Abstract
The emetic type of foodborne disease caused by Bacillus cereus is produced by the small peptide toxin cereulide. The genetic locus encoding the Ces nonribosomal peptide synthetase (CesNRPS) multienzyme machinery is located on a 270 kb megaplasmid, designated pCER270, which shares its backbone with the Bacillus anthracis toxin plasmid pXO1. Although the ces genes are plasmid-borne, the chromosomally encoded pleiotropic transcriptional factors CodY and AbrB are key players in the control of ces transcription. Since these proteins only repress cereulide synthesis during earlier growth phases, other factors must be involved in the strict control of ces expression and its embedment in the bacterial life cycle. In silico genome analysis revealed that pCER270 carries a putative ArsR/SmtB family transcription factor showing high homology to PagR from B. anthracis. As PagR plays a crucial role in the regulation of the protective antigen gene pagA, which forms part of anthrax toxin, we used a gene-inactivation approach, combined with electrophoretic mobility shift assays and a bacterial two-hybrid system for dissecting the role of the PagR homologue PagRBc in the regulation of cereulide synthesis. Our results highlight that the plasmid-encoded transcriptional regulator PagRBc plays an important role in the complex and multilayered process of cereulide synthesis.
Keywords:
Bacillus cereus; pagR; cereulide; transcription factor; homologue; Bacillus anthracis; toxins 1. Introduction
Bacillus cereus is a major causative agent of two distinct forms of gastroenteritis diseases linked to food poisoning—emesis and diarrhea—as well as extra-intestinal infections, including endocarditis, endophthalmitis, and septicemia [1,2,3,4,5].
Most of the virulence factors of B. cereus, such as the diarrhea-causing enterotoxins, are located on the chromosome, while the ces genes – that are encoding the non-ribosomal peptide synthetase CesNRPS for the assembly of the emetic toxin cereulide—are located on a 270 kb plasmid pCER270. The megaplasmid pCER270 shares its origin of replication and its backbone with plasmid pXO1 from Bacillus anthracis [6,7]. The conserved state of pXO1 and pXO1-like plasmids is thought to reflect the relatively recent evolution of B. anthracis from a parental B. cereus subgroup [8]. The 182 kb pXO1 plasmid carries the anthrax toxin genes cya, lef and pagA as well as their major regulators pagR and atxA [2,9]. AtxA is known to act as the master virulence regulator in B. anthracis, exerting positive control on the anthrax toxin genes as well as the biosynthetic operon for the capsule synthesis, encoded on a second virulence plasmid pXO2 [10,11,12,13,14]. The weak autorepressor pagR, which is co-transcribed with pagA, acts in a complex signal-transduction cascade that controls the expression of virulence factors [15,16]. PagR exerts its negative control on pagA by directly binding to the pagAR promoter and is also involved in the transcriptional regulation of the chromosomally encoded S-layer genes sap and eag [15].
While considerable progress has been achieved in dissecting the regulatory circuits of anthrax toxin production in B. anthracis, much less is known about the regulation of cereulide toxin biosynthesis in emetic B. cereus. The ces locus consists of seven coding sequences (CDSs), the individually transcribed cesH and the polycistronically transcribed cesPTABCD gene cluster [17,18,19,20]. cesH encodes a putative hydrolase, cesP encodes a 4′-phosphopanthetheinyl transferase (PPTase) responsible for the activation of CesNRPS (nonribosomal peptide synthesis), cesT is a type-II thioesterase (TEII) with a proofreading function, cesAB encodes the structural cereulide synthetase genes and cesCD encodes an ABC transporter, recently shown to be directly involved in the tethering of the CesNRPS to the membrane [21]. The polycistronic transcription of cesPTABCD, which is driven by the main ces promoter P1, is strictly regulated and tightly linked to the physiological status of the cell [17,22,23,24].
In previous studies, knockout mutagenesis has shown that the transcriptional regulator PlcR, which is known to play a central role in the pathology of enterotoxigenic B. cereus [25], was not involved in the regulation of the emetic toxin cereulide [26]. However, the synthesis of cereulide is controlled by the Spo0A phosphorelay [26] and CodY [22]. In the early growth stages, the chromosomally encoded AbrB binds to the cesP promoter region and represses the ces transcription until abrB transcription is ceased by Spo0A [26]. Furthermore, CodY has been described to act as a master regulator interlinking synthesis of the emetic toxin and enterotoxins with the general metabolism [22]. However, since CodY, as well as AbrB, are only repressing cereulide synthesis during the earlier growth phases, other factors have to be involved in the strict control of ces expression during the bacterial life cycle. Indeed, it has been reported that CesH, which is part of the ces locus, is taking part in the transcriptional control of cereulide synthesis [20,27]. Since cesH transcription is upregulated at a later growth phase than the ces operon, CesH may contribute indirectly to the shutdown of ces mRNA synthesis after entering the stationary phase by degrading metabolites or signaling molecules. The direct action of CesH as a transcription factor is unlikely because it encodes for a bona fide hydrolase [27].
In silico search for putative transcription factors encoded on the megaplasmid pCER270 in emetic B. cereus revealed two ArsR/SmtB family members, showing high sequence similarity with PagR from B. anthracis. The ArsR/SmtB family is widely distributed throughout non-pathogenic and pathogenic bacteria including Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa or Mycobacterium tuberculosis [28]. Members of the ArsR/SmtB protein family act primarily as prokaryotic transcriptional repressors, which regulate the expression of genes associated with metal(loid) sequestration or efflux in Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria [29,30]. Originally, ArsR/SmtB family members were described as metalloregulators and named after their founding members, the regulatory protein ArsR of the plasmid-encoded arsenical resistance operon in Escherichia coli and SmtB, which represses the transcription of a class II metallothionein gene smtA in Synechococcus PCC7942 [31,32]. Despite the original described function of ArsR/SmtB family in metal sensing and metal homeostasis, other ArsR/SmtB family members show a broad variety of regulatory functions, such as in symbiosis, biofilm formation, stress response and virulence [28]. For instance, ArsR/SmtB transcriptional regulators involved in the control of virulence factors have been described in Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Rv2034), Vibrio cholera (HlyU) and B. anthracis (PagR), [33,34,35]. Despite their diverse regulatory functionality, the ArsR/SmtB family shows a common tertiary structure consisting of five α-helices (α1-α5) and a typical hairpin flanked by the two anti-parallel β-sheets (β1 and β2), which enable homodimer formation [30].
In this study, we aimed at deciphering the potential role of the two PagR homologous ArsR/SmtB family transcriptional factors located on the pCER270 plasmid for cereulide bio-synthesis in emetic B. cereus. A gene-inactivation approach combined with electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSA) and a bacterial adenylate cyclase-based two-hybrid system (BACTH) allowed us to identify the first plasmid-encoded transcriptional regulator involved in the control of cereulide synthesis. This permitted us to gain further insights into the mechanisms orchestrating the interplay between chromosomally and plasmid-encoded factors controlling cereulide synthesis.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Identification of PagR-like ArsR/SmtB Family Regulators on the pCER270 Plasmid
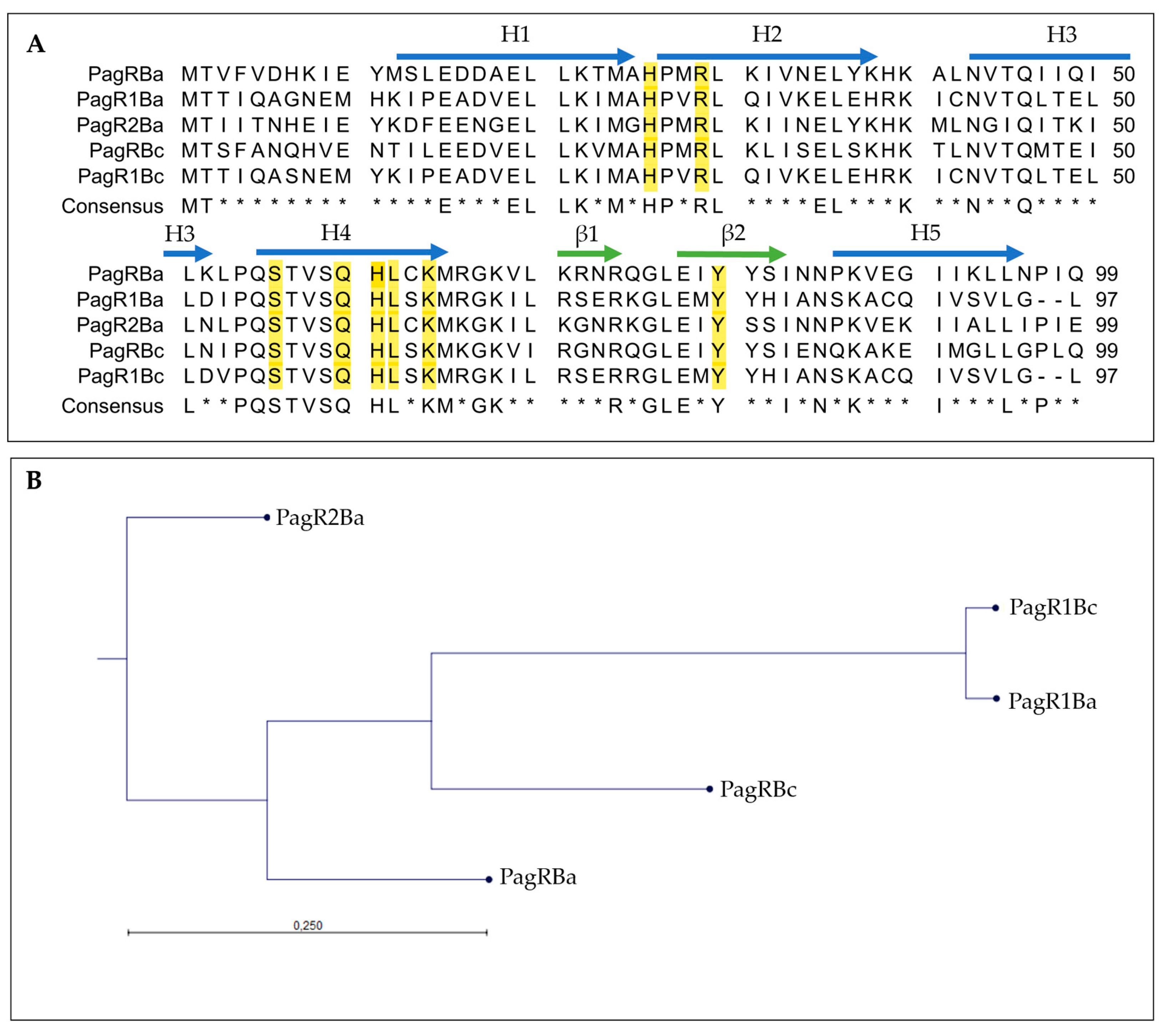
We carried out an in silico analysis of the pCER270 sequence (GenBank accession number: DQ889676.1) to identify plasmid-encoded transcription factors potentially involved in the control of ces expression. We found two genes, BCAH187_RS28375 and BCAH187_RS28695, predicted to encode ArsR/SmtB family proteins, which we designated pagRBc and pagR1Bc, respectively. BCAH187_RS28375 and BCAH187_RS28695 are encoded on the sense strand, while des ces gene cluster cesHPTABCD is encoded on the anti-sense strand of pCER270 (see Supplementary Figure S1). The distance between the ces genes cluster and pagRBc is 102.5 kb, while pagR1Bc is located at a distance of 22 kb to the ces genes. Although pagRBc and pagR1Bc show sequence homology, there are no homologous genes found in their proximities (for details of the genetic pagR loci, see Supplementary Figure S2). However, a BlastP search revealed that PagRBc (YP_002335935.1) and PagR1Bc (ACJ82764.1) of emetic B. cereus show high similarity with B. anthracis PagR (PagRBa) and its homologues encoded on the B. anthracis virulence plasmids pXO1 (designated PagR1Ba) and pXO2 (designated PagR2Ba) (Figure 1A). The three-dimensional structure of PagR has been solved by multi-wavelength anomalous diffraction (MAD) and it was demonstrated that PagR bears the typical characteristics of an ArsR/SmtB family member, such as dimeric structure and a winged helix–turn–helix (HTH) DNA-binding domain, but lacks the classical metal-binding motifs [33]. A comparison of B. anthracis PagR and the PagR homologues of the emetic B. cereus and B. anthracis revealed that two specific protein motifs, “PQSTVSQHL” and “GLE”, are conserved in all PagR homologues (Figure 1A). The first motif represents the DNA recognition sequence α-helix α4 (also known as αR), ensures contact with the major groove of DNA and mediates protein–DNA interactions. The α4 is highly conserved and characteristic for the ArsR/SmtB family members [28]. Further, the three residues S56, Q60 and L62 in α4 of PagR are thought to interact with the DNA major groove [33]. The second motif, “GLE”, is located between the two β-sheets β1 and β2, forming a hairpin structure. Notably, the latter motif is also found in CadC, the transcriptional regulatory protein of the cadmium resistance system of S. aureus and Listeria monocytogenes [29]. In silico analysis of the protein sequences revealed that the residues, which are known to be crucial for DNA interactions of ArsR/SmtB repressors, are present in all PagR homologues (Figure 1A), indicating that these proteins are indeed ArsR/SmtB family members with yet to explore functionalities. With the exception of PagR2Ba, the residue Y81, which has been reported recently to be important for DNA binding of target gene promoters [36] and to be a potential tyrosine kinase phosphorylation site in PagR [16], is conserved in all PagR homologues. It is thus tempting to speculate that the PagR homologues share common molecular mechanisms.
