Overexpression of miR-125a-5p Inhibits Hepatocyte Proliferation through the STAT3 Regulation In Vivo and In Vitro
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
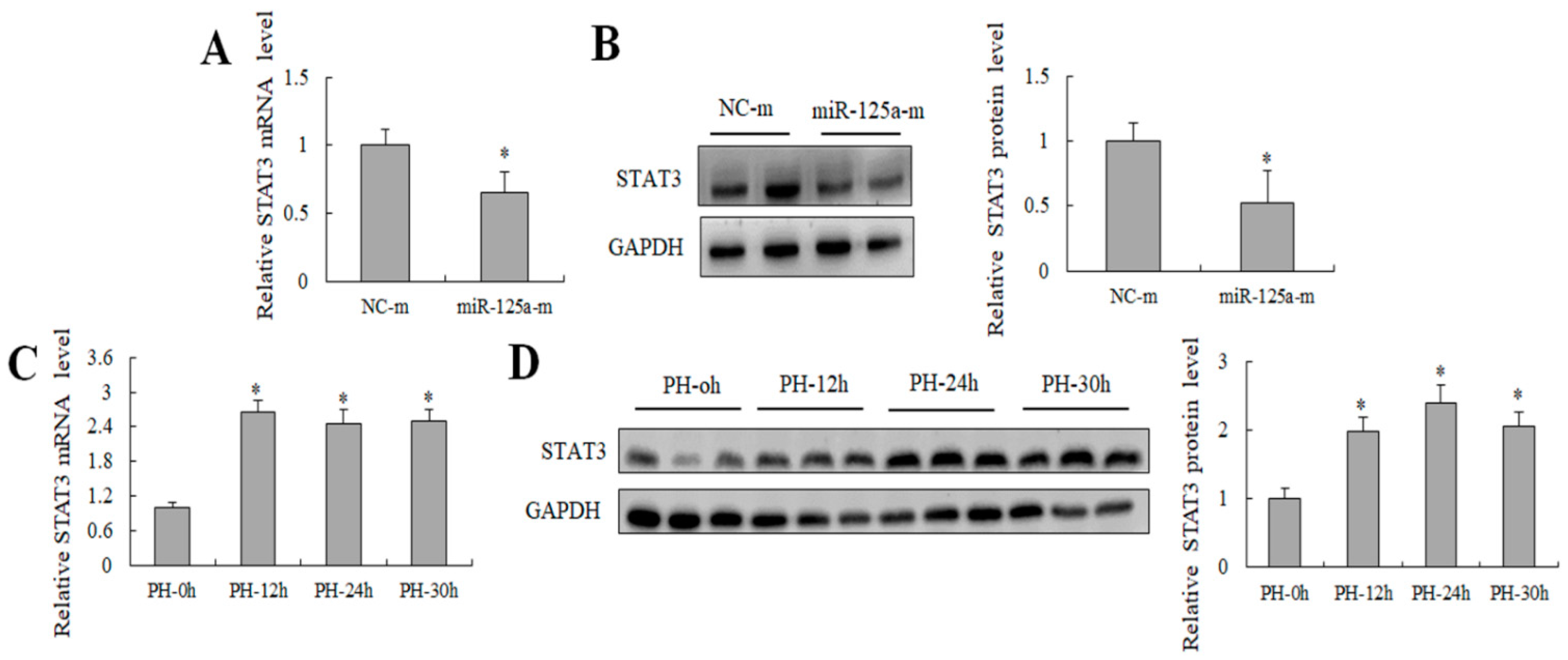
2.1. miR-125a Was Associated with Rat Liver Regeneration
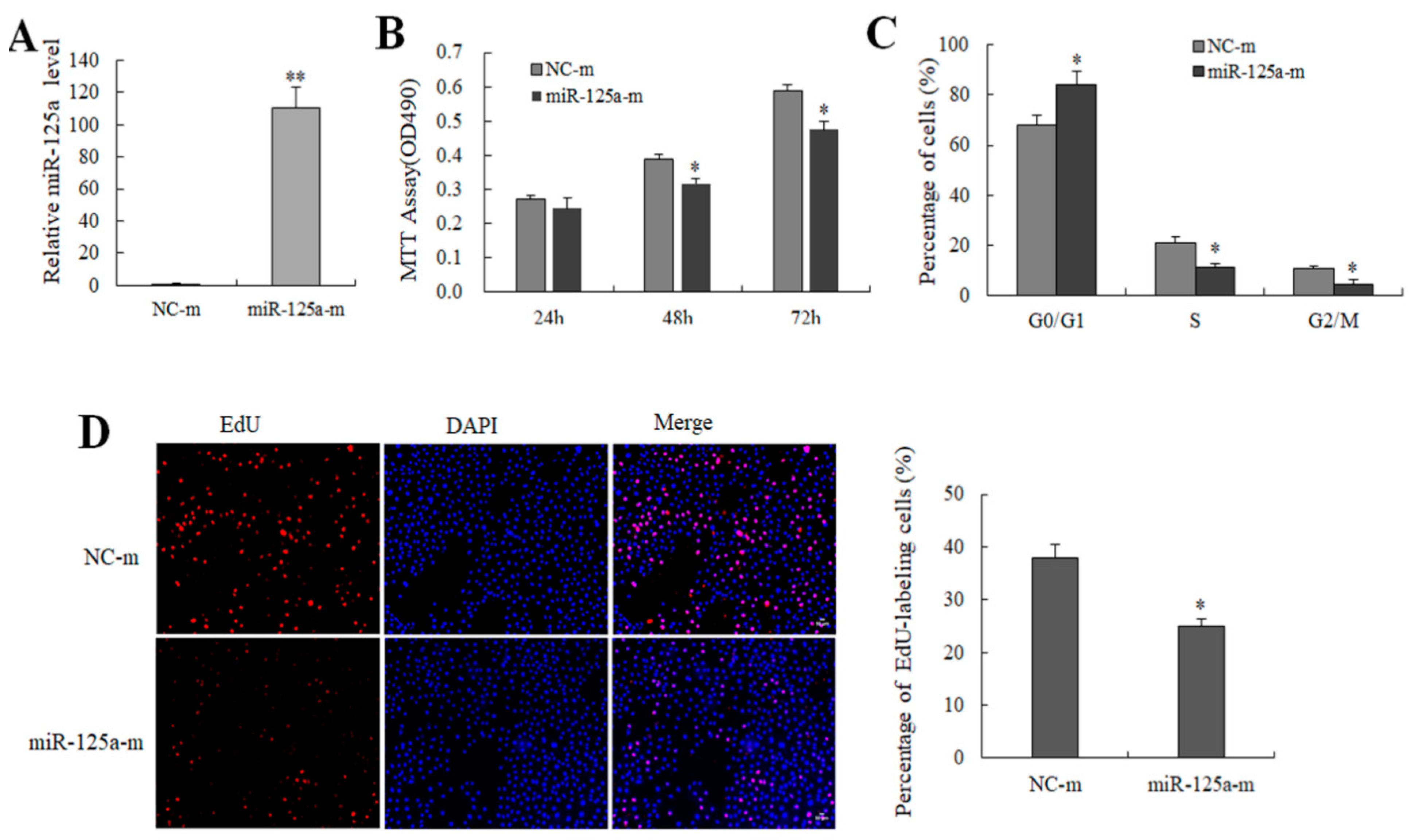
2.2. miR-125a Reduced Hepatocytes Proliferation
2.3. miR-125a Induced Hepatocytes Apoptosis
2.4. miR-125a Was Negatively Correlated with STAT3 Level In Vivo and Negatively Regulated STAT3 Level In Vitro
2.5. STAT3 Was the Direct Target of miR-125a in Rat Hepatocytes
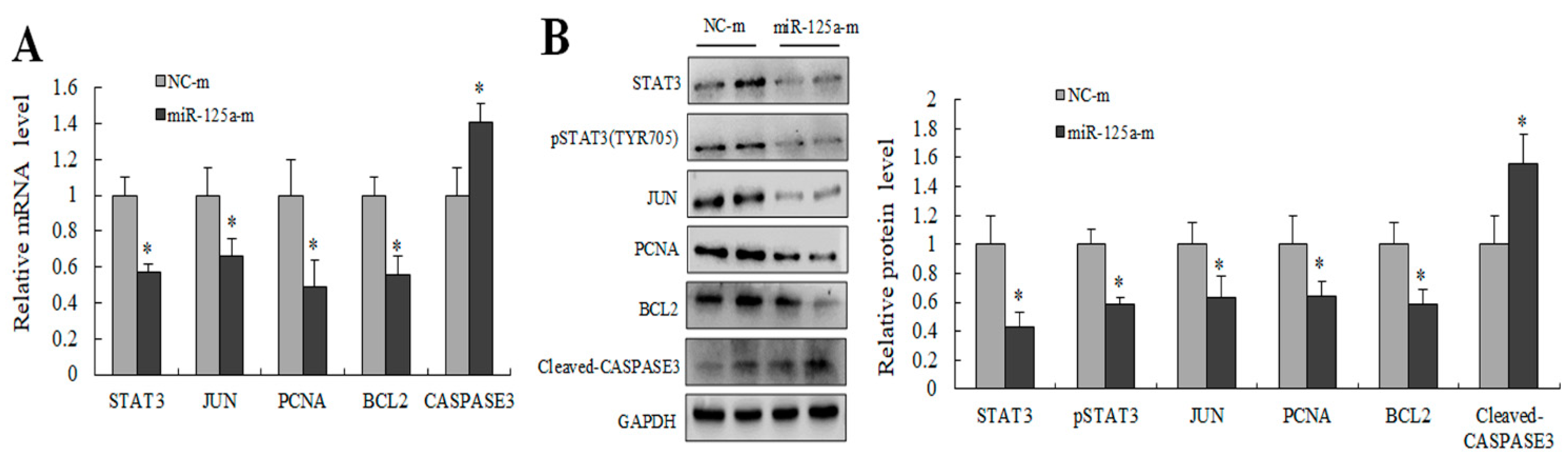
2.6. miR-125a Inhibited Hepatocytes Proliferation through STAT3/P-STAT3/JUN/BCL2 Axis
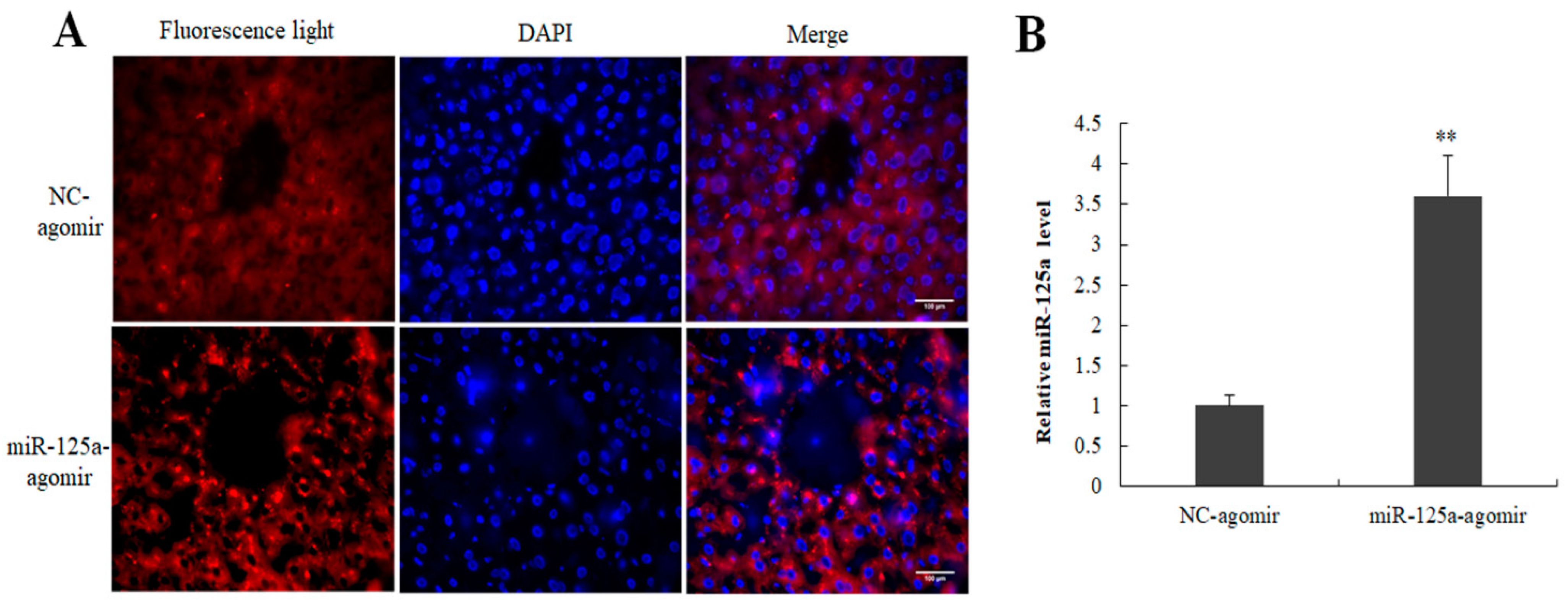
2.7. Expression of miR-125a Agomir in Mouse Liver
2.8. miR-125a Inhibited LR through STAT3/p-STAT3/JUN/BCL2 Axis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. PH Model Preparation and Tail Vein Injection
4.2. Fluorescence Observation
4.3. Immunohistochemistry
4.4. Biochemical Index Analysis
4.5. miRNA High-Throughput Sequencing and Analysis
4.6. Cell Culture and Transfection
4.7. MTT Assay
4.8. EdU Proliferation Assay
4.9. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.10. Cell Apoptosis
4.11. Luciferase Vector Acquisition and Detection
4.12. RNA Acquisition and qRT-PCR
4.13. Western Blot Analysis
4.14. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Li, S.; Mo, D.; Ma, J.; Ni, R.; Yang, Q.; He, J.; Luo, L. Tel2 regulates redifferentiation of bipotential progenitor cells via Hhex during zebrafish liver regeneration. Cell Rep. 2022, 39, 110596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Zhou, Y.; Qian, C.; Wang, D.; Yang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Sun, J.; Ni, R.; Yang, Q.; Chen, J.; et al. DNA methylation maintenance at the p53 locus initiates biliary-mediated liver regeneration. NPJ Regen. Med. 2022, 7, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, G.; Song, Y.; Li, N.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Jiao, S.; Wei, M.; Yu, B.; Wang, Y.; et al. Myeloid peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α deficiency accelerates liver regeneration via IL-6/STAT3 pathway after 2/3 partial hepatectomy in mice. Hepatobiliary Surg. Nutr. 2022, 11, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Chen, X.; Chang, C.; Wang, G.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, F. Transcriptome analysis of hepatocytes after partial hepatectomy in rats. Dev. Genes Evol. 2010, 220, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalopoulos, G.K.; DeFrances, M.C. Liver regeneration. Science 1997, 276, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Song, Y.; Bei, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xiao, J.; Yang, C. Telocytes in liver regeneration: Possible roles. