Ciliary Neurotrophic Factor (CNTF) and Its Receptors Signal Regulate Cementoblasts Apoptosis through a Mechanism of ERK1/2 and Caspases Signaling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
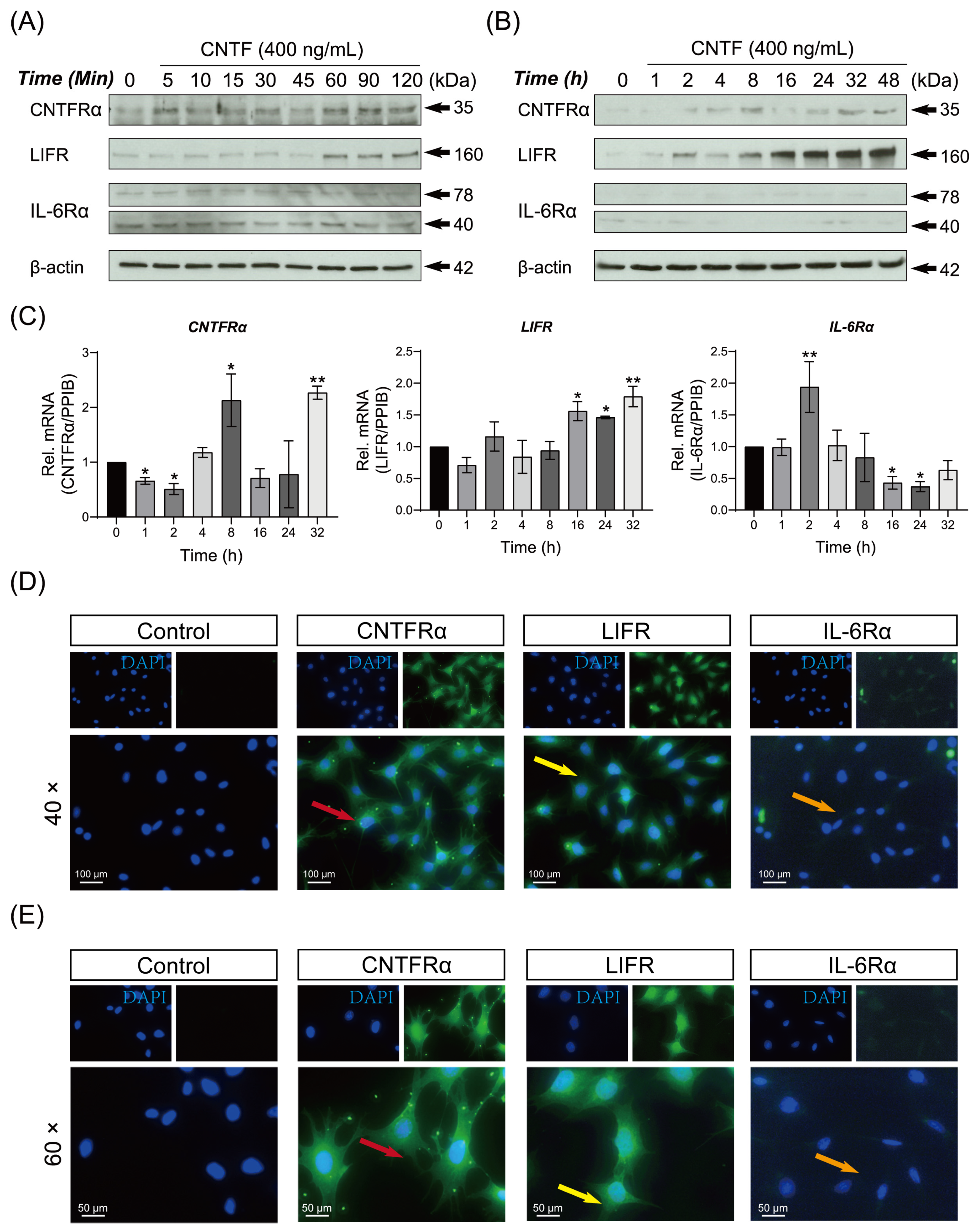
2.1. Ciliary Neurotrophic Factor Facilities the Expression of CNTF-Receptor Complex mRNA and Protein in Cementoblasts
2.2. CNTF Induces Initial Activation of the Cytokine Receptor GP130 and Promotes GP130 Phosphorylation in OCCM-30 Cells
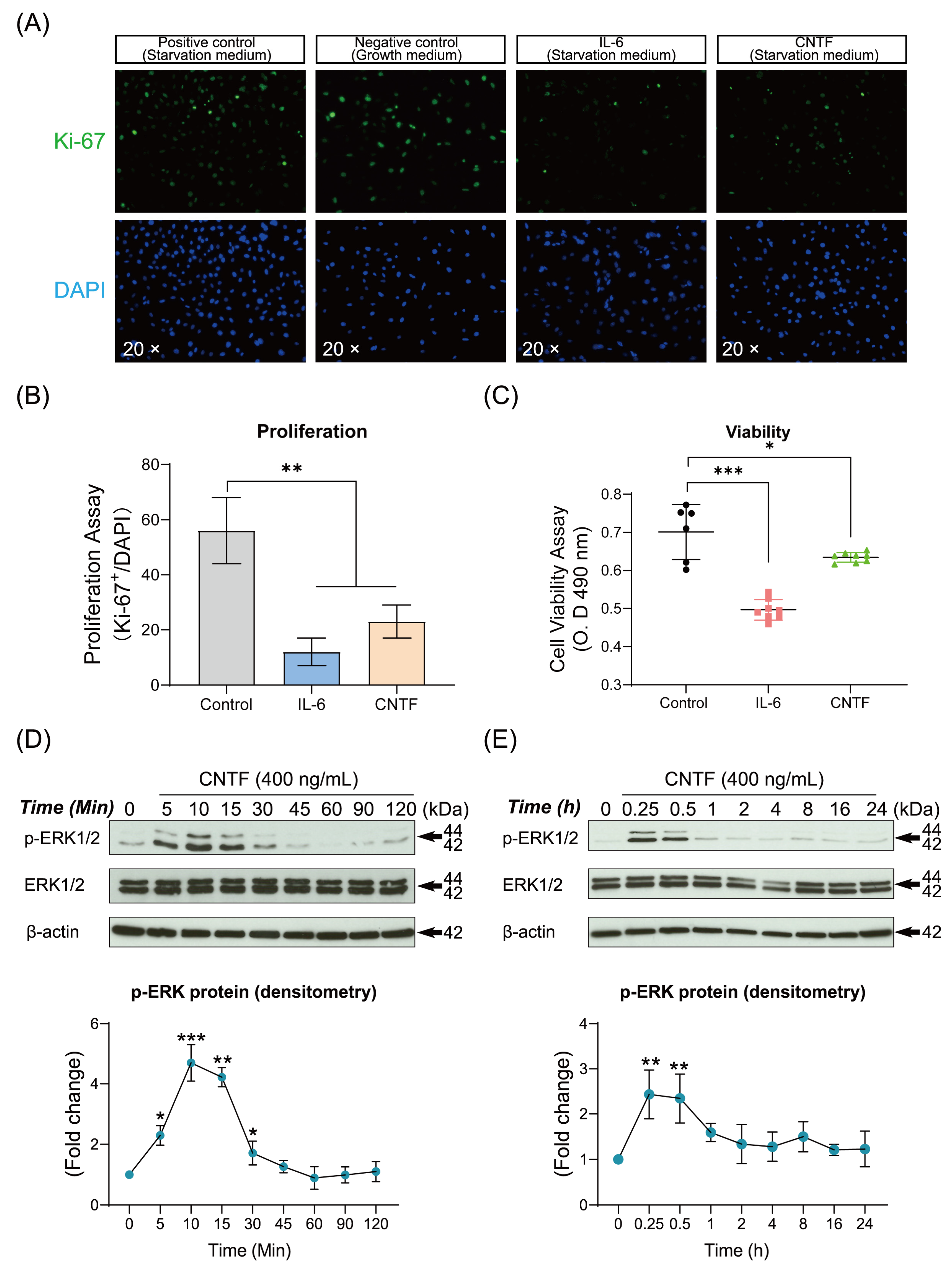
2.3. CNTF Decreases the Cell Viability, Proliferation and Induced Phosphorylated ERK1/2 Expression of Cementoblasts
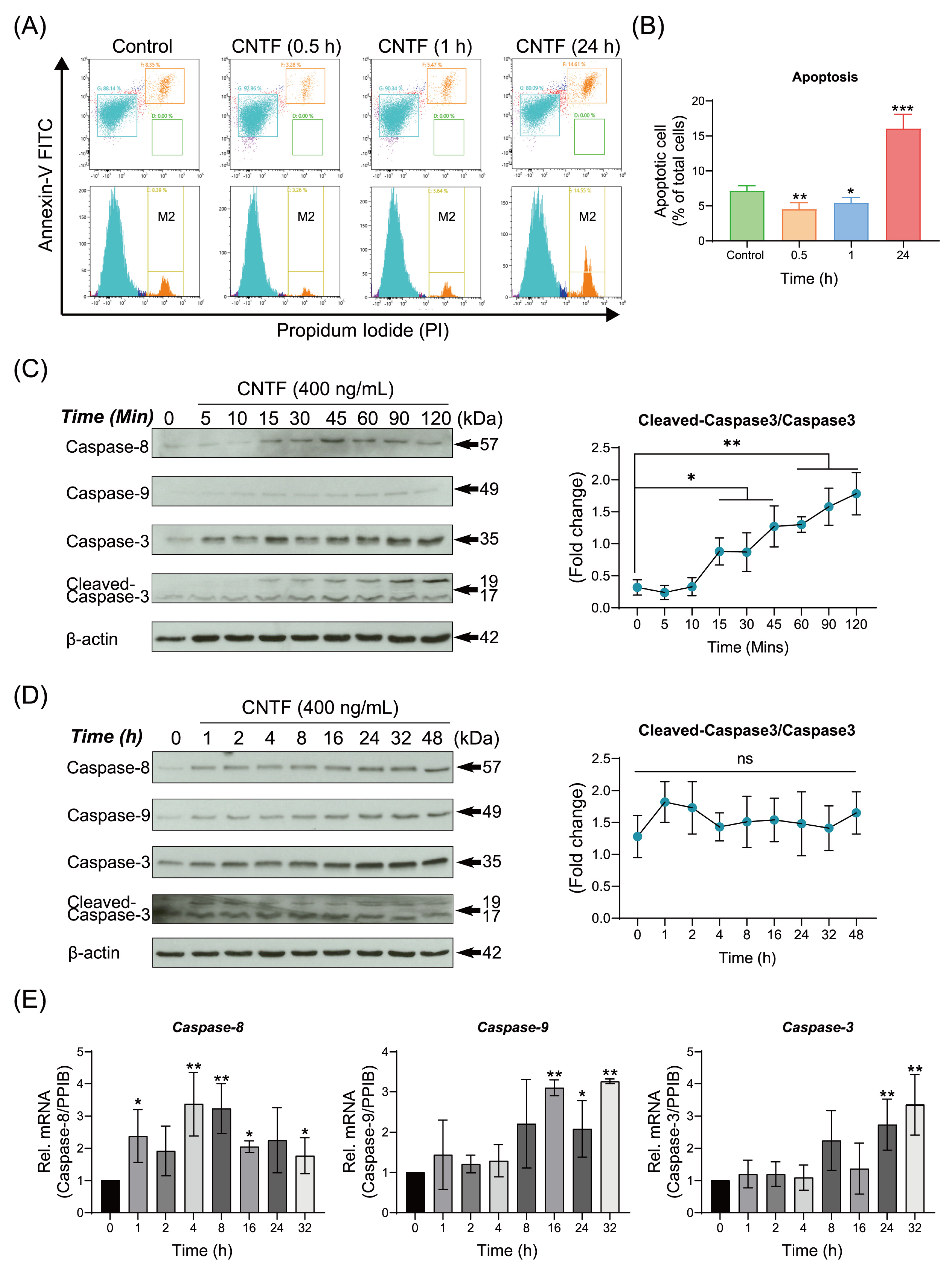
2.4. CNTF Regulates Cementoblasts Apoptosis and Activates the Caspases Signaling Pathway
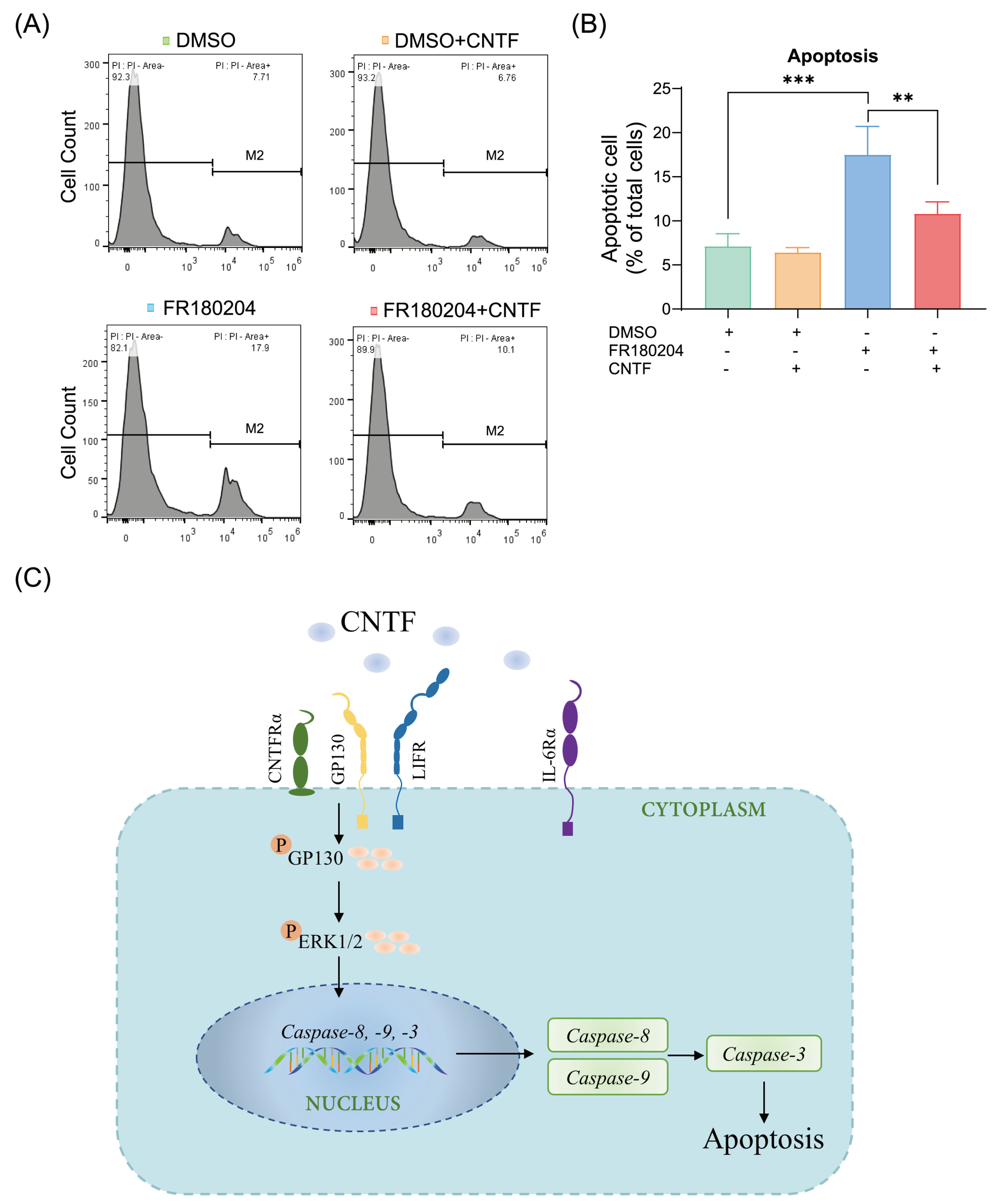
2.5. ERK1/2 Is Involved in the Modulation of CNTF-Induced Apoptosis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Cell Stimulation and Pharmacological Inhibitor
4.3. MTS Viability Assay
4.4. Cell Proliferation Assay
4.5. RNA Isolation, Reverse Transcription and RT-qPCR
4.6. Immunofluorescence (IF)
4.7. Apoptosis Detection with Flow Cytometry Analysis
4.8. Western Blotting (WB)
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stockli, K.A.; Lottspeich, F.; Sendtner, M.; Masiakowski, P.; Carroll, P.; Gotz, R.; Lindholm, D.; Thoenen, H. Molecular cloning, expression and regional distribution of rat ciliary neurotrophic factor. Nature 1989, 342, 920–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.F.; Mismer, D.; Lile, J.D.; Armes, L.G.; Butler, E.T., 3rd; Vannice, J.L.; Collins, F. Purification, cloning, and expression of ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF). Science 1989, 246, 