BST2, a Novel Inhibitory Receptor, Is Involved in NK Cell Cytotoxicity through Its Cytoplasmic Tail Domain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Cytoplasmic Tail of BST2 Has an ITIM Motif
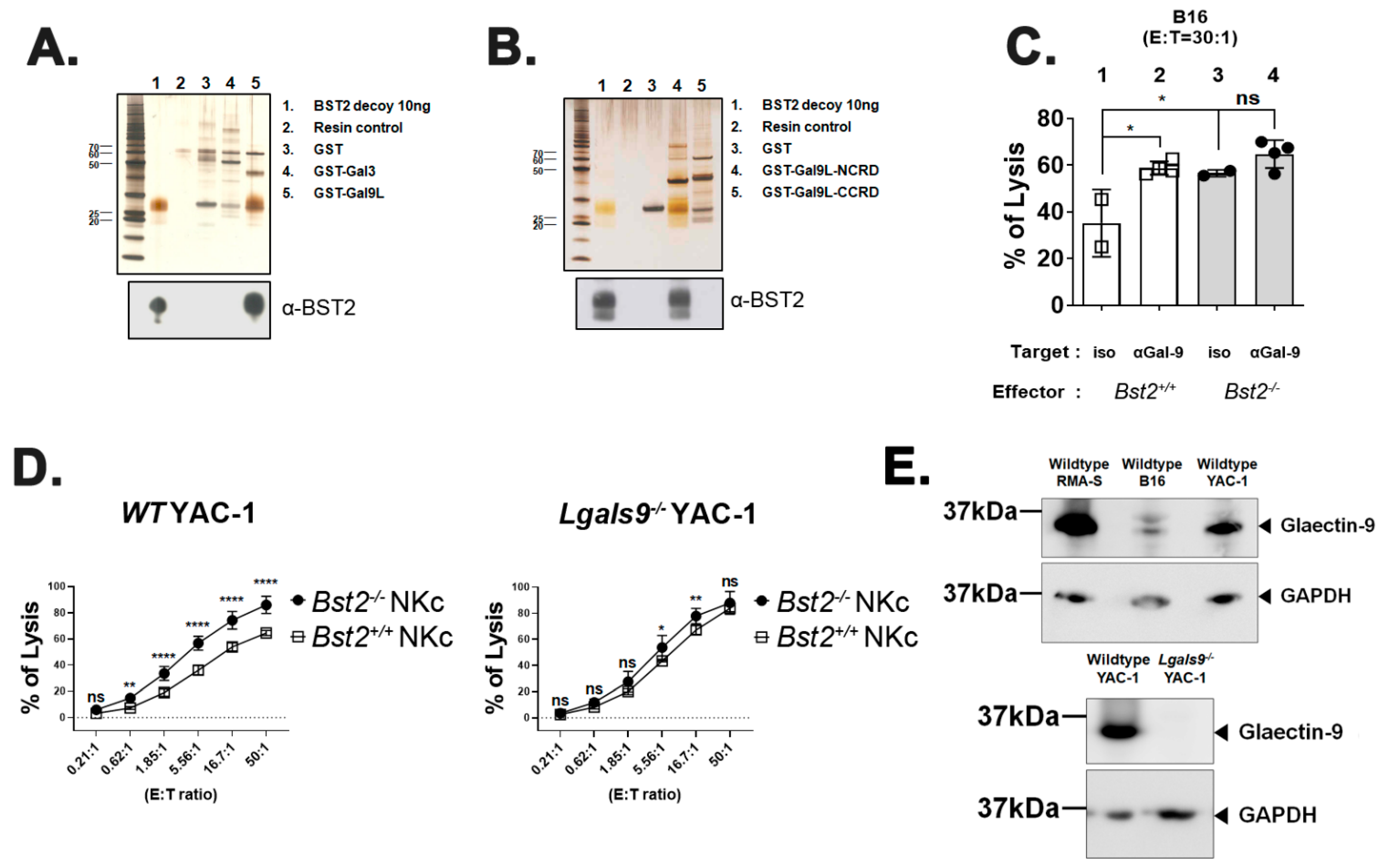
2.2. BST2 Can Bind to Galectin-8 and Galectin-9
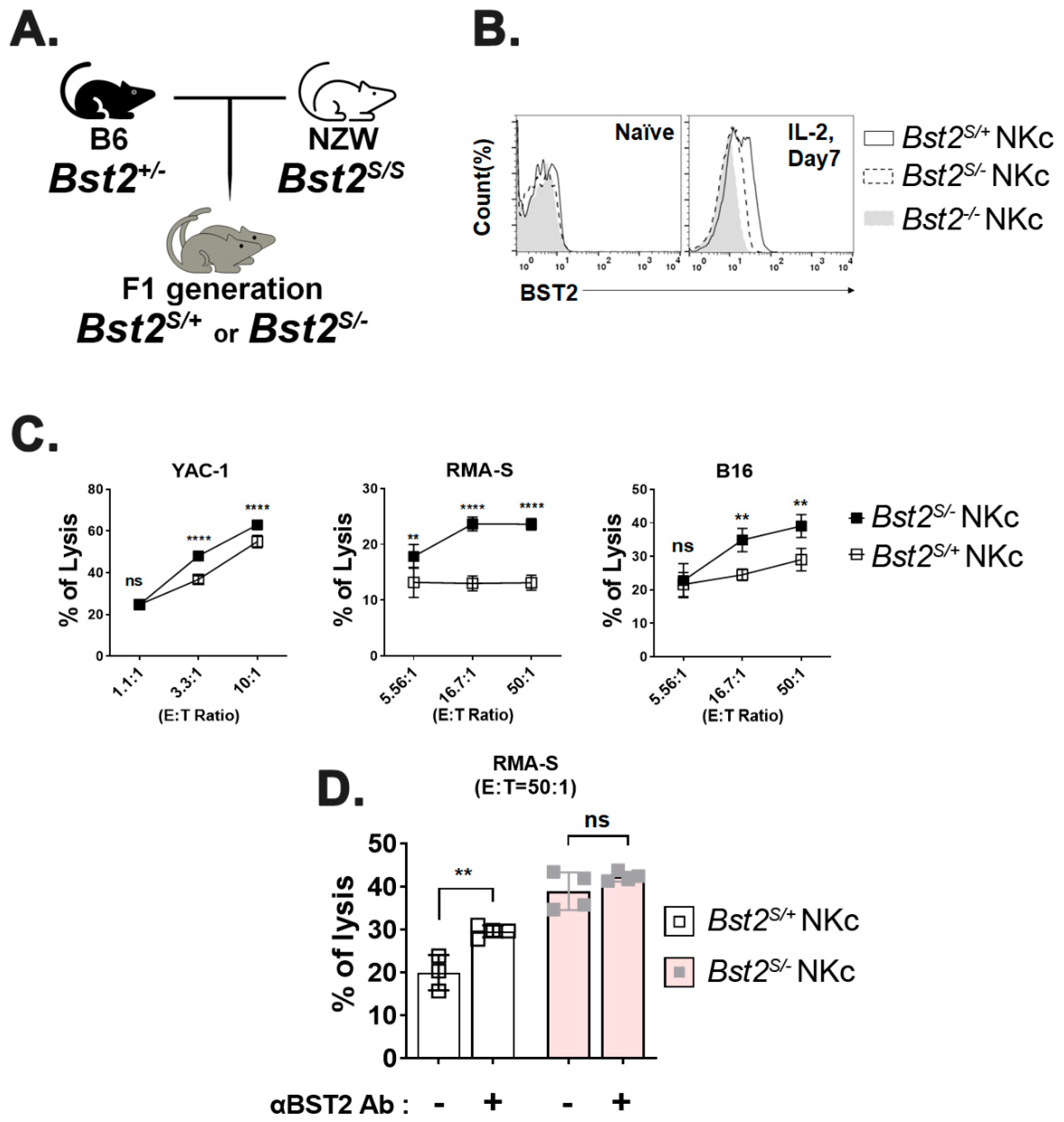
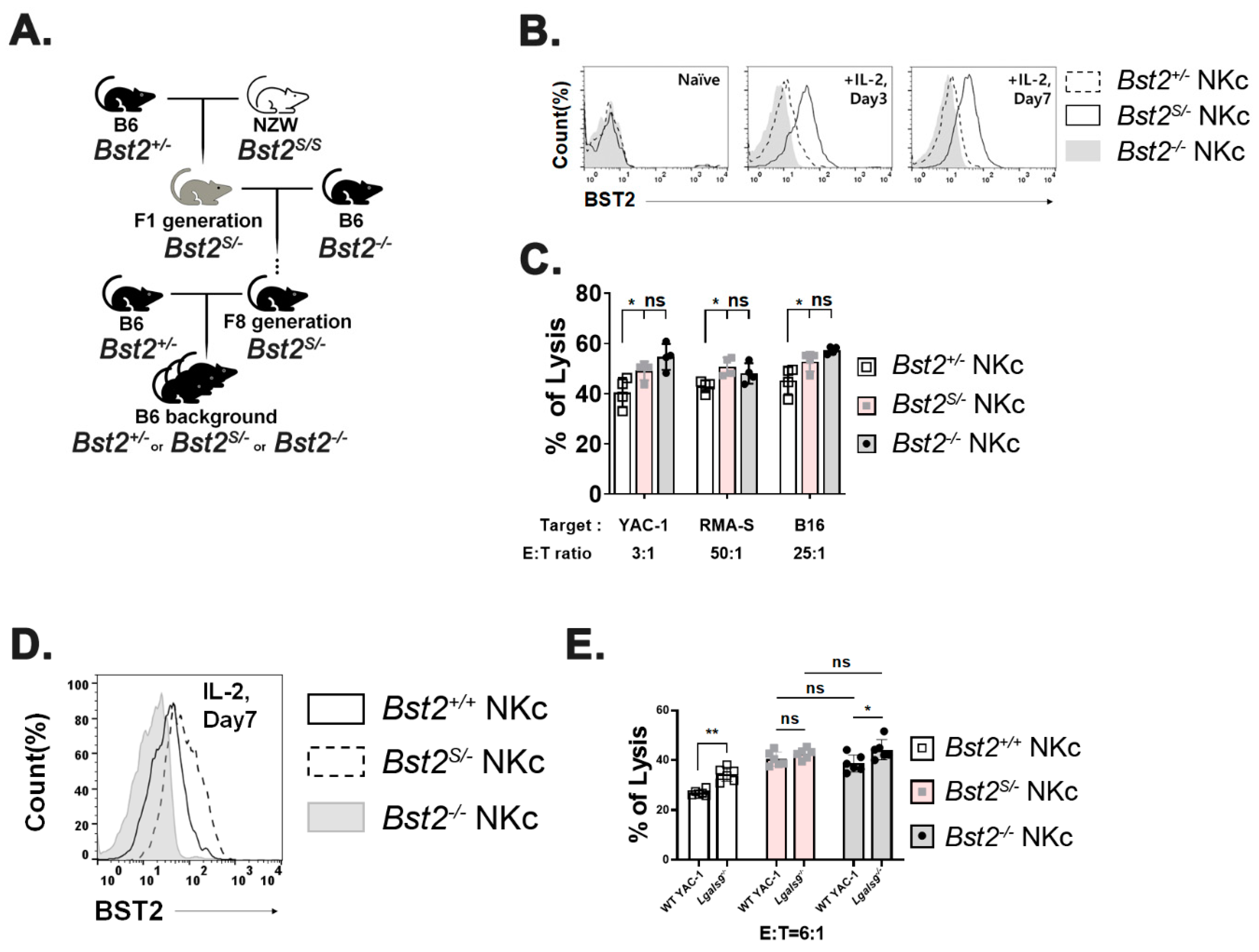
2.3. Long Isoform of BST2 Critically Downregulates the Cytotoxicity of NK Cells
2.4. Cytoplasmic Tail ITIM Motif in BST2 Is Involved in NK Cell Cytotoxicity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines and Mice
4.2. Cell Line Gene Knock out
4.3. Preparation of NK Cells
4.4. Preparation of OT1 Cells
4.5. Cytotoxic Assay
4.6. Flow Cytometry
4.7. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.8. Pull-Down Assay and Western Blot Analysis
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruiz, A.; Lau, D.; Mitchell, R.S.; Hill, M.S.; Schmitt, K.; Guatelli, J.C.; Stephens, E.B. BST-2 mediated restriction of simian-human immunodeficiency virus. Virology 2010, 406, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kupzig, S.; Korolchuk, V.; Rollason, R.; Sugden, A.; Wilde, A.; Banting, G. Bst-2/HM1.24 is a raft-associated apical membrane protein with an unusual topology. Traffic 2003, 4, 694–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocka, L.J.; Bates, P. Identification of alternatively translated Tetherin isoforms with differing antiviral and signaling activities. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, B.S.; Smith, D.S.; Li, S.X.; Guo, K.; Hasenkrug, K.J.; Santiago, M.L. A single nucleotide polymorphism in tetherin promotes retrovirus restriction in vivo. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galão, R.P.; Pickering, S.; Curnock, R.; Neil, S.J.D. Retroviral retention activates a Syk-dependent HemITAM in human tetherin. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 16, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, M.T.; Lanier, L.L. Natural killer cell education and tolerance. Cell 2010, 142, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, C.T.; Gamble, J.R.; Vadas, M.A.; Jackson, D.E. Recruitment and activation of SHP-1 protein-tyrosine phosphatase by human platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (PECAM-1). Identification of immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif-like binding motifs and substrates. