GmIAA27 Encodes an AUX/IAA Protein Involved in Dwarfing and Multi-Branching in Soybean
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterization of the dmbn Mutant
2.2. Cytological Observations
2.3. Mapping of dmbn Gene with BSA-Seq
2.4. Fine Mapping of the GmIAA27 Gene
2.5. Functional Confirmation by Arabidopsis Transformation
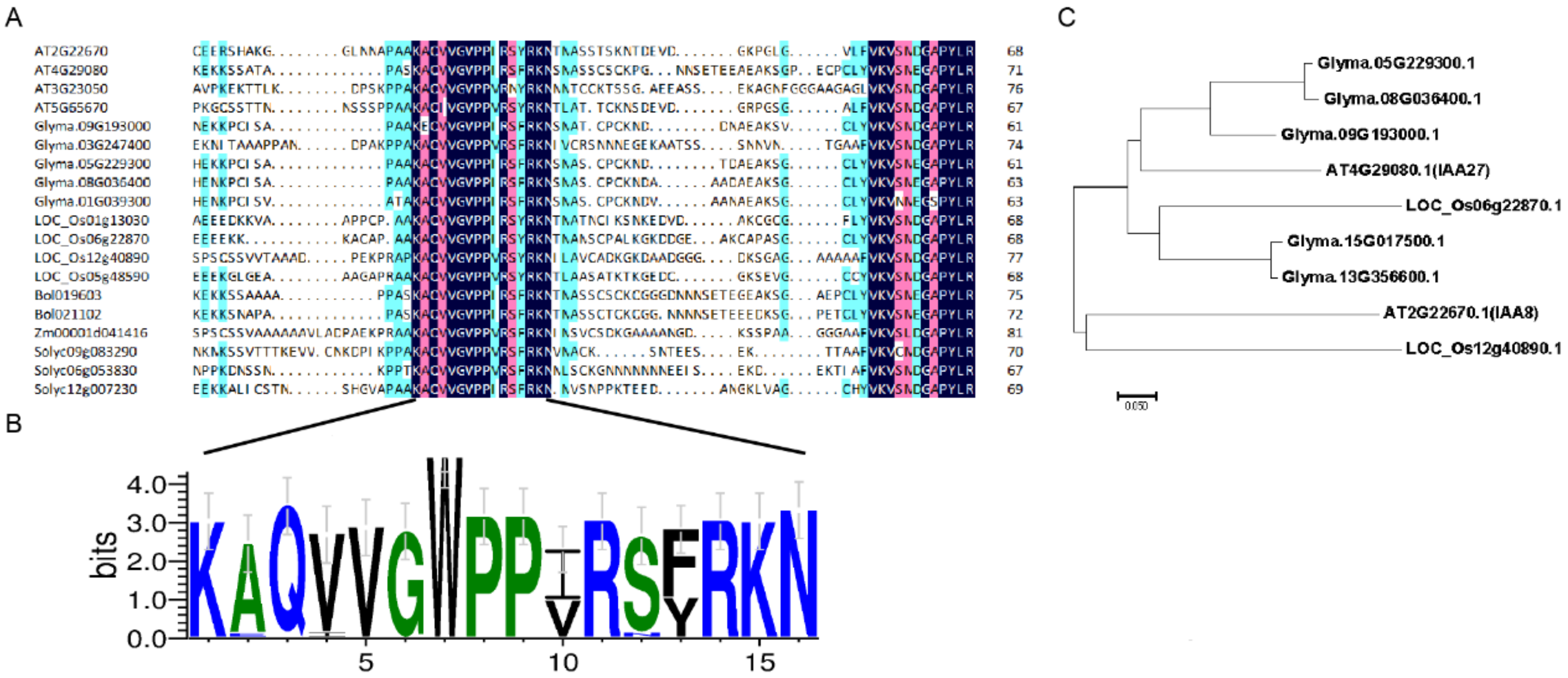
2.6. Subcellular Localization of GmIAA27 and Sequence Analysis
2.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Validation of GmIAA27 Genes
2.8. Mutation of GmIAA27 Affects Its Interactions with GmTIR1 under NAA Treatment
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
4.2. DNA Extraction and Genetic Mapping
4.3. RNA Extraction and Real-Time Quantitative PCR
4.4. Cytological Observation
4.5. Subcellular Localization
4.6. Multiple-Sequence Alignment
4.7. Genetic Transformation of Arabidopsis
4.8. In Vitro Pulldown Assay
4.9. Co-Immunoprecipitation
4.10. Yeast Two-Hybrid Assay
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hartman, G.L.; West, E.D.; Herman, T.K. Crops that feed the World 2. Soybean—worldwide production, use, and constraints caused by pathogens and pests. Food Sec. 2011, 3, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, P.; Caballero-Anthony, M.; Lassa, J.; Nair, T. Towards Asia 2025: Policy and technology imperatives. Summary of the main findings of the second international conference on Asian food security held in Singapore on 21–22 August 2014. Agric. Food Sec. 2015, 7, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jamet, J.P.; Chaumet, J.M. Soybean in China, adaptating to the liberalization. Ocl. Oils. Fat. Crop. Li 2016, 23, D604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huyghe, C. Genetics and genetic modifications of plant architecture in grain legumes: A review. Agronomie 1998, 18, 383–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, P.; Lauer, J.G. Response of soybean yield components to management system and planting date. Agron. J. 2004, 96, 1372–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, R.L. Two genes affecting stem termination in soybeans1. Crop Sci. 1972, 12, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Watanabe, S.; Uchiyama, T.; Kong, F.; Kanazawa, A.; Xia, Z.; Nagamatsu, A.; Arai, M.; Yamada, T.; Kitamura, K.; et al. The soybean stem growth habit gene Dt1 is an ortholog of Arabidopsis TERMINAL FLOWER1. Plant Physiol. 2010, 153, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ping, J.; Liu, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhao, M.; Li, Y.; She, M.; Sui, Y.; Lin, F.; Liu, X.; Tang, Z.; et al. Dt2 is a gain-of-function mads-domain factor gene that specifies semideterminacy in soybean. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 2831–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.F.; Guo, Y.; Ou, L.; Hong, H.L.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.X.; Guo, B.F.; Zhang, L.J.; Qiu, L.J. Identification of the dwarf gene GmDW1 in soybean (Glycine max L.) by combining mapping-by-sequencing and linkage analysis. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2018, 131, 1001–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Su, C.; Yun, J.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Cao, D.; Zhao, F.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, M.; et al. Genetic improvement of the shoot architecture and yield in soya bean plants via the manipulation of GmmiR156b. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilfoyle, T.J.; Hagen, G. Auxin response factors. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2007, 10, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Grones, P.; Stéphanie, R. Auxin signaling, a big question to be addressed by small molecules. