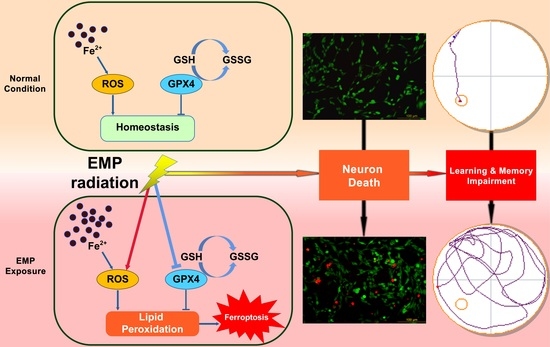
Lipid Peroxides Mediated Ferroptosis in Electromagnetic Pulse-Induced Hippocampal Neuronal Damage via Inhibition of GSH/GPX4 Axis
Abstract
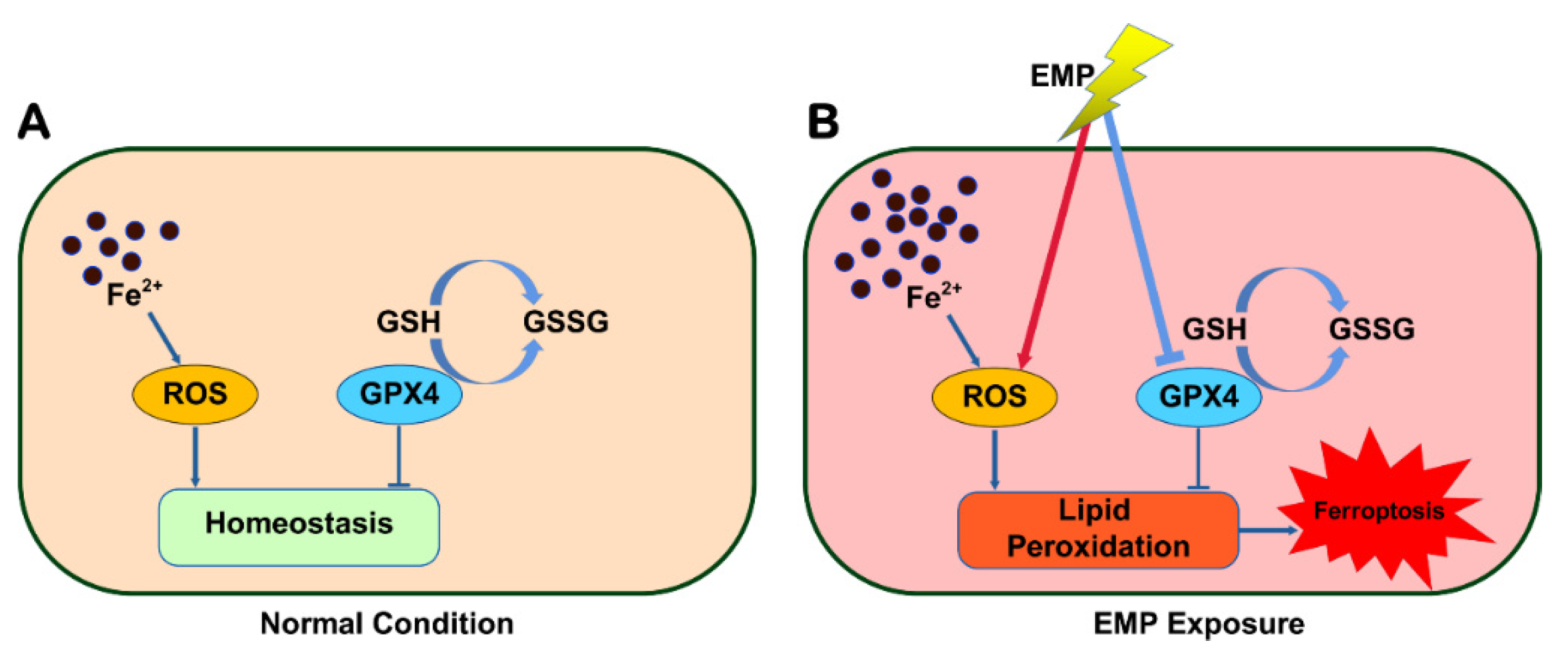
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Increase in Temperature during EMP Exposure Was Less Than 1 °C
2.2. EMP Exposure Could Induce Spatial Learning and Memory Impairment in Rats
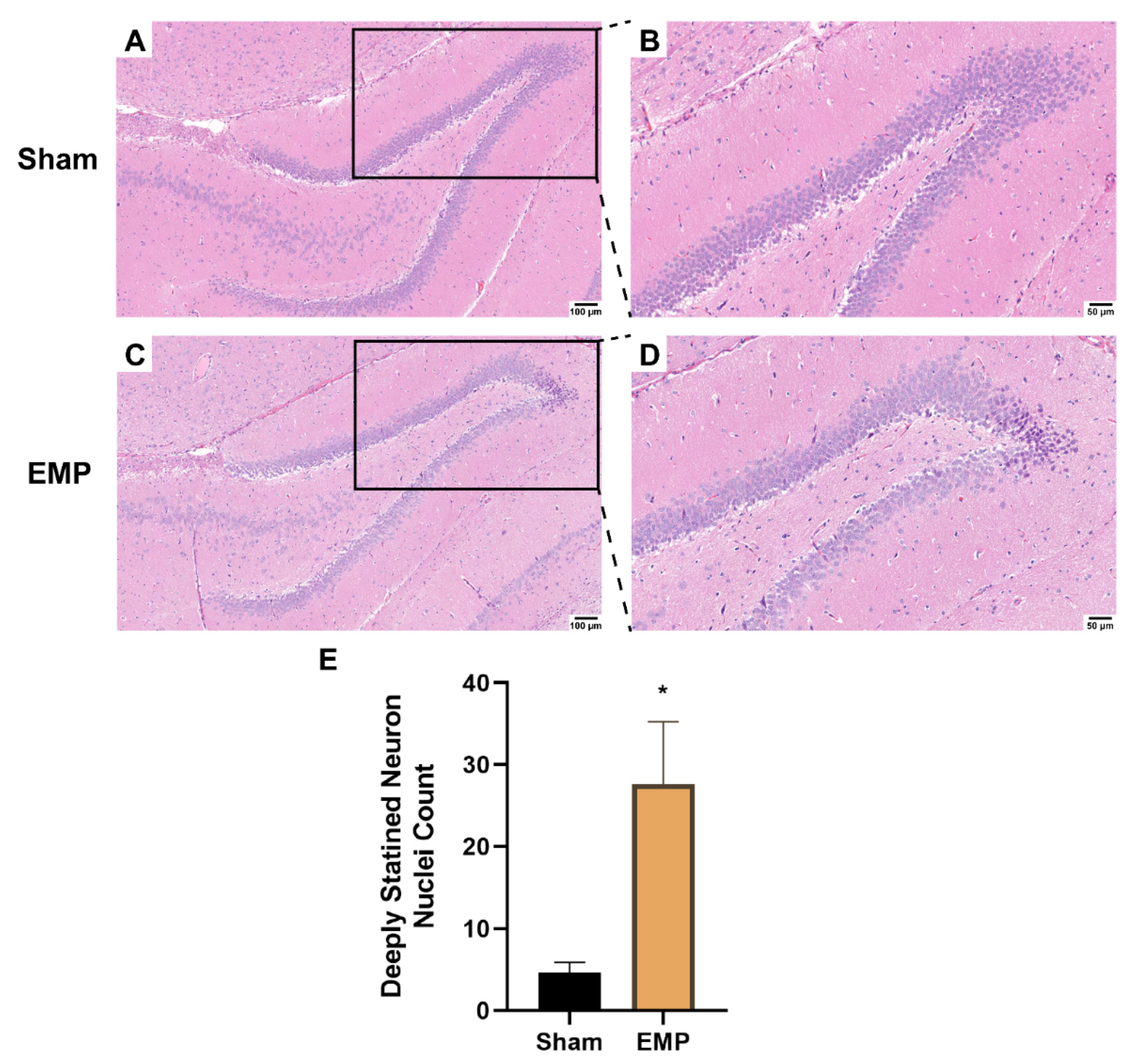
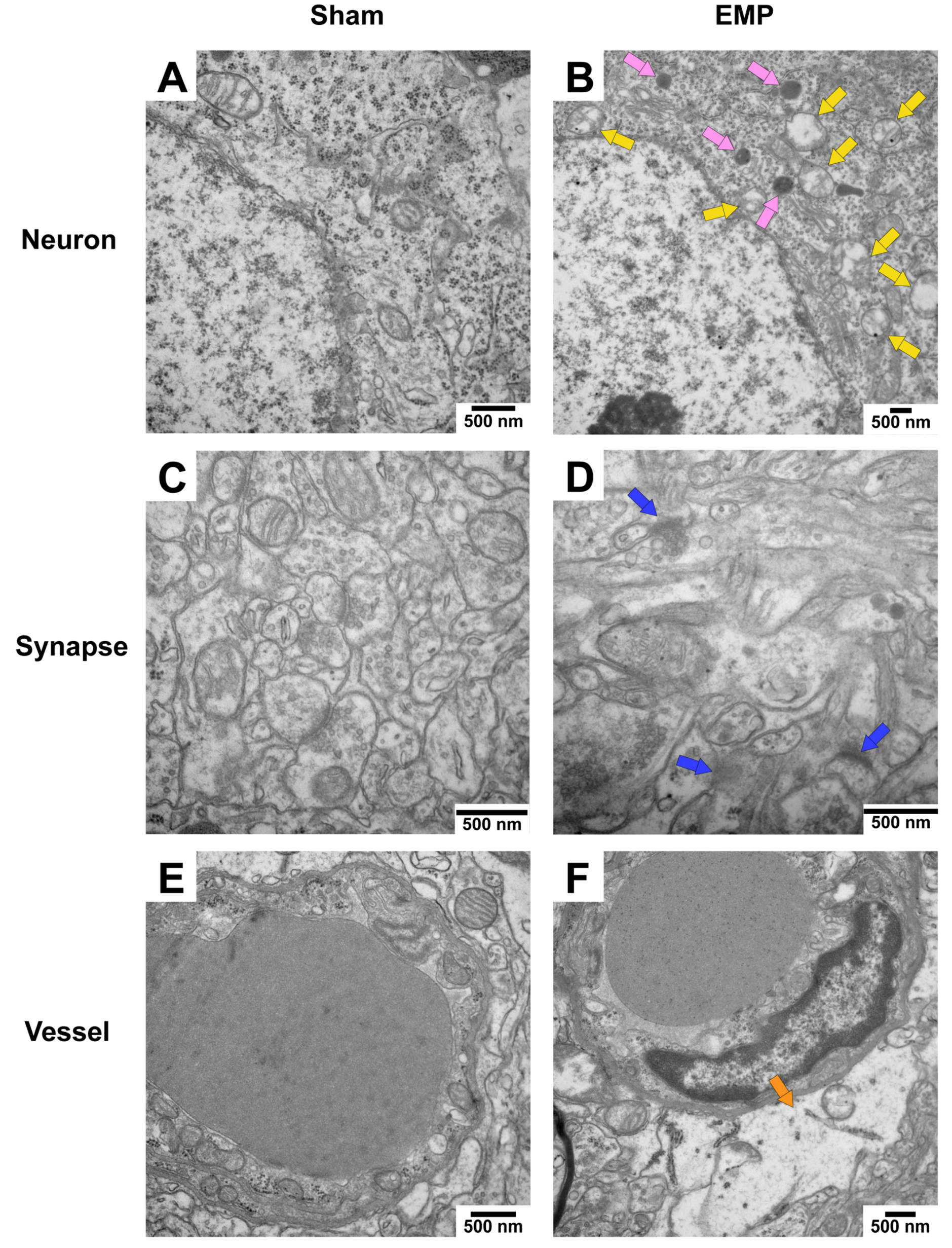
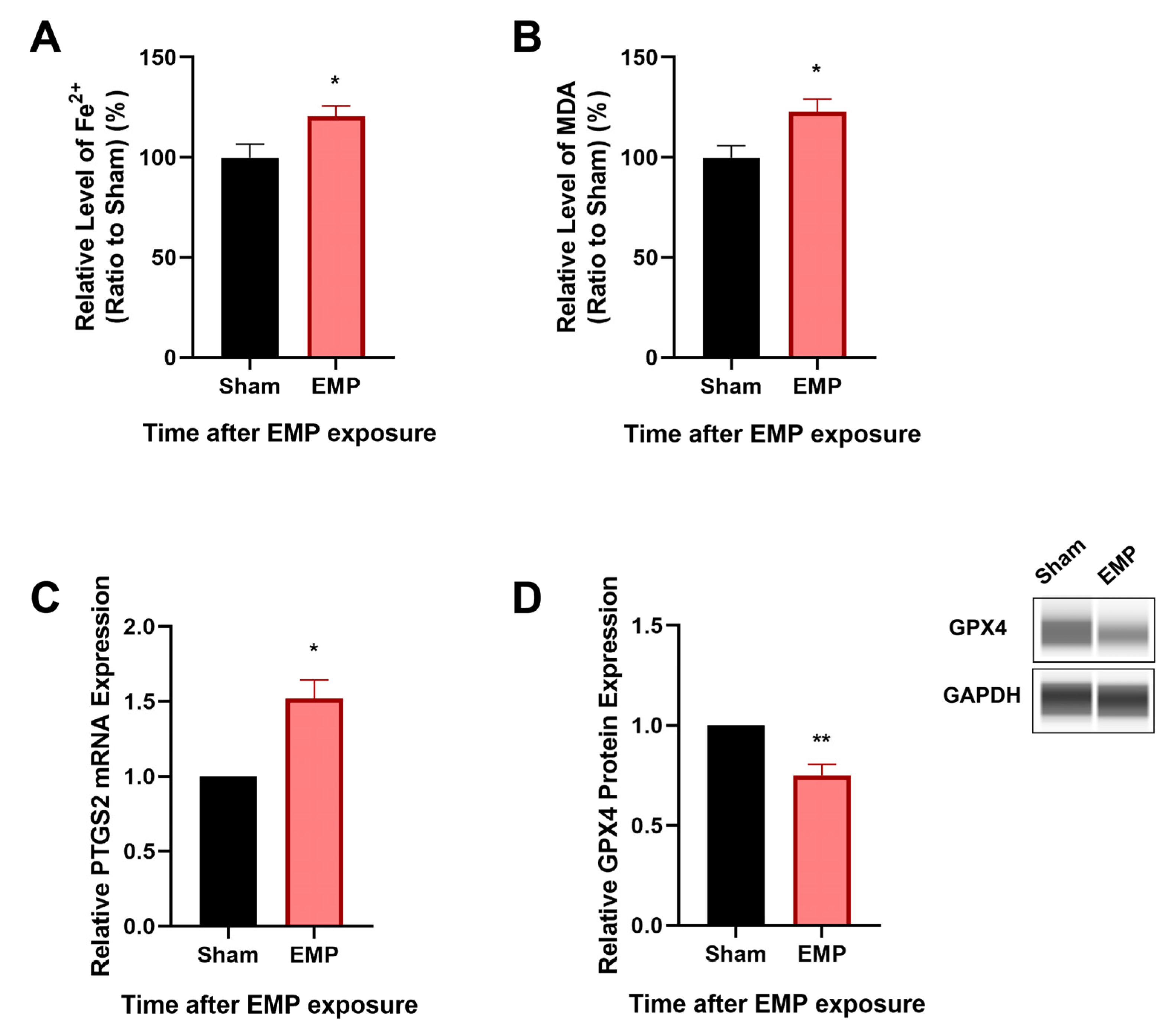
2.3. EMP-Induced Neuronal Injury in Rat Hippocampus Was Associated with Ferroptosis
2.4. EMP-Induced Cell Death in HT22 Neurons Was Associated with Ferroptosis
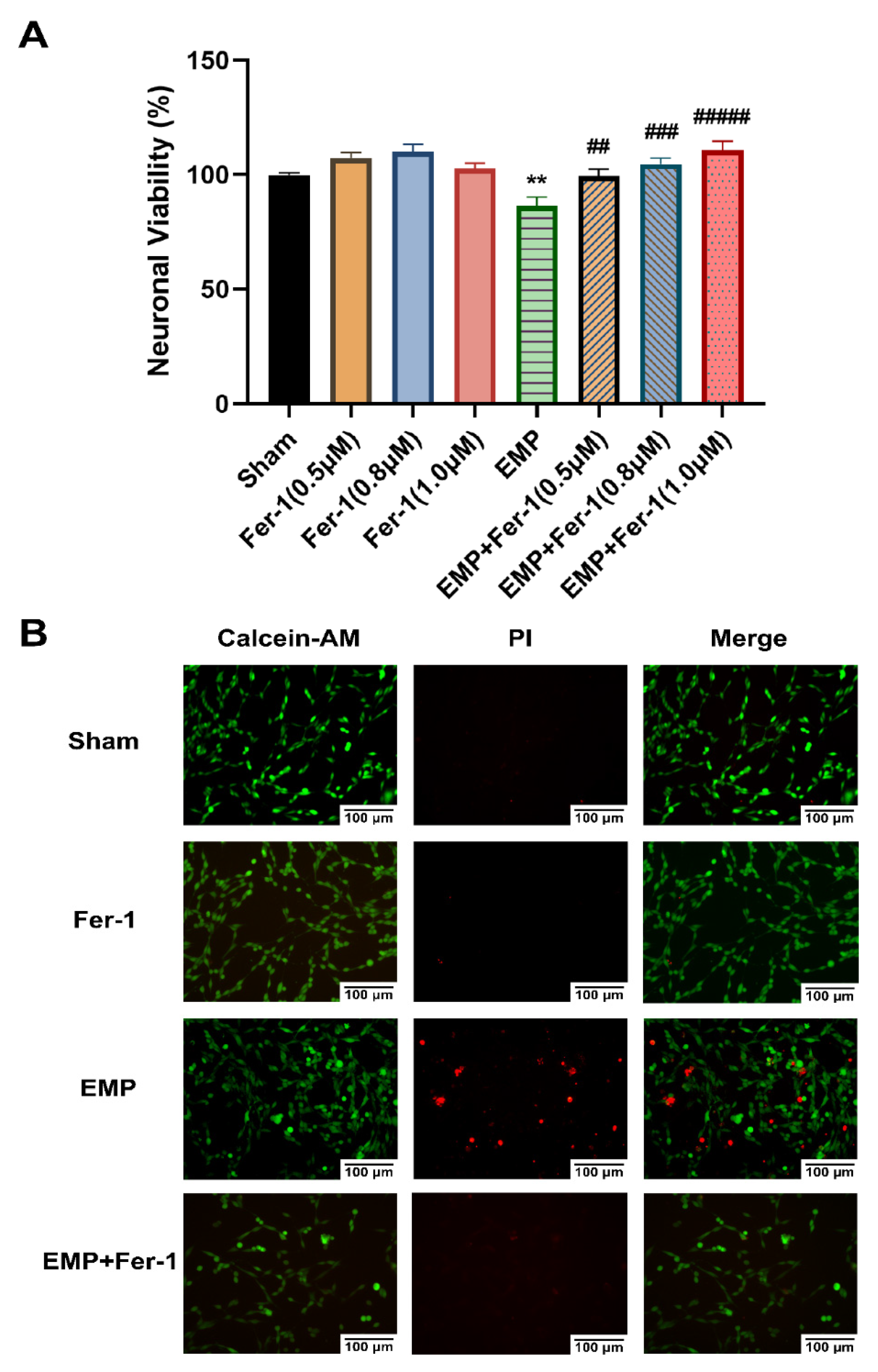
2.5. EMP-Induced Ferroptotic Cell Death in HT22 Neurons Could Be Alleviated by Fer-1
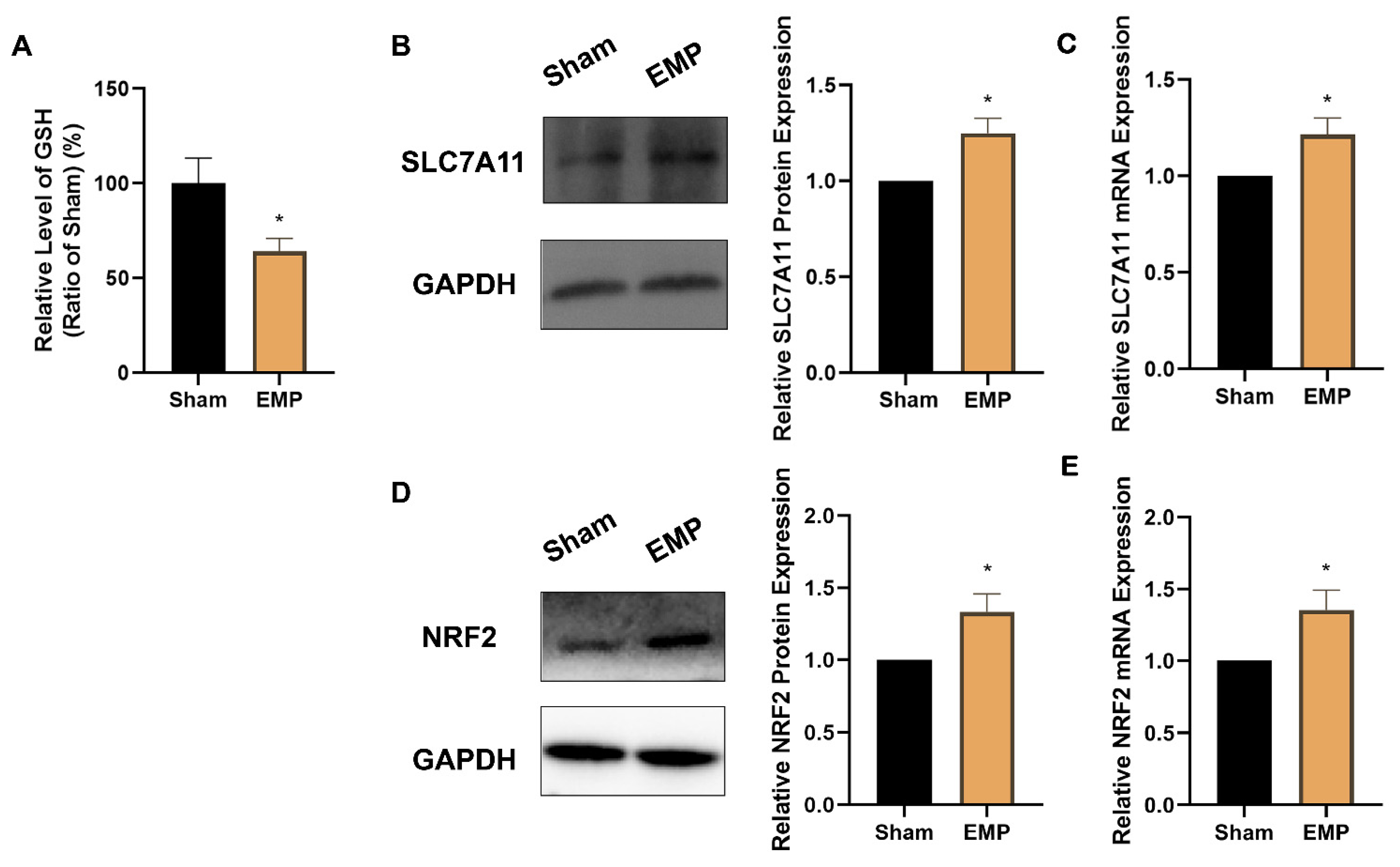
2.6. EMP Exposure Could Affect the Antioxidant System in HT22 Neurons
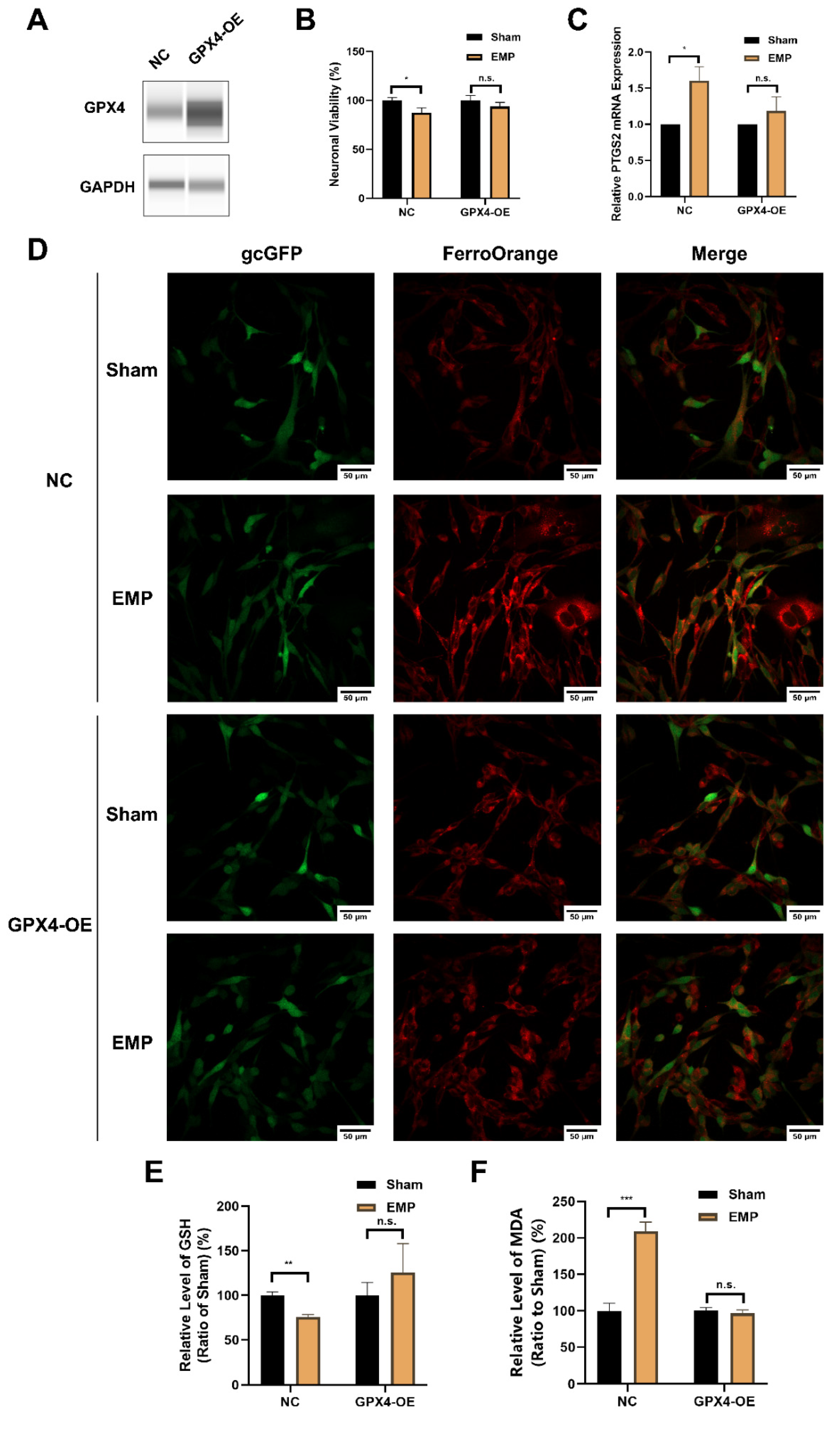
2.7. GPX4 Alleviated EMP-Induced Ferroptotic Neuronal Death in HT22 Neurons by Inhibiting Lipid Peroxides Accumulation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Groups
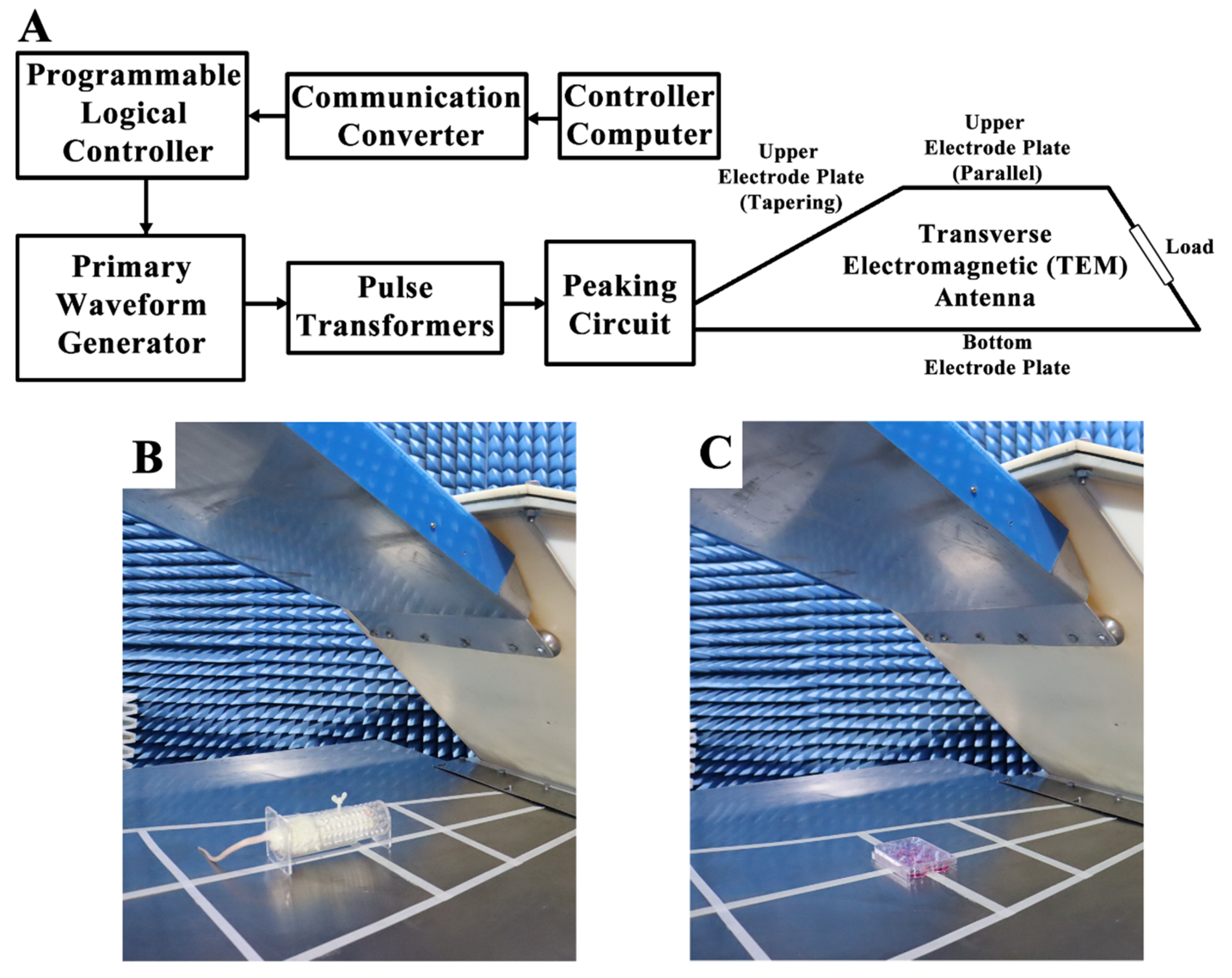
4.2. EMP Exposure
4.3. Morris Water Maze (MWM)
4.4. Sample Collection
4.5. HE Staining
4.6. TEM Analysis
4.7. HT22 Cell Cultures
4.8. Cell Transfection
4.9. Cell Viability Assay
4.10. Cell Death Assay
4.11. Iron Level Assessment
4.12. Lipid Peroxidation Assessment
4.13. GSH Assessment
4.14. Real-Time PCR Analysis
4.15. Western Blotting
4.16. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- World Health Organization. The Overview of Electromagnetic Fields. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/electromagnetic-fields#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Qiu, L.B.; Ding, G.R.; Li, K.C.; Wang, X.W.