Taking a Breather: Advances in Interleukin 5 Inhibition for Asthma Relief
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. IL-5 in Asthma
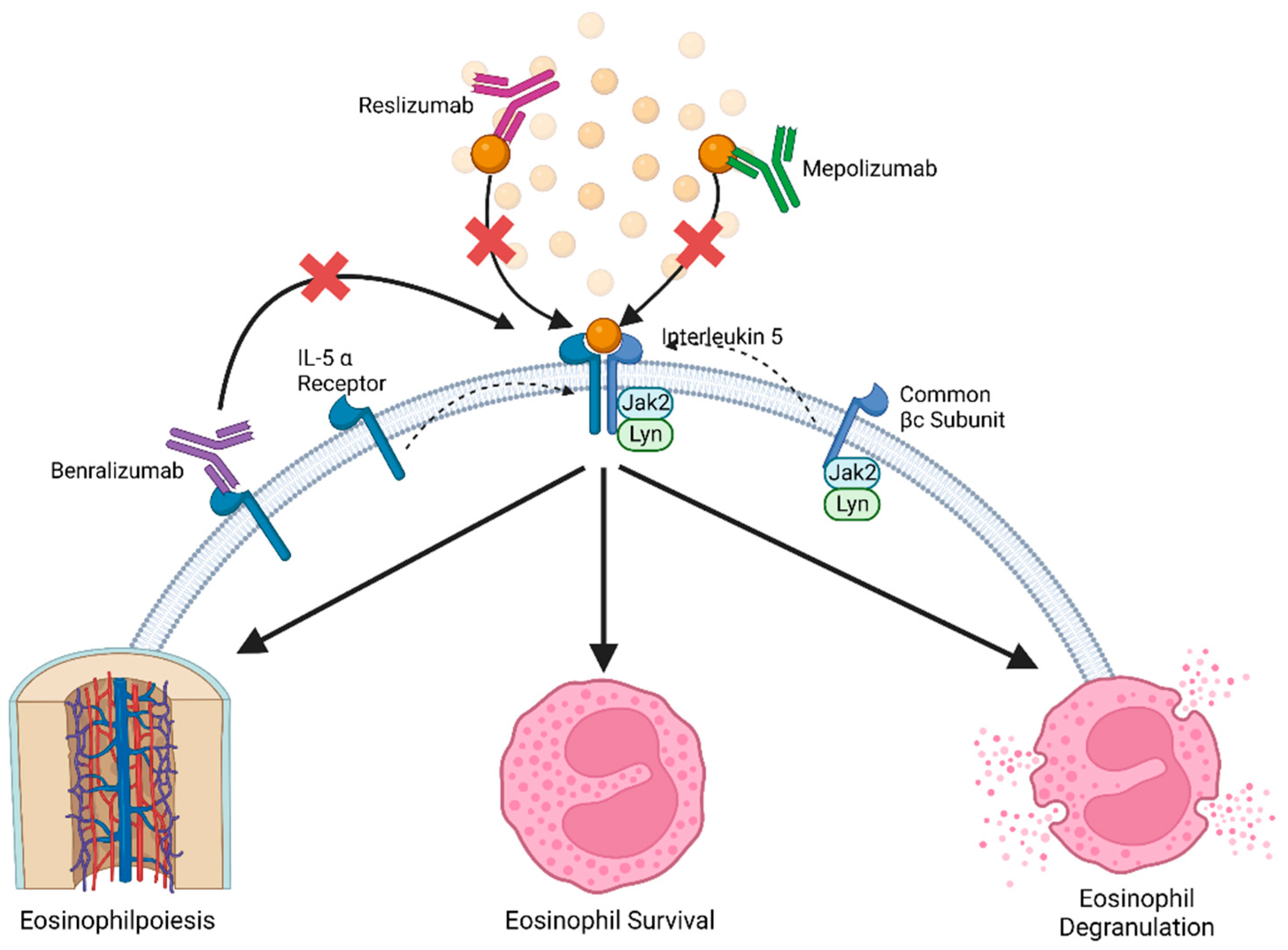
3. IL-5 Pathway in Eosinophils
4. IL-5 in Clinical Intervention
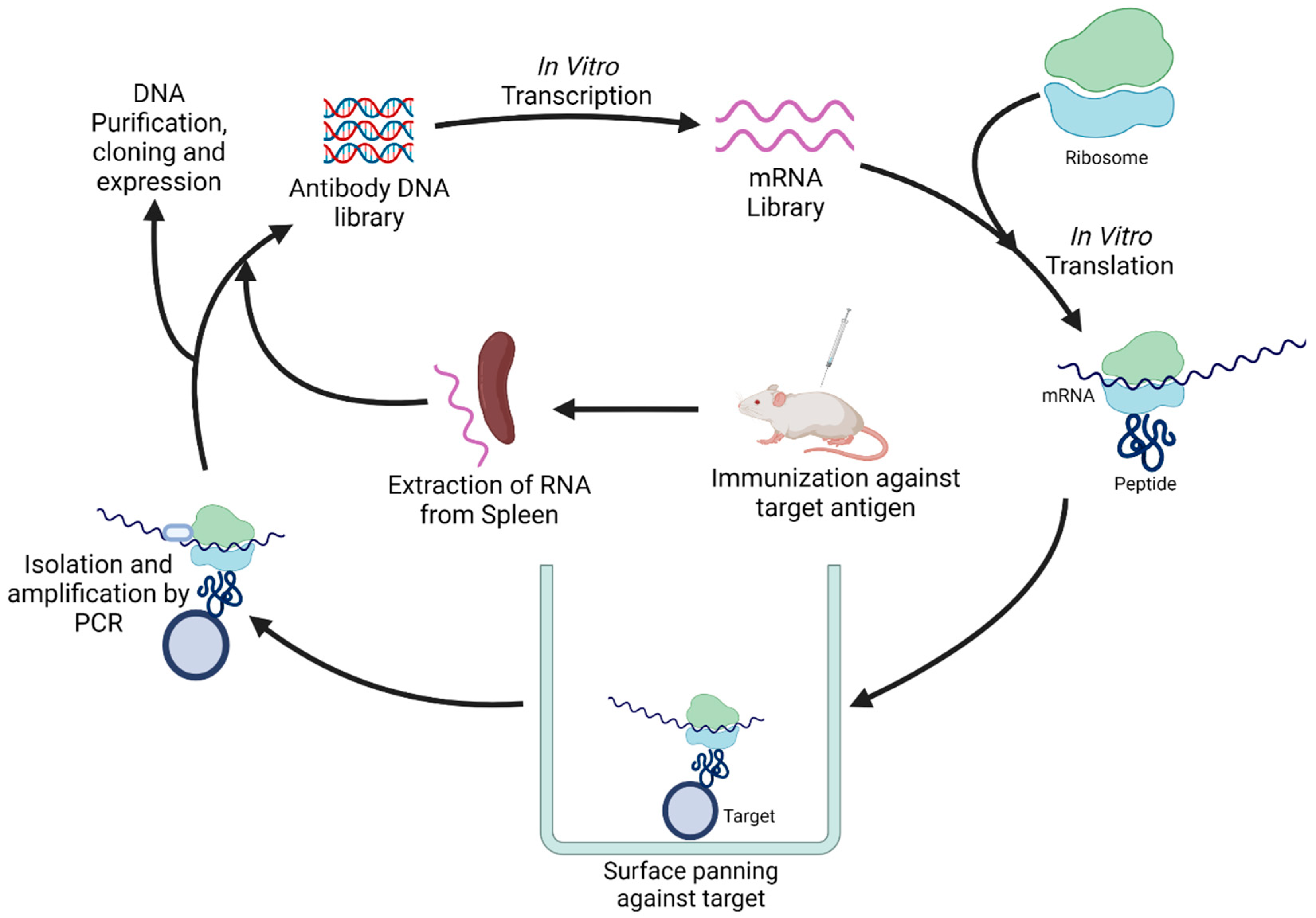
5. Novel Antibody Discovery Methods
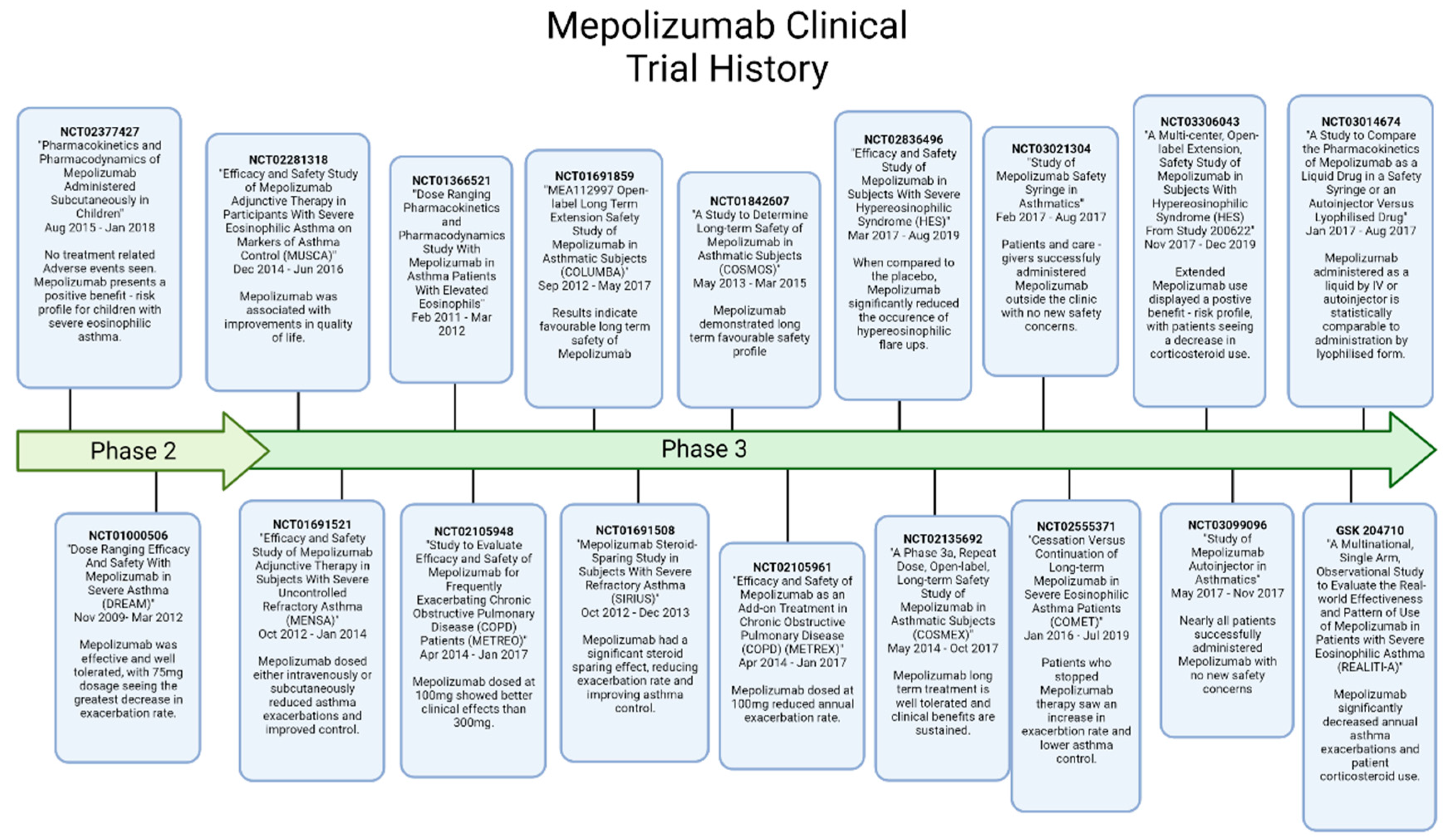
6. Mepolizumab
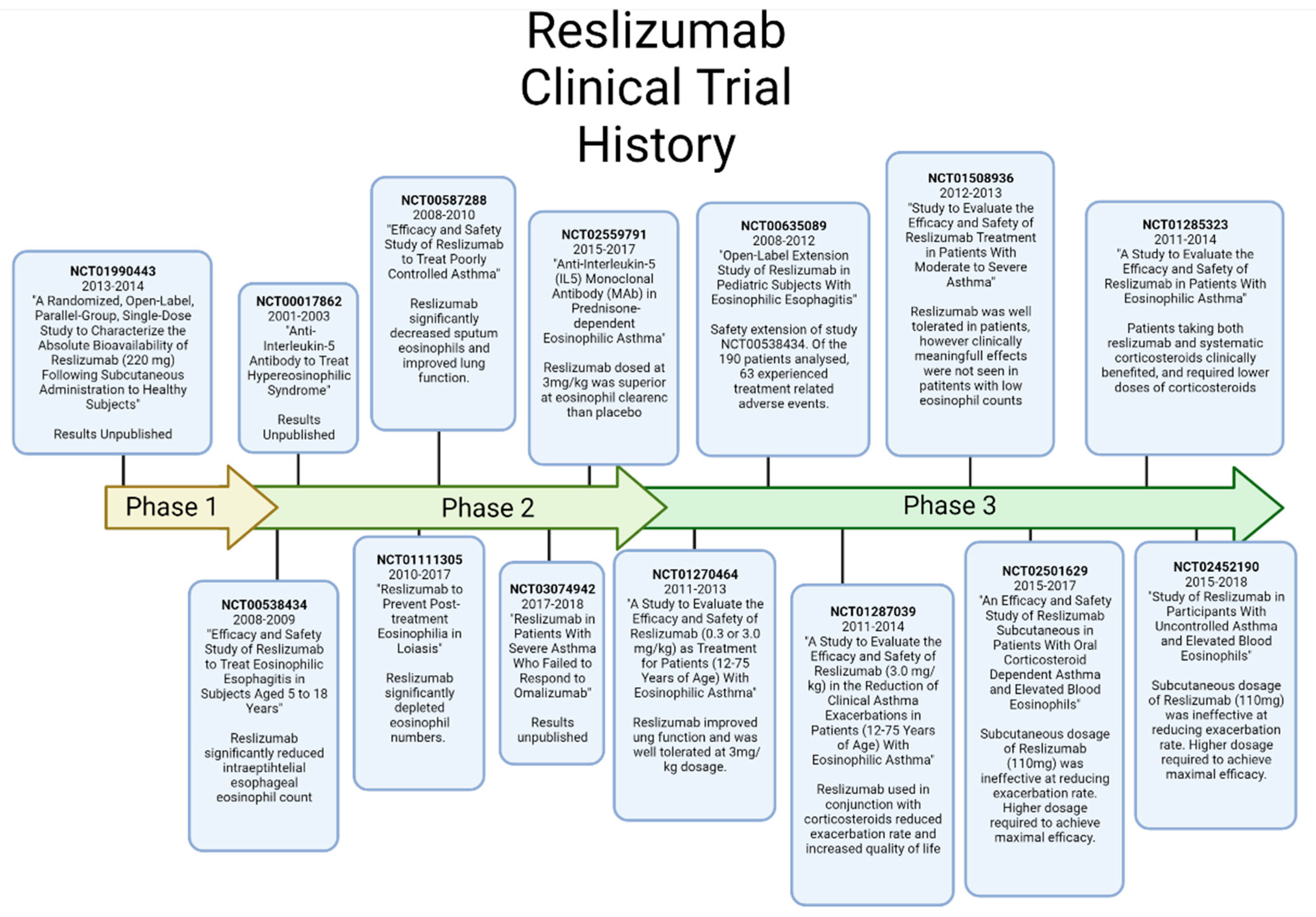
7. Reslizumab
8. Benralizumab
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dougan, M.; Dranoff, G.; Dougan, S.K. GM-CSF, IL-3, and IL-5 Family of Cytokines: Regulators of Inflammation. Immunity 2019, 50, 796–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, T.; Rothenberg, M.E.; Gordon, S. The Regulatory Function of Eosinophils. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaia, C.; Paoletti, G.; Puggioni, F.; Racca, F.; Pelaia, G.; Canonica, G.W.; Heffler, E. Interleukin-5 in the Pathophysiology of Severe Asthma. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagnasco, D.; Caminati, M.; Ferrando, M.; Aloè, T.; Testino, E.; Canonica, G.W.; Passalacqua, G. Anti-IL-5 and IL-5Ra: Efficacy and Safety of New Therapeutic Strategies in Severe Uncontrolled Asthma. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 5698212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlidis, S.; Takahashi, K.; Kwong, F.N.K.; Xie, J.; Hoda, U.; Sun, K.; Elyasigomari, V.; Agapow, P.; Loza, M.; Baribaud, F.; et al. “T2-high” in severe asthma related to blood eosinophil, exhaled nitric oxide and serum periostin. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1800938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esnault, S.; Johansson, M.W.; Mathur, S.K. Eosinophils, beyond IL-5. Cells 2021, 10, 2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuruvilla, M.E.; Lee, F.E.-H.; Lee, G.B. Understanding Asthma Phenotypes, Endotypes, and Mechanisms of Disease. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2019, 56, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahi, N.; Singh, N.R.; Heard, S.; Loutsios, C.; Summers, C.; Solanki, C.K.; Solanki, K.; Balan, K.K.; Ruparelia, P.; Peters, A.M.; et al. Use of 111-Indium–labeled autologous eo-sinophils to establish the in vivo kinetics of human eosinophils in healthy subjects. Blood 2012, 120, 4068–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, M.; Kephart, G.M.; Talley, N.J.; Wagner, J.M.; Sarr, M.G.; Bonno, M.; McGovern, T.; Gleich, G.J. Eosinophil infiltration and degranulation in normal human tissue. Anat. Rec. 1998, 252, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gans, M.D.; Gavrilova, T. Understanding the immunology of asthma: Pathophysiology, biomarkers, and treatments for asthma endotypes. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2020, 36, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, H.; Lambrecht, B.N. The basic immunology of asthma. Cell 2021, 184, 1469–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, O.; Suphioglu, C. Recent Advances in the Inhibition of the IL-4 Cytokine Pathway for the Treatment of Aller-gen-Induced Asthma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouro, T.; Takatsu, K. IL-5- and eosinophil-mediated inflammation: From discovery to therapy. Int. Immunol. 