.; Zhou, C.; Shen, G.W.; Wang, X.Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Xiao, S.J. MicroRNA19b inhibitors can attenuate the STAT3 signaling pathway in NPC C6661 cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.C.; Meng, W.W.; Qu, Y.H.; Zhou, M.X.; He, J.; Lv, P.; Ming, L. Expression of circulating microRNA-20a and let-7a in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 4660–4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zou, X.; Wu, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, T.; Liu, P.; Zhu, W.; Zhu, J. Identification of a 7-microRNA signature in plasma as promising biomarker for nasopharyngeal carcinoma detection. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 1230–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Xiang, J.; Wu, M.; Xiong, W.; Tang, H.; Deng, M.; Li, X.; Liao, Q.; Su, B.; Luo, Z.; et al. Circulating miR-17, miR-20a, miR-29c, and miR-223 combined as non-invasive biomarkers in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Kyung, H.M. Identification of eight meta-signature miRNAs as potential biomarkers for oropharyngeal cancers. Cancer Genet. 2019, 233–234, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, T.; Wong, D.T.W. Liquid Biopsy in Head and Neck Cancer: Promises and Challenges. J. Dent. Res. 2018, 97, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, F.; Sun, R.; Deng, N.; Guo, T.; Cao, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zou, B.; Zhang, S.; Jing, T.; et al. miR-29a/b enhances cell migration and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression by regulating SPARC and COL3A1 gene expression. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.L.; Li, H.X.; Yang, Y.Y.; Su, Y.L.; Lian, J.S.; Li, T.; Xu, J.; Wang, X.N.; Jin, N.; Liu, X.F. MiR-31 is a potential biomarker for diagnosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2018, 11, 4339–4345. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ansari, M.H.; Irani, S.; Edalat, H.; Amin, R.; Mohammadi Roushandeh, A. Deregulation of miR-93 and miR-143 in human esophageal cancer. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 3097–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Fan, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, X. Expression of miR-93-5p in patients with esophageal carcinoma and its relationship with the curative effect and prognosis of radiotherapy. Cell Mol. Biol. 2020, 66, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, R.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Yang, C. MicroRNA-105 plays an independent prognostic role in esophageal cancer and acts as an oncogene. Cancer Biomark. 2020, 27, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.J.; Yang, B.B. Identification of core miRNA prognostic markers in patients with laryngeal cancer using bioinformatics analysis. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2021, 278, 1613–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Sun, Z.; Wang, D.; Du, T. MiR-106b-5p regulates esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression by binding to HPGD. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zeng, G.; Jiang, Y. The Emerging Roles of miR-125b in Cancers. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazumder, S.; Datta, S.; Ray, J.G.; Chaudhuri, K.; Chatterjee, R. Liquid biopsy: miRNA as a potential biomarker in oral cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. 2019, 58, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Wang, J.; Shan, C.; Jia, Q.; Bian, Y.; Zhang, H. Circular RNA ZNF609 promotes laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma progression by upregulating epidermal growth factor receptor via sponging microRNA-134-5p. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 6929–6941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.J.; Shen, W.G.; Peng, S.Y.; Cheng, H.W.; Kao, S.Y.; Lin, S.C.; Chang, K.W. miR-134 induces oncogenicity and metastasis in head and neck carcinoma through targeting WWOX gene. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 134, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerer, I.; Unger, K.; Braselmann, H.; Schuettrumpf, L.; Maihoefer, C.; Baumeister, P.; Kirchner, T.; Niyazi, M.; Sage, E.; Specht, H.M.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as prognostic therapy biomarkers in head and neck cancer patients. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, R.J.; Xiao, D.W.; Liao, L.D.; Chen, T.; Xie, Z.F.; Huang, W.Z.; Wang, W.S.; Jiang, T.F.; Wu, B.L.; Li, E.M.; et al. MiR-142-3p as a potential prognostic biomarker for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 105, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Li, J.; Zhou, C.; Lv, C.; Tian, M. MiR-142-3p Suppresses SOCS6 Expression and Promotes Cell Proliferation in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 36, 1743–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wu, J.; Wu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Deng, Y.; Liao, J.; Liu, H.; Peng, H. A novel microRNA-based signature predicts prognosis among nasopharyngeal cancer patients. Exp. Biol. Med. 2021, 246, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, B.G.; Anczykowski, M.Z.; Ihler, F.; Bertlich, M.; Spiegel, J.L.; Haubner, F.; Canis, M.; Kuffer, S.; Hess, J.; Unger, K.; et al. MicroRNA-182-5p and microRNA-205-5p as potential biomarkers for prognostic stratification of p16-positive oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Biomark. 2022, 33, 331–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.S.; Liu, X.B.; Wong, B.Y.; Ng, R.W.; Yuen, A.P.; Wei, W.I. Mature miR-184 as Potential Oncogenic microRNA of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Tongue. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 2588–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, T.S.; Ho, W.K.; Chan, J.Y.; Ng, R.W.; Wei, W.I. Mature miR-184 and squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue. Sci. World J. 2009, 9, 130–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghffari, M.; Asadi, M.; Shanaehbandi, D.; Bornehdeli, S.; Sadeghzadeh, M.; Mohammad Reza Khani, H.; Ghasembaglou, S. Aberrant Expression of miR-103, miR-184, miR-378, miR-497 and miR-506 in Tumor Tissue from Patients with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Regulates the Clinical Picture of the Patients. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2020, 21, 1311–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahran, F.; Ghalwash, D.; Shaker, O.; Al-Johani, K.; Scully, C. Salivary microRNAs in oral cancer. Oral Dis. 2015, 21, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.J.; Lin, J.S.; Cheng, H.W.; Hsu, Y.H.; Cheng, C.Y.; Lin, S.C. Plasma miR-187* is a potential biomarker for oral carcinoma. Clin. Oral Investig. 2017, 21, 1131–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.C.; Kao, S.Y.; Chang, J.C.; Liu, Y.C.; Yu, E.H.; Tseng, S.H.; Liu, C.J.; Chang, K.W. Up-regulation of miR-187 modulates the advances of oral carcinoma by targeting BARX2 tumor suppressor. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 61355–61365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, G.; Cao, Y.; Wang, P.; Song, H.; Bie, T.; Li, M.; Huai, D. miR-200b-3p in plasma is a potential diagnostic biomarker in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Biomarkers 2018, 23, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Carvalho, A.C.; Scapulatempo-Neto, C.; Maia, D.C.; Evangelista, A.F.; Morini, M.A.; Carvalho, A.L.; Vettore, A.L. Accuracy of microRNAs as markers for the detection of neck lymph node metastases in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, C.; Liu, K.; Lv, M.; Li, B.; Lan, Z.; Chen, W.; Kang, M. Expression and Possible Molecular Mechanisms of microRNA-205-5p in Patients With Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 19, 1533033820980110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, A.M.; Heaford, A.C.; Trask, D.K. Detection of metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma using the relative expression of tissue-specific mir-205. Transl. Oncol. 2008, 1, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibuki, Y.; Nishiyama, Y.; Tsutani, Y.; Emi, M.; Hamai, Y.; Okada, M.; Tahara, H. Circulating microRNA/isomiRs as novel biomarkers of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hezova, R.; Kovarikova, A.; Srovnal, J.; Zemanova, M.; Harustiak, T.; Ehrmann, J.; Hajduch, M.; Sachlova, M.; Svoboda, M.; Slaby, O. MiR-205 functions as a tumor suppressor in adenocarcinoma and an oncogene in squamous cell carcinoma of esophagus. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 8007–8018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Lu, C.; Yang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zhong, J.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Huang, G.; Peng, X.; Liu, K.; et al. A panel of three serum microRNA can be used as potential diagnostic biomarkers for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachibana, H.; Sho, R.; Takeda, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yoshida, Y.; Narimatsu, H.; Otani, K.; Ishikawa, S.; Fukao, A.; Asao, H.; et al. Circulating miR-223 in Oral Cancer: Its Potential as a Novel Diagnostic Biomarker and Therapeutic Target. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Lv, L.; Liu, X.; Jiang, X.; Yin, Q.; Hao, Y.; Xiao, L. MiR-223 promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma proliferation and migration by regulating FBXW7. Cancer Biomark. 2019, 24, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, X.