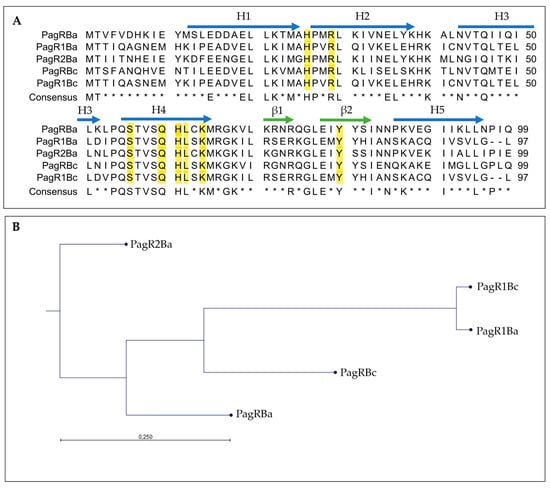
Figure 1.
Amino acid sequence analysis of B. anthracis PagR (PagRBa) and its homologues on plasmids pXO1, pXO2 and pCER270. (A): Multiple sequence alignment of PagR homologues in emetic B. cereus and B. anthracis. The protein sequences of PagRBc (YP_002335935.1) from the emetic reference strain B. cereus F4810/72 and PagR1Bc (ACJ82764.1) were aligned to the two PagR protein sequences of B. anthracis Sterne encoded on pXO1 (PagR and PagR1) and the PagR homologue of B. anthracis Pasteur PagR2 encoded on pXO2 (for details of genome location, see Supplementary Figure S2). Sequences were retrieved from NCBI GenBank as follows: PagRBa (WP_000215715.1), PagR1Ba (AAD32441.1) and PagR2Ba (AJH31838.1). The consensus sequence is shown as identical amino acid residues in all PagRs in capital letters. Residues essential for DNA binding and physiological protein structure are highlighted in yellow [33]. Alpha helices (H1 to H5) are labelled with blue arrows and β-Sheets (β1 and β2) are labelled with green arrows. Asterisks * indicates amino acids not conserved in all sequences. (B): Protein similarity tree of the different PagR homologues based on the amino acid sequences of homologues from B. cereus (abbreviation: Bc) and B. anthracis (abbreviation: Ba) was calculated. The tree was constructed with the neighbor-joining method employing CLC Workbench Qiagen software. The Jukes–Cantor model was used for protein distance measurements.
Overall, PagR1Bc and PagR1Ba show the highest similarity among the PagR homologues, while PagR2Ba was found to be the most distantly related PagR homologue (Figure 1B). PagR1Bc and PagR1Ba differ only in four amino acid residues. Since these changes in the primary structure are located before or after the α-helices α1 to α5 and the β-sheets β 1 and β 2, it is tempting to speculate that both proteins are identical or very similar in their functional characteristics. The high similarity between PagR1Bc and PagR1Ba was also pinpointed by the results from a pairwise sequence alignment of PagR homologues performed by the Emboss Needle Algorithm to show an optimal sequence alignment consisting of identity, similarity, score and gaps (Supplementary Figure S3). This analysis revealed an identity of 95.9% and a similarity of 99.0% of PagR1Bc to PagR1Ba, while PagRBc and PagR1Bc only share an identity of 54.5% and a similarity of 73.7%. Interestingly, PagRBc showed the highest identity (63.6%) and similarity (78.8%) to PagRBa, which indicates that PagRBc might be a functional homologue of PagRBa.
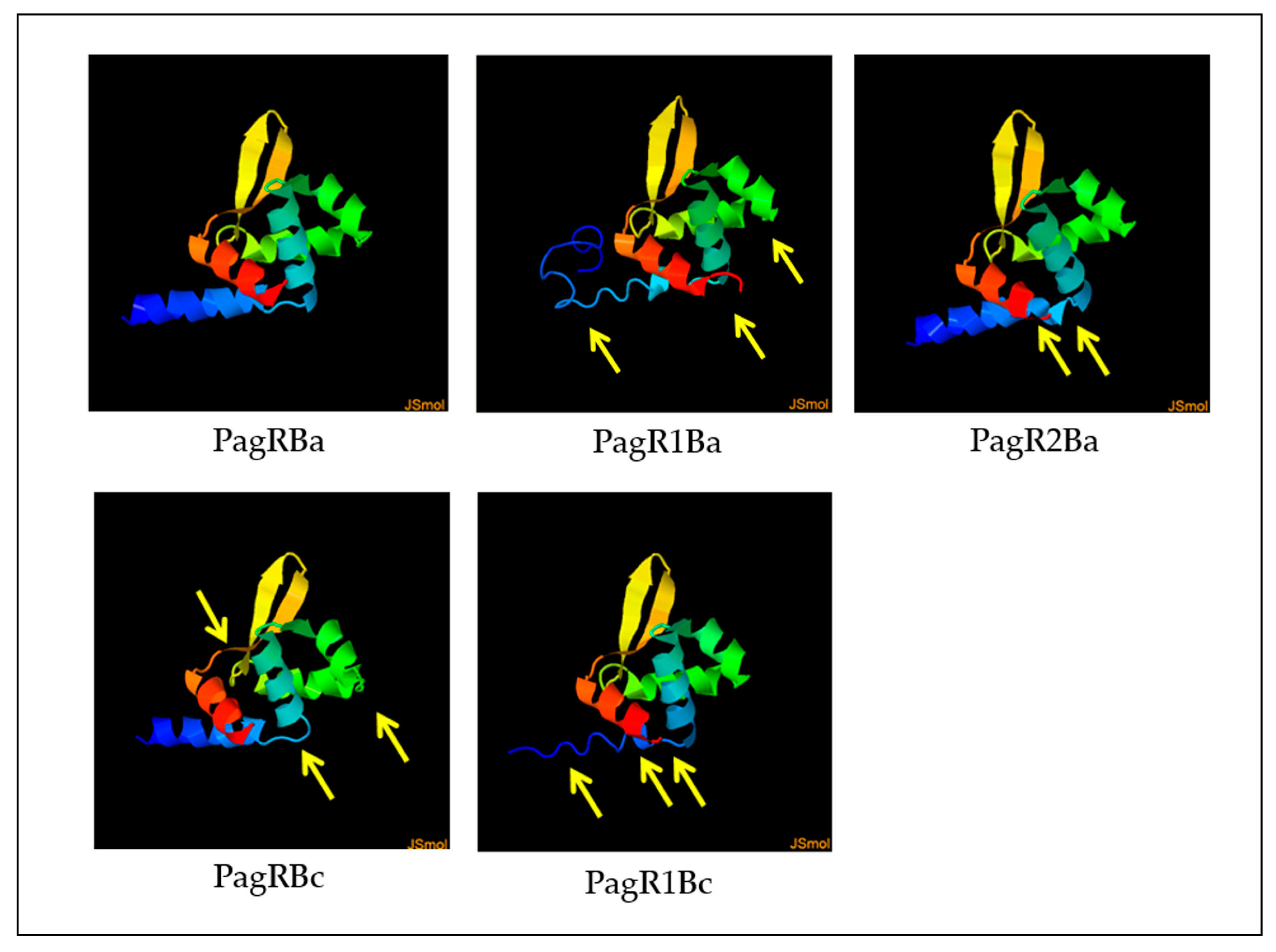
We next employed the Phyre2 online tool [37] to construct predictive 3D models of PagR homologues, based on the crystal protein structure and a 3D model of PagR (PagRBa) of B. anthracis [33]. As depicted in Figure 2, all PagR homologues show similar 3D structures resembling the typical architecture of ArsR/SmtB family transcription repressors, which leads to the unique structural folding of family members in the following order α1α2α3α4β1β2α5 [29,30]. However, while PagRBa, PagRBc and PagRBa2 are predicted to form all five α-helices (α1-α5) and the typical hairpin flanked by the two antiparallel β-sheets β1 and β2, the α1 helix seems to be only partially conserved in PagR1Ba and PagR1Bc.

Figure 2.
Predictive 3D protein models of PagR homologues. Structure models were constructed by the Phyre2 online tool, based on the crystal structure of PagR from B. anthracis [33]. Differences in protein folding are marked with yellow arrows of PagR homologues of emetic reference strain B. cereus F4810/72 and B. anthracis Sterne. Designations of PagR homologues as shown in Figure 1.
2.2. In Vitro Binding of PagR Homologues to the ces Promoter Region
Since PagR is a DNA binding protein that exerts negative control of pagAR transcription in B. anthracis by direct binding to the pagAR promoter [16], we investigated the binding affinity of His6-tagged B. cereus PagR homologues (PagRBc, PagR1Bc) and the original His6-tagged PagR from B. anthracis (PagRBa) to the main promoter region of the ces operon in emetic B. cereus.
