Ligand-Specific Nano-Contrast Agents Promote Enhanced Breast Cancer CT Detection at 0.5 mg Au
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
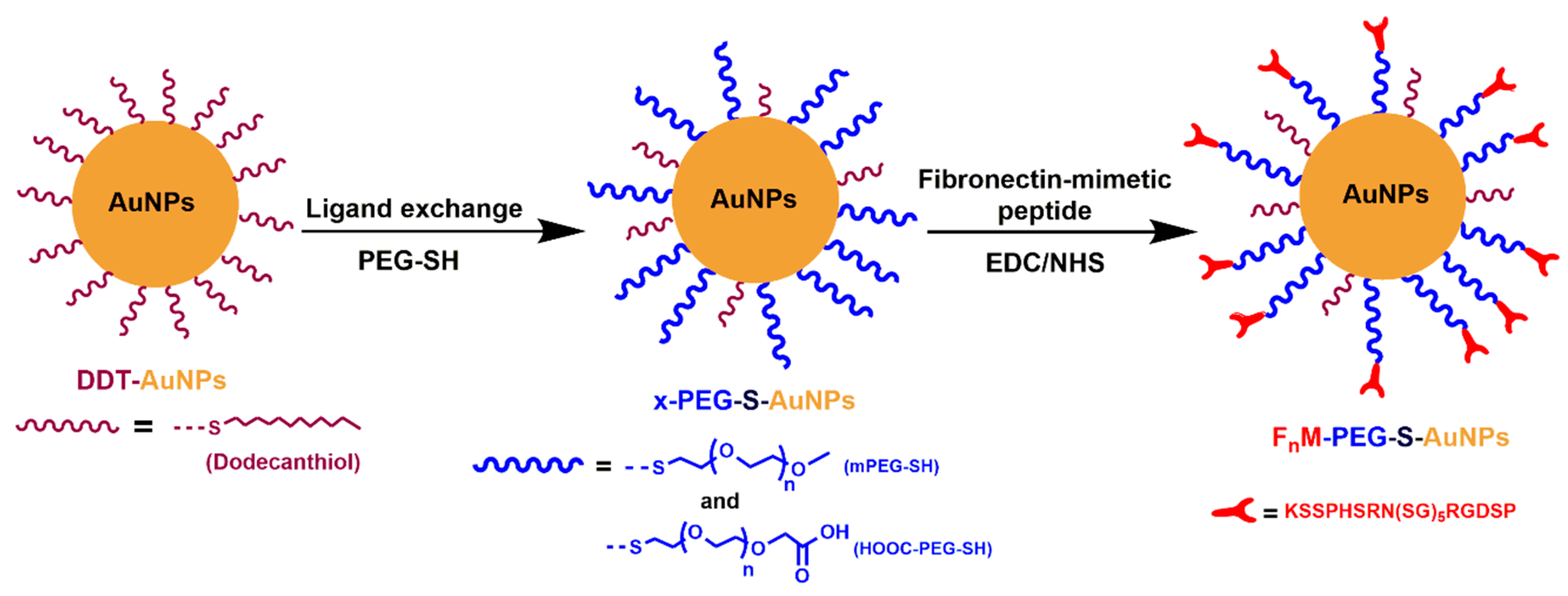
2.1. Dodecanethiol-Coated Gold Nanoparticles (C12-S-AuNPs)
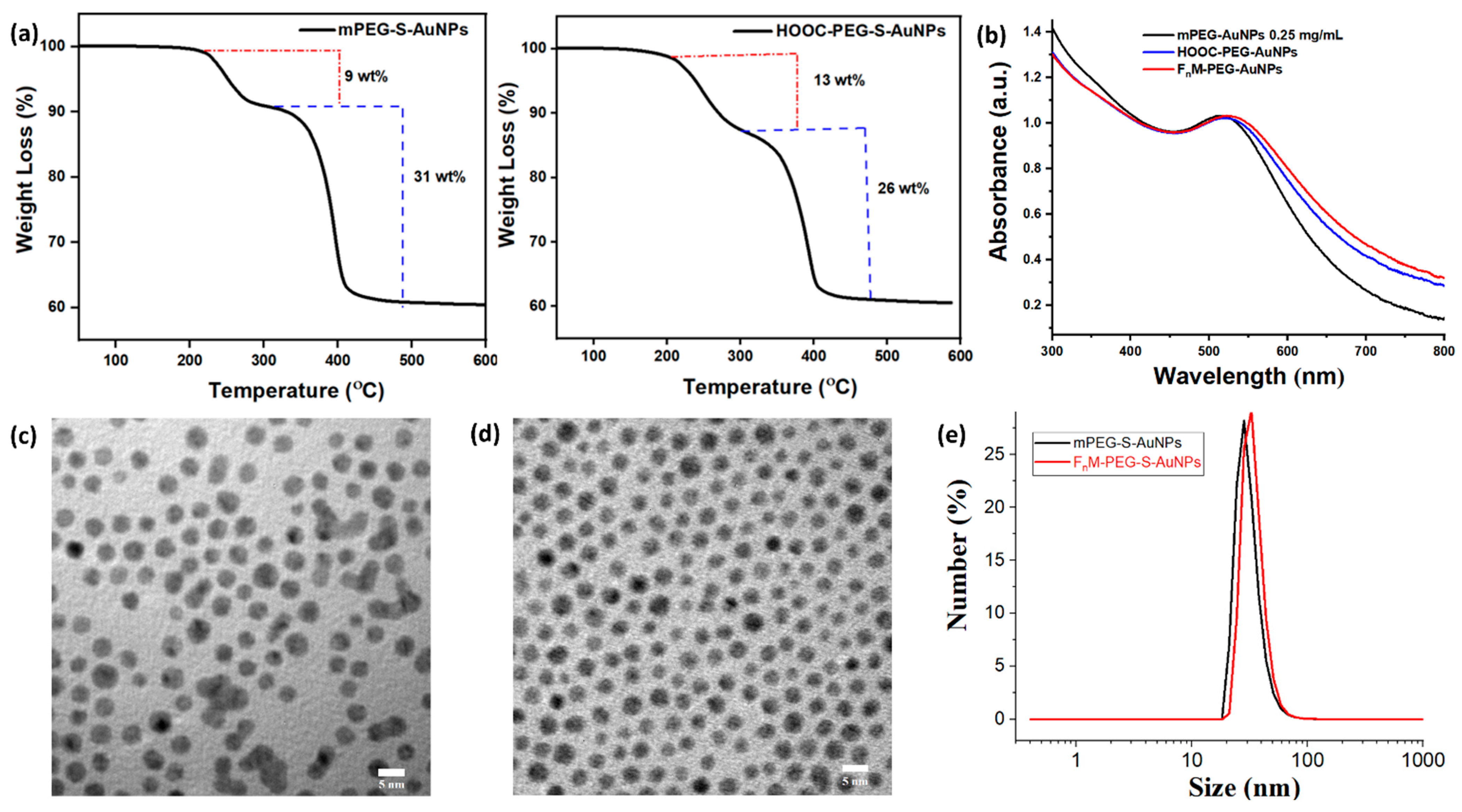
2.2. Synthesis of Hydrophilic PEG-Coated Gold Nanoparticles (x-PEG-S-AuNPs)
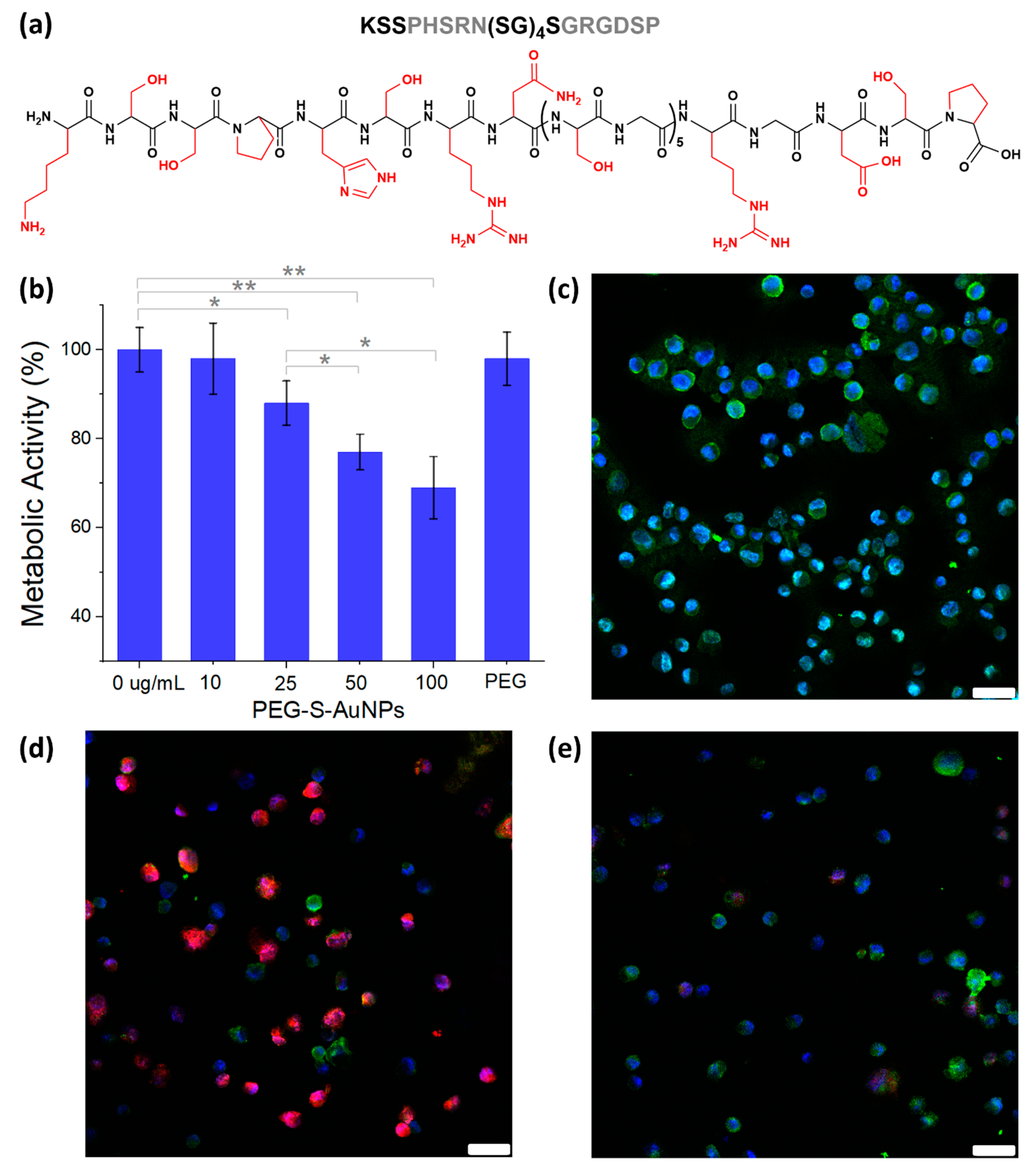
2.3. Synthesis of Ligand-Specific PEG-Gold Nanoparticles (FnM-PEG-S-AuNPs)
2.4. Fibroblasts Metabolic Activity and Binding Studies with MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells
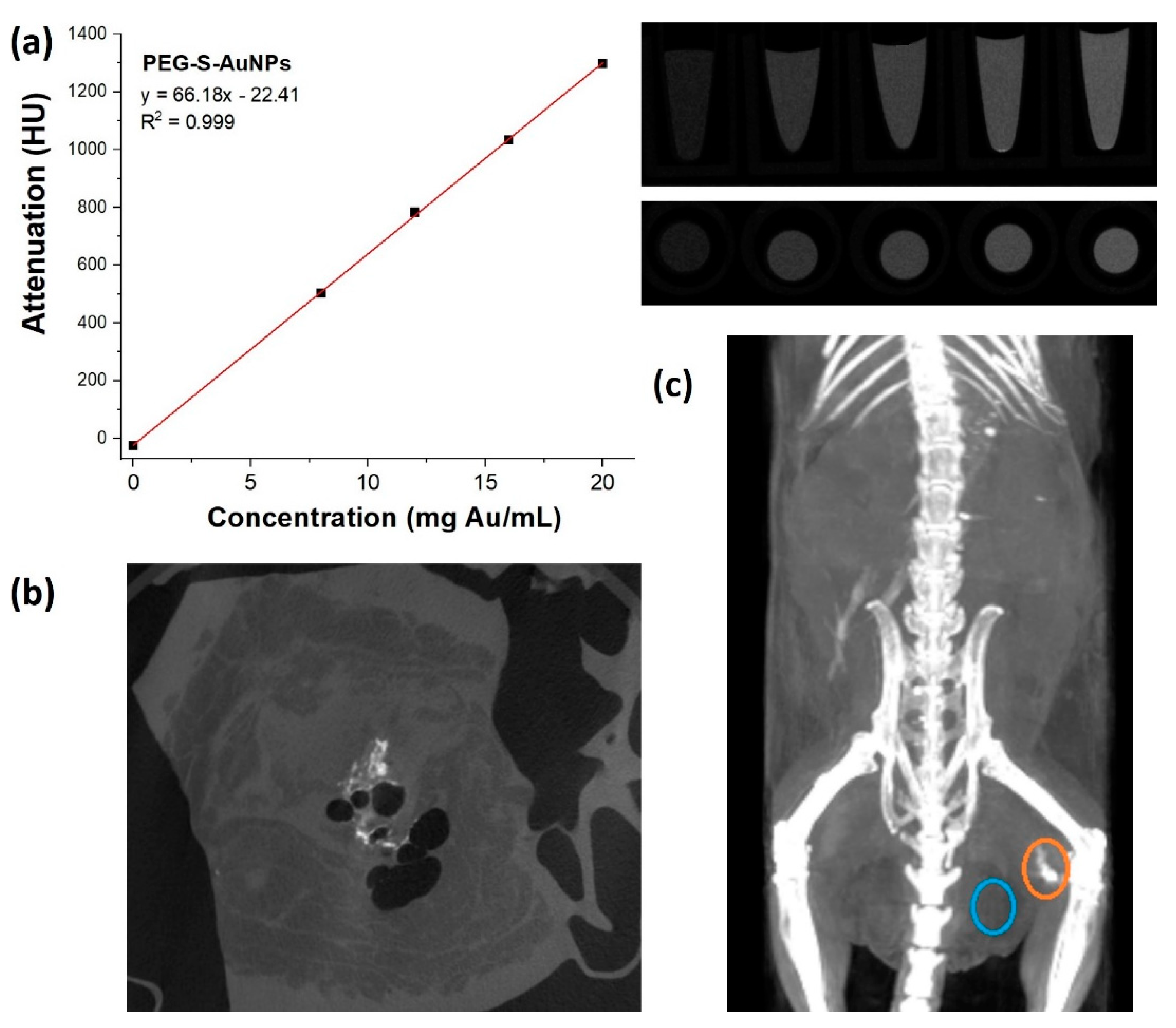
2.5. Quantification of mPEG-S-AuNP Contrast Agent in Solution and Ex Vivo Using a DE Micro-CT
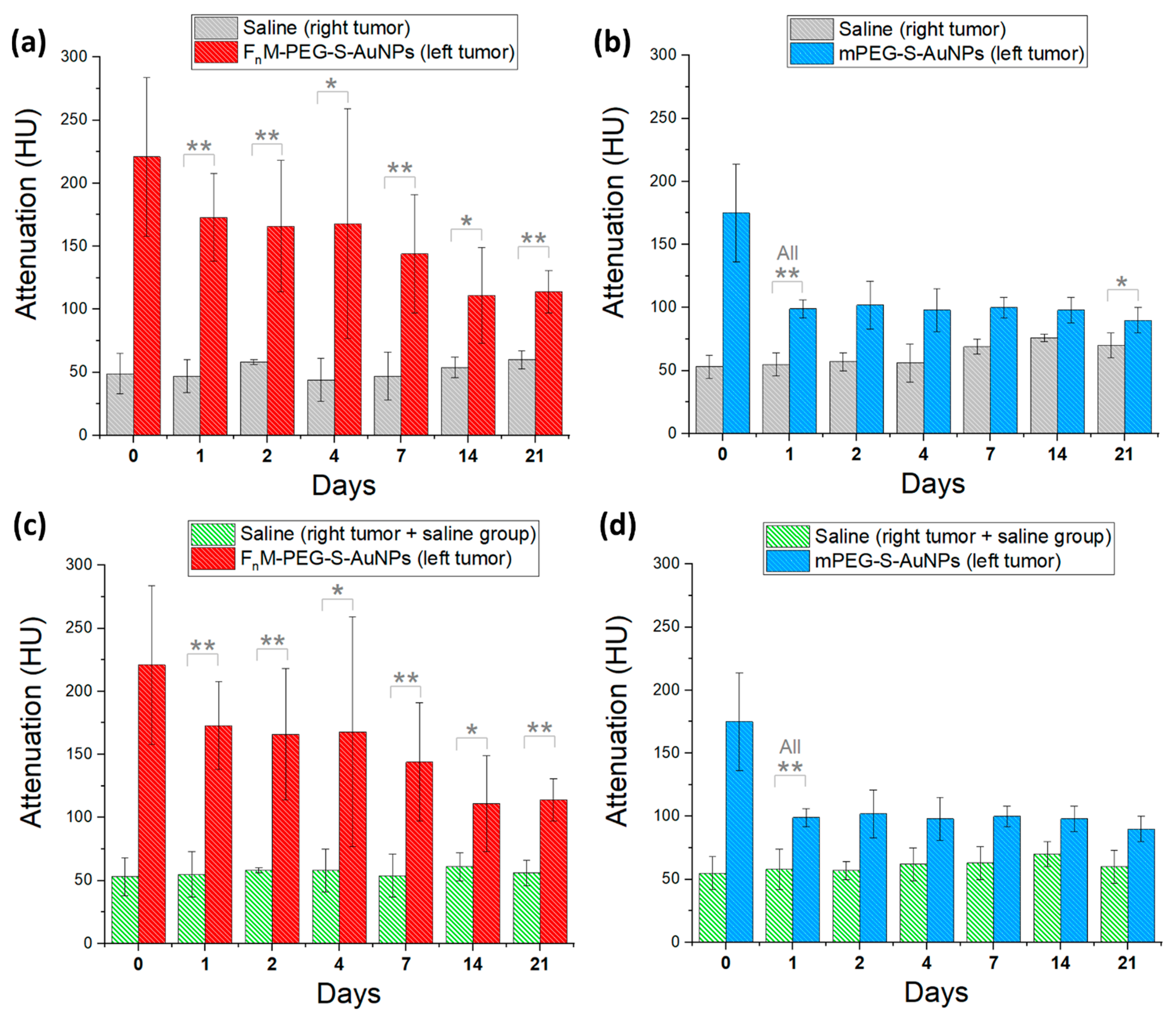
2.6. Animal Studies of Au-Based Contrast Agents Using a Triple (−) Breast Cancer Model
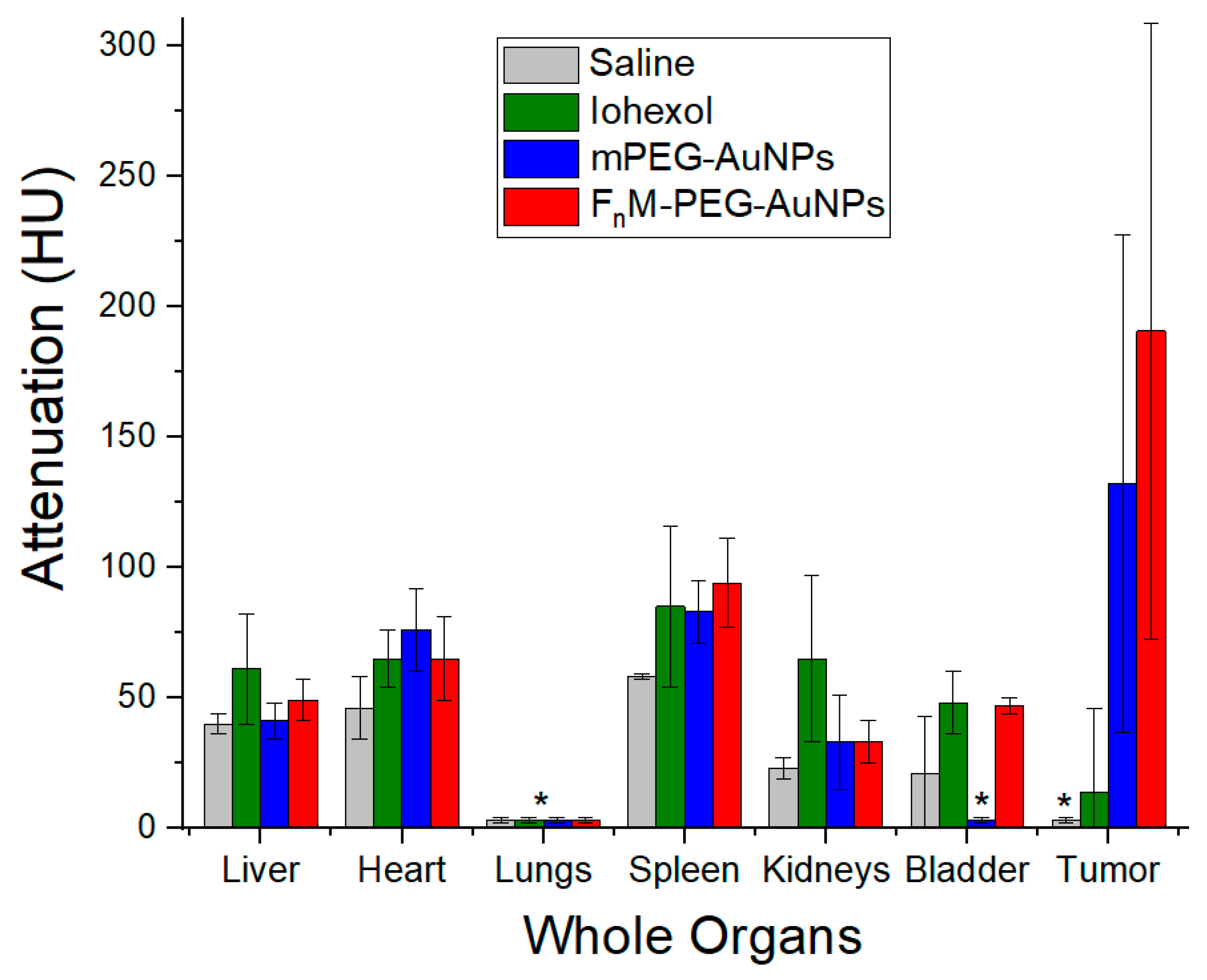
2.7. NP Biodistribution Studies/Contrast Retention and Accumulation in Tumors
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harris, J.R.; Lippman, M.E.; Veronesi, U.; Willett, W. Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 1992, 27, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelsey, J.L.; Gammon, M.D.; John, E.M. Reproductive Factors and Breast Cancer. Epidemiol. Rev. 1993, 15, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Key, T.J.; Verkasalo, P.K.; Banks, E. Epidemiology of Breast Cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2001, 2, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmore, J.G.; Armstrong, K.; Lehman, C.D.; Fletcher, S.W. Screening for Breast Cancer. JAMA 2005, 293, 1245–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennecke, H.; Yerushalmi, R.; Woods, R.; Cheang, M.C.U.; Voduc, D.; Speers, C.H.; Nielsen, O.T.; Gelmon, K. Metastatic Behavior of Breast Cancer