Structural Evolution of Delta (B.1.617.2) and Omicron (BA.1) Spike Glycoproteins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
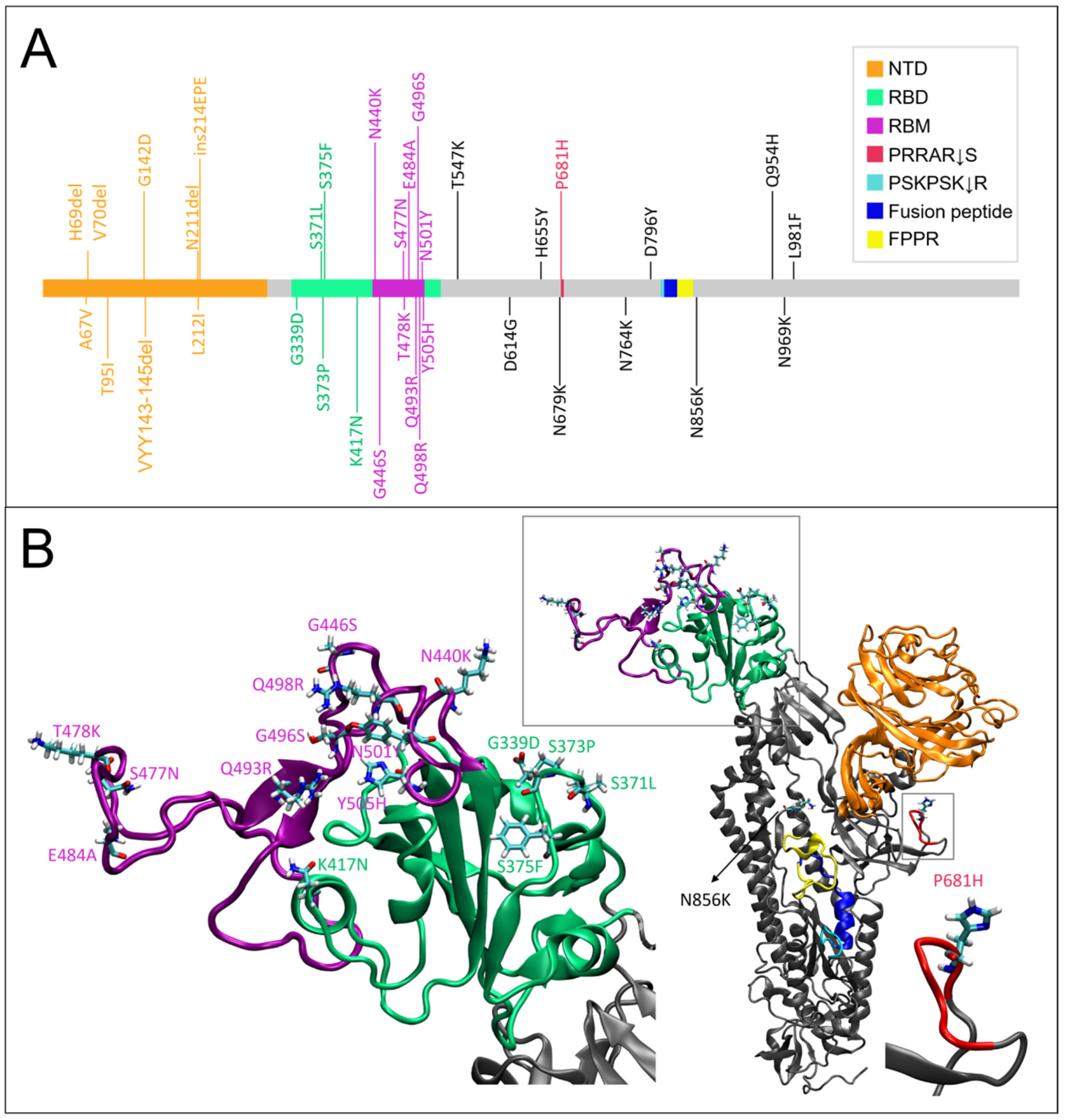
2. Results
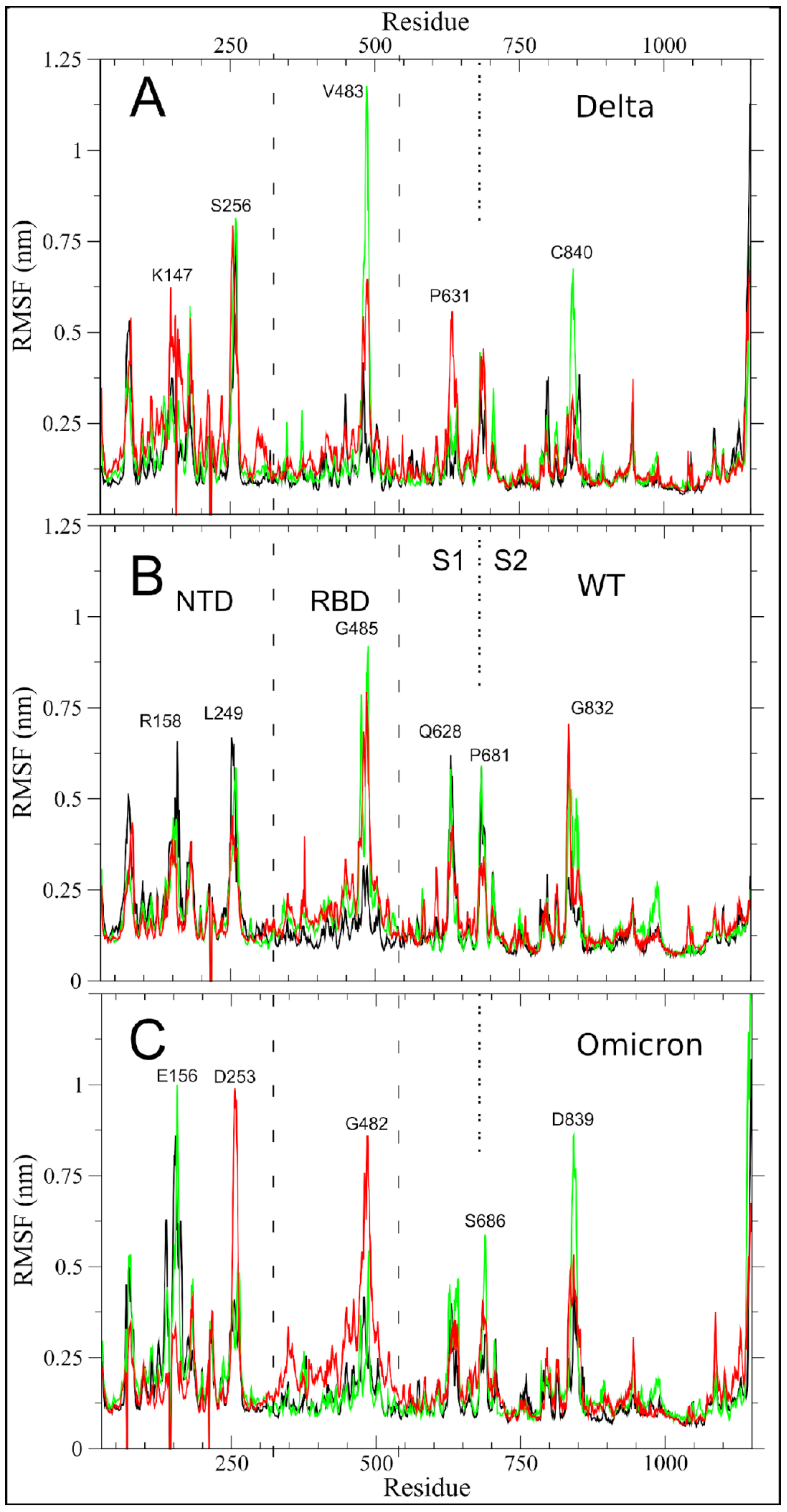
2.1. Altered Flexibility in the Delta and Omicron S Glycoprotein
2.2. Altered Long-Range Correlated Motions in Delta and Omicron S Glycoprotein
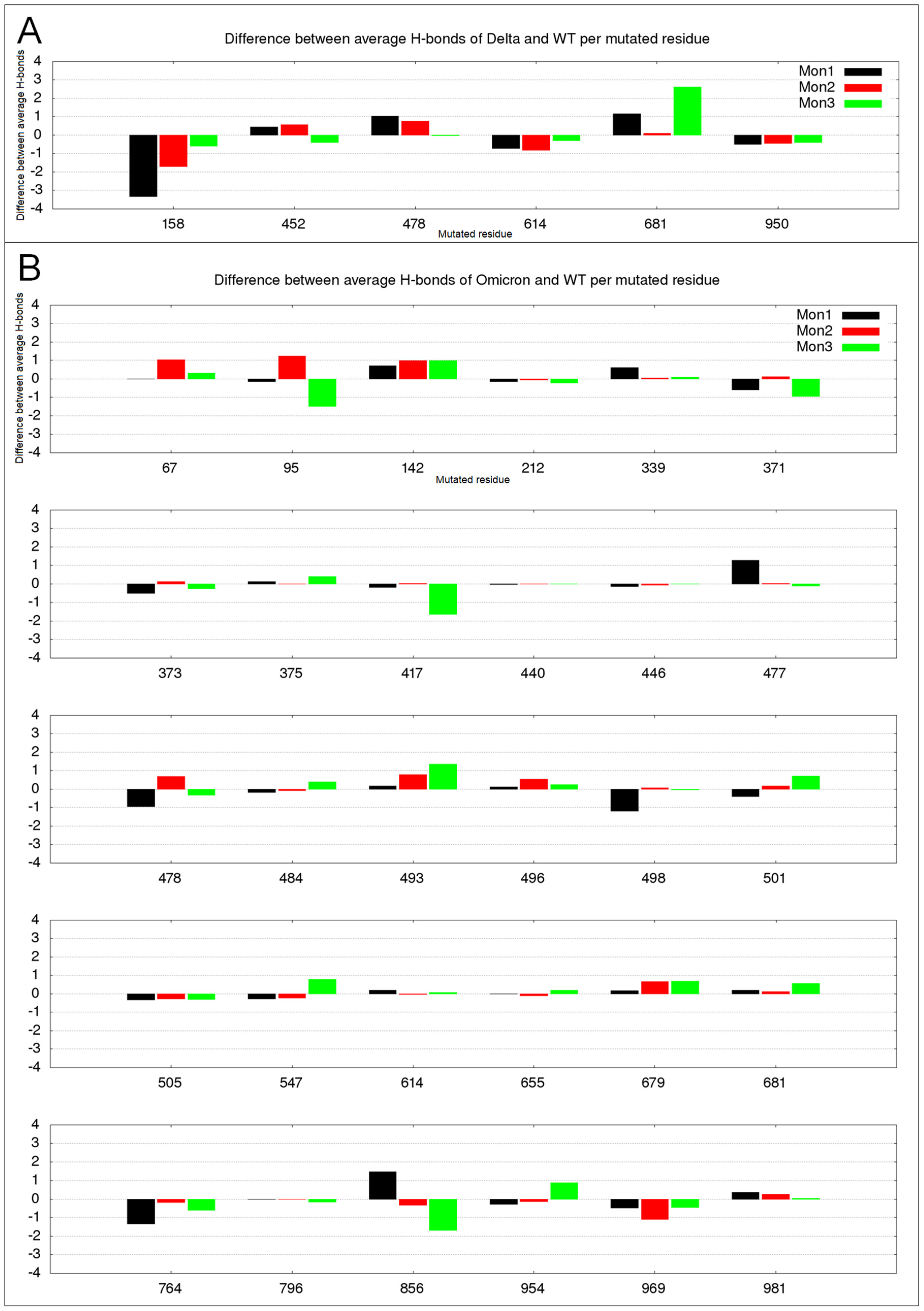