1023–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruttgen, A.; Grotzinger, J.; Kurapkat, G.; Weis, J.; Simon, R.; Thier, M.; Schroder, M.; Heinrich, P.; Wollmer, A.; Comeau, M.; et al. Human ciliary neurotrophic factor: A structure-function analysis. Biochem. J. 1995, 309 Pt 1, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, B.; Kovaleva, M.; Sun, Y.; Regenhard, P.; Matthews, V.; Grotzinger, J.; Rose-John, S.; Kallen, K.J. Signaling of human ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF) revisited. The interleukin-6 receptor can serve as an alpha-receptor for CTNF. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 9528–9535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heinrich, P.C.; Behrmann, I.; Muller-Newen, G.; Schaper, F.; Graeve, L. Interleukin-6-type cytokine signalling through the gp130/Jak/STAT pathway. Biochem. J. 1998, 334 Pt 2, 297–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davis, S.; Yancopoulos, G.D. The molecular biology of the CNTF receptor. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1993, 5, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taga, T.; Kishimoto, T. Gp130 and the interleukin-6 family of cytokines. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1997, 15, 797–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasquin, S.; Sharma, M.; Gauchat, J.-F. Ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF): New facets of an old molecule for treating neurodegenerative and metabolic syndrome pathologies. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015, 26, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perugini, J.; Di Mercurio, E.; Tossetta, G.; Severi, I.; Monaco, F.; Reguzzoni, M.; Tomasetti, M.; Dani, C.; Cinti, S.; Giordano, A. Biological Effects of Ciliary Neurotrophic Factor on hMADS Adipocytes. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steinberg, G.R.; Watt, M.J.; Ernst, M.; Birnbaum, M.J.; Kemp, B.E.; Jorgensen, S.B. Ciliary neurotrophic factor stimulates muscle glucose uptake by a PI3-kinase-dependent pathway that is impaired with obesity. Diabetes 2009, 58, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fantone, S.; Tossetta, G.; Montironi, R.; Senzacqua, M.; Marzioni, D.; Mazzucchelli, R. Ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF) and its receptor (CNTFRalpha) signal through MAPK/ERK pathway in human prostate tissues: A morphological and biomolecular study. Eur. J. Histochem. 2020, 64, 3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezende, L.F.; Vieira, A.S.; Negro, A.; Langone, F.; Boschero, A.C. Ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF) signals through STAT3-SOCS3 pathway and protects rat pancreatic islets from cytokine-induced apoptosis. Cytokine 2009, 46, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, J.; von Bremen, J.; Ruiz-Heiland, G.; Ruf, S. Adiponectin as Well as Compressive Forces Regulate in vitro beta-Catenin Expression on Cementoblasts via Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Activation. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 645005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, J.; von Bremen, J.; Groeger, S.; Ruiz-Heiland, G.; Ruf, S. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha acts as a bridge factor for crosstalk between ERK1/2 and caspases in hypoxia-induced apoptosis of cementoblasts. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 9710–9723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brentnall, M.; Rodriguez-Menocal, L.; De Guevara, R.L.; Cepero, E.; Boise, L.H. Caspase-9, caspase-3 and caspase-7 have distinct roles during intrinsic apoptosis. BMC Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Algeciras-Schimnich, A.; Barnhart, B.C.; Peter, M.E. Apoptosis