TRIOBP-1 Protein Aggregation Exists in Both Major Depressive Disorder and Schizophrenia, and Can Occur through Two Distinct Regions of the Protein
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Insoluble TRIOBP-1 Is Found in the Brains of Patients with Major Depressive Disorder and Schizophrenia, Indicating Its Aggregation in Both Conditions
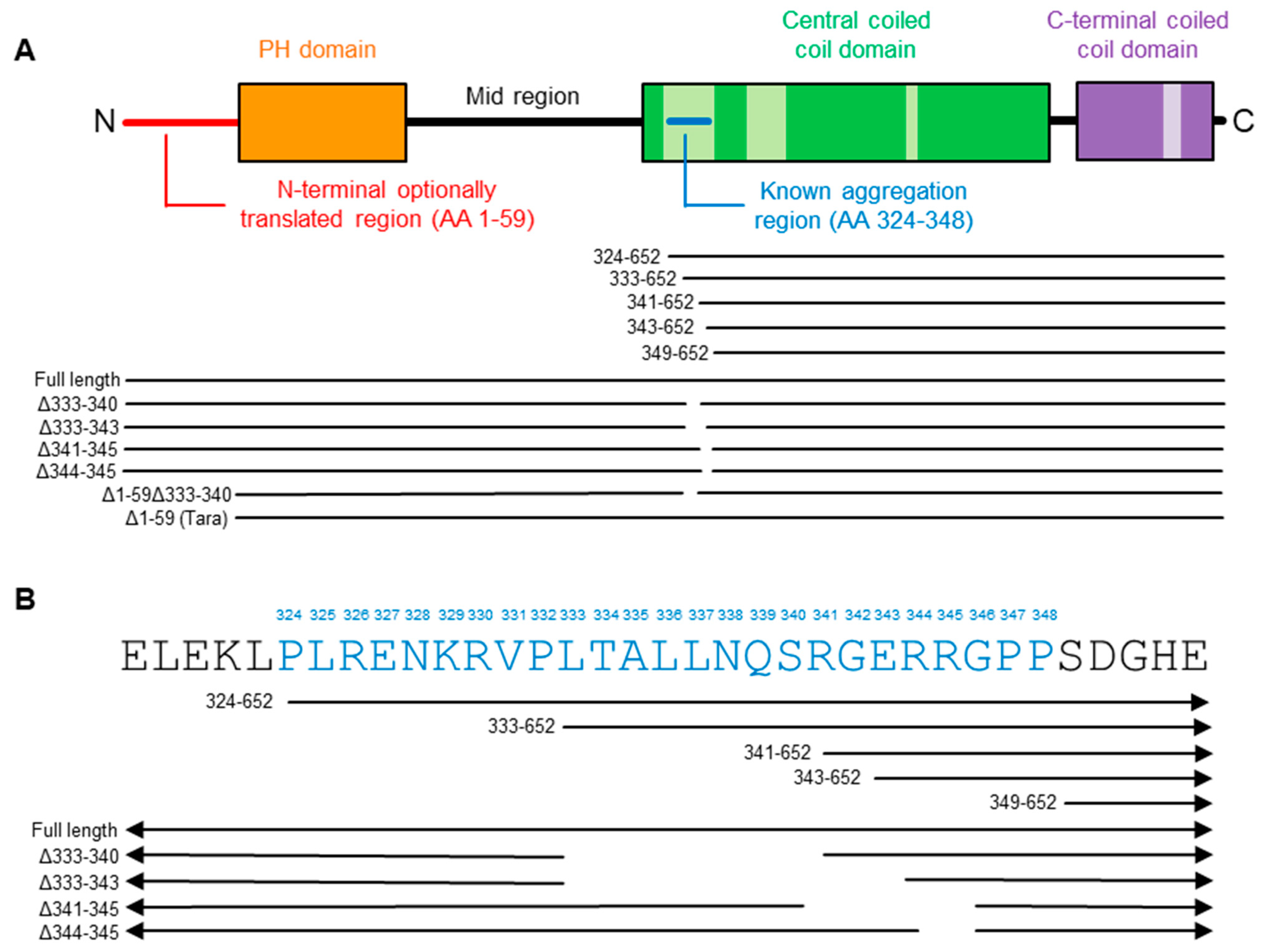
2.2. Refining the Aggregation Domain of TRIOBP-1, Using C-Terminal Constructs
2.3. Aggregation of TRIOBP-1 Can Arise through Its Isoform-Specific N-Terminal Unstructured Region
2.4. Aggregation of TRIOBP-1 Can Occur through Either Its Optionally Translated N-Terminus, or a Loop near the Center of the Protein
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Brain Samples
4.2. High Stringency Insoluble Protein Fraction Purification Protocol
4.3. Low Stringency Insoluble Protein Fraction Purification Protocol
4.4. Plasmids
4.5. Antibodies
4.6. Cell Culture
4.7. Western Blotting
4.8. Immunocytochemistry and Microscopy
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trubetskoy, V.; Pardiñas, A.F.; Qi, T.; Panagiotaropoulou, G.; Awasthi, S.; Bigdeli, T.B.; Bryois, J.; Chen, C.-Y.; Dennison, C.A.; Hall, L.S.; et al. Mapping genomic loci implicates genes and synaptic biology in schizophrenia. Nature 2022, 604, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leliveld, S.R.; Bader, V.; Hendriks, P.; Prikulis, I.; Sajnani, G.; Requena, J.R.; Korth, C. Insolubility of Disrupted-in-Schizophrenia 1 disrupts oligomer-dependent interactions with Nuclear Distribution Element 1 and is associated with sporadic mental disease. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 3839–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradshaw, N.J.; Korth, C. Protein misassembly and aggregation as potential convergence points for non-genetic causes of chronic mental illness. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 936–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bousman, C.A.; Luza, S.; Mancuso, S.G.; Kang, D.; Opazo, C.M.; Mostaid, M.S.; Cropley, V.; McGorry, P.; Weickert, C.S.; Pantelis, C.; et al. Elevated ubiquitinated proteins in brain and blood of individuals with schizophrenia. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nucifora, L.G.; MacDonald, M.L.; Lee, B.J.; Peters, M.E.; Norris, A.L.; Orsburn, B.C.; Yang, K.; Gleason, K.; Margolis, R.L.; Pevsner, J.; et al. Increased protein insolubility in brains from a subset of patients with schizophrenia. Am. J. Psychiatry 2019, 176, 730–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, M.R.; Meador-Woodruff, J.H. Intracellular compartment-specific proteasome dysfunction in postmortem cortex in schizophrenia patients. Mol. Psychiatry 2020, 25, 776–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottis, P.; Bader, V.; Trossbach, S.V.; Kretzschmar, H.; Michel, M.; Leliveld, S.R.; Korth, C. Convergence of two independent mental disease genes on the protein level: Recruitment of dysbindin to cell-invasive Disrupted-in-Schizophrenia 1 aggresomes. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 70, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, V.; Tomppo, L.; Trossbach, S.V.; Bradshaw, N.J.; Prikulis, I.; Leliveld, S.R.; Lin, C.