Naegleria fowleri Cathepsin B Induces a Pro-Inflammatory Immune Response in BV-2 Microglial Cells via NF-κB and AP-1 Dependent-MAPK Signaling Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Recombinant NfCB (rNfCB)
2.2. Cultivation of BV-2 Microglial Cells and Treatment of rNfCB
2.3. Analysis of the Pro-Inflammatory Immune Response in BV-2 Microglial Cells Induced by rNfCB
2.4. Investigation of MAPK Signaling Pathways in BV-2 Microglial Cells Stimulated by rNfCB
2.5. Investigation of NF-κB Involvement in BV-2 Microglial Cells Stimulated by rNfCB
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. rNfCB Does Not Induce Cytotoxicity to BV-2 Microglial Cells
3.2. rNfCB Induces the Expression of TLR-2, TLR-4, and MyD88 in BV-2 Microglial Cells
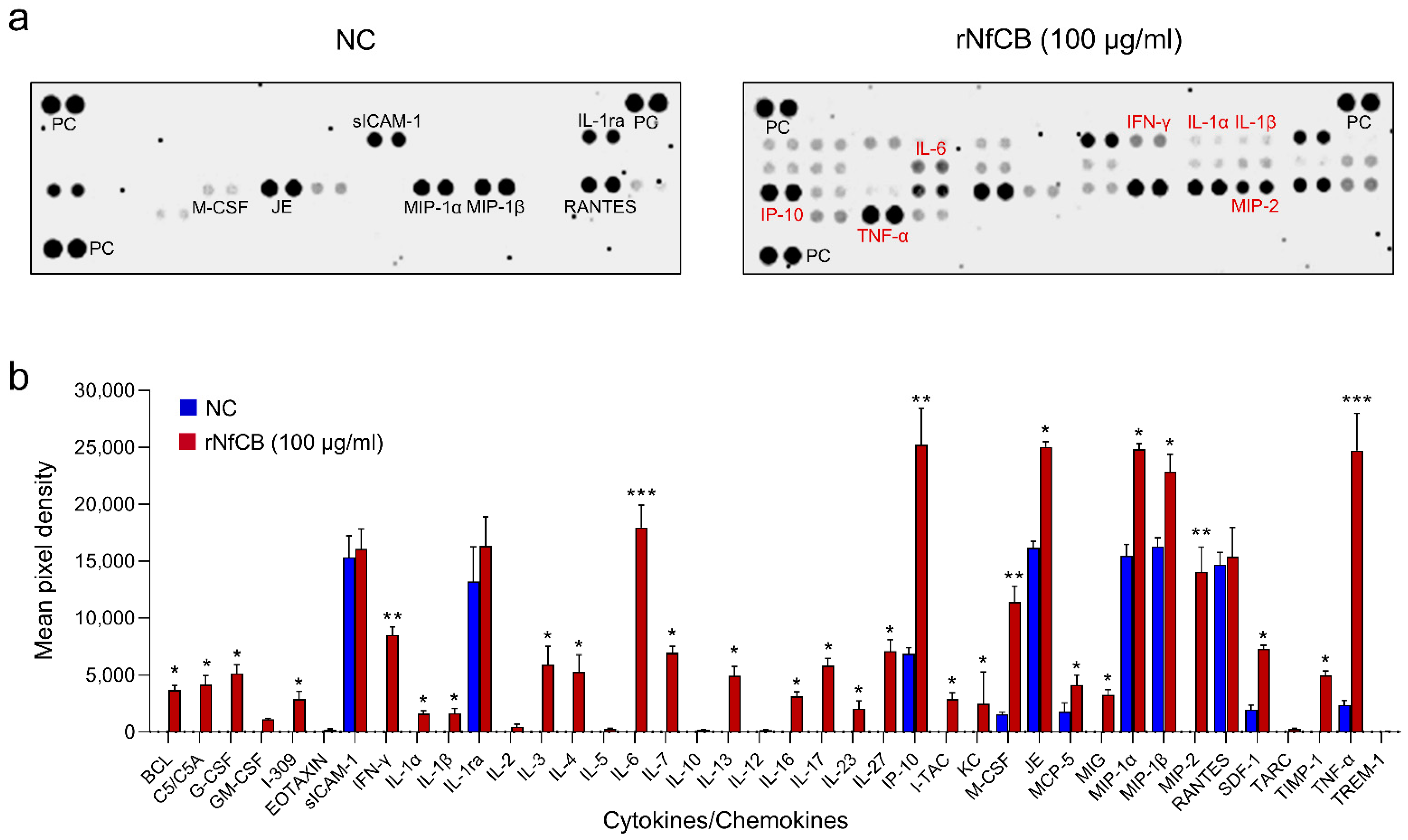
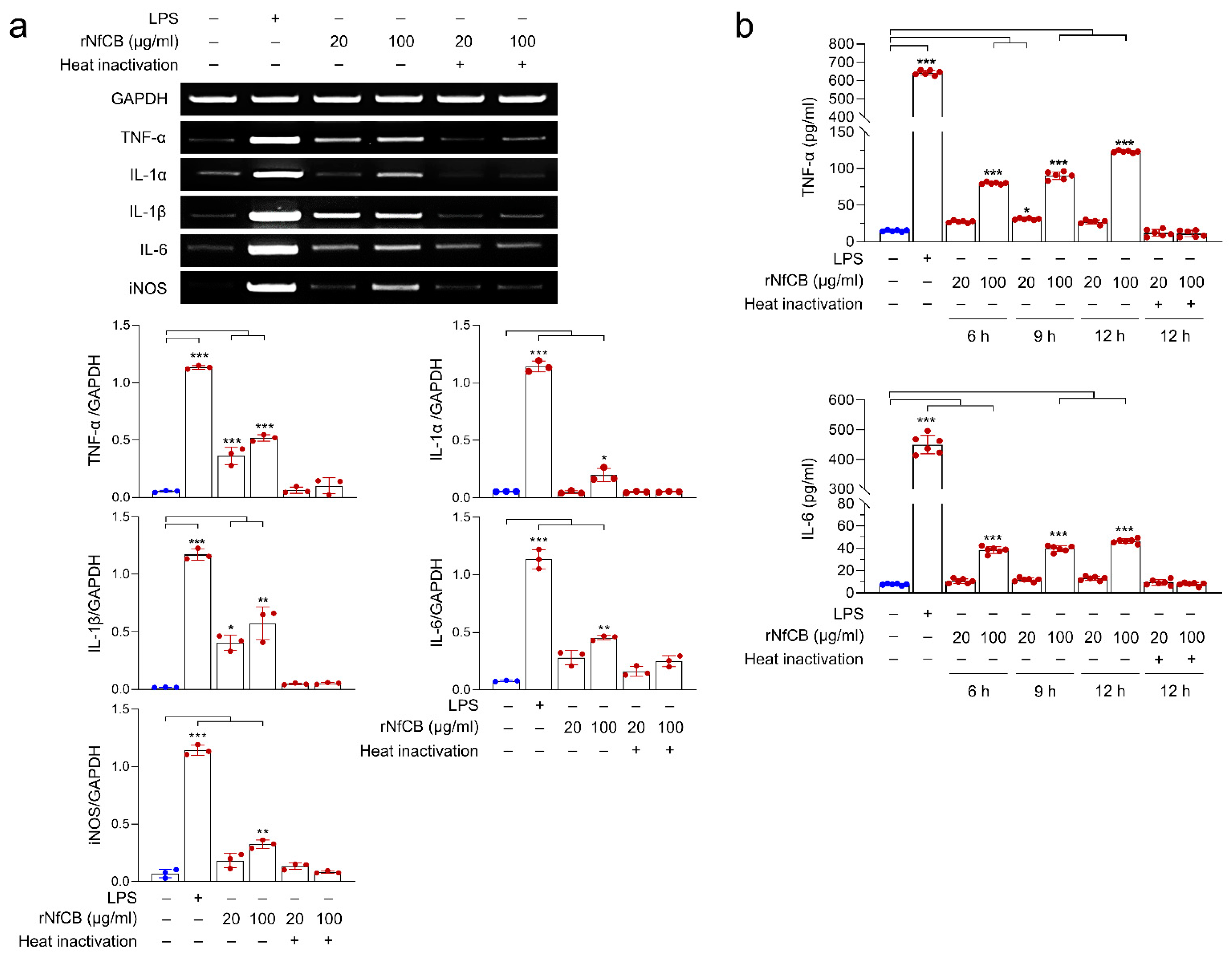
3.3. rNfCB Induces the Enhanced Production of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in BV-2 Microglial Cells
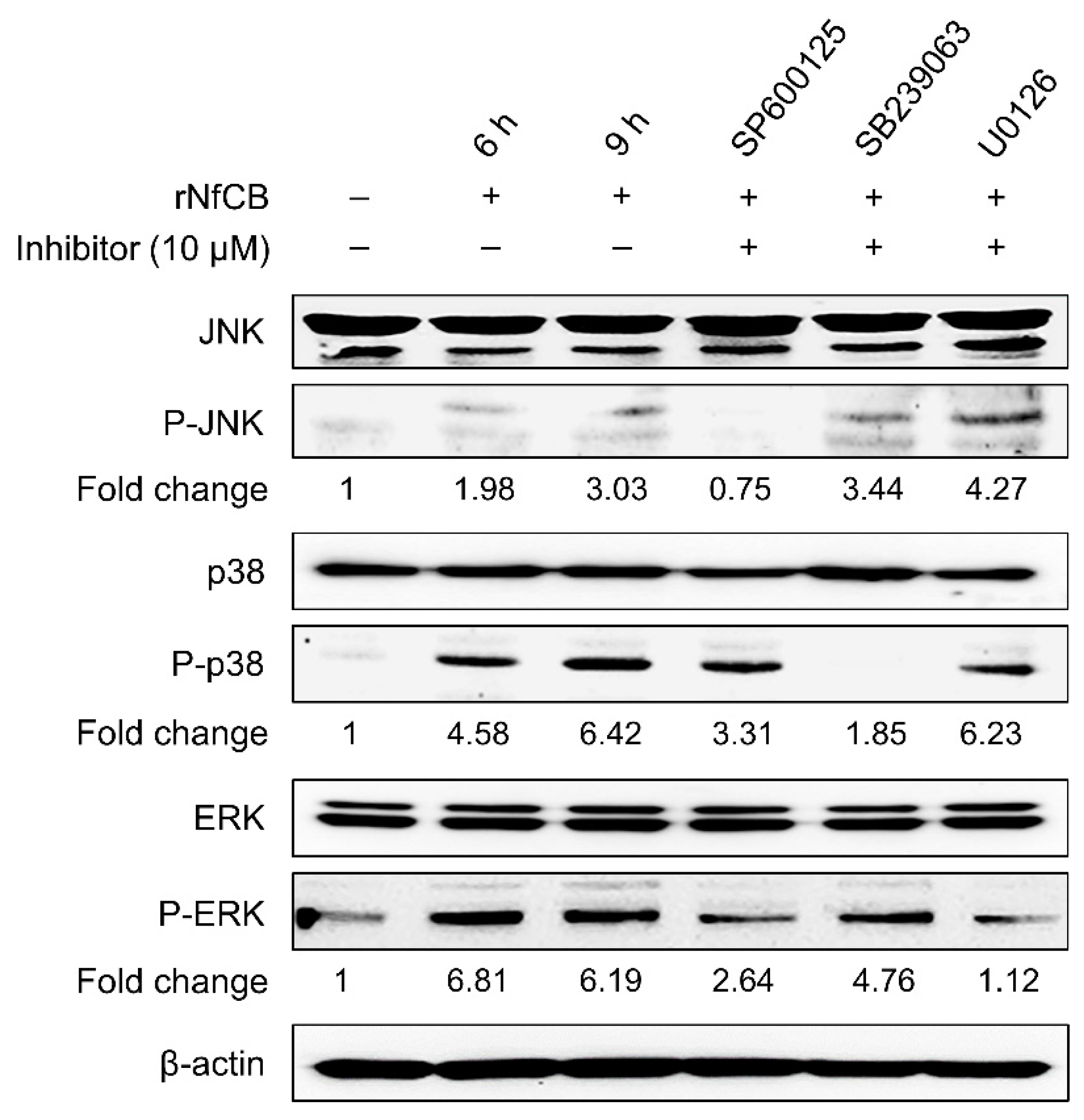
3.4. Production of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Are Mediated by the MAPK Pathway
