Antiviral Drugs Screening for Swine Acute Diarrhea Syndrome Coronavirus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
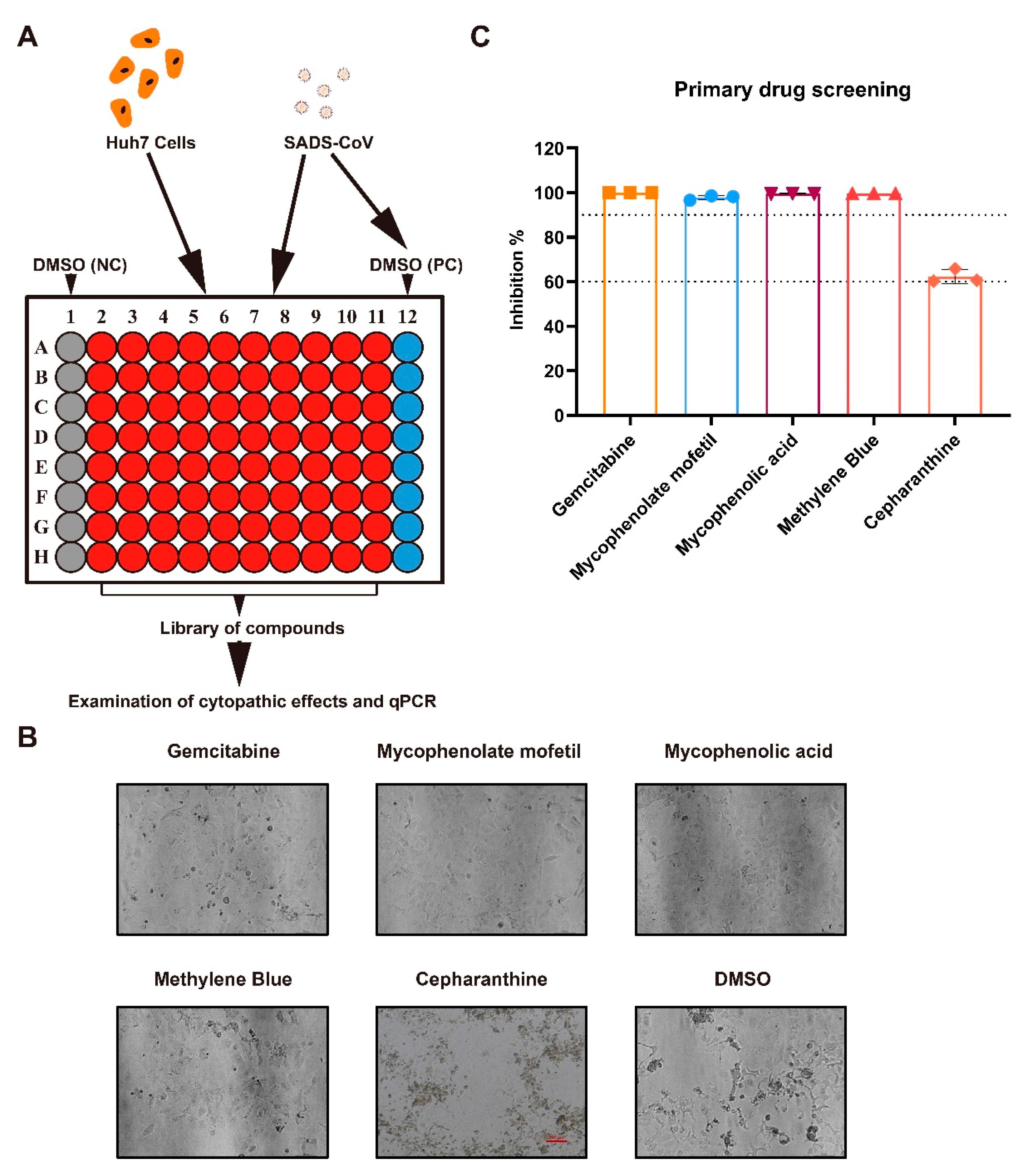
2.1. Antiviral Drug Screening and Evaluation
2.2. Preliminary Identification of Potential Antiviral Targets
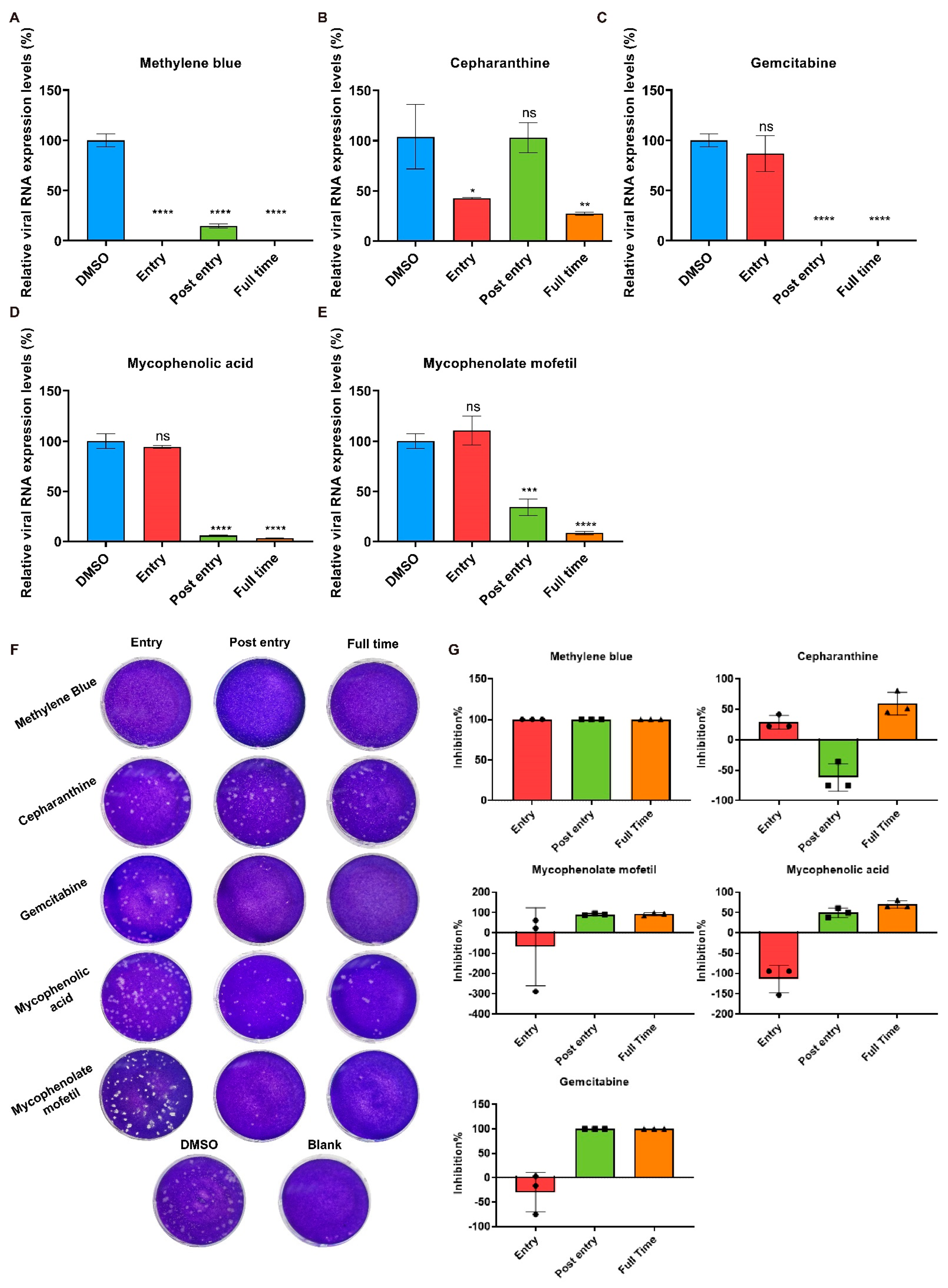
2.3. Cepharanthine Inhibits SADS-CoV Entry
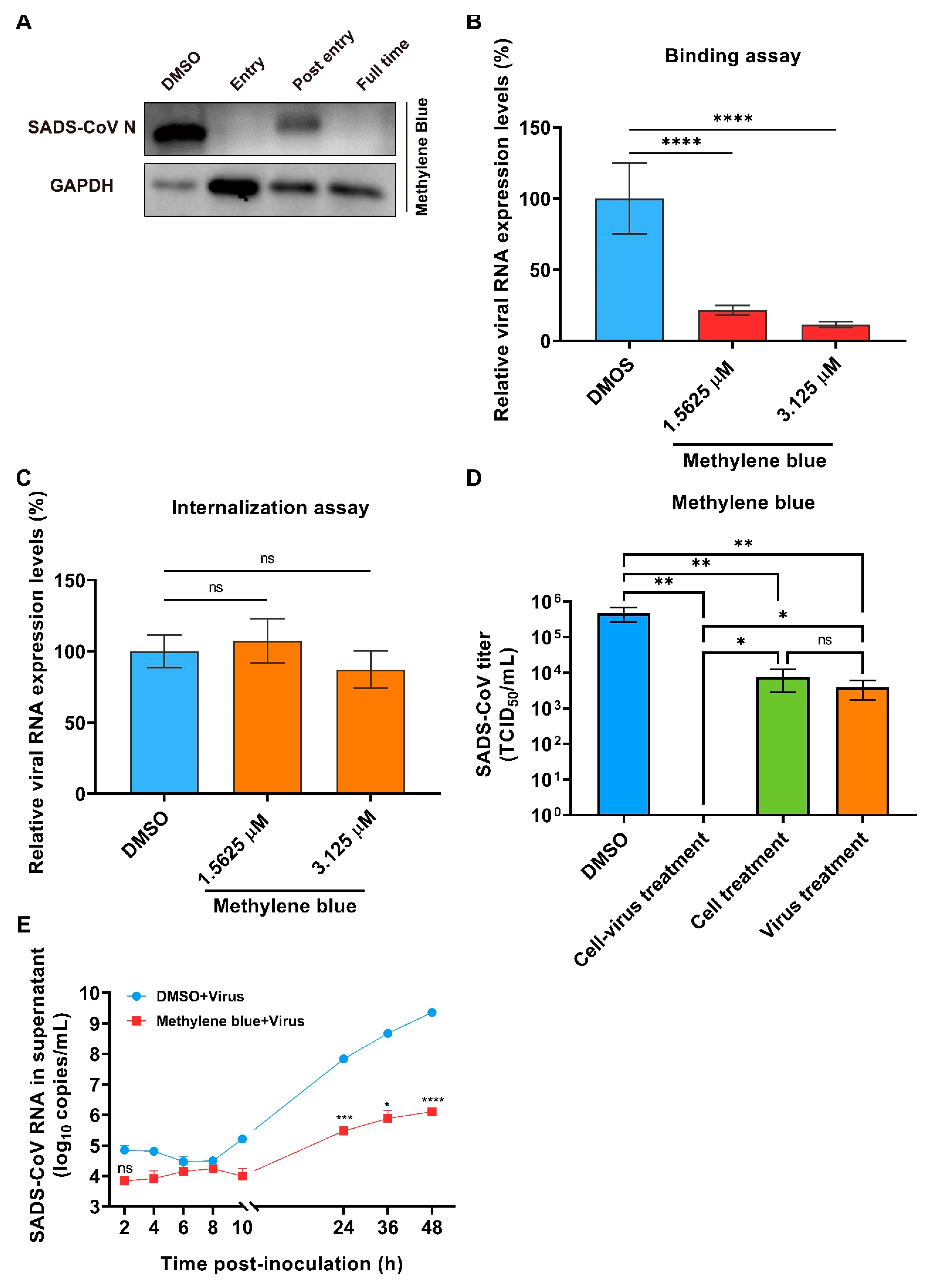
2.4. Methylene Blue Is an Inhibitor for SADS-CoV Infection
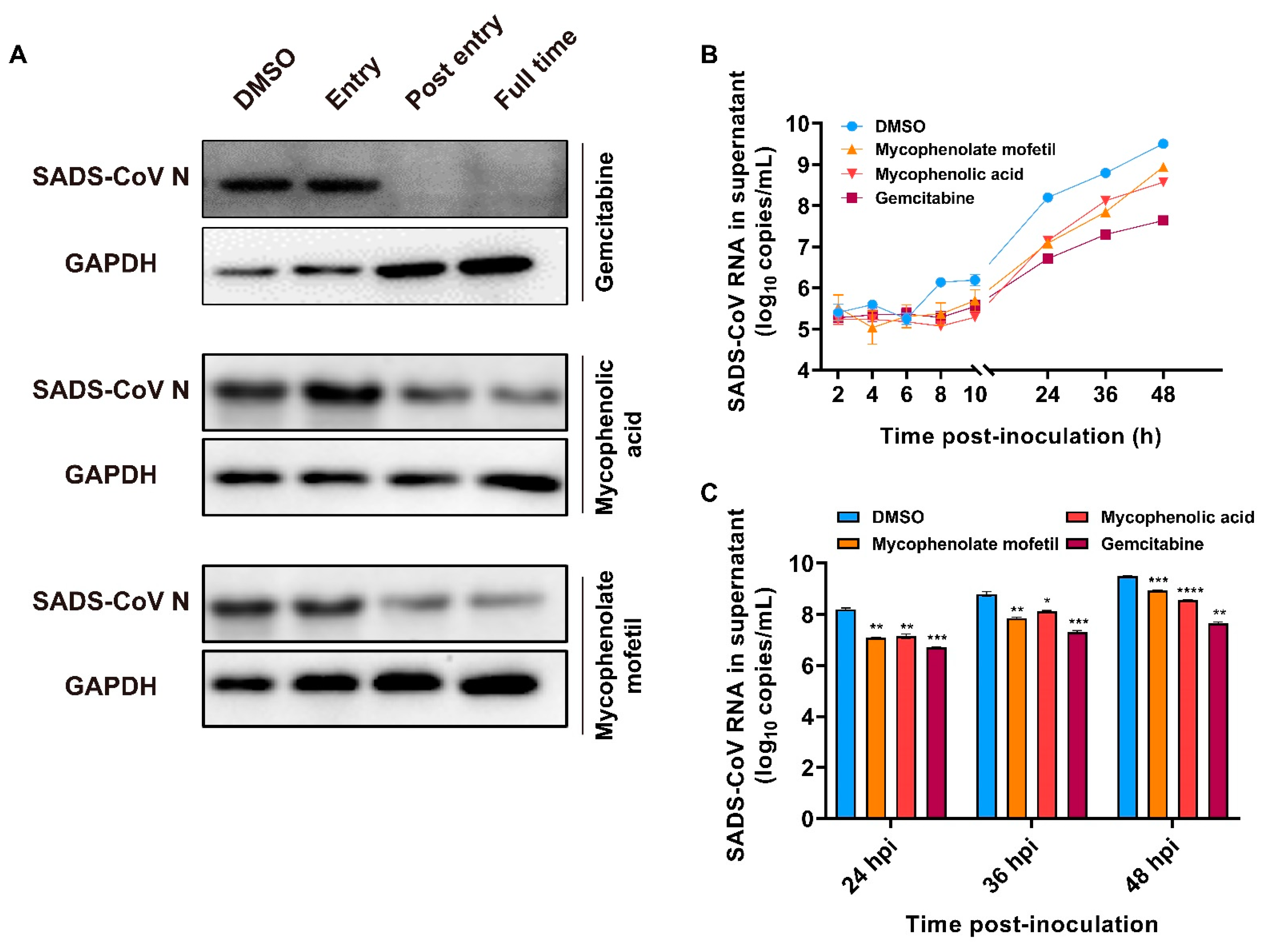
2.5. Effects of Gemcitabine, Mycophenolate mofetil, and Mycophenolic Acid after SADS-CoV Entry
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Line and Viruses
4.2. Compound Library
4.3. Primary Screening for Antiviral Compounds
4.4. Viral RNA Extraction and Quantification
4.5. Antiviral and Cytotoxicity Assays
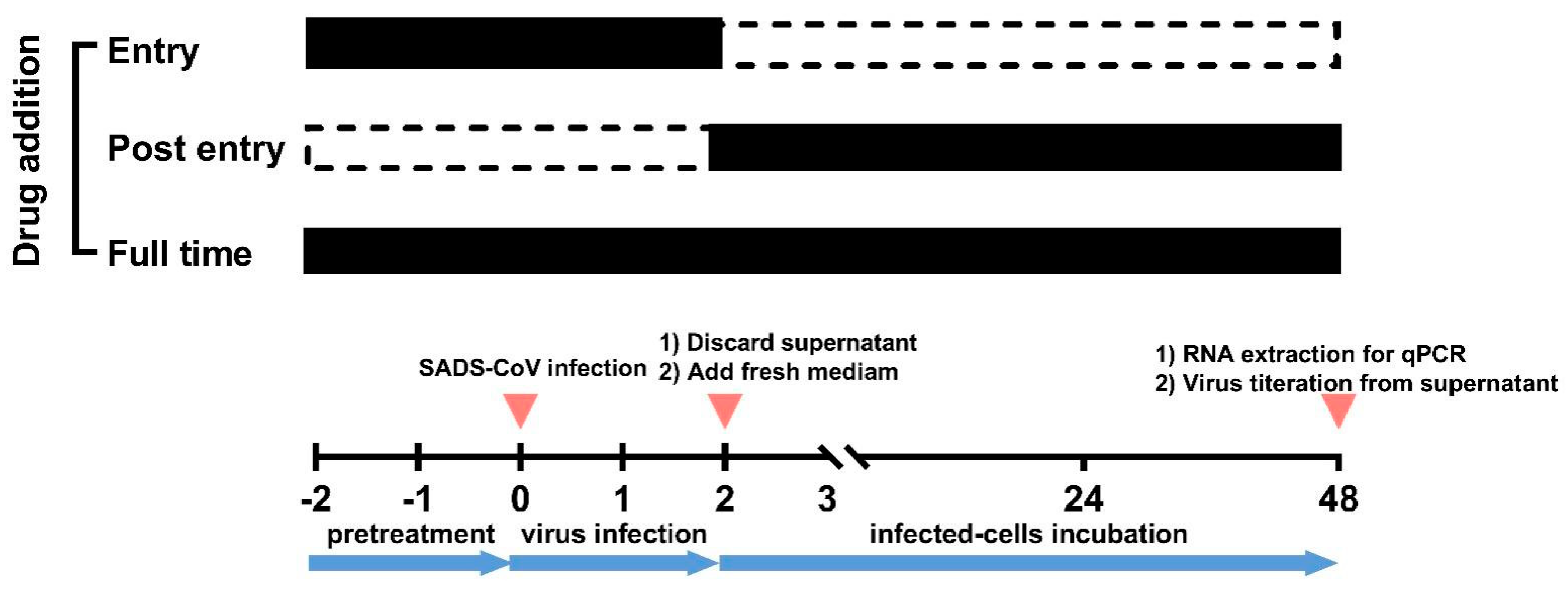
4.6. Time-of-Addition Assay
4.7. Plaque Assay and TCID50 Assay
4.8. Western Blotting
4.9. Virus Binding and Internalization Assay
4.10. Examination of Compounds Effect on Virus Entry
4.11. Virus Growth Kinetics Assay
4.12. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karim, S.; Karim, Q.A. Omicron SARS-CoV-2 variant: A new chapter in the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet 2021, 398, 2126–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Li, J.; Zhou, Q.; Xu, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, C.; Wen, Z.; Cao, Y. A New Bat-HKU2-like Coronavirus in Swine, China, 2017. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1607–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Vlasova, A.N.; Kenney, S.P.; Saif, L.J. Emerging and re-emerging coronaviruses in pigs. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2019, 34, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Fan, H.; Lan, T.; Yang, X.L.; Shi, W.F.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.W.; Xie, Q.M.; Mani, S.; et al. Fatal swine acute diarrhoea syndrome caused by an HKU2-related coronavirus of bat origin. Nature 2018, 556, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, H.; Wang, Y.; Perčulija, V.; Saeed, A.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Jan, S.S.; Li, Y.; Zhu, P.; Ouyang, S. Cryo-electron Microscopy Structure of the Swine Acute Diarrhea Syndrome Coronavirus Spike Glycoprotein Provides Insights into Evolution of Unique Coronavirus Spike Proteins. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e01301-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Qiao, S.; Guo, R.; Wang, X. Cryo-EM structures of HKU2 and SADS-CoV spike glycoproteins provide insights into coronavirus evolution. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Geng, R.; Li, B.; Chen, J.; Zhao, K.; Zheng, X.S.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, P.; Yang, X.L.; et al. Broad Cell Tropism of SADS-CoV In Vitro Implies Its Potential Cross-Species Infection Risk. Virol. Sin. 2021, 36, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.L.; Qin, P.; Wang, B.; Liu, Y.; Xu, G.H.; Peng, L.; Zhou, J.; Zhu, S.J.; Huang, Y.W. Broad Cross-Species Infection of Cultured Cells by Bat HKU2-Related Swine Acute Diarrhea Syndrome Coronavirus and Identification of Its Replication in Murine Dendritic Cells In Vivo Highlight Its Potential for Diverse Interspecies Transmission. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e01448-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, C.E.; Yount, B.L.; Graham, R.L.; Leist, S.R.; Hou, Y.J.; Dinnon, K.H., 3rd; Sims, A.C.; Swanstrom, J.; Gully, K.; Scobey, T.D.; et al. Swine acute diarrhea syndrome coronavirus replication in primary human cells reveals potential susceptibility to infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 26915–26925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.H.; Wang, L.Q.; Liu, W.L.; An, X.P.; Liu, Z.D.; He, X.Q.; Song, L.H.; Tong, Y.G. Repurposing of clinically approved drugs for treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 in a 2019-novel coronavirus-related coronavirus model. Chin. Med. J. 2020, 133, 1051–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, M.; Qin, H.; Lin, H.; An, X.; Shi, Z.; Song, L.; Yang, X.; Fan, H.; Tong, Y. Artemether, Artesunate, Arteannuin B, Echinatin, Licochalcone B and Andrographolide Effectively Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 and Related Viruses In Vitro. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 680127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- V’kovski, P.; Kratzel, A.; Steiner, S.; Stalder, H.; Thiel, V. Coronavirus biology and replication: Implications for SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailly, C. Cepharanthine: An update of its mode of action, pharmacological properties and medical applications. Phytomedicine 2019, 62, 152956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogosnitzky, M.; Okediji, P.; Koman, I. Cepharanthine: A review of the antiviral potential of a Japanese-approved alopecia drug in COVID-19. Pharmacol. Rep. 2020, 72, 1509–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabholkar, N.; Gorantla, S.; Dubey, S.K.; Alexander, A.; Taliyan, R.; Singhvi, G. Repurposing methylene blue in the management of COVID-19: Mechanistic aspects and clinical investigations. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 142, 112023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Lang, Y.; Sakamuru, S.; Samrat, S.; Trudeau, N.; Kuo, L.; Rugenstein, N.; Tharappel, A.; D’Brant, L.; Koetzner, C.A.; et al. Methylene blue is a potent and broad-spectrum inhibitor against Zika virus in vitro and in vivo. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 2404–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.J.; Kim, C.; Cho, S. Gemcitabine and Nucleos(t)ide Synthesis Inhibitors Are Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Drugs that Activate Innate Immunity. Viruses 2018, 10, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siebert, A.; Prejs, M.; Cholewinski, G.; Dzierzbicka, K. New Analogues of Mycophenolic Acid. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 734–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Duan, X.; Yang, L.; Nilsson-Payant, B.E.; Wang, P.; Duan, F.; Tang, X.; Yaron, T.M.; Zhang, T.; Uhl, S.; et al. Identification of SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors using lung and colonic organoids. Nature 2021, 589, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manchala, N.R.; Dungdung, R.; Trivedi, P.; Unniyampurath, U.; Pilankatta, R. Mycophenolic acid (MPA) modulates host cellular autophagy progression in sub genomic dengue virus-2 replicon cells. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 137, 103762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, J.; Parekh, H.K.; Ho, W. Mycophenolate mofetil inhibits hepatitis C virus replication in human hepatic cells. Virus Res. 2012, 168, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.; Yap, T.; Martyres, R.; Kern, J.S.; Varigos, G.; Scardamaglia, L. The association of mycophenolate mofetil and human herpes virus infection. J. Dermatolog. Treat. 2020, 31, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.E.; Min, J.S.; Jang, M.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Shin, Y.S.; Song, J.H.; Kim, H.R.; Kim, S.; Jin, Y.H.; Kwon, S. Natural Bis-Benzylisoquinoline Alkaloids-Tetrandrine, Fangchinoline, and Cepharanthine, Inhibit Human Coronavirus OC43 Infection of MRC-5 Human Lung Cells. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohashi, H.; Watashi, K.; Saso, W.; Shionoya, K.; Iwanami, S.; Hirokawa, T.; Shirai, T.; Kanaya, S.; Ito, Y.; Kim, K.S.; et al. Potential anti-COVID-19 agents, cepharanthine and nelfinavir, and their usage for combination treatment. iScience 2021, 24, 102367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, K.; Hattori, S.; Komizu, Y.; Kariya, R.; Ueoka, R.; Okada, S. Cepharanthine inhibited HIV-1 cell-cell