2.3. Hydrogen Bond Variation in Delta and Omicron Mutated Residues
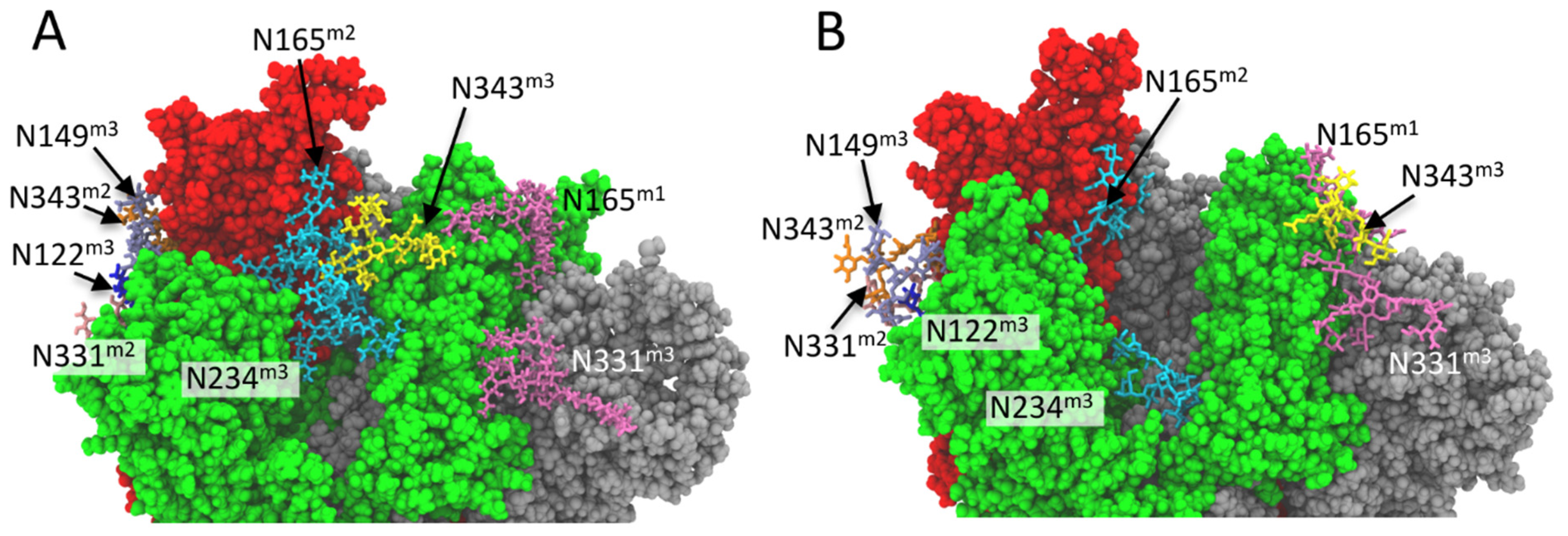
2.4. N-Glycan-RBD Domain Interaction in Delta and Omicron Variants
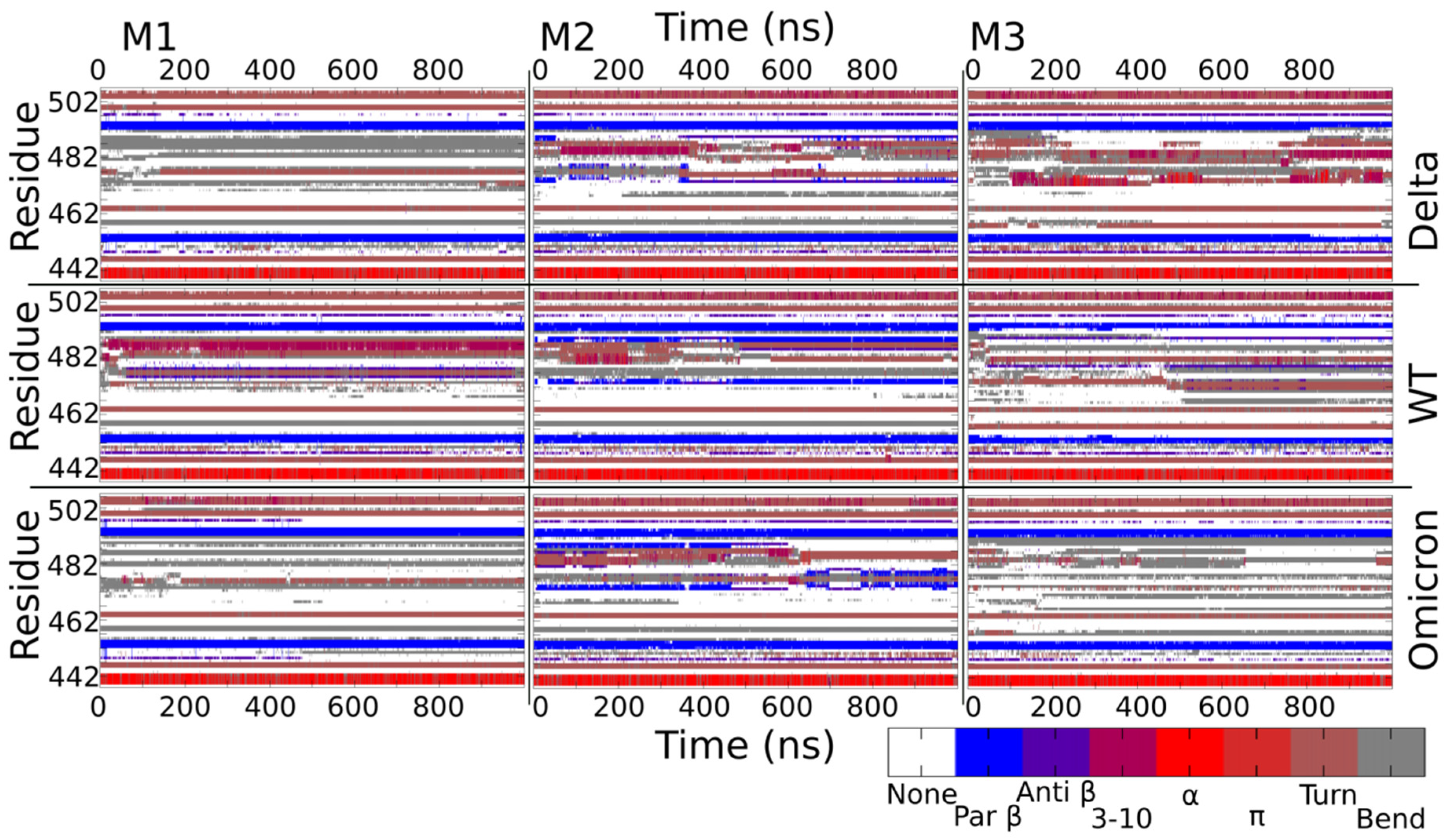
2.5. Secondary Structure Variation in Delta and Omicron Key Regions
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Modeling of S Glycoproteins Starting Structures
4.2. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
4.3. Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SP | Structural proteins |
| NSP | Non-structural proteins |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus disease 2019 |
| VUM | Variants under monitoring |
| VOC | Variant of concern |
| VOI | Variant of interest |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| CDC | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |
| WT | Wild-type |
| RMSF | Root mean square fluctuations |
| MD | Molecular dynamics |
| RBM | Receptor binding motif |
| RBD | Receptor binding domain |
| ACE2 | Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 |
| NTD | N-terminal domain |
| FP | Fusion peptide |
| FCS | Furin-like cleavage site |
| ED | Essential dynamics |
| FPPR | Fusion peptide proximal region |
References
- Ksiazek, T.G.; Erdman, D.; Goldsmith, C.S.; Zaki, S.R.; Peret, T.; Emery, S.; Tong, S.; Urbani, C.; Comer, J.A.; Lim, W.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus Associated with Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1953–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.-J.; Ni, Z.-Y.; Hu, Y.; Liang, W.-H.; Ou, C.-Q.; He, J.-X.; Liu, L.; Shan, H.; Lei, C.-L.; Hui, D.S.C.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/en/activities/tracking-SARS-CoV-2-variants (accessed on 26 May 2022).
