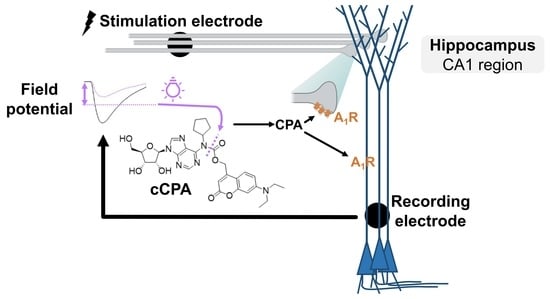
Ex Vivo Feedback Control of Neurotransmission Using a Photocaged Adenosine A1 Receptor Agonist
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Design and Synthesis of cCPA
2.2. Light-Triggered Release of CPA
2.3. Proof-of-Principle: Closed-Loop Photopharmacological Control of Neurotransmission
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis of Caged CPA Compound
3.2. Adenosine A1 Receptor Competitive Binding Assay
3.3. Acute Hippocampal Slice Recordings with a Multielectrode Array
3.3.1. Slice Preparation
3.3.2. Electrophysiological Recordings
3.3.3. Experimental Paradigms
3.3.4. Data Analysis
3.3.5. Statistical Analysis
3.3.6. Chemicals
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Svenningsson, P.; Hall, H.; Sedvall, G.; Fredholm, B.B. Distribution of Adenosine Receptors in the Postmortem Human Brain: An Extended Autoradiographic Study. Synapse 1997, 27, 322–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, A.; Holschbach, M.H.; Meyer, P.T.; Boy, C.; Herzog, H.; Olsson, R.A.; Coenen, H.H.; Zilles, K. In Vivo Imaging of Adenosine A1 Receptors in the Human Brain with [18F]CPFPX and Positron Emission Tomography. Neuroimage 2003, 19, 1760–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredholm, B.B.; IJzerman, A.P.; Jacobson, K.A.; Klotz, K.N.; Linden, J. International Union of Pharmacology. XXV. Nomenclature and Classification of Adenosine Receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2001, 53, 527–552. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spanoghe, J.; Larsen, L.E.; Craey, E.; Manzella, S.; Van Dycke, A.; Boon, P.; Raedt, R. The Signaling Pathways Involved in the Anticonvulsive Effects of the Adenosine A1 Receptor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benarroch, E.E. Adenosine and Its Receptors: Multiple Modulatory Functions and Potential Therapeutic Targets for Neurologic Disease. Neurology 2008, 70, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borea, P.A.; Gessi, S.; Merighi, S.; Vincenzi, F.; Varani, K. Pharmacology of Adenosine Receptors: The State of the Art. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 1591–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boison, D. Adenosine Dysfunction in Epilepsy. Glia 2012, 60, 1234–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, Y.; Yang, R.; Li, L.; Xu, X.; Liang, S. Purinergic Signaling: A Potential Therapeutic Target for Depression and Chronic Pain. Purinergic Signal. 2021, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricart-Ortega, M.; Font, J.; Llebaria, A. GPCR Photopharmacology. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2019, 488, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.M.; Silva, E.; Reis, R.L. Light-Triggered Release of Photocaged Therapeutics—Where Are We Now? J. Control Release 2019, 298, 154–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brieke, C.; Rohrbach, F.; Gottschalk, A.; Mayer, G.; Heckel, A. Light-Controlled Tools. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 8446–8476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Font, J.; López-Cano, M.; Notartomaso, S.; Scarselli, P.; Di Pietro, P.; Bresolí-Obach, R.; Battaglia, G.; Malhaire, F.; Rovira, X.; Catena, J.; et al. Optical Control of Pain in Vivo with a Photoactive MGlu5 Receptor Negative Allosteric Modulator. eLife 2017, 6, e23545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taura, J.; Nolen, E.G.; Cabré, G.; Hernando, J.; Squarcialupi, L.; López-Cano, M.; Jacobson, K.A.; Fernández-Dueñas, V.; Ciruela, F. Remote Control of Movement Disorders Using a Photoactive Adenosine A2Areceptor Antagonist. J. Control Release 2018, 283, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Cano, M.; Font, J.; Aso, E.; Sahlholm, K.; Cabré, G.; Giraldo, J.; De Koninck, Y.; Hernando, J.; Llebaria, A.; Fernández-Dueñas, V.; et al. Remote Local Photoactivation of Morphine Produces Analgesia without Opioid-Related Adverse Effects. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Cano, M.; Filgaira, I.; Nolen, E.G.; Cabré, G.; Hernando, J.; Tosh, D.K.; Jacobson, K.A.; Soler, C.; Ciruela, F. Optical Control of Adenosine A3 Receptor Function in Psoriasis. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 170, 105731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Rode, D.L.; Peterka, D.S.; Yuste, R.; Rothman, S.M. Optical Control of Focal Epilepsy In Vivo with Caged γ-Aminobutyric Acid. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 71, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glukhova, A.; Thal, D.M.; Nguyen, A.T.; Vecchio, E.A.; Jörg, M.; Scammells, P.J.; May, L.T.; Sexton, P.M.; Christopoulos, A. Structure of the Adenosine A1 Receptor Reveals the Basis for Subtype Selectivity. Cell 2017, 168, 867–877.