Medical Advances in Hepatitis D Therapy: Molecular Targets
Abstract
:1. Introduction
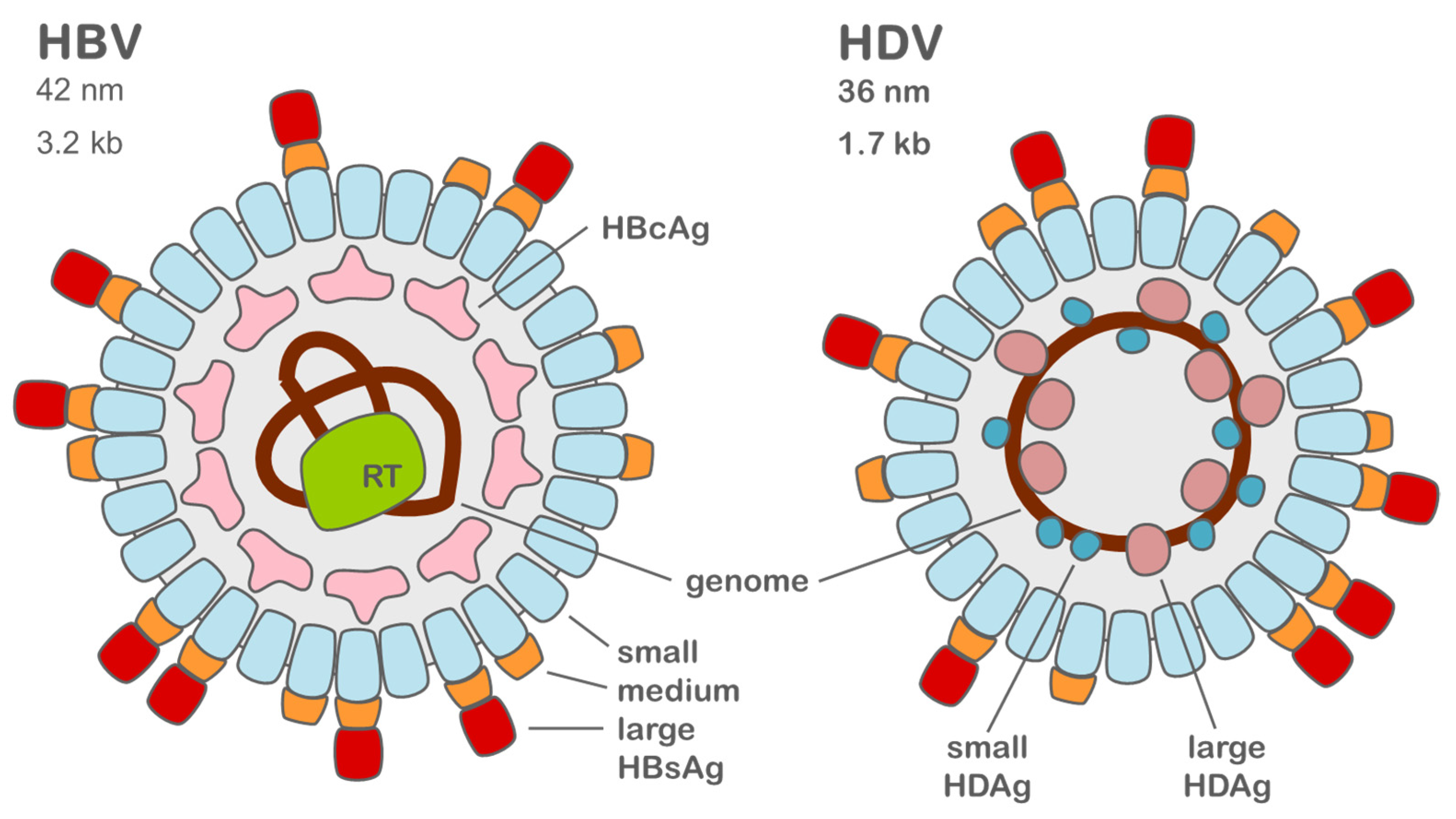
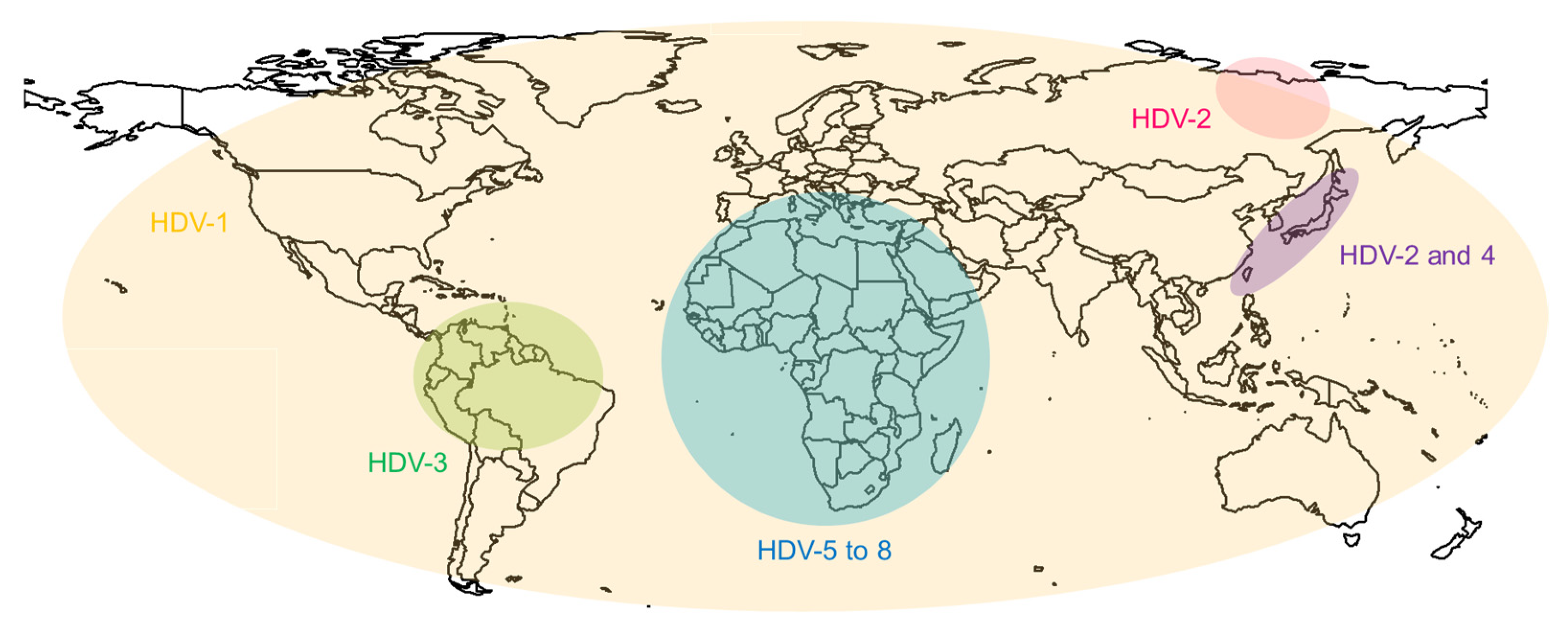
2. Molecular Biology of HDV and HBV
3. Current Therapy
3.1. Cytokines
3.2. Reverse Transcriptase
3.3. Sodium Taurocholate Co-Transporting Polypeptide
4. Potential Therapy Targets
4.1. Farnesyltransferase
4.2. HBV Surface Antigen and Subviral Particles
4.3. Additional Targets
5. Conclusions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stockdale, A.; Kreuels, B.; Henrion, M.; Giorgi, E.; Kyomuhangi, I.; de Martel, C.; Hutin, Y.; Geretti, A. The global prevalence of hepatitis D virus infection: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.B.; Lai, M.M.C. Isoprenylation mediates direct protein-protein interactions between hepatitis large delta antigen and hepatitis B virus surface antigen. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 7659–7662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnius, L.; Taylor, J.; Mason, W.S.; Sureau, C.; Deny, P.; Norder, H.; Ictv Report, C. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Deltavirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 1565–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarado-Mora, M.V.; Locarnini, S.; Rizzetto, M.; Pinho, J.R.R. An update on HDV: Virology, pathogenesis and treatment. Antivir. Ther. 2013, 18, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kos, A.; Dijkema, R.; Arnberg, A.C.; van der Meide, P.H.; Schellekens, H. The hepatitis delta (δ) virus possesses a circular RNA. Nature 1986, 323, 558–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, S.; Chang, M.-F.; Shieh, C.-K.; Kamahora, T.; Vannier, D.M.; Govindarajan, S.; Lai, M.M.C. Molecular cloning and sequencing of a human hepatitis delta (δ) virus RNA. Nature 1987, 329, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodrum, G.; Pelchat, M. Insight into the Contribution and Disruption of Host Processes during HDV Replication. Viruses 2018, 11, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedemeyer, H.; Manns, M.P. Epidemiology, pathogenesis and management of hepatitis D: Update and challenges ahead. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 7, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.M.; Changchien, C.S.; Chung, J.C.; Liaw, Y.F. Characterization of a new genotype II hepatitis delta virus from Taiwan. J. Med. Virol. 1996, 49, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado-Mora, M.V.; Romano, C.M.; Gomes-Gouvêa, M.S.; Gutierrez, M.F.; Carrilho, F.J.; Pinho, J.R. Dynamics of hepatitis D (delta) virus genotype 3 in the Amazon region of South America. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2011, 11, 1462–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dény, P. Hepatitis delta virus genetic variability: From genotypes I, II, III to eight major clades? Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2006, 307, 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivaniushina, V.; Radjef, N.; Alexeeva, M.; Gault, E.; Semenov, S.; Salhi, M.; Kiselev, O.; Dény, P. Hepatitis delta virus genotypes I and II cocirculate in an endemic area of Yakutia, Russia. J. Gen. Virol. 2001, 82, 2709–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurdaydin, C.; Idilman, R.; Bozkaya, H.; Bozdayi, A.M. Natural history and treatment of chronic delta hepatitis. J. Viral Hepat. 2010, 17, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, M.Y.; Chao, M.; Taylor, J. Initiation of replication of the human hepatitis delta virus genome from cloned DNA: Role of delta antigen. J. Virol. 1989, 63, 1945–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.-L.; Chen, P.-J.; Tu, S.-J.; Wang, C.-J.; Chen, D.