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.B.; Wang, X.J.; Hagen, G.; Guilfoyle, T.J. AUX/IAA proteins are active repressors, and their stability and activity are modulated by auxin. Plant Cell 2001, 13, 2809–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roosjen, M.; Paque, S.; Weijers, D. Auxin response factors, output control in auxin biology. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harper, R.M.; Stowe-Evans, E.L.; Luesse, D.R.; Muto, H.; Tatematsu, K.; Watahiki, M.K.; Yamamoto, K.; Liscum, E. The NPH4 locus encodes the auxin response factor ARF7, a conditional regulator of differential growth in aerial arabidopsis tissue. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 757–770. [Google Scholar]
- Abel, S.; Oeller, P.W.; Theologis, A. Early auxin-induced genes encode short-lived nuclear proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainley, D.; Wilson, P.; Barton, K.; Ballard, G.; Nur, N.; Karl, B. Diet and foraging effort of Adelie penguins in relation to pack-ice conditions in the southern Ross Sea. Polar Microbiol. 1998, 20, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, G.; Guilfoyle, T. Auxin-responsive gene expression, genes, promoters and regulatory factors. Plant Mol. Biol. 2002, 49, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, D. Changes in auxin response from mutations in an AUX/IAA Gene. Science 1998, 279, 1371–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liscum, E.; Reed, J.W. Genetics of Aux/IAA and ARF action in plant growth and development. Plant Mol. Biol. 2002, 49, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Li, H.; Song, J.; Zhao, B.; Guo, C.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; King, G.J.; Liu, K. An auxin signaling gene BnaA3.IAA7 contributes to improved plant architecture and yield heterosis in rapeseed. New Phytol. 2019, 222, 837–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, P.; Walker, L.M.; Young, J.C.; Sonawala, A.; Timpte, C.; Estelle, M.; Reed, J.W. AXR2 encodes a member of the AUX/IAA protein family. New Phytol. 2000, 123, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaabouni, S.; Jones, B.; Delalande, C.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Mila, I.; Frasse, P.; Latche, A.; Pech, J.C.; Bouzayen, M. Sl-IAA3, a tomato Aux/IAA at the crossroads of auxin and ethylene signalling involved in differential growth. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 1349–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Wang, B.; Li, Z.; Guo, T.; Zhao, J.; Guan, Z.; Liu, K. Identification and characterization of a new dwarf locus DS-4 encoding an Aux/IAA7 protein in Brassica napus. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2019, 132, 1435–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.S.; Zeng, L.; Thyssen, G.N.; Delhom, C.D.; Kim, H.J.; Li, P.; Fang, D.D. Mapping by sequencing in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) line MD52ne identified candidate genes for fiber strength and its related quality attributes. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2016, 129, 1071–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiroki, T.; Akira, A.; Kentaro, Y.; Shunichi, K.; Satoshi, N.; Chikako, M.; Aiko, U.; Hiroe, U.; Muluneh, T.; Shohei, T.; et al. QTL-seq, rapid mapping of quantitative trait loci in rice by whole genome resequencing of DNA from two bulked populations. Plant J. 2013, 74, 174–183. [Google Scholar]