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Z.G.; Tosh, D.K.; Jain, S.; Yu, J.; Suresh, R.R.; Jacobson, K.A. A1 adenosine receptor agonists, antagonists, and allosteric modulators. In The Adenosine Receptors; Borea, P.A., Varani, K., Gessi, S., Merighi, S., Vincenzi, F., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 59–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosh, D.K.; Rao, H.; Bitant, A.; Salmaso, V.; Mannes, P.; Lieberman, D.I.; Vaughan, K.L.; Mattison, J.A.; Rothwell, A.C.; Auchampach, J.A.; et al. Design and In Vivo Characterization of A1 Adenosine Receptor Agonists in the Native Ribose and Conformationally Constrained (N)-Methanocarba Series. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 1502–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mendonça, A.; Ribeiro, J.A. Influence of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Agonists on the Inhibitory Effects of Adenosine A1 Receptor Activation in the Rat Hippocampus. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 121, 1541–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sebastião, A.M.; Cunha, R.A.; De Mendonça, A.; Ribeiro, J.A. Modification of Adenosine Modulation of Synaptic Transmission in the Hippocampus of Aged Rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 131, 1629–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebola, N.; Coelho, J.E.; Costenla, A.R.; Lopes, L.V.; Parada, A.; Oliveira, C.R.; Soares-da-Silva, P.; De Mendonça, A.; Cunha, R.A. Decrease of Adenosine A1 Receptor Density and of Adenosine Neuromodulation the Hippocampus of Kindled Rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 18, 820–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benians, A.; Leaney, J.L.; Milligan, G.; Tinker, A. The Dynamics of Formation and Action of the Ternary Complex Revealed in Living Cells Using a G-Protein-Gated K+ Channel as a Biosensor. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 10851–10858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yun, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, R.; Chen, W.; Liu, C.; Wang, R.; Hou, Z.; Yu, Z.; Sun, Y.; IJzerman, A.P.; et al. Long Residence Time Adenosine A 1 Receptor Agonists Produce Sustained Wash-Resistant Antilipolytic Effect in Rat Adipocytes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 164, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gielen, F.; Wadman, W.J. Closed Loop Neuromodulation for Suppression of Epileptic Activity. U.S. Patent 6671555 B2, 30 December 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Gielen, F.; Wadman, W.J. Closed Loop Neuromodulation for Suppression of Epileptic Activity. U.S. Patent 7006872 B2, 28 February 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, V.; Chamberlain, S.D. Novel Photoinduced Functionalized C-Alkylations in Purine Systems. J. Org. Chem. 1985, 50, 5069–5075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadler, A.; Reither, G.; Feng, S.; Stein, F.; Reither, S.; Müller, R.; Schultz, C. The fatty acid composition of diacylglycerols determines local signaling patterns. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 6330–6334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, S. Regioselective alkylation of the exocyclic nitrogen of adenine and adenosine by the Mitsunobu reaction. Tetrahedron Lett. 2010, 51, 2948–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Craey, E.; Hulpia, F.; Spanoghe, J.; Manzella, S.; Larsen, L.E.; Sprengers, M.; De Bundel, D.; Smolders, I.; Carrette, E.; Delbeke, J.; et al. Ex Vivo Feedback Control of Neurotransmission Using a Photocaged Adenosine A1 Receptor Agonist. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8887. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23168887
Craey E, Hulpia F, Spanoghe J, Manzella S, Larsen LE, Sprengers M, De Bundel D, Smolders I, Carrette E, Delbeke J, et al. Ex Vivo Feedback Control of Neurotransmission Using a Photocaged Adenosine A1 Receptor Agonist. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(16):8887. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23168887
Chicago/Turabian StyleCraey, Erine, Fabian Hulpia, Jeroen Spanoghe, Simona Manzella, Lars E. Larsen, Mathieu Sprengers, Dimitri De Bundel, Ilse Smolders, Evelien Carrette, Jean Delbeke, and et al. 2022. "Ex Vivo Feedback Control of Neurotransmission Using a Photocaged Adenosine A1 Receptor Agonist" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 16: 8887. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23168887
APA StyleCraey, E., Hulpia, F., Spanoghe, J., Manzella, S., Larsen, L. E., Sprengers, M., De Bundel, D., Smolders, I., Carrette, E., Delbeke, J., Vonck, K., Boon, P., Van Calenbergh, S., Wadman, W. J., & Raedt, R. (2022). Ex Vivo Feedback Control of Neurotransmission Using a Photocaged Adenosine A1 Receptor Agonist. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(16), 8887. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23168887