-Y.; Ishizuka, K.; Sawa, A.; Ramos, A.; et al. Proteomic, genomic and translational approaches identify CRMP1 for a role in schizophrenia and its underlying traits. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 4406–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradshaw, N.J.; Bader, V.; Prikulis, I.; Lueking, A.; Müllner, S.; Korth, C. Aggregation of the protein TRIOBP-1 and its potential relevance to schizophrenia. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nucifora, L.G.; Wu, Y.C.; Lee, B.J.; Sha, L.; Margolis, R.L.; Ross, C.A.; Sawa, A.; Nucifora Jr, F.C. A mutation in NPAS3 that segregates with schizophrenia in a small family leads to protein aggregation. Mol. Neuropsychiatry 2016, 2, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seipel, K.; O’Brien, S.P.; Iannotti, E.; Medley, Q.G.; Streuli, M. Tara, a novel F-actin binding protein, associates with the Trio guanine nucleotide exchange factor and regulates actin cytoskeletal organization. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riazuddin, S.; Khan, S.N.; Ahmed, Z.M.; Ghosh, M.; Caution, K.; Nazli, S.; Kabra, M.; Zafar, A.U.; Chen, K.; Naz, S.; et al. Mutations in TRIOBP, which encodes a putative cytoskeletal-organizing protein, are associated with nonsyndromic recessive deafness. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2006, 78, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahin, H.; Walsh, T.; Sobe, T.; Abu Sa’ed, J.; Abu Rayan, A.; Lynch, E.D.; Lee, M.K.; Avraham, K.B.; King, M.-C.; Kanaan, M. Mutations in a novel isoform of TRIOBP that encodes a filamentous-actin binding protein are responsible for DFNB28 recessive nonsyndromic hearing loss. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2006, 78, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaharija, B.; Samardžija, B.; Bradshaw, N.J. The TRIOBP isoforms and their distinct roles in actin stabilization, deafness, mental illness, and cancer. Molecules 2020, 25, 4967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradshaw, N.J.; Yerabham, A.S.K.; Marreiros, R.; Zhang, T.; Nagel-Steger, L.; Korth, C. An unpredicted aggregation-critical region of the actin-polymerizing protein TRIOBP-1/Tara, determined by elucidation of its domain structure. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 9583–9598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmierczak, M.; Kazmierczak, P.; Peng, A.W.; Harris, S.L.; Shah, P.; Puel, J.-L.; Lenoir, M.; Franco, S.J.; Schwander, M. Pejvakin, a candidate stereociliary rootlet protein, regulates hair cell function in a cell-autonomous manner. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 3447–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samardžija, B.; Radonja, A.P.; Zaharija, B.; Bergman, M.; Renner, É.; Palkovits, M.; Rubeša, G.; Bradshaw, N.J. Protein aggregation of NPAS3, implicated in mental illness, is not limited to the V304I mutation. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.-H.; Kwak, Y.; Woo, Y.; Park, C.; Lee, S.-A.; Lee, H.; Park, S.J.; Suh, Y.; Suh, B.K.; Goo, B.S.; et al. Regulation of the actin cytoskeleton by the Ndel1-Tara complex is critical for cell migration. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, Y.; Kim, S.J.; Suh, B.K.; Kwak, Y.; Jung, H.-J.; Nhung, T.T.M.; Mun, D.J.; Hong, J.-H.; Noh, S.