2009, 21, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopf, M.; Brombacher, F.; Hodgkin, P.D.; Ramsay, A.J.; Milbourne, E.A.; Dai, W.J.; Ovington, K.S.; Behm, C.A.; Köhler, G.; Young, I.G.; et al. IL-5-Deficient Mice Have a Developmental Defect in CD5+ B-1 Cells and Lack Eosinophilia but Have Normal Antibody and Cytotoxic T Cell Responses. Immunity 1996, 4, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulkerson, P.C.; Rothenberg, M.E. Targeting eosinophils in allergy, inflammation and beyond. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusano, S.; Kukimoto-Niino, M.; Hino, N.; Ohsawa, N.; Ikutani, M.; Takaki, S.; Sakamoto, K.; Hara-Yokoyama, M.; Shirouzu, M.; Takatsu, K.; et al. Structural basis of interleukin-5 dimer recognition by its α receptor. Protein Sci. 2012, 21, 850–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molfino, N.A.; Gossage, D.; Kolbeck, R.; Parker, J.M.; Geba, G.P. Molecular and clinical rationale for therapeutic targeting of interleukin-5 and its receptor. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2012, 42, 712–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossjohn, J.; McKinstry, W.J.; Woodcock, J.M.; McClure, B.J.; Hercus, T.R.; Parker, M.W.; Lopez, A.F.; Bagley, C.J. Structure of the activation domain of the GM-CSF/IL-3/IL-5 receptor common beta-chain bound to an antagonist. Blood 2000, 95, 2491–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varricchi, G.; Bagnasco, D.; Borriello, F.; Heffler, E.; Canonica, G.W. Interleukin-5 pathway inhibition in the treatment of eosinophilic respiratory disorders: Evidence and unmet needs. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 16, 186–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellman, C.; Halldén, G.; Hylander, B.; Lundahl, J. Regulation of the interleukin-5 receptor α -subunit on peripheral blood eosinophils from healthy subjects. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2003, 131, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broughton, S.E.; Dhagat, U.; Hercus, T.R.; Nero, T.L.; Grimbaldeston, M.A.; Bonder, C.S.; Lopez, A.F.; Parker, M.W. The GM-CSF/IL-3/IL-5 cytokine receptor family: From ligand recognition to initiation of signaling. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 250, 277–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-X.; Leonard, W.J. The Common Cytokine Receptor γ Chain Family of Cytokines. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, a028449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Katagiri, T.; Takaki, S.; Kikuchi, Y.; Hitoshi, Y.; Yonehara, S.; Tsukada, S.; Kitamura, D.; Watanabe, T.; Witte, O.; et al. IL-5 receptor-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation of SH2/SH3-containing proteins and activation of Bruton’s tyrosine and Janus 2 kinases. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 180, 2101–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, N.; Kouro, T.; Yamada, A.; Koike, M.; Hanai, N.; Ishikawa, T.; Takatsu, K. JAK2 and JAK1 constitutively associate with an interleukin-5 (IL-5) receptor alpha and betac subunit, respectively, and are activated upon IL-5 stimulation. Blood 1998, 91, 2264–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouro, T.; Kikuchi, Y.; Kanazawa, H.; Hirokawa, K.; Harada, N.; Shiiba, M.; Wakao, H.; Takaki, S.; Takatsu, K. Critical proline residues of the cytoplasmic domain of the IL-5 receptor α chain and its function in IL-5-mediated activation of JAK kinase and STAT5. Int. Immunol. 