- Tribhuvan, K.U.; Sandhya; Kumar, K.; Sevanthi, M.A.; Gaikwad, K. MutMap: A versatile tool for identification of mutant loci and mapping of genes. Indian J. Plant Physiol. 2018, 23, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rym, F.; Hiroki, T.; Muluneh, T.; Akira, A.; Satoshi, N.; Hiroki, Y.; Shailendra, S.; Shiveta, S.; Hiroyuki, K.; Hideo; et al. MutMap+, genetic mapping and mutant identification without crossing in rice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68529. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, T.; Chi, W.; Huang, L.; Qu, M.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Z.Q.; Chen, Z.J.; Tian, D.; Gui, Y.; Chen, X.; et al. Bulked segregant analysis coupled with whole-genome sequencing (BSA-Seq) mapping identifies a novel pi21 haplotype conferring basal resistance to rice blast disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zheng, Y.; Bai, F.; Liu, Y.; Deng, S.; Liu, X.; Wang, L. Bulked segregant analysis coupled with whole-genome sequencing (BSA-Seq) and identification of a novel locus, qGL3.5, that regulates grain length. Res. Sq. 2021, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvaa, M.P.; Zaccaronb, A.Z.; Bluhmb, B.H.; Rupeb, J.C.; Wooda, L.; Mozzonia, L.A.; Masona, R.E.; Yinglinga, S.; Pereiraa, A. Bulked segregant analysis using next-generation sequencing for identification of genetic loci for charcoal rot resistance in soybean. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2020, 109, 101440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasch, R.M.; Weigand, C.; Perez, P.T.; Palmer, R.G.; Sandhu, D. Molecular mapping of two environmentally sensitive male-sterile mutants in soybean. J. Hered. 2011, 102, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashelford, K.E.; Eriksson, M.E.; Allen, C.M.; Amore, R.D.; Johansson, M.; Gould, P.D.; Suzanne, K.P.; Millar, A.J.; Hall, N.; Anthony, H. Full genome re-sequencing reveals a novel circadian clock mutation in Arabidopsis. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akira, A.; Shunichi, K.; Kentaro, Y.; Satoshi, N.; Hiroki, T.; Hiroyuki, K.; Hideo, M.; Kakoto, Y.; Chikako, M.; Muluneh, T.; et al. Genome sequencing reveals agronomically important loci in rice using MutMap. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 174–178. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, W.J.; Kim, M.Y.; Kang, Y.J.; Sangrea, S.; Minviluz, G.S.; Gary, S.; Suk-Ha, L. Genome-wide analysis of mutations in a dwarf soybean mutant induced by fast neutron bombardment. Euphytica 2015, 203, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, Y.; Berendzen, K.W.; Xu, C.; Piepho, H.P.; Hochholdinger, F. Diversity of stability, localization, interaction and control of downstream gene activity in the Maize Aux/IAA protein family. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arase, F.; Nishitani, H.; Egusa, M.; Nishimoto, N.; Sakurai, S.; Sakamoto, N.; Kaminaka, H. IAA8 involved in lateral root formation interacts with the TIR1 auxin receptor and ARF transcription factors in Arabidopsis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Zhou, J.J.; Zhang, J.Z. Aux/IAA gene family in plants, molecular structure, regulation, and function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.L.; You, J.; Xiong, L. Characterization of OsIAA1 gene, a member of rice Aux/IAA family involved in auxin and brassinosteroid hormone responses and plant morphogenesis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2009, 70, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felipe, D.; Memelink, J.; Offringa, R. Auxin-induced, SCF(TIR1)-mediated poly-ubiquitination marks AUX/IAA proteins for degradation. Plant J. 2009, 59, 100–109. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, W.M.; Kepinski, S.; Rouse, D.; Leyser, O.; Estelle, M. Auxin regulates SCFTIR1-dependent degradation of AUX/IAA proteins. Nature 2001, 414, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmasiri, N.; Dharmasiri, S.; Estelle, M. The F-box protein TIR1 is an auxin receptor. Nature 2005, 435, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Harter, K.; Theologis, A. Protein–protein interactions among the Aux/IAA proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 11786–11791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abel, S.; Theologis, A. Early genes and auxin action. Plant Physiol. 