Dependent and Independent Functions of Caspases. In Madame Curie Bioscience Database; Landes Bioscience: Austin, TX, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, N.; Batt, M.K.; Cronier, B.A.; Jackson, M.C.; Garza, J.L.B.; Trinh, D.S.; Mason, C.O.; Spearry, R.P.; Bhattacharya, S.; Robitz, R.; et al. Ciliary neurotrophic factor receptor regulation of adult forebrain neurogenesis. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 1241–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bellido, T.; Stahl, N.; Farruggella, T.J.; Borba, V.; Yancopoulos, G.D.; Manolagas, S.C. Detection of receptors for interleukin-6, interleukin-11, leukemia inhibitory factor, oncostatin M, and ciliary neurotrophic factor in bone marrow stromal/osteoblastic cells. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 97, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allan, E.H.; Hilton, D.J.; Brown, M.A.; Evely, R.S.; Yumita, S.; Metcalf, D.; Gough, N.M.; Ng, K.W.; Nicola, N.A.; Martin, T.J. Osteoblasts display receptors for and responses to leukemia-inhibitory factor. J. Cell Physiol. 1990, 145, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodan, S.B.; Wesolowski, G.; Hilton, D.J.; Nicola, N.A.; Rodan, G.A. Leukemia inhibitory factor binds with high affinity to preosteoblastic RCT-1 cells and potentiates the retinoic acid induction of alkaline phosphatase. Endocrinology 1990, 127, 1602–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonni, A.; Sun, Y.; Nadal-Vicens, M.; Bhatt, A.; Frank, D.A.; Rozovsky, I.; Stahl, N.; Yancopoulos, G.D.; Greenberg, M.E. Regulation of gliogenesis in the central nervous system by the JAK-STAT signaling pathway. Science 1997, 278, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taga, T. The signal