1996, 8, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazdrak, K.; Olszewska-Pazdrak, B.; Stafford, S.; Garofalo, R.P.; Alam, R. Lyn, Jak2, and Raf-1 Kinases Are Critical for the Antiapoptotic Effect of Interleukin 5, whereas only Raf-1 Kinase Is Essential for Eosinophil Activation and Degranulation. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 188, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parray, H.A.; Shukla, S.; Samal, S.; Shrivastava, T.; Ahmed, S.; Sharma, C.; Kumar, R. Hybridoma technology a versatile method for isolation of monoclonal antibodies, its applicability across species, limitations, advancement and future perspectives. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 85, 106639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanack, K.; Messerschmidt, K.; Listek, M. Antibodies and Selection of Monoclonal Antibodies. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 917, 11–22. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C. Hybridoma Technology for the Generation of Monoclonal Antibodies. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 901, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hnasko, R.M.; Stanker, L.H. Hybridoma Technology. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1318, 15–28. [Google Scholar]
- Tomita, M.; Tsumoto, K. Hybridoma technologies for antibody production. Immunotherapy 2011, 3, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parola, C.; Neumeier, D.; Reddy, S.T. Integrating high-throughput screening and sequencing for monoclonal antibody discovery and engineering. Immunology 2018, 153, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.P. Filamentous fusion phage: Novel expression vectors that display cloned antigens on the virion surface. Science 1985, 228, 1315–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledsgaard, L.; Kilstrup, M.; Karatt-Vellatt, A.; McCafferty, J.; Laustsen, A.H. Basics of Antibody Phage Display Technology. Toxins 2018, 10, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherf, G.M.; Cochran, J.R. Applications of Yeast Surface Display for Protein Engineering. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1319, 155–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelini, A.; Chen, T.F.; de Picciotto, S.; Yang, N.J.; Tzeng, A.; Santos, M.S.; Van Deventer, J.A.; Traxlmayr, M.W.; Wittrup, K.D. Protein Engineering and Selection Using Yeast Surface Display. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1319, 3–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teymennet-Ramírez, K.V.; Martínez-Morales, F.; Trejo-Hernández, M.R. Yeast Surface Display System: Strategies for Improvement and Biotechnological Applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 9, 794742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gera, N.; Hussain, M.; Rao, B. Protein selection using yeast surface display. Methods 2013, 60, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunamneni, A.; Ogaugwu, C.; Bradfute, S.; Durvasula, R. Ribosome Display Technology: Applications in Disease Diagnosis and Control. Antibodies 2020, 9, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keating, G.M. Mepolizumab: First Global Approval. Drugs 2015, 75, 2163–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldar, P.; Brightling, C.E.; Hargadon, B.; Gupta, S.; Monteiro, W.; Sousa, A.; Marshall, R.P.; Bradding, P.; Green, R.H.; Wardlaw, A.J.; et al. Mepolizumab and exacerbations of refractory eosinophilic asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 973–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mkorombindo, T.; Dransfield, M.T. Mepolizumab in the treatment of eosinophilic chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2019, 14, 14–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CADTH Common Drug Reviews. Mepolizumab (Nucala); Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pavord, I.D.; Bel, E.H.; Bourdin, A.; Chan, R.; Han, J.K.; Keene, O.N.; Liu, M.C.; Martin, N.; Papi, A.; Roufosse, F.; et al. From DREAM to REALITI-A and beyond: Mepolizumab for the treatment of eosinophil-driven diseases. Allergy 2022, 77, 778–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettiol, A.; Urban, M.L.; Dagna, L.; Cottin, V.; Franceschini, F.; Del Giacco, S.; Schiavon, F.; Neumann, T.; Lopalco, G.; Novikov, P.; et al. Mepolizumab for Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis: A European Multicenter Observational Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leckie, M.J.; ten Brinke, A.; Khan, J.; Diamant, Z.; O’connor, B.J.; Walls, C.M.; Mathur, A.K.; Cowley, H.C.; Chung, K.F.; Djukanovic, R.; et al. Effects of an interleukin-5 blocking monoclonal antibody on eosinophils, airway hyper-responsiveness, and the late asthmatic response. Lancet 2000, 356, 2144–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldhoff, J.M.; Darsow, U.; Werfel, T.; Katzer, K.; Wulf, A.; Laifaoui, J.; Hijnen, D.; Plotz, S.; Knol, E.; Kapp, A.; et al. Anti-IL-5 recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody (Mepolizumab) for the treatment of atopic dermatitis. Allergy 2005, 60, 693–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TGA. Australian Product Information—NUCALA (Mepolizumab). In Care DoHaA; GlaxoSmithKline Australia: Ermington, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.; Pouliquen, I.; Austin, D.; Price, R.G.; Kempsford, R.; Steinfeld, J.; Bradford, E.S.; Yancey, S.W. Subcutaneous mepolizumab in children aged 6 to 11 years with severe eosinophilic asthma. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2019, 54, 1957–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavord, I.D.; Korn, S.; Howarth, P.; Bleecker, E.R.; Buhl, R.; Keene, O.N.; Ortega, H.; Chanez, P. Mepolizumab for severe eosinophilic asthma (DREAM): A multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2012, 380, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chupp, G.L.; Bradford, E.S.; Albers, F.C.; Bratton, D.J.; Wang-Jairaj, J.; Nelsen, L.M.; Trevor, J.L.; Magnan, A.; Brinke, A.T. Efficacy of mepolizumab add-on therapy on health-related quality of life and