-J.; Kim, S.; et al. Sequential phosphorylation of NDEL1 by the DYRK2-GSK3β complex is critical for neuronal morphogenesis. eLife 2019, 8, e50850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Xu, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Slavin, S.; Kumar, S.; Koroleva, M.; Luo, J.; Wu, X.; et al. The novel coronary artery disease risk gene JCAD/KIAA1462 promotes endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 2398–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, J.-C.; Han, X.; Hsiao, C.-T.; Yates Iii, J.R.; Waterman, C.M. Analysis of the myosin-II-responsive focal adhesion proteome reveals a role for β-Pix in negative regulation of focal adhesion maturation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, T.; Yamazaki, Y.; Adachi, M.; Okawa, K.; Fort, P.; Uji, M.; Tsukita, S.; Tsukita, S. Tara up-regulates E-cadherin transcription by binding to the Trio RhoGEF and inhibiting Rac signaling. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 193, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, J.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, L.; Yu, H.; Yu, J.; Liu, X.; Fu, C.; Wang, X.; Ke, Y.; Huang, H.; et al. The 68-kDa Telomeric Repeat binding Factor 1 (TRF1)-Associated Protein (TAP68) interacts with and recruits TRF1 to the spindle pole during mitosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 14145–14156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lan, J.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, J.; Dou, Z.; Huang, H. Expression, purification, and characterization of Tara, a novel telomere repeat-binding factor 1 (TRF1)-binding protein. Protein Expr. Purif. 2007, 55, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottis, P.; Topic, B.; Loos, M.; Li, K.W.; de Souza Silva, M.A.; Schulz, D.; Smit, A.B.; Huston, J.P.; Korth, C. Aging-induced proteostatic changes in the rat hippocampus identify ARP3, NEB2 and BRAG2 as a molecular circuitry for cognitive impairment. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, B.; Ingram, E.; Takao, M.; Smith, M.J.; Jakes, R.; Virdee, K.; Yoshida, H.; Holzer, M.; Craxton, M.; Emson, P.C.; et al. Abundant tau filaments and nonapoptotic neurodegeneration in transgenic mice expressing human P301S tau protein. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 9340–9351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trossbach, S.V.; Bader, V.; Hecher, L.; Pum, M.E.; Masoud, S.T.; Prikulis, I.; Schäble, S.; de Souza Silva, M.A.; Su, P.; Boulat, B.; et al. Misassembly of full-length Disrupted-in-Schizophrenia 1 protein is linked to altered dopamine homeostasis and behavioral deficits. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 1561–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, C.; Bretteville, A.; Planel, E. Biochemical isolation of insoluble tau in transgenic mouse models of tauopathies. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 849, 473–491. [Google Scholar]