transducer gp130 is shared by interleukin-6 family of haematopoietic and neurotrophic cytokines. Ann. Med. 1997, 29, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGregor, N.E.; Poulton, I.J.; Walker, E.C.; Pompolo, S.; Quinn, J.M.W.; Martin, T.J.; Sims, N.A. Ciliary neurotrophic factor inhibits bone formation and plays a sex-specific role in bone growth and remodeling. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2010, 86, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askmyr, M.; White, K.E.; Jovic, T.; King, H.A.; Quach, J.M.; Maluenda, A.C.; Baker, E.K.; Smeets, M.F.; Walkley, C.R.; Purton, L.E. Ciliary neurotrophic factor has intrinsic and extrinsic roles in regulating B cell differentiation and bone structure. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martens, W.; Bronckaers, A.; Politis, C.; Jacobs, R.; Lambrichts, I. Dental stem cells and their promising role in neural regeneration: An update. Clin. Oral Investig. 2013, 17, 1969–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Xu, S. ERK1/2 MAP kinases in cell survival and apoptosis. IUBMB Life 2006, 58, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, J.; Groeger, S.; Meyle, J.; Ruf, S. MAPK and β-Catenin signaling: Implication and interplay in orthodontic tooth movement. Front. Biosci. 2022, 27, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartel, F.V.; Holl, M.; Arshad, M.; Aslam, M.; Gunduz, D.; Weyand, M.; Micoogullari, M.; Abdallah, Y.; Piper, H.M.; Noll, T. Transient hypoxia induces ERK-dependent anti-apoptotic cell survival in endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2010, 298, C1501-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vondracek, J.; Soucek, K.; Sheard, M.A.; Chramostova, K.; Andrysik, Z.; Hofmanova, J.; Kozubik, A. Dimethyl sulfoxide potentiates death