markers of asthma control in severe eosinophilic asthma (MUSCA): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multicentre, phase 3b trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017, 5, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, H.G.; Liu, M.C.; Pavord, I.D.; Brusselle, G.G.; Fitzgerald, J.M.; Chetta, A.; Humbert, M.; Katz, L.E.; Keene, O.N.; Yancey, S.W.; et al. Mepolizumab Treatment in Patients with Severe Eosinophilic Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1198–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouliquen, I.J.; Kornmann, O.; Barton, S.V.; Price, J.A.; Ortega, H.G. Characterization of the relationship between dose and blood eosinophil response following subcutaneous administration of mepolizumab. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 53, 1015–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavord, I.D.; Chanez, P.; Criner, G.J.; Kerstjens, H.A.; Korn, S.; Lugogo, N.; Martinot, J.-B.; Sagara, H.; Albers, F.C.; Bradford, E.S.; et al. Mepolizumab for Eosinophilic Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1613–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, S.; Moore, W.; Gibson, P.G.; Leigh, R.; Bourdin, A.; Maspero, J.; Barros, M.; Buhl, R.; Howarth, P.; Albers, F.C.; et al. Assessment of the long-term safety of mepolizumab and durability of clinical response in patients with severe eosinophilic asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 1742–1751.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bel, E.H.; Wenzel, S.E.; Thompson, P.J.; Prazma, C.M.; Keene, O.N.; Yancey, S.W.; Ortega, H.G.; Pavord, I.D. Oral Glucocorticoid-Sparing Effect of Mepolizumab in Eosinophilic Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lugogo, N.; Domingo, C.; Chanez, P.; Leigh, R.; Gilson, M.J.; Price, R.G.; Yancey, S.W.; Ortega, H.G. Long-term Efficacy and Safety of Mepolizumab in Patients with Severe Eosinophilic Asthma: A Multi-center, Open-label, Phase IIIb Study. Clin. Ther. 2016, 38, 2058–2070.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinfeld, J.; Rofousse, F.; Kahn, J.-E.; Gleich, G.; Rothenberg, M.; Wardlaw, A.; Kirby, S.Y.; Gilson, M.; Bentley, J.; Bradford, E.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Mepolizumab in Hypereosinophilic Syndrome: A Phase III, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 1397–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, S.; Brusselle, G.G.; Bel, E.H.; FitzGerald, J.M.; Masoli, M.; Korn, S.; Kato, M.; Albers, F.C.; Bradford, E.S.; Gilson, M.J.; et al. Long-term Safety and Clinical Benefit of Mepolizumab in Patients with the Most Severe Eosinophilic Asthma: The COSMEX Study. Clin. Ther. 2019, 41, 2041–2056.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bel, E.H.; Bernstein, D.I.; Bjermer, L.; Follows, R.; Bentley, J.H.; Pouliquen, I.; Bradford, E. Usability of mepolizumab single-use prefilled syringe for patient self-administration. J. Asthma 2020, 57, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, W.C.; Kornmann, O.; Humbert, M.; Poirier, C.; Bel, E.H.; Kaneko, N.; Smith, S.G.; Martin, N.; Gilson, M.J.; Price, R.G.; et al. Stopping versus continuing long-term mepolizumab treatment in severe eosinophilic asthma (COMET study). Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 59, 2100396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleich, G.J.; Roufosse, F.; Chupp, G.; Faguer, S.; Walz, B.; Reiter, A.; Yancey, S.W.; Bentley, J.H.; Steinfeld, J.; García, G.R.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Mepolizumab in Hypereosinophilic Syndrome: An Open-Label Extension Study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 4431–4440.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, D.; Pavord, I.D.; Chapman, K.R.; Follows, R.; Bentley, J.H.; Pouliquen, I.; Bradford, E. Usability of mepolizumab single-use prefilled autoinjector for patient self-administration. J. Asthma 2020, 57, 987–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabbir, S.; Pouliquen, I.; Bentley, J.; Bradford, E.; Kaisermann, M.; Albayaty, M. The Pharmacokinetics and Relative Bioavailability of Mepolizumab 100 mg Liquid Formulation Administered Subcutaneously to Healthy Participants: A Randomized Trial. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2020, 9, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harrison, T.; Canonica, G.W.; Chupp, G.; Lee, J.; Schleich, F.; Welte, T.; Valero, A.; Gemzoe, K.; Maxwell, A.; Joksaite, S.; et al. Real-world mepolizumab in the prospective severe asthma REALITI-A study: Initial analysis. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 2000151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, M.; Mathur, S.; Hargreave, F.; Boulet, L.P.; Xie, F.; Young, J.; Wilkins, H.J.; Henkel, T.; Nair, P. Reslizumab for poorly controlled, eosinophilic asthma: A randomized, placebo-controlled study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 184, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, M.; Zangrilli, J.E.; Wechsler, M.E.; Bateman, E.D.; Brusselle, G.G.; Bardin, P.; Murphy, K.; Maspero, J.F.; O’Brien, C.; Korn, S. Reslizumab for inadequately controlled asthma with elevated blood eosinophil counts: Results from two multicentre, parallel, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trials. Lancet Respir. Med. 2015, 3, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, T.W.; Chanez, P.; Menzella, F.; Canonica, G.W.; Louis, R.; Cosio, B.G.; Lugogo, N.L.; Mohan, A.; Burden, A.; McDermott, L.; et al. Onset of effect and impact on health-related quality of life, exacerbation rate, lung function, and nasal polyposis symptoms for patients with severe eosinophilic asthma treated with benralizumab (ANDHI): A randomised, controlled, phase 3b trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 260–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TGA. Australian Product Information—CINQAIR (Reslizumab). In Care DoHaA; GlaxoSmithKline Australia: Ermington, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Spergel, J.M.; Rothenberg, M.E.; Collins, M.H.; Furuta, G.T.; Markowitz, J.E.; Fuchs, G., III; O’Gorman, M.A.; Abonia, J.P.; Young, J.; Henkel, T.; et al. Reslizumab in children and adolescents with eosinophilic esophagitis: Results of a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, F.; Herrick, J.; Makiya, M.; Ramanathan, R.; Thompson, R.; Rampertaap, S.; Stoddard, J.; Ware, J.; Fay, M.P.; Holland-Thomas, N.; et