Achromobacter spp. Adaptation in Cystic Fibrosis Infection and Candidate Biomarkers of Antimicrobial Resistance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
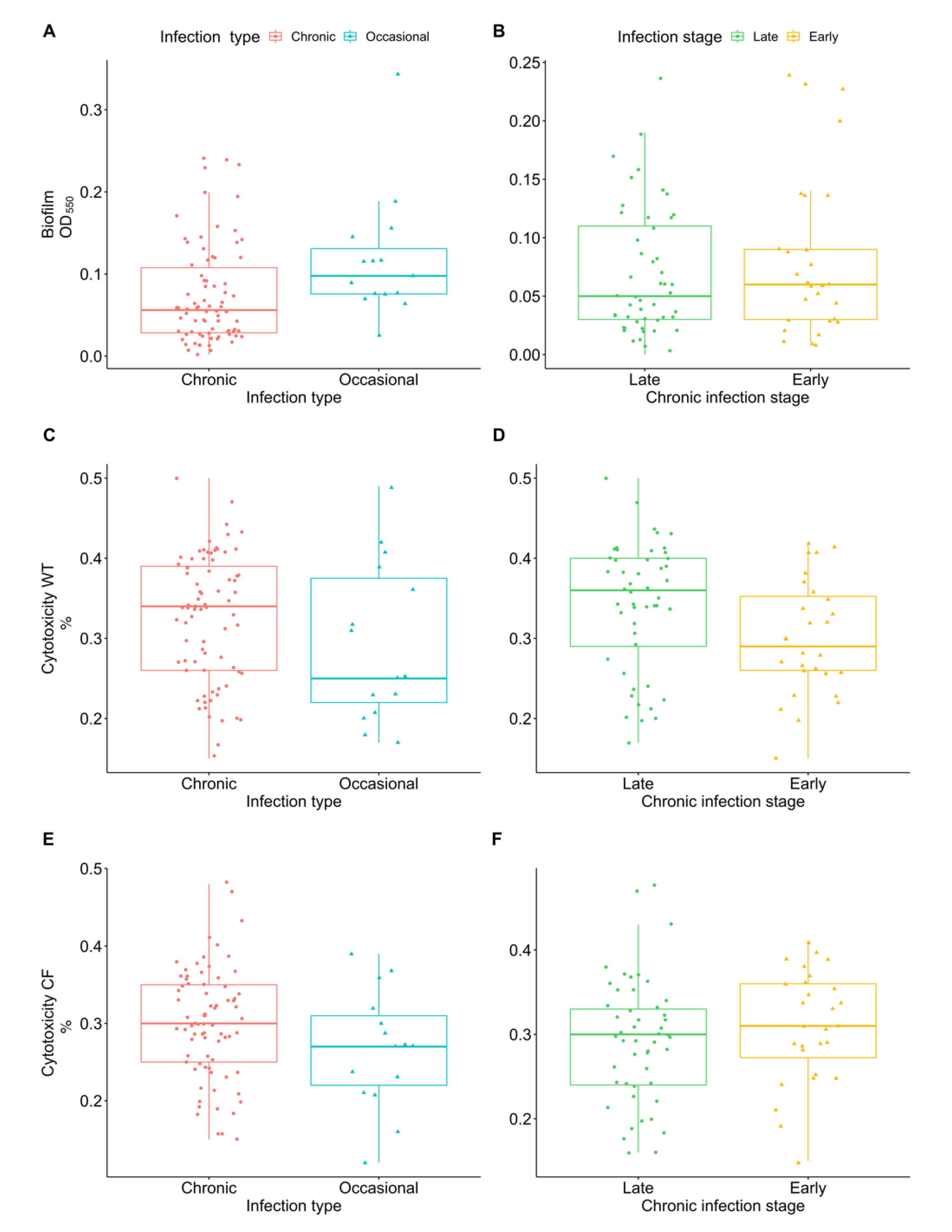
2.1. Virulence
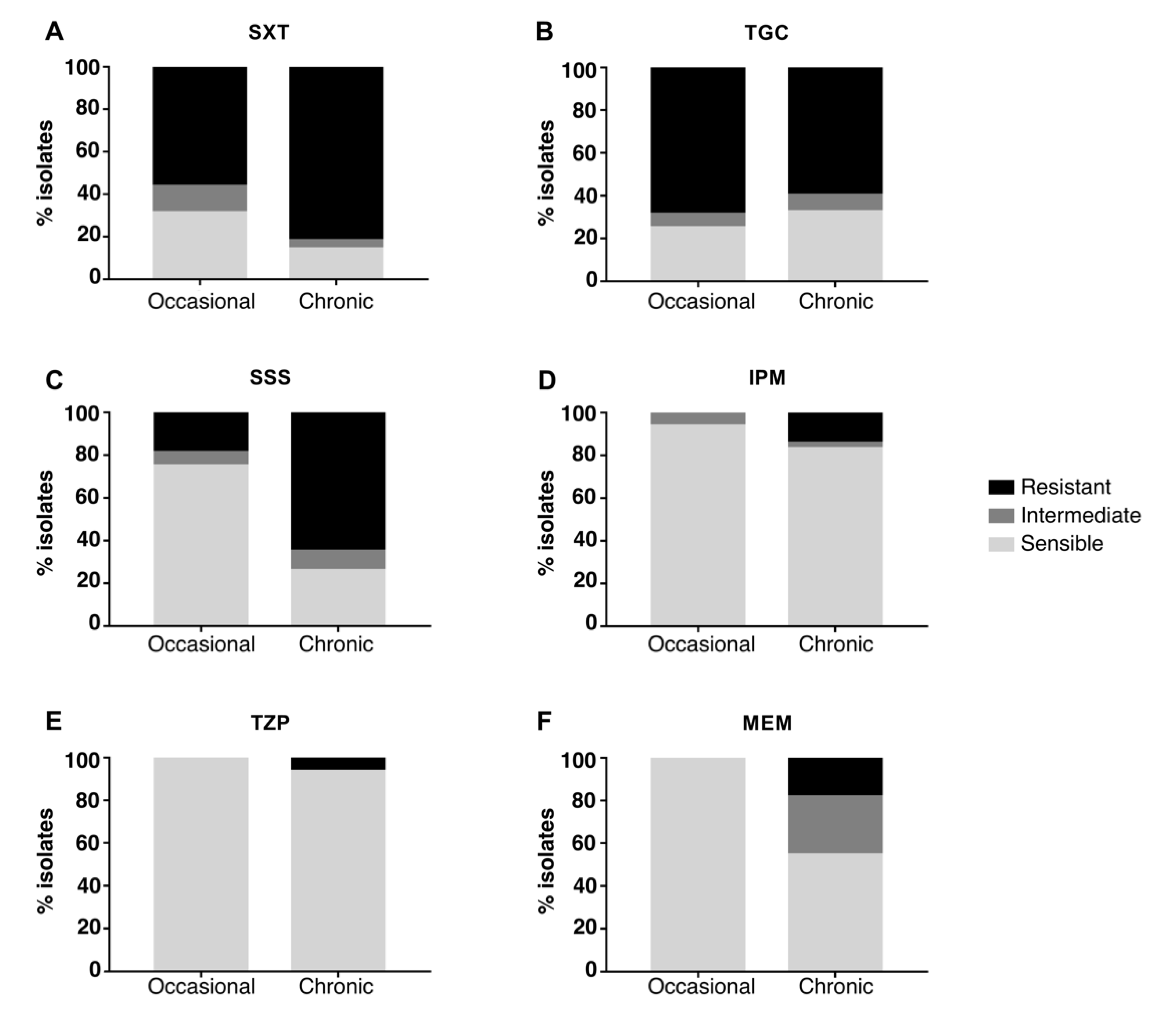
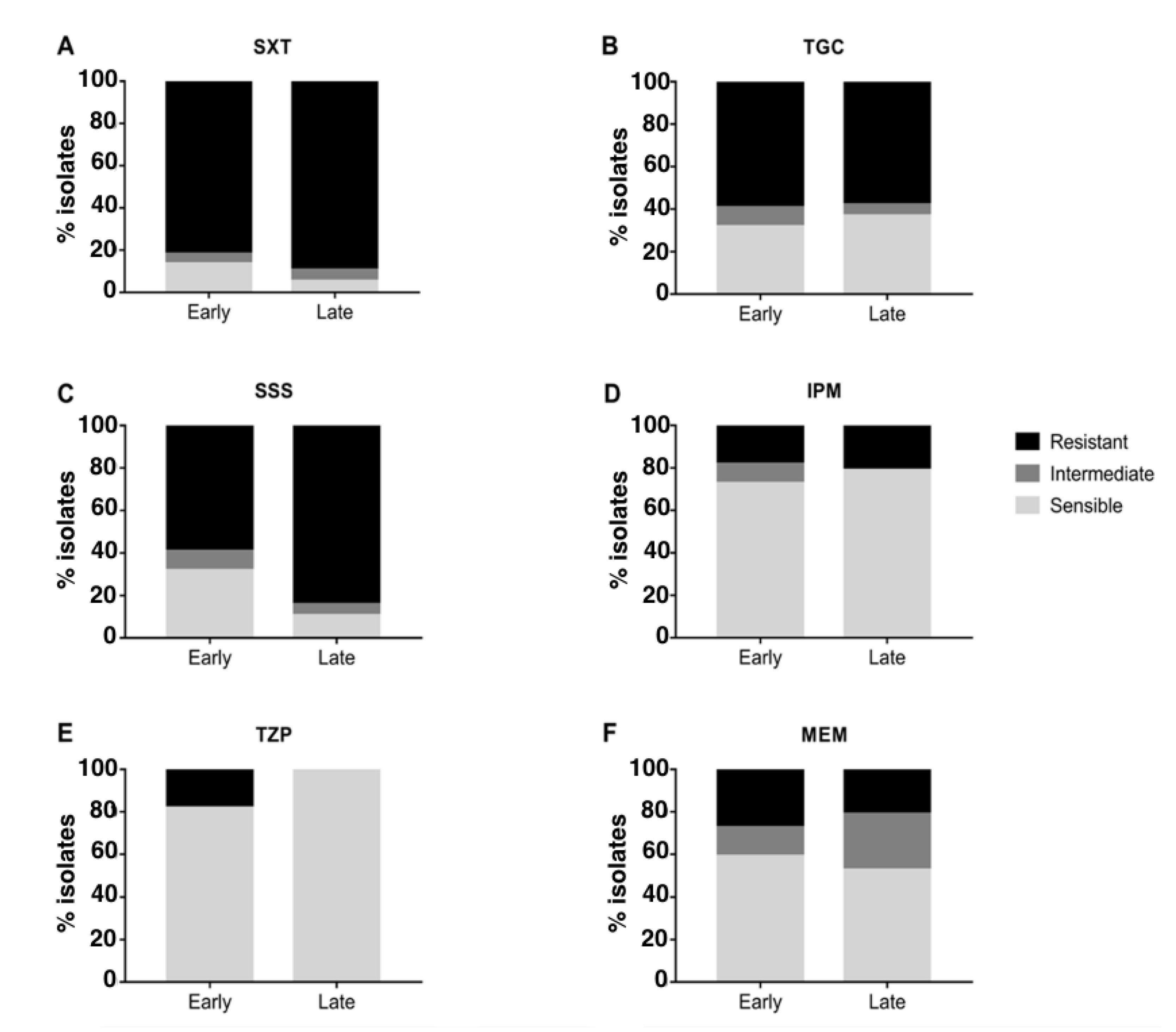
2.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility
2.3. Biomarkers of Antimicrobial Resistance
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Samples Collection
4.2. Virulence Testing
4.3. Biofilm Formation Assay
4.4. Cytotoxicity Testing
4.5. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
4.6. Statistical Analysis
4.7. Identification of Genetic Loci Associated with Virulence, Biofilm, Cytotoxicity and Antimicrobial Resistance
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Firmida, M.C.; Pereira, R.H.V.; Silva, E.A.S.R.; Marques, E.A.; Lopes, A.J. Clinical impact of Achromobacter xylosoxidans colonization/infection in patients with cystic fibrosis. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2016, 49, e5097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swenson, C.E.; Sadikot, R.T. Achromobacter Respiratory Infections. Annals ATS 2015, 12, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veschetti, L.; Sandri, A.; Patuzzo, C.; Melotti, P.; Malerba, G.; Lleo, M.M. Genomic characterization of Achromobacter species isolates from chronic and occasional lung infection in cystic fibrosis patients. Microbial. Genomics. 2021, 7, 000606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Hu, Y.; Gong, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, G. Comparative genome characterization of Achromobacter members reveals potential genetic determinants facilitating the adaptation to a pathogenic lifestyle. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 6413–6425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, R.P.; Levy, C.E.; Yano, T. A heat-stable cytotoxic factor produced by Achromobacter xylosoxidans isolated from Brazilian patients with CF is associated with in vitro increased proinflammatory cytokines. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2012, 11, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeukens, J.; Freschi, L.; Vincent, A.T.; Emond-Rheault, J.