Discovery of the First Highly Selective Antagonist of the GluK3 Kainate Receptor Subtype
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
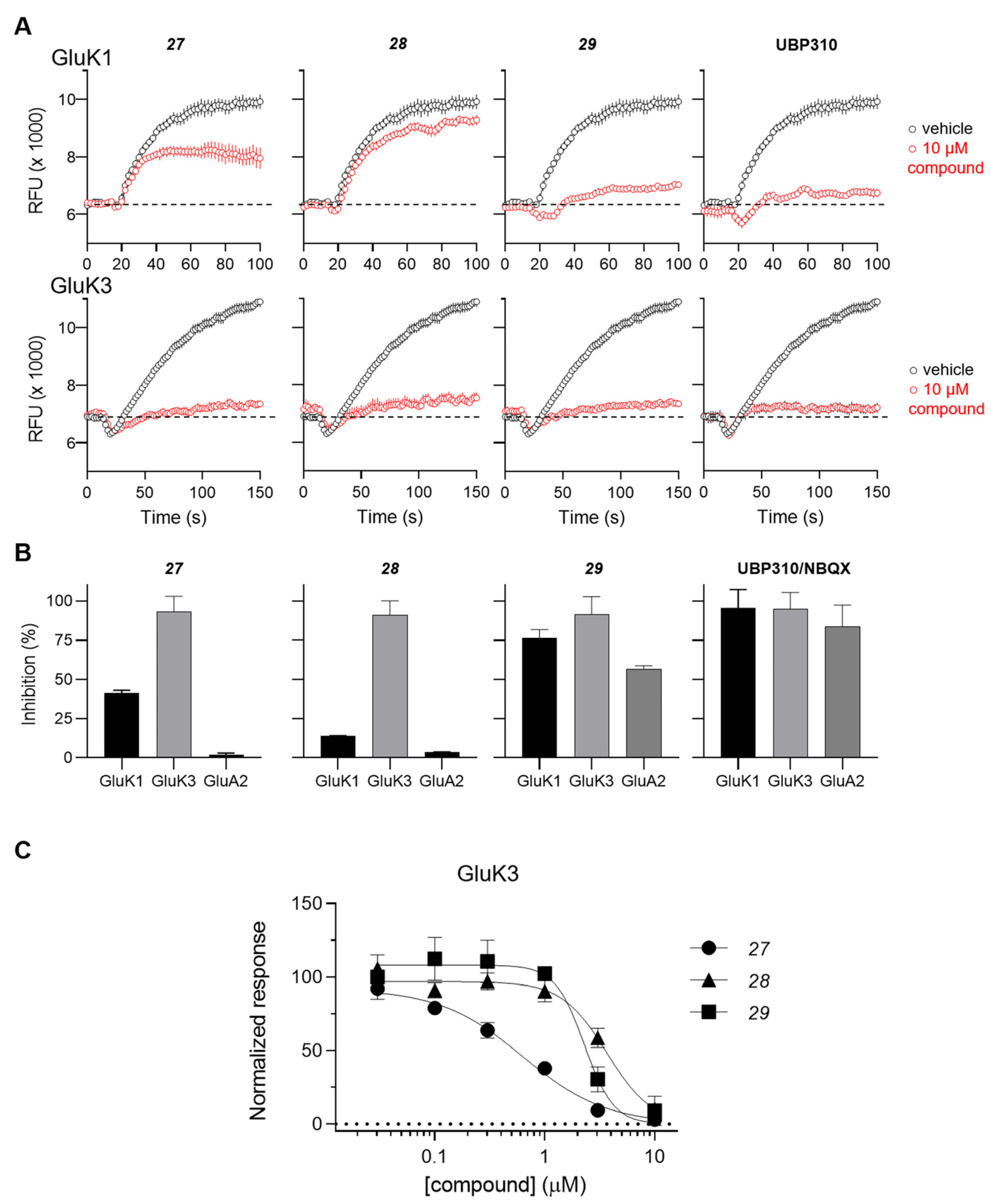
2.2. Pharmacological Characterization
2.2.1. Binding Pharmacology
2.2.2. Functional Pharmacology
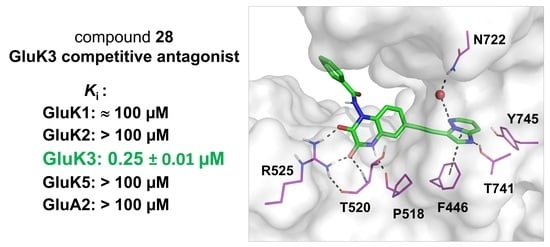
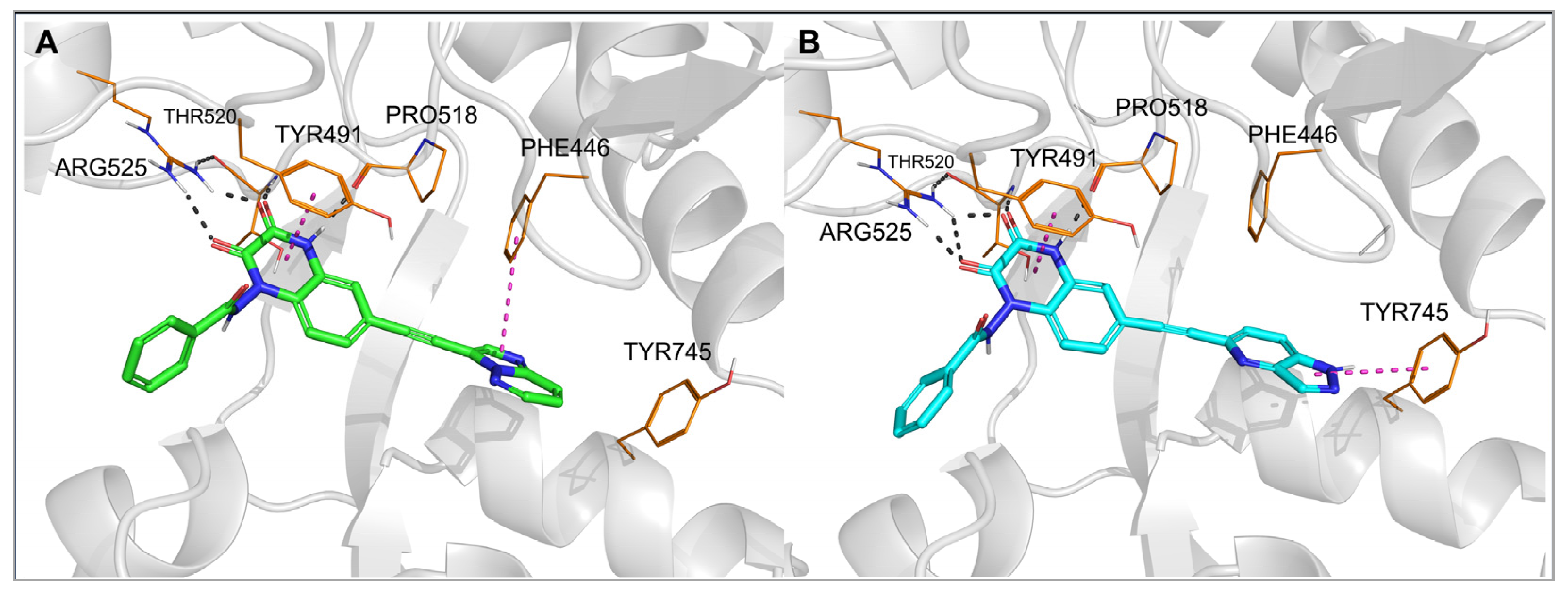
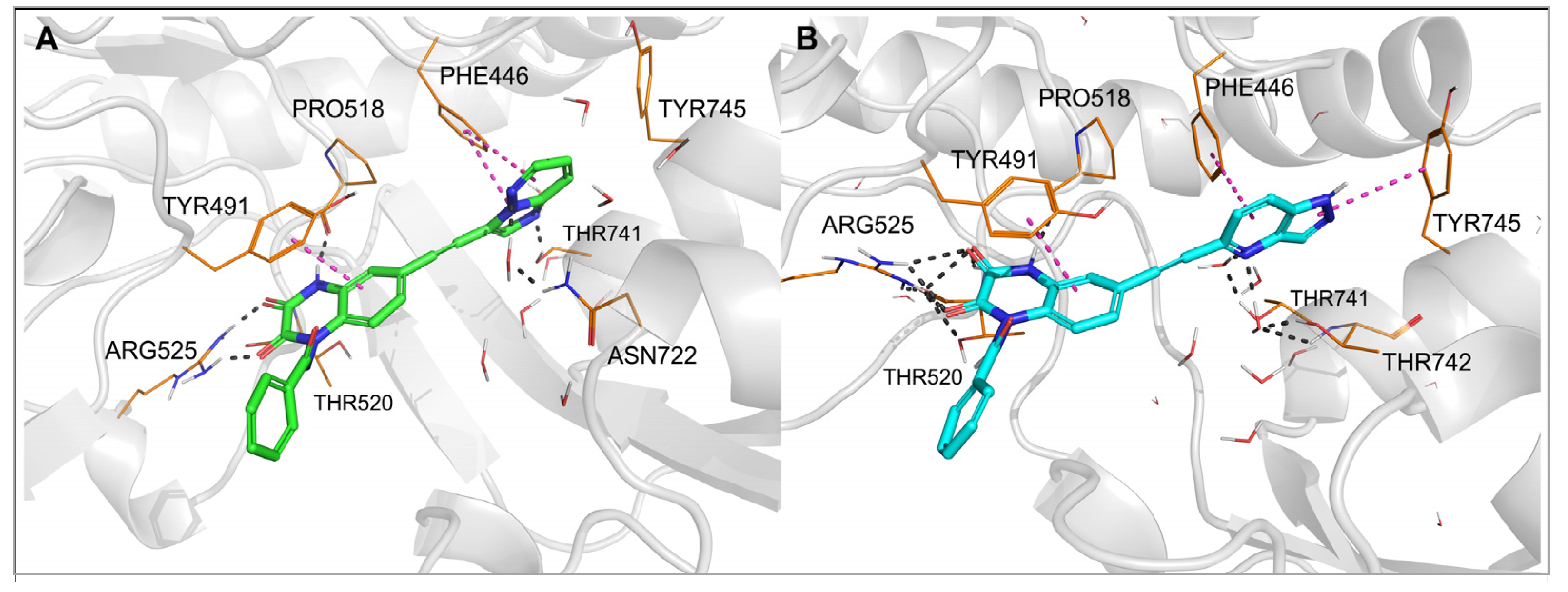
2.3. Molecular Modeling
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.2. Pharmacology
3.2.1. Receptor-Binding Studies
3.2.2. Intracellular Ca2+ Assay
3.2.3. mGluR2 Functional Assay
3.2.4. mGluR4/5 Functional Assay
3.3. Molecular Modeling
3.3.1. Homology Modeling
3.3.2. Docking Studies
3.3.3. Molecular Dynamics
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hansen, K.B.; Wollmuth, L.P.; Bowie, D.; Furukawa, H.; Menniti, F.S.; Sobolevsky, A.I.; Swanson, G.T.; Swanger, S.A.; Greger, I.H.; Nakagawa, T.; et al. Structure, function, and pharmacology of glutamate receptor ion channels. Pharmacol. Rev. 2021, 73, 298–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholefield, C.L.; Atlason, P.T.; Jane, D.E.; Molnár, E. Assembly and trafficking of homomeric and heteromeric kainate receptors with impaired ligand binding sites. Neurochem. Res. 2019, 44, 585–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, A.J.; Gurung, S.; Henley, J.M.; Nakamura, Y.; Wilkinson, K.A. Exciting times: New advances towards nnderstanding the regulation and roles of kainate receptors. Neurochem. Res. 2019, 44, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negrete-Díaz, J.V.; Falcón-Moya, R.; Rodríguez-Moreno, A. Kainate receptors: From synaptic activity to disease. FEBS J. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valbuena, S.; Lerma, J. Kainate receptors, homeostatic gatekeepers of synaptic plasticity. Neuroscience 2021, 456, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, P.S.; Perrais, D.; Coussen, F.; Barhanin, J.; Bettler, B.; Mann, J.R.; Malva, J.O.; Heinemann, S.F.; Mulle, C. GluR7 