al. A Randomized, Placebo-controlled, Double-blind Pilot Study of Single-dose Humanized Anti-IL5 Antibody (Reslizumab) for the Reduction of Eosinophilia Following Diethylcarbamazine Treatment of Loa Infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e1624–e1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, M.; Aleman Paramo, F.; Kjarsgaard, M.; Salter, B.; Nair, G.; LaVigne, N.; Radford, K.; Sehmi, R.; Nair, P. Weight-adjusted Intravenous Reslizumab in Severe Asthma with Inadequate Response to Fixed-Dose Subcutaneous Mepolizumab. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 197, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjermer, L.; Lemiere, C.; Maspero, J.; Weiss, S.; Zangrilli, J.; Germinaro, M. Reslizumab for Inadequately Controlled Asthma with Elevated Blood Eosinophil Levels: A Randomized Phase 3 Study. Chest 2016, 150, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corren, J.; Weinstein, S.; Janka, L.; Zangrilli, J.; Garin, M. Phase 3 Study of Reslizumab in Patients with Poorly Controlled Asthma: Effects Across a Broad Range of Eosinophil Counts. Chest 2016, 150, 799–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, J.A.; Virchow, J.C.; Murphy, K.; Maspero, J.F.; Jacobs, J.; Adir, Y.; Humbert, M.; Castro, M.; Marsteller, D.A.; McElhattan, J.; et al. Effect of fixed-dose subcutaneous reslizumab on asthma exacerbations in patients with severe uncontrolled asthma and corticosteroid sparing in patients with oral corticosteroid-dependent asthma: Results from two phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 461–474. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Castro, M.; Wenzel, S.E.; Bleecker, E.R.; Pizzichini, E.; Kuna, P.; Busse, W.W.; Gossage, D.L.; Ward, C.K.; Wu, Y.; Wang, B.; et al. Benralizumab, an anti-interleukin 5 receptor alpha monoclonal antibody, versus placebo for uncontrolled eosinophilic asthma: A phase 2b randomised dose-ranging study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2014, 2, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brightling, C.E.; Bleecker, E.R.; Panettieri, R.A.; Bafadhel, M.; She, D.; Ward, C.K.; Xu, X.; Birrell, C.; van der Merwe, R. Benralizumab for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and sputum eosinophilia: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2a study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2014, 2, 891–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FitzGerald, J.M.; Bleecker, E.R.; Nair, P.; Korn, S.; Ohta, K.; Lommatzsch, M.; Ferguson, G.T.; Busse, W.W.; Barker, P.; Sproule, S.; et al. Benralizumab, an anti-interleukin-5 receptor α monoclonal antibody, as add-on treatment for patients with severe, uncontrolled, eosinophilic asthma (CALIMA): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 2016, 388, 2128–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleecker, E.R.; FitzGerald, J.M.; Chanez, P.; Papi, A.; Weinstein, S.F.; Barker, P.; Sproule, S.; Gilmartin, G.; Aurivillius, M.; Werkström, V.; et al. Efficacy and safety of benralizumab for patients with severe asthma uncontrolled with high-dosage inhaled corticosteroids and long-acting β2-agonists (SIROCCO): A randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 2016, 388, 2115–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TGA. Australian Product Information—FASENRA (Benralizumab). In Care DoHaA; GlaxoSmithKline Australia: Ermington, Australia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nowak, R.M.; Parker, J.M.; Silverman, R.A.; Rowe, B.H.; Smithline, H.; Khan, F.; Fiening, J.P.; Kim, K.; Molfino, N.A. A randomized trial of benralizumab, an antiinterleukin 5 receptor α monoclonal antibody, after acute asthma. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2015, 33, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criner, G.J.; Celli, B.R.; Brightling, C.E.; Agusti, A.; Papi, A.; Singh, D.; Sin, D.D.; Vogelmeier, C.F.; Sciurba, F.C.; Bafadhel, M.; et al. Benralizumab for the Prevention of COPD Exacerbations. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1023–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, W.W.; Bleecker, E.R.; FitzGerald, J.M.; Ferguson, G.T.; Barker, P.; Sproule, S.; Olsson, R.; Martin, U.J.; Goldman, M.; Yañez, A.; et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of benralizumab in patients with severe, uncontrolled asthma: 1-year results from the BORA phase 3 extension trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panettieri, R.A., Jr.; Welte, T.; Shenoy, K.V.; Korn, S.; Jandl, M.; Kerwin, E.M.; Feijoo, R.; Barker, P.; Olsson, R.F.; Martin, U.J. Onset of Effect, Changes in Airflow Obstruction and Lung Volume, and Health-Related Quality of Life Improvements with Benralizumab for Patients with Severe Eosinophilic Asthma: Phase IIIb Randomized, Controlled Trial (SOLANA). J. Asthma Allergy 2020, 13, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chupp, G.; Lugogo, N.L.; Kline, J.N.; Ferguson, G.T.; Hirsch, I.; Goldman, M.; Zangrilli, J.G.; Trudo, F. Rapid onset of effect of benralizumab on morning peak expiratory flow in severe, uncontrolled asthma. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019, 122, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korn, S.; Bourdin, A.; Chupp, G.; Cosio, B.G.; Arbetter, D.; Shah, M.; Gil, E.G. Integrated Safety and Efficacy among Patients Receiving Benralizumab for up to 5 Years. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 4381–4392.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Massey, O.W.; Suphioglu, C. Taking a Breather: Advances in Interleukin 5 Inhibition for Asthma Relief. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911166
Massey OW, Suphioglu C. Taking a Breather: Advances in Interleukin 5 Inhibition for Asthma Relief. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(19):11166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911166
Chicago/Turabian StyleMassey, Oliver William, and Cenk Suphioglu. 2022. "Taking a Breather: Advances in Interleukin 5 Inhibition for Asthma Relief" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 19: 11166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911166
APA StyleMassey, O. W., & Suphioglu, C. (2022). Taking a Breather: Advances in Interleukin 5 Inhibition for Asthma Relief. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(19), 11166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911166