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, X.; He, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, W. MicroRNA expression profiling analysis in serum for nasopharyngeal carcinoma diagnosis. Gene 2020, 727, 144243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, D.; Shan, X.; Zhou, X.; Qi, L.W.; Wu, L.; Zhu, J.; Cheng, W.; Zhang, H.; et al. A novel serum microRNA signature to screen esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2017, 6, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, J.; Liu, J.N.; Sun, C. Mechanism and Role of the Neuropeptide LGI1 Receptor ADAM23 in Regulating Biomarkers of Ferroptosis and Progression of Esophageal Cancer. Dis. Markers 2021, 2021, 9227897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, H.F.; Chang, K.W.; Cheng, H.W.; Liu, C.J. Upregulation of miR-372 and -373 associates with lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis of oral carcinomas. Laryngoscope 2015, 125, E365–E370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.A.; Weng, S.L.; Yang, S.F.; Chou, C.H.; Huang, W.C.; Tu, S.J.; Chang, T.H.; Huang, C.N.; Jong, Y.J.; Huang, H.D. A Three-MicroRNA Signature as a Potential Biomarker for the Early Detection of Oral Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romani, C.; Salviato, E.; Paderno, A.; Zanotti, L.; Ravaggi, A.; Deganello, A.; Berretti, G.; Gualtieri, T.; Marchini, S.; D’Incalci, M.; et al. Genome-wide study of salivary miRNAs identifies miR-423-5p as promising diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Theranostics 2021, 11, 2987–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolandparva, F.; Hashemi Nasab, M.S.; Mohamadnia, A.; Garajei, A.; Farhadi Nasab, A.; Bahrami, N. Early Diagnosis of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma (OSCC) by miR-138 and miR-424-5p Expression as a Cancer Marker. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2021, 22, 2185–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Yang, X.; Luo, Y.; Ren, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, N. Serum miR-483-5p: A novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Nan, J.; Dong, L.; Zhang, C.; Li, H.; Na, R.; He, H.; Wang, Y. Upregulated miR-483-5p expression as a prognostic biomarker for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Biomark. 2017, 19, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Hong, L. Prediction value of miR-483 and miR-214 in prognosis and multidrug resistance of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Genet. Test Mol. Biomark. 2013, 17, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.; Wang, C.; Guan, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, D.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Zen, K.; et al. Diagnostic and prognostic implications of a serum miRNA panel in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, X.H.; Cui, C.; Ruan, H.L.; Xue, W.Q.; Zhang, S.D.; Hu, Y.Z.; Zhou, X.X.; Jia, W.H. Plasma microRNA profiling in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients reveals miR-548q and miR-483-5p as potential biomarkers. Chin. J. Cancer 2014, 33, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langevin, S.; Kuhnell, D.; Parry, T.; Biesiada, J.; Huang, S.; Wise-Draper, T.; Casper, K.; Zhang, X.; Medvedovic, M.; Kasper, S. Comprehensive microRNA-sequencing of exosomes derived from head and neck carcinoma cells in vitro reveals common secretion profiles and potential utility as salivary biomarkers. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 82459–82474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, J.; Bao, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, W.; Xu, Q. Serum miR-626 and miR-5100 are Promising Prognosis Predictors for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Theranostics 2019, 9, 920–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.H.; Hu, X.D.; Yan, Y. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway participates in the effect of miR-626 on oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting RASSF4. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2021, 50, 1005–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hufbauer, M.; Maltseva, M.; Meinrath, J.; Lechner, A.; Beutner, D.; Huebbers, C.U.; Akgul, B. HPV16 increases the number of migratory cancer stem cells and modulates their miRNA expression profile in oropharyngeal cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 1426–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ries, J.; Vairaktaris, E.; Agaimy, A.; Kintopp, R.; Baran, C.; Neukam, F.W.; Nkenke, E. miR-186, miR-3651 and miR-494: Potential biomarkers for oral squamous cell carcinoma extracted from whole blood. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 1429–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ries, J.; Baran, C.; Wehrhan, F.; Weber, M.; Neukam, F.W.; Krautheim-Zenk, A.; Nkenke, E. Prognostic significance of altered miRNA expression in whole blood of OSCC patients. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 3467–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Fan, W. Low expression of miR-let-7a promotes cell growth and invasion through the regulation of c-Myc in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Cycle 2020, 19, 1983–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Du, N.; Xu, C.; Liang, R.; Ren, H.; et al. Nano Let7b sensitization of eliminating esophageal cancer stemlike cells is dependent on blockade of Wnt activation of symmetric division. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 51, 1077–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Lu, J.; Wang, F.; Liu, X.; Peng, X.; Yu, B.; Zhao, F.; Li, X. Dynamic Changes in Plasma MicroRNAs Have Potential Predictive Values in Monitoring Recurrence and Metastasis of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 7329195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minor, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, F.; Song, J.; Jimeno, A.; Wang, X.-J.; Lu, X.; Gross, N.; Kulesz-Martin, M.; Wang, D.; et al. Methylation of microRNA-9 is a specific and sensitive biomarker for oral and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas. Oral Oncol. 2012, 48, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hersi, H.M.; Raulf, N.; Gaken, J.; Folarin, N.; Tavassoli, M. MicroRNA-9 inhibits growth and invasion of head and neck cancer cells and is a predictive biomarker of response to plerixafor, an inhibitor of its target CXCR4. Mol. Oncol. 2018, 12, 2023–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, R.; Xu, T.; Wu, W.; Zhang, R.; Wang, C.; Huang, H.; Calin, C.A.; Yang, H.; et al. Hsa-miR-24-3p increases nasopharyngeal carcinoma radiosensitivity by targeting both the 3′UTR and 5′UTR of Jab1/CSN5. Oncogene 2016, 35, 6096–6108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.; Zheng, S.; Liu, T.; Liu, Q.; Dai, F.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Y.; Sheyhidin, I.; Lu, X. Down-regulated miR-26a promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion via negative regulation of MTDH in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 2114–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jia, L.F.; Wei, S.B.; Gan, Y.H.; Guo, Y.; Gong, K.; Mitchelson, K.; Cheng, J.; Yu, G.Y. Expression, regulation and roles of miR-26a and MEG3 in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 2282–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liang, Y.; Lv, H.; Meng, H.; Xiong, G.; Guan, X.; Chen, X.; Bai, Y.; Wang, K. miR-26a and miR-26b inhibit esophageal squamous cancer cell proliferation through suppression of c-MYC pathway. Gene 2017, 625, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumoto, I.; Hanazawa, T.; Kinoshita, T.; Kikkawa, N.; Koshizuka, K.; Goto, Y.; Nishikawa, R.; Chiyomaru, T.; Enokida, H.; Nakagawa, M.; et al. MicroRNA expression signature of oral squamous cell carcinoma: Functional role of microRNA-26a/b in the modulation of novel cancer pathways. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Z.; Chang, K.; Fan, C.; Zhang, Y. MiR-26a/miR-26b represses tongue squamous cell carcinoma progression by targeting PAK1. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syllaios, A.; Sakellariou, S.; Garmpis, N.; Sarlani, E.; Damaskos, C.; Apostolou, K.; Kykalos, S.; Gazouli, M.; Karavokyros, I.; Schizas, D. The role of miR-101 in esophageal and gastric cancer. Per. Med. 2021, 18, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiam, K.; Mayne, G.C.; Watson, D.I.; Woodman, R.J.; Bright, T.F.; Michael, M.Z.; Karapetis, C.S.; Irvine, T.; Phillips, W.A.; Hummel, R.; et al. Identification of microRNA Biomarkers of Response to Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy in Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Using Next Generation Sequencing. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 25, 2731–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jia, R.Z.; Diao, S.; He, J.; Jia, L. miRNA-101 Targets TGF-betaR1 to Retard the Progression of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Oncol. Res. 2020, 28, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, R.S.; Zhang, E.X.; Sun, Q.F.; Ye, Z.J.; Liu, J.W.; Zhou, D.H.; Tang, Y. Integrated analysis of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA network in squamous cell carcinoma of tongue. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Meng, L.; Liu, F.; Sang, M.; Wang, G. Hypermethylation-mediated inactivation of miR-124 predicts poor prognosis and promotes tumor growth at least partially through targeting EZH2/H3K27me3 in ESCC. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2019, 36, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Wang, Q.Q.; Li, H.; Ye, T.; Gao, F.; Liu, Y.C. miR-124 radiosensitizes human esophageal cancer cell TE-1 by targeting CDK4. Genet. Mol. Res. 2016, 15, 15027893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, H.; Hirasaki, M.; Kogashiwa, Y.; Kuba, K.; Ebihara, Y.; Nakahira, M.; Sakai, A.; Okuda, A.; Sugasawa, M. Predicting the radiosensitivity of HPV-negative oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma using miR-130b. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2021, 141, 640–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duz, M.B.; Karatas, O.F.; Guzel, E.; Turgut, N.F.; Yilmaz, M.; Creighton, C.J.; Ozen, M. Identification of miR-139-5p as a saliva biomarker for tongue squamous cell carcinoma: A pilot study. Cell. Oncol. 2016, 39, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Cao, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Li, C.; Liu, L.; Xu, G. Progression of squamous cell carcinoma is regulated by miR-139-5p/CXCR4. Front. Biosci. Landmark Ed. 2020, 25, 1732–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Jin, J.; Ma, T.; Zhai, H. MiR-139-5p inhibits the tumorigenesis and progression of oral squamous carcinoma cells by targeting HOXA9. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 3730–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, R. Prognostic Value of MicroRNAs in Esophageal Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2018, 9, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Li, J. Downregulation of miR-138 predicts poor prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Biomark. 2017, 20, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokobori, T.; Suzuki, S.; Tanaka, N.; Inose, T.; Sohda, M.; Sano, A.; Sakai, M.; Nakajima, M.; Miyazaki, T.; Kato, H.; et al. MiR-150 is associated with poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via targeting the EMT inducer ZEB1. Cancer Sci. 2013, 104, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yue, W.; Xie, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, S.; Dang, W.; Xin, S.; Yang, L.; Zhai, X.; Cao, P.; et al. The fourmicroRNA signature identified by bioinformatics analysis predicts the prognosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 42, 1767–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yue, P.Y.; Ha, W.Y.; Lau, C.C.; Cheung, F.M.; Lee, A.W.; Ng, W.T.; Ngan, R.K.; Yau, C.C.; Kwong, D.L.; Lung, H.L.; et al. MicroRNA profiling study reveals miR-150 in association with metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, G.H.; Ma, Z.H.; Wang, X. Long non-coding RNA CCAT1 is a prognostic biomarker for the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma via miR-181a-mediated Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Cell Cycle 2019, 18, 2902–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.T.; Tong, X.; Zhang, Z.X.; Sun, Y.Y.; Yan, W.; Xu, Z.M.; Fu, W.N. MYCT1 represses apoptosis of laryngeal cancerous cells through the MAX/miR-181a/NPM1 pathway. FEBS J. 2019, 286, 3892–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Ye, L.; Chang, T.; Li, X.; Li, X. microRNA-195-Cdc42 axis acts as a prognostic factor of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 6871–6879. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, C.Y.; Zhang, W.W.; Xiang, J.L.; Wang, X.H.; Li, J.; Wang, J.L. Identification of microRNAs as novel biomarkers for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: A study based on The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and bioinformatics. Chin. Med. J. 2019, 132, 2213–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Wang, J.; Ye, K.; Du, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, W. Reduced miR-203 predicts metastasis and poor survival in esophageal carcinoma. Aging 2019, 11, 12114–12130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Lin, Y.; Fan, L.; Kuang, W.; Zheng, L.; Wu, J.; Shang, P.; Wang, Q.; Tan, J. miR-203 inhibits cell proliferation and promotes cisplatin induced cell death in tongue squamous cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 473, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.Q.; Yi, H.M.; Ye, X.; Zhu, J.F.; Yi, H.; Li, L.N.; Xiao, T.; Yuan, L.; Li, J.Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; et al. MiRNA-203 Reduces Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Radioresistance by Targeting IL8/AKT Signaling. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 2653–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhuang, Z.; Yu, P.; Xie, N.; Wu, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, M.; Tao, Y.; Wang, W.; Yin, H.; Zou, B.; et al. MicroRNA-204-5p is a tumor suppressor and potential therapeutic target in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Theranostics 2020, 10, 1433–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, F.; Zhou, X. miR-204-5p regulates cell proliferation and metastasis through inhibiting CXCR4 expression in OSCC. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 82, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Wu, Y.; He, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Liu, Q.; Qu, X.; Li, W.; Wen, S.; et al. MicroRNA-204-5p inhibits invasion and metastasis of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma by suppressing forkhead box C1. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 2356–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yao, Y.; Meng, F.; Qian, X.; Jiang, X.; Li, X.; Gao, Z.; Gao, L. Predictive Value of Serum miR-10b, miR-29c, and miR-205 as Promising Biomarkers in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Screening. Medicine 2015, 94, e1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, T.; Jimenez, L.; Kawachi, N.; Fan, J.-B.; Chen, J.; Belbin, T.; Ramnauth, A.; Loudig, O.; Keller, C.E.; Smith, R.; et al. Low-level expression of miR-375 correlates with poor outcome and metastasis while altering the invasive properties of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 180, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salazar, C.; Calvopina, D.; Punyadeera, C. miRNAs in human papilloma virus associated oral and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2014, 14, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faur, C.I.; Rotaru, H.; Osan, C.; Jurj, A.; Roman, R.C.; Moldovan, M.; Chirila, M.; Hedesiu, M. Salivary exosomal microRNAs as biomarkers for head and neck cancer detection-a literature review. Maxillofac. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2021, 43, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garajei, A.; Parvin, M.; Mohammadi, H.; Allameh, A.; Hamidavi, A.; Sadeghi, M.; Emami, A.; Brand, S. Evaluation of the Expression of miR-486-3p, miR-548-3p, miR-561-5p and miR-509-5p in Tumor Biopsies of Patients with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Pathogens 2022, 11, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Chen, H.; Han, C.; Fu, D.; Zhou, L.; Jin, G.; Wang, F.; Wang, D.; Chen, Y.; Ma, L.; et al. miR-486-5p expression pattern in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, gastric cancer and its prognostic value. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 15840–15853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Guan, S.; Chen, X.; Liu, B.; Liu, F.; Han, L.; Un Nesa, E.; Song, Q.; Bao, C.; Wang, X.; et al. Clinical potential of miR-3651 as a novel prognostic biomarker for esophageal squamous cell cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 465, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ries, J.; Baran, C.; Wehrhan, F.; Weber, M.; Motel, C.; Kesting, M.; Nkenke, E. The altered expression levels of miR-186, miR-494 and miR-3651 in OSCC tissue vary from those of the whole blood of OSCC patients. Cancer Biomark. 2019, 24, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, X.; Gao, J.; Sun, Q.W.; Wang, C.X.; Deng, W.; Mao, G.Y.; Li, H.Q.; Guo, S.S.; Cheng, J.; Wu, Y.N.; et al. MiR-34a inhibits the proliferation, migration, and invasion of oral squamous cell carcinoma by directly targeting SATB2. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 4856–4864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, W.; Liu, Y.E.; Zheng, Y.; Qu, L. MiR-429 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma growth by targeting ZEB1. Med. Sci. Monit. 2015, 21, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, M.; Zhan, J.; Xie, J.; Zhu, L.; Chen, L.; Luo, X.; Sheng, X.; Liu, T.; Zhang, S.; Lu, Z. MiR-125a-5p inhibits cell proliferation, cell cycle progression, and migration while promoting apoptosis in head and neck cancers by targeting ERBB3. Auris Nasus Larynx 2021, 48, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Liu, M.D.; Wu, H.; Pang, P.; Wang, S.; Li, Z.N.; Sun, C.F.; Liu, F.Y. Overexpression of hsa-miR-125a-5p enhances proliferation, migration and invasion of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines by upregulating C-C chemokine receptor type 7. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 9703–9710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, F.Y.; Gan, C.W.; Wang, M.X.; Sun, B.C.; Li, F.J.; Qiu, Y.H.; Wang, K. MiR-146a-5p inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells by regulating NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 3717–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Li, Y.S.; Huang, J.T.; Lan, S.H.; Wang, Y.F.; Lai, W.W.; Wang, Y.C.; Lin, Y.J.; Liu, H.S.; et al. MicroRNA-146a suppresses tumor malignancy via targeting vimentin in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells with lower fibronectin membrane assembly. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumoto, I.; Kikkawa, N.; Matsushita, R.; Kato, M.; Kurozumi, A.; Nishikawa, R.; Goto, Y.; Koshizuka, K.; Hanazawa, T.; Enokida, H.; et al. Tumor-suppressive microRNAs (miR-26a/b, miR-29a/b/c and miR-218) concertedly suppressed metastasis-promoting LOXL2 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J. Hum. Genet 2016, 61, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.H.; Hsu, W.L.; Tseng, Y.J.; Liu, D.W.; Weng, C.F. Involvement of DNMT 3B promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and gene expression profile of invasive head and neck squamous cell carcinomas cell lines. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.K.; Bär, C.; Thum, T. miR-21, Mediator, and Potential Therapeutic Target in the Cardiorenal Syndrome. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyahara, N.; Benazzo, A.; Oberndorfer, F.; Iwasaki, A.; Laszlo, V.; Döme, B.; Hoda, M.A.; Jaksch, P.; Klepetko, W.; Hoetzenecker, K. MiR-21 in Lung Transplant Recipients With Chronic Lung Allograft Dysfunction. Transpl. Int. 2021, 35, 10184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yin, Z.; Wang, F.; Han, Z.; Wang, Y.; Huang, S.; Hu, T.; Guo, M.; Lei, P. Hydrogen exerts neuroprotection by activation of the miR-21/PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β pathway in an in vitro model of traumatic brain injury. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 4061–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Bei, Y.; Shen, S.; Huang, P.; Shi, J.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Q.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xu, T.; et al. miR-21-3p controls sepsis-associated cardiac dysfunction via regulating SORBS2. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2016, 94, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L. Hyperoside prevents sepsis-associated cardiac dysfunction through regulating cardiomyocyte viability and inflammation via inhibiting miR-21. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 138, 111524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.; Huang, J.J.; Xu, W.H.; Jin, X.J.; Li, J.P.; Tang, Y.J.; Huang, X.F.; Cui, H.J.; Sun, G.B.; Li, R.L.; et al. MiR-21/miR-375 ratio is an independent prognostic factor in patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 1775–1785. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Cui, L. A robust six-miRNA prognostic signature for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 8799–8811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Li, G.; Zhong, R.; Du, D.; Meng, R.; Kong, W.; Lu, M. Identification of a six microRNA signature as a novel potential prognostic biomarker in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 21579–21590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganci, F.; Sacconi, A.; Manciocco, V.; Covello, R.; Benevolo, M.; Rollo, F.; Strano, S.; Valsoni, S. Altered peritumoral microRNA expression predicts head and neck cancer patients with a high risk of recurrence. Mod. Pathol. 2017, 30, 1387–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hess, J.; Unger, K.; Maihoefer, C. A Five-MicroRNA Signature Predicts Survival and Disease Control of Patients with Head and Neck Cancer Negative for HPV Infection. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 1505–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, L.; Wu, Y.; Feng, M.; Xue, X.; Fan, Y. A novel seven-miRNA prognostic model to predict overall survival in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 4340–4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Boohaker, R.J.; Jiang, C.; Boohaker, J.R.; Xu, B. A radiosensitivity MiRNA signature validated by the TCGA database for head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 34649–34657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sun, W.; Lui, V.W.Y.; Wei, Y.; Chen, F.; Wen, W. Prediction of radiotherapy response with a 5-microRNA signature-based nomogram in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, T.; Koo, K.; Cheng, L.; Vella, L.J.; Hill, A.F.; Reynolds, E.; Nastri, A.; Cirillo, N.; Seers, C. Predicting the Presence of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Using Commonly Dysregulated MicroRNA in Oral Swirls. Cancer Prev. Res. 2018, 11, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, S.C.; Liao, C.T.; Peng, C.H.; Cheng, A.J.; Chen, S.J.; Huang, C.G.; Hsieh, W.P.; Yen, T.C. MicroRNAs MiR-218, MiR-125b, and Let-7g predict prognosis in patients with oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, A.J.; Wang, S.; Kutler, D.I.; Carvajal, R.D.; Philipone, E.; Wang, T.; Peters, S.M.; LaRoche, D.; Hernandez, B.Y.; McDowell, B.D.; et al. MicroRNA-based risk scoring system to identify early-stage oral squamous cell carcinoma patients at high-risk for cancer-specific mortality. Head Neck 2020, 42, 1699–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervigne, N.K.; Reis, P.P.; Machado, J.; Sadikovic, B.; Bradley, G.; Galloni, N.N.; Pintilie, M.; Jurisica, I.; Perez-Ordonez, B.; Gilbert, R.; et al. Identification of a microRNA signature associated with progression of leukoplakia to oral carcinoma. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 4818–4829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, G.; Gay, H.A.; Chernock, R.D.; Zhang, T.R.; Luo, J.; Thorstad, W.L.; Lewis, J.S., Jr.; Wang, X. A microRNA expression signature for the prognosis of oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer 2013, 119, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, P.; Chernock, R.D.; Yang, Z.; Lang Kuhs, K.A.; Lewis, J.S.; Luo, J. A MicroRNA Expression Signature as Prognostic Marker for Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer 2021, 113, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, A.B.; Lin, A.; Xu, W.; Waldron, L.; Perez-Ordonez, B.; Weinreb, I.; Shi, W.; Bruce, J.; Huang, S.H.; O’Sullivan, B.; et al. Potentially prognostic miRNAs in HPV-associated oropharyngeal carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2154–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Lu, Z.; Gross, N.; Li, G. A 3-miRNA signature predicts survival of patients with hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma after post-operative radiotherapy. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 8280–8291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.Q.; Liu, J.; Chen, H.B.; Dai, W.J.; Zhou, L.Q.; Xie, C.W.; Li, J.C. A novel three-microRNA signature for predicting survival in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J. Dent. Sci. 2022, 17, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Xu, Y. Identification of a 3-miRNA Signature Associated With the Prediction of Prognosis in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 823603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreimer, A.R.; Clifford, G.M.; Boyle, P.; Franceschi, S. Human papillomavirus types in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas worldwide: A systematic review. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2005, 14, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brakenhoff, R.H.; Wagner, S.; Klussmann, J.P. Molecular Patterns and Biology of HPV-Associated HNSCC. In HPV Infection in Head and Neck Cancer; Golusiński, W., Leemans, C.R., Dietz, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 37–56. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.J.; Zheng, M.; Cao, M.X.; Zhang, W.L.; Huang, M.C.; Dai, L.; Tang, Y.L.; Liang, X.H. Distinguishable Prognostic miRNA Signatures of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Cancer With or Without HPV Infection. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 614487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Näsman, A.; Holzhauser, S.; Kostopoulou, O.N.; Zupancic, M.; Ährlund-Richter, A.; Du, J.; Dalianis, T. Prognostic Markers and Driver Genes and Options for Targeted Therapy in Human-Papillomavirus-Positive Tonsillar and Base-of-Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Viruses 2021, 13, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajer, C.B.; Garnæs, E.; Friis-Hansen, L.; Norrild, B.; Therkildsen, M.H.; Glud, M.; Rossing, M.; Lajer, H.; Svane, D.; Skotte, L.; et al. Erratum: The role of miRNAs in human papilloma virus (HPV)-associated cancers: Bridging between HPV-related head and neck cancer and cervical cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 117, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wald, A.I.; Hoskins, E.E.; Wells, S.I.; Ferris, R.L.; Khan, S.A. Alteration of microRNA profiles in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck cell lines by human papillomavirus. Head Neck 2011, 33, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ludwig, S.; Sharma, P.; Wise, P.; Sposto, R.; Hollingshead, D.; Lamb, J.; Lang, S.; Fabbri, M.; Whiteside, T.L. mRNA and miRNA Profiles of Exosomes from Cultured Tumor Cells Reveal Biomarkers Specific for HPV16-Positive and HPV16-Negative Head and Neck Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojtechova, Z.; Sabol, I.; Salakova, M.; Smahelova, J.; Zavadil, J.; Turek, L.; Grega, M.; Klozar, J.; Prochazka, B.; Tachezy, R. Comparison of the miRNA profiles in HPV-positive and HPV-negative tonsillar tumors and a model system of human keratinocyte clones. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Hu, S.Q.; Pu, Y.M.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.X. A HPV16-related prognostic indicator for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, S. HPV+ HNSCC-derived exosomal miR-9-5p inhibits TGF-β signaling-mediated fibroblast phenotypic transformation through NOX4. Cancer Sci. 2022, 113, 1475–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, D.L.; Davis, J.W.; Taylor, K.H.; Johnson, J.; Shi, Z.; Williams, R.; Atasoy, U.; Lewis, J.S., Jr.; Stack, M.S. Identification of a human papillomavirus-associated oncogenic miRNA panel in human oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma validated by bioinformatics analysis of the Cancer Genome Atlas. Am. J. Pathol. 2015, 185, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tong, F.; Mao, X.; Zhang, S.; Xie, H.; Yan, B.; Wang, B.; Sun, J.; Wei, L. HPV + HNSCC-derived exosomal miR-9 induces macrophage M1 polarization and increases tumor radiosensitivity. Cancer Lett. 2020, 478, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirghani, H.; Ugolin, N.; Ory, C.; Goislard, M.; Lefevre, M.; Baulande, S.; Hofman, P.; Guily, J.L.; Chevillard, S.; Lacave, R. Comparative analysis of micro-RNAs in human papillomavirus-positive versus -negative oropharyngeal cancers. Head Neck 2016, 38, 1634–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peacock, B.; Rigby, A.; Bradford, J.; Pink, R.; Hunter, K.; Lambert, D.; Hunt, S. Extracellular vesicle microRNA cargo is correlated with HPV status in oropharyngeal carcinoma. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2018, 47, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayne, G.C.; Woods, C.M.; Dharmawardana, N.; Wang, T.; Krishnan, S.; Hodge, J.C.; Foreman, A.; Boase, S.; Carney, A.S.; Sigston, E.A.W.; et al. Cross validated serum small extracellular vesicle microRNAs for the detection of oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MicroRNA Markers in Head and Neck Cancers. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04305366 (accessed on 26 June 2022).
- Tertiary Prevention of Head and Neck Cancer With a Dietary Intervention. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT02869399 (accessed on 26 June 2022).
- Expression & Epigenetic Silencing of MicroRNA for Predicting Therapeutic Response and Prognosis of HPV-negative HNSCC. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT03953443 (accessed on 26 June 2022).
- Hemopurifier Plus Pembrolizumab in Head and Neck Cancer. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04453046 (accessed on 26 June 2022).
- Neoadjuvant Nivolumab for Oral Cancer Combined With FDG and Anti-PD-L1 PET/CT Imaging for Response Prediction. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT03843515 (accessed on 26 June 2022).
- Study on the Interplay Between Twist1 and Other EMT Regulators Through microRNA-29 Family. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT01927354 (accessed on 26 June 2022).
- The Role of microRNA-29b in the Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT02009852 (accessed on 26 June 2022).