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2014, 18, 1720–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Haan, L.; van der Lely, S.J.; Warps, A.K.; Hofsink, Q.; Olthof, P.B.; de Keijzer, M.J.; Lionarons, D.A.; Mendes-Dias, L.; Bruinsma, B.G.; Uygun, K.; et al. Post-hepatectomy liver regeneration in the context of bile acid homeostasis and the gut-liver signaling axis. J. Clin. Transl. Res. 2018, 4, 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Abu Rmilah, A.; Zhou, W.; Nelson, E.; Lin, L.; Amiot, B.; Nyberg, S.L. Understanding the marvels behind liver regeneration. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Dev. Biol. 2019, 8, e340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalopoulos, G.K. Hepatostat: Liver regeneration and normal liver tissue maintenance. Hepatology 2017, 65, 1384–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, J.; Xu, L.; Li, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Xu, M. Diabetes mellitus and postoperative blood glucose value help predict posthepatectomy liver failure in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2021, 12, 2377–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.Y. Activation of the EGFR-PI3K-CaM pathway by PRL-1-overexpressing placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorates liver cirrhosis via ER stress-dependent calcium. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Zhang, M.; Han, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Pang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, B.; Wu, W.; Qi, R.; Zhang, T. Differential microRNAs expression profiles in liver from three different lifestyle modification mice models. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, L.P.; Lau, N.C.; Garrett-Engele, P.; Grimson, A.; Schelter, J.M.; Castle, J.; Bartel, D.P.; Linsley, P.S.; Johnson, J.M. Microarray analysis shows that some microRNAs downregulate large numbers of target mRNAs. Nature 2005, 433, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terkelsen, T.; Russo, F.; Gromov, P.; Haakensen, V.D.; Brunak, S.; Gromova, I.; Krogh, A.; Papaleo, E. Secreted breast tumor interstitial fluid microRNAs and their target genes are associated with triple-negative breast cancer, tumor grade, and immune infiltration. Breast Cancer Res. 2020, 22, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latorre, J.; Ortega, F.J.; Liñares-Pose, L.; Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Lluch, A.; Comas, F.; Oliveras-Cañellas, N.; Ricart, W.; Höring, M.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Compounds that modulate AMPK activity and hepatic steatosis impact the biosynthesis of microRNAs required to maintain lipid homeostasis in hepatocytes. EBioMedicine 2020, 53, 102697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Sharma, A.D.; Roll, G.R.; Ng, R.; Lee, A.Y.; Blelloch, R.H.; Frandsen, N.M.; Willenbring, H. MicroRNAs control hepatocyte proliferation during liver regeneration. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1735–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geng, X.; Chang, C.; Zang, X.; Sun, J.; Li, P.; Guo, J.; Xu, C. Integrative proteomic and microRNA analysis of the priming phase during rat liver regeneration. Gene 2016, 575, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahm, A.M.; Wang, A.W.; Wang, Y.J.; Schug, J.; Wangensteen, K.J.; Kaestner, K.H. A High-Content Screen Identifies MicroRNAs That Regulate Liver Repopulation After Injury in Mice. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1044–1057.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez, R.T.; Wendlandt, E.; Galle, C.S.; Keck, K.; McCaffrey, A.P. MicroRNA-21 is upregulated during the proliferative phase of liver regeneration, targets Pellino-1, and inhibits NF-kappaB signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2010, 298, G535–G541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.J.; Chan, W.H.; Leung, W.Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, C.S. MicroRNA-21 promotes proliferation of rat hepatocyte BRL-3A by targeting FASLG. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 4150–4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Song, M.; Chen, W.; Dimitrova-Shumkovska, J.; Zhao, Y.; Cao, Y.; Song, Y.; Yang, W.; Wang, F.; Xiang, Y.; et al. MicroRNA-21 Contributes to Liver Regeneration by Targeting PTEN. Med. Sci. Monit. 2016, 22, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Hyun, J.; Wang, S.; Lee, C.; Jung, Y. MicroRNA-378 is involved in hedgehog-driven epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in hepatocytes of regenerating liver. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ju, W.Q.; Yuan, X.P.; Zhu, X.F.; Wang, D.P.; He, X.S. MiR-26a regulates mouse hepatocyte proliferation via directly targeting the 3’ untranslated region of CCND2 and CCNE2. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2016, 15, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Chen, H.; Wang, L.; Yang, S.; Fu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Miao, M.; Jiao, B. Down-regulation of MiR-127 facilitates hepatocyte proliferation during rat liver regeneration. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, B.; Dong, R.; Shi, D.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Miao, M.; Jiao, B. Down-regulation of miR-23b may contribute to activation of the TGF-β1/Smad3 signalling pathway during the termination stage of liver regeneration. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tu, W.; Gong, J.; Song, J.; Tian, D.; Wang, Z. MiR-20a/TCF4 axis-mediated inhibition of hepatocytes proliferation impairs liver regeneration in mice PHx model by regulating CDC2 and CDC6. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 5220–5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuhara, Y.; Hirasawa, A.; Li, X.K.; Kawasaki, M.; Fujino, M.; Funeshima, N.; Katsuma, S.; Shiojima, S.; Yamada, M.; Okuyama, T.; et al. Gene expression profile in the regenerating rat liver after partial hepatectomy. J. Hepatol. 2003, 38, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Guo, E.; Yang, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, S.; Jiang, X.; Hu, Q.; Dirsch, O.; Dahmen, U.; Zhang, C.; et al. Young plasma reverses age-dependent alterations in hepatic function through the restoration of autophagy. Aging Cell 2018, 17, e12708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, L.; Li, Y.; Yin, L.; Qi, Y.; Sun, H.; Sun, P.; Xu, M.; Tang, Z.; Peng, J. MiR-125a-5p ameliorates hepatic glycolipid metabolism disorder in type 2 diabetes mellitus through targeting of STAT3. Theranostics 2018, 8, 5593–5609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.D.; Gao, Z.J.; Zheng, G.D. MiR-125a-5p inhibits cancer stem cells phenotype and epithelial to mesenchymal transition in glioblastoma. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2020, 66, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Huang, J. MiR-125a regulates HAS1 and inhibits the proliferation, invasion and metastasis by targeting STAT3 in non-small cell lung cancer cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2020, 121, 3197–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Ma, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, P.; Yu, T. Reduced miR-125a-5p level in non-small-cell lung cancer is associated with tumour progression. Open Biol. 2018, 8, 180118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Sun, S.; Shi, J.; Cao, F.; Han, X.; Chen, Z. MicroRNA-125a-5p plays a role as a tumor suppressor in lung carcinoma cells by directly targeting STAT3. Tumour Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317697579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Xiao, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, Q. MiR-125a/b inhibits tumor-associated macrophages mediated in cancer stem cells of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting CD90. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 3046–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xue, C.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, X.; Xian, H.; Huang, Z. Suppression of microRNA-125a-5p upregulates the TAZ-EGFR signaling pathway and promotes retinoblastoma proliferation. Cell. Signal. 2016, 28, 850–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Sun, X.; Han, K.; Zhu, H.; Min, D.; Lin, S. Long Non-coding RNA MRUL Contributes to Osteosarcoma Progression Through the miR-125a-5p/FUT4 Axis. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Q.; Wang, N.; Ren, L.; Tian, J.; Yang, S.; Cheng, H. MiR-125a-5p post-transcriptionally suppresses GALNT7 to inhibit proliferation and invasion in cervical cancer cells via the EGFR/PI3K/AKT pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minini, M.; Senni, A.; He, X.; Proietti, S.; Liguoro, D.; Catizone, A.; Giuliani, A.; Mancini, R.; Fuso, A.; Cucina, A.; et al. MiR-125a-5p impairs the metastatic potential in breast cancer via IP(6)K1 targeting. Cancer Lett. 2021, 520, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosca, N.; Castiello, F.; Coppola, N.; Trotta, M.C.; Sagnelli, C.; Pisaturo, M.; Sagnelli, E.; Russo, A.; Potenza, N. Functional interplay between hepatitis B virus X protein and human miR-125a in HBV infection. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 449, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Q.; Tang, S.; Xia, L.; Du, R.; Fan, R.; Gao, L.; Jin, J.; Liang, S.; Chen, Z.; Xu, G.; et al. Ectopic expression of MiR-125a inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting MMP11 and VEGF. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Noh, J.H.; Jung, K.H.; Eun, J.W.; Bae, H.J.; Kim, M.G.; Chang, Y.G.; Shen, Q.; Park, W.S.; Lee, J.Y.; et al. Sirtuin7 oncogenic potential in human hepatocellular carcinoma and its regulation by the tumor suppressors MiR-125a-5p and MiR-125b. Hepatology 2013, 57, 1055–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yao, Q.; Li, R.; Jin, Y. Isoflurane induces liver injury by modulating the expression of miR-125a-5p. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2021, 45, 101732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceyzériat, K.; Abjean, L.; Carrillo-de Sauvage, M.A.; Ben Haim, L.; Escartin, C. The complex STATes of astrocyte reactivity: How are they controlled by the JAK-STAT3 pathway? Neuroscience 2016, 330, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hillmer, E.J.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.S.; Watowich, S.S. STAT3 signaling in immunity. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016, 31, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zimmers, T.A.; Fishel, M.L.; Bonetto, A. STAT3 in the systemic inflammation of cancer cachexia. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 54, 28–41. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Z.; Wu, G.; Fan, C.; Xu, J.; Jiang, S.; Yan, X.; Di, S.; Ma, Z.; Hu, W.; Yang, Y. The emerging role of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 in cerebral ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke. Prog. Neurobiol. 2016, 137, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furtek, S.L.; Backos, D.S.; Matheson, C.J.; Reigan, P. Strategies and Approaches of Targeting STAT3 for Cancer Treatment. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Chng, W.J. Biological Hallmarks and Emerging Strategies to Target STAT3 Signaling in Multiple Myeloma. Cells 2022, 11, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, N.; Feng, G.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xie, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Ou, L.; Pei, X.; Liu, N.; et al. Embryonic stem cell preconditioned microenvironment suppresses tumorigenic properties in breast cancer. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2016, 7, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marshall, K.M.; He, S.; Zhong, Z.; Atkinson, C.; Tomlinson, S. Dissecting the complement pathway in hepatic injury and regeneration with a novel protective strategy. J. Exp. Med. 2014, 211, 1793–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tao, Y.; Wang, M.; Chen, E.; Tang, H. Liver Regeneration: Analysis of the Main Relevant Signaling Molecules. Mediators Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 4256352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fujiyoshi, M.; Ozaki, M. Molecular mechanisms of liver regeneration and protection for treatment of liver dysfunction and diseases. J. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Sci. 2011, 18, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaper, F.; Rose-John, S. Interleukin-6: Biology, signaling and strategies of blockade. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015, 26, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuest, M.; Willim, K.; MacNelly, S.; Fellner, N.; Resch, G.P.; Blum, H.E.; Hasselblatt, P. The transcription factor c-Jun protects against sustained hepatic endoplasmic reticulum stress thereby promoting hepatocyte survival. Hepatology 2012, 55, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepniak, E.; Ricci, R.; Eferl, R.; Sumara, G.; Sumara, I.; Rath, M.; Hui, L.; Wagner, E.F. C-Jun/AP-1 controls liver regeneration by repressing p53/p21 and p38 MAPK activity. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 2306–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tolomeo, M.; Cascio, A. The Multifaced Role of STAT3 in Cancer and Its Implication for Anticancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zugowski, C.; Lieder, F.; Müller, A.; Gasch, J.; Corvinus, F.M.; Moriggl, R.; Friedrich, K. STAT3 controls matrix metalloproteinase-1 expression in colon carcinoma cells by both direct and AP-1-mediated interaction with the MMP-1 promoter. Biol. Chem. 2011, 392, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roderfeld, M.; Padem, S.; Lichtenberger, J.; Quack, T.; Weiskirchen, R. Schistosoma mansoni Egg-Secreted Antigens Activate Hepatocellular Carcinoma-Associated Transcription Factors c-Jun and STAT3 in Hamster and Human Hepatocytes. Hepatology 2020, 72, 626–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, T.; Li, S.; Li, J.; Yin, F.; Hua, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lin, B.; Wang, H.; Zou, D.; Zhou, Z.; et al. Natural product pectolinarigenin inhibits osteosarcoma growth and metastasis via SHP-1-mediated STAT3 signaling inhibition. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Liao, S.; Bennett, S.; Tang, H.; Song, D.; Wood, D.; Zhan, X.; Xu, J. STAT3 and its targeting inhibitors in osteosarcoma. Cell Prolif. 2021, 54, e12974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Chang, C.; Gao, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, F.; Xu, C. MiR-429 regulates rat liver regeneration and hepatocyte proliferation by targeting JUN/MYC/BCL2/CCND1 signaling pathway. Cell. Signal. 2018, 50, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, J.P.; Diallo, A.; Cruceanu, C.; Fiori, L.M.; Laboissiere, S.; Guillet, I.; Fontaine, J.; Ragoussis, J.; Benes, V.; Turecki, G.; et al. Biomarker discovery: Quantification of microRNAs and other small non-coding RNAs using next generation sequencing. BMC Med. Genom. 2015, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




| Enriched KEGG Pathways | p-Value | Genes |
|---|---|---|
| JAK-STAT signaling pathway | 0.0066 | CSF3, PTPN6, GRB2, IL6ST, CTF1, IL6R, IL24, BCL2L1, STAT3, IL11, LEP, PIAS3, IL4R, SOS2, PIK3CA, PIK3R5, IFNGR2, EPO, THPO |
| Proteoglycans in cancer | 0.0089 | CDX2, THRB, MED22, RFXANK, MED20, CBFB, TAF7L, FOXS1, POU4F3, CTDSP1, RBPJL, ZFP518A, TBL1XR1, FOXJ1, LDB1, TADA2B, MLXIPL, FOXN1, GRHL3, GRHL2, NRIP1, BRWD1, HNF4A, MED15, ETV3L, VEGFA, ZFP395, TADA3, TFCP2L1, ABCA2, ZFP110, MSX2, TAL2, FOXH1, VDR, NPAS1, MSX3, FOXQ1, ELK4, OVOL1, TFDP2, ETV4, SIM1, EPO, RFX5, ZMYM3, FOXA1, KLF16, MAFK, FOXP3, ZFP444, SNAI1, STAT3, SOD2, NOTCH1, SP1, ETS1, MAPK14, LOC100911917, MLX, BNC1, KDM4C |
| Insulin resistance | 0.0216 | PPARA, MLXIPL, CREB5, PPP1R3A, CPT1A, STAT3, PPP1R3D, TNFRSF1A, PPP1CA, RPS6KA1, RPS6KA2, MLX, GYS1, PIK3CA, SLC27A6, PIK3R5, PTPN1, SLC27A4 |
| HIF-1 signaling pathway | 0.0263 | FLT1, EDN1, MKNK2, MKNK1, IL6R, STAT3, EIF4EBP1, TFRC, PLCG1, VEGFA, SERPINE1, PIK3CA, PIK3R5, CAMK2B, EGF, IFNGR2, EPO |
| Enriched Biological Processes | No. of Genes | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| negative regulation of apoptotic process | 70 | 0.00323 |
| positive regulation of transcription, DNA-templated | 71 | 0.02048 |
| negative regulation of neuron death | 11 | 0.03945 |
| negative regulation of cell death | 15 | 0.04121 |
| positive regulation of cell proliferation | 61 | 0.04763 |
| positive regulation of cell migration | 37 | 0.00028 |
| positive regulation of apoptotic process | 45 | 0.02398 |
| negative regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway | 8 | 0.01467 |
| positive regulation of JUN kinase activity | 10 | 0.01670 |
