Viral Clearance and Neuroinflammation in Acute TMEV Infection Vary by Host Genetic Background
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Genetic Background, as Represented by Different Mouse Strains, Influenced Clinical Symptom Variability Following TMEV Infection
2.2. Female and Male Mice Did Not Exhibit Significant Differences in TMEV-Induced Clinical Signs during the Acute Phase of Viral Infection
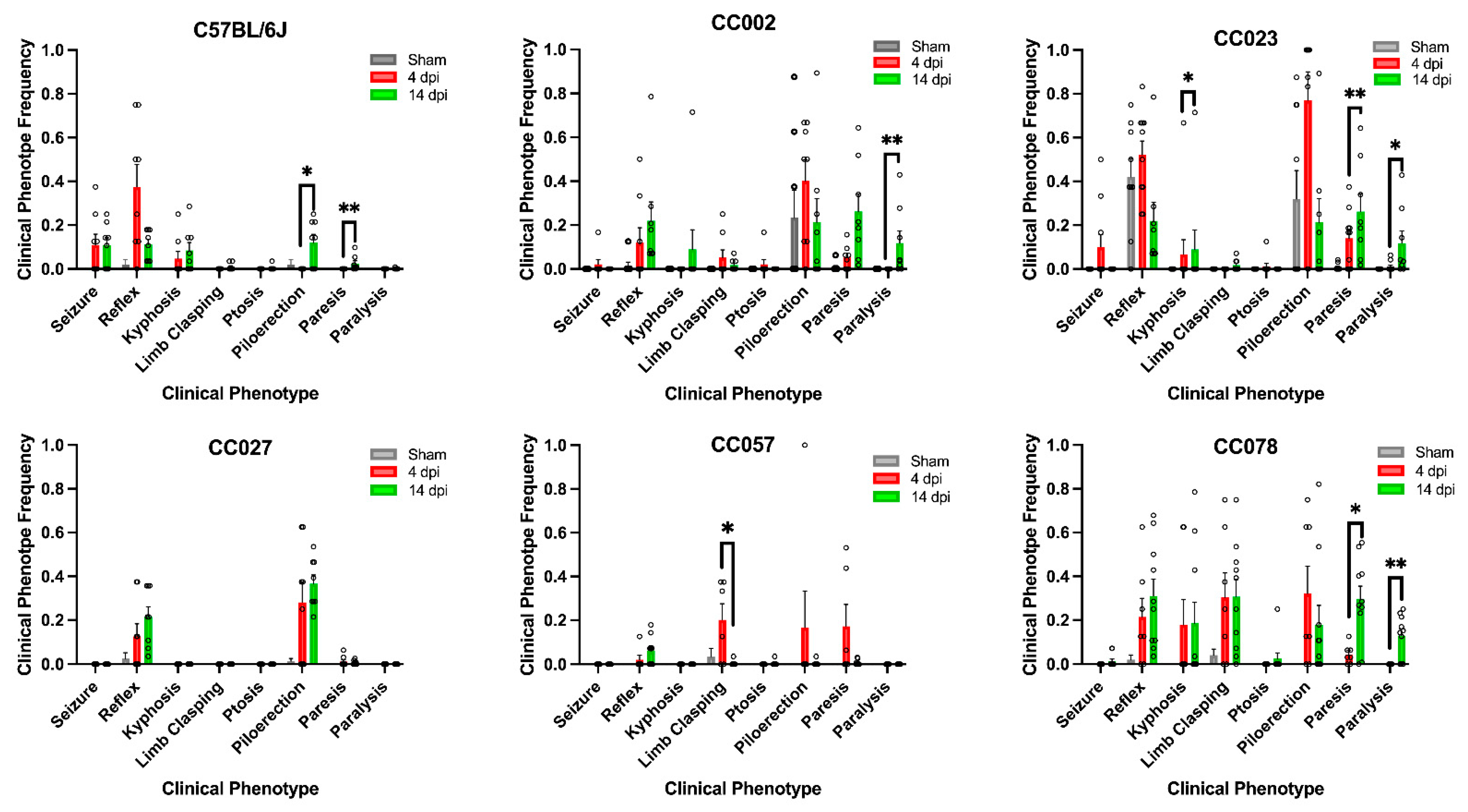
2.3. Frequencies of TMEV-Induced Phenotypes Varied by Strain between 4 dpi and 14 dpi
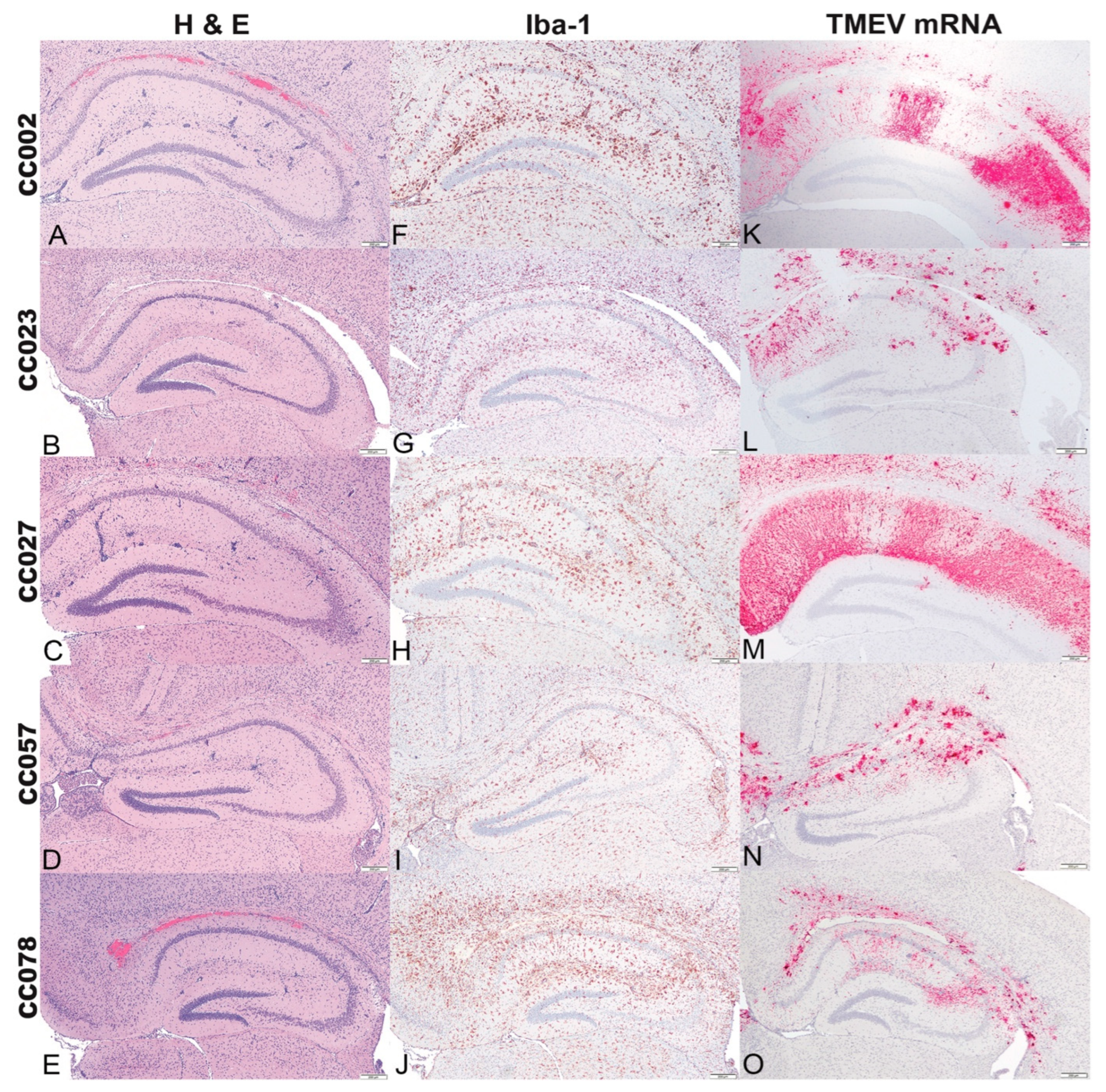
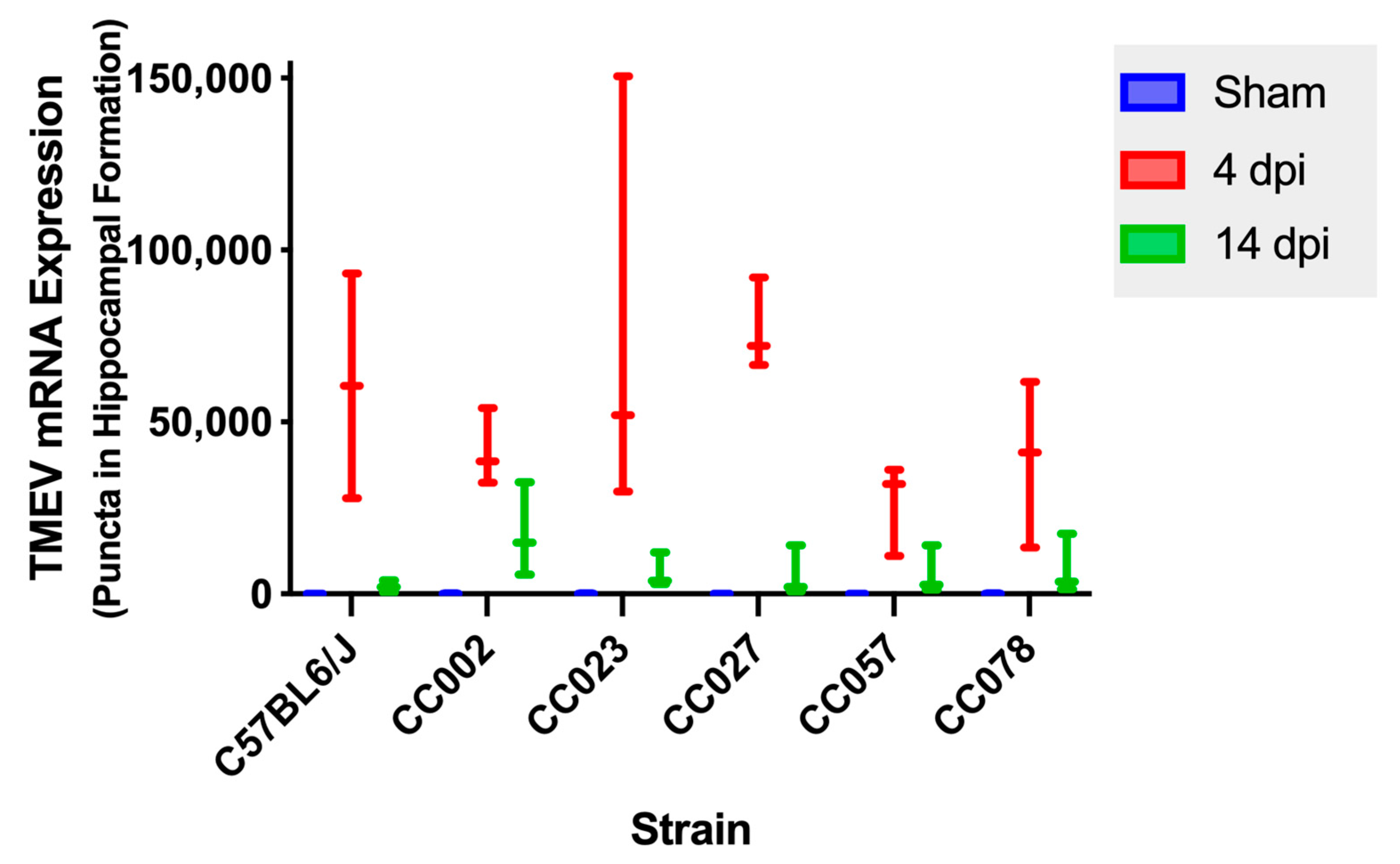
2.4. Histologic Lesions of the Brain, Iba-1 Immunolabeling, and TMEV mRNA Expression in the Hippocampal Formation Demonstrated the Influences of Genetic Background
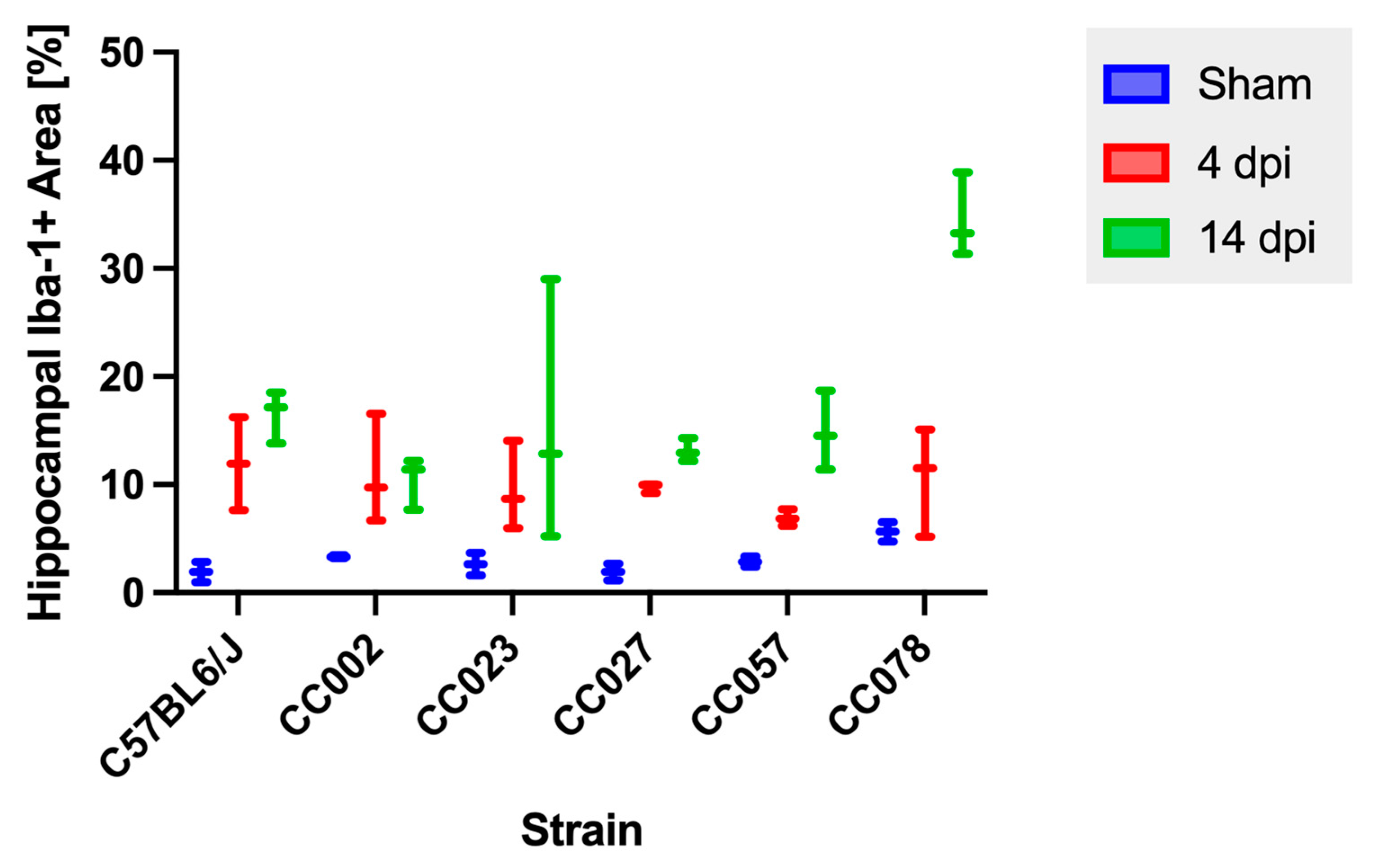
2.5. Hippocampal Microglial/Macrophage Reactivity Varied over Time and by Genetic Background
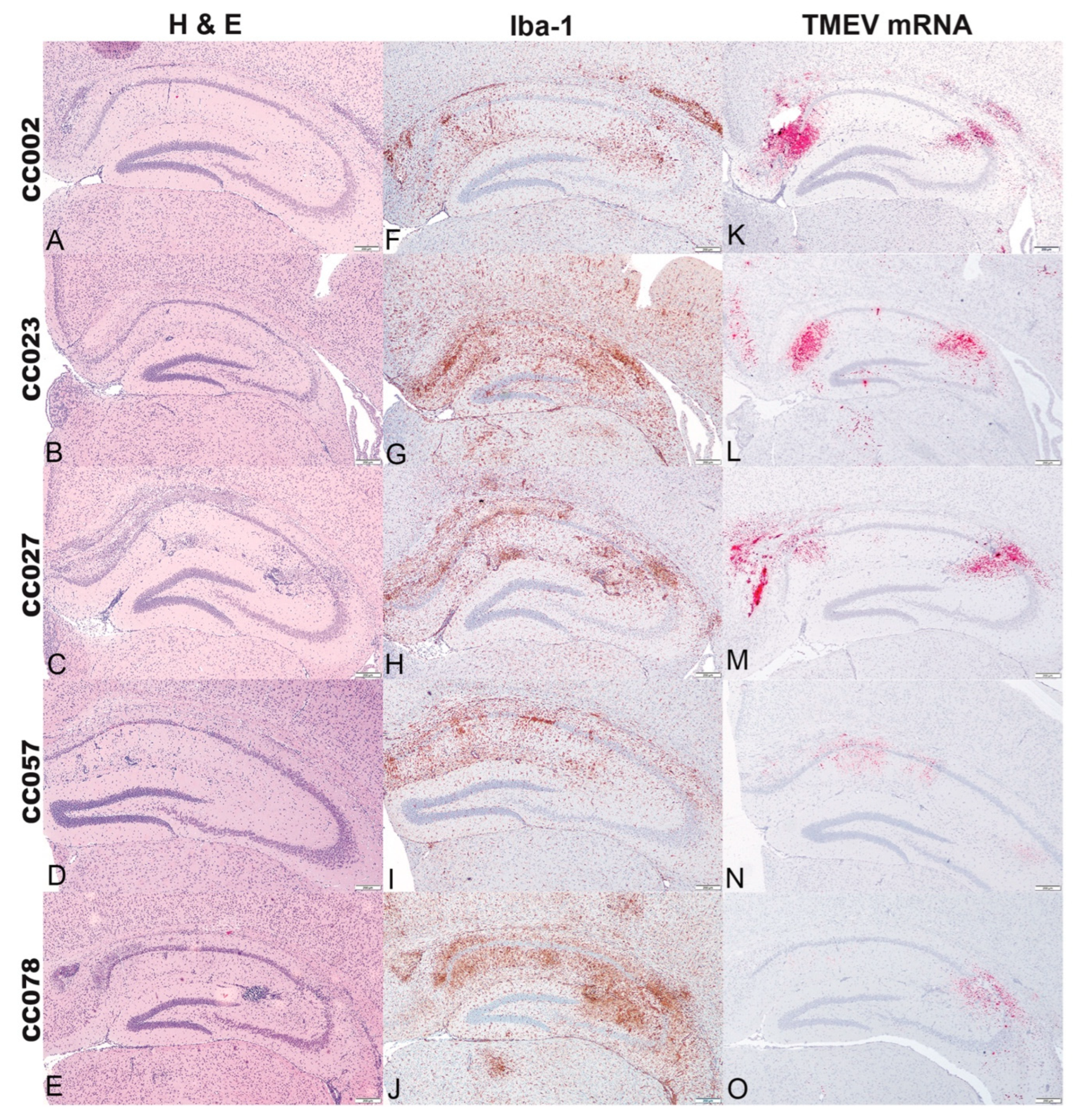
2.6. TMEV mRNA Expression Decreased between 4 dpi and 14 dpi in All Strains
2.7. Microglial/Macrophage Reactivity Was Correlated with Viral Load at 4 dpi
2.8. Several Loci of Interest Were Associated with Lesion Distribution and Microglial/Macrophage Reactivity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mouse Care
4.2. Evaluation of Clinical Signs
4.3. Euthanasia and Tissue Collection
4.4. Histology
4.5. Iba-1 Immunohistochemistry of the Hippocampal Formation
4.6. RNA In Situ Hybridization of the Hippocampal Formation
4.7. Digital Analysis of Iba-1 Immunohistochemistry and RNA In Situ Hybridization
4.8. Statistical Analysis
4.9. Genetic Association Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Donati, D. Viral infections and multiple sclerosis. Drug Discov. Today Dis. Models 2020, 32, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.C.; Feuer, R.; Cashman, N.; Luo, H. Enteroviral Infection: The Forgotten Link to Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis? Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.; Boltz, D.; McClaren, J.; Pani, A.K.; Smeyne, M.; Korff, A.; Webster, R.; Smeyne, R.J. Inflammatory effects of highly pathogenic H5N1 influenza virus infection in the CNS of mice. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 1545–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itzhaki, R.F.; Wozniak, M.A. Herpes simplex virus type 1, apolipoprotein E, and cholesterol: A dangerous liaison in Alzheimer′s disease and other disorders. Prog. Lipid Res. 2006, 45, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, B.C.; Rothbarth, P.H.; van der Meche, F.G.; Herbrink, P.; Schmitz, P.I.; de Klerk, M.A.; van Doorn, P.A. The spectrum of antecedent infections in Guillain-Barre syndrome: A case-control study. Neurology 1998, 51, 1110–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karatas, H.; Gurer, G.; Pinar, A.; Soylemezoglu, F.; Tezel, G.G.; Hascelik, G.; Akalan, N.; Tuncer, S.; Ciger, A.; Saygi, S. Investigation of HSV-1, HSV-2, CMV, HHV-6 and HHV-8 DNA by real-time PCR in surgical resection materials of epilepsy patients with mesial temporal lobe sclerosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2008, 264, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, S.; Perry, A.; Ironside, J.; Budka, H. Greenfield′s Neuropathology-Two Volume Set; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, R.C.; Lockwood, A.H.; Sonawane, B.R. Neurodegenerative diseases: An overview of environmental risk factors. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 1250–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churchill, G.A.; Airey, D.C.; Allayee, H.; Angel, J.M.; Attie, A.D.; Beatty, J.; Beavis, W.D.; Belknap, J.K.; Bennett, B.; Berrettini, W. The Collaborative Cross, a community resource for the genetic analysis of complex traits. Nature Genet. 2004, 36, 1133. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Threadgill, D.W.; Hunter, K.W.; Williams, R.W. Genetic dissection of complex and quantitative traits: From fantasy to reality via a community effort. Mamm. Genome 2002, 13, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noll, K.E.; Ferris, M.T.; Heise, M.T. The Collaborative Cross: A systems genetics resource for studying host-pathogen interactions. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 25, 484–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Canto, M.C.; Kim, B.S.; Miller, S.D.; Melvold, R.W. Theiler′s murine encephalomyelitis virus (TMEV)-induced demyelination: A model for human multiple sclerosis. Methods 1996, 10, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DePaula-Silva, A.B.; Hanak, T.J.; Libbey, J.E.; Fujinami, R.S. Theiler′s murine encephalomyelitis virus infection of SJL/J and C57BL/6J mice: Models for multiple sclerosis and epilepsy. J. Neuroimmunol. 