Subtypes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 3271–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiadi, Z.; Lianos, G.D.; Ignatiadou, E.; Harissis, H.V.; Mitsis, M. Breast Cancer in Young Women: An Overview. Updates Surg. 2017, 69, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlin, S.S. Epidemiology of Breast Cancer in Women. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1152, 9–29. [Google Scholar]
- Momose, A.; Takeda, T.; Itai, Y.; Hirano, K. Phase-Contrast X-ray Computed Tomography for Observing Biological Soft Tissues. Nat. Med. 1996, 2, 473–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulus, M.J.; Gleason, S.S.; Kennel, S.J.; Hunsicker, P.R.; Johnson, D.K. High resolution X-ray Computed Tomography: An Emerging Tool for Small Animal Cancer Research. Neoplasia 2000, 2, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangheri, B.; Messa, C.; Picchio, M.; Gianolli, L.; Landoni, C.; Fazio, F. PET/CT and Breast Cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2004, 31, S135–S142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhl, C.K.; Schrading, S.; Leutner, C.C.; Morakkabati-Spitz, N.; Wardelmann, E.; Fimmers, R.; Kuhn, W.; Schild, H.H. Mammography, Breast Ultrasound, and Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Surveillance of Women at High Familial Risk for Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 8469–8476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalender, W.A. X-ray Computed Tomography. Phys. Med. Biol. 2006, 51, R29–R43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, E.L.; Eubank, W.B.; Mankoff, D.A. FDG PET, PET/CT, and Breast Cancer Imaging. Radiographics 2007, 27, S215–S229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, K.M.; Dean, J.; Comulada, W.S.; Lee, S.-J. Breast Cancer Detection Using Automated Whole Breast Ultrasound and Mammography in Radiographically Dense Breasts. Eur. Radiol. 