-G.; Kukavica-Ibrulj, I.; Charette, S.J.; Levesque, R.C. A Pan-Genomic Approach to Understand the Basis of Host Adaptation in Achromobacter. Genome Biol. Evol. 2017, 9, 1030–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, T.H.; Hansen, M.A.; Jensen, P.Ø.; Hansen, L.; Riber, L.; Cockburn, A.; Kolpen, M.; Rønne Hansen, C.; Ridderberg, W.; Eickhardt, S.; et al. Complete Genome Sequence of the Cystic Fibrosis Pathogen Achromobacter xylosoxidans NH44784-1996 Complies with Important Pathogenic Phenotypes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiester, S.E.; Arivett, B.A.; Schmidt, R.E.; Beckett, A.C.; Ticak, T.; Carrier, M.V.; Ghosh, R.; Ohneck, E.J.; Metz, M.L.; Sellin Jeffries, M.K.; et al. Iron-Regulated Phospholipase C Activity Contributes to the Cytolytic Activity and Virulence of Acinetobacter baumannii. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veschetti, L.; Sandri, A.; Krogh Johansen, H.; Lleò, M.M.; Malerba, G. Hypermutation as an Evolutionary Mechanism for Achromobacter xylosoxidans in Cystic Fibrosis Lung Infection. Pathogens 2020, 9, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S.M.; Nørskov-Lauritsen, N.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Meyer, R.L. Achromobacter Species Isolated from Cystic Fibrosis Patients Reveal Distinctly Different Biofilm Morphotypes. Microorganisms 2016, 4, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantam, J.; Subbaraman, L.N.; Jones, L. Adhesion of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Achromobacter xylosoxidans, Delftia acidovorans, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia to contact lenses under the influence of an artificial tear solution. Biofouling 2020, 36, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay, A.K.; Willcox, M.D.P. Adhesion of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, Delftia acidovorans, and Achromobacter xylosoxidans to Contact Lenses. Eye Contact Lens 2018, 44 (Suppl. S2), S120–S126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridderberg, W.; Nielsen, S.M.; Nørskov-Lauritsen, N. Genetic Adaptation of Achromobacter sp. during Persistence in the Lungs of Cystic Fibrosis Patients. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trancassini, M.; Iebba, V.; Citerà, N.; Tuccio, V.; Magni, A.; Varesi, P.; De Biase, R.V.; Totino, V.; Santangelo, F.; Gagliardi, A.; et al. Outbreak of Achromobacter xylosoxidans in an Italian Cystic fibrosis center: Genome variability, biofilm production, antibiotic resistance, and motility in isolated strains. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almuzara, M.; Limansky, A.; Ballerini, V.; Galanternik, L.; Famiglietti, A.; Vay, C. In vitro susceptibility of Achromobacter spp. isolates: Comparison of disk diffusion, Etest and agar dilution methods. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2010, 35, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrielaite, M.; Bartell, J.A.; Nørskov-Lauritsen, N.; Pressler, T.; Nielsen, F.C.; Johansen, H.K.; Marvig, R.L. Transmission and antibiotic resistance of Achromobacter in cystic fibrosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e02911-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiley, R.A.; Sheikh, N.P.; Mushtaq, N.; Hagi-Pavli, E.; Personne, Y.; Javaid, D.; Waite, R.D. Differential Potentiation of the Virulence of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Cystic Fibrosis Liverpool Epidemic Strain by Oral Commensal Streptococci. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 209, 769–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.J.-Y.; Loh, J.M.S.; Proft, T. Galleria mellonella infection models for the study of bacterial diseases and for antimicrobial drug testing. Virulence 2016, 7, 214–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandri, A.; Haagensen, J.A.J.; Veschetti, L.; Johansen, H.K.; Molin, S.; Malerba, G.; Signoretto, C.; Boaretti, M.; Lleo, M.M. Adaptive Interactions of Achromobacter spp. with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Cystic Fibrosis Chronic Lung Co-Infection. Pathogens 2021, 10, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quereda, J.J.; Cossart, P. Regulating Bacterial Virulence with RNA. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 71, 263–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, J.A.; Raghavan, R. Modulation of bacterial fitness and virulence through antisense RNAs. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 10, 596277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayama, S.; Koba, Y.; Shigemoto, N.; Kuwahara, R.; Kakuhama, T.; Kimura, K.; Hisatsune, J.; Onodera, M.; Yokozaki, M.; Ohge, H.; et al. Imipenem-Susceptible, Meropenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Producing OXA-181 in Japan. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 1379–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isler, B.; Kidd, T.J.; Stewart, A.G.; Harris, P.; Paterson, D.L. Achromobacter Infections and Treatment Options. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e01025-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livermore, D.M.; Mushtaq, S.; Warner, M.; Woodford, N. Comparative in vitro activity of sulfametrole/trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim and other agents against multiresistant Gram-negative bacteria. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 1050–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, I.; Peleg, A. Stenotrophomonas, Achromobacter, and Nonmelioid Burkholderia Species: Antimicrobial Resistance and Therapeutic Strategies. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 36, 099–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veschetti, L.; Sandri, A.; Patuzzo, C.; Melotti, P.; Malerba, G.; Lleò, M.M. Mobilome Analysis of Achromobacter spp. Isolates from Chronic and Occasional Lung Infection in Cystic Fibrosis Patients. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.H. ABC transporters as multidrug resistance mechanisms and the development of chemosensitizers for their reversal. Cancer Cell Int. 2005, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, C.; Jumas-Bilak, E.; Michon, A.-L.; Chiron, R.; Marchandin, H. Impact of High Diversity of Achromobacter Populations within Cystic Fibrosis Sputum Samples on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jaillard, M.; Lima, L.; Tournoud, M.; Mahé, P.; van Belkum, A.; Lacroix, V.; Jacob, L. A fast and agnostic method for bacterial genome-wide association studies: Bridging the gap between k-mers and genetic events. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Antimicrobial | Associated with | Node ID | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | q-Value | Annotation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IPM | Resistance | n1316743 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 8.4 × 10−23 | Arginine-tRNA ligase |
| IPM | Resistance | n284357 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 8.4 × 10−23 | Diguanylate cyclase (GGDEF domain) with GAF sensor |