is an essential subunit of presynaptic kainate autoreceptors at hippocampal mossy fiber synapses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 12181–12186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerma, J.; Marques, J.M. Kainate receptors in health and disease. Neuron 2013, 80, 292–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, R.H.; Eastwood, S.L.; Harrison, P.J. Distribution of kainate receptor subunit mRNAs in human hippocampus, neocortex and cerebellum, and bilateral reduction of hippocampal GluR6 and KA2 transcripts in schizophrenia. Brain Res. 1997, 751, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takago, H.; Oshima-Takago, T. Pre- and postsynaptic ionotropic glutamate receptors in the auditory system of mammals. Hear. Res. 2018, 362, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcón-Moya, R.; Rodríguez-Moreno, A. Metabotropic actions of kainate receptors modulating glutamate release. Neuropharmacology 2021, 197, 108696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrete-Díaz, J.V.; Sihra, T.S.; Flores, G.; Rodríguez-Moreno, A. Non-canonical mechanisms of presynaptic kainate receptors controlling glutamate release. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Moreno, A.; Sihra, T.S. Metabotropic actions of kainate receptors in the control of glutamate release in the hippocampus. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2011, 717, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sihra, T.S.; Rodríguez-Moreno, A. Presynaptic kainate receptor-mediated bidirectional modulatory actions: Mechanisms. Neurochem. Int. 2013, 62, 982–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrais, D.; Pinheiro, P.S.; Jane, D.E.; Mulle, C. Antagonism of recombinant and native GluK3-containing kainate receptors. Neuropharmacology 2009, 56, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcón-Moya, R.; Sihra, T.S.; Rodríguez-Moreno, A. Kainate receptors: Role in epilepsy. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsch, B.; Reis, J.; Gasior, M.; Kaminski, R.M.; Rogawski, M.A. Role of GluK1 kainate receptors in seizures, epileptic discharges, and epileptogenesis. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 5765–5775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valbuena, S.; Lerma, J. Losing balance: Kainate receptors and psychiatric disorders comorbidities. Neuropharmacology 2021, 191, 108558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, M. Cortical kainate receptors and behavioral anxiety. Mol. Brain 2017, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffer, H.H.; Heinemann, S.F. Association of the human kainate receptor GluR7 gene (GRIK3) with recurrent major depressive disorder. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2007, 144b, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Y.; Bhatia, M.S.; Mediratta, P.K.; Sharma, K.K.; Negi, H.; Chosdol, K.; Sinha, S. Association between the ionotropic glutamate receptor kainate3 (GRIK3) Ser310Ala polymorphism and schizophrenia in the Indian population. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 10, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, G.; Ismail Kucukali, C.; Orhan, N.; Ozkok, E.; Zengin, A.; Aydin, M.; Kara, I. Are GRIK3 (T928G) gene variants in schizophrenia patients different from those in their first-degree relatives? Psychiatry Res. 2010, 175, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samengo, I.; Curro, D.; Navarra, P.; Barrese, V.; Taglialatela, M.; Martire, M. Molecular and pharmacological evidence for a facilitatory functional role of pre-synaptic GLUK2/3 kainate receptors on GABA release in rat trigeminal caudal nucleus. Eur. J. Pain 2012, 16, 1148–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, M.J.; Bogaert, L.; Hicks, C.A.; Bond, A.; Ward, M.A.; Ebinger, G.; Ornstein, P.L.; Michotte, Y.; Lodge, D. LY377770, a novel iGlu5 kainate receptor antagonist with neuroprotective effects in global and focal cerebral ischaemia. Neuropharmacology 2000, 39, 1575–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, B.; Alt, A.; Ogden, A.M.; Gates, M.; Dieckman, D.K.; Clemens-Smith, A.; Ho, K.H.; Jarvie, K.; Rizkalla, G.; Wright, R.A.; et al. Pharmacological characterization of the competitive GLUK5 receptor antagonist decahydroisoquinoline LY466195 in vitro and in vivo. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 318, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubisch, W.; Behl, B.; Henn, C.; Hofmann, H.P.; Reeb, J.; Regner, F.; Vierling, M. Pyrrolylquinoxalinediones carrying a piperazine residue represent highly potent and selective ligands to the homomeric kainate receptor GluR5. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2002, 12, 2113–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolman, N.P.; More, J.C.; Alt, A.; Knauss, J.L.; Pentikainen, O.T.; Glasser, C.R.; Bleakman, D.; Mayer, M.L.; Collingridge, G.L.; Jane, D.E. Synthesis and pharmacological characterization of N3-substituted willardiine derivatives: Role of the substituent at the 5-position of the uracil ring in the development of highly potent and selective GLUK5 kainate receptor antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 1558–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, J.C.A.; Nistico, R.; Dolman, N.P.; Clarke, V.R.J.; Alt, A.J.; Ogden, A.M.; Buelens, F.P.; Troop, H.M.; Kelland, E.E.; Pilato, F.; et al. Characterisation of UBP296: A novel, potent and selective kainate receptor antagonist. Neuropharmacology 2004, 47, 46–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulie, C.B.M.; Larsen, Y.; Leteneur, C.; Barthet, G.; Bjørn-Yoshimoto, W.E.; Malhaire, F.; Nielsen, B.; Pin, J.-P.; Mulle, C.; Pickering, D.S.; et al. (S)-2-Mercaptohistidine: A first selective orthosteric GluK3 antagonist. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2022, 13, 1580–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honoré, T.; Davies, S.N.; Drejer, J.; Fletcher, E.J.; Jacobsen, P.; Lodge, D.; Nielsen, F.E. Quinoxalinediones: Potent competitive non-NMDA glutamate receptor antagonists. Science 1988, 241, 701–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheardown, M.J.; Nielsen, E.O.; Hansen, A.J.; Jacobsen, P.; Honore, T. 2,3-Dihydroxy-6-nitro-7-sulfamoyl-benzo(F)quinoxaline: A neuroprotectant for cerebral ischemia. Science 1990, 247, 571–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catarzi, D.; Colotta, V.; Varano, F. Competitive AMPA receptor antagonists. Med. Res. Rev. 2007, 27, 239–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Møllerud, S.; Hansen, R.B.; Pallesen, J.; Temperini, P.; Pasini, D.; Bornholt, J.; Nielsen, B.; Mamedova, E.; Chalupnik, P.; Paternain, A.V.; et al. N-(7-(1 H-Imidazol-1-yl)-2,3-dioxo-6-(trifluoromethyl)-3,4-dihydroquinoxalin-1(2 H)-yl)benzamide, a new kainate receptor selective antagonist and analgesic: Synthesis, X-ray crystallography, structure-affinity relationships, and in vitro and in vivo pharmacology. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 4685–4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallesen, J.; Møllerud, S.; Frydenvang, K.; Pickering, D.S.; Bornholdt, J.; Nielsen, B.; Pasini, D.; Han, L.; Marconi, L.; Kastrup, J.S.; et al. N1-substituted quinoxaline-2,3-diones as kainate receptor antagonists: X-ray crystallography, structure−affinity relationships, and in vitro pharmacology. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 1841–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löscher, W.; Lehmann, H.; Behl, B.; Seemann, D.; Teschendorf, H.J.; Hofmann, H.P.; Lubisch, W.; Höger, T.; Lemaire, H.G.; Gross, G. A new pyrrolyl-quinoxalinedione series of non-NMDA glutamate receptor antagonists: Pharmacological characterization and comparison with NBQX and valproate in the kindling model of epilepsy. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1999, 11, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrödinger Release 2021-4; LigPrep; Epik; Protein Preparation Wizard; Macromodel; Glide; Prime; MM-GBSA. Schrödinger, LLC.: New York, NY, USA, 2021.
