Fused Cells between Human-Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Monocytes Keep Stemness Properties and Acquire High Mobility
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
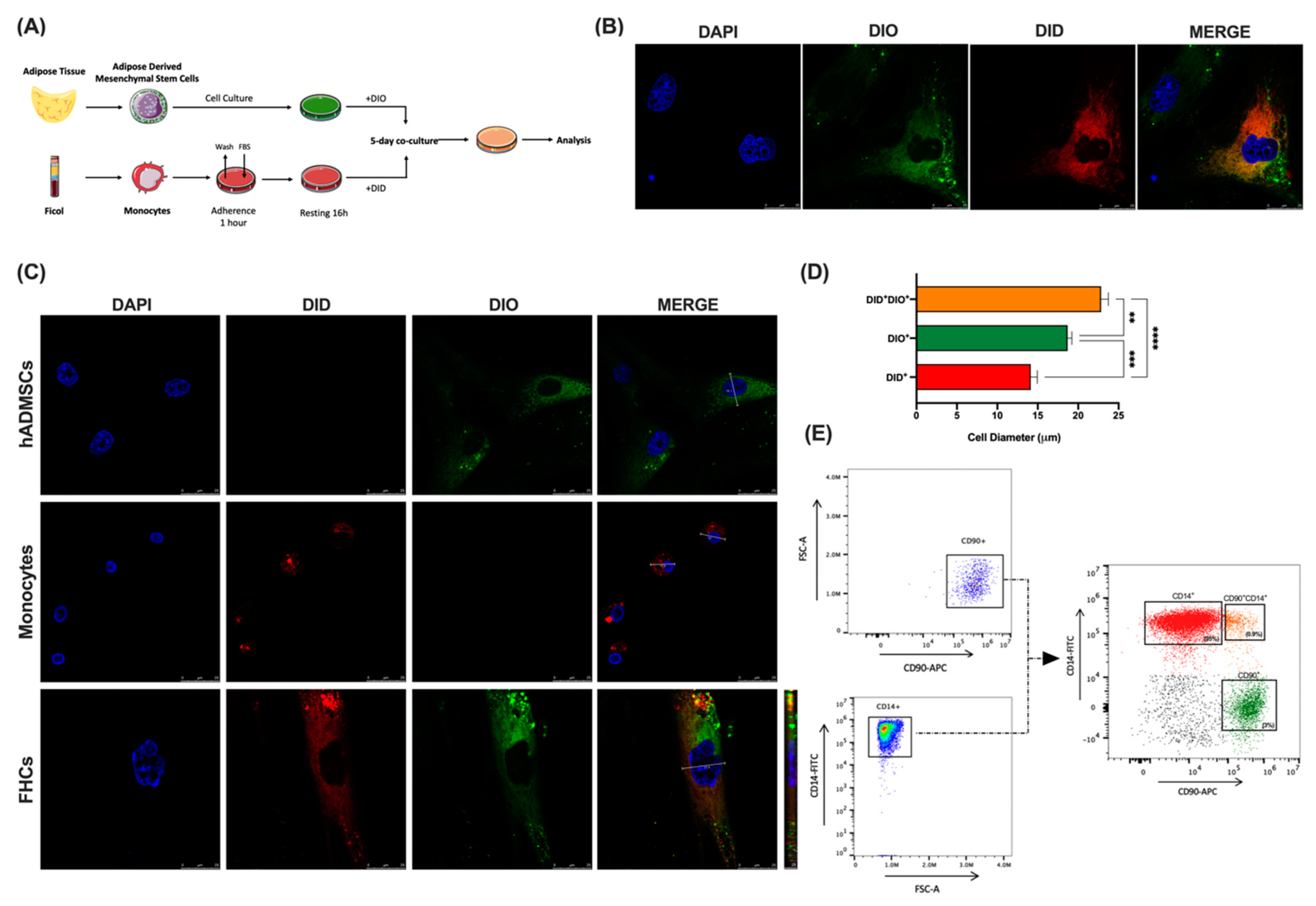
2.1. Co-Culture of hADMSCs with Human Monocytes Ex Vivo Yields a New Hybrid Entity
2.2. Pro-Inflammatory Phenotype Favours FHC Formation
2.3. Foam Hybrid Cells Generated after Co-Culture Exhibit Strong Immunomodulatory Features
2.4. Foam Hybrid Cells Display High Migratory and Proliferative Abilities
2.5. Foam Hybrid Cells Maintain Stem Cell Properties after Co-Culture
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Human Samples
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Vital Colorant Assay
4.4. Cell Sorting and Flow Cytometry Analysis
4.5. Real Time Quantitative PCR Analysis
4.6. In Vitro Modulation of Monocyte Polarisation Status
4.7. Soluble Cytokines Quantification
4.8. Soluble Immune-Checkopoint Quantification
4.9. ELISA Assay
4.10. In Vitro Proliferation Assays
4.11. Transwell Migration Assay
4.12. hADMSC Differentiation and Staining
4.13. Animals
4.14. Immunohistochemistry
4.15. Statistical Analysis
4.16. Ethics Approval
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, X.; Liu, G.; Halim, A.; Ju, Y.; Luo, Q.; Song, G. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Migration and Tissue Repair. Cells 2019, 8, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnecchi, M.; Danieli, P.; Malpasso, G.; Ciuffreda, M.C. Paracrine Mechanisms of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Tissue Repair. In Mesenchymal Stem Cells; Gnecchi, M., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 1416, pp. 123–146. ISBN 978-1-4939-3582-6. [Google Scholar]
- Konno, M.; Hamabe, A.; Hasegawa, S.; Ogawa, H.; Fukusumi, T.; Nishikawa, S.; Ohta, K.; Kano, Y.; Ozaki, M.; Noguchi, Y.; et al. Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Regenerative Medicine. Dev. Growth Differ. 2013, 55, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuk, P.A.; Zhu, M.; Mizuno, H.; Huang, J.; Futrell, J.W.; Katz, A.J.; Benhaim, P.; Lorenz, H.P.; Hedrick, M.H. Multilineage Cells from Human Adipose Tissue: Implications for Cell-Based Therapies. Tissue Eng. 2001, 7, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardo, E.; DelaRosa, O.; Mancheño-Corvo, P.; Menta, R.; Ramírez, C.; Büscher, D. Toll-like Receptor–Mediated Signaling in Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells: Implications for Immunogenicity and Immunosuppressive Potential. Tissue Eng. Part A 2009, 15, 1579–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Xu, L.; Zwingenberger, S.; Gibon, E.; Goodman, S.B.; Li, G. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Homing to Improve Bone Healing. J. Orthop. Transl. 2017, 9, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggenhofer, E.; Benseler, V.; Kroemer, A.; Popp, F.C.; Geissler, E.K.; Schlitt, H.J.; Baan, C.C.; Dahlke, M.H.; Hoogduijn, M.J. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Are Short-Lived and Do Not Migrate beyond the Lungs after Intravenous Infusion. Front. Immun. 