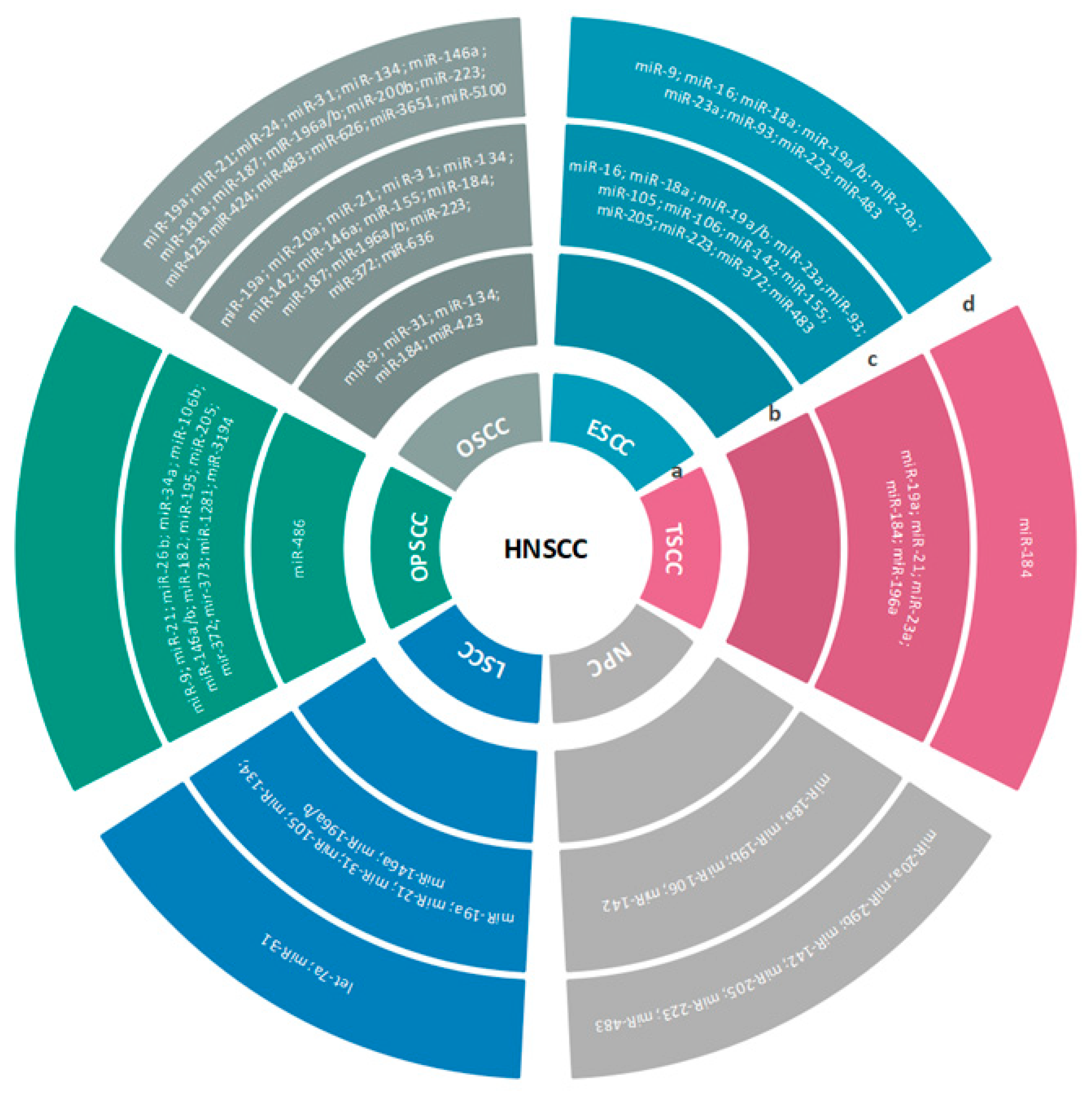
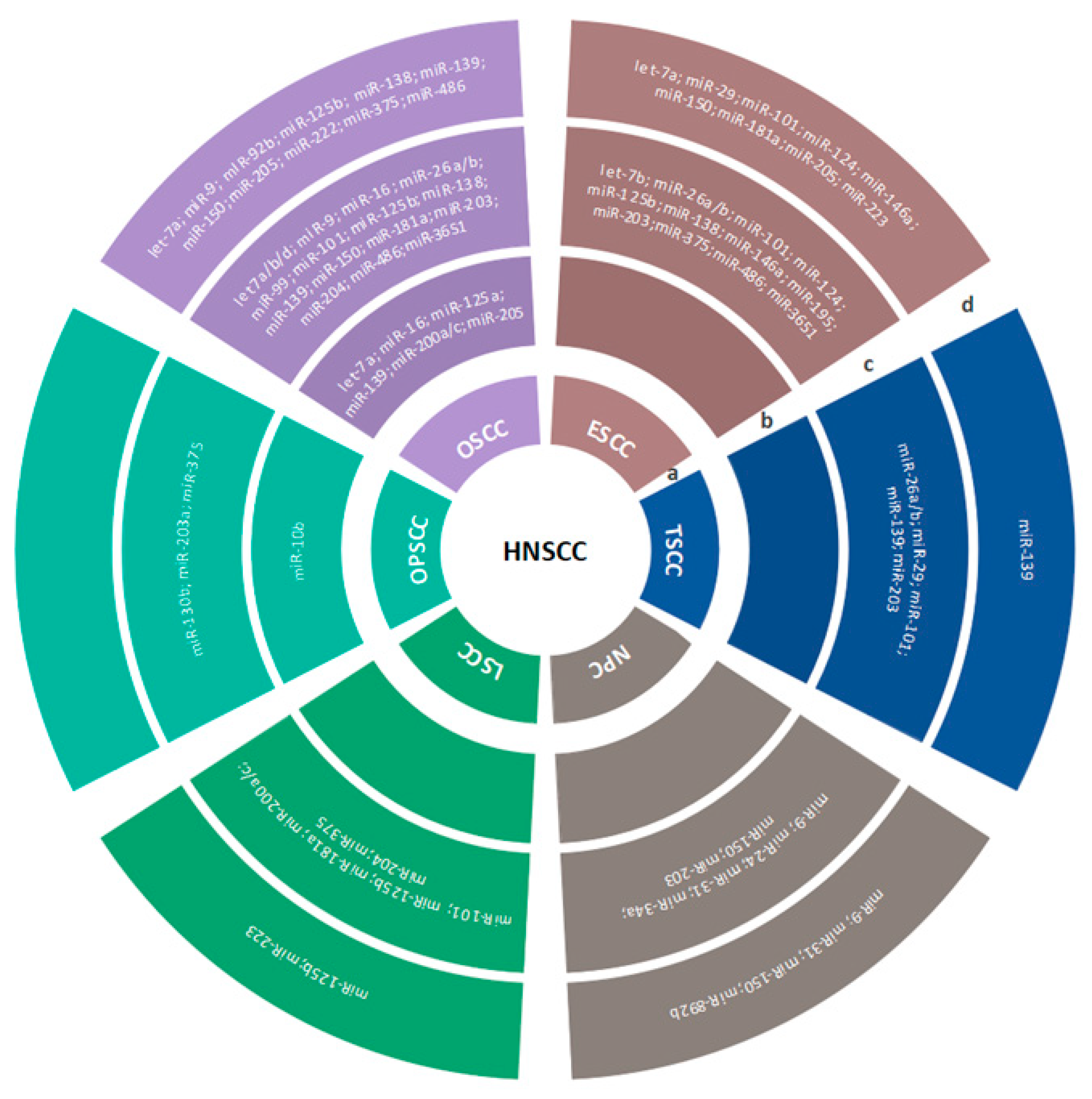

| miRNA | Tumor Site | Sample Type | Biomarker Role | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| let-7a | LSCC | Serum | Diagnosis | [298] |
| miR-9 | OSCC | Saliva | Prognosis and diagnosis | [299] |
| ESCC | Plasma | Prognosis and diagnosis | [300] | |
| OPSCC | Tumor tissue | Recurrence and detection of HPV+ patients | [301] | |
| miR-16 | ESCC | Tumor tissue/serum | Early detection and prognosis | [278,302] |
| miR-18a | NPC | Tumor tissue | Prediction metastasis and therapeutic target | [303] |
| ESCC | Tumor tissue/plasma | Prognosis, detection, and disease monitoring | [304,305,306] | |
| miR-19a | OSCC | Serum/tumor tissue | Diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy | [115,307] |
| TSCC | Tumor tissue | Prognosis | [308] | |
| ESCC | Plasma/tumor tissue | Early detection and prediction of progression-free and overall survival | [304,309] | |
| LSCC | Tumor tissue | Prognosis and differential diagnosis | [310] | |
| miR-19b | ESCC | Plasma/tumor tissue | Prognosis and metastasis prediction | [311,312] |
| NPC | Tumor tissue | Prediction reduced patient survival and therapeutic target | [313,314] | |
| miR-20a | ESCC | Serum | Diagnosis | [315] |
| NPC | Serum/plasma | Detection and prognosis | [316,317] | |
| OSCC | Tumor tissue | Prognosis | [162] | |
| miR-21 | OSCC | Tumor tissue/plasma | Prognosis | [36,56,57] |
| LSCC | Tumor tissue | Prognosis and prediction of lymph node metastasis | [34] | |
| TSCC | Tumor tissue | Prediction of chemoresistance | [59] | |
| OPSCC | Tumor tissue | Prediction and therapy | [318] | |
| miR-23a | ESCC | Tumor tissue/plasma | Prognosis and prediction of chemoresistance | [261,264] |
| TSCC | Tumor tissue | Prediction of chemoresistance | [265] | |
| miR-24 | OSCC | Plasma | Prognosis | [319] |
| miR-26b | OPSCC | Tumor tissue | Prediction and therapy | [318] |
| miR-29b | NPC | Serum | Prognosis | [320] |
| miR-31 | OSCC | Tumor tissue/plasma/saliva | Prognosis and diagnosis, early detection marker, and disease monitoring | [46,148,154] |
| HNSCC | Tumor tissue/serum | Prognosis and diagnosis | [147,321] | |
| LSCC | Plasma/tumor tissue | Early detection | [155] | |
| miR-34a | OPSCC | Tumor tissue | Detection and HPV stratification | [109] |
| miR-93 | ESCC | Tumor tissue/serum | Prognosis and prediction of metastasis and radiotherapy | [322,323] |
| miR-105 | ESCC/LSCC | Tumor tissue | Prognosis | [324,325] |
| miR-106 | ESCC | Tumor tissue | Diagnosis | [11,326] |
| OPSCC | Tumor tissue | Prediction and therapy | [318] | |
| miR-125b | NPC | Tumor tissue | Prognosis | [327] |
| miR-134 | OSCC | Plasma/serum/saliva/tumor tissue | Metastasis detection, prognosis, and diagnosis | [299,328] |
| LSCC | Tumor tissue | Prognosis and targeted therapy | [329] | |
| HNSCC | Tumor tissue/plasma | Prediction of poor survival | [330] | |
| miR-142 | HNSCC | Plasma/tumor tissue | Prognosis and therapy monitoring, discrimination of HPV-positive patients | [245,331] |
| ESCC/OSCC | Tumor tissue | Prognosis | [274,332] | |
| NPC | Tumor tissue/serum | Potential therapy target, prognosis, and prediction of metastasis | [333,334] | |
| miR-146a | OSCC/LSCC | Tumor tissue | Prognosis | [7] |
| OSCC | Plasma | Disease detection | [242] | |
| miR-146a/b | OPSCC | Tumor tissue | Prediction and therapy | [318] |
| miR-155 | HNSCC | Plasma/serum/tumor tissue | Prognosis and therapy | [64,229] |
| ESCC, OSCC | Tumor tissue | Diagnosis and prognosis and therapy target | [224,226] | |
| miR-181a | OSCC | Plasma | Prognosis of lymph node metastasis | [211] |
| miR-182 | OPSCC | Tumor tissue | Prognosis | [335] |
| miR-184 | TSCC | Tumor tissue/plasma | Early detection | [336,337] |
| OSCC | Tumor tissue/saliva | Diagnosis and prognosis | [338,339] | |
| miR-186 | HNSCC | Plasma | Prognosis and therapy monitoring | [331] |
| miR-187 | OSCC | Tumor tissue/plasma | Diagnosis and metastasis prediction | [340,341] |
| miR-195 | HNSCC | Tumor tissue/plasma | Prognosis and therapy monitoring | [331] |
| OPSCC | Tumor tissue | Prediction and therapy | [318] | |
| miR-196a | OSCC | Tumor tissue/plasma | Diagnosis, early detection, and prediction of recurrence and patients’ survival | [57,171,175] |
| HNSCC | Tumor tissue | Prognosis and response to radiotherapy | [173] | |
| LSCC | Tumor tissue | Diagnosis and therapy | [180] | |
| TSCC | Tumor tissue | Prediction of lymph node metastasis | [179] | |
| miR-196b | LSCC | Tumor tissue | Prognosis and potential therapeutic target | [176,177] |
| OSCC | Plasma | Early detection | [171] | |
| miR-200b | OSCC | Plasma | Diagnosis | [342] |
| miR-203 | HNSCC | Tumor tissue | Diagnosis and metastasis detection | [164,343] |
| miR-205 | HNSCC | Tumor tissue/plasma | Prognosis, diagnosis, and metastasis detection | [343,344,345] |
| ESCC | Tumor tissue | Diagnosis and therapy | [346,347] | |
| NPC | Plasma/serum | Disease detection | [316,348] | |
| OPSCC | Tumor tissue | Prognosis and HPV stratification | [335] | |
| miR-223 | OSCC | Tumor tissue/serum | Prognosis and therapy target | [349,350] |
| NPC | Serum | Prognosis and detection | [351] | |
| ESCC | Tumor tissue/serum/plasma | Prognosis and diagnosis | [305,352] | |
| HNSCC | Tumor tissue/plasma | Therapy and disease monitoring | [36] | |
| miR-372 | OSCC | Tumor tissue | Prognosis and therapy resistance | [162] |
| ESCC | Tumor tissue | Prognosis | [353] | |
| OPSCC | Tumor tissue | Prognosis and metastasis detection | [354] | |
| miR-373 | OPSCC | Tumor tissue | Metastasis detection | [354] |
| miR-374b | HNSCC | Plasma | Prognosis and disease monitoring | [331] |
| miR-423 | OSCC | Plasma/saliva | Early detection and disease monitoring | [355,356] |
| miR-424 | OSCC | Serum | Detection | [357] |
| miR-483 | OSCC | Serum | Diagnosis and prognosis | [358] |
