Recurrent Translocations in Topoisomerase Inhibitor-Related Leukemia Are Determined by the Features of DNA Breaks Rather Than by the Proximity of the Translocating Genes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
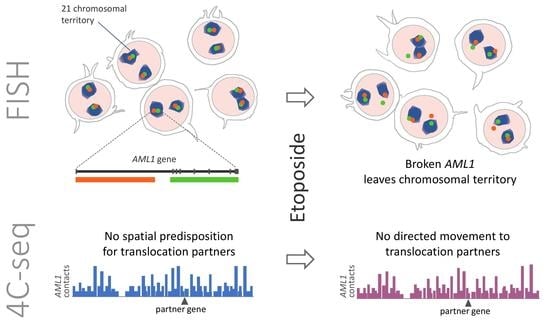
2.1. Etoposide Treatment Leads to the Formation of DSBs in AML1 Followed by Separation of the Break Ends
2.2. The Distribution of AML1 Alleles Relative to the Chromosomal Territory Boundaries Changes after Etoposide Treatment
2.3. MLL and AML1 Do Not Demonstrate Increased Contact Frequency with Their TI-Related Rearrangement Partners in Both Control and Etoposide-Treated Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. 3D-FISH
4.3. Image Processing
4.4. 3C and 4C-seq Libraries
| 4C-AML1-H | CAGGTGAGTGTGGAGGTAGAGAG |
| 4C-AML1-D | CTTGGTTCCCCAGCTGAGAT |
| 4C-MLL-H | ATAGGCTCCATGTTGGCTCA |
| 4C-MLL-D | CACAGGATACAAAGCAGAACTACTC |
| 4C-CCND1-H | CCTGCCAACTTCGGTGTCC |
| 4C-CCND1-D | AAGTTACCCGAGGCGGAGTC |
4.5. 4C-seq Analysis
4.6. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Riccio, A.A.; Schellenberg, M.J.; Williams, R.S. Molecular Mechanisms of Topoisomerase 2 DNA–Protein Crosslink Resolution. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitiss, J.L. Targeting DNA Topoisomerase II in Cancer Chemotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pommier, Y.; Leo, E.; Zhang, H.; Marchand, C. DNA Topoisomerases and Their Poisoning by Anticancer and Antibacterial Drugs. Chem. Biol. 2010, 17, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.-C.; Li, Y.-C.; Wang, Y.-R.; Li, T.-K.; Chan, N.-L. On the Structural Basis and Design Guidelines for Type II Topoisomerase-Targeting Anticancer Drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 10630–10640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hevener, K.E.; Verstak, T.A.; Lutat, K.E.; Riggsbee, D.L.; Mooney, J.W. Recent Developments in Topoisomerase-Targeted Cancer Chemotherapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2018, 8, 844–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunting, S.F.; Nussenzweig, A. End-Joining, Translocations and Cancer. Nat. Cancer 2013, 13, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieber, M.R.; Gu, J.; Lu, H.; Shimazaki, N.; Tsai, A.G. Nonhomologous DNA end joining (NHEJ) and chromosomal translocations in humans. Subcell Biochem. 2010, 50, 279–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratain, M.J.; Rowley, J.D. Therapy-Related Acute Myeloid Leukemia Secondary to Inhibitors of Topoisomerase II: From the Bedside to the Target Genes. Ann. Oncol. 1992, 3, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNerney, M.E.; Godley, L.A.; Le Beau, M.M. Therapy-Related Myeloid Neoplasms: When Genetics and Environment Collide. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 513–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, S. Therapy-Related Myelodysplasia and Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Semin. Oncol. 2013, 40, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kayser, S.; Döhner, K.; Krauter, J.; Köhne, C.H.; Horst, H.A.; Held, G.; Von Lilienfeld-Toal, M.; Wilhelm, S.; Kündgen, A.; Götze, K.; et al. The Impact of Therapy-Related Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) on Outcome in 2853 Adult Patients with Newly Diagnosed AML. Blood 2011, 117, 2137–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoch, C.; Kern, W.; Schnittger, S.; Hiddemann, W.; Haferlach, T. Karyotype Is an Independent Prognostic Parameter in Therapy-Related Acute Myeloid Leukemia (t-AML): An Analysis of 93 Patients with t-AML in Comparison to 1091 Patients with de Novo AML. Leukemia 2004, 18, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.; Cowell, I. The Role of Topoisomerase II Beta on Breakage and Proximity of RUNX1 to Partner Alleles RUNX1T1 and EVI1. Genes 2014, 128, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowley, J.D.; Olney, H.J. International Workshop on the Relationship of Prior Therapy to Balanced Chromosome Aberrations in Therapy-Related Myelodysplastic Syndromes and Acute Leukemia: Overview Report. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2002, 33, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, R.C.; Dou, Y. Hijacked in Cancer: The KMT2 (MLL) Family of Methyltransferases. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, M.G.; Jenner, R.G.; Chevalier, B.; Nakamura, T.; Croce, C.M.; Canaani, E.; Young, R.A. Global and Hox-Specific Roles for the MLL1 Methyltransferase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 8603–8608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichikawa, M.; Goyama, S.; Asai, T.; Kawazu, M.; Nakagawa, M.; Takeshita, M.; Chiba, S.; Ogawa, S.; Kurokawa, M. AML1/Runx1 Negatively Regulates Quiescent Hematopoietic Stem Cells in Adult Hematopoiesis. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 4402–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Braekeleer, E.; Douet-Guilbert, N.; Morel, F.; Le Bris, M.J.; Férec, C.; De Braekeleer, M. RUNX1 Translocations and Fusion Genes in Malignant Hemopathies. Future Oncol. 2011, 7, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen-Bjergaard, J.; Andersen, M.K.; Andersen, M.T.; Christiansen, D.H. Genetics of Therapy-Related Myelodysplasia and Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Leukemia 2008, 22, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, T.; Taga, T.; Takagi, M.; Kawasaki, H.; Koh, K.; Taki, T.; Adachi, S.; Manabe, A.; Ishida, Y. Nationwide Survey of Therapy-Related Leukemia in Childhood in Japan. Int. J. Hematol. 2018, 108, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafson, S.A.; Lin, P.; Chen, S.S.; Chen, L.; Abruzzo, L.V.; Luthra, R.; Medeiros, L.J.; Wang, S.A. Therapy-Related Acute Myeloid Leukemia with t(8;21) (Q22;Q22) Shares Many Features with de Novo Acute Myeloid Leukemia with t(8;21)(Q22;Q22) but Does Not Have a Favorable Outcome. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2009, 131, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sood, R.; Kamikubo, Y.; Liu, P. Role of RUNX1 in Hematological Malignancies. Blood 2017, 129, 2070–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.; Oshikawa, G.; Akiyama, H.; Ishida, S.; Nagao, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Miura, O. Acute Myeloid Leukemia with t(3;21)(Q26.2;Q22) Developing Following Low-Dose Methotrexate Therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis and Expressing Two AML1/MDS1/EVI1 Fusion Proteins: A Case Report. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, Y.; Izumi, T.; Kanamori, H.; Davis, E.M.; Miura, Y.; Larson, R.A.; Le Beau, M.M.; Ozawa, K.; Rowley, J.D. T(1;3)(P36;P21) Is a Recurring Therapy-Related Translocation. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2002, 34, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duhoux, F.P.; Ameye, G.; Montano-Almendras, C.P.; Bahloula, K.; Mozziconacci, M.J.; Laibe, S.; Wlodarska, I.; Michaux, L.; Talmant, P.; Richebourg, S.; et al. PRDM16 (1p36) Translocations Define a Distinct Entity of Myeloid Malignancies with Poor Prognosis but May Also Occur in Lymphoid Malignancies. Br. J. Haematol. 