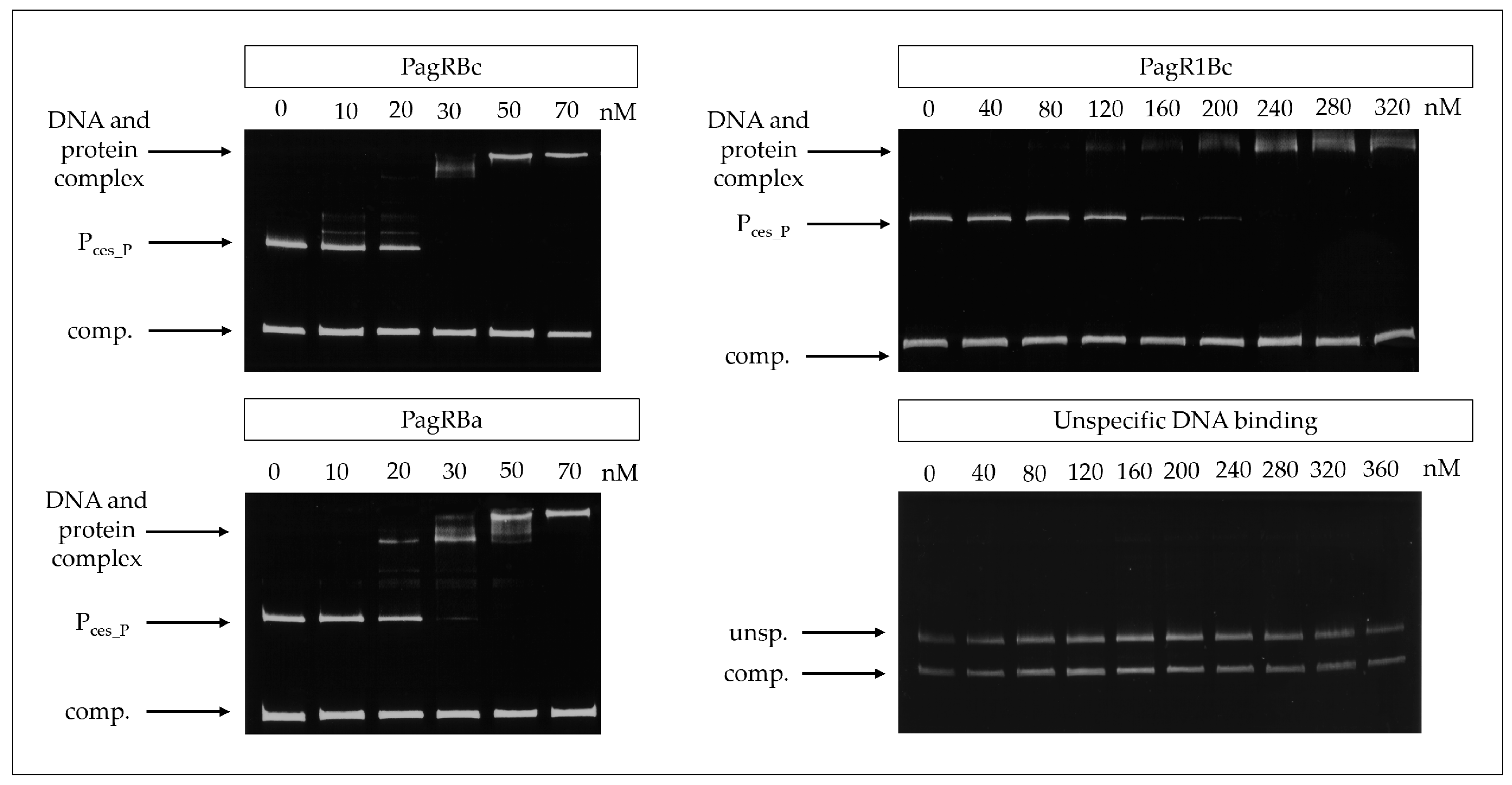
For this, PagRBa, PagRBc, and PagR1Bc were heterologously expressed in Escherichia coli and the DNA-binding affinity of the purified proteins to the main ces promoter was tested by an electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA). The promoter of the S-layer protein Eag, which is one of the main targets for PagR in B. anthracis [15], served as a positive control. Randomly amplified DNA fragments from emetic B. cereus F4810/72 served as a negative control. All three PagRs were able to bind the cesP probe containing the main ces promoter, while no specific interaction was observed within the unspecific DNA fragments (Figure 3). The highest binding affinity for the ces promoter was observed for PagRBc and PagRBa with an estimated equilibrium constant KD of about 25 nM, whereas the binding of PagR1Bc was about six-fold weaker (KD ≈ 150 nM). Notably, PagRBa and PagRBc showed a comparable binding affinity for the eag promoter of B. anthracis and emetic B. cereus (KD of 20 to 25 nM), whereas the binding affinity of PagR1Bc to the eag promoter was much weaker (Supplementary Figure S4). Furthermore, our in vitro binding studies revealed that PagRBa as well as PagRBc formed two distinct protein–DNA complexes of different sizes, with an increase of the slower migrating complex at higher concentration of PagRBc and PagRBa, respectively (Figure 3 and Supplementary Figure S4). Previously, it has been reported that S. aureus CadC forms two protein–DNA complexes of different sizes. In line with our current findings, a shift to the higher molecular complex was observed with increasing amounts of CadC, possibly reflecting the binding of a second dimer to the DNA and the formation of a tetramer [38]. Although it has been reported that the binding of PagR dimers only covers 2.5 helical turns [33], it is known from DNase footprinting data that PagR binds to protect the DNA regions from the transcription at a length of nearly five helical turns [15]. Thus, it is tempting to speculate that PagR and its homologues may form tetrameric protein-DNA complexes to protect DNA regions from transcription in vivo. However, further studies, which are clearly beyond the scope of the current study, will be necessary to fully understand these highly dynamic and complex protein-DNA interactions.

Figure 3.
Gel mobility shift assay to determine the in vitro affinity of PagR homologues (PagRBc, PagR1Bc and PagRBa) to the ces gene promoter region of emetic B. cereus. The PagR homologues’ potential to bind to the ces promoter (Pces_P) was conducted in vitro using different amounts (0 nM up to 360 nM) of DNA comprising the promoter region of the ces operon or equimolar amounts of a competitive negative control DNA fragment (comp.), respectively. PagR concentrations are indicated in nM concerning the monomer on the top of each panel. Specificity of binding was further tested by using randomly amplified DNA from B. cereus (unsp.) with the competitive negative control DNA fragment (comp.) and increasing concentrations of purified PagR1Bc (lower right panel). A representative result from three independent experiments is shown.
Overall, our experiments demonstrate that PagRBc binds to the main promoter of the ces operon in vitro, suggesting that PagRBc may act as a transcriptional regulator of the cereulide synthetase gene cluster. Furthermore, the similar binding affinities of PagRBa and PagRBc for the ces and the eag promoter foster the hypothesis that these two proteins are not only structurally but also functionally homologues. Thus, we next invested their protein–protein interactions.
2.3. Interactions of PagR Homologues Identified by a Bacterial Two-Hybrid Assay
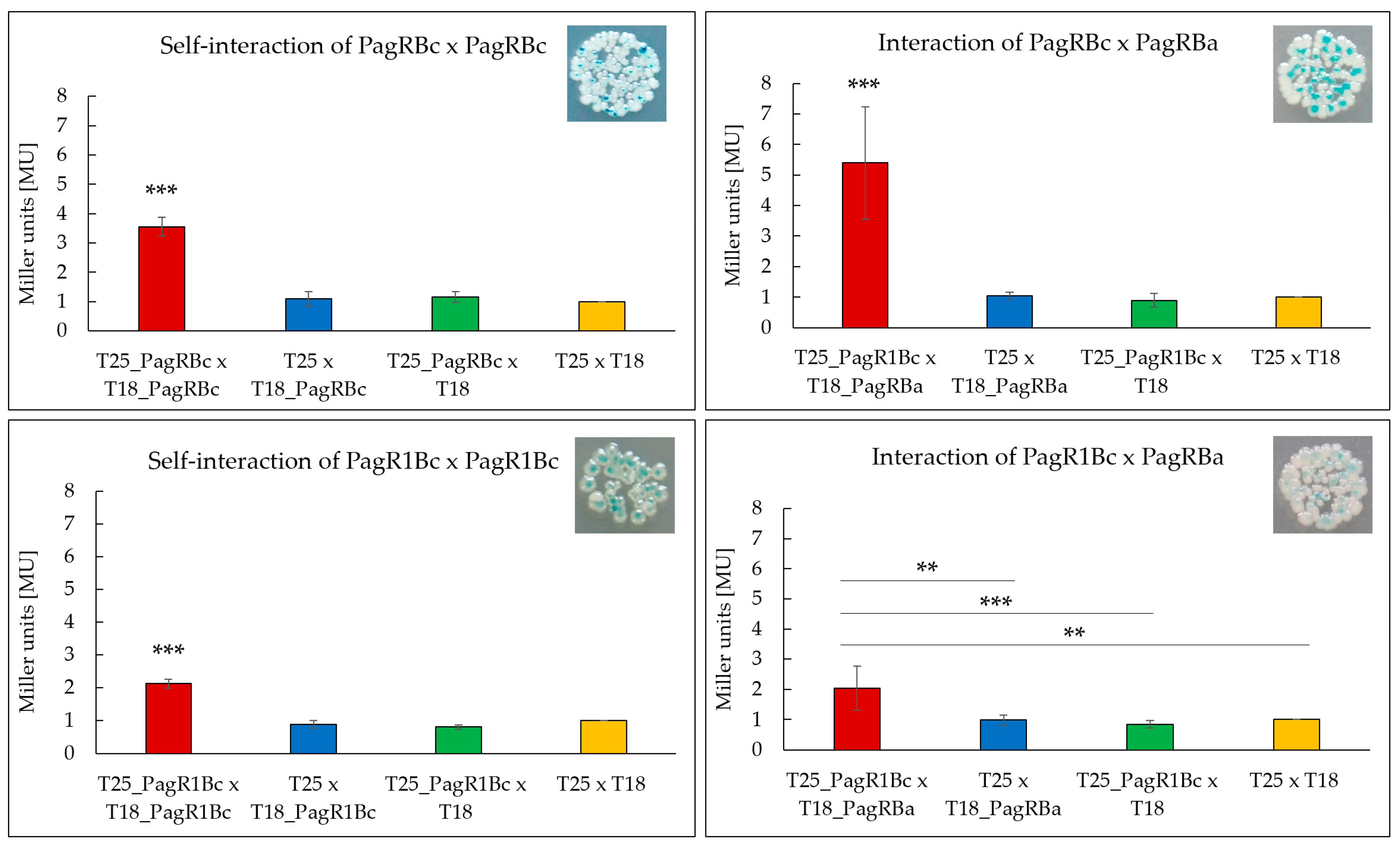
To test the ability of the B. cereus PagR homologues to form homodimers, which are the characteristic features of ArsR/SmtB family repressors [30], we used a bacterial adenylate cyclase-based two-hybrid system (BACTH) that allows testing protein interactions in vivo [39]. Both B. cereus PagR homologues were co-expressed with N-terminal and C-terminal fusions to the adenylate cyclase (cya) fragments T18 and T25, respectively, and tested for the formation of blue colonies on X-Gal/IPTG agar plates, thereby indicating protein interactions. To determine the affinity of the protein interactions, the enzymatic activity of β-galactosidase was additionally quantified in bacterial extracts by using the Miller Assay [40]. As depicted in Figure 4, the self-interaction of PagRBc was about 1.75-fold stronger than the self-interaction of PagR1Bc. The comparably weaker self-interaction of PagRBc might be explained by the lack of a folded α-helix α1 (Figure 2). Helices α1 and α5 have been reported to build the core of the binding surface for PagR dimers [33], which is crucial for the correct positioning of the α4 (=αR) helix for protein–DNA interaction.