-S. The Large Form of Hepatitis delta Antigen is Crucial for Assembly of Hepatitis delta Virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 8490–8494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, W.S.; Bayer, M.; Taylor, J. Assembly of hepatitis delta virus particles. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 2310–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, M.; Hsieh, S.Y.; Taylor, J. Role of two forms of hepatitis delta virus antigen: Evidence for a mechanism of self-limiting genome replication. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 5066–5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sureau, C.; Negro, F. The hepatitis delta virus: Replication and pathogenesis. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, S102–S116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, M.Y.; Sharmeen, L.; Dinter-Gottlieb, G.; Taylor, J. Characterization of self-cleaving RNA sequences on the genome and antigenome of human hepatitis delta virus. J. Virol. 1988, 62, 4439–4444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C.; Chang, T.C.; Lin, C.W.; Tsui, H.L.; Chu, P.B.C.; Chen, B.S.; Huang, Z.S.; Wu, H.N. Nucleic acid binding properties of the nucleic acid chaperone domain of hepatitis delta antigen. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 6481–6492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.Z.; Lin, J.H.; Chao, M.; McKnight, K.; Lai, M.M. RNA-binding activity of hepatitis delta antigen involves two arginine-rich motifs and is required for hepatitis delta virus RNA replication. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 2221–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daigh, L.H.; Griffin, B.L.; Soroush, A.; Mamedov, M.R.; Casey, J.L. Arginine-Rich Motifs Are Not Required for Hepatitis Delta Virus RNA Binding Activity of the Hepatitis Delta Antigen. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 8665–8674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poisson, F.; Roingeard, P.; Baillou, A.; Dubois, F.; Bonelli, F.; Calogero, R.A.; Goudeau, A. Characterization of RNA-binding domains of hepatitis delta antigen. J. Gen. Virol. 1993, 74, 2473–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenn, J.S.; Watson, J.A.; Havel, C.M.; White, J.M. Identification of a Prenylation Site in Delta Virus Large Antigen. Science 1992, 256, 1331–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Z.; Chen, P.J.; Lai, M.M.; Chen, D.S. Isoprenylation of large hepatitis delta antigen is necessary but not sufficient for hepatitis delta virus assembly. Virology 1994, 199, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hourioux, C.; Sureau, C.; Poisson, F.; Brand, D.; Goudeau, A.; Roingeard, P. Interaction between hepatitis delta virus-encoded proteins and hepatitis B virus envelope protein domains. J. Gen. Virol. 1998, 79, 1115–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazinski, D.W.; Taylor, J.M. Relating structure to function in the hepatitis delta virus antigen. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 2672–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, J.; Mason, W.S. Replication of the genome of a hepatitis B-like virus by reverse transcription of an RNA intermediate. Cell 1982, 29, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.K.; Jeevan-Raj, B.; Netter, H.J. Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Subviral Particles as Protective Vaccines and Vaccine Platforms. Viruses 2020, 12, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhong, G.C.; Xu, G.W.; He, W.H.; Jing, Z.Y.; Gao, Z.C.; Huang, Y.; Qi, Y.H.; Peng, B.; Wang, H.M.; et al. Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide is a functional receptor for human hepatitis B and D virus. eLife 2012, 1, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lott, L.; Beames, B.; Notvall, L.; Lanford, R.E. Interaction between Hepatitis B Virus Core Protein and Reverse Transcriptase. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 11479–11489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levrero, M.; Pollicino, T.; Petersen, J.; Belloni, L.; Raimondo, G.; Dandri, M. Control of cccDNA function in hepatitis B virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2009, 51, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuttleman, J.S.; Pourcel, C.; Summers, J. Formation of the pool of covalently closed circular viral DNA in hepadnavirus-infected cells. Cell 1986, 47, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanetti, A.R.; Van Damme, P.; Shouval, D. The global impact of vaccination against hepatitis B: A historical overview. Vaccine 2008, 26, 6266–6273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyon, M.; Deakin, J.A.; Gallagher, J.T. Liver heparan sulfate structure. A novel molecular design. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 11208–11215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, A.; Gripon, P.; Urban, S. Hepatitis B virus infection initiates with a large surface protein–dependent binding to heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Hepatology 2007, 46, 1759–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urban, S. Liver capsule: Entry and entry inhibition of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis delta virus into hepatocytes. Hepatology 2016, 63, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Y.; Lempp, F.A.; Mehrle, S.; Nkongolo, S.; Kaufman, C.; Fälth, M.; Stindt, J.; Königer, C.; Nassal, M.; Kubitz, R.; et al. Hepatitis B and D Viruses Exploit Sodium Taurocholate Co-transporting Polypeptide for Species-Specific Entry into Hepatocytes. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1070–1083.e1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defenbaugh, D.A.; Johnson, M.; Chen, R.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Casey, J.L. Hepatitis Delta Antigen Requires a Minimum Length of the Hepatitis Delta Virus Unbranched Rod RNA Structure for Binding. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 4548–4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudima, S.; Wu, S.Y.; Chiang, C.M.; Moraleda, G.; Taylor, J. Origin of hepatitis delta virus mRNA. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 7204–7210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, W.-H.; Chen, Y.-S.; Chen, P.-J. Nucleolar Targeting of Hepatitis Delta Antigen Abolishes Its Ability to Initiate Viral Antigenomic RNA Replication. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.K.; Lazinski, D.W. Replicating hepatitis delta virus RNA is edited in the nucleus by the small form of ADAR1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15118–15123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poison, A.G.; Bass, B.L.; Casey, J.L. RNA editing of hepatitis delta virus antigenome by dsRNA-adenosine deaminase. Nature 1996, 380, 454–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.X.; Chao, M.; Hsieh, S.Y.; Sureau, C.; Nishikura, K.; Taylor, J. A specific base transition occurs on replicating hepatitis delta virus RNA. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, J.L. Control of ADAR1 editing of hepatitis delta virus RNAs. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2012, 353, 123–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.F.; Baker, S.C.; Soe, L.H.; Kamahora, T.; Keck, J.G.; Makino, S.; Govindarajan, S.; Lai, M.M. Human hepatitis delta antigen is a nuclear phosphoprotein with RNA-binding activity. J. Virol. 1988, 62, 2403–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavanez, J.P.; Cunha, C.; Silva, M.C.; David, E.; Monjardino, J.; Carmo-Fonseca, M. Hepatitis delta virus ribonucleoproteins shuttle between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. RNA 2002, 8, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.H.; Rutter, W.J. Regulation of secretion of the hepatitis B virus major surface antigen by the preS-1 protein. J. Virol. 