2012, 156, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, M.K.; Christiansen, D.H.; Jensen, B.A.; Ernst, P.; Hauge, G.; Pedersen-Bjergaard, J. Therapy-Related Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia with MLL Rearrangements Following DNA Topoisomerase II Inhibitors, an Increasing Problem: Report on Two New Cases and Review of the Literature since 1992. Br. J. Haematol. 2001, 114, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowell, I.G.; Austin, C.A. Mechanism of Generation of Therapy Related Leukemia in Response to Anti-Topoisomerase II Agents. J. Environ. Res. Public 2012, 9, 2075–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorman, A.V.; Hagemeijer, A.; Charrin, C.; Rieder, H.; Secker-walker, L.M. Clinical Profile of 53 Patients. Leukemia 1998, 12, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, C.; Burmeister, T.; Strehl, S.; Schneider, B.; Hubert, D.; Zach, O.; Haas, O.; Klingebiel, T.; Dingermann, T.; Marschalek, R. Spliced MLL Fusions: A Novel Mechanism to Generate Functional Chimeric MLL-MLLT1 Transcripts in t(11;19)(Q23;P13.3) Leukemia. Leuk. Off. J. Leuk. Soc. Am. Leuk. Res. Fund UK 2007, 21, 588–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavau, C.; Du, C.; Thirman, M.; Zeleznik-Le, N. Chromatin-Related Properties of CBP Fused to MLL Generate a Myelodysplastic-like Syndrome That Evolves into Myeloid Leukemia. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 4655–4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoo, B.J.; Nam, M.H.; Sung, H.J.; Lim, C.S.; Lee, C.K.; Cho, Y.J.; Lee, K.N.; Yoon, S.Y. A Case of Therapy-Related Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia with t(11;19) (Q23;P13.3) and MLL/MLLT1 Gene Rearrangement. Korean J. Lab. Med. 2011, 31, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, W.; Tang, G.; Wang, E.; Kim, Y.; Cloe, A.; Shen, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Loghavi, S.; Hu, A.Y.; et al. T(11;16)(Q23;P13)/KMT2A-CREBBP in Hematologic Malignancies: Presumptive Evidence of Myelodysplasia or Therapy-Related Neoplasm? Ann. Hematol. 2020, 99, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cremer, M.; von Hase, J.; Volm, T.; Brero, A.; Kreth, G.; Walter, J.; Fischer, C.; Solovei, I.; Cremer, C.; Cremer, T. Non-Random Radial Higher-Order Chromatin Arrangements in Nuclei of Diploid Human Cells. Chromosome Res. 2001, 9, 541–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieberman-Aiden, E.; van Berkum, N.L.; Williams, L.; Imakaev, M.; Ragoczy, T.; Telling, A.; Amit, I.; Lajoie, B.R.; Sabo, P.J.; Dorschner, M.O.; et al. Comprehensive Mapping of Long-Range Interactions Reveals Folding Principles of the Human Genome. Science 2009, 326, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremer, T.; Cremer, M. Chromosome Territories. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a003889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosin, L.F.; Crocker, O.; Isenhart, R.L.; Nguyen, S.C.; Xu, Z.; Joyce, E.F. Chromosome Territory Formation Attenuates the Translocation Potential of Cells. Elife 2019, 8, e49553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; McCord, R.P.; Ho, Y.-J.; Lajoie, B.R.; Hildebrand, D.G.; Simon, A.C.; Becker, M.S.; Alt, F.W.; Dekker, J. Chromosomal Translocations Are Guided by the Spatial Organization of the Genome. Cell 2012, 148, 908–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engreitz, J.M.; Agarwala, V.; Mirny, L.A. Three-Dimensional Genome Architecture Influences Partner Selection for Chromosomal Translocations in Human Disease. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathitruangsak, C.; Righolt, C.H.; Klewes, L.; Tung Chang, D.; Kotb, R.; Mai, S. Distinct and Shared Three-Dimensional Chromosome Organization Patterns in Lymphocytes, Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance and Multiple Myeloma. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aymard, F.; Aguirrebengoa, M.; Guillou, E.; Javierre, B.M.; Bugler, B.; Arnould, C.; Rocher, V.; Iacovoni, J.S.; Biernacka, A.; Skrzypczak, M.; et al. Genome-Wide Mapping of Long-Range Contacts Unveils Clustering of DNA Double-Strand Breaks at Damaged Active Genes. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2017, 24, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soutoglou, E.; Dorn, J.F.; Sengupta, K.; Jasin, M.; Nussenzweig, A.; Ried, T.; Danuser, G.; Misteli, T. Positional Stability of Single Double-Strand Breaks in Mammalian Cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Nakamura, M.; Abbott, T.R.; Zhao, D.; Luo, K.; Yu, C.; Nguyen, C.M.; Lo, A.; Daley, T.P.; La Russa, M.; et al. CRISPR-Mediated Live Imaging of Genome Editing and Transcription. Science 2019, 365, 1301–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glukhov, S.I.; Rubtsov, M.A.; Alexeyevsky, D.A.; Alexeevski, A.V.; Razin, S.V.; Iarovaia, O.V. The Broken MLL Gene Is Frequently Located Outside the Inherent Chromosome Territory in Human Lymphoid Cells Treated with DNA Topoisomerase II Poison Etoposide. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bystritskiy, A.A.; Razin, S.V. Breakpoint Clusters: Reason or Consequence? Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2004, 14, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falk, M.; Lukasova, E.; Gabrielova, B.; Ondrej, V.; Kozubek, S. Chromatin Dynamics during DSB Repair. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2007, 1773, 1534–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aten, J.A.; Stap, J.; Krawczyk, P.M.; van Oven, C.H.; Hoebe, R.A.; Essers, J.; Kanaar, R. Dynamics of DNA Double-Strand Breaks Revealed by Clustering of Damaged Chromosome Domains. Science 2004, 303, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsden, D.A.; Nussenzweig, A. Mechanisms Driving Chromosomal Translocations: Lost in Time and Space. Oncogene 2021, 40, 4263–4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roukos, V.; Voss, T.C.; Schmidt, C.K.; Lee, S.; Wangsa, D.; Misteli, T. Spatial Dynamics of Chromosome Translocations in Living Cells. Science 2013, 341, 660–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarle, R.; Zhang, Y.; Frock, R.L.; Lewis, S.M.; Molinie, B.; Ho, Y.J.; Myers, D.R.; Choi, V.W.; Compagno, M.; Malkin, D.J.; et al. Genome-Wide Translocation Sequencing Reveals Mechanisms of Chromosome Breaks and Rearrangements in B Cells. Cell 2011, 147, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, I.A.; Resch, W.; Jankovic, M.; Oliveira, T.; Yamane, A.; Nakahashi, H.; Di Virgilio, M.; Bothmer, A.; Nussenzweig, A.; Robbiani, D.F.; et al. Translocation-Capture Sequencing Reveals the Extent and Nature of Chromosomal Rearrangements in B Lymphocytes. Cell 2011, 147, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hakim, O.; Resch, W.; Yamane, A.; Klein, I.; Kieffer-Kwon, K.-R.; Jankovic, M.; Oliveira, T.; Bothmer, A.; Voss, T.C.; Ansarah-Sobrinho, C.; et al. DNA Damage Defines Sites of Recurrent Chromosomal Translocations in B Lymphocytes. Nature 2012, 484, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krawczyk, P.M.; Borovski, T.; Stap, J.; Cijsouw, T.; ten Cate, R.; Medema, J.P.; Kanaar, R.; Franken, N.A.P.; Aten, J.A. Chromatin Mobility Is Increased at Sites of DNA Double-Strand Breaks. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 2127–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantidze, O.L.; Razin, S.V. Chromatin Loops, Illegitimate Recombination, and Genome Evolution. BioEssays 2009, 31, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canela, A.; Maman, Y.; Huang, S.