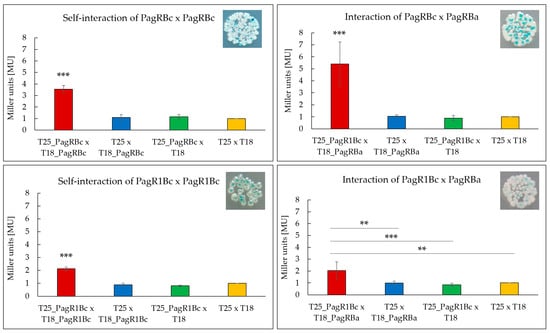
Figure 4.
Screening of interacting PagR homologues of emetic B. cereus F4810/72 and B. anthracis Sterne strain by a Bacterial Two-Hybrid System Assay (BACTH assay). Self-interactions of the PagR proteins PagRBc and PagR1Bc are shown as well as the interactions of PagRBc × PagRBa and PagR1Bc × PagRBa. The efficacies of complementation between the indicated hybrid proteins were quantified by β-galactosidase assay (in Miller units [MU]). A color change to blue of the colonies indicates an interaction, respectively. Representative results from three independent experiments are shown, respectively. Statistically significant differences between the sample compared to the three controls are denoted as follows: ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
In addition, we expressed pagRBa fused to the N-terminal cya fragment T18 together with each of the B. cereus pagR homologues fused to the C-terminal cya fragment T25 to investigate whether the predicted structural homologies are also reflected in functional interactions in vivo. As expected, the PagRBa showed stronger interactions with PagRBc (about 2.5-fold) than with PagR1Bc, reflecting once more the strong structural homologies between PagRBa and PagRBc. Since PagRBa is known to repress the expression of the anthrax toxin component pagA, we next tested the effect of PagRBc on the synthesis of the cereulide toxin by generating a pagRBc gene-deletion mutant.
2.4. Phenotypic Characterization of a pagRBc Gene-Deletion Mutant
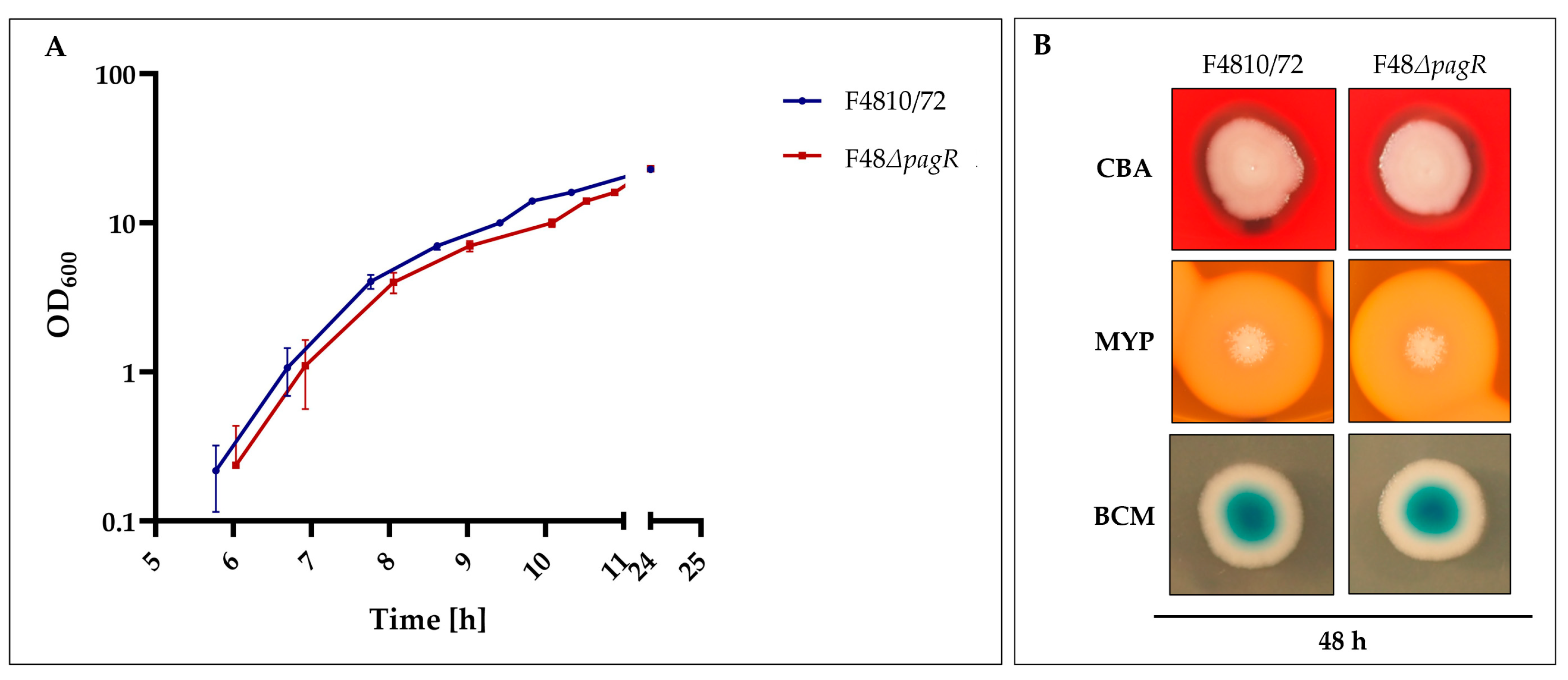
To assess the effect of PagRBc on cereulide biosynthesis, a single null mutant strain was constructed by allelic gene replacement of the pagRBc ORF in the emetic B. cereus reference strain F4810/72, resulting in the double-crossover pagRBc::spc strain F48ΔpagR. The growth of the pagRBc null mutant strain starts slightly later than the wild type but the increase in OD is similar (Figure 5A).
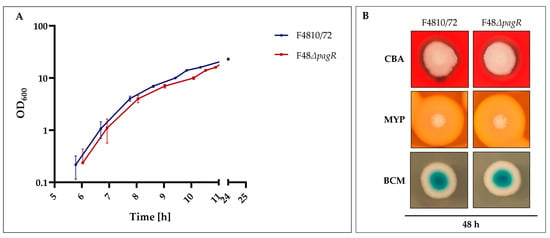
Figure 5.
Growth and colony phenotypes of emetic B. cereus F4810/72 and its isogenic F48∆pagR mutant. (A): Growth curves of wild-type and F48ΔpagR mutant. Strains were cultivated in LB broth at 30 °C. The growth was monitored by measuring the optical density at 600 nm (OD600), shown are averages with standard deviations from three independent experiments. (B): Strains were grown on Columbia blood agar (CBA), Mannitol egg yolk polymyxin agar (MYP) and Brilliance Bacillus cereus agar (BCM), incubated at 30 °C for 48 h.
Furthermore, the F48ΔpagR and the wild-type strain F4810/72 did not exhibit differences in hemolysis nor in phosphatidylcholine- and phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipases (PC-PLC and PI-PLC), as tested by growth at 30 °C on Columbia blood agar (CBA), Mannitol egg yolk polymyxin agar (MYP) and Brilliance Bacillus cereus agar (BCM), respectively (Figure 5B). These results suggest that PagR does not affect these chromosomally encoded virulence factors, which belong to the PlcR regulon [25].
2.5. PagRBc Acts as a Repressor of Cereulide Synthetase Gene Expression
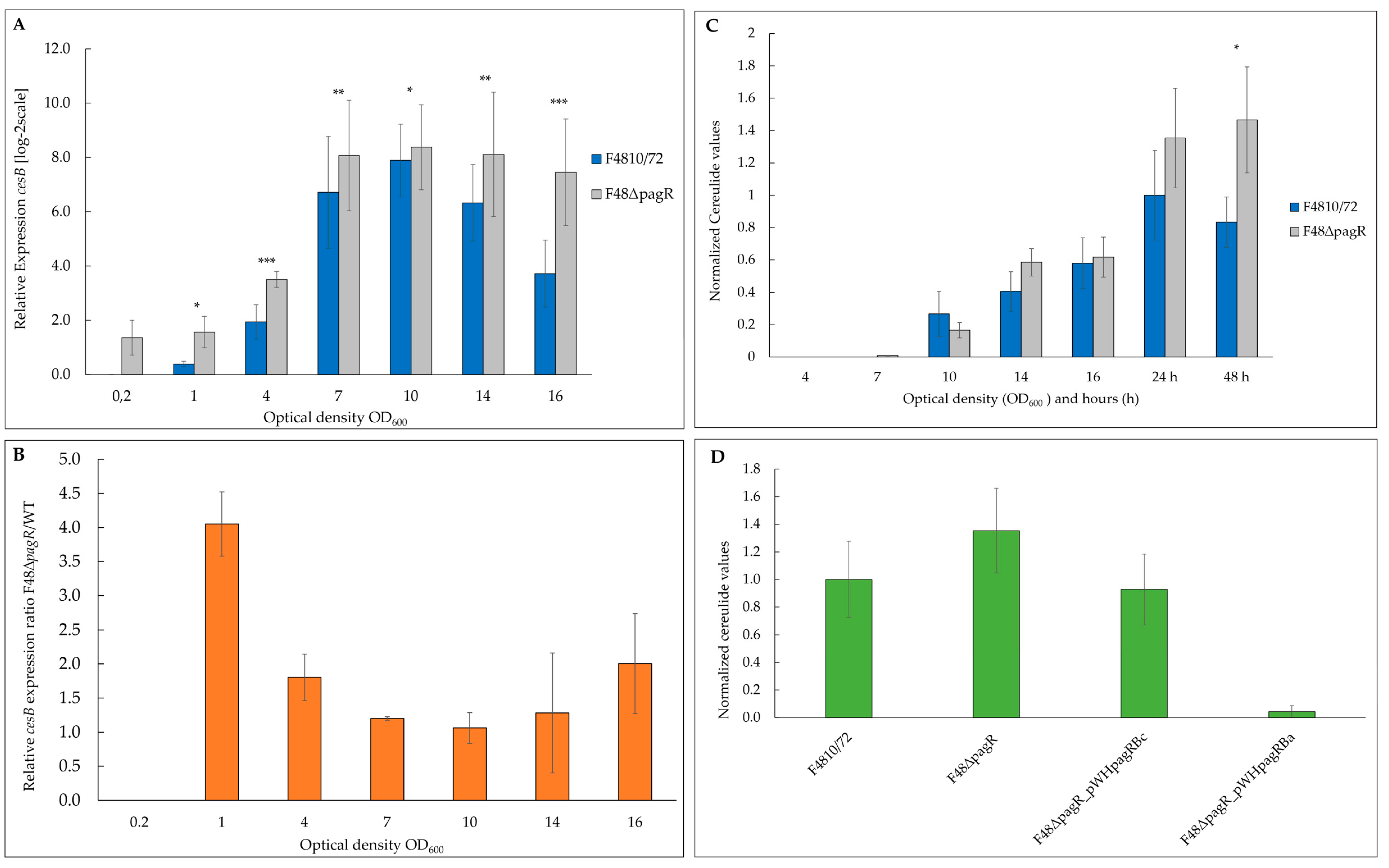
To examine the impact of PagRBc on ces transcription, we performed qRT-PCR-based quantification of mRNA levels. To compensate for slight growth delay of the mutant compared to its parental, we isolated RNA from cultures sampled at the same OD600 and monitored ces transcription from OD600 of 0.2 to 16 (Figure 6A). While the expression of ces in the wild-type strain was restricted to the late exponential/early stationary phase, the absence of pagRBc resulted in an approx. four-fold enhanced synthesis of ces mRNA during the early growth phase (Figure 6B). Generally, the ces mRNA levels in the pagRBc null mutant were significantly higher during the different growth phases, although both strains reached the highest ces transcription levels around the same OD600. In the wild-type B. cereus F4810/72, maximum ces transcription peaked at OD600 of 10 and declined thereafter, while the ces mRNA levels in the isogenic F48∆pagR mutant stayed constantly high. These results indicate that the pCER270 encoded pagRBc acts as a transcriptional repressor of the cereulide toxin synthetase operon ces.
