27-Hydroxycholesterol-Induced Dysregulation of Cholesterol Metabolism Impairs Learning and Memory Ability in ApoE ε4 Transgenic Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
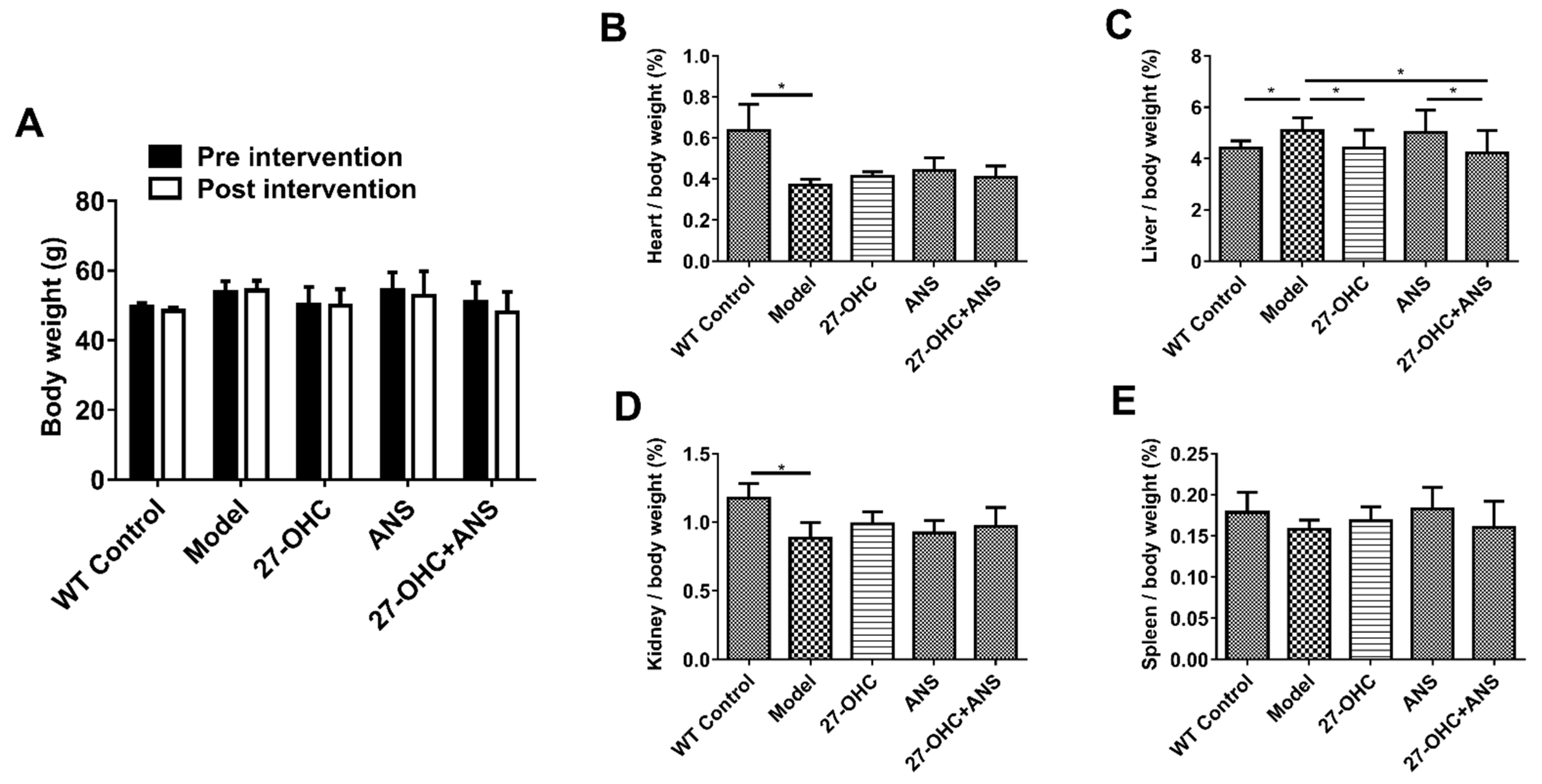
2.1. Bodyweight and Organ Coefficient of Mice
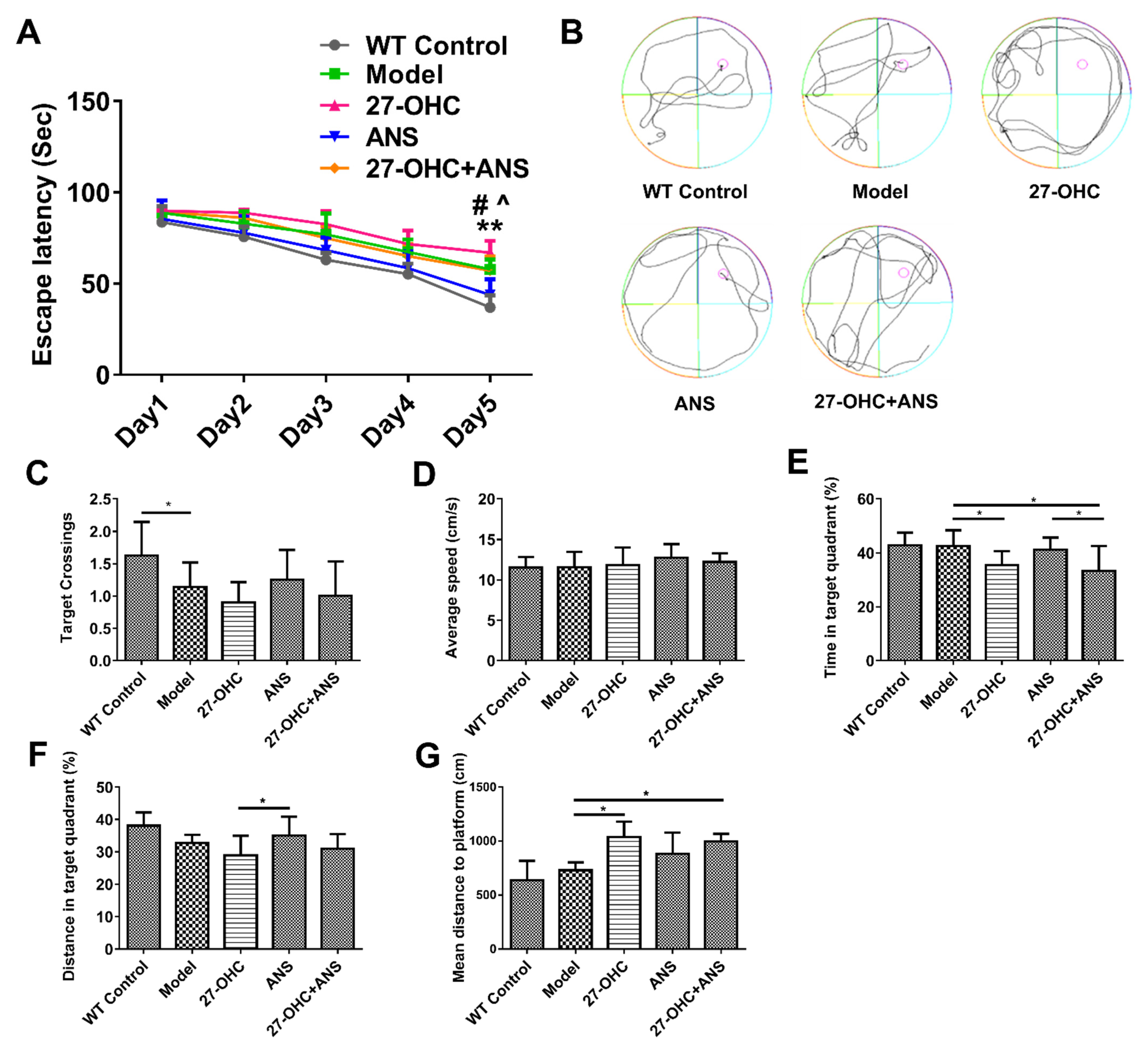
2.2. Morris Water Maze
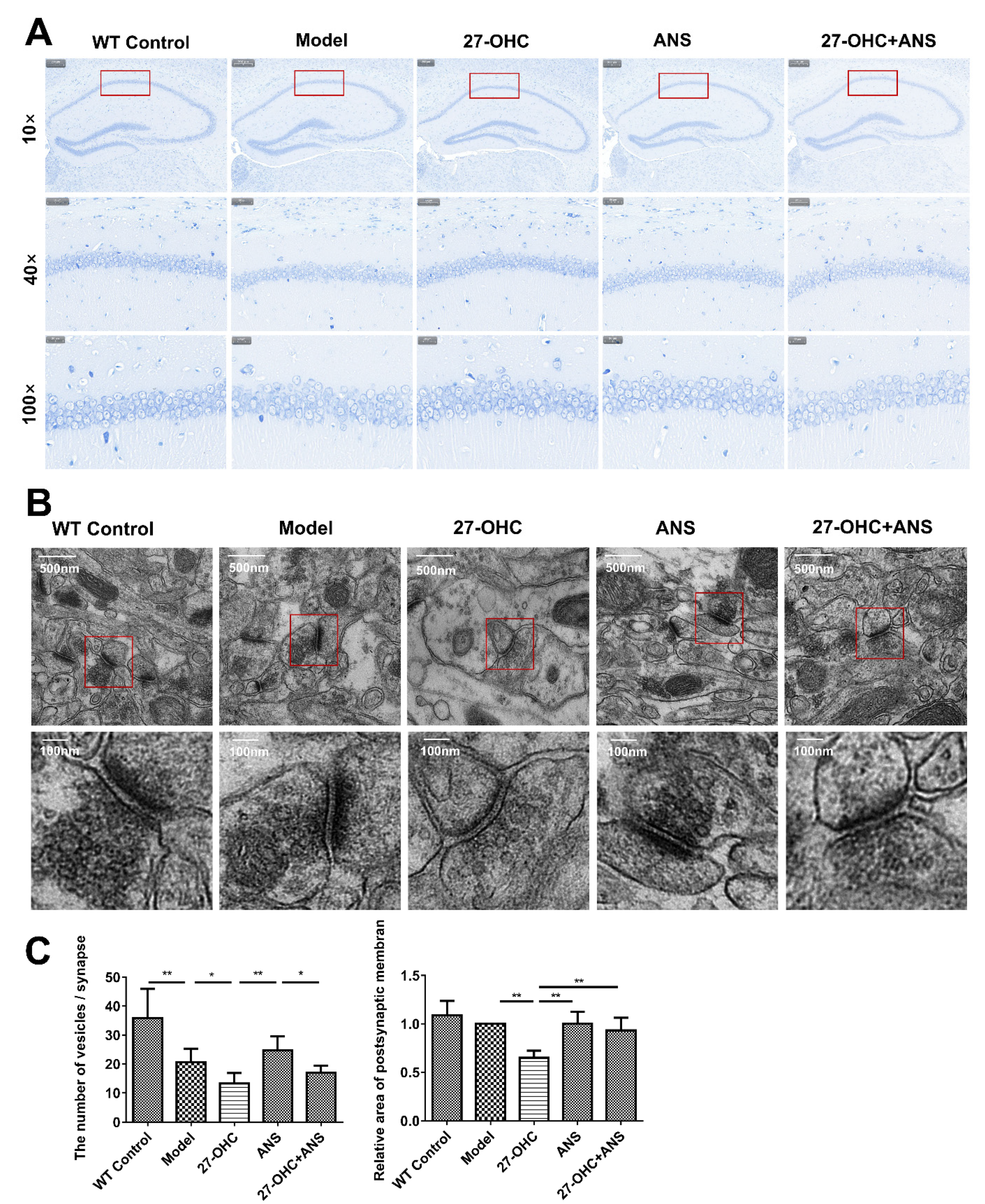
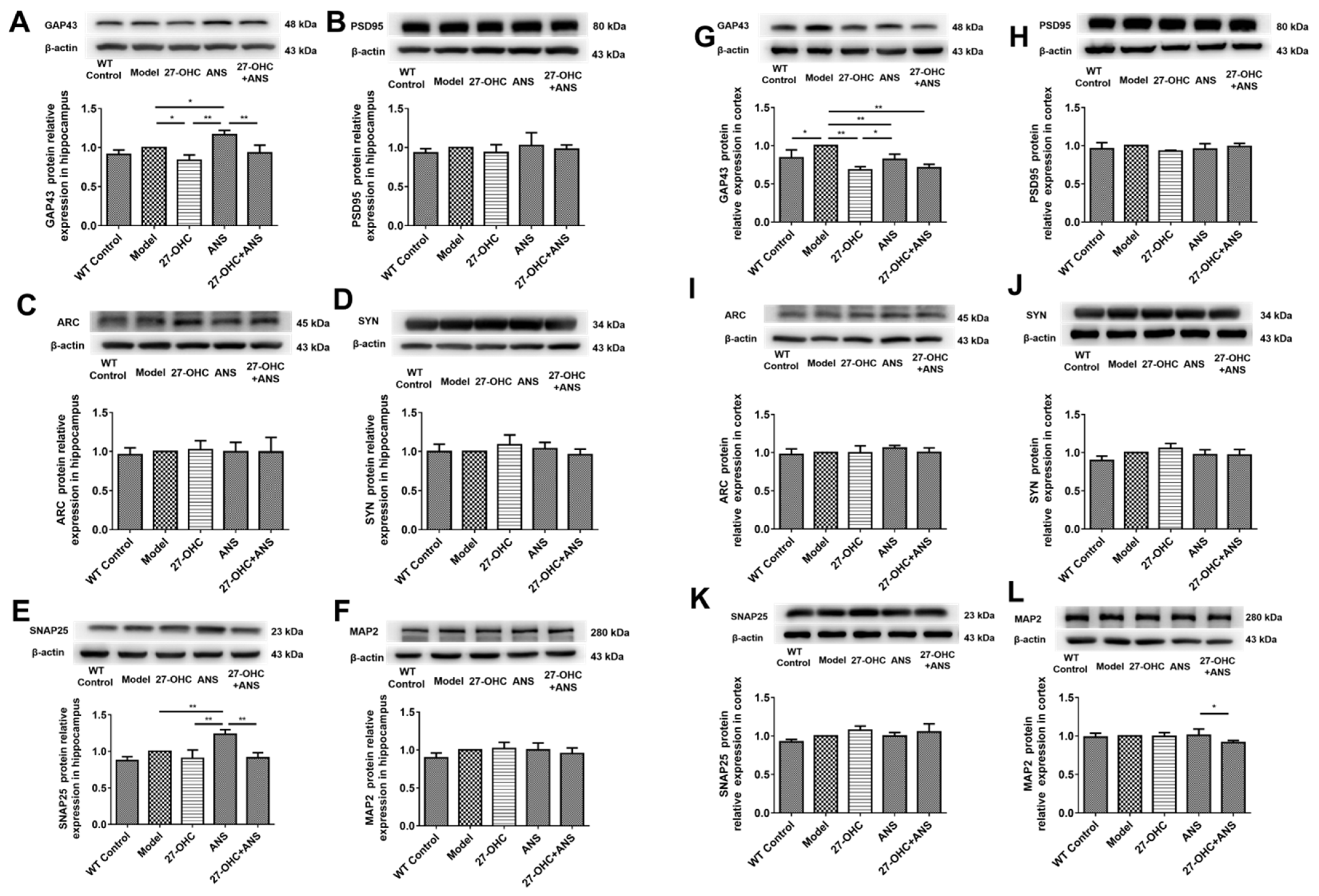
2.3. 27-OHC Damages Brain Tissue Structure and Nerve Synapses in Mice
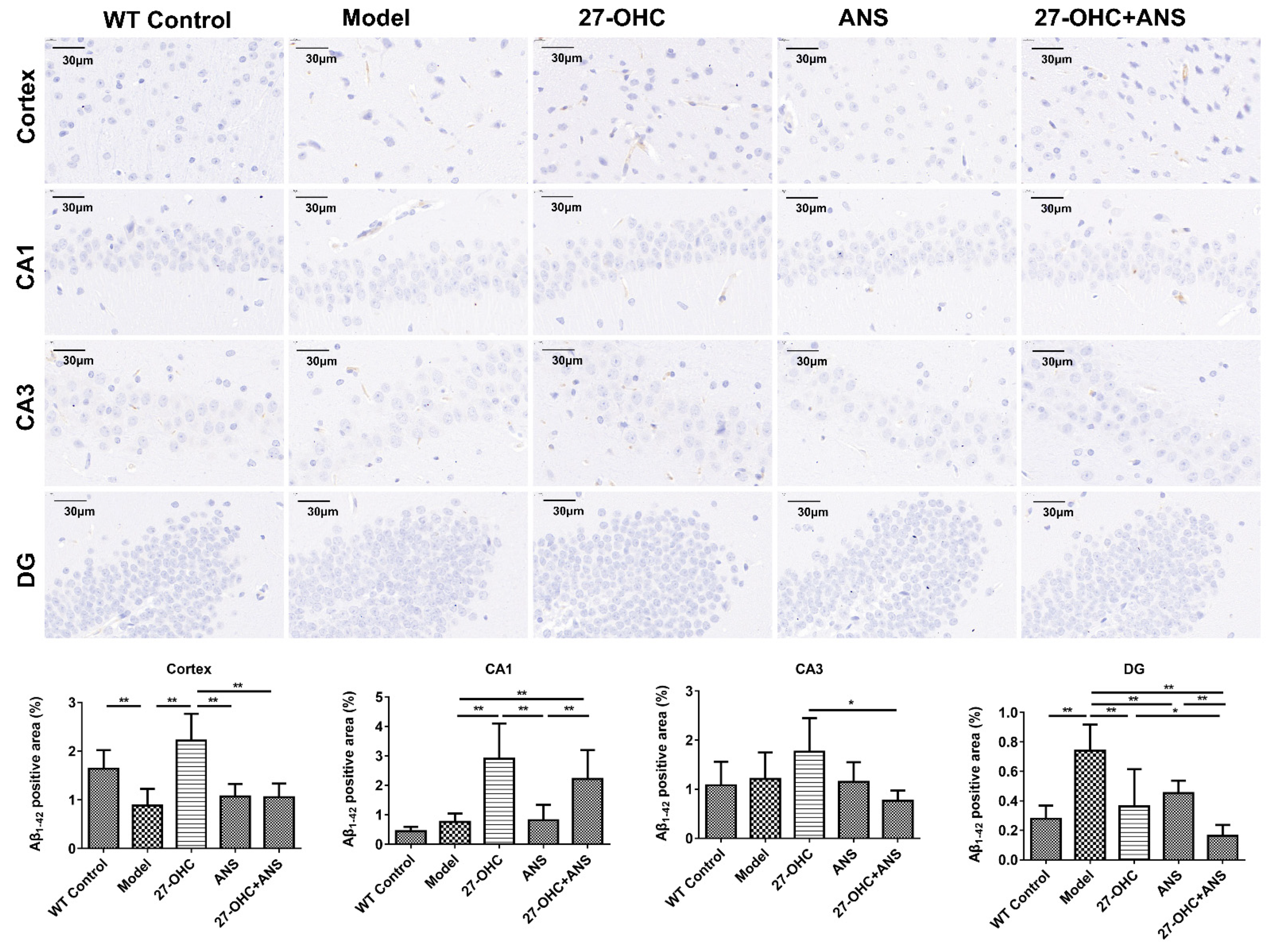
2.4. 27-OHC Increases Aβ Burden in Hippocampus and Cortex of ApoE4 Mice
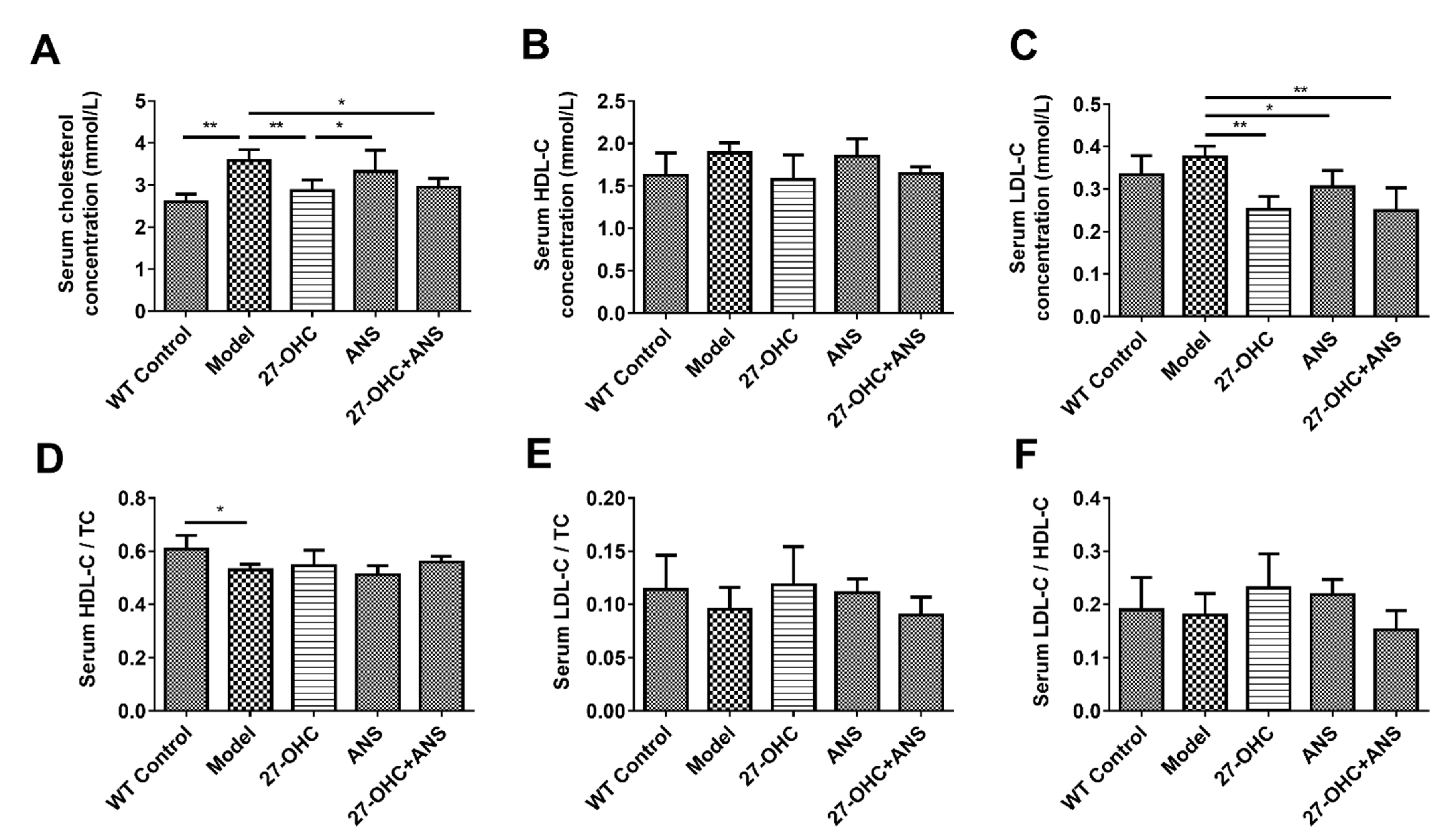
2.5. Serum Cholesterol Levels
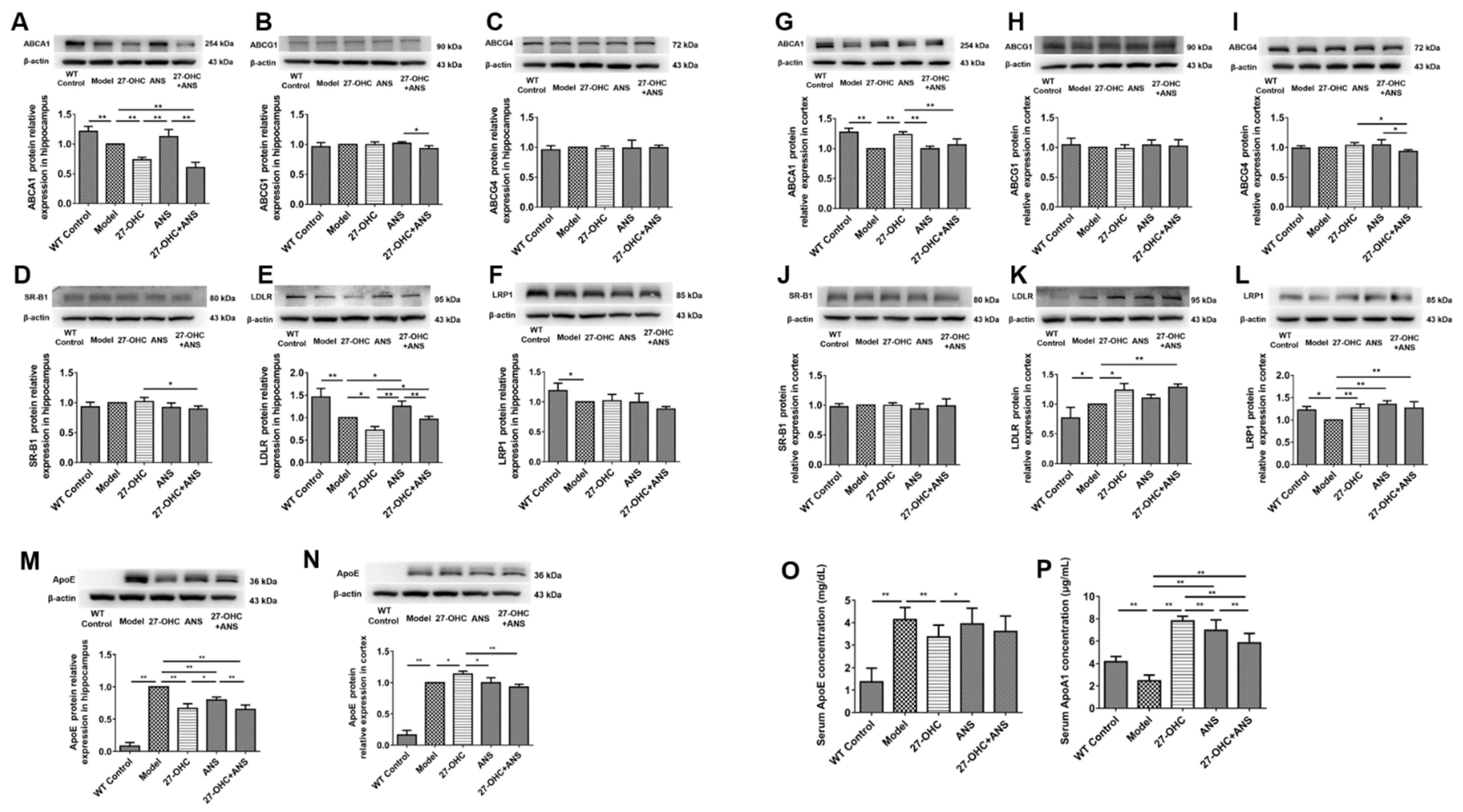
2.6. 27-OHC Affects Brain Cholesterol Transport
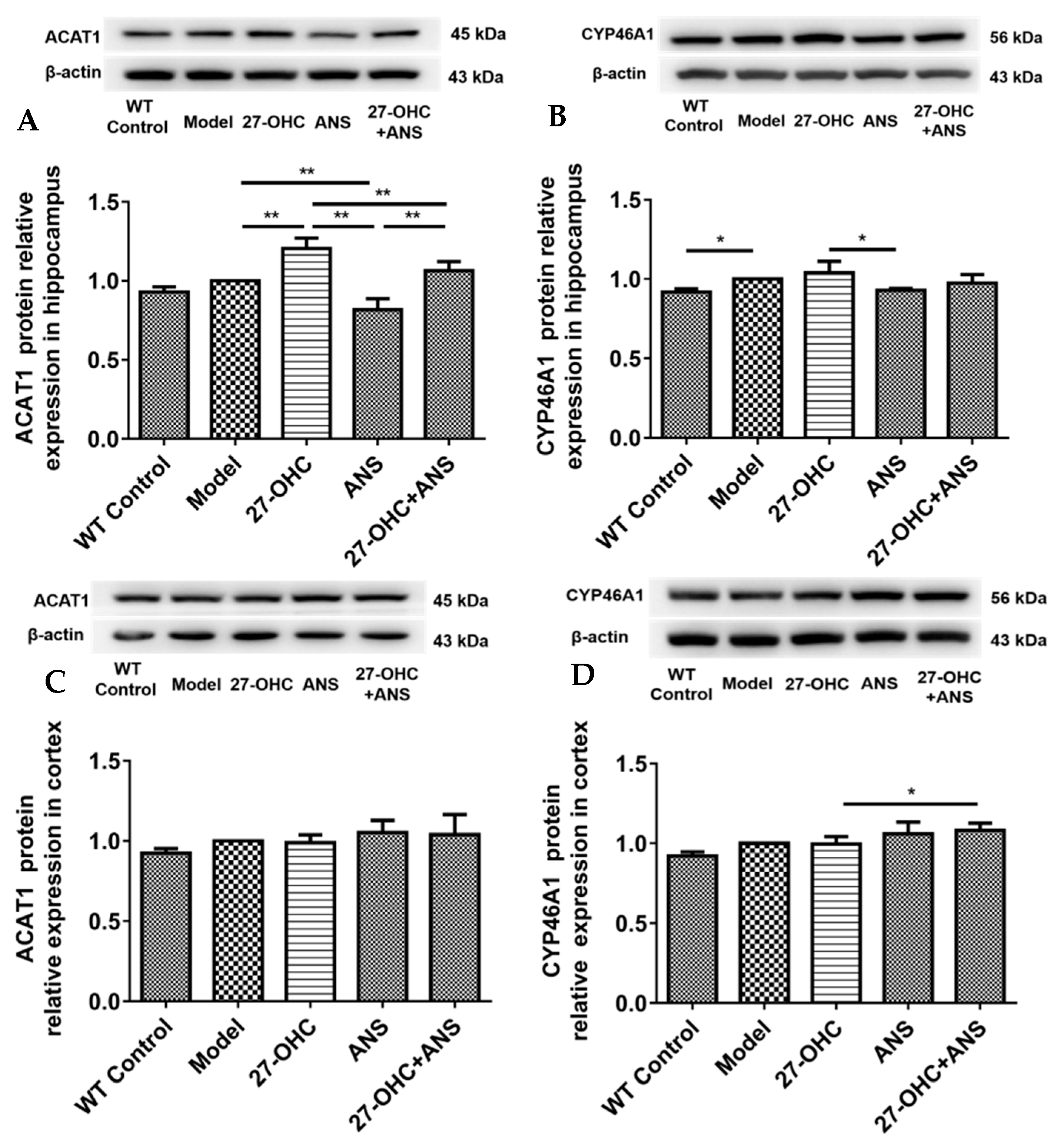
2.7. 27-OHC Affects Brain Cholesterol Conversion
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Treatments
4.2. Morris Water Maze
4.3. Nissl Staining
4.4. Transmission Electron Microscope
4.5. Immunohistochemistry
4.6. Biochemical Assays
4.7. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
4.8. Western-Blotting Analysis
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- DeTure, M.A.; Dickson, D.W. The neuropathological diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2019, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez, A.; Singh, S.K.; Churruca, M.; Maccioni, R.B. Alzheimer’s Disease and Tau Self-Assembly: In the Search of the Missing Link. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitali, C.; Wellington, C.L.; Calabresi, L. HDL and cholesterol handling in the brain. Cardiovasc. Res. 2014, 103, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, J.; Yang, H.; Song, B.L. Mechanisms and regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 225–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Q. Cholesterol metabolism and homeostasis in the brain. Protein Cell 2015, 6, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carmona, S.; Hardy, J.; Guerreiro, R. The genetic landscape of Alzheimer disease. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2018, 148, 395–408. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Lv, C.; An, Y.; Liu, Q.; Rong, H.; Tao, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, R. Increased Levels of 27-Hydroxycholesterol Induced by Dietary Cholesterol in Brain Contribute to Learning and Memory Impairment in Rats. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1700531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, L.; Hao, L.; Ju, M.; Xiao, R. High cholesterol and 27-hydroxycholesterol contribute to phosphorylation of tau protein by impairing autophagy causing learning and memory impairment in C57BL/6J mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2022, 106, 109016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staurenghi, E.; Giannelli, S.; Testa, G.; Sottero, B.; Leonarduzzi, G.; Gamba, P. Cholesterol Dysmetabolism in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Starring Role for Astrocytes? Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutemberezi, V.; Guillemot-Legris, O.; Muccioli, G.G. Oxysterols: From cholesterol metabolites to key mediators. Prog. Lipid Res. 2016, 64, 152–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurkinden, L.; Sviridov, D.; Vogt, B.; Escher, G. Sterol 27-hydroxylase gene dosage and the antiatherosclerotic effect of Rifampicin in mice. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20171162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.D.; Yu, H.L.; Ma, W.W.; Liu, Q.R.; Han, J.; Wang, H.; Xiao, R. 27-Hydroxycholesterol contributes to disruptive effects on learning and memory by modulating cholesterol metabolism in the rat brain. Neuroscience 2015, 300, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarrouk, A.; Hammouda, S.; Ghzaiel, I.; Hammami, S.; Khamlaoui, W.; Ahmed, S.H.; Lizard, G.; Hammami, M. Association Between Oxidative Stress and Altered Cholesterol Metabolism in Alzheimer’s Disease Patients. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2020, 17, 823–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; An, Y.; Yu, H.; Lu, Y.; Feng, L.; Wang, C.; Xiao, R. Relationship between oxysterols and mild cognitive impairment in the elderly: A case-control study. Lipids Health Dis. 2016, 15, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; An, Y.; Ma, W.; Yu, H.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, T.; Xiao, R. 27-Hydroxycholesterol contributes to cognitive deficits in APP/PS1 transgenic mice through microbiota dysbiosis and intestinal barrier dysfunction. J. Neuroinflammation 2020, 17, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, T.; Liu, W.; Wang, L.; Hao, L.; Ju, M.; Xiao, R. 