| ESCC | Tumor tissue/serum | Prognosis and therapy target | [359,360,361] | |
| NPC | Plasma | Prognosis | [362] | |
| miR-486 | OPSCC | Saliva | Detection and early diagnosis | [363] |
| miR-626 | OSCC | Serum/tumor tissue | Prognosis | [364,365] |
| miR-1281 | OPSCC | Tumor tissue | Therapy target and metastasis detection | [366] |
| miR-3194 | OPSCC | Tumor tissue | HPV patients’ stratification, metastasis detection, and therapy target | [366] |
| miR-3651 | OSCC | Whole blood | Prognosis, metastasis monitoring, and detection of the recurrence | [367,368] |
| miR-5100 | OSCC | Serum | Prognosis | [364] |
| miRNA | Tumor Site | Sample | Biomarker Role | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| let-7a | HNSCC/OSCC | Saliva/tumor tissue | Early detection and poor prognosis | [117,369] |
| ESCC | Serum | Diagnosis | [315] | |
| let-7b | ESCC/OSCC | Tumor tissue | Therapy target | [370] |
| let-7d | HNSCC/OSCC | Tumor tissue | Progression | [112,114] |
| miR-9 | NPC | Tumor tissue/plasma | Recurrence, metastasis, and disease monitoring | [194,371] |
| OSCC | Tumor tissue/serum | Prognosis | [197,372] | |
| HNSCC | Tumor tissue | Prediction and therapy resistance | [198,373] | |
| miR-10b | OPSCC | Saliva | Detection | [363] |
| miR-16 | OSCC | Tumor tissue | Tumor suppression and prognosis | [273,275] |
| OSCC | Saliva | Early diagnosis | [276] | |
| miR-24 | NPC | Tumor tissue | Prognosis of recurrence, radioresistance | [374] |
| miR-26a | ESCC | Tumor tissue | Prediction of metastasis | [375] |
| TSCC | Tumor tissue | Prognosis | [376] | |
| miR-26b | HNSCC | Plasma/Serum | Early detection, prognosis, and therapeutic evaluation | [41,64] |
| miR-26a/b | ESCC/OSCC/TSCC | Tumor tissue | Prevention and therapeutic target | [377,378,379] |
| miR-29 | TSCC | Tumor tissue | Progression and therapy target | [295] |
| ESCC | Serum | Prediction and radioresistance | [297] | |
| miR-31 | NPC | Peripheral blood | Tumor suppression, early diagnosis, and therapeutic target | [151] |
| miR-34a | HNSCC | Tumor tissue | Tumor suppression, diagnosis, and therapeutic target | [104,105] |
| NPC | Tumor tissue | Prognosis | [110] | |
| miR-92b | OSCC | Plasma | Metastasis detection | [42] |
| miR-93 | HNSCC | Saliva | Radiotherapy monitoring | [134] |
| miR-99 | OSCC | Tumor tissue/serum | Clinical outcome, early detection of disease, and prognosis | [75,87] |
| HNSCC | Plasma | Prognosis | [36] | |
| miR-101 | HNSCC/ESCC | Tumor tissue/serum | Diagnosis and prediction of metastasis | [42,380,381] |
| OSCC | Tumor tissue | Prognosis and therapeutic target | [162,382] | |
| TSCC/LSCC | Tumor tissue | Diagnosis and therapeutic target | [383] | |
| miR-124 | NPC/ESCC | Tumor tissue/plasma | Prognosis and chemosensitivity | [371,384,385] |
| miR-125a | OSCC | Saliva | Diagnosis and prediction | [133,134] |
| HNSCC | Tumor tissue | Prognosis and therapy target | [166] | |
| miR-125b | OSCC/HNSCC | Serum/tumor tissue | Prognosis, early diagnosis, and prediction Development and progression | [83,116,162] |
| LSCC | Tumor tissue/plasma | Early detection and progression | [159,163] | |
| ESCC | Tumor tissue | Prognosis | [161] | |
| miR-130b | OPSCC | Tumor tissue | Progression and radioresistance | [386] |
| miR-139 | OSCC/TSCC | Saliva/tumor tissue/serum | Prognosis, early detection, disease monitoring, therapeutic targeτ | [116,387,388,389] |
| miR-146a | ESCC | Tumor tissue/serum | Tumor suppression and prognosis | [244] |
| miR-138 | OSCC/ESCC | Serum/tumor tissue | Early detection, metastasis, and prognosis | [357,390,391] |
| miR-150 | ESCC/OSCC | Plasma/tumor tissue | Prediction of overall survival and metastasis and early detection | [328,355,392] |
| NPC | Tumor tissue/serum | Diagnosis, prognosis, personalized treatment, and prediction of metastasis | [348,393,394] | |
| miR-181a | OSCC | Tumor tissue | Progression | [395] |
| LSCC | Tumor tissue | Early diagnosis and treatment target | [210,396] | |
| ESCC | Plasma/serum | Diagnosis and prognosis | [214,215] | |
| miR-195 | ESCC | Tumor tissue | Diagnosis, patient classification, and prognosis | [397,398] |
| miR-200a | HNSCC/OSCC | Saliva | Detection and radiotherapy monitoring | [133,134] |
| miR-200a/c | LCSS | Tumor tissue | Prognosis and disease recurrence | [130] |
| OSCC | Saliva/oral rinse | Disease detection | [63] | |
| miR-203 | ESCC | Tumor tissue | Prognosis and detection of metastasis | [390,399] |
| OPSCC | Tumor tissue | Prediction and therapy | [318] | |
| OSCC/TSCC/NPC | Tumor tissue | Prediction and radiotherapy resistance | [400,401] | |
| miR-204 | HNSCC | Tumor tissue | Prognosis and therapeutic target | [402] |
| OSCC/LSCC | Tumor tissue | Prognosis of overall survival and therapeutic target | [175,403,404] | |
| miR-205 | OSCC/ESCC | Saliva/serum | Diagnosis, prognosis, and disease monitoring | [299,335,405] |
| miR-222 | OSCC | Plasma | Early detection | [355] |
| miR-223 | LSCC | Serum | Diagnosis | [298] |
| miR-375 | HNSCC | Tumor tissue | Prognosis and prediction of metastasis | [68,406] |
| LSCC/ESCC | Tumor tissue | Overall survival and prognosis | [34,68] | |
| OSCC | Plasma | Monitoring recurrence after surgery | [42] | |
| OPSCC | Tumor tissue | Prognosis | [407] | |
| miR-486 | OSCC | Plasma/saliva/tumor tissue | Early diagnosis and recurrence | [42,408,409] |
| ESCC | Tumor tissue | Prognosis | [410] | |
| miR-892b | NPC | Plasma | Monitor recurrence and metastasis | [371] |
| miR-3651 | OSCC/ESCC | Tumor tissue | Diagnosis and prognosis | [411,412] |
| miRNA | Function | Experimental Set-Up | Target Gene or Signaling Pathway | HNC Subtypes | References | Cellular Functions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-21 | Oncogenic | In vitro | PTEN | OSCC | [45] | Proliferation, invasion, metastasis, apoptosis |
| p53 | [46] | |||||
| p63 | [47] | |||||
| PDCD4 | [48,49,50] | |||||