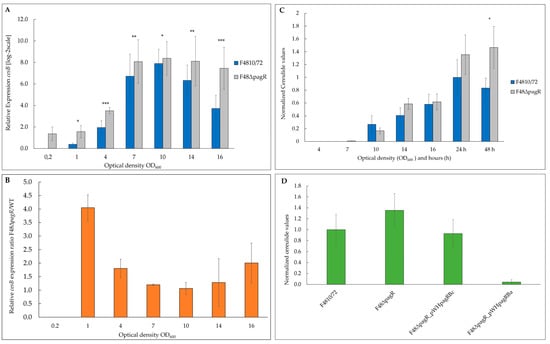
Figure 6.
PagRBc represses cereulide toxin synthesis. The emetic reference strain B. cereus F4810/72 (wt) and its isogenic F48∆pagR mutant were grown in LB broth at 30 °C. Total RNA was extracted from B. cereus F4810/72 and F48∆pagR, harvested at indicated optical densities. Gene expression of ces and amounts of the cereulide toxin was determined at the OD600 as indicated. (A) The kinetics of ces transcription in F48∆pagR and its wild-type parent were determined by qRT-PCR. Levels of ces expression were determined by qRT-PCR and normalized to 16S rrn levels of the same sample preparations. The expression level of ces gene obtained for the wild-type strain at an OD600 of 0.2 (external calibrator sample) was set to 1 (R = 1) by default, and all other expression levels were compared relative to this condition using the REST method [41]. Data were calculated from at least two independent qPCR measurements from three independent biological replicates. Statistically significant differences between the strains are denoted as follows: * p < 0.01, ** p < 0.001, *** p < 0.0001. (B) Results of a comparative REST analysis of the relative cesB transcription levels of F48∆pagR and the wild-type strain. The rrn-normalized cesB expression values in F48∆pagR are depicted as log-2 ratios relative to the normalized cesB expression values of the wild-type strain at the same optical densities. Statistically significant differences in the cesB mRNA levels between the strains are indicated as denoted in (A). (C,D) The amount of cereulide in F48∆pagR, the wild-type strain and the pagRBc complementation strains was determined by UPLC-MS/MS. (C) Samples from F48∆pagR and the wild-type strain were analyzed at the OD600s and hours indicated. (D) In addition, cereulide was determined in F48∆pagR complemented in trans with pagRBc (F48∆pagR_pWHpagRBc) and pagRBa (F48∆pagR_pWHpagRBa), respectively; using a xylose-inducible promoter. Cereulide levels were calculated relative to the cereulide amount of the wild-type strain F4810/72 at 24 h. Samples were taken from three independent experiments shown as averages with standard deviations.
In line with the results from the ces expression studies, the cereulide toxin was detectable earlier (at an OD600 of 7) by ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) in the mutant F48∆pagR than in the B. cereus F4810/72 wild-type strain, and higher toxin levels were observed after 24 and 48 h (Figure 6C).
Since we found PagR (PagRBa) from B. anthracis not only to be structurally similar to B. cereus PagRBc but also to share functional characteristics with PagRBc, we examined if a heterologous PagRBa complementation strain could downregulate the increased cereulide production observed in the pagRBc null mutant. In parallel, we re-introduced pagRBc into F48∆pagR to generate a homologous complementation strain, in order to prove whether the increased cereulide production indeed would result from the deletion of pagRBc. Thus, we amplified pagR from B. anthracis Sterne and pagRBc from B. cereus F4810/72, respectively, fused the genes to a xylose-inducible promoter in the B. cereus expression vector pWH1520 and introduced these plasmid constructs into the F48∆pagR mutant. As expected, the induction of pagRBc with 0.1% xylose in the new strain—designated F48∆pagR_pWHpagRBc—reduced the cereulide levels to those observed in the wild-type F4810/72 strain. Furthermore, the induction of pagRBa with 0.1% xylose in the pagRBa complemented mutant strain—designated F48∆pagR_pWHpagRBa—led to a strong reduction of cereulide levels (Figure 6D). These results demonstrate that PagR plays a significant role in the regulation of cereulide biosynthesis. Furthermore, they show that besides B. cereus PagRBc, the structurally related PagR from B. anthracis substitutes the function of indigenous PagRBc in cereulide biosynthesis. The strong repressing effect of PagRBa on cereulide production observed in the heterologous complementation mutant indicates that PagR is able to form stable dimers, which mediate strong protein-DNA interactions.
Due to the high structural and functional homologies of PagRBa and PagRBc, we analyzed if the promoter regions of their target genes eag and ces comprise any conserved binding sites (see Supplementary Figure S5). However, as expected, no common binding site could be identified. Typically, ArsR/SmtB family members form dimeric or tetrameric proteins with a winged HTH-binding region and bind often imperfect inverted repeat motifs or imperfect palindromes [28,30]. Indeed, PagR (PagRBa) binds to DNA regions either symmetrically (to the sap promoter) or asymmetrically (to pagA and eag promoters, respectively), [15]. Thus, it is tempting to speculate that the pagR homologues in B. anthracis as well as in B. cereus follow a similar logic for binding to specific DNA regions. Another intriguing question that requires attention is the evolutionary origin of the PagR homologues encoded on the virulence plasmids of B. anthracis and emetic B. cereus, respectively. Although B. cereus pCER270 and B. anthracis pXO1 share a common backbone [7] and pagR1Ba and pagR1Bc are flanked by some homologous genes, the genetic organization of pagRBa and pagRBc is different (Supplementary Figure S2). There are no homologous genes found in the flanking genetic regions of pagRBa and pagRBc except for a Tn3 family transposase and its recombinase, which might be remnants from an ancient transition event. In contrast to pagRBa, which is known to be bicistronically transcribed with pagA [16], pagRBc is transcribed monocistronically, independently of the gene at its 5‘-proximity, designated hyp1 (see Supplementary Figure S6). Thus, further studies will be necessary to fully decipher the molecular functionality of PagRBc and its role in the virulence of emetic B. cereus.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
A list of all bacterial strains used in this study is provided in Table 1. If not indicated otherwise, E. coli strains were routinely grown in LB broth (LB) or on LB agar plates at 37 °C. The emetic reference strain B. cereus F4810/72 and its derivatives were grown at 30 °C in LB broth or on LB agar plates. For kinetic inoculation of the main cultures with a final inoculum of 103 CFU/mL of 100 mL fresh LB broth in baffled flasks, the emetic reference strain B. cereus F4810/72 and its derivatives were pre-cultivated for 16 h, as described previously [23,42]. Optical densities at 600 nm (OD600) were recorded using a Biospectrometer Basic (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany). To remain within the linear absorption capacity of the instrument, samples exceeding an OD600 of 1 were measured as 1:10 dilutions in fresh growth medium and samples exceeding an OD600 of 10 were measured 1:100 diluted, respectively, and extrapolated. The following antibiotics were added to the media when necessary: ampicillin (120 µg/mL), kanamycin (50 µg/mL) or 5-aminolevulonic acid (5ALA), [stock concentration: 50 mg/mL, final concentration 50 µg/mL) for E. coli; chloramphenicol (5 µg/mL) or tetracycline (10 µg/mL) for B. cereus.

Table 1.
Bacterial strains used in this study.
3.2. General Molecular Methods
DNA isolation, manipulation, transformation of E. coli, plasmid preparation, protein separation by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting was carried out according to standard procedures [47,48]. For cloning purposes and generation of gel mobility assay samples as well as protein samples, genomic DNA of the emetic B. cereus F4810/72, and the B. anthracis Sterne strain served as a template. DNA amplification was carried out with Phusion High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase (Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, USA). The oligonucleotides (synthesized by Eurofins Ebersberg, Germany) used for plasmid construction and strain manipulation are listed in Supplementary Table S1. An overview of plasmids used is provided in Supplementary Table S2. All constructs were verified by restriction enzyme digest and Sanger DNA sequencing (LGC Genomics, GmbH, Berlin, Germany). E. coli strains were transformed by heat shock and B. cereus strains by electroporation as described previously [19]. Conjugation was carried out according to Thoma and Schober [43] as described below (see Section 3.7).
3.3. Construction of E. coli Protein Expression Strains for Electrophoretic Mobility-Shift Assay (EMSA)
For recombinant protein expression, DNA fragments encoding pagRBc and pagR1Bc were amplified from genomic DNA of emetic B. cereus F4810/72 by using the following primer pairs: PagRNco_F/PagRXho_R and PagR1Nde_F/PagR1Xho_R (Supplementary Table S1). DNA fragments encoding pagR of B. anthracis Sterne strain were amplified from genomic DNA using the primer pairs: PagRBaNco_F/PagRBaXho_R (Supplementary Table S1). Probes were designed to achieve N-terminal or C-terminal His6-tag. Start and Stop codons were integrated and/or replaced in/with the respective restriction site. The amplified, digested and purified fragments were cloned into the expression vector pET28b(+). Constructs were verified by PCR and Sanger DNA-sequencing using the primers pET28b_for and pET28b_rev. For protein overexpression, the plasmids were introduced into E. coli BL21 (DE3) by transformation.