1987, 61, 782–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patzer, E.J.; Nakamura, G.R.; Yaffe, A. Intracellular transport and secretion of hepatitis B surface antigen in mammalian cells. J. Virol. 1984, 51, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huovila, A.P.; Eder, A.M.; Fuller, S.D. Hepatitis B surface antigen assembles in a post-ER, pre-Golgi compartment. J. Cell Biol. 1992, 118, 1305–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asselah, T.; Loureiro, D.; Tout, I.; Castelnau, C.; Boyer, N.; Marcellin, P.; Mansouri, A. Future treatments for hepatitis delta virus infection. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Protzer, U. Control of Hepatitis B Virus by Cytokines. Viruses 2017, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Cheng, X.; Blossey, C.K.; Wisskirchen, K.; Esser, K.; Protzer, U. Secreted Interferon-Inducible Factors Restrict Hepatitis B and C Virus Entry In Vitro. J. Immunol. Res. 2017, 2017, 4828936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Y.; Aliyari, R.; Chikere, K.; Li, G.; Marsden, M.D.; Smith, J.K.; Pernet, O.; Guo, H.; Nusbaum, R.; Zack, J.A.; et al. Interferon-inducible cholesterol-25-hydroxylase broadly inhibits viral entry by production of 25-hydroxycholesterol. Immunity 2013, 38, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belloni, L.; Allweiss, L.; Guerrieri, F.; Pediconi, N.; Volz, T.; Pollicino, T.; Petersen, J.; Raimondo, G.; Dandri, M.; Levrero, M. IFN-alpha inhibits HBV transcription and replication in cell culture and in humanized mice by targeting the epigenetic regulation of the nuclear cccDNA minichromosome. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.-H.; Baek, K.-W.; Cho, E.-Y.; Ahn, B.-Y. PKR-dependent mechanisms of interferon-α for inhibiting hepatitis B virus replication. Mol. Cells 2011, 32, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, R.C.; Nie, H.; Cai, D.W.; Zhang, J.M.; Liu, H.Y.; Yan, R.; Cuconati, A.; Block, T.M.; Guo, J.T.; Guo, H.T. Inhibition of Hepatitis B Virus Replication by the Host Zinc Finger Antiviral Protein. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.Q.; Dai, J.; Bai, L.; Tang, H. The efficacy of zinc finger antiviral protein against hepatitis B virus transcription and replication in tansgenic mouse model. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Zhao, X.S.; Cai, D.W.; Liu, Y.J.; Block, T.M.; Guo, J.T.; Guo, H.T. The Interferon-Inducible Protein Tetherin Inhibits Hepatitis B Virus Virion Secretion. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 9200–9212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deterding, K.; Wedemeyer, H. Beyond Pegylated Interferon-Alpha: New Treatments for Hepatitis Delta. AIDS Rev. 2019, 21, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleijfer, S.; Bannink, M.; Van Gool, A.R.; Kruit, W.H.; Stoter, G. Side effects of interferon-alpha therapy. Pharm. World Sci. 2005, 27, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherrington, J.M.; Allen, S.J.W.; Bischofberger, N.; Chen, M.S. Kinetic interaction of the diphosphates of 9-(2-phosphonylmethoxyethyl)adenine and other anti-HIV active purine congeners with HIV reverse transcriptase and human DNA polymerases α, β and γ. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 1995, 6, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumada, H.; Koike, K.; Suyama, K.; Ito, H.; Itoh, H.; Sugiura, W. Efficacy and safety of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate rescue therapy for chronic hepatitis B patients who failed other nucleos(t)ide analogs. Hepatol. Res. 2017, 47, 1032–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niro, G.A.; Ciancio, A.; Tillman, H.L.; Lagget, M.; Olivero, A.; Perri, F.; Fontana, R.; Little, N.; Campbell, F.; Smedile, A.; et al. Lamivudine therapy in chronic delta hepatitis: A multicentre randomized-controlled pilot study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 22, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canbakan, B.; Senturk, H.; Tabak, F.; Akdogan, M.; Tahan, V.; Mert, A.; Sut, N.; Ozaras, R.; Midilli, K.; Ozbay, G. Efficacy of interferon α-2b and lamivudine combination treatment in comparison to interferon α-2b alone in chronic delta hepatitis: A randomized trial. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 21, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurdaydin, C.; Bozkaya, H.; Sentürk, H.; Fried, M.W.; Akdoǧan, M.; Schinazi, F.R.; Çetinkaya, H.; Erden, E.; Bozdayi, M.; Deǧertekin, H.; et al. Treatment of chronic hepatitis D with lamivudine vs. lamivudine + interferon vs. interferon: A randomized controlled clinical trial. J. Hepatol. 2000, 32, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananthanarayanan, M.; Ng, O.C.; Boyer, J.L.; Suchy, F.J. Characterization of cloned rat liver Na(+)-bile acid cotransporter using peptide and fusion protein antibodies. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 1994, 267, G637–G643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Ananthanarayanan, M.; Stieger, B.; Meier, P.J.; Suchy, F.J.; Anwer, M.S. Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide is a serine, threonine phosphoprotein and is dephosphorylated by cyclic adenosine monophosphate. Hepatology 1998, 28, 1629–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagenbuch, B.; Meier, P.J. Molecular cloning, chromosomal localization, and functional characterization of a human liver Na+/bile acid cotransporter. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 93, 1326–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagenbuch, B.; Dawson, P. The sodium bile salt cotransport family SLC10. Pflügers Arch. 2004, 447, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallen, S.; Mareninova, O.; Branden, M.; Sachs, G. Organization of the membrane domain of the human liver sodium/bile acid cotransporter. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 7253–7266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinman, S.A.; Carruth, M.W.; Dawson, P.A. Bile acid uptake via the human apical sodium-bile acid cotransporter is electrogenic. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 34691–34695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doring, B.; Lutteke, T.; Geyer, J.; Petzinger, E. The SLC10 carrier family: Transport functions and molecular structure. Curr. Top. Membr. 2012, 70, 105–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosters, A.; Karpen, S.J. Bile acid transporters in health and disease. Xenobiotica 2008, 38, 1043–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkongolo, S.; Ni, Y.; Lempp, F.A.; Kaufman, C.; Lindner, T.; Esser-Nobis, K.; Lohmann, V.; Mier, W.; Mehrle, S.; Urban, S. Cyclosporin A inhibits hepatitis B and hepatitis D virus entry by cyclophilin-independent interference with the NTCP receptor. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogomolov, P.; Alexandrov, A.; Voronkova, N.; Macievich, M.; Kokina, K.; Petrachenkova, M.; Lehr, T.; Lempp, F.A.; Wedemeyer, H.; Haag, M.; et al. Treatment of chronic hepatitis D with the entry inhibitor myrcludex B: First results of a phase Ib/IIa study. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedemeyer, H.; Schöneweis, K.; Bogomolov, P.; Vorokova, N.; Chulanov, V.; Stepanova, T.; Allweiss, L.; Dandri, M.; Ciesek, S.; Dittmer, U.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of 10 mg Myrcludex B/IFNa Combination Therapy in Patients with Chronic HBV/HDV Co-Infection. Z Gastroenterol. 