27-Hydroxycholesterol Promotes the Transfer of Astrocyte-Derived Cholesterol to Neurons in Co-cultured SH-SY5Y Cells and C6 Cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 580599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; An, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yu, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Tao, L.; Xiao, R. 27-Hydroxycholesterol Alters Synaptic Structural and Functional Plasticity in Hippocampal Neuronal Cultures. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2019, 78, 238–247. [Google Scholar]
- An, Y.; Zhang, D.D.; Yu, H.L.; Ma, W.W.; Lu, Y.H.; Liu, Q.R.; Xiao, R. 27-Hydroxycholesterol regulates cholesterol synthesis and transport in C6 glioma cells. Neurotoxicology 2017, 59, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Strickland, M.R.; Soranno, A.; Holtzman, D.M. Apolipoprotein E: Structural Insights and Links to Alzheimer Disease Pathogenesis. Neuron 2021, 109, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.I.; Jeong, W.; Lim, H.; Cho, S.; Lee, H.; Jang, Y.; Cho, J.; Bae, S.; Lin, Y.T.; Tsai, L.H.; et al. APOE4-carrying human astrocytes oversupply cholesterol to promote neuronal lipid raft expansion and Abeta generation. Stem Cell Rep. 2021, 16, 2128–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolova, L.G.; Risacher, S.L.; Duran, T.; Stage, E.C.; Goukasian, N.; West, J.D.; Do, T.M.; Grotts, J.; Wilhalme, H.; Nho, K.; et al. Associations of the Top 20 Alzheimer Disease Risk Variants With Brain Amyloidosis. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 328–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharbi-Meliani, A.; Dugravot, A.; Sabia, S.; Regy, M.; Fayosse, A.; Schnitzler, A.; Kivimaki, M.; Singh-Manoux, A.; Dumurgier, J. The association of APOE epsilon4 with cognitive function over the adult life course and incidence of dementia: 20 years follow-up of the Whitehall II study. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2021, 13, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, J.; Betensky, R.A.; Hyman, B.T.; Serrano-Pozo, A. Association of APOE Genotype With Heterogeneity of Cognitive Decline Rate in Alzheimer Disease. Neurology 2021, 96, e2414–e2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Yamada, K.; Liddelow, S.A.; Smith, S.T.; Zhao, L.; Luo, W.; Tsai, R.M.; Spina, S.; Grinberg, L.T.; Rojas, J.C.; et al. ApoE4 markedly exacerbates tau-mediated neurodegeneration in a mouse model of tauopathy. Nature 2017, 549, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutsodendris, N.; Nelson, M.R.; Rao, A.; Huang, Y. Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer’s Disease: Findings, Hypotheses, and Potential Mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2022, 17, 73–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, Y.; Zhao, N.; Caulfield, T.R.; Liu, C.C.; Bu, G. Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer disease: Pathobiology and targeting strategies. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 501–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.A. APOE at the BBB: Pericyte-Derived Apolipoprotein E4 Diminishes Endothelial Cell Barrier Function. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanfranco, M.F.; Ng, C.A.; Rebeck, G.W. ApoE Lipidation as a Therapeutic Target in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.L.; Wang, Y.Y.; Liu, X.G.; Kuo, S.H.; Liu, N.; Song, Q.Y.; Wang, M.W. Cholesterol, 24-Hydroxycholesterol, and 27-Hydroxycholesterol as Surrogate Biomarkers in Cerebrospinal Fluid in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Meta-Analysis. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2016, 51, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandebring-Matton, A.; Goikolea, J.; Bjorkhem, I.; Paternain, L.; Kemppainen, N.; Laatikainen, T.; Ngandu, T.; Rinne, J.; Soininen, H.; Cedazo-Minguez, A.; et al. 27-Hydroxycholesterol, cognition, and brain imaging markers in the FINGER randomized controlled trial. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2021, 13, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.C.; Liu, C.C.; Kanekiyo, T.; Xu, H.; Bu, G. Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer disease: Risk, mechanisms and therapy. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 9, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, J.Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, B.H.; Xu, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, H.J. Brain Homotopic Connectivity in Mild Cognitive Impairment APOE-epsilon4 Carriers. Neuroscience 2020, 436, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xi, Y.; Yu, H.; An, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tao, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, T.; Xiao, R. 27-hydroxycholesterol promotes Abeta accumulation via altering Abeta metabolism in mild cognitive impairment patients and APP/PS1 mice. Brain Pathol. 