3.4. Production and Purification of Heterologous Proteins PagRBc-His6, PagR1-His6 of Emetic B. cereus and PagR-His6 of B. anthracis
Proteins were produced with E. coli BL21 (DE3) as soluble, N-terminal or C-terminal His6-tag fusions as previously described [22]. Protein production was induced by adding 1 mM IPTG to exponentially growing cells with an OD600 of 0.6. After 3 h incubation, cells were harvested at 6000× g, at 4 °C, 10 min and washed twice with washing buffer A [50 mM Tris pH 7.5, 50 mM KCl, 1 mM DTT, 0.5 mM Pefabloc (Roth, Karlsruhe, Germany)]. For protein purification, cells were resuspended in 3 mL Ni-NTA Native Lysis Buffer [50 mM NaH2PO4, 300 mM NaCl, 10 mM Imidazole, pH 8] containing 5 mM Pefabloc (Roth, Karlsruhe, Germany) and 3 µL of Benzonase [20,000 units], (Thermo Fisher, USA). Cells were disrupted twice with a French press (1 kbar) and cellular debris was removed by two times 20 min centrifugation step at 15,700 rpm at 4 °C. The supernatant was loaded onto Ni-NTA affinity columns (Qiagen, Chatsworth, CA, USA) pre-equilibrated with lysis buffer. The column was washed with 10 column volumes (CV) of washing buffer [50 mM NaH2PO4, 300 mM NaCl, 20 mM imidazole, pH 8.0] and the protein was eluted in elution buffer [50 mM NaH2PO4, 300 mM NaCl, 250 mM imidazole, pH 8.0]. The eluted fractions were dialyzed with the 10-fold BS buffer [50 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.5, 50 mM KCl, 10 mM MgCl2, 0.5 mM Na2EDTA, pH 8.0, 10% glycerol] using ultrafiltration columns with a 10 kDa cut-off (Vivaspin 500 concentrators (Sartorius AG, Goettingen, Germany)). Protein purity was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and total protein concentrations were determined with Pierce BCA Protein Assay Kit (Thermo Fisher, MA, USA), using bovine serum albumin as a standard.
3.5. Gel Mobility Shift Assay
Affinities of His6-tagged transcription factors PagR, PagR1 of B. cereus F4810/72 and PagR of B. anthracis Sterne to the promoter region of the ces gene were analyzed with nonradioactive native PAGE in gel mobility shift assays [49]. To analyze the binding to the ces promoter, a 523 bp fragment covering the main promoter region of cesPII [17], the ces promoter was amplified with the primer pairs: cesPII_for and cesPII_rev (Supplementary Table S1). The binding reactions contained increasing amounts (0 ng up to 360 ng) of PagR-His6, PagR1-His6 of B. cereus F4810/72 and PagR-His6 of B. anthracis Sterne and the cesPII promoter fragment in binding buffer [50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 750 mM KCl, 2.5 mM Na2EDTA (pH 8.0), 0.5% Triton X-100, 62.5% glycerin (v/v), 1 mM dithiothreitol (DTT)]. To monitor nonspecific binding, equimolar amounts of a randomly amplified 301 bp DNA fragment (EMSAunspec7), originating from the cesH coding sequence of B. cereus F4810/72, served as competing DNA as described previously [26]. To further test the specificity of DNA-binding, PagR1-His6 was incubated with EMSAunspec7 and a second randomly amplified 201 bp DNA fragment (EMSAunspec8), origination from the cesP coding sequence of B. cereus F4810/72. The binding reaction was carried out as described above. Samples were incubated at RT for 30 min before being loaded onto a 10% native polyacrylamide gel which was run in pre-chilled TBE buffer at 120 V for 3 h at 4 °C. Gels were stained in ethidium bromide solution and visualized by UV irradiation.
3.6. Bacterial Two-Hybrid System (BACTH) and β-Galactosidase Assay
The genes pagR1Bc (NCBI locus tag: BCAH187_RS28695) and pagRBc (NCBI locus tag: BCAH187_RS28375) of the emetic B. cereus F4810/72, located on the pCER270 megaplasmid, and the pagRBa gene (NCBI locus tag AW20_RS00175) of B. anthracis (located on the pXO1-plasmid) were amplified (Supplementary Table S1) and cloned into the pKT25, pKNT25, pUT18 and pUTC18C BACTH expression vectors (Cat no: EUK001, Euromedex, Souffelweyersheim, France), (Table 1). The cloning procedure of the BACTH and the β-galactosidase assay were performed as recently described [21]. The respective plasmids were introduced into E. coli BTH101 cya-host strain by heat-shock transformation. The procedure is based on the functional complementation of two subunits of the adenylate cyclase (Cya) T18 and T25 fused with the putatively interacting partners as previously described [39,50]. Each protein was tagged on the N- and C-terminus by both subunits of Cya (T18 and T25). For each putative interaction, all possible combinations were tested in order to assess homo- as well as heterodimers by cotransforming plasmid constructs into E. coli BTH101 cells and plating them on LB X-gal/IPTG agar and LB IPTG for ß-galactosidase assay. The cells were incubated for 24 h at 30 °C, followed by incubation for 20 h at RT and for 20 h at 18 °C. For the β-galactosidase assay, cells were harvested from the LB-IPTG plates and resuspended in 1 mL Z-buffer (10 mM KCl, 10 mM MgSO4, 0.27% β-mercaptoethanol, Na-phosphate butter with pH of 7). The cell densities at OD600 were adjusted to 0.4 to 0.7, cells were permeabilized using β-mercaptoethanol, SDS and chloroform. The enzymatic reaction was carried out at 28 °C and started by adding 4 mg/mL ortho-Nitrophenyl-β-galactoside-sodium-phosphate buffer. After the samples turned yellow, the reactions were stopped with 1 M Na2CO3. The ß-galactosidase assay was carried out according to [50] and values were expressed in Miller Units [MU].
3.7. Construction of the B. cereus pagRBc Null Mutant Strain F48ΔpagR
To construct a pagRBc deletion mutant of the emetic B. cereus reference strain F4810/72, DNA regions of approximately 1500 bp flanking the pagRBc gene (NCBI locus tag: BCAH187_RS28375) were amplified with the primer pairs: pagRFl1_F/pagRFl1_R and pagRFl2_F/pag2Fl2_R for the flanking regions of pagRBc gene from emetic B. cereus F4810/72 DNA (Supplementary Table S1). The fragments were digested with KpnI/SacI and XhoI/XbaI, respectively. The amplification of a chloramphenicol-resistance cassette (1200 bp) from plasmid pAD123 [51] was carried out with the primer pairs CmEcoRI_F/CmEcoRI_R. The remaining fragment and the pCR 2.1 TOPO plasmid were digested with EcoRI and ligated by heat-shock transformation in E. coli TOP10 cells to result in pCR 2.1 TOPO/Cm construct (control primers for the insert were M13-F/M13-R). Both flanking region fragments were cloned into the chloramphenicol cassette containing plasmid pCR 2.1 TOPO/Cm. The construct was cut (KpnI/XbaI) and cloned into the similarly digested conjugative suicide pAT113 plasmid [52]. This plasmid was introduced into a diparental mating system with E. coli ST18, which was used to replace pagRBc with the chloramphenicol cassette in emetic B. cereus F4810/72 as described previously [43]. In brief, the diparental mating system is performed with E. coli ST18 strain, a hemA deletion mutant defective in tetrapyrrole biosynthesis, where the hemA mutation can easily be complemented by the addition of 5-aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA). The counterselection of the mating system is carried out by standard media and optimal growth conditions for the recipient strains. The conjugation was performed with the emetic B. cereus wild-type strain F4810/72 to yield the null mutant, designated F48ΔpagR. Gene deletion and integration of the resistance cassette was confirmed by PCR and sequencing using the primer pairs: pagRK1_F/pagRK1_R and pagRK2_F/pagRK2_R.
3.8. Expression of pagR Homologues in the pagRBc Null Mutant F48ΔpagR
To complement the pagRBc null mutant with pagR homologues from B. cereus as well as with pagR from B. anthracis, the respective genes were amplified from DNA of B. cereus F4801/72 and B. anthracis Sterne using the primers listed in Table S1. and introduced into pWH1520 plasmid to obtain pWH::pagRBc and pWH::pagRBa, in which the expression of pagR homologues is under control of a xylose-inducible promoter [53]. The plasmids were passaged through the non-methylating E. coli strain INV 110 and introduced into F48ΔpagR by electroporation. The successful uptake of the plasmids was verified by by PCR and subsequent sequencing of the PCR fragments with the primer pairs pWH1520_F/pWH1520_R (Supplementary Table S1). To induce the expression of the pagR homologues in F48ΔpagR, the cultures were kinetically inoculated 103 CFU/mL as described above and induced with D-xylose to a final concentration of 0.1% (v/v), respectively, harvested at 24 h for determination of cereulide toxin levels.
3.9. Transcriptional Analysis of cesB Expression by qRT-PCR
Transcription of the cesB gene in the B. cereus pagRBc null mutant F48ΔpagR and its parental strain was analyzed by qRT-PCR as described previously [23,42]. For RNA isolation, 2 mL to 5 mL bacterial culture was harvested (10,000× g, 4 °C, and 2 min) at different optical densities. The supernatant was discarded and the cell pellets were directly frozen using liquid nitrogen. Pellets were stored at −80 °C until RNA extraction. RNA was isolated from frozen cell pellets via TRIzol Reagent (Invitrogen, Thermo Fisher, USA) and homogenized with FastPrep®-24 Ribolyser of MP (2 times of 45 s, in between samples were chilled on ice for 30 s, speed 6.5) using 0.1 mm ZnSn beads in 2 mL screw-top tubes. Phase separation was carried out with chloroform and nucleic acid was precipitated with 75% ethanol. RNA concentration was measured by Nanodrop™ 2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher, USA). Samples were diluted in a ratio 1:10 or 1:100, respectively, to get 1 µg final volume for cDNA synthesis with iScript™ gDNA Clear Synthesis Kit (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Vienna, Austria). The cDNA was diluted in a ratio 1:25 for qRT-PCR performance. For qRT-PCR analysis, we used SSO Advanced Universal SYBR Green Supermix (Bio-Rad Laboratories, USA) according to manufacturer instructions. For each reaction, 10 µL of SYBR Green, 2.5 µL of primer_F (3 µM) and 2.5 µL primer_R (3 µM) was used. Primers for qRT-PCR are listed in Table S1. To every qRT-PCR reaction mix, 5 µL of 1:25 diluted cDNA was added (final volume of 20 µL). Reactions were run on Bio-Rad Cycler (Bio-Rad Laboratories, USA, CFX96 Real-Time System C1000 Touch). To monitor gene expression, the REST method (Relative Expression Software Tool) was used according to [41], the mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time PCR. As an internal calibrator, (with a relative expression value of 1.00) the ces gene expression at an OD600 of 0.2 was chosen. Sample-to-sample variation was corrected by using the 16S rDNA gene as a reference (rrn), [54]. Mean values and standard deviations were calculated from three independent experiments and two independent measurements. Statistically significant differences (p < 0.5, p < 0.01 and p < 0.001) compared to the wild-type reference strain B. cereus F4810/72 were calculated with a paired, two-tailed Student’s t-test.
3.10. Cereulide Quantification by Means of Ultraperformance Liquid Chromatography (UPLC) Tandem Mass Spectrometry (MS/MS)
Samples of 5 mL were taken from bacterial cultures at a specific OD600 of 4, 7, 10, 14, 16 as well as 24 h and 48 h and centrifuged at 8000× g, 2 min, 4 °C. Pellets were stored at −80 °C until further processing. For cereulide extraction, about 50 mg of bacterial mass was weighted by pipetting and re-suspended in the respective amount of ethanol absolute. The cereulide extraction was performed as previously described [42].