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 28332–28340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daeron, M.; Jaeger, S.; Du Pasquier, L.; Vivier, E. Immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motifs: A quest in the past and future. Immunol. Rev. 2008, 224, 11–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandstadter, J.D.; Yang, Y. Natural killer cell responses to viral infection. J. Innate Immun. 2011, 3, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, C.A.; Laugier-Anfossi, F.; Vély, F.; Saulquin, X.; Riedmuller, J.; Tisserant, A.; Gauthier, L.; Romagné, F.; Ferracci, G.; Arosa, F.A.; et al. Recognition of peptide-MHC class I complexes by activating killer immunoglobulin-like receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 13224–13229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakoo, S.I.; Carrington, M. KIR and disease: A model system or system of models? Immunol. Rev. 2006, 214, 186–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, S.; Groh, V.; Wu, J.; Steinle, A.; Phillips, J.H.; Lanier, L.L.; Spies, T. Activation of NK cells and T cells by NKG2D, a receptor for stress-inducible MICA. Science 1999, 285, 727–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrow, A.D.; Martin, C.J.; Colonna, M. The Natural Cytotoxicity Receptors in Health and Disease. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prager, I.; Watzl, C. Mechanisms of natural killer cell-mediated cellular cytotoxicity. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2019, 105, 1319–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Antonio, B.; Suñe, G.; Perez-Amill, L.; Castella, M.; Urbano-Ispizua, A. Natural Killer Cells: Angels and Devils for Immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretta, L.; Ciccone, E.; Mingari, M.C.; Biassoni, R.; Moretta, A. Human natural killer cells: Origin, clonality, specificity, and receptors. Adv. Immunol. 1994, 55, 341–380. [Google Scholar]