2010, 20, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, M.; Morris, E. MRI for Breast Cancer Screening, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Lancet 2011, 378, 1804–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusic, H.; Grinstaff, M.W. X-ray Computed Tomography Contrast Agents. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 1641–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torchilin, V.P.; Frank-Kamenetsky, M.D.; Wolf, G.L. CT Visualization of Blood Pool in Rats by Using Long-Circulating, Iodine-Containing Micelles. Acad. Radiol. 1999, 6, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leike, J.U.; Schneider, T.; Wagner, S.E.; Rössling, G.L.; Krause, W.; Brandl, M. Biodistribution and Computed tomography Blood-Pool Imaging Properties of Polyethylene Glycol-Coated Iopromide-Carrying Liposomes. Investig. Radiol. 1997, 32, 44–50. [Google Scholar]
- Kao, C.-Y.; Hoffman, E.A.; Beck, K.C.; Bellamkonda, R.V.; Annapragada, A.V. Long-Residence-Time Nano-scale Liposomal Iohexol for X-ray–based Blood Pool Imaging. Acad. Radiol. 2003, 10, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukundan, S., Jr.; Ghaghada, K.B.; Badea, C.T.; Kao, C.-Y.; Hedlund, L.W.; Provenzale, J.M.; Johnson, G.A.; Chen, E.; Bellamkonda, R.V.; Annapragada, A.V. A Liposomal Nanoscale Contrast Agent for Preclinical CT in Mice. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2006, 186, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyafil, F.; Cornily, J.C.; Feig, J.E.; Gordon, R.; Vucic, E.; Amirbekian, V.; Fisher, E.A.; Fuster, V.; Feldman, L.J.; Fayad, Z.A. Noninvasive Detection of Macrophages Using a Nanoparticulate Contrast Agent for Computed Tomography. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karathanasis, E.; Suryanarayanan, S.; Balusu, S.R.; McNeeley, K.; Sechopoulos, I.; Karellas, A.; Annapragada, A.V.; Bellamkonda, R.V. Imaging Nanoprobe for Prediction of Outcome of Nanoparticle Chemotherapy by Using Mammography. Radiology 2009, 250, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clark, D.P.; Ghaghada, K.; Moding, E.J.; Kirsch, D.G.; Badea, C.T. In vivo Characterization of Tumor Vasculature Using Iodine and Gold Nanoparticles and Dual Energy Micro-CT. Phys. Med. Biol. 2013, 58, 1683–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashton, J.R.; Clark, D.P.; Moding, E.J.; Ghaghada, K.; Kirch, D.G.; West, J.L.; Badea, C.T. Dual-Energy Micro-CT Functional Imaging of Primary Lung Cancer in Mice Using Gold and Iodine Nanoparticle Contrast Agents: A Validation Study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88129. [Google Scholar]
- Rabin, O.; Perez, J.M.; Grimm, J.; Wojtkiewicz, G.; Weissleder, R. An X-ray Computed Tomography Imaging Agent Based on Long-Circulating Bismuth Sulphide Nanoparticles. Nat. Mater. 2006, 5, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getzin, M.; Garfield, J.J.; Rundle, D.S.; Krueger, U.; Gkikas, M.; Wang, G. Increased Separability of K-edge Nanoparticles by Photon-Counting Detectors for Spectral μCΤ. J. Xray Sci. Technol. 2018, 26, 707–726. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, K.; Getzin, M.; Garfield, J.J.; Suvarnapathaki, S.; Camci-Unal, G.; Wang, G.; Gkikas, M. Nanophosphor-Based Contrast Agents for Spectral X-ray Imaging. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarty, S.; Hix, J.M.L.; Wiewiora, K.A.; Volk, M.C.; Kenyon, E.; Shuboni-Mulligan, D.D.; Blanco-Fernandez, B.; Kiupel, M.; Thomas, J.; Sempere, L.F.; et al. Tantalum Oxide Nanoparticles as Versatile Contrast Agents for X-ray Computed Tomography. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 7720–7734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hainfeld, J.F.; Slatkin, D.N.; Focella, T.M.; Smilowitz, H.M. Gold Nanoparticles: A New X-ray Contrast Agent. Br. J. Radiol. 2006, 79, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Park, S.; Lee, J.H.; Jeong, Y.Y.; Jon, S. Antibiofouling Polymer-Coated Gold Nanoparticles as a Contrast Agent for in Vivo X-ray Computed Tomography Imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 7661–7665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Q.-Y.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, K.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Byun, S.J.; Kim, K.W.; Park, S.H.; Juhng, S.K.; Yoon, K.-H. Colloidal Gold Nanoparticles as a Blood-Pool Contrast Agent for X-ray Computed Tomography in Mice. Investig. Radiol. 2007, 42, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-A.; Kim, H.-K.; Kim, J.-H.; Jeong, S.-W.; Jung, J.-C.; Lee, G.-H.; Lee, J.; Chang, Y.; Kim, T.-J. Gold Nanoparticles Functionalized by Gadolinium–DTPA Conjugate of Cysteine as a Multimodal Bioimaging Agent. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 2287–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Zheng, L.; Chen, Q.; Shen, M.; Guo, R.; Wang, H.; Cao, X.; Zhang, G.; Shi, X. PEGylated Dendrimer-Entrapped Gold Nanoparticles for In Vivo Blood Pool and Tumor Imaging by CT. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 1107–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.-D.; Luo, Z.; Chen, C.; Song, S.; Yuan, X.; Shen, X.; Wang, H.; Sun, Y.; Gao, K.; Zhang, L.; et al. Ultrasmall Glutathione-Protected Gold Nanoclusters as Next Generation Radiotherapy Sensitizers with High Tumor Uptake and High Renal Clearance. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popovtzer, R.; Agrawal, A.; Kotov, N.A.; Popovtzer, A.; Balter, J.; Carey, T.E.; Kopelman, R. Targeted Gold Nanoparticles Enable Molecular CT Imaging of Cancer. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 4593–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormode, D.P.; Skajaa, T.; van Schooneveld, M.M.; Koole, R.; Jarzyna, P.; Lobatto, M.E.; Calcagno, C.; Barazza, A.; Gordon, R.E.; Zanzonico, P.; et al. Nanocrystal Core High-Density Lipoproteins: A Multimodality Contrast Agent Platform. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 3715–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanda, N.; Kattumuri, V.; Shukla, R.; Zambre, A.; Katti, K.; Upendran, A.; Kulkarni, R.R.; Kan, P.; Fent, G.M.; Casteel, S.W.; et al. Bombesin Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles Show in Vitro and in Vivo Cancer Receptor Specificity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 8760–8765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormode, D.P.; Roessl, E.; Thran, A.; Skajaa, T.; Gordon, R.E.; Schlomka, J.P.; Fuster, V.; Fisher, E.A.; Mulder, W.J.M.; Proska, R.; et al. Atherosclerotic Plaque Composition: Analysis with Multicolor CT and Targeted Gold Nanoparticle. Radiology 2010, 256, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hainfeld, J.F.; O’Connor, M.J.; Dilmanian, F.A.; Slatkin, D.N.; Adams, D.J.; Smilowitz, H.M. Micro-CT Enables Microlocalisation and Quantification of Her2-Targeted Gold Nanoparticles within Tumour Regions. Br. J. Radiol. 2011, 84, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuveni, T.; Motiei, M.; Romman, Z.; Popovtzer, A.; Popovtzer, R. Targeted Gold Nanoparticles Enable Molecular CT Imaging of Cancer: An in vivo Study. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 2859–2864. [Google Scholar]