2020, 58, e2–e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jachs, M.; Schwarz, C.; Panzer, M.; Binter, T.; Aberle, S.W.; Hartl, L.; Dax, K.; Aigner, E.; Stättermayer Albert, F.; Munda, P.; et al. Response-guided long-term treatment of chronic hepatitis D patients with bulevirtide—Results of a “real world” study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 56, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, C.; Chromy, D.; Bangert, C.; Schwarz, M.; Jachs, M.; Reiberger, T.; Gschwantler, M. Immediate-type hypersensitivity reaction to bulevirtide and successful desensitization in a patient with HBV/HDV-associated compensated cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 254–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrendt, P.; Traidl, S.; Böker, K.H.W.; Wedemeyer, H.; Deterding, K. T-cell driven allergic cutaneous reaction complicating treatment of hepatitis delta virus infection with bulevirtide. Liver Int. 2022, 42, 1770–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, P.J.; Seabra, M.C. Protein prenyltransferases. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 5289–5292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seabra, M.C.; Reiss, Y.; Casey, P.J.; Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L. Protein farnesyltransferase and geranylgeranyltransferase share a common α subunit. Cell 1991, 65, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompliano, D.L.; Schaber, M.D.; Mosser, S.D.; Omer, C.A.; Shafer, J.A.; Gibbs, J.B. Isoprenoid diphosphate utilization by recombinant human farnesyl-protein transferase: Interactive binding between substrates and a preferred kinetic pathway. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 8341–8347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, T.S.; Terry, K.L.; Casey, P.J.; Beese, L.S. Crystallographic Analysis of CaaX Prenyltransferases Complexed with Substrates Defines Rules of Protein Substrate Selectivity. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 343, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.B.; Casey, P.J.; Beese, L.S. Reaction path of protein farnesyltransferase at atomic resolution. Nature 2002, 419, 645–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.J.; Moomaw, J.F.; Overton, L.; Kost, T.A.; Casey, P.J. High level expression of mammalian protein farnesyltransferase in a baculovirus system. The purified protein contains zinc. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 9675–9680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, K.T.; Beese, L.S. Structural biology of protein farnesyltransferase and geranylgeranyltransferase type I. J. Lipid Res. 2006, 47, 681–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moomaw, J.F.; Casey, P.J. Mammalian protein geranylgeranyltransferase. Subunit composition and metal requirements. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 17438–17443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Casey, P.J. Protein prenylation: Unique fats make their mark on biology. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, C.; Canini, L.; Dahari, H.; Zhao, X.; Uprichard, S.L.; Haynes-Williams, V.; Winters, M.A.; Subramanya, G.; Cooper, S.L.; Pinto, P.; et al. Oral prenylation inhibition with lonafarnib in chronic hepatitis D infection: A proof-of-concept randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2A trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yurdaydin, C.; Keskin, O.; Yurdcu, E.; Çalişkan, A.; Önem, S.; Karakaya, F.; Kalkan, Ç.; Karatayli, E.; Karatayli, S.; Choong, I.; et al. A phase 2 dose-finding study of lonafarnib and ritonavir with or without interferon alpha for chronic delta hepatitis. Hepatology 2022, 75, 1551–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurdaydin, C.; Keskin, O.; Kalkan, Ç.; Karakaya, F.; Çalişkan, A.; Karatayli, E.; Karatayli, S.; Bozdayi, A.M.; Koh, C.; Heller, T.; et al. Optimizing lonafarnib treatment for the management of chronic delta hepatitis: The LOWR HDV-1 study. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1224–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beilstein, F.; Blanchet, M.; Vaillant, A.; Sureau, C. Nucleic Acid Polymers Are Active against Hepatitis Delta Virus Infection In Vitro. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01416-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaillant, A. Nucleic acid polymers: Broad spectrum antiviral activity, antiviral mechanisms and optimization for the treatment of hepatitis B and hepatitis D infection. Antivir. Res. 2016, 133, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaillant, A. REP 2139: Antiviral Mechanisms and Applications in Achieving Functional Control of HBV and HDV Infection. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaillant, A.; Juteau, J.-M.; Lu, H.; Liu, S.; Lackman-Smith, C.; Ptak, R.; Jiang, S. Phosphorothioate oligonucleotides inhibit human immunodeficiency virus type 1 fusion by blocking gp41 core formation. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 1393–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dane, D.S.; Cameron, C.H.; Briggs, M. Virus-like particles in serum of patients with Australia-antigen-associated hepatitis. Lancet 1970, 295, 695–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mahtab, M.; Bazinet, M.; Vaillant, A. Safety and Efficacy of Nucleic Acid Polymers in Monotherapy and Combined with Immunotherapy in Treatment-Naive Bangladeshi Patients with HBeAg+ Chronic Hepatitis B Infection. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanlandschoot, P.; Van Houtte, F.; Roobrouck, A.; Farhoudi, A.; Leroux-Roels, G. Hepatitis B virus surface antigen suppresses the activation of monocytes through interaction with a serum protein and a monocyte-specific receptor. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 1281–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Meng, Z.; Jiang, M.; Pei, R.; Trippler, M.; Broering, R.; Bucchi, A.; Sowa, J.-P.; Dittmer, U.; Yang, D.; et al. Hepatitis B virus suppresses toll-like receptor–mediated innate immune responses in murine parenchymal and nonparenchymal liver cells. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.S.; Ren, G.X.; Hu, Y.W.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Yuan, Z.H. HBsAg Inhibits IFN-alpha Production in Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells through TNF-alpha and IL-10 Induction in Monocytes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata, J.E.; Bishop, M.R.; Tarantolo, S.R.; Angle, C.R.; Swanson, S.A.; Iversen, P.L. Evidence of Enhanced Iron Excretion During Systemic Phosphorothioate Oligodeoxynucleotide Treatment. J. Clin. Toxicol. 2000, 38, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazinet, M.; Pantea, V.; Placinta, G.; Moscalu, I.; Cebotarescu, V.; Cojuhari, L.; Jimbei, P.; Iarovoi, L.; Smesnoi, V.; Musteata, T.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of 48 Weeks REP 2139 or REP 2165, Tenofovir Disoproxil, and Pegylated Interferon Alfa-2a in Patients with Chronic HBV Infection Naive to Nucleos(t)ide Therapy. Gastroenterology 2020, 8, 2180–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano, V. Hot News: Hepatitis B Gene Therapy Coming to Age. AIDS Rev. 2018, 20, 125–127. [Google Scholar]