- Wagtmann, N.; Rajagopalan, S.; Winter, C.C.; Peruzzi, M.; Long, E.O. Killer cell inhibitory receptors specific for HLA-C and HLA-B identified by direct binding and by functional transfer. Immunity 1995, 3, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlhofer, F.M.; Ribaudo, R.K.; Yokoyama, W.M. MHC class I alloantigen specificity of Ly-49+ IL-2-activated natural killer cells. Nature 1992, 358, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotte, A.; Jin, J.Y.; Lemaire, V. Mechanistic overview of immune checkpoints to support the rational design of their combinations in cancer immunotherapy. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, F.-C.; Chen, H.-Y.; Kuo, C.-C.; Sytwu, H.-K. Role of Galectins in Tumors and in Clinical Immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yu, Y.; Koehn, C.D.; Zhang, Z.; Su, K. Galectins in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Clin. Cell. Immunol. 2013, 4, 1000164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golden-Mason, L.; McMahan, R.H.; Strong, M.; Reisdorph, R.; Mahaffey, S.; Palmer, B.E.; Cheng, L.; Kulesza, C.; Hirashima, M.; Niki, T.; et al. Galectin-9 functionally impairs natural killer cells in humans and mice. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 4835–4845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Guo, H.; Geng, J.; Zheng, X.; Wei, H.; Sun, R.; Tian, Z. Tumor-released Galectin-3, a soluble inhibitory ligand of human NKp30, plays an important role in tumor escape from NK cell attack. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 33311–33319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.T.; Rabinovich, G.A. Galectins as modulators of tumour progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elola, M.; Ferragut, F.; Delgado, V.; Nugnes, L.; Gentilini, L.; Laderach, D.; Troncoso, M.; Compagno, D.; Wolfenstein-Todel, C.; Rabinovich, G. Expression, localization and function of galectin-8, a tandem-repeat lectin, in human tumors. Histol. Histopathol. 2014, 29, 1093–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staub, E.; Rosenthal, A.; Hinzmann, B. Systematic identification of immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motifs in the human proteome. Cell. Signal. 