| miR-375 | Onco-suppressor | In vitro | XPR1 | ESCC | [61] | Proliferation, migration, invasion |
| HNF1β | LSCC | [65] | ||||
| PDK1 | NPC | [60] | ||||
| USP1 | [66] | |||||
| miR-99 | Onco-suppressor | In vitro | IGF1R mTOR | HNSCC | [77] | Proliferation, migration, invasion |
| miR-34a | Onco-suppressor | In vitro | FLOT-2 MEK/ERK1/2 | HNSCC | [105] | Proliferation, migration, invasion, EMT |
| SATB2 | OSCC | [413] | ||||
| let-7 family | Onco-suppressor | In vitro | Nanog, K-RAS, CASPASE3, IL-8 | HNSCC | [113,123,124] | Proliferation, metastasis, chemosensitivity |
| miR-200 family | Onco-suppressor | In vitro | ZEB1/2, BMI1 | OSCC | [135,414] | Proliferation, migration, metastasis, malignant CSC-like properties |
| miR-31 | Oncogenic | In silico | FIH | HNSCC | [149] | Angiogenesis |
| miR-125a | Onco-suppressor/Oncogenic | In vitro | ERBB2 and ERBB3/CCR7 | HNSCC | [166,415,416] | Proliferation, metastasis, invasion |
| miR-125b | Onco-suppressor | In vitro | HMGA2 | ESCC | [161] | Proliferation, migration, invasion |
| miR-196a | Oncogenic | In vitro | ANXA1, MAMDC2, HOXB8, p27 (CDKN1B) | HNSCC/OSCC | [173,174] | Proliferation, migration, invasion, EMT, radioresistance |
| miR-196b | Oncogenic | In vitro | SOCS2, PCDH-17, ANXA1 | LSCC/HNSCC | [176,177,178] | proliferation, invasion, apoptosis |
| miR-9 | Onco-suppressor | In vitro | CXCR4, Wnt/β-catenin | HNSCC | [373] | Proliferation, colony formation |
| miR-181a | Onco-suppressor | In vitro | MAX/miR-181a/NPM1 pathway, ATF2 | LSCC | [210,396] | Proliferation, colony formation, migration, apoptosis |
| LNC RNA CCAT1 | OSCC/NPC | [395,396] | Proliferation, migration, drug resistance | |||
| miR-155 | Oncogenic | In vitro | CDC73, ARID2 | OSCC | [225,229] | Proliferation, invasion, apoptosis |
| mir-146a | Oncogenic | In vitro | IRAK1-NF-κB | ESCC OSCC | [246,417] | Proliferation, apoptosis invasion |
| Onco-suppressor | In vitro | Snail Vimentin E-cadherin | ESCC | [244,418] | ||
| miR-23a | Onco-suppressor | In vitro | SIX1 | OPSCC | [256] | Growth, proliferation, chemoresistance, invasion |
| Oncogenic | In vitro | HIF1AN | OSCC | [261] | ||
| Oncogenic | In vitro | PTEN | ESCC | [262] | ||
| miR-16 | Onco-suppressor | In vitro/in vivo | TLK1, BCL2L2 | OSCC | [273,275] | Proliferation, viability, apoptosis |
| BPDE/RAR-β2 | ESCC | [278] | ||||
| miR-29 | Onco-suppressor | In vitro/in vivo | LAMC2 ITGA6 | HNSCC | [291] | Proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, EMT |
| ITGB1 | HNSCC | [292] | ||||
| LOXL2 | HNSCC | [419] | ||||
| DNMT3B | HNSCC | [420] | ||||
| Sp1/PTEN/p-AKT | TSCC | [295] | ||||
| TIAM1 | NPC | [294] |
| miRNA | Tumor Site | Sample Type | Biomarker Role | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-383, miR-615, miR-877 | HNSCC | Serum | Diagnostic | [277] |
| miR-9, miR-134, miR-191 | HNSCC | Saliva | Diagnostic | [191] |
| miR-21-5p, miR-28-3p, miR-142-3p, miR-191-5p, miR-186-5p, miR-197-3p, miR-425-5p, miR-590-5p | HNSCC | Plasma | Diagnostic | [331] |
| miR-204-5p, miR-499a-5p, miR-498-5p, miR-4714-3p, miR-30a-5p, miR-1-5p, miR-548f-3p, miR-518a-3p, miR-155-3p, miR-365a-5p, miR-196b-5p | HNSCC | (Bioinformatic analysis/TCGA) | Prognostic | [24] |
| miR-99a-5p, miR-758-5p, miR-329-3p, miR-137-3p, miR-1229-3p, miR-3187-3p | HNSCC | Tumor tissue | Prognostic | [427] |
| let-7c, miR-125b-2, miR-129-1, miR-337, miR-654, miR-99a | HNSCC | Tumor tissue (TCGA) | Prognostic | [428] |
| miR-21-3p, miR-21-5p, miR-96-5p, miR-429 | HNSCC | Tumor tissue | Prognostic | [429] |
| let-7g-3p, miR-6508-5p, miR-210-5p, miR-4306, miR-7161-3p | HNSCC | Tumor tissue | Prognostic | [430] |
| miR-142-3p, miR-186-5p, miR-195-5p, miR-374b-5p, miR-574-3p | HNSCC | Plasma | Prognostic | [331] |
| miR-499a, miR-548k, miR-3619, miR-99a, miR-137, miR-3170, miR-654 | HNSCC | Tumor tissue (TCGA) | Prognostic | [431] |
| miR-16, miR-29b, miR-150, miR-1254, let-7e | HNSCC | Cell lines (TCGA) | Predictive (radiotherapy) | [432] |
| miR-99a, miR-31, miR-410, miR-424, miR-495 | HNSCC | Tumor tissue (TCGA) | Predictive (radiotherapy) | [433] |
| miR-6510-3p, miR-34c-5p | OSCC | Tumor tissue | Diagnostic | [7] |
| miR-31-5p, miR-21-5p, miR-125b-5p, miR-99a-5p, miR-100-5p, let-7c-5p, miR-24-3p, miR-30c | OSCC | Saliva (Oral Swirls) | Diagnostic | [434] |
| miR-196a, miR-196b | OSCC | Plasma | Diagnostic | [171] |
| miR-218, miR-125b, let-7g | OSCC | Tumor tissue | Prognostic | [435] |
| miR-127-3p, miR-4736, miR-655-3p | OSCC | Tumor tissue | Prognostic | [436] |
| miR-21, miR-181b, miR-345 | OSCC | Tumor tissue | Susceptibility/risk | [437] |
| miR-21, miR-375 | TSCC | Oral (Brush) Cytology, tumor tissue | Diagnostic (screening) | [49] |
| miR-142-3p, miR-31, miR-146a, miR-26b, miR-24, miR-193b | OPSCC | Tumor tissue | Prognostic | [438] |
| miR-27a-3p, miR-455-5p, miR-203a-3p, miR-584-5p, miR-24-3p, miR-548k, miR-126-3p, miR-126-5p, miR-365a-5p, miR-98-5p, miR-151b, miR-361-3p, miR-374c-5p, miR-150-5p, miR-374b-5p, miR-107, miR-125b-5p, miR-1287-5p, miR-146a-5p, miR-106a-5p, miR-15b-5p, miR-20b-5p, miR-532-3p, miR-361-5p, miR-363-3p, miR-625-3p | OPSCC | Tumor tissue | Prognostic | [439] |
| miR-107, miR-151, miR-492 | OPSCC | Tumor tissue | Prognostic | [440] |
| miR-20b, miR-107, miR-151, miR-182, miR-361 | OPSCC | Tumor tissue | Prognostic | [440] |
| miR-151, miR-152, miR-324-5p, miR-361, miR-492 | OPSCC | Tumor tissue | Prognostic | [440] |
| miR-449a-5p, miR-6510-3p, miR-133a-5p | LSCC | Tumor tissue | Diagnostic | [7] |
| miR-31-3p, miR-196a-5p | LSCC | Plasma | Diagnostic | [155] |
| miR-200a-3p, miR-30b-5p, miR-4451 | HSCC | Tumor tissue | Prognostic | [441] |
| miR-29c, miR-30e, miR-93 | NPC | Tumor tissue (GEO) | Prognostic | [442] |
| ebv-miR-BART19-3p, miR-135b, miR-141 | NPC | Tumor tissue (GEO)/cell line | Prognostic | [443] |
| miR-142-3p, miR-29c, miR-30e | NPC | (Bioinformatic analysis/GEO) | Prognostic | [334] |