1996, 111, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, M.; Yabe, N.; Ichikawa, T.; Yamamoto, Y.Y.; Yoshizumi, T.; Hasunuma, K.; Matsui, M. DFL1, an auxin-responsive GH3 gene homologue, negatively regulates shoot cell elongation and lateral root formation, and positively regulates the light response of hypocotyl length. Plant J. 2001, 25, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takase, T.; Nakazawa, M.; Ishikawa, A.; Kawashima, M.; Ichikawa, T.; Takahashi, N.; Shimada, H.; Manabe, K.; Matsui, M. ydk1-D, an auxin-responsive GH3 mutant that is involved in hypocotyl and root elongation. Plant J. 2004, 37, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Jiang, L.; Ma, Y.; Wei, Z.; Hong, H.; Liu, Z.; Lei, J.; Liu, Y.; Guan, R.; Guo, Y.; et al. Development and utilization of a new chemically-induced soybean library with a high mutation density. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2017, 59, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saghai-Maroof, M.A. Ribosomal DNA spacer-length polymorphisms in barley, mendelian inheritance, chromosomal location, and population dynamics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 81, 8014–8018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.; Jia, G.; Zhu, Y.; Grant, D.; Nelson, R.T.; Hwang, E.Y.; Hyten, D.L.; Cregan, P.B. Abundance of ssr motifs and development of candidate polymorphic SSR markers (BARCSOYSSR_1.0) in soybean. Crop Sci. 2010, 50, 1950–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, D.E.; Tong, G.L.; Guo, X.; Melito, S.; Wang, K.; Bayless, A.M.; Wang, J.; Hughes, T.J.; Willis, D.K.; Clemente, T.E.; et al. Copy number variation of multiple genes at Rhg1 mediates nematode resistance in soybean. Science 2012, 338, 1206–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Henriques, R.; Lin, S.S.; Niu, Q.W.; Chua, N.H. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana using the floral dip method. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Ren, Y.; Wang, Y.; Peng, C.; Zhou, K. OsVPS9A functions cooperatively with OsRAB5A to regulate post-golgi dense vesicle-mediated storage protein trafficking to the protein storage vacuole in rice endosperm cells. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 1919–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, B.; Wu, H.; Guo, Y.; Gao, H.; Wei, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Qiu, L. GmIAA27 Encodes an AUX/IAA Protein Involved in Dwarfing and Multi-Branching in Soybean. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8643. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158643
Su B, Wu H, Guo Y, Gao H, Wei Z, Zhao Y, Qiu L. GmIAA27 Encodes an AUX/IAA Protein Involved in Dwarfing and Multi-Branching in Soybean. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(15):8643. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158643
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Bohong, Haitao Wu, Yong Guo, Huawei Gao, Zhongyan Wei, Yuyang Zhao, and Lijuan Qiu. 2022. "GmIAA27 Encodes an AUX/IAA Protein Involved in Dwarfing and Multi-Branching in Soybean" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 15: 8643. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158643
APA StyleSu, B., Wu, H., Guo, Y., Gao, H., Wei, Z., Zhao, Y., & Qiu, L. (2022). GmIAA27 Encodes an AUX/IAA Protein Involved in Dwarfing and Multi-Branching in Soybean. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(15), 8643. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158643