- Pøhlsgaard, J.; Frydenvang, K.; Madsen, U.; Kastrup, J.S. Lessons from more than 80 structures of the GluA2 ligand-binding domain in complex with agonists, antagonists and allosteric modulators. Neuropharmacology 2011, 60, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demmer, C.S.; Rombach, D.; Liu, N.; Nielsen, B.; Pickering, D.S.; Bunch, L. Revisiting the quinoxalinedione scaffold in the construction of new ligands for the ionotropic glutamate receptors. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 2477–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcaide, A.; Marconi, L.; Marek, A.; Haym, I.; Nielsen, B.; Møllerud, S.; Jensen, M.; Conti, P.; Pickering, D.S.; Bunch, L. Synthesis and pharmacological characterization of the selective GluK1 radioligand (S)-2-amino-3-(6-[3H]-2,4-dioxo-3,4- dihydrothieno [3,2-d]pyrimidin-1(2H)-yl)propanoic acid ([3H]-NF608). MedChemComm 2016, 7, 2136–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Møllerud, S.; Pinto, A.; Marconi, L.; Frydenvang, K.; Thorsen, T.S.; Laulumaa, S.; Venskutonyte, R.; Winther, S.; Moral, A.M.C.; Tamborini, L.; et al. Structure and affinity of two bicyclic glutamate analogues at AMPA and kainate receptors. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 2056–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagot, E.; Pickering, D.S.; Pu, X.; Umberti, M.; Stensbøl, T.B.; Nielsen, B.; Chapelet, M.; Bolte, J.; Gefflaut, T.; Bunch, L. Chemo-enzymatic synthesis of a series of 2,4-syn-functionalized (S)-glutamate analogues: New insight into the structure-activity relation of ionotropic glutamate receptor subtypes 5, 6, and 7. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 4093–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Poulie, C.B.M.; Liu, N.; Jensen, A.A.; Bunch, L. Design, synthesis, and pharmacological characterization of heterobivalent ligands for the putative 5-HT(2A)/mGlu(2) receptor complex. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 9928–9949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, B.; Sali, A. Comparative Protein Structure Modeling Using MODELLER. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2016, 54, 5.6.1–5.6.37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Kim, B.-H.; Grishin, N.V. PROMALS3D: A tool for multiple protein sequence and structure alignments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 2295–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterhouse, A.; Bertoni, M.; Bienert, S.; Studer, G.; Tauriello, G.; Gumienny, R.; Heer, F.T.; De Beer, T.A.P.; Rempfer, C.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W296–W303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 2.5.2; Schrödinger, LLC.: New York, NY, USA, 2021.
- Phillips, J.C.; Hardy, D.J.; Maia, J.D.C.; Stone, J.E.; Ribeiro, J.V.; Bernardi, R.C.; Buch, R.; Fiorin, G.; Hénin, J.; Jiang, W.; et al. Scalable molecular dynamics on CPU and GPUarchitectures with NAMD. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 153, 44130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| cmpd | R | Ki (µM) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GluK1 | GluK2 | GluK3 | GluK5 | GluA2 | ||
| DNQX 1 | 0.65 ± 0.03 | 2.1 ± 0.3 | 0.36 ± 0.03 | 7.1 ± 0.9 | 0.25 ± 0.01 | |