receptor-mediated apoptosis in the human myeloid leukemia U937 cell line through enhancement of mitochondrial membrane depolarization. Leuk. Res. 2006, 30, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egli, R.J.; Sckell, A.; Fraitzl, C.R.; Felix, R.; Ganz, R.; Hofstetter, W.; Leunig, M. Cryopreservation with dimethyl sulfoxide sustains partially the biological function of osteochondral tissue. Bone 2003, 33, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Errico, J.A.; Berry, J.E.; Ouyang, H.; Strayhorn, C.L.; Windle, J.J.; Somerman, M.J. Employing a transgenic animal model to obtain cementoblasts in vitro. J. Periodontol. 2000, 71, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yong, J.; Gröger, S.; Meyle, J.; Ruf, S. Immunorthodontics: Role of HIF-1α in the Regulation of (Peptidoglycan-Induced) PD-L1 Expression in Cementoblasts under Compressive Force. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, J.; von Bremen, J.; Ruiz-Heiland, G.; Ruf, S. Adiponectin Interacts In-Vitro with Cementoblasts Influencing Cell Migration, Proliferation and Cementogenesis Partly Through the MAPK Signaling Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 585346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, J.; Li, P.; Mizrahi, I.K.; Franzen, R.; Groeger, S.; Ruf, S.; Gutknecht, N.; Marques, M.M. Effect of Low-Level Er: YAG (2940 nm) laser irradiation on the photobiomodulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase cellular signaling pathway of rodent cementoblasts. Front. Biosci. 2022, 27, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, J.; Groeger, S.; Ruf, S.; Ruiz-Heiland, G. Influence of leptin and compression in GAS-6 mediated homeostasis of periodontal ligament cell. Oral Dis. 2021; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, J.; Groeger, S.E.; Ruiz-Heiland, G.; Ruf, S. Selection