The mass spectrometric analysis was performed using a WatersXevo TQ-S mass spectrometer (Waters, Manchester, UK) combined with an Acquity UPLC i-class core system (Waters, Milford, MA, USA), as described previously [55]. The UPLC-MS/MS system was equipped with a 2.1 × 150 mm, 1.7μm, UPLC CSH C18 column (Waters, Manchester, UK). Measurements were executed in the positive electrospray ionization (ESI) mode as described previously [55]. The UPLC Xevo TQ-S system was operated with MassLynxTM 4.1 SCN 813 Software (Waters, Manchester, UK), and analysis and data processing were completed using TargetLynx (Waters, Manchester, UK). By means of the multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode, the ammonium adducts of cereulide (m/z 1170.7→qualifier: m/z 172.2, 314.2; quantifier: m/z 357.2) were analyzed for a duration of 25 ms. The analysis of MS-data was performed as described [56]. All samples were measured in two different dilutions as duplicates. Mean values and standard deviations were calculated from three independent experiments.
3.11. Sequence Analysis
For the emetic reference strain B. cereus F4810/72, the genomic information was retrieved from the NCBI website (GenBank accession numbers NC_011655.1 and CP001179.1) and used for homology search and analysis of the pagR sequence. For the reference B. anthracis Sterne strain (GenBank accession number CP009540.1) and for the reference B. anthracis Pasteur strain (GenBank accession number CP009475.1), the genome information was also retrieved from the NCBI website were used for homologue search and analysis of the pagR sequence.
The DNA and amino acid sequences were accessed from the NCBI database. Protein homology search was performed by using BLAST (http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi) and as well as PATRIC (https://patricbrc.org/), accessed on 6 August 2022. Multiple sequence alignments were carried out with CLC Workbench Qiagen Software and SnapGene Software (GSL Biotech, USA). The published annotations of the characteristic protein domains of the crystal structure of PagR of B. anthracis was used according to [33]. Phylogenetic tree analyses were performed with the construction method neighbor joining and the distance measurement with the Jukes–Cantor model, including bootstrap analysis via CLC Workbench Qiagen Software.
For sequence homology analysis of proteins, the database Emboss Needle program [57] was used (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/psa/emboss_needle/), accessed on 9 august 2022, due to an optimal sequence alignment, applying the Needleman-Wunsch algorithm.
Predictive 3D protein models were constructed using the Phyre2 online tool (http://www.sbg.bio.ic.ac.uk/phyre2/html/page.cgi?id=index), accessed on 29 august 2021, by adding the protein sequence, respectively [37].
4. Conclusions
In summary, our work provides novel insights into the complex regulatory circuits governing the non-ribosomal biosynthesis of the depsipeptide toxin cereulide by the CesNRPS. As shown previously, different levels of regulation are involved in the tight control of cereulide production [24]. The chromosomally encoded global regulator CodY, which senses the physiological status of the cell and orchestrates virulence factor expression in emetic B. cereus, as well as the pleiotropic transition state regulator AbrB, plays an important role as repressors of ces transcription in early growth phases. Both have been shown to act on the timing of ces expression by direct binding to the central promoter cesP [22,26]. In addition, CesH, which forms part of the ces gene locus, has been shown to influence the ces expression, but most likely by an indirect mechanism [27] yet to be explored. Furthermore, the ABC transporter CesCD contributes to cereulide production through its recently described non-canonical function in CesNRPS assembly [21].
With the identification of the PagR homologue PagRBc, which represents the first pCER270-encoded transcription factor described to be involved in ces transcription, we add a new piece to this still not entirely completed puzzle of virulence gene regulation in emetic B. cereus (Figure 7). Furthermore, PagRBc is the first ArsR/SmtB family member shown to be involved in the regulation of non-ribosomal assembly of cereulide by CesNRPS, highlighting the structural and functional diversity of factors involved in the tight control of ces expression. The homologous PagR (PagRBa) in B. anthracis has been shown to act in a complex cascade of signaling transduction that orchestrates the expression of virulence factors at the right time and in the right place [10,15,58]. It is therefore expected from our now-expanded understanding that PagRBc plays a similar role in the fine tuning of virulence factor expression in emetic B. cereus.
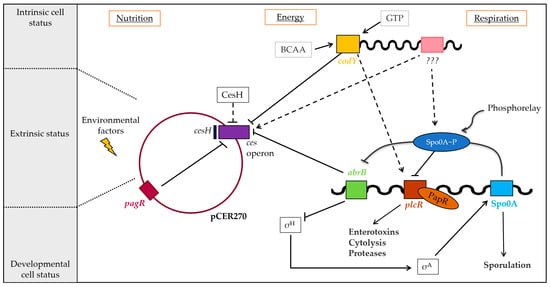
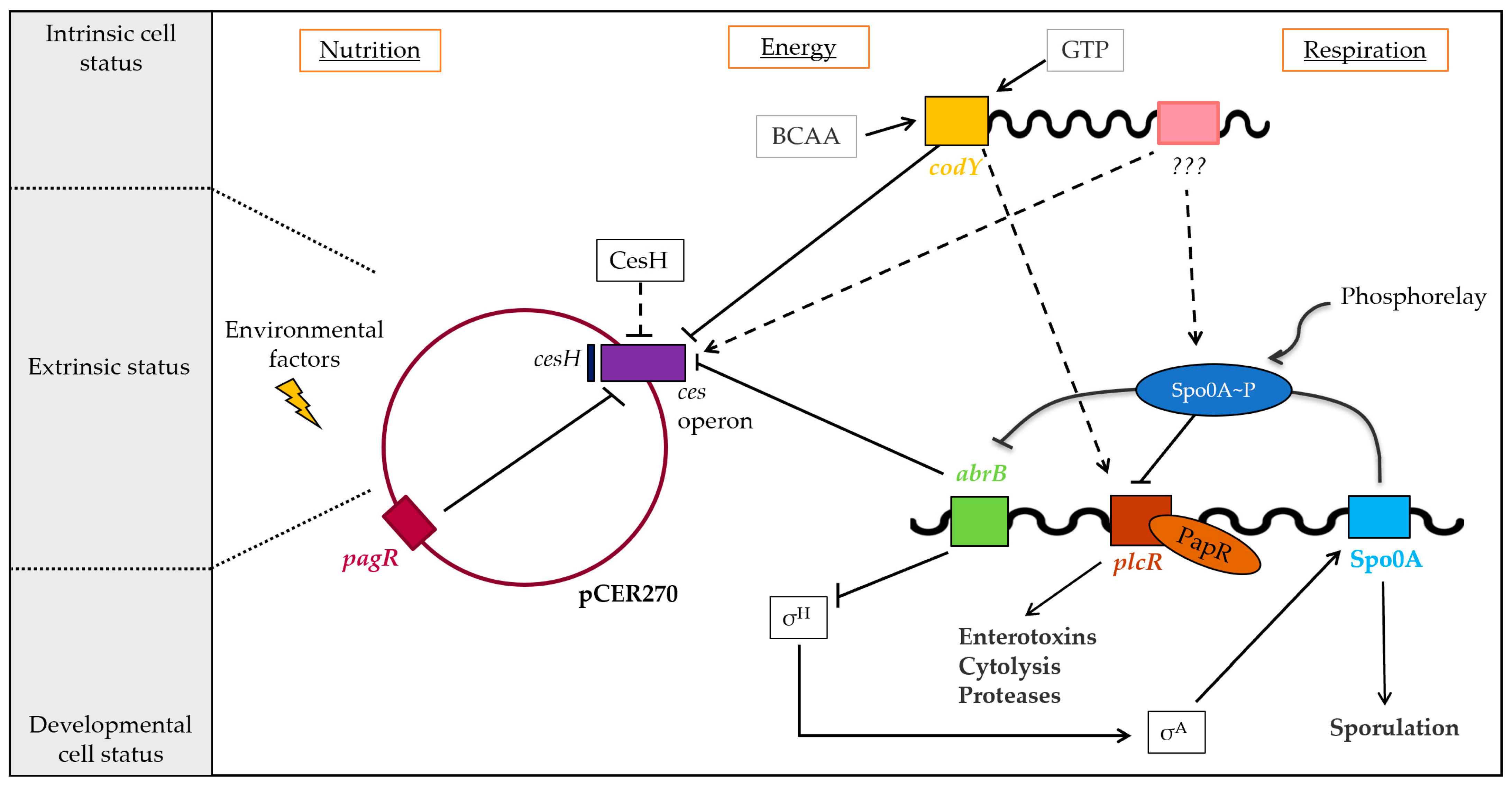
Figure 7.
Regulation of cereulide toxin synthesis of emetic B. cereus. Cereulide toxin synthesis is a complex and multilayered process, orchestrated by the interplay of chromosomally and plasmid-encoded factors controlling the toxin synthesis at the transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels. The ces operon is tightly controlled by the chromosomally encoded global transcriptional regulators CodY and the transition phase regulator AbrB that belongs to the Spo0A regulon, but not by the pleiotropic B. cereus virulence regulator PlcR. The putative hydrolase CesH, encoded adjacent to the ces operon, indirectly controls cereulide biosynthesis, while the ArsR/SmtB family repressor PagRBc on pCER270 plasmid exerts control of ces transcription. Solid arrows: transcriptional regulation; dashed arrows: indirect regulatory effects (adapted from [24]).