2004, 16, 435–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, A.D.; Trowsdale, J. You say ITAM and I say ITIM, let’s call the whole thing off: The ambiguity of immunoreceptor signalling. Eur. J. Immunol. 2006, 36, 1646–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemoto, Y.; Furuta, M.; Sato, M.; Kubo, M.; Hashimoto, Y. Isolation and characterization of a novel HS1 SH3 domain binding protein, HS1BP3. Int. Immunol. 1999, 11, 1957–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Taylor, V.C.; Buckley, C.D.; Douglas, M.; Cody, A.J.; Simmons, D.L.; Freeman, S.D. The myeloid-specific sialic acid-binding receptor, CD33, associates with the protein-tyrosine phosphatases, SHP-1 and SHP-2. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 11505–11512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Lostao, L.; Anel, A.; Pardo, J. How Do Cytotoxic Lymphocytes Kill Cancer Cells? Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 5047–5056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alter, G.; Malenfant, J.M.; Altfeld, M. CD107a as a functional marker for the identification of natural killer cell activity. J. Immunol. Methods 2004, 294, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-H.; Zhou, W.-H.; Tao, Y.; Wang, S.-C.; Jiang, Y.-L.; Zhang, D.; Piao, H.-L.; Fu, Q.; Li, D.-J.; Du, M.-R. The Galectin-9/Tim-3 pathway is involved in the regulation of NK cell function at the maternal–fetal interface in early pregnancy. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 13, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.X.; Barrett, B.S.; Heilman, K.J.; Messer, R.J.; Liberatore, R.A.; Bieniasz, P.D.; Kassiotis, G.; Hasenkrug, K.J.; Santiago, M.L. Tetherin promotes the innate and adaptive cell-mediated immune response against retrovirus infection in vivo. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.; Bover, L.; Cho, M.; Wen, X.; Hanabuchi, S.; Bao, M.; Rosen, D.B.; Wang, Y.-H.; Shaw, J.L.; Du, Q.; et al. Regulation of TLR7/9 responses in plasmacytoid dendritic cells by BST2 and ILT7 receptor interaction. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 1603–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivier, E.; Nunès, J.A.; Vély, F. Natural Killer Cell Signaling Pathways. Science 2004, 306, 1517–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orange, J.S. Formation and function of the lytic NK-cell immunological synapse. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, H.; Miyaji, M.; Kosugi, A.; Nagafuku, M.; Okazaki, T.; Mimori, T.; Amakawa, R.; Fukuhara, S.; Domae, N.; Bloom, E.T.; et al. Lipid rafts as the signaling scaffold for NK cell activation: Tyrosine phosphorylation and association of LAT with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and phospholipase C-γ following CD2 stimulation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2002, 32, 2188–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Tan, Y.; Fan, A.; Liao, Z.; Liu, H.; Wei, P. Molecular Dynamics of the Recruitment of Immunoreceptor Signaling Module DAP12 Homodimer to Lipid Raft Boundary Regulated by PIP2. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Pertierra, E.; Cernuda-Morollón, E.; Brdička, T.; Hoøejši, V.; López-Larrea, C. L-plastin is involved in NKG2D recruitment into lipid rafts and NKG2D-mediated NK cell migration. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2014, 96, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billcliff, P.G.; Rollason, R.; Prior, I.; Owen, D.M.; Gaus, K.; Banting, G. CD317/tetherin is an organiser of membrane microdomains. J. Cell Sci 2013, 126 Pt 7, 1553–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlén, M.; Fagerberg, L.; Hallström, B.M.; Lindskog, C.; Oksvold, P.; Mardinoglu, A.; Sivertsson, Å.; Kampf, C.; Sjöstedt, E.; Asplund, A.; et al. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science 2015, 347, 1260419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecoeur, H.; Février, M.; Garcia, S.; Rivière, Y.; Gougeon, M.-L. A novel flow cytometric assay for quantitation and multiparametric characterization of cell-mediated cytotoxicity. J. Immunol. Methods 2001, 253, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neri, S.; Mariani, E.; Meneghetti, A.; Cattini, L.; Facchini, A. Calcein-acetyoxymethyl cytotoxicity assay: Standardization of a method allowing additional analyses on recovered effector cells and supernatants. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2001, 8, 1131–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, H.; Park, S.H.; Ye, S.K.; Kim, M. IFN-gamma-induced BST2 mediates monocyte adhesion to human endothelial cells. Cell. Immunol. 2011, 267, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, F.; Seip, N.; Maertens, B.; Block, H.; Kubicek, J. Chapter Nine—Purification of GST-Tagged Proteins. In Methods in Enzymology; Lorsch, J.R., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; Volume 559, pp. 127–139. [Google Scholar]


| Gene | Species | Amino acid Sequence Alongside ITIM Motif | ITIM Tyrosine Residue | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BST2 | Human | MASTSYDYCRVPMEDGDKRC… | Y8 | |
| Bst2 | Mouse | MAPSFYHYLPVPMDEMGGKQGWGS… | Y6 | |
| Hs1bp3 | Mouse | …GHVEYQILVVTR…VSKKYSEIEEFYQKLSSRY… | Y41, Y71, Y78 | [28] |
| CD33 | Human | …ELHYASLNFH…STEYSEVRTQ | Y340, Y358 | [29] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, J.; Yi, E.; Jeong, S.K.; Park, S.; Park, S.-H. BST2, a Novel Inhibitory Receptor, Is Involved in NK Cell Cytotoxicity through Its Cytoplasmic Tail Domain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11395. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911395
Oh J, Yi E, Jeong SK, Park S, Park S-H. BST2, a Novel Inhibitory Receptor, Is Involved in NK Cell Cytotoxicity through Its Cytoplasmic Tail Domain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(19):11395. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911395
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Jinsoo, Eunbi Yi, Soo Kyung Jeong, Sehoon Park, and Se-Ho Park. 2022. "BST2, a Novel Inhibitory Receptor, Is Involved in NK Cell Cytotoxicity through Its Cytoplasmic Tail Domain" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 19: 11395. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911395
APA StyleOh, J., Yi, E., Jeong, S. K., Park, S., & Park, S.-H. (2022). BST2, a Novel Inhibitory Receptor, Is Involved in NK Cell Cytotoxicity through Its Cytoplasmic Tail Domain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(19), 11395. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911395