| NBQX | 2.6 ± 0.1 | 5.4 ± 1.2 | 3.4 ± 0.6 | 152 ± 23 | 0.077 ± 0.010 | |
| 1 2 | Ph | >100 | ≈100 | 2.9 ± 0.3 | >100 | 24 ± 6 |
| 5 | 3-Me-Ph | ≈100 | ≈100 | 1.4 ± 0.4 | >100 | >100 |
| 6 | 4-Me-Ph | ≥100 | nd | 6.1 ± 0.8 | nd | nd |
| 7 | 4-Et-Ph | >100 | >100 | 20 ± 1 | >100 | >100 |
| 8 | 4-nPr-Ph | >100 | >100 | 50 ± 12 | >100 | >100 |
| 9 | 4-iPr-Ph | >100 | >100 | 38 ± 10 | >100 | >100 |
| 10 | 4-Cl-Ph | >100 | >100 | 3.5 ± 0.7 | >100 | >100 |
| 11 | 4-CF3-Ph | ≈100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 12 | 4-MeO-Ph | >100 | >100 | 8.3 ± 0.4 | >100 | >100 |
| 13 | 4-PhO-Ph | ≥100 | nd | 7.9 ± 0.7 | nd | nd |
| 14 | 3-COOH-Ph | >100 | >100 | 28 ± 2 | >100 | >100 |
| 15 | 4-COOH-Ph | >100 | >100 | 31 ± 4 | >100 | >100 |
| 16 | 4-NH2SO2-Ph | >100 | >100 | ≈100 | >100 | >100 |
| 17 | 4-FSO2-Ph | 1.1 ± 0.4 | >100 | 8.1 ± 0.4 | >100 | ≈100 |
| 18 | 2-OH-Ph | >100 | nd | 14 ± 2 | nd | nd |
| 19 | 3-OH-Ph | >100 | >100 | 3.2 ± 0.6 | >100 | ≈100 |
| 20 | 4-OHCH2-Ph | ≈100 | >100 | 5.8 ± 1.5 | >100 | >100 |
| 21 | 2-NH2-Ph | 14 ± 2 | nd | 1.0 ± 0.1 | nd | nd |
| 22 | 3-NH2-Ph | >100 | nd | ≈100 | nd | nd |
| 23 | 4-NH2-Ph | >100 | >100 | 1.4 ± 0.2 | >100 | >100 |
| 24 | 4-N(CH3)2-Ph | 39 ± 4 | nd | 24 ± 4 | nd | nd |
| 25 | pyridin-4-yl | >100 | >100 | 25 ± 6 | >100 | >100 |
| 26 | 6-hydroxypyridin-3-yl | >100 | >100 | 11 ± 1 | >100 | >100 |
| 27 | pyrimidin-5-yl | 11 ± 2 | 12 ± 2 | 0.28 ± 0.02 | >100 | >100 |
| 28 | 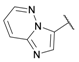 | ≈100 | >100 | 0.25 ± 0.01 | >100 | >100 |
| 29 | 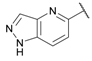 | 0.15 ± 0.05 | 0.091 ± 0.015 | 0.13 ± 0.03 | 3.8 ± 0.1 | 0.23 ± 0.02 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chałupnik, P.; Vialko, A.; Pickering, D.S.; Hinkkanen, M.; Donbosco, S.; Møller, T.C.; Jensen, A.A.; Nielsen, B.; Bay, Y.; Kristensen, A.S.; et al. Discovery of the First Highly Selective Antagonist of the GluK3 Kainate Receptor Subtype. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8797. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158797
Chałupnik P, Vialko A, Pickering DS, Hinkkanen M, Donbosco S, Møller TC, Jensen AA, Nielsen B, Bay Y, Kristensen AS, et al. Discovery of the First Highly Selective Antagonist of the GluK3 Kainate Receptor Subtype. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(15):8797. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158797
Chicago/Turabian StyleChałupnik, Paulina, Alina Vialko, Darryl S. Pickering, Markus Hinkkanen, Stephanie Donbosco, Thor C. Møller, Anders A. Jensen, Birgitte Nielsen, Yasmin Bay, Anders S. Kristensen, and et al. 2022. "Discovery of the First Highly Selective Antagonist of the GluK3 Kainate Receptor Subtype" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 15: 8797. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158797
APA StyleChałupnik, P., Vialko, A., Pickering, D. S., Hinkkanen, M., Donbosco, S., Møller, T. C., Jensen, A. A., Nielsen, B., Bay, Y., Kristensen, A. S., Johansen, T. N., Łątka, K., Bajda, M., & Szymańska, E. (2022). Discovery of the First Highly Selective Antagonist of the GluK3 Kainate Receptor Subtype. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(15), 8797. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158797