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, Y.C.; Li, Y.R.; Guo, G.Z. The role of protein kinase C in the opening of blood-brain barrier induced by electromagnetic pulse. Toxicology 2010, 273, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.B.; Li, J.; Liu, J.Y.; Zeng, L.H.; Wan, Y.; Li, Y.R.; Ren, D.; Guo, G.Z. Effect of electromagnetic pulses (EMP) on associative learning in mice and a preliminary study of mechanism. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2011, 87, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, B.; Xu, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Han, L.-C.; Li, L.-Y.; Wu, G.-L.; Hou, Y.-N.; Guo, G.-Z.; Wang, Q.; et al. Neuroprotective effects of sevoflurane against electromagnetic pulse-induced brain injury through inhibition of neuronal oxidative stress and apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, D.-P.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Xu, S.-L.; Kuang, F.; Lang, H.-Y.; Wang, Y.-F.; An, G.-Z.; Li, J.-H.; Guo, G.-Z. Electromagnetic pulse exposure induces overexpression of beta amyloid protein in rats. Arch. Med. Res. 2013, 44, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.-P.; Li, J.-H.; Zhang, J.; Xu, S.-L.; Kuang, F.; Lang, H.-Y.; Wang, Y.-F.; An, G.-Z.; Li, J.; Guo, G.-Z. Long-term electromagnetic pulse exposure induces Abeta deposition and cognitive dysfunction through oxidative stress and overexpression of APP and BACE1. Brain. Res. 2016, 1642, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Chen, Q.; Hu, J.F.; Lin, Y.Y.; Lin, J.J.; Guo, Q.Y.; Yue, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zeng, L.; Li, J. Effect of ultra-wide-band electromagnetic pulses on blood-brain barrier permeability in rats. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 2775–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.Y.; Cai, C.K.; Zhang, X.J.; Sun, X.D. Isoflurane preconditioning effects on brain damage induced by electromagnetic pulse radiation through epigenetic modification of BDNF gene transcription. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2020, 9, 3418–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Nie, Q.; Sun, X.D. BDNF-TrkB signaling is involved in the histopathological damage, synaptic protein loss and inflammatory response caused by an electromagnetic pulse in rat brain cortex. Neuroreport 2019, 30, 550–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Deng, B.; Zhang, X.J.; Lv, M.M.; Zhao, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.D.; Han, R.L.; Sun, X.D. Isoflurane preconditioning attenuates brain injury induced by electromagnetic pulse via the TLR4/NFB signaling pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 9653494. [Google Scholar]
- Dixon, S.J.; Lemberg, K.M.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Skouta, R.; Zaitsev, E.M.; Gleason, C.E.; Patel, D.N.; Bauer, A.J.; Cantley, A.M.; Yang, W.S.; et al. Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 2012, 149, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockwell, B.R.; Angeli, J.P.F.; Bayir, H.; Bush, A.I.; Conrad, M.; Dixon, S.J.; Fulda, S.; Gascón, S.; Hatzios, S.K.; Kagan, V.E.; et al. Ferroptosis: A regulated cell death nexus linking metabolism, redox biology, and disease. Cell 2017, 171, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Chen, X.; Kang, R.; Kroemer, G. Ferroptosis: Molecular mechanisms and health implications. Cell. Res. 2021, 31, 107–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedmann Angeli, J.P.F.; Schneider, M.; Proneth, B.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Tyurin, V.A.; Hammond, V.J.; Herbach, N.; Aichler, M.; Walch, A.; Eggenhofer, E.; et al. Inactivation of the ferroptosis regulator Gpx4 triggers acute renal failure in mice. Nat. Cell. Biol. 2014, 16, 1180–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do