2012, 3, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saat, T.C.; van den Engel, S.; Bijman-Lachger, W.; Korevaar, S.S.; Hoogduijn, M.J.; IJzermans, J.N.M.; de Bruin, R.W.F. Fate and Effect of Intravenously Infused Mesenchymal Stem Cells in a Mouse Model of Hepatic Ischemia Reperfusion Injury and Resection. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 5761487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggenhofer, E.; Luk, F.; Dahlke, M.H.; Hoogduijn, M.J. The Life and Fate of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogle, B.M.; Cascalho, M.; Platt, J.L. Biological Implications of Cell Fusion. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörnen, J.; Myklebost, O.; Dittmar, T. Cell Fusion of Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells and Breast Cancer Cells Leads to the Formation of Hybrid Cells Exhibiting Diverse and Individual (Stem Cell) Characteristics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horsley, V.; Pavlath, G.K. Forming a Multinucleated Cell: Molecules That Regulate Myoblast Fusion. Cells Tissues Organs 2004, 176, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagers, A.J.; Weissman, I.L. Plasticity of Adult Stem Cells. Cell 2004, 116, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomerantz, J.; Blau, H.M. Nuclear Reprogramming: A Key to Stem Cell Function in Regenerative Medicine. Nat. Cell Biol. 2004, 6, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espagnolle, N.; Balguerie, A.; Arnaud, E.; Sensebé, L.; Varin, A. CD54-Mediated Interaction with Pro-Inflammatory Macrophages Increases the Immunosuppressive Function of Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Stem Cell Rep. 2017, 8, 961–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Fu, C.; Song, L.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Ma, G.; Shen, C. Exposure to Supernatants of Macrophages That Phagocytized Dead Mesenchymal Stem Cells Improves Hypoxic Cardiomyocytes Survival. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 165, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggini, J.; Mirkin, G.; Bognanni, I.; Holmberg, J.; Piazzón, I.M.; Nepomnaschy, I.; Costa, H.; Cañones, C.; Raiden, S.; Vermeulen, M.; et al. Mouse Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Turn Activated Macrophages into a Regulatory-Like Profile. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguirre, L.A.; Montalbán-Hernández, K.; Avendaño-Ortiz, J.; Marín, E.; Lozano, R.; Toledano, V.; Sánchez-Maroto, L.; Terrón, V.; Valentín, J.; Pulido, E.; et al. Tumor Stem Cells Fuse with Monocytes to Form Highly Invasive Tumor-Hybrid Cells. OncoImmunology 2020, 9, 1773204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano-Rodríguez, R.; Avendaño-Ortíz, J.; Montalbán-Hernández, K.; Ruiz-Rodríguez, J.C.; Ferrer, R.; Martín-Quirós, A.; Maroun-Eid, C.; González-López, J.J.; Fàbrega, A.; Terrón, V.; et al. SIGLEC5: An Immune Checkpoint Ligand in Sepsis; Infectious Diseases (except HIV/AIDS). medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Becker, A.; Van Hummelen, P.; Bakkus, M.; Vande Broek, I.; De Wever, J.; De Waele, M.; Van Riet, I. Migration of Culture-Expanded Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells through Bone Marrow Endothelium Is Regulated by Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 and Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-3. Haematologica 