transmission and cell-free infection via modification of cell membrane fluidity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 2115–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cagno, V.; Medaglia, C.; Cerny, A.; Cerny, T.; Zwygart, A.C.; Cerny, E.; Tapparel, C. Methylene Blue has a potent antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 and H1N1 influenza virus in the absence of UV-activation in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano, M.; Cid, J.; Müller, T.H. Plasma treated with methylene blue and light: Clinical efficacy and safety profile. Transfus. Med. Rev. 2013, 27, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Kim, D.E.; Jang, K.S.; Kim, S.J.; Cho, S.; Kim, C. Gemcitabine, a broad-spectrum antiviral drug, suppresses enterovirus infections through innate immunity induced by the inhibition of pyrimidine biosynthesis and nucleotide depletion. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 115315–115325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.N.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Li, X.D.; Xiong, J.; Xiao, S.Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.R.; Deng, C.L.; Yang, X.L.; Wei, H.P.; et al. Gemcitabine, lycorine and oxysophoridine inhibit novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) in cell culture. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 1170–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Niu, J.; Wang, C.; Huang, B.; Wang, W.; Zhu, N.; Deng, Y.; Wang, H.; Ye, F.; Cen, S.; et al. High-Throughput Screening and Identification of Potent Broad-Spectrum Inhibitors of Coronaviruses. J. Virol. 