2017, 308, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerhauser, I.; Hansmann, F.; Ciurkiewicz, M.; Löscher, W.; Beineke, A. Facets of theiler′s murine encephalomyelitis virus-induced diseases: An update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libbey, J.E.; Kirkman, N.J.; Smith, M.C.; Tanaka, T.; Wilcox, K.S.; White, H.S.; Fujinami, R.S. Seizures following picornavirus infection. Epilepsia 2008, 49, 1066–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawley, K.S.; Rech, R.R.; Elenwa, F.; Han, G.; Perez Gomez, A.A.; Amstalden, K.; Welsh, C.J.; Young, C.R.; Threadgill, D.W.; Brinkmeyer-Langford, C.L. Host genetic diversity drives variable central nervous system lesion distribution in chronic phase of Theiler′s Murine Encephalomyelitis Virus (TMEV) infection. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westphal, A.; Cheng, W.; Yu, J.; Grassl, G.; Krautkrämer, M.; Holst, O.; Föger, N.; Lee, K.-H. Lysosomal trafficking regulator Lyst links membrane trafficking to toll-like receptor–mediated inflammatory responses. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 227–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Lacrampe, A.; Hu, F. Physiological and pathological functions of TMEM106B: A gene associated with brain aging and multiple brain disorders. Acta Neuropathol. 2021, 141, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Hartley, T.; Baird, S.; Venkateswaran, S.; Simons, C.; Wolf, N.I.; Boycott, K.M.; Dyment, D.A.; Kernohan, K.D. Lysosomal dysfunction in TMEM106B hypomyelinating leukodystrophy. Neurol. Genet. 2018, 4, e288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, R.S.; Garber, C.; Funk, K.E.; Salimi, H.; Soung, A.; Kanmogne, M.; Manivasagam, S.; Agner, S.; Cain, M. Neuroinflammation During RNA Viral Infections. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 37, 73–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Sluijs, L.; Pijlman, G.P.; Kammenga, J.E. Why do individuals differ in viral susceptibility? A story told by model organisms. Viruses 2017, 9, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldridge, R.; Osorio, D.; Amstalden, K.; Edwards, C.; Young, C.R.; Cai, J.J.; Konganti, K.; Hillhouse, A.; Threadgill, D.W.; Welsh, C.J.; et al. Antecedent presentation of neurological phenotypes in the Collaborative Cross reveals four classes with complex sex-dependencies. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkmeyer-Langford, C.L.; Rech, R.; Amstalden, K.; Kochan, K.J.; Hillhouse, A.E.; Young, C.; Welsh, C.J.; Threadgill, D.W. Host genetic background influences diverse neurological responses to viral infection in mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckwalter, M.R.; Nga, P.T.; Gouilh, M.A.; Fiette, L.; Bureau, J.-F.; Laird, M.E.; Buchrieser, J.; Ozden, S.; Cheval, J.; Eloit, M. Identification of a novel neuropathogenic Theiler′s murine encephalomyelitis virus. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 6893–6905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, K.A.A.; Wilcox, K.S.; Fujinami, R.S.; White, H.S. Theiler′s virus infection chronically alters seizure susceptibility. Epilepsia 2010, 51, 1418–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bröer, S.; Hage, E.; Käufer, C.; Gerhauser, I.; Anjum, M.; Li, L.; Baumgärtner, W.; Schulz, T.F.; Löscher, W. Viral mouse models of multiple sclerosis and epilepsy: Marked differences in neuropathogenesis following infection with two naturally occurring variants of Theiler′s virus BeAn strain. Neurobiol. Dis. 2017, 99, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkman, N.J.; Libbey, J.E.; Wilcox, K.S.; White, H.S.; Fujinami, R.S. Innate but not adaptive immune responses contribute to behavioral seizures following viral infection. Epilepsia 2010, 51, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libbey, J.E.; Kennett, N.J.; Wilcox, K.S.; White, H.S.; Fujinami, R.S. Lack of correlation of central nervous system inflammation and neuropathology with the development of seizures following acute virus infection. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 8149–8157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loewen, J.L.; Barker-Haliski, M.L.; Dahle, E.J.; White, H.S.; Wilcox, K.S. Neuronal Injury, Gliosis, and Glial Proliferation in Two Models of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2016, 75, 366–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, P.; Pavelko, K.; Leibowitz, J.; Lin, X.; Rodriguez, M. CD4+ and CD8+ T cells make discrete contributions to demyelination and neurologic disease in a viral model of multiple sclerosis. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 7320–7329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipton, H.L. Theiler′s virus infection in mice: An unusual biphasic disease process leading to demyelination. Infect. Immun. 1975, 11, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, R.B.; Gekker, G.; Hu, S.; Sheng, W.S.; Cheeran, M.; Lokensgard, J.R.; Peterson, P.K. Role of microglia in central nervous system infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 17, 942–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhatbar, C.; Prinz, M. The roles of microglia in viral encephalitis: From sensome to therapeutic targeting. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waltl, I.; Käufer, C.; Gerhauser, I.; Chhatbar, C.; Ghita, L.; Kalinke, U.; Löscher, W. Microglia have a protective role in viral encephalitis-induced seizure development and hippocampal damage. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 74, 186–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, G.; Medeiros Geraldo, L.H.; Gedeao Salomao, N.; Viana Paes, M.; Regina Souza Lima, F.; Carvalho Alcantara Gomes, F. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and glial cells: Insights and perspectives. Brain Behav. Immun. Health 2020, 7, 100127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, N.H. Exosomes Secreted by Microglia Contribute to Virus Persistence and Demyelinating Disease. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, USA, September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Perez Gomez, A.A.; Karmakar, M.; Carroll, R.J.; Lawley, K.S.; Amstalden, K.; Young, C.R.; Threadgill, D.W.; Welsh, C.J.; Brinkmeyer-Langford, C. Genetic and immunological contributors to virus-induced paralysis. Brain Behav. Immun. Health 2021, 18, 100395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmeyer-Langford, C.; Amstalden, K.; Konganti, K.; Hillhouse, A.; Lawley, K.; Perez-Gomez, A.; Young, C.R.; Welsh, C.J.; Threadgill, D.W. Resilience in Long-Term Viral Infection: Genetic Determinants and Interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.M.S.; DePaula-Silva, A.B.; Doty, D.J.; Truong, A.; Libbey, J.E.; Fujinami, R.S. Microglial cell depletion is fatal with low level picornavirus infection of the central nervous system. J. Neurovirol. 