| IPM | Resistance | n1001723 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 8.4 × 10−23 | ABC transporter |
| IPM | Resistance | n1228398 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 8.4 × 10−23 | Type II secretory pathway component GspD |
| IPM | Resistance | n1320154 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 8.4 × 10−23 | AraC family transcriptional regulator |
| IPM | Resistance | n119911 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 8.4 × 10−23 | NA |
| IPM | Resistance | n1360642 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 8.4 × 10−23 | General secretion pathway protein GspN |
| IPM | Resistance | n1607259 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 8.4 × 10−23 | Fe2+-dicitrate sensor, membrane component, FecR |
| IPM | Resistance | n1496359 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 8.4 × 10−23 | Glutathione S-transferase family protein |
| MEM | Resistance | n382985 | 88.9 | 97.1 | 1.3 × 10−2 | ABC transporter ATP-binding protein |
| MEM | Resistance | n776344 | 88.9 | 97.1 | 1.3 × 10−2 | Hypothetical protein |
| MEM | Resistance | n1454097 | 88.9 | 97.1 | 1.3 × 10−2 | ABC transporter ATP-binding protein |
| SSS | Susceptibility | n477893 | 81.3 | 86.1 | 2.8 × 10−3 | Hypothetical protein |
| SSS | Susceptibility | n1248808 | 81.3 | 86.1 | 2.8 × 10−3 | ABC transporter ATP-binding protein |
| SSS | Susceptibility | n888310 | 81.3 | 86.1 | 2.8 × 10−3 | Aminomethyl-transferring glycine dehydrogenase |
| SXT | Susceptibility | n1221225 | 85.7 | 100.0 | 7.6 × 10−9 | NA |
| SXT | Susceptibility | n1593088 | 85.7 | 100.0 | 7.6 × 10−9 | 16S rRNA (uracil(1498)-N(3))-methyltransferase |
| SXT | Susceptibility | n222900 | 85.7 | 100.0 | 7.6 × 10−9 | NA |
| SXT | Susceptibility | n979447 | 85.7 | 100.0 | 7.6 × 10−9 | DNA mismatch repair endonuclease MutL |
| SXT | Susceptibility | n120539 | 85.7 | 100.0 | 7.6 × 10−9 | Efflux RND transporter periplasmic adaptor subunit |
| SXT | Susceptibility | n335885 | 85.7 | 100.0 | 7.6 × 10−9 | Efflux RND transporter periplasmic adaptor subunit |
| SXT | Susceptibility | n71145 | 85.7 | 100.0 | 7.6 × 10−9 | M61 family metallopeptidase |
| SXT | Susceptibility | n346933 | 85.7 | 100.0 | 7.6 × 10−9 | Acyl-CoA synthetase |