2019, 29, 558–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mast, N.; Lin, J.B.; Pikuleva, I.A. Marketed Drugs Can Inhibit Cytochrome P450 27A1, a Potential New Target for Breast Cancer Adjuvant Therapy. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 88, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- John, A.; Reddy, P.H. Synaptic basis of Alzheimer’s disease: Focus on synaptic amyloid beta, P-tau and mitochondria. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 65, 101208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Flores, R.; La Joie, R.; Chetelat, G. Structural imaging of hippocampal subfields in healthy aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. 2015, 309, 29–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pelucchi, S.; Gardoni, F.; Di Luca, M.; Marcello, E. Synaptic dysfunction in early phases of Alzheimer’s Disease. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2022, 184, 417–438. [Google Scholar]
- Merino-Serrais, P.; Loera-Valencia, R.; Rodriguez-Rodriguez, P.; Parrado-Fernandez, C.; Ismail, M.A.; Maioli, S.; Matute, E.; Jimenez-Mateos, E.M.; Bjorkhem, I.; DeFelipe, J.; et al. 27-Hydroxycholesterol Induces Aberrant Morphology and Synaptic Dysfunction in Hippocampal Neurons. Cereb. Cortex 2019, 29, 429–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loera-Valencia, R.; Vazquez-Juarez, E.; Munoz, A.; Gerenu, G.; Gomez-Galan, M.; Lindskog, M.; DeFelipe, J.; Cedazo-Minguez, A.; Merino-Serrais, P. High levels of 27-hydroxycholesterol results in synaptic plasticity alterations in the hippocampus. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.Y.; Kwon, O.H.; Chung, S. Preferred Endocytosis of Amyloid Precursor Protein from Cholesterol-Enriched Lipid Raft Microdomains. Molecules 2020, 25, 5490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, D.M.; Liu, W.; Portelius, E.; Bayram, S.; Yasvoina, M.; Ho, S.H.; Smits, H.; Ali, S.S.; Steinberg, R.; Pegasiou, C.M.; et al. First effects of rising amyloid-beta in transgenic mouse brain: Synaptic transmission and gene expression. Brain A J. Neurol. 2015, 138 Pt 7, 1992–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dankner, R.; Ben Avraham, S.; Harats, D.; Chetrit, A. ApoE Genotype, Lipid Profile, Exercise, and the Associations With Cardiovascular Morbidity and 18-Year Mortality. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2020, 75, 1887–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, Y. Plasma cholesterol in Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal dementia. Transl. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malloy, S.I.; Altenburg, M.K.; Knouff, C.; Lanningham-Foster, L.; Parks, J.S.; Maeda, N. Harmful effects of increased LDLR expression in mice with human APOE*4 but not APOE*3. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Go, G.W.; Mani, A. Low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) family orchestrates cholesterol homeostasis. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2012, 85, 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, M.; Khan, S. Plasma Lipids as Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2020, 12, e12008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchi, C.; Adorni, M.P.; Caffarra, P.; Ronda, N.; Spallazzi, M.; Barocco, F.; Galimberti, D.; Bernini, F.; Zimetti, F. ABCA1- and ABCG1-mediated cholesterol efflux capacity of cerebrospinal fluid is impaired in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Lipid Res. 2019, 60, 1449–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, V.; Wang, S.; Sima, J.; Bar, R.; Liraz, O.; Gundimeda, U.; Parekh, T.; Chan, J.; Johansson, J.O.; Tang, C.; et al. ApoE4 Alters ABCA1 Membrane Trafficking in Astrocytes. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 9611–9622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, F.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Tan, C.; Wang, Q.; Xie, C.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging, I. APOE genotype moderates the relationship between LRP1 polymorphism and cognition across the Alzheimer’s disease spectrum via disturbing default mode network. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2021, 27, 1385–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.S.; Chan, S.L.; Hill, A.F.; Guillemin, G.J.; Garner, B. Impact of 27-hydroxycholesterol on amyloid-beta peptide production and ATP-binding cassette transporter expression in primary human neurons. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2009, 16, 121–131. [Google Scholar]