| angiogenesis | 30 | 0.00546 |
| positive regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway | 10 | 0.01030 |
| cell migration | 30 | 0.01378 |
| positive regulation of MAP kinase activity | 12 | 0.01442 |
| miRNA and Genes | Pimers Sequences (5′→3′) |
|---|---|
| miR-125a RT | GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTA TTCGCACTGGATACGACTCACAG |
| miR-125a FP | TCCCTGAGACCCTTTAACCT |
| miR-125a RP | GTGCAGGGTCCGAGGT |
| U6 FP | CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA |
| U6 RP | AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT |
| r-STAT3 FP | GTGGAAAAGGACATCAGTGGCA |
| r-STAT3 RP | CTTGGTCTTCAGGTAAGGGGCA |
| r-JUN FP | GGCTGTTCATCTGTTTGTCTTCAT |
| r-JUN RP | CCCTTTTCTTTACGGTCTCGGT |
| r-CASPASE3 FP | GAGCTGGACTGCGGTATTGAG |
| r-CASPASE3 RP | AACCATGACCCGTCCCTTGA |
| r-BCL2 FP | CGACCTCTGTTTGATTTCTCCTG |
| r-BCL2 RP | CTTTTCATATTTGTTTGGGGCA |
| r-PCNA FP | GGGTGAAGTTTTCTGCGAGTG |
| r-PCNA RP | GGAGACAGTGGAGTGGCTTTT |
| r-GAPDH FP | AAGATGGTGAAGGTCGGTGTGA |
| r-GAPDH RP | TCGCTCCTGGAAGATGGTGAT |
| m-STAT3 FP | AACCTCCAGGACGACTTTGATTT |
| m-STAT3 RP | GTTTCTTAATTTGTTGGCGGGTC |
| m-JUN FP | CAGAGTTGCACTGAGTGTGGC |
| m-JUN RP | GCAGTTGGTGAGAAAATGAAGAC |
| m-CASPASE3 FP | GTCTGACTGGAAAGCCGAAACTCT |
| m-CASPASE3 RP | AAAGGGACTGGATGAACCACGAC |
| m-BCL2 FP | GCCACCTGTGGTCCATCTGA |
| m-BCL2 RP | GAGACAGCCAGGAGAAATCAAAC |
| m-PCNA FP | TTGCACGTATATGCCGAGACC |
| m-PCNA RP | GGTGAACAGGCTCATTCATCTCT |
| m-GAPDH FP | TGGCCTTCCGTGTTCCTAC |
| m-GAPDH RP | GAGTTGCTGTTGAAGTCGCA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Qin, J.; Ye, B.; Xu, C.; Yu, G. Overexpression of miR-125a-5p Inhibits Hepatocyte Proliferation through the STAT3 Regulation In Vivo and In Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8661. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158661
Zhang C, Zhao Y, Wang Q, Qin J, Ye B, Xu C, Yu G. Overexpression of miR-125a-5p Inhibits Hepatocyte Proliferation through the STAT3 Regulation In Vivo and In Vitro. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(15):8661. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158661
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Chunyan, Yabin Zhao, Qiwen Wang, Jianru Qin, Bingyu Ye, Cunshuan Xu, and Guoying Yu. 2022. "Overexpression of miR-125a-5p Inhibits Hepatocyte Proliferation through the STAT3 Regulation In Vivo and In Vitro" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 15: 8661. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158661
APA StyleZhang, C., Zhao, Y., Wang, Q., Qin, J., Ye, B., Xu, C., & Yu, G. (2022). Overexpression of miR-125a-5p Inhibits Hepatocyte Proliferation through the STAT3 Regulation In Vivo and In Vitro. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(15), 8661. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158661