2019, 25, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.; Zhang, W.; Gu, J.; Shen, K.; Luo, H.; Yang, Y. Novel mutations of STXBP2 and LYST associated with adult haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis with Epstein-Barr virus infection: A case report. BMC Med. Genet. 2019, 20, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuan, M.I.; Jaeger, H.K.; Balemba, O.B.; O′Dowd, J.M.; Duricka, D.; Hannemann, H.; Marx, E.; Teissier, N.; Gabrielli, L.; Bonasoni, M.P.; et al. Human Cytomegalovirus Interactions with the Basement Membrane Protein Nidogen 1. J. Virol. 2020, 95, e01506–e01520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, A.M.; Rademakers, R. What we know about TMEM106B in neurodegeneration. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 132, 639–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baggen, J.; Persoons, L.; Vanstreels, E.; Jansen, S.; Van Looveren, D.; Boeckx, B.; Geudens, V.; De Man, J.; Jochmans, D.; Wauters, J. Genome-wide CRISPR screening identifies TMEM106B as a proviral host factor for SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, S.C.; Polymenidou, M.; Cleveland, D.W. Converging mechanisms in ALS and FTD: Disrupted RNA and protein homeostasis. Neuron 2013, 79, 416–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bignall, K.E. Ontogeny of levels of neural organization: The righting reflex as a model. Exp. Neurol. 1974, 42, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, P.; Fielding, R.; Ameis, K.M.; Vacca-Galloway, L.L. A novel behavioral method to detect motoneuron disease in Wobbler mice aged three to seven days old. Brain Res. 1998, 813, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.R.; Storts, R.; Welsh, T.H.; Welsh, C.J.R.; Meagher, M.W. Social stress alters the severity of acute Theiler′s virus infection. J. Neuroimmunol. 2004, 148, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappas, S.S.; Darr, K.; Holley, S.M.; Cepeda, C.; Mabrouk, O.S.; Wong, J.-M.T.; Lewitt, T.M.; Paudel, R.; Houlden, H.; Kennedy, R.T.; et al. Forebrain deletion of the dystonia protein torsinA causes dystonic-like movements and loss of striatal cholinergic neurons. eLife 2015, 4, e08352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondori, N.R.; Paul, P.; Robbins, J.P.; Liu, K.; Hildyard, J.C.W.; Wells, D.J.; de Belleroche, J.S. Characterisation of the pathogenic effects of the in vivo expression of an ALS-linked mutation in D-amino acid oxidase: Phenotype and loss of spinal cord motor neurons. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burrer, R.; Buchmeier, M.J.; Wolfe, T.; Ting, J.P.C.; Feuer, R.; Iglesias, A.; Von Herrath, M.G. Exacerbated Pathology of Viral Encephalitis in Mice with Central Nervous System-Specific Autoantibodies. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 170, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Campbell, T.; Meagher, M.W.; Sieve, A.; Scott, B.; Storts, R.; Welsh, T.H.; Welsh, C.J.R. The Effects of Restraint Stress on the Neuropathogenesis of Theiler′s Virus Infection: I. Acute Disease. Brain Behav. Immun. 2001, 15, 235–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieve, A.N.; Steelman, A.J.; Young, C.R.; Storts, R.; Welsh, T.H.; Welsh, C.J.R.; Meagher, M.W. Chronic restraint stress during early Theiler′s virus infection exacerbates the subsequent demyelinating disease in SJL mice. J. Neuroimmunol. 2004, 155, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, C. Allograft inflammatory factor-1/Ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1 is specifically expressed by most subpopulations of macrophages and spermatids in testis. Cell Tissue Res. 2007, 330, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertram, C.A.; Klopfleisch, R. The pathologist 2.0: An update on digital pathology in veterinary medicine. Vet. Pathol. 2017, 54, 756–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riber-Hansen, R.; Vainer, B.; Steiniche, T. Digital image analysis: A review of reproducibility, stability and basic requirements for optimal results. Apmis 2012, 120, 276–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konganti, K.; Ehrlich, A.; Rusyn, I.; Threadgill, D.W. gQTL: A Web Application for QTL Analysis Using the Collaborative Cross Mouse Genetic Reference Population. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2018, 8, 2559–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Mouse Strain | Hippocampal Formation | † Hippo. Adj. | Striatum | Thalamus | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| * Field CA1 | * Field CA2 | * Field CA3 | Caudate-Putamen | Septal Nuclei | Nucleus Accumbens | ||||
| 4 dpi–early acute | C57BL/6J | 0.86 | 0.86 | 0.29 | 0 | 0.29 | 0.29 | 0 | 0.29 |
| CC002 | 1 | 1 | 0.13 | 0.25 | 0.50 | 0.625 | 0.25 | 0.50 | |