- Ghann, W.E.; Aras, O.; Fleiter, T.; Daniel, M.-C. Syntheses and Characterization of Lisinopril-Coated Gold Nanoparticles as Highly Stable Targeted CT Contrast Agents in Cardiovascular Diseases. Langmuir 2012, 28, 10398–10408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shroff, K.; Kokkoli, E. PEGylated Liposomal Doxorubicin Targeted to α5β1-Expressing MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells. Langmuir 2012, 28, 4729–4736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirgoz, D.; Garg, A.; Kokkoli, E. PR_b-Targeted PEGylated Liposomes for Prostate Cancer Therapy. Langmuir 2008, 24, 13518–13524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffner, F.; Ray, A.M.; Dontenwill, M. Integrin α5β1, the Fibronectin Receptor, as a Pertinent Therapeutic Target in Solid Tumors. Cancers 2013, 5, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, T.; Kumata, K.; Xie, L.; Yui, J.; Wakizaka, H.; Fujibayashi, Y.; Zhang, M.-R.; Saga, T. Development of the Fibronectin-Mimetic Peptide KSSPHSRN(SG)5RGDSP as a Novel Radioprobe for Molecular Imaging of the Cancer Biomarker α5β1 Integrin. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 38, 1722–1731. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, H.; He, G.; Yan, S.; Chen, C.; Song, L.; Rosol, T.J.; Deng, X. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Is There a Treatment on the Horizon? Oncotarget 2017, 8, 1913–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Yan, L.; Maji, T.; Lévêque, G.; Gkikas, M.; Fytas, G. Harnessing Polymer Grafting to Control the Shape of Plasmonic Nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 127, 074302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torchilin, V.P.; Trubetskoy, V.S. Which Polymers can Make Nanoparticulate Drug Carriers Long-Circulating? Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1995, 16, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redick, S.D.; Settles, D.L.; Briscoe, G.; Erickson, H.P. Defining Fibronectin’s Cell Adhesion Synergy Site by Site-directed Mutagenesis. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 149, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillo, A.K.; Ochsenhirt, S.E.; McCarthy, J.B.; Fields, G.B.; Tirrell, M. Adhesion of α5β1 Receptors to Biomimetic Substrates Constructed from Peptide Amphiphiles. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 1493–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardilovich, A.; Kokkoli, E. Biomimetic Peptide-Amphiphiles for Functional Biomaterials: The Role of GRGDSP and PHSRN. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 950–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramesh, K.; Truong, A.; Wang, Y.; Rusckowski, M.; Gkikas, M. Ligand-Specific Nano-Contrast Agents Promote Enhanced Breast Cancer CT Detection at 0.5 mg Au. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9926. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23179926
Ramesh K, Truong A, Wang Y, Rusckowski M, Gkikas M. Ligand-Specific Nano-Contrast Agents Promote Enhanced Breast Cancer CT Detection at 0.5 mg Au. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(17):9926. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23179926
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamesh, Kalyan, Alice Truong, Yuzhen Wang, Mary Rusckowski, and Manos Gkikas. 2022. "Ligand-Specific Nano-Contrast Agents Promote Enhanced Breast Cancer CT Detection at 0.5 mg Au" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 17: 9926. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23179926
APA StyleRamesh, K., Truong, A., Wang, Y., Rusckowski, M., & Gkikas, M. (2022). Ligand-Specific Nano-Contrast Agents Promote Enhanced Breast Cancer CT Detection at 0.5 mg Au. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(17), 9926. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23179926