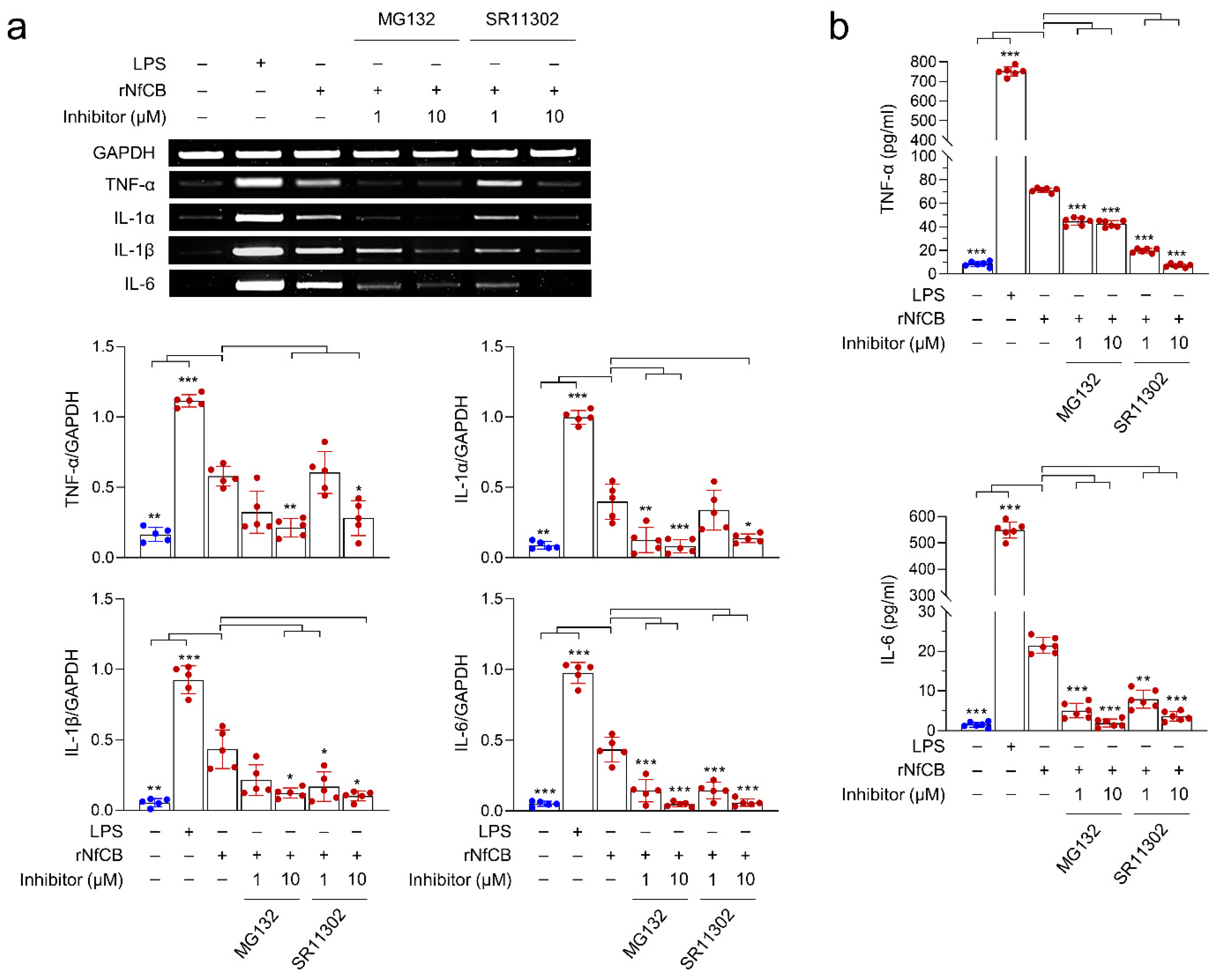
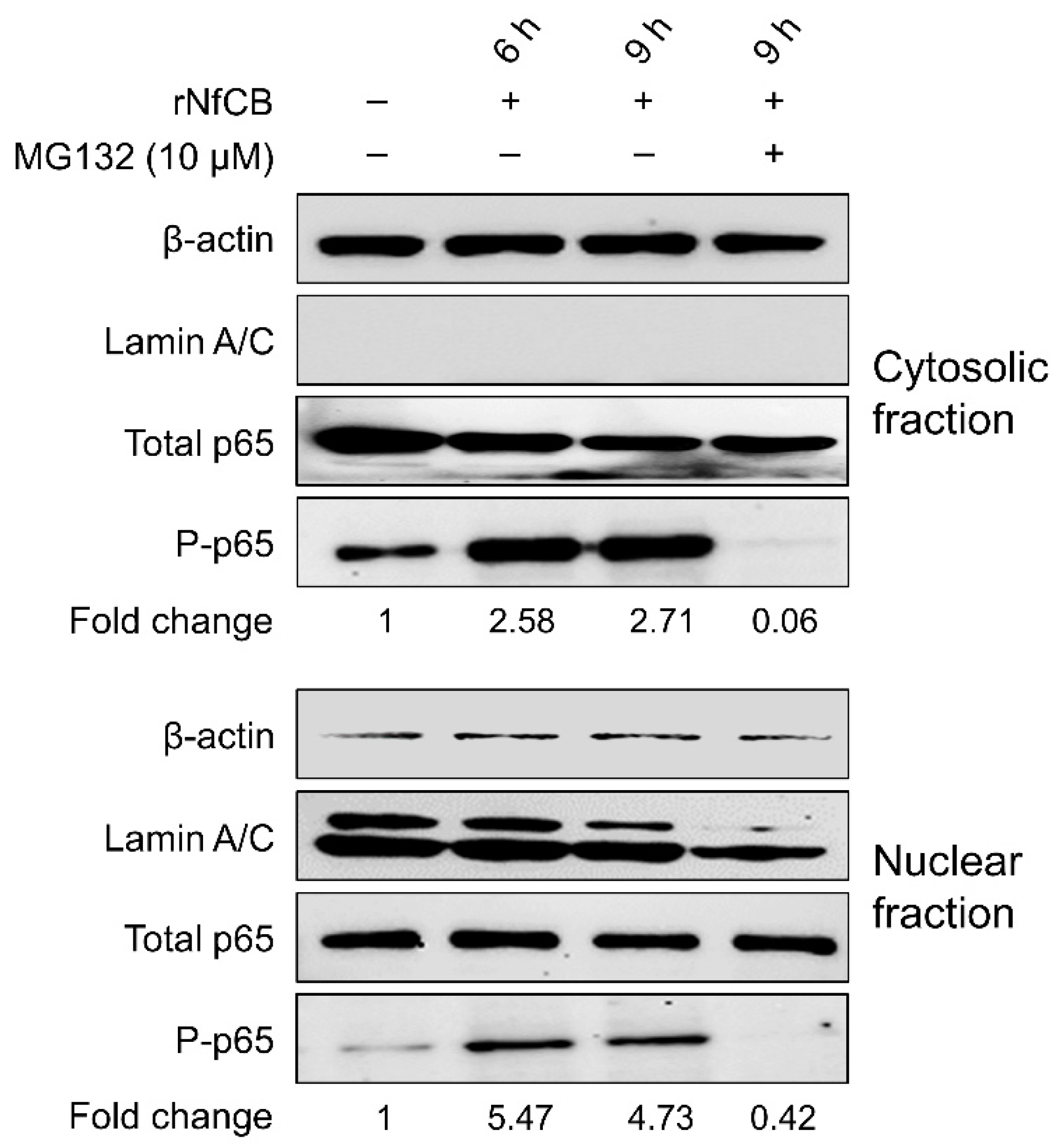
3.5. rNfCB-Induced Pro-Inflammatory Immune Response of BV-2 Microglial Cells Is Regulated via NF-κB and AP-1 Signaling Pathways
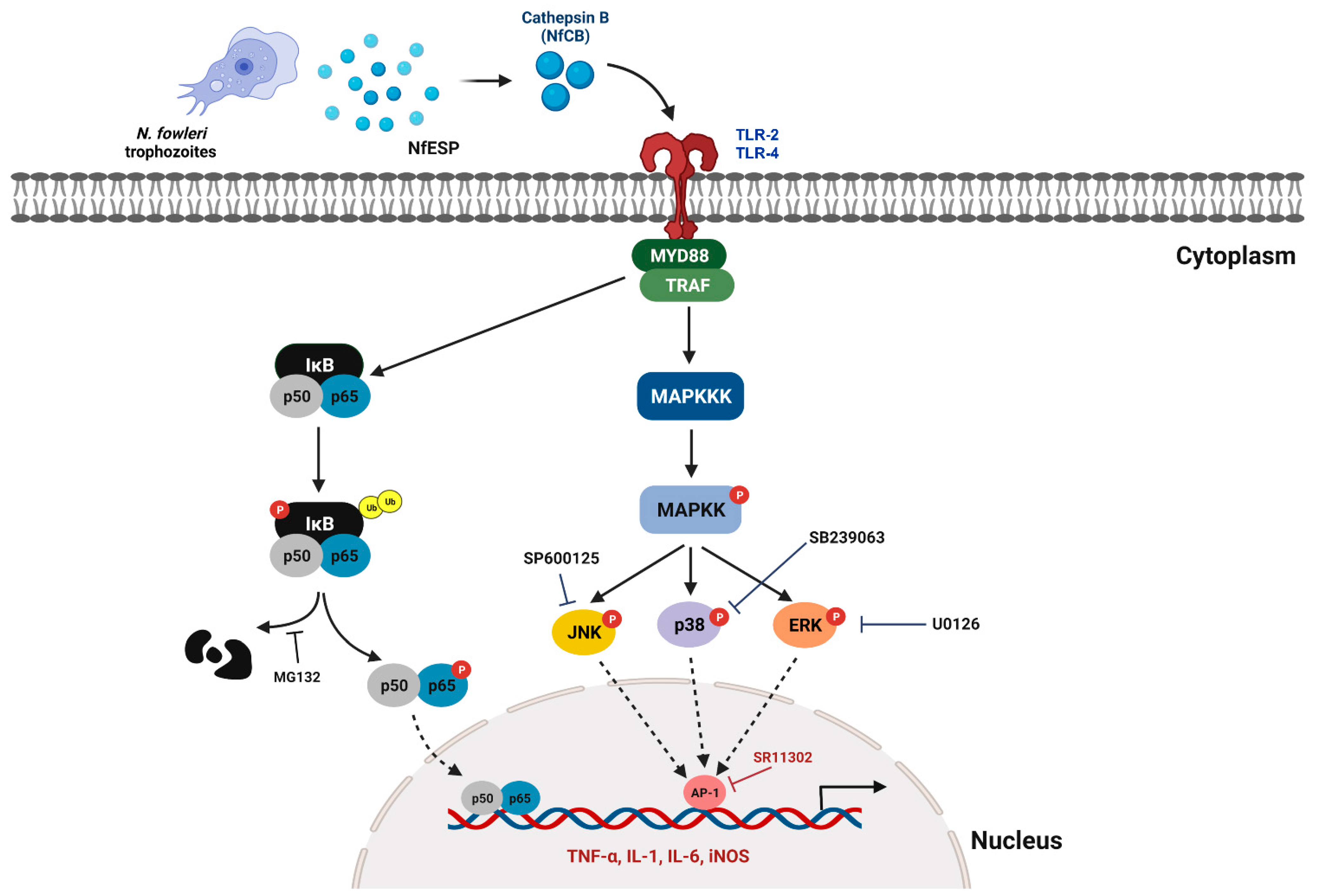
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grace, E.; Asbill, S.; Virga, K. Naegleria fowleri: Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment options. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 6677–6681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervantes-Sandoval, I.; de Jesús Serrano-Luna, J.; García-Latorre, E.; Tsutsumi, V.; Shibayama, M. Mucins in the host defence against Naegleria fowleri and mucinolytic activity as a possible means of evasion. Microbiology 2008, 154, 3895–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervantes-Sandoval, I.; Serrano-Luna, J.d.J.; Meza-Cervantes, P.; Arroyo, R.; Tsutsumi, V.; Shibayama, M. Naegleria fowleri induces MUC5AC and proinflammatory cytokines in human epithelial cells via ROS production and EGFR activation. Microbiology 2009, 155, 3739–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Marciano-Cabral, F.; Cabral, G.A. The immune response to Naegleria fowleri amebae and pathogenesis of infection. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 51, 243–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, R.; Ali, I.K.M.; Cope, J.R.; Khan, N.A. Biology and pathogenesis of Naegleria fowleri. Acta Trop. 2016, 164, 375–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Yang, A.H.; Sohn, H.J.; Kim, D.; Song, K.J.; Shin, H.J. Immunodominant antigens in Naegleria fowleri excretory-secretory proteins were potential pathogenic factors. Parasitol. Res. 2009, 105, 1675–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kang, J.M.; Kim, T.I.; Kim, J.H.; Sohn, H.J.; Na, B.K.; Shin, H.J. Excretory and Secretory Proteins of Naegleria fowleri Induce Inflammatory Responses in BV-2 Microglial Cells. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2017, 64, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKerrow, J.H.; Caffrey, C.; Kelly, B.; Loke, P.; Sajid, M. Proteases in parasitic diseases. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2006, 1, 497–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, P.J. Falcipain cysteine proteases of malaria parasites: An update. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Proteins Proteom. 2020, 1868, 140362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, A.; Roy, M.; Jyoti, A.; Kaushik, S.; Verma, K.; Srivastava, V.K. Cysteine proteases: Battling pathogenic parasitic protozoans with omnipresent enzymes. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 249, 126784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Que, X.; Reed, S.L. Cysteine proteinases and the pathogenesis of amebiasis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allain, T.; Fekete, E.; Buret, A.G. Giardia Cysteine Proteases: The Teeth behind the Smile. Trends Parasitol. 2019, 35, 636–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siqueira-Neto, J.L.; Debnath, A.; McCall, L.I.; Bernatchez, J.A.; Ndao, M.; Reed, S.L.; Rosenthal, P.J. Cysteine proteases in protozoan parasites. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano-Luna, J.; Cervantes-Sandoval, I.; Tsutsumi, V.; Shibayama, M. A biochemical comparison of proteases from pathogenic Naegleria fowleri and non-pathogenic Naegleria gruberi. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2007, 54, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, J.H.; Sohn, H.J.; Yang, H.J.; Na, B.K.; Chwae, Y.J.; Park, S.; Kim, K.; Shin, H.J. Novel cathepsin B and cathepsin B-like cysteine protease of Naegleria fowleri excretory-secretory proteins and their biochemical properties. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 2765–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W.N.I.H. Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehrmann, J.; Matsumoto, Y.; Kreutzberg, G.W. Microglia: Intrinsic immuneffector cell of the brain. Brain Res. Rev. 1995, 20, 269–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popiolek-Barczyk, K.; Mika, J. Targeting the Microglial Signaling Pathways: New Insights in the Modulation of Neuropathic Pain. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 2908–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thameem Dheen, S.; Kaur, C.; Ling, E.-A. Microglial Activation and its Implications in the Brain Diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2007, 14, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, Y.H.; Jeong, S.R.; Kim, J.H.; Song, K.J.; Kim, K.; Park, S.; Sohn, S.; Shin, H.J. Cytopathic changes and pro-inflammatory cytokines induced by Naegleria fowleri trophozoites in rat microglial cells and protective effects of an anti-Nfa1 antibody. Parasite Immunol. 2005, 27, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.J.; Park, C.E.; Kim, J.H.; Sohn, H.J.; Lee, J.; Jung, S.Y.; Shin, H.J. Naegleria fowleri lysate induces strong cytopathic effects and pro-inflammatory cytokine release in rat microglial cells. Korean J. Parasitol. 2011, 49, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.A.; Nam, Y.H.; Min, A.; Kim, K.A.; Nozaki, T.; Saito-Nakano, Y.; Mirelman, D.; Shin, M.H. Entamoeba histolytica-secreted cysteine proteases induce IL-8 production in human mast cells via a PAR2-independent mechanism. Parasite 2014, 21, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, C.P.; Neves, B.M.; Lourenço, Á.; Cruz, M.T.; Martins, J.D.; Silva, A.; Pereira, S.; Sousa, M.d.C. Giardia lamblia decreases NF-κB p65RelA protein levels and modulates LPS-induced pro-inflammatory response in macrophages. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beutler, B. Inferences, questions and possibilities in Toll-like receptor signalling. Nature 2004, 430, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Castillo, M.; Santos-Argumedo, L.; Galván-Moroyoqui, J.M.; Serrano-Luna, J.; Shibayama, M. Toll-like receptors participate in Naegleria fowleri recognition. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollock, K.G.J.; McNeil, K.S.; Mottram, J.C.; Lyons, R.E.; Brewer, J.M.; Scott, P.; Coombs, G.H.; Alexander, J. The Leishmania mexicana cysteine protease, CPB2.8, induces potent Th2 responses. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 1746–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lê, H.G.; Kang, J.-M.; Võ, T.C.; Na, B.-K. Naegleria fowleri Cathepsin B Induces a Pro-Inflammatory Immune Response in BV-2 Microglial Cells via NF-κB and AP-1 Dependent-MAPK Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8388. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158388
Lê HG, Kang J-M, Võ TC, Na B-K. Naegleria fowleri Cathepsin B Induces a Pro-Inflammatory Immune Response in BV-2 Microglial Cells via NF-κB and AP-1 Dependent-MAPK Signaling Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(15):8388. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158388
Chicago/Turabian StyleLê, Hương Giang, Jung-Mi Kang, Tuấn Cường Võ, and Byoung-Kuk Na. 2022. "Naegleria fowleri Cathepsin B Induces a Pro-Inflammatory Immune Response in BV-2 Microglial Cells via NF-κB and AP-1 Dependent-MAPK Signaling Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 15: 8388. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158388
APA StyleLê, H. G., Kang, J.-M., Võ, T. C., & Na, B.-K. (2022). Naegleria fowleri Cathepsin B Induces a Pro-Inflammatory Immune Response in BV-2 Microglial Cells via NF-κB and AP-1 Dependent-MAPK Signaling Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(15), 8388. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158388