and validation of reference gene for RT-qPCR studies in co-culture system of mouse cementoblasts and periodontal ligament cells. BMC Res. Notes 2022, 15, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, L.C.; Marfell, B.J.; Scott, A.P.; Waterhouse, N.J. Quantitation of Apoptosis and Necrosis by Annexin V Binding, Propidium Iodide Uptake, and Flow Cytometry. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2016, 2016, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yong, J.; Groeger, S.; von Bremen, J.; Ruf, S. Ciliary Neurotrophic Factor (CNTF) and Its Receptors Signal Regulate Cementoblasts Apoptosis through a Mechanism of ERK1/2 and Caspases Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8335. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158335
Yong J, Groeger S, von Bremen J, Ruf S. Ciliary Neurotrophic Factor (CNTF) and Its Receptors Signal Regulate Cementoblasts Apoptosis through a Mechanism of ERK1/2 and Caspases Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(15):8335. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158335
Chicago/Turabian StyleYong, Jiawen, Sabine Groeger, Julia von Bremen, and Sabine Ruf. 2022. "Ciliary Neurotrophic Factor (CNTF) and Its Receptors Signal Regulate Cementoblasts Apoptosis through a Mechanism of ERK1/2 and Caspases Signaling" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 15: 8335. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158335
APA StyleYong, J., Groeger, S., von Bremen, J., & Ruf, S. (2022). Ciliary Neurotrophic Factor (CNTF) and Its Receptors Signal Regulate Cementoblasts Apoptosis through a Mechanism of ERK1/2 and Caspases Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(15), 8335. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158335