- Scholtzova, H.; Chianchiano, P.; Pan, J.; Sun, Y.; Goñi, F.; Mehta, P.D.; Wisniewski, T. Amyloid β and Tau Alzheimer’s disease related pathology is reduced by Toll-like receptor 9 stimulation. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2014, 2, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, C.; Lan, J.; Yu, J.; Jin, C.; Huang, H. Phosphorylation of Tara by Plk1 is essential for faithful chromosome segregation in mitosis. Exp. Cell Res. 2012, 318, 2344–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.-Y.; Shen, Y.; Xu, Q. Propagation of dysbindin-1B aggregates: Exosome-mediated transmission of neurotoxic deposits. Neuroscience 2015, 291, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamburg, H.; Trossbach, S.V.; Bader, V.; Chwiesko, C.; Kipar, A.; Sauvage, M.; Crum, W.R.; Vernon, A.C.; Bidmon, H.J.; Korth, C. Simultaneous effects on parvalbumin-positive interneuron and dopaminergic system development in a transgenic rat model for sporadic schizophrenia. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zandi, P.P.; Jaffe, A.E.; Goes, F.S.; Burke, E.E.; Collado-Torres, L.; Huuki-Myers, L.; Seyedian, A.; Lin, Y.; Seifuddin, F.; Pirooznia, M.; et al. Amygdala and anterior cingulate transcriptomes from individuals with bipolar disorder reveal downregulated neuroimmune and synaptic pathways. Nat. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campeau, E.; Ruhl, V.E.; Rodier, F.; Smith, C.L.; Rahmberg, B.L.; Fuss, J.O.; Campisi, J.; Yaswen, P.; Cooper, P.K.; Kaufman, P.D. A versatile viral system for expression and depletion of proteins in mammalian cells. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, J.C.; Wellenreuther, R.; Poustka, A.; Pepperkok, R.; Wiemann, S. Systematic subcellular localization of novel proteins identified by large-scale cDNA sequencing. EMBO Rep. 2000, 1, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JASP Team. JASP (Version 0.14.1) [Computer Software]; JASP Team: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zaharija, B.; Odorčić, M.; Hart, A.; Samardžija, B.; Marreiros, R.; Prikulis, I.; Juković, M.; Hyde, T.M.; Kleinman, J.E.; Korth, C.; et al. TRIOBP-1 Protein Aggregation Exists in Both Major Depressive Disorder and Schizophrenia, and Can Occur through Two Distinct Regions of the Protein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11048. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911048
Zaharija B, Odorčić M, Hart A, Samardžija B, Marreiros R, Prikulis I, Juković M, Hyde TM, Kleinman JE, Korth C, et al. TRIOBP-1 Protein Aggregation Exists in Both Major Depressive Disorder and Schizophrenia, and Can Occur through Two Distinct Regions of the Protein. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(19):11048. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911048
Chicago/Turabian StyleZaharija, Beti, Maja Odorčić, Anja Hart, Bobana Samardžija, Rita Marreiros, Ingrid Prikulis, Maja Juković, Thomas M. Hyde, Joel E. Kleinman, Carsten Korth, and et al. 2022. "TRIOBP-1 Protein Aggregation Exists in Both Major Depressive Disorder and Schizophrenia, and Can Occur through Two Distinct Regions of the Protein" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 19: 11048. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911048
APA StyleZaharija, B., Odorčić, M., Hart, A., Samardžija, B., Marreiros, R., Prikulis, I., Juković, M., Hyde, T. M., Kleinman, J. E., Korth, C., & Bradshaw, N. J. (2022). TRIOBP-1 Protein Aggregation Exists in Both Major Depressive Disorder and Schizophrenia, and Can Occur through Two Distinct Regions of the Protein. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(19), 11048. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911048