In addition, our work revealed that the newly identified PagR homologues PagR1Bc and PagR1Ba are nearly identical and also show a conserved genetic organization of their gene neighborhood, suggesting that they are functionally and structurally interchangeable. Notably, both genes are located on megaplasmids, which carry the key virulence determinants of emetic B. cereus (pCER270) and B. anthracis (pXO1 Ba), respectively. Thus, further studies should dissect the function of these PagR-like transcription factors for the pathophysiology of emetic B. cereus and B. anthracis.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijms231911479/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.E.-S.; methodology, E.M.K., M.K., A.G.-M., G.G., T.D.S., E.F.; formal analysis, E.M.K., M.K., A.G.-M., E.F.; investigation, E.M.K., M.K., A.G.-M., E.F.; resources, M.E.-S., G.G.; writing—original draft preparation, E.M.K., M.E.-S.; writing—review and editing, M.E.-S., M.K., A.G.-M., G.G., T.D.S., E.F.; visualization, E.M.K., M.E.-S.; supervision, M.E.-S.; project administration, M.E.-S.; funding acquisition, M.E.-S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article or Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
We thank Susanna Leiter and Tatjana Svoboda for their excellent technical assistance and Rilana Wiechert for her help in establishing the EMSA assays and Stefan Schulz for his help with data analysis. We accept Open Access Funding by the University of Veterinary Medicine Vienna.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dietrich, R.; Jeßberger, N.; Ehling-Schulz, M.; Märtlbauer, E.; Granum, P.E. The food poisoning toxins of Bacillus cereus. Toxins 2021, 13, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehling-Schulz, M.; Koehler, T.M.; Lereclus, D. The Bacillus cereus group: Bacillus species with pathogenic potential. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messelhäußer, U.; Ehling-Schulz, M. Bacillus cereus–A Multifaceted Opportunistic Pathogen. Curr. Clin. Microbiol. Rep. 2018, 5, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottone, E.J. Bacillus cereus, a volatile human pathogen. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 382–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drobniewski, F.A. Bacillus cereus and related species. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1993, 6, 324–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehling-Schulz, M.; Guinebretiere, M.H.; Monthán, A.; Berge, O.; Fricker, M.; Svensson, B. Toxin gene profiling of enterotoxic and emetic Bacillus cereus. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 260, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasko, D.A.; Rosovitz, M.J.; Økstad, O.A.; Fouts, D.E.; Jiang, L.; Cer, R.Z.; Kolstø, A.B.; Gill, S.R.; Ravel, J. Complete sequence analysis of novel plasmids from emetic and periodontal Bacillus cereus isolates reveals a common evolutionary history among the B. cereus-group plasmids, including Bacillus anthracis pXO1. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baillie, L.; Read, T.D. Bacillus anthracis, a bug with attitude! Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2001, 4, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, T.M. Bacillus anthracis genetics and virulence gene regulation. In Anthrax; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2002; pp. 143–164. [Google Scholar]
- Perego, M.; Hoch, J.A. Commingling regulatory systems following acquisition of virulence plasmids by Bacillus anthracis. Trends Microbiol. 2008, 16, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouet, A. AtxA, a Bacillus anthracis global virulence regulator. Res. Microbiol. 2010, 161, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, J.L.; Raynor, M.J.; Ty, M.C.; Hadjifrangiskou, M.; Koehler, T.M. A dual role for the Bacillus anthracis master virulence regulator AtxA: Control of sporulation and anthrax toxin production. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCall, R.M.; Sievers, M.E.; Fattah, R.; Ghirlando, R.; Pomerantsev, A.P.; Leppla, S.H. Bacillus anthracis virulence regulator AtxA binds specifically to the pagA promoter region. J. Bacteriol. 2019, 201, e00569-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Z.; Sirard, J.; Mock, M.; Koehler, T.M. The atxA gene product activates transcription of the anthrax toxin genes and is essential for virulence. Mol. Microbiol. 1995, 16, 1171–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mignot, T.; Mock, M.; Fouet, A. A plasmid-encoded regulator couples the synthesis of toxins and surface structures in Bacillus anthracis. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 47, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmaster, A.R.; Koehler, T.M. Autogenous regulation of the Bacillus anthracis pag operon. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 4485–4492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dommel, M.K.; Frenzel, E.; Strasser, B.; Blöchinger, C.; Scherer, S.; Ehling-Schulz, M. Identification of the main promoter directing cereulide biosynthesis in emetic Bacillus cereus and its application for real-time monitoring of ces gene expression in foods. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 1232–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magarvey, N.A.; Ehling-Schulz, M.; Walsh, C.T. Characterization of the cereulide NRPS alpha-hydroxy acid specifying modules: Activation of alpha-keto acids and chiral reduction on the assembly line. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 10698–10699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehling-Schulz, M.; Vukov, N.; Schulz, A.; Shaheen, R.; Andersson, M.; Märtlbauer, E.; Scherer, S.; Shaheen, R.; Scherer, S. Identification and Partial Characterization of the Nonribosomal Peptide Synthetase Gene Responsible for Cereulide Production in Emetic Bacillus cereus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehling-Schulz, M.; Fricker, M.; Grallert, H.; Rieck, P.; Wagner, M.; Scherer, S. Cereulide synthetase gene cluster from emetic Bacillus cereus: Structure and location on a mega virulence plasmid related to Bacillus anthracis toxin plasmid pXO1. BMC Microbiol. 2006, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gacek-Matthews, A.; Chromiková, Z.; Sulyok, M.; Lücking, G.; Barák, I.; Ehling-Schulz, M. Beyond Toxin Transport: Novel Role of ABC Transporter for Enzymatic Machinery of Cereulide NRPS Assembly Line. MBio 2020, 11, e01577-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenzel, E.; Doll, V.; Pauthner, M.; Lücking, G.; Scherer, S.; Ehling-Schulz, M. CodY orchestrates the expression of virulence determinants in emetic Bacillus cereus by impacting key regulatory circuits. Mol. Microbiol. 2012, 85, 67–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dommel, M.K.; Lücking, G.; Scherer, S.; Ehling-Schulz, M. Transcriptional kinetic analyses of cereulide synthetase genes with respect to growth, sporulation and emetic toxin production in Bacillus cereus. Food Microbiol. 2011, 28, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehling-Schulz, M.; Frenzel, E.; Gohar, M. Food-bacteria interplay: Pathometabolism of emetic Bacillus cereus. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gohar, M.; Faegri, K.; Perchat, S.; Ravnum, S.; Økstad, O.A.; Gominet, M.; Kolstø, A.B.; Lereclus, D. The PlcR virulence regulon of Bacillus cereus. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lücking, G.; Dommel, M.K.; Scherer, S.; Fouot, A.; Ehling-Schulz, M. Cereulide synthesis in emetic Bacillus cereus is controlled by the transition state regulator AbrB, but not by the virulence regulator PlcR. Microbiology 2009, 155, 922–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lücking, G.; Frenzel, E.; Rütschle, A.; Marxen, S.; Stark, T.D.; Hofmann, T.; Scherer, S.; Ehling-Schulz, M. Ces locus embedded proteins control the non-ribosomal synthesis of the cereulide toxin in emetic Bacillus cereus on multiple levels. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.; Li, Q.; Xie, L.; Xie, J. Molecular mechanisms underlying the function diversity of ArsR family metalloregulator. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2017, 27, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busenlehner, L.S.; Pennella, M.A.; Giedroc, D.P. The SmtB/ArsR family of metalloregulatory transcriptional repressors: Structural insights into prokaryotic metal resistance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 27, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, R.P.; Samanta, S.; Patra, S.; Sarkar, D.; Saha, A.; Singh, M.K. Metal homeostasis in bacteria: The role of ArsR–SmtB family of transcriptional repressors in combating varying metal concentrations in the environment. Biometals 2017, 30, 459–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.H.; Rosen, B.P. Regulation of the ars operon: The arsR gene product is a negative regulatory protein. Mol. Microbiol. 1991, 5, 1331–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morby, A.P.; Turner, J.S.; Huckle, J.W.; Robinson, N.J. SmtB is a metal-dependent repressor of the cyanobacterial metallothionein gene smtA: Identification of a Zn inhibited DNA-protein complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993, 21, 921–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Volkov, A.; Veldore, V.H.; Hoch, J.A.; Varughese, K.I. Crystal structure of the transcriptional repressor PagR of Bacillus anthracis. Microbiology 2010, 156, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gao, C.-H.; Yang, M.; He, Z.-G. An ArsR-like transcriptional factor recognizes a conserved sequence motif and positively regulates the expression of phoP in mycobacteria. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 411, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, R.P.; Chakrabarti, P. Molecular modeling and characterization of Vibrio cholerae transcription regulator HlyU. BMC Struct. Biol. 2006, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsi, I.D.; Koehler, T.M. Overlapping and Distinct Functions of the Paralogous PagR Regulators of Bacillus anthracis. J. Bacteriol. 2022, 204, e00208-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, L.A.; Mezulis, S.; Yates, C.M.; Wass, M.N.; Sternberg, M.J.E. The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, G.; Silver, S. CadC, the transcriptional regulatory protein of the cadmium resistance system of Staphylococcus aureus plasmid pI258. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 4437–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimova, G.; Pidoux, J.; Ullmann, A.; Ladant, D. A bacterial two-hybrid system based on a reconstituted signal transduction pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 5752–5756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.H. Experiments in Molecular Genetics; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory: New York, NY, USA, 1972; pp. 328–330. [Google Scholar]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT–PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 2002–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranzler, M.; Stollewerk, K.; Rouzeau-Szynalski, K.; Blayo, L.; Sulyok, M.; Ehling-Schulz, M. Temperature exerts control of Bacillus cereus emetic toxin production on post-transcriptional levels. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoma, S.; Schobert, M. An improved Escherichia coli donor strain for diparental mating. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 294, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterne, M. Variation in Bacillus anthracis. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Sci. Anim. Ind. 1937, 8, 271–348. [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull, P.C.; Kramer, J.M.; Jørgensen, K.; Gilbert, R.J.; Melling, J. Properties and production characteristics of vomiting, diarrheal, and necrotizing toxins of Bacillus cereus. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1979, 32, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehling-Schulz, M.; Svensson, B.; Guinebretiere, M.H.; Lindbäck, T.; Andersson, M.; Schulz, A.; Fricker, M.; Christiansson, A.; Granum, P.E.; Märtlbauer, E.; et al. Emetic toxin formation of Bacillus cereus is restricted to a single evolutionary lineage of closely related strains. Microbiology 2005, 151, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, D.W.; Sambrook, J. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Cold Spring Harbor: New York, NY, USA, 2001; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Ausubel, F.M.; Brent, R.; Kingston, R.E.; Moore, D.D.; Seidman, J.G.; Smith, J.A.; Struhl, K. (Eds.) Current Protocols in Molecular Biology; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Hellman, L.M.; Fried, M.G. Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) for detecting protein-nucleic acid interactions. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 1849–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.H.; Schuler, C.; Ward, J.; Wylie, F.; Frea, T.; Delbene, R.; Faubert, B.; Frea, B.; Frea, A.; Hildebrand, B. A Short Course in Bacterial Genetics; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, A.K.; Handelsman, J. A vector for promoter trapping in Bacillus cereus. Gene 1999, 226, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trieu-Cuot, P.; Carlier, C.; Martin, P.; Courvalin, P. Plasmid transfer by conjugation from Escherichia coli to gram positive bacteria. FEMS Micorbiol. Lett. 1987, 48, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rygus, T.; Hillen, W. Inducible high-level expression of heterologous genes in Bacillus megaterium using the regulatory elements of the xylose-utilization operon. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1991, 35, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martineau, F.; Picard, F.J.; Roy, P.H.; Ouellette, M.; Bergeron, M.G.; Martineau, F.; Bergeron, M.G. Species-specific and ubiquitous DNA-based assays for rapid identification of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Species-Specific and Ubiquitous DNA-Based Assays for Rapid Identification of Staphylococcus epidermidis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 34, 2888–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marxen, S.; Stark, T.D.; Rutschle, A.; Lucking, G.; Frenzel, E.; Scherer, S.; Ehling-Schulz, M.; Hofmann, T. Multiparametric Quantitation of the Bacillus cereus Toxins Cereulide and Isocereulides A–G in Foods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 8307–8313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, T.; Stark, T.; Hofmann, T.; Ehling-Schulz, M. Development of a stable isotope dilution analysis for the quantification of the Bacillus cereus toxin cereulide in foods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madeira, F.; Pearce, M.; Tivey, A.R.N.; Basutkar, P.; Lee, J.; Edbali, O.; Madhusoodanan, N.; Kolesnikov, A.; Lopez, R. Search and sequence analysis tools services from EMBL-EBI in 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W276–W279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouet, A.; Mock, M. Regulatory networks for virulence and persistence of Bacillus anthracis. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2006, 9, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).