- Gorbalenya, A.E.; Baker, S.C.; Baric, R.S.; de Groot, R.J.; Drosten, C.; Gulyaeva, A.A.; Haagmans, B.L.; Lauber, C.; Leontovich, A.M.; Neuman, B.W.; et al. The Species Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Related Coronavirus: Classifying 2019-NCoV and Naming It SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gordon, D.E.; Jang, G.M.; Bouhaddou, M.; Xu, J.; Obernier, K.; White, K.M.; O’Meara, M.J.; Rezelj, V.V.; Guo, J.Z.; Swaney, D.L.; et al. A SARS-CoV-2 Protein Interaction Map Reveals Targets for Drug Repurposing. Nature 2020, 583, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.A.; VanInsberghe, D.; Koelle, K. Insights from SARS-CoV-2 Sequences. Science 2021, 371, 466–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, Q.; Inchakalody, V.P.; Merhi, M.; Mestiri, S.; Taib, N.; Moustafa Abo El-Ella, D.; Bedhiafi, T.; Raza, A.; Al-Zaidan, L.; Mohsen, M.O.; et al. Emerging COVID-19 Variants and Their Impact on SARS-CoV-2 Diagnosis, Therapeutics and Vaccines. Ann. Med. 2022, 54, 524–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SARS-CoV-2 Variant Classifications and Definitions. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/variants/variant-classifications.html (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- Stefanelli, P.; Trentini, F.; Guzzetta, G.; Marziano, V.; Mammone, A.; Sane Schepisi, M.; Poletti, P.; Molina Grané, C.; Manica, M.; del Manso, M.; et al. Co-Circulation of SARS-CoV-2 Alpha and Gamma Variants in Italy, February and March 2021. Euro Surveill. Bull. Eur. Sur Les Mal. Transm. Eur. Commun. Dis. Bull. 2022, 27, 2100429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colavita, F.; Meschi, S.; Gruber, C.E.M.; Rueca, M.; Vairo, F.; Matusali, G.; Lapa, D.; Giombini, E.; de Carli, G.; Spaziante, M.; et al. Virological and Serological Characterisation of SARS-CoV-2 Infections Diagnosed After MRNA BNT162b2 Vaccination Between December 2020 and March 2021. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 815870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliamonte, M.S.; Mavian, C.; Zainabadi, K.; Cash, M.N.; Lednicky, J.A.; Magalis, B.R.; Riva, A.; Deschamps, M.M.; Liautaud, B.; Rouzier, V.; et al. Rapid Emergence and Spread of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Gamma (P.1) Variant in Haiti. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 74, 2057–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracking Omicron and Other Coronavirus Variants—The New York Times. Available online: https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2021/health/coronavirus-variant-tracker.html (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- Adam, D. What Scientists Know about New, Fast-Spreading Coronavirus Variants. Nature 2021, 594, 19–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EpiCentro—Portale Di Epidemiologia per Gli Operatori Sanitari. Available online: https://www.epicentro.iss.it/ (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- Mallapaty, S. Where Did Omicron Come from? Three Key Theories. Nature 2022, 602, 26–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Pérez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 MRNA Covid-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, L.A.; Anderson, E.J.; Rouphael, N.G.; Roberts, P.C.; Makhene, M.; Coler, R.N.; McCullough, M.P.; Chappell, J.D.; Denison, M.R.; Stevens, L.J.; et al. An MRNA Vaccine against SARS-CoV-2—Preliminary Report. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1920–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez Bernal, J.; Andrews, N.; Gower, C.; Gallagher, E.; Simmons, R.; Thelwall, S.; Stowe, J.; Tessier, E.; Groves, N.; Dabrera, G.; et al. Effectiveness of Covid-19 Vaccines against the B.1.617.2 (Delta) Variant. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Self, W.H.; Sandkovsky, U.; Reilly, C.S.; Vock, D.M.; Gottlieb, R.L.; Mack, M.; Golden, K.; Dishner, E.; Vekstein, A.; Ko, E.R.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Two Neutralising Monoclonal Antibody Therapies, Sotrovimab and BRII-196 plus BRII-198, for Adults Hospitalised with COVID-19 (TICO): A Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 622–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/covid-19/variants-concern (accessed on 26 May 2022).