| CC023 | 0.9 | 0.40 | 0.10 | 0.50 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.30 | |
| CC027 | 1 | 0.71 | 0 | 0 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0 | 0 | |
| CC057 | 1 | 0.29 | 0 | 0.14 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0 | 0.29 | |
| CC078 | 0.63 | 0.50 | 0 | 0 | 0.25 | 0.38 | 0 | 0.13 | |
| 14 dpi–late acute | C57BL/6J | 0.86 | 0.86 | 0.38 | 0 | 0.13 | 0.38 | 0 | 0.63 |
| CC002 | 1 | 0.75 | 0 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.63 | 0 | 0.50 | |
| CC023 | 0.63 | 0.38 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.25 | 0.13 | 0.63 | |
| CC027 | 1 | 0.88 | 0 | 0 | 0.13 | 0 | 0 | 0.38 | |
| CC057 | 0.89 | 0.67 | 0 | 0.22 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.56 | |
| CC078 | 1 | 0.36 | 0 | 0.09 | 0.55 | 0.36 | 0 | 0.36 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lawley, K.S.; Rech, R.R.; Perez Gomez, A.A.; Hopkins, L.; Han, G.; Amstalden, K.; Welsh, C.J.; Young, C.R.; Jones-Hall, Y.; Threadgill, D.W.; et al. Viral Clearance and Neuroinflammation in Acute TMEV Infection Vary by Host Genetic Background. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810482
Lawley KS, Rech RR, Perez Gomez AA, Hopkins L, Han G, Amstalden K, Welsh CJ, Young CR, Jones-Hall Y, Threadgill DW, et al. Viral Clearance and Neuroinflammation in Acute TMEV Infection Vary by Host Genetic Background. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(18):10482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810482
Chicago/Turabian StyleLawley, Koedi S., Raquel R. Rech, Aracely A. Perez Gomez, Laura Hopkins, Gang Han, Katia Amstalden, C. Jane Welsh, Colin R. Young, Yava Jones-Hall, David W. Threadgill, and et al. 2022. "Viral Clearance and Neuroinflammation in Acute TMEV Infection Vary by Host Genetic Background" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 18: 10482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810482
APA StyleLawley, K. S., Rech, R. R., Perez Gomez, A. A., Hopkins, L., Han, G., Amstalden, K., Welsh, C. J., Young, C. R., Jones-Hall, Y., Threadgill, D. W., & Brinkmeyer-Langford, C. L. (2022). Viral Clearance and Neuroinflammation in Acute TMEV Infection Vary by Host Genetic Background. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(18), 10482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810482