| SXT | Susceptibility | n1069885 | 85.7 | 100.0 | 7.6 × 10−9 | Helix-turn-helix domain-containing protein |
| SXT | Susceptibility | n1157928 | 85.7 | 100.0 | 7.6 × 10−9 | Helix-turn-helix domain-containing protein |
| SXT | Susceptibility | n527920 | 85.7 | 100.0 | 7.6 × 10−9 | Patatin-like phospholipase family protein |
| Rome-n (Patients) | Verona-n (Patients) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chronic infection isolates | 36 (7) | E: 6 (4) | 43 (17) | E: 24 (10) |
| L: 30 (7) | L: 19 (10) | |||
| Occasional infection isolates | 5 (5) | 11 (9) | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sandri, A.; Veschetti, L.; Saitta, G.M.; Passarelli Mantovani, R.; Carelli, M.; Burlacchini, G.; Preato, S.; Sorio, C.; Melotti, P.; Montemari, A.L.; et al. Achromobacter spp. Adaptation in Cystic Fibrosis Infection and Candidate Biomarkers of Antimicrobial Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9265. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23169265
Sandri A, Veschetti L, Saitta GM, Passarelli Mantovani R, Carelli M, Burlacchini G, Preato S, Sorio C, Melotti P, Montemari AL, et al. Achromobacter spp. Adaptation in Cystic Fibrosis Infection and Candidate Biomarkers of Antimicrobial Resistance. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(16):9265. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23169265
Chicago/Turabian StyleSandri, Angela, Laura Veschetti, Giulia Maria Saitta, Rebeca Passarelli Mantovani, Maria Carelli, Gloria Burlacchini, Sara Preato, Claudio Sorio, Paola Melotti, Anna Lisa Montemari, and et al. 2022. "Achromobacter spp. Adaptation in Cystic Fibrosis Infection and Candidate Biomarkers of Antimicrobial Resistance" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 16: 9265. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23169265
APA StyleSandri, A., Veschetti, L., Saitta, G. M., Passarelli Mantovani, R., Carelli, M., Burlacchini, G., Preato, S., Sorio, C., Melotti, P., Montemari, A. L., Fiscarelli, E. V., Patuzzo, C., Signoretto, C., Boaretti, M., Lleò, M. M., & Malerba, G. (2022). Achromobacter spp. Adaptation in Cystic Fibrosis Infection and Candidate Biomarkers of Antimicrobial Resistance. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(16), 9265. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23169265