- Rife Magalis, B.; Rich, S.; Tagliamonte, M.S.; Mavian, C.; Cash, M.N.; Riva, A.; Marini, S.; Amador, D.M.; Zhang, Y.; Shapiro, J.; et al. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Delta Vaccine Breakthrough Transmissibility in Alachua County, Florida. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, ciac197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalis, B.R.; Mavian, C.; Tagliamonte, M.; Rich, S.N.; Cash, M.; Riva, A.; Loeb, J.C.; Norris, M.; Amador, D.M.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Low-Frequency Variants in Mildly Symptomatic Vaccine Breakthrough Infections Presents a Doubled-Edged Sword. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 3192–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliamonte, M.S.; Abid, N.; Borocci, S.; Sangiovanni, E.; Ostrov, D.A.; Kosakovsky Pond, S.L.; Salemi, M.; Chillemi, G.; Mavian, C. Multiple Recombination Events and Strong Purifying Selection at the Origin of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein Increased Correlated Dynamic Movements. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borocci, S.; Cerchia, C.; Grottesi, A.; Sanna, N.; Prandi, I.G.; Abid, N.; Beccari, A.R.; Chillemi, G.; Talarico, C. Altered Local Interactions and Long-Range Communications in UK Variant (B.1.1.7) Spike Glycoprotein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Outbreak.Info. Available online: https://outbreak.info/situation-reports/delta (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- White, J.M.; Whittaker, G.R. Fusion of Enveloped Viruses in Endosomes. Traffic 2016, 17, 593–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amadei, A.; Linssen, A.B.M.; Berendsen, H.J.C. Essential Dynamics of Proteins. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 1993, 17, 412–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, T.; Peng, H.; Sterling, S.M.; Walsh, R.M.J.; Rawson, S.; Rits-Volloch, S.; Chen, B. Distinct Conformational States of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein. Science 2020, 369, 1586–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, H.; Fadda, E.; Crispin, M. Principles of SARS-CoV-2 Glycosylation. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2022, 75, 102402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casalino, L.; Gaieb, Z.; Goldsmith, J.A.; Hjorth, C.K.; Dommer, A.C.; Harbison, A.M.; Fogarty, C.A.; Barros, E.P.; Taylor, B.C.; McLellan, J.S.; et al. Beyond Shielding: The Roles of Glycans in the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 1722–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harbison, A.M.; Fogarty, C.A.; Phung, T.K.; Satheesan, A.; Schulz, B.L.; Fadda, E. Fine-Tuning the Spike: Role of the Nature and Topology of the Glycan Shield in the Structure and Dynamics of the SARS-CoV-2 S. Chem. Sci. 2022, 13, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sztain, T.; Ahn, S.-H.; Bogetti, A.T.; Casalino, L.; Goldsmith, J.A.; Seitz, E.; McCool, R.S.; Kearns, F.L.; Acosta-Reyes, F.; Maji, S.; et al. A Glycan Gate Controls Opening of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein. Nat. Chem. 2021, 13, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, A.; Bertoni, M.; Bienert, S.; Studer, G.; Tauriello, G.; Gumienny, R.; Heer, F.T.; de Beer, T.A.P.; Rempfer, C.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Homology Modelling of Protein Structures and Complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W296–W303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walls, A.C.; Park, Y.-J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Wall, A.; McGuire, A.T.; Veesler, D. Structure, Function, and Antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein. Cell 2020, 181, 281–292.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, B. P-LINCS: A Parallel Linear Constraint Solver for Molecular Simulation. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2008, 4, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrinello, M.; Rahman, A. Polymorphic Transitions in Single Crystals: A New Molecular Dynamics Method. J. Appl. Phys. 1981, 52, 7182–7190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussi, G.; Donadio, D.; Parrinello, M. Canonical Sampling through Velocity Rescaling. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 126, 014101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Darden, T.; York, D.; Pedersen, L. Particle Mesh Ewald: An N⋅log(N) Method for Ewald Sums in Large Systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 10089–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maier, J.A.; Martinez, C.; Kasavajhala, K.; Wickstrom, L.; Hauser, K.E.; Simmerling, C. Ff14SB: Improving the Accuracy of Protein Side Chain and Backbone Parameters from Ff99SB. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2015, 11, 3696–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kirschner, K.N.; Yongye, A.B.; Tschampel, S.M.; González-Outeiriño, J.; Daniels, C.R.; Foley, B.L.; Woods, R.J. GLYCAM06: A Generalizable Biomolecular Force Field. Carbohydrates. J. Comput. Chem. 2008, 29, 622–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mark, P.; Nilsson, L. Structure and Dynamics of the TIP3P, SPC, and SPC/E Water Models at 298 K. J. Phys. Chem. A 2001, 105, 9954–9960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van verSpoel, D.; Lindahl, E.; Hess, B.; Groenhof, G.; Mark, A.E.; Berendsen, H.J.C. GROMACS: Fast, Flexible, and Free. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1701–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, D.R.; Cheatham, T.E. PTRAJ and CPPTRAJ: Software for Processing and Analysis of Molecular Dynamics Trajectory Data. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2013, 9, 3084–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daura, X.; Gademann, K.; Jaun, B.; Seebach, D.; van Gunsteren, W.F.; Mark, A.E. Peptide Folding: When Simulation Meets Experiment. Angew. Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual Molecular Dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrignanò, T.; Gioiosa, S.; Flati, T.; Cestari, M.; Picardi, E.; Chiara, M.; Fratelli, M.; Amente, S.; Cirilli, M.; Tangaro, M.A.; et al. ELIXIR-IT HPC@CINECA: High Performance Computing Resources for the Bioinformatics Community. BMC Bioinform. 2020, 21, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prandi, I.G.; Mavian, C.; Giombini, E.; Gruber, C.E.M.; Pietrucci, D.; Borocci, S.; Abid, N.; Beccari, A.R.; Talarico, C.; Chillemi, G. Structural Evolution of Delta (B.1.617.2) and Omicron (BA.1) Spike Glycoproteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8680. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158680
Prandi IG, Mavian C, Giombini E, Gruber CEM, Pietrucci D, Borocci S, Abid N, Beccari AR, Talarico C, Chillemi G. Structural Evolution of Delta (B.1.617.2) and Omicron (BA.1) Spike Glycoproteins. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(15):8680. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158680
Chicago/Turabian StylePrandi, Ingrid Guarnetti, Carla Mavian, Emanuela Giombini, Cesare E. M. Gruber, Daniele Pietrucci, Stefano Borocci, Nabil Abid, Andrea R. Beccari, Carmine Talarico, and Giovanni Chillemi. 2022. "Structural Evolution of Delta (B.1.617.2) and Omicron (BA.1) Spike Glycoproteins" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 15: 8680. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158680
APA StylePrandi, I. G., Mavian, C., Giombini, E., Gruber, C. E. M., Pietrucci, D., Borocci, S., Abid, N., Beccari, A. R., Talarico, C., & Chillemi, G. (2022). Structural Evolution of Delta (B.1.617.2) and Omicron (BA.1) Spike Glycoproteins. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(15), 8680. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158680