2007, 92, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Guo, Y.; Xia, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhang, F.; Guo, L.; Liu, Y.; Yin, T.; Gao, C.; et al. Resistin Promotes Cardiac Homing of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Functional Recovery after Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion via the ERK1/2-MMP-9 Pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2019, 316, H233–H244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Fuentes, D.E.; Fernández-Garza, L.E.; Samia-Meza, J.A.; Barrera-Barrera, S.A.; Caplan, A.I.; Barrera-Saldaña, H.A. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Current Clinical Applications: A Systematic Review. Arch. Med. Res. 2021, 52, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Nicola, M.; Carlo-Stella, C.; Magni, M.; Milanesi, M.; Longoni, P.D.; Matteucci, P.; Grisanti, S.; Gianni, A.M. Human Bone Marrow Stromal Cells Suppress T-Lymphocyte Proliferation Induced by Cellular or Nonspecific Mitogenic Stimuli. Blood 2002, 99, 3838–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krampera, M.; Glennie, S.; Dyson, J.; Scott, D.; Laylor, R.; Simpson, E.; Dazzi, F. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Inhibit the Response of Naive and Memory Antigen-Specific T Cells to Their Cognate Peptide. Blood 2003, 101, 3722–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabat, M.; Bobkov, I.; Kumar, S.; Grumet, M. Trends in Mesenchymal Stem Cell Clinical Trials 2004-2018: Is Efficacy Optimal in a Narrow Dose Range? Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2020, 9, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankrum, J.; Karp, J.M. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy: Two Steps Forward, One Step Back. Trends Mol. Med. 2010, 16, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karp, J.M.; Leng Teo, G.S. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Homing: The Devil Is in the Details. Cell Stem Cell 2009, 4, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Poll, D.; Parekkadan, B.; Borel Rinkes, I.H.M.; Tilles, A.W.; Yarmush, M.L. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Protection and Repair of Injured Vital Organs. Cell Mol. Bioeng. 2008, 1, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Billet, S.; Choudhury, D.; Cheng, R.; Haldar, S.; Fernandez, A.; Biondi, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, H.; Bhowmick, N.A. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Interact with Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells to Promote Cancer Progression and Drug Resistance. Neoplasia 2021, 23, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merle, C.; Lagarde, P.; Lartigue, L.; Chibon, F. Acquisition of Cancer Stem Cell Capacities after Spontaneous Cell Fusion. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalbán-Hernández, K.; Cantero-Cid, R.; Casalvilla-Dueñas, J.C.; Avendaño-Ortiz, J.; Marín, E.; Lozano-Rodríguez, R.; Terrón-Arcos, V.; Vicario-Bravo, M.; Marcano, C.; Saavedra-Ambrosy, J.; et al. Colorectal Cancer Stem Cells Fuse with Monocytes to Form Tumour Hybrid Cells with the Ability to Migrate and Evade the Immune System. Cancers 2022, 14, 3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, A.R.R.; Dahlke, M.H. Immunomodulation by Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs): Mechanisms of Action of Living, Apoptotic, and Dead MSCs. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dittmar, T.; Entschladen, F. Migratory Properties of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. In Mesenchymal Stem Cells—Basics and Clinical Application I; Weyand, B., Dominici, M., Hass, R., Jacobs, R., Kasper, C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 117–136. ISBN 978-3-642-35671-1. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Ding, L.; Wang, L.; Cao, Y.; Zhu, H.; Lu, J.; Li, X.; Song, T.; Hu, Y.; Dai, J. Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Scaffolds Facilitate Collagen Degradation via Upregulation of MMP-9 in Rat Uterine Scars. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, S.L.; Duchi, S.; Onofrillo, C.; Di Bella, C.; Choong, P.F.M. Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Use of Cartilage Tissue Engineering: The Need for a Rapid Isolation Procedure. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 8947548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Montalbán-Hernández, K.; Casado-Sánchez, C.; Avendaño-Ortiz, J.; Casalvilla-Dueñas, J.C.; Bonel-Pérez, G.C.; Prado-Montero, J.; Valentín-Quiroga, J.; Lozano-Rodríguez, R.; Terrón-Arcos, V.; de la Bastida, F.R.; et al. Fused Cells between Human-Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Monocytes Keep Stemness Properties and Acquire High Mobility. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9672. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23179672
Montalbán-Hernández K, Casado-Sánchez C, Avendaño-Ortiz J, Casalvilla-Dueñas JC, Bonel-Pérez GC, Prado-Montero J, Valentín-Quiroga J, Lozano-Rodríguez R, Terrón-Arcos V, de la Bastida FR, et al. Fused Cells between Human-Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Monocytes Keep Stemness Properties and Acquire High Mobility. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(17):9672. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23179672
Chicago/Turabian StyleMontalbán-Hernández, Karla, Cesar Casado-Sánchez, José Avendaño-Ortiz, José Carlos Casalvilla-Dueñas, Gloria C. Bonel-Pérez, Julia Prado-Montero, Jaime Valentín-Quiroga, Roberto Lozano-Rodríguez, Verónica Terrón-Arcos, Fátima Ruiz de la Bastida, and et al. 2022. "Fused Cells between Human-Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Monocytes Keep Stemness Properties and Acquire High Mobility" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 17: 9672. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23179672
APA StyleMontalbán-Hernández, K., Casado-Sánchez, C., Avendaño-Ortiz, J., Casalvilla-Dueñas, J. C., Bonel-Pérez, G. C., Prado-Montero, J., Valentín-Quiroga, J., Lozano-Rodríguez, R., Terrón-Arcos, V., de la Bastida, F. R., Córdoba, L., Laso-García, F., Diekhorst, L., del Fresno, C., & López-Collazo, E. (2022). Fused Cells between Human-Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Monocytes Keep Stemness Properties and Acquire High Mobility. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(17), 9672. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23179672