- Thi, E.P.; Dhillon, A.P.; Ardzinski, A.; Bidirici-Ertekin, L.; Cobarrubias, K.D.; Cuconati, A.; Kondratowicz, A.S.; Kwak, K.; Li, A.H.L.; Miller, A.; et al. ARB-1740, a RNA Interference Therapeutic for Chronic Hepatitis B Infection. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Zhao, Q.; Sheraz, M.; Cheng, J.; Qi, Y.; Su, Q.; Cuconati, A.; Wei, L.; Du, Y.; Li, W.; et al. HBV core protein allosteric modulators differentially alter cccDNA biosynthesis from de novo infection and intracellular amplification pathways. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlicksup, C.J.; Wang, J.C.; Francis, S.; Venkatakrishnan, B.; Turner, W.W.; VanNieuwenhze, M.; Zlotnick, A. Hepatitis B virus core protein allosteric modulators can distort and disrupt intact capsids. eLife 2018, 7, e31473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gane, E.; Liu, A.; Yuen, M.F.; Schwabe, C.; Bo, Q.; Das, S.; Gao, L.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.; Coakley, E.; et al. LBO-003-RO7049389, a core protein allosteric modulator, demonstrates robust anti-HBV activity in chronic hepatitis B patients and is safe and well tolerated. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, S101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrier, E.R.; Weiss, A.; Bach, C.; Heydmann, L.; Turon-Lagot, V.; Kopp, A.; El Saghire, H.; Crouchet, E.; Pessaux, P.; Garcia, T.; et al. Combined small molecule and loss-of-function screen uncovers estrogen receptor alpha and CAD as host factors for HDV infection and antiviral targets. Gut 2020, 69, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löffler, M.; Fairbanks, L.D.; Zameitat, E.; Marinaki, A.M.; Simmonds, H.A. Pyrimidine pathways in health and disease. Trends Mol. Med. 2005, 11, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decorsiere, A.; Mueller, H.; van Breugel, P.C.; Abdul, F.; Gerossier, L.; Beran, R.K.; Livingston, C.M.; Niu, C.; Fletcher, S.P.; Hantz, O.; et al. Hepatitis B virus X protein identifies the Smc5/6 complex as a host restriction factor. Nature 2016, 531, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, C.M.; Xu, Y.; Li, F.; Nio, K.; Reszka-Blanco, N.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Su, L. Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Promotes Degradation of SMC5/6 to Enhance HBV Replication. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 2846–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekiba, K.; Otsuka, M.; Ohno, M.; Yamagami, M.; Kishikawa, T.; Seimiya, T.; Suzuki, T.; Tanaka, E.; Ishibashi, R.; Funato, K.; et al. Pevonedistat, a Neuronal Precursor Cell-Expressed Developmentally Down-Regulated Protein 8-Activating Enzyme Inhibitor, Is a Potent Inhibitor of Hepatitis B Virus. Hepatology 2019, 69, 1903–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etzion, O.; Hamid, S.S.; Lurie, Y.; Gane, E.; Bader, N.; Yardeni, D.; Nevo-Shor, A.; Channa, S.; Mawani, M.; Parkash, O.; et al. PS-052-End of study results from LIMT HDV study: 36% durable virologic response at 24 weeks post-treatment with pegylated interferon lambda monotherapy in patients with chronic hepatitis delta virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vogt, A.; Wohlfart, S.; Urban, S.; Mier, W. Medical Advances in Hepatitis D Therapy: Molecular Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10817. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810817
Vogt A, Wohlfart S, Urban S, Mier W. Medical Advances in Hepatitis D Therapy: Molecular Targets. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(18):10817. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810817
Chicago/Turabian StyleVogt, Amelie, Sabrina Wohlfart, Stephan Urban, and Walter Mier. 2022. "Medical Advances in Hepatitis D Therapy: Molecular Targets" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 18: 10817. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810817
APA StyleVogt, A., Wohlfart, S., Urban, S., & Mier, W. (2022). Medical Advances in Hepatitis D Therapy: Molecular Targets. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(18), 10817. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810817