- La Joie, R.; Perrotin, A.; Barre, L.; Hommet, C.; Mezenge, F.; Ibazizene, M.; Camus, V.; Abbas, A.; Landeau, B.; Guilloteau, D.; et al. Region-specific hierarchy between atrophy, hypometabolism, and beta-amyloid (Abeta) load in Alzheimer’s disease dementia. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 16265–16273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Corona, A.W.; Kodoma, N.; Casali, B.T.; Landreth, G.E. ABCA1 is Necessary for Bexarotene-Mediated Clearance of Soluble Amyloid Beta from the Hippocampus of APP/PS1 Mice. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. Off. J. Soc. NeuroImmune Pharmacol. 2016, 11, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basak, J.M.; Verghese, P.B.; Yoon, H.; Kim, J.; Holtzman, D.M. Low-density lipoprotein receptor represents an apolipoprotein E-independent pathway of Abeta uptake and degradation by astrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 13959–13971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, D.E.; Pietrzik, C.U.; Baum, L.; Chevallier, N.; Merriam, D.E.; Kounnas, M.Z.; Wagner, S.L.; Troncoso, J.C.; Kawas, C.H.; Katzman, R.; et al. Modulation of amyloid beta-protein clearance and Alzheimer’s disease susceptibility by the LDL receptor-related protein pathway. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 106, 1159–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schreurs, B.G.; Sparks, D.L. Dietary high cholesterol and trace metals in the drinking water increase levels of ABCA1 in the rabbit hippocampus and temporal cortex. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2016, 49, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Mahley, R.W. Apolipoprotein E: Structure and function in lipid metabolism, neurobiology, and Alzheimer’s diseases. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 72 Pt A, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinez-Martinez, A.B.; Torres-Perez, E.; Devanney, N.; Del Moral, R.; Johnson, L.A.; Arbones-Mainar, J.M. Beyond the CNS: The many peripheral roles of APOE. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 138, 104809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, R.B.; Oliveira, T.G.; Cortes, E.P.; Honig, L.S.; Duff, K.E.; Small, S.A.; Wenk, M.R.; Shui, G.; Di Paolo, G. Comparative lipidomic analysis of mouse and human brain with Alzheimer disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 2678–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alavez-Rubio, J.S.; Juarez-Cedillo, T. ACAT1 as a Therapeutic Target and its Genetic Relationship with Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2019, 16, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodero, A.O. 24S-hydroxycholesterol: Cellular effects and variations in brain diseases. J. Neurochem. 