| miRNA | Tumor Site | Sample Type | Biomarker Role | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-9, miR-134, miR-196b, miR-210, miR-455 | HNSCC | Saliva | Early-stage detection and HPV+ patients’ stratification | [190] |
| miR-191, miR-196b, miR-210, miR-222 | HNSCC | Saliva | HPV+ patients’ stratification | [190] |
| miR-378a-3p, miR-16-1-3p, miR-493-3p, miR-380-5p, miR-376c-3p, miR-338-5p | HNSCC | Tumor tissue (TCGA/GDAC) | The prognosis and detection of HPV+ patients | [446] |
| miR-324-5p, miR-4764-3p, miR-107, miR-1234, miR-3144-3p, miR-3176, miR-3177-3p, miR-4267, miR-4418, miR-615-3p, miR-668, miR-99b-3p, miR-675-3p, miR-584-5p, miR-212-3p, miR-18b-5p, miR-18a5p, miR-138-1-3p, miR-135b-5p, miR-1246, miR-4764-3p, miR-857, miR-7-2-3p | OPSCC | Tumor tissue | The detection of HPV+ patients | [456] |
| miR-363-3p, miR-551b-3p, miR-20b-5p, miR-20b-3p, miR-143-3p, miR-106a-5p, miR-9-5p (miR-9-1), miR-9-5p (miR-9-2), miR-9-5p (miR-9-3), miR-99a-3p, miR-99a-5p, miR-9-3p (miR-9-1), miR-193a-5p, let-7b-3p | OPSCC | Cell line | Early detection and patient stratification | [457] |
| miR-206/miR-494-3p, U6 snRNA/miR-150-5p, miR-532-3p/miR-574-3p, miR-125a-5p/miR-193b-3p, miR-1274b/miR-27a-3p, miR-494-3p/miR-150-5p, miR-193a-5p/U6 snRNA, miR-27a-3p/miR-93-5p, ath-miR-159a/miR-152-3p, ath-miR-159a/miR-494-3p, miR-375-3p/miR-483-5p | OPSCC | Serum (EVs) | The detection of HPV+ patients | [458] |
| Identifier | Official Title | Clinical Phase | Target miRNAs | Sample Type | Purpose | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT04305366 | MicroRNA Markers in Head and Neck Cancers | N/A | N/D | Fine needle aspiration biopsy, serum, saliva | To investigate the miRNA signature of samples and to develop biomarkers for surveillance of HNSCC patients. | [459] |
| NCT02869399 | A Randomized Phase II Study for Tertiary Prevention of Squamocellular Cancer of Head and Neck (SCCHN) With a Dietary Intervention | II | N/D | Saliva, plasma | To investigate the role of diet as a risk factor for HNSCC recurrence and secondary tumor development, to identify saliva and plasma miRNAs, and to evaluate their change in inflammatory cytokine profile during the course of dietary intervention. | [460] |
| NCT03953443 | INST 1008: Expression and Epigenetic Silencing of MicroRNA for Predicting the Therapeutic Response and Prognosis of HPV- negative Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC) | N/A | N/D | Tumor tissue, normal tissue | To assess the association between miR expression and miR promoter methylation and the response to therapy and prognosis in primary HPV-negative HNSCC patients. | [461] |
| NCT04453046 | Depleting Exosomes to Improve Response to Immune Therapy in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Cancer: An Early Feasibility Phase I Clinical Trial | I | N/D | Blood | To determine whether the use of Hemopurifier before treatment with pembrolizumab is low-risk and well-tolerated by the patients and whether it leads to reduced levels of exosomes in the blood and to identify immunoinhibitory proteins and miRNA profiles for the evaluation of effectiveness of combination treatment in decreasing immune suppression in patients with recurrent/metastatic HNSCC. | [462] |
| NCT03843515 | Safety and Tolerability of Neoadjuvant Nivolumab for Locally Advanced Resectable Oral Cancer Combined With [18F] BMS-986192/[18F]-FDG PET Imaging and Immunomonitoring for Response Prediction | I | N/D | Tumor tissue, plasma | To further evaluate tumor PD-L1 expression as a predictive biomarker and to investigate the immunophenotype of the patient and tumor, as well as the presence of neoantigens and other potential biomarkers such as plasma vesicle miRNAs. | [463] |
| NCT01927354 | Observational Study on the Investigation of the Molecular Mechanism and Clinical Significance of the Interplay Between Twist1 and Other EMT Regulators Through microRNA-29 Family | N/A | miR-29 family | Tumor tissue | To delineate the regulatory mechanism of the Twist1-miR-29s-SIN3A axis, to investigate the molecular interplay between Twist1 and Snail through Twist1-miR-29s-SIN3A signal pathway, and to elucidate the molecular basis and pathophysiologic significance of Twist1-Snail interaction under hypoxic environment. | [464] |
| NCT02009852 | The Role of microRNA-29b in the Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma | N/A | miR-29b | Tumor tissue, serum, saliva | To identify a prognostic significance for miR-29b in oral cancer. | [465] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thomaidou, A.C.; Batsaki, P.; Adamaki, M.; Goulielmaki, M.; Baxevanis, C.N.; Zoumpourlis, V.; Fortis, S.P. Promising Biomarkers in Head and Neck Cancer: The Most Clinically Important miRNAs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8257. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158257
Thomaidou AC, Batsaki P, Adamaki M, Goulielmaki M, Baxevanis CN, Zoumpourlis V, Fortis SP. Promising Biomarkers in Head and Neck Cancer: The Most Clinically Important miRNAs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(15):8257. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158257
Chicago/Turabian StyleThomaidou, Arsinoe C., Panagiota Batsaki, Maria Adamaki, Maria Goulielmaki, Constantin N. Baxevanis, Vassilis Zoumpourlis, and Sotirios P. Fortis. 2022. "Promising Biomarkers in Head and Neck Cancer: The Most Clinically Important miRNAs" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 15: 8257. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158257
APA StyleThomaidou, A. C., Batsaki, P., Adamaki, M., Goulielmaki, M., Baxevanis, C. N., Zoumpourlis, V., & Fortis, S. P. (2022). Promising Biomarkers in Head and Neck Cancer: The Most Clinically Important miRNAs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(15), 8257. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158257