Van, B.; Gouel, F.; Jonneaux, A.; Timmerman, K.; Gele, P.; Petrault, M.; Bastide, M.; Laloux, C.; Moreau, C.; Bordet, R.; et al. Ferroptosis, a newly characterized form of cell death in Parkinson’s disease that is regulated by PKC. Neurobiol. Dis. 2016, 94, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambright, W.S.; Fonseca, R.S.; Chen, L.J.; Na, R.; Ran, Q.T. Ablation of ferroptosis regulator glutathione peroxidase 4 in forebrain neurons promotes cognitive impairment and neurodegeneration. Redox. Biol. 2017, 12, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzel, S.E.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Zhao, J.M.; St Croix, C.M.S.; Dar, H.H.; Mao, G.W.; Tyurin, V.A.; Anthonymuthu, T.S.; Kapralov, A.A.; Amoscato, A.A.; et al. PEBP1 wardens ferroptosis by enabling lipoxygenase generation of lipid death signals. Cell 2017, 171, 628–641.e626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alim, I.; Caulfield, J.T.; Chen, Y.X.; Swarup, V.; Geschwind, D.H.; Ivanova, E.; Seravalli, J.; Ai, Y.; Sansing, L.H.; Ste.Marie, E.J.; et al. Selenium drives a transcriptional adaptive program to block ferroptosis and treat stroke. Cell 2019, 177, 1262–1279.e1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Liu, Y.Y.; Dai, R.J.; Ismail, N.; Su, W.J.; Li, B. Ferroptosis and its potential role in human diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, H.H.; Anthonymuthu, T.S.; Ponomareva, L.A.; Souryavong, A.B.; Shurin, G.V.; Kapralov, A.O.; Tyurin, V.A.; Lee, J.S.; Mallampalli, R.K.; Wenzel, S.E.; et al. A new thiol-independent mechanism of epithelial host defense against pseudomonas aeruginosa: INOS/NO sabotage of theft-ferroptosis. Redox. Biol. 2021, 45, 102045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Fang, Y.; Gu, Q. Mechanisms of modulation of ferroptosis and its role in central nervous system diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 657033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Cong, J.; Xian, H.; Cao, X.; Sun, C.; Wu, K. The effects of electromagnetic pulse on fluidity and lipid peroxidation of mitochondrial membrane. Chin. J. Ind. Hyg. Occup. Dis. 2002, 20, 266–268. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.S.; SriRamaratnam, R.; Welsch, M.E.; Shimada, K.; Skouta, R.; Viswanathan, V.S.; Cheah, J.H.; Clemons, P.A.; Shamji, A.F.; Clish, C.B.; et al. Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell 2014, 156, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigelius-Flohé, R.; Maiorino, M. Glutathione peroxidases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2013, 1830, 3289–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, T.Y.; Wang, H.C.; Li, Q.Q.; Cheng, Y.; Gao, Y.; Fang, X.X.; Ma, X.; Chen, G.; Gao, C.; Gu, Z.; et al. Deletion of ferritin H in neurons counteracts the protective effect of melatonin against traumatic brain injury-induced ferroptosis. J. Pineal. Res. 2021, 70, e12704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Q.Q.; Liu, J.C.; Wang, G.Q. Ferroptosis, a regulated neuronal cell death type after intracerebral hemorrhage. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 591874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Kon, N.; Li, T.; Wang, S.-J.; Su, T.; Hibshoosh, H.; Baer, R.; Gu, W. Ferroptosis as a p53-mediated activity during tumour suppression. Nature 2015, 520, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, S.J.; Stockwell, B.R. The role of iron and reactive oxygen species in cell death. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014, 10, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.S.; Kim, K.J.; Gaschler, M.M.; Patel, M.; Shchepinov, M.S.; Stockwell, B.R. Peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids by lipoxygenases drives ferroptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E4966–E4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursini, F.; Maiorino, M. Lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis: The role of GSH and GPx4. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 152, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotnik, T.; Rems, L.; Tarek, M.; Miklavčič, D. Membrane electroporation and electropermeabilization: Mechanisms and models. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2019, 48, 63–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakhomova, O.N.; Khorokhorina, V.A.; Bowman, A.M.; Rodaite, R. Oxidative effects of nanosecond pulsed electric field exposure in cells and cell-free media. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2012, 527, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azan, A.; Untereiner, V.; Descamps, L.; Merla, C.; Gobinet, C.; Breton, M.; Piot, O.; Mir, L.M. Comprehensive characterization of the interaction between pulsed electric fields and live cells by confocal Raman microspectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 10790–10797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, S.J.; Patel, D.N.; Welsch, M.; Skouta, R.; Lee, E.D.; Thomas, A.G.; Gleason, C.E.; Tatonetti, N.; Slusher, B.S.; Stockwell, B.R.; et al. Pharmacological inhibition of cystine-glutamate exchange induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and ferroptosis. eLife 2014, 3, e02523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibt, T.M.; Proneth, B.; Conrad, M. Role of GPX4 in ferroptosis and its pharmacological implication. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 133, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, F.M.; Liu, J.; Tang, D.L.; Kang, R. Oxidative damage and antioxidant defense in ferroptosis. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 586578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skouta, R.; Dixon, S.J.; Wang, J.; Dunn, D.E.; Orman, M.; Shimada, K.; Rosenberg, P.A.; Lo, D.C.; Weinberg, J.M.; Linkermann, A.; et al. Ferrostatins inhibit oxidative lipid damage and cell death in diverse disease models. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 4551–4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; An, P.; Xie, E.J.; Wu, Q.; Fang, X.X.; Gao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; et al. Characterization of ferroptosis in murine models of hemochromatosis. Hepatology 2017, 66, 449–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.X.; Cai, Z.X.; Wang, H.; Han, D.; Cheng, Q.; Zhang, P.; Gao, F.; Yu, Y.; Song, Z.; Wu, Q.; et al. Loss of cardiac ferritin H facilitates cardiomyopathy via Slc7a11-mediated ferroptosis. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, T.X.; Huang, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, T.; Zang, S.; Guan, K.; Xiong, Y.; Liu, J.; Yuan, H. Targeting ferroptosis alleviates methionine-choline deficient (MCD)-diet induced NASH by suppressing liver lipotoxicity. Liver. Int. 2020, 40, 1378–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.P.; Yan, F.; Deng, R.H.; Gu, R.; Zhang, X.W.; Bai, J. Thioredoxin-1 rescues MPP+/MPTP-induced ferroptosis by increasing glutathione peroxidase 4. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 3187–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.Q.; Lu, Y.Y.; Peng, G.J.; Li, J.J.; Li, W.J.; Li, M.; Wang, H.; Liu, L.; Zhao, Q. Furin inhibits epithelial cell injury and alleviates experimental colitis by activating the Nrf2-Gpx4 signaling pathway. Dig. Liver. Dis. 2021, 53, 1276–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.Y.; Zhu, J.H.; Yuan, G.X.; Li, D.; Wen, Y.; Huang, S.L.; Lv, Z.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, J. The effects of selenium on GPX4-mediated lipid peroxidation and apoptosis in germ cells. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2021, 42, 1016–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorhees, C.V.; Williams, M.T. Morris water maze: Procedures for assessing spatial and related forms of learning and memory. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 848–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lai, Y.; Dong, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Yao, B.; Xu, X.; Zou, Y.; Zhao, H.; et al. Lipid Peroxides Mediated Ferroptosis in Electromagnetic Pulse-Induced Hippocampal Neuronal Damage via Inhibition of GSH/GPX4 Axis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9277. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23169277
Lai Y, Dong J, Wu Y, Zhao L, Wang H, Zhang J, Yao B, Xu X, Zou Y, Zhao H, et al. Lipid Peroxides Mediated Ferroptosis in Electromagnetic Pulse-Induced Hippocampal Neuronal Damage via Inhibition of GSH/GPX4 Axis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(16):9277. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23169277
Chicago/Turabian StyleLai, Yunfei, Ji Dong, You Wu, Li Zhao, Hui Wang, Jing Zhang, Binwei Yao, Xinping Xu, Yong Zou, Haixia Zhao, and et al. 2022. "Lipid Peroxides Mediated Ferroptosis in Electromagnetic Pulse-Induced Hippocampal Neuronal Damage via Inhibition of GSH/GPX4 Axis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 16: 9277. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23169277
APA StyleLai, Y., Dong, J., Wu, Y., Zhao, L., Wang, H., Zhang, J., Yao, B., Xu, X., Zou, Y., Zhao, H., Yue, H., Song, Y., Wang, H., & Peng, R. (2022). Lipid Peroxides Mediated Ferroptosis in Electromagnetic Pulse-Induced Hippocampal Neuronal Damage via Inhibition of GSH/GPX4 Axis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(16), 9277. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23169277