2021, 157, 899–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahn, T.; Clark, C.; Kerksiek, A.; Lewczuk, P.; Lutjohann, D.; Popp, J. Cholesterol metabolites and plant sterols in cerebrospinal fluid are associated with Alzheimer’s cerebral pathology and clinical disease progression. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 205, 105785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Cui, S.; Hao, L.; Liu, W.; Wang, L.; Ju, M.; Feng, W.; Xiao, R. Regulation of Th17/Treg Balance by 27-Hydroxycholesterol and 24S-Hydroxycholesterol Correlates with Learning and Memory Ability in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Hao, L.; Wang, T.; Liu, W.; Wang, L.; Ju, M.; Feng, W.; Xiao, R. 27-Hydroxycholesterol-Induced Dysregulation of Cholesterol Metabolism Impairs Learning and Memory Ability in ApoE ε4 Transgenic Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11639. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911639
Wang Y, Hao L, Wang T, Liu W, Wang L, Ju M, Feng W, Xiao R. 27-Hydroxycholesterol-Induced Dysregulation of Cholesterol Metabolism Impairs Learning and Memory Ability in ApoE ε4 Transgenic Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(19):11639. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911639
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yushan, Ling Hao, Tao Wang, Wen Liu, Lijing Wang, Mengwei Ju, Wenjing Feng, and Rong Xiao. 2022. "27-Hydroxycholesterol-Induced Dysregulation of Cholesterol Metabolism Impairs Learning and Memory Ability in ApoE ε4 Transgenic Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 19: 11639. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911639
APA StyleWang, Y., Hao, L., Wang, T., Liu, W., Wang, L., Ju, M., Feng, W., & Xiao, R. (2022). 27-Hydroxycholesterol-Induced Dysregulation of Cholesterol Metabolism Impairs Learning and Memory Ability in ApoE ε4 Transgenic Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(19), 11639. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911639