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnard, D.L.; Day, C.W.; Bailey, K.; Heiner, M.; Montgomery, R.; Lauridsen, L.; Winslow, S.; Hoopes, J.; Li, J.K.; Lee, J.; et al. Enhancement of the infectivity of SARS-CoV in BALB/c mice by IMP dehydrogenase inhibitors, including ribavirin. Antivir. Res. 2006, 71, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, F.; Matsuyama, S.; Kawase, M.; Hishiki, T.; Katoh, H.; Takeda, M. Antiviral activities of mycophenolic acid and IMD-0354 against SARS-CoV-2. Microbiol. Immunol. 2020, 64, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamba, V.; Sangkuhl, K.; Sanghavi, K.; Fish, A.; Altman, R.B.; Klein, T.E. PharmGKB summary: Mycophenolic acid pathway. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2014, 24, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Q.; de Ruiter, P.E.; Metselaar, H.J.; Kwekkeboom, J.; de Jonge, J.; Tilanus, H.W.; Janssen, H.L.; van der Laan, L.J. Mycophenolic acid augments interferon-stimulated gene expression and inhibits hepatitis C Virus infection in vitro and in vivo. Hepatology 2012, 55, 1673–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
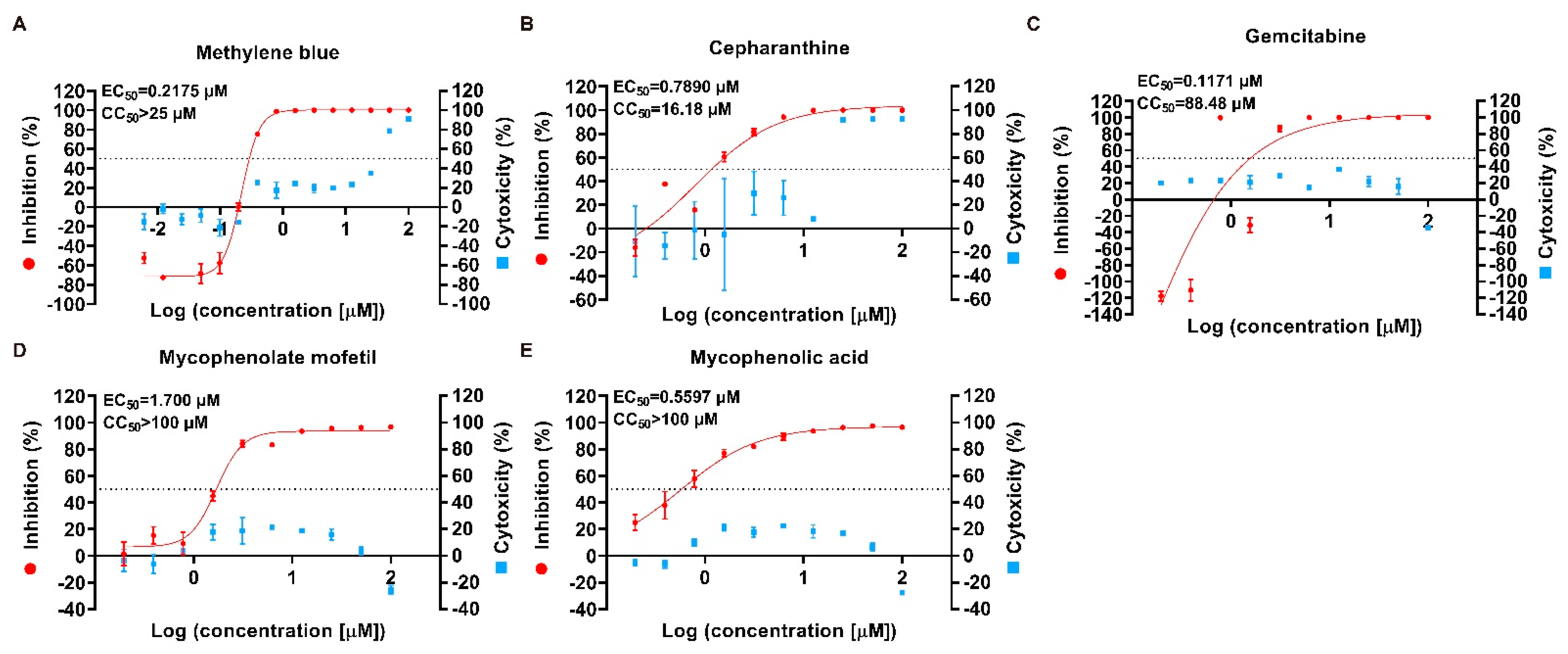

| Compound Name | CAS No. | Bioactivity | SADS-CoV | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC50 (μM) | CC50 (μM) | SI | |||
| Methylene blue | 61-73-4 | Antidote, disinfectant, antiviral | 0.2175 | >25 | >114.94 |
| Cepharanthine | 481-49-2 | Antiinflammatory, antineoplastic, antiviral | 0.789 | 16.18 | 20.51 |