-Y.N.; Wutz, G.; Tang, W.; Zagnoli-Vieira, G.; Callen, E.; Wong, N.; Day, A.; Peters, J.M.; et al. Topoisomerase II-Induced Chromosome Breakage and Translocation Is Determined by Chromosome Architecture and Transcriptional Activity. Mol. Cell 2019, 75, 252–266.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantidze, O.L.; Razin, S.V. Chemotherapy-Related Secondary Leukemias: A Role for DNA Repair by Error-Prone Non-Homologous End Joining in Topoisomerase II—Induced Chromosomal Rearrangements. Gene 2007, 391, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strissel, P.L.; Strick, R.; Tomek, R.J.; Roe, B.A.; Rowley, J.D.; Zeleznik-Le, N.J. DNA Structural Properties of AF9 Are Similar to MLL and Could Act as Recombination Hot Spots Resulting in MLL/AF9 Translocations and Leukemogenesis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2000, 9, 1671–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Strissel, P.; Strick, R.; Chen, J.; Nucifora, G.; Le Beau, M.M.; Larson, R.A.; Rowley, J.D.; Le Beau, M.M. Genomic DNA Breakpoints in AML1/RUNX1 and ETO Cluster with Topoisomerase II DNA Cleavage and DNase I Hypersensitive Sites in t(8;21) Leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 3070–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gole, B.; Wiesmüller, L. Leukemogenic rearrangements at the mixed lineage leukemia gene (MLL)-multiple rather than a single mechanism. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2015, 3, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannunzio, N.R.; Watanabe, G.; Lieber, M.R. Nonhomologous DNA End-Joining for Repair of DNA Double-Strand Breaks. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 10512–10523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzhin, A.V.; Velichko, A.K.; Razin, S.V.; Kantidze, O.L. Automated Analysis of Cell Cycle Phase-Specific DNA Damage Reveals Phase-Specific Differences in Cell Sensitivity to Etoposide. J. Cell. Biochem. 2016, 117, 2209–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashkevich, A.N.; Martin, O.A.; Smith, A.J.; Redon, C.E.; Bonner, W.M.; Martin, R.F.; Lobachevsky, P.N. ΓH2AX Foci as a Measure of DNA Damage: A Computational Approach to Automatic Analysis. Mutat. Res. Fundam. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2011, 711, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddig, A.; Roggenbuck, D.; Reinhold, D. Comparison of Different Immunoassays for ΓH2AX Quantification. J. Lab. Precis. Med. 2018, 3, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Saha, S.; Wang, W.; Saha, L.K.; Huang, S.-Y.N.; Pommier, Y. Excision Repair of Topoisomerase DNA-Protein Crosslinks (TOP-DPC). DNA Repair 2020, 89, 102837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, C.A.; Strande, N.T.; Wyatt, D.W.; Pryor, J.M.; Ramsden, D.A. Nonhomologous End Joining: A Good Solution for Bad Ends. DNA Repair 2014, 17, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubtsov, M.A.; Glukhov, S.I.; Allinne, J.; Pichugin, A.; Vassetzky, Y.S.; Razin, S.V.; Iarovaia, O.V. Treatment of Lymphoid Cells with the Topoisomerase II Poison Etoposide Leads to an Increased Juxtaposition of AML1 and ETO genes on the surface of nucleoli. Biopolym. Cell 2011, 27, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, U.; Schwenk, H.-U.; Bornkamm, G. Characterization of EBV-genome Negative “Null” and “T” Cell Lines Derived from Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Leukemic Transformed Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Int. J. Cancer 1977, 19, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syljuåsen, R.G.; McBride, W.H. Radiation-induced apoptosis and cell cycle progression in Jurkat T cells. Radiat. Res. 1999, 152, 328–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremer, M.; Müller, S.; Köhler, D.; Brero, A.; Solovei, I. Cell Preparation and Multicolor FISH in 3D Preserved Cultured Mammalian Cells. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2007, 2007, pdb.prot4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Splinter, E.; de Wit, E.; van de Werken, H.J.G.; Klous, P.; de Laat, W. Determining Long-Range Chromatin Interactions for Selected Genomic Sites Using 4C-Seq Technology: From Fixation to Computation. Methods 2012, 58, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gushchanskaya, E.S.; Artemov, A.V.; Ulyanov, S.V.; Logacheva, M.D.; Penin, A.A.; Kotova, E.S.; Akopov, S.B.; Nikolaev, L.G.; Iarovaia, O.V.; Sverdlov, E.D.; et al. The Clustering of CpG Islands May Constitute an Important Determinant of the 3D Organization of Interphase Chromosomes. Epigenetics 2014, 9, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krijger, P.H.L.; Geeven, G.; Bianchi, V.; Hilvering, C.R.E.; de Laat, W. 4C-Seq from Beginning to End: A Detailed Protocol for Sample Preparation and Data Analysis. Methods 2020, 170, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borovkov, A.A. Mathematical Statistics; Sobolev Institute of Mathematics: Novosibirsk, Russia, 1997; p. 32. [Google Scholar]





| Gene | Translocation | Partner | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| t(8;21)(q22;q22) | ETO (RUNX1T1) | [13,14,19,20,21] | |
| AML1 (RUNX1) | t(3;21)(q26.2;q22) | MDS1-EVI1 (MECOM, PRDM3) | [22,23] |
| t(1;21)(p36;q21) | PRDM16 | [24,25] | |
| t(9;11)(p22;q23) | AF9 (MLLT3) | [14,20] | |
| t(4;11)(q21;q23) | AF4 (AFF1, MLLT2) | [26,27] | |
| MLL (KMT2A) | t(19;11)(q13;q23) | ELL | [20,28] |
| t(11;19)(q23;p13.3) | ENL (MLLT1) | [20,28,29] | |
| t(11;16)(q23;p13) | CREBBP | [30,31,32] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lomov, N.A.; Viushkov, V.S.; Ulianov, S.V.; Gavrilov, A.A.; Alexeyevsky, D.A.; Artemov, A.V.; Razin, S.V.; Rubtsov, M.A. Recurrent Translocations in Topoisomerase Inhibitor-Related Leukemia Are Determined by the Features of DNA Breaks Rather Than by the Proximity of the Translocating Genes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9824. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23179824
Lomov NA, Viushkov VS, Ulianov SV, Gavrilov AA, Alexeyevsky DA, Artemov AV, Razin SV, Rubtsov MA. Recurrent Translocations in Topoisomerase Inhibitor-Related Leukemia Are Determined by the Features of DNA Breaks Rather Than by the Proximity of the Translocating Genes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(17):9824. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23179824
Chicago/Turabian StyleLomov, Nikolai A., Vladimir S. Viushkov, Sergey V. Ulianov, Alexey A. Gavrilov, Daniil A. Alexeyevsky, Artem V. Artemov, Sergey V. Razin, and Mikhail A. Rubtsov. 2022. "Recurrent Translocations in Topoisomerase Inhibitor-Related Leukemia Are Determined by the Features of DNA Breaks Rather Than by the Proximity of the Translocating Genes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 17: 9824. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23179824
APA StyleLomov, N. A., Viushkov, V. S., Ulianov, S. V., Gavrilov, A. A., Alexeyevsky, D. A., Artemov, A. V., Razin, S. V., & Rubtsov, M. A. (2022). Recurrent Translocations in Topoisomerase Inhibitor-Related Leukemia Are Determined by the Features of DNA Breaks Rather Than by the Proximity of the Translocating Genes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(17), 9824. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23179824