| Gemcitabine | 95058-81-4 | Antineoplastic, antiviral | 0.1171 | 88.48 | 755.59 |
| Mycophenolate mofetil | 115007-34-6 | Immune suppressant, antineoplastic, antiviral | 1.7 | >100 | 58.82 |
| Mycophenolic acid | 24280-93-1 | Immune suppressant, antineoplastic, antiviral | 0.5597 | >100 | 178.67 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; You, Y.; Wang, S.; Jiang, L.; Tian, L.; Zhu, S.; An, X.; Song, L.; Tong, Y.; Fan, H. Antiviral Drugs Screening for Swine Acute Diarrhea Syndrome Coronavirus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11250. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911250
Chen Y, You Y, Wang S, Jiang L, Tian L, Zhu S, An X, Song L, Tong Y, Fan H. Antiviral Drugs Screening for Swine Acute Diarrhea Syndrome Coronavirus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(19):11250. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911250
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yangzhen, Yecheng You, Shuqi Wang, Lin Jiang, Lili Tian, Shaozhou Zhu, Xiaoping An, Lihua Song, Yigang Tong, and Huahao Fan. 2022. "Antiviral Drugs Screening for Swine Acute Diarrhea Syndrome Coronavirus" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 19: 11250. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911250
APA StyleChen, Y., You, Y., Wang, S., Jiang, L., Tian, L., Zhu, S., An, X., Song, L., Tong, Y., & Fan, H. (2022). Antiviral Drugs Screening for Swine Acute Diarrhea Syndrome Coronavirus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(19), 11250. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911250






