Quantitative Proteomic Analysis Reveals Yeast Cell Wall Products Influence the Serum Proteome Composition of Broiler Chickens
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Overview of LC-MS/MS Results
2.2. Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Serum from Broilers Fed a GHP1 Supplemented Diet vs. Serum from Broilers Fed on a Control Diet
2.3. Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Serum from Broilers Fed a GHP2 Supplemented Diet vs. Serum from Broilers Fed a Control Diet
2.4. Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Serum from Broilers Fed a GHP3 Supplemented Diet vs. Serum from Broilers Fed on a Control Diet
3. Discussion
3.1. Overview
3.2. Individual Proteins of Note
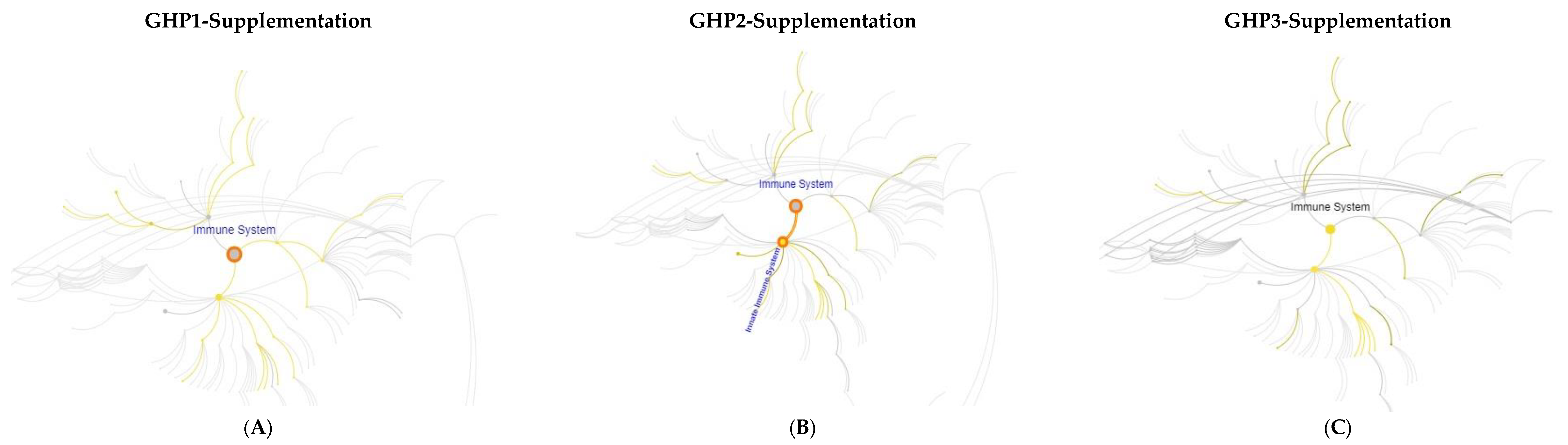
3.3. Immunological Effects
3.4. Effects on Metabolism
3.5. Vitamin A Transport
3.6. Effect of Organic Selenium Supplementation
4. Materials and Methods
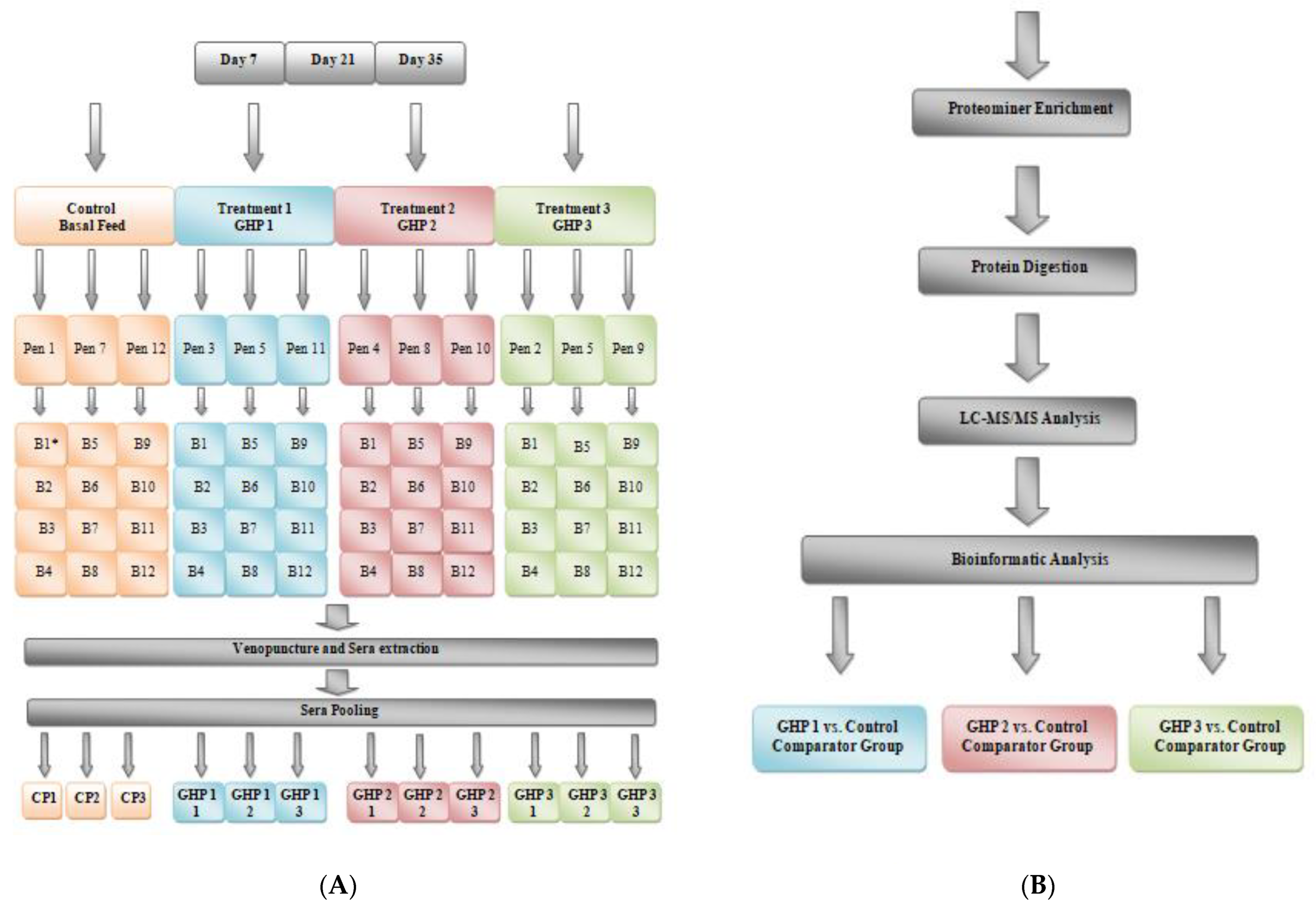
4.1. Experimental Design, Sample Collection and Preservation
4.2. ProteoMiner™ Serum Enrichment Evaluation
4.3. Upgraded ProteoMiner™ Processing for Serum Enrichment
4.4. Protein Digestion and Q-Exactive Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) Analysis
4.5. Label-Free Quantitative (LFQ) Proteomic Analysis Using MaxQuant and Perseus
4.6. A1AGP Immunoassay
4.7. Software and Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Y.; Iji, P.A.; Choct, M. Dietary modulation of gut microflora in broiler chickens: A review of the role of six kinds of alternatives to in-feed antibiotics. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 2009, 65, 97–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, B.J.; Lohakare, J.D.; Moon, W.K.; Lee, S.L.; Park, Y.H.; Hahn, T.W. Effects of supplementation of β-glucan on the growth performance and immunity in broilers. Res. Vet. Sci. 2006, 80, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalonso, N.; Goldman, G.H.; Gern, R.A.M.M. β-(1→3),(1→6)-Glucans: Medicinal activities, characterization, biosynthesis and new horizons. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 7893–7906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhang, H.J.; Yu, S.H.; Wu, S.G.; Yoon, I.; Quigley, J.; Gao, Y.P.; Qi, G.H. Effects of Yeast Culture in Broiler Diets on Performance and Immunomodulatory Functions. Poult. Sci. 2008, 87, 1377–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodridge, H.S.; Wolf, A.J.; Underhill, D.M. β-glucan recognition recognition by the innate immune system. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 230, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoving, L.R.; van der Zande, H.J.P.; Pronk, A.; Guigas, B.; Willems van Dijk, K.; van Harmelen, V. Dietary yeast-derived mannan oligosaccharides have immune-modulatory properties but do not improve high fat diet-induced obesity and glucose intolerance. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, S.K.; Beck, B.R.; Kim, D.; Park, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.D.; Ringø, E. Prebiotics as immunostimulants in aquaculture: A review. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 40, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCaffrey, C.; Corrigan, A.; Moynagh, P.; Murphy, R. Effect of yeast cell wall supplementation on intestinal integrity, digestive enzyme activity and immune traits of broilers. Br. Poult. Sci. 2021, 62, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, P.J.; Kelley, J.L.; Kogan, G.; Ensley, H.E.; Kalbfleisch, J.H.; Browder, I.W.; Williams, D.L. Human monocyte scavenger receptors are pattern recognition receptors for (1-3)-beta-D-glucans. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2002, 72, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majtán, J.; Kogan, G.; Kovácová, E.; Bíliková, K.; Simúth, J. Stimulation of TNF-alpha release by fungal cell wall polysaccharides. J. Biosci. 1998, 60, 921–926. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, K.; Goff, J.P.; Schmerr, M.J.; Stabel, J.R.; Inumaru, S.; Yokomizo, Y. Activation of Immune Cells in Bovine Mammary Gland Secretions by Zymosan-Treated Bovine Serum. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 1852–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Trincado, C.A.; Murtaugh, M.P. β-Glucan enhancement of T cell IFNγ response in swine. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2004, 102, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogan, G.; Kocher, A. Role of yeast cell wall polysaccharides in pig nutrition and health protection. Livest. Sci. 2007, 109, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacher, M.F.A.; Kamran, Z.; Ahsan, U.; Ahmad, S.; Koutoulis, K.C.; Qutab Ud Din, H.G.; Cengiz, Ö. Use of mannan oligosaccharide in broiler diets: An overview of underlying mechanisms. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 2017, 73, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, G.; Czop, J.K. Stimulation of human monocyte beta-glucan receptors by glucan particles induces production of TNF-alpha and IL-1 beta. Int. J. Immunopharmacol. 1992, 14, 1363–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashidhara, R.; Devegowda, G. Effect of dietary mannan oligosaccharide on broiler breeder production traits and immunity. Poult. Sci. 2003, 82, 1319–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spring, P.; Wenk, C.; Dawson, K.A.; Newman, K.E. The effects of dietary mannaoligosaccharides on cecal parameters and the concentrations of enteric bacteria in the ceca of salmonella-challenged broiler chicks. Poult. Sci. 2000, 79, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaseyed, T.; Bergström, J.H.; Gustafsson, J.K.; Ermund, A.; Birchenough, G.M.H.; Schütte, A.; van der Post, S.; Svensson, F.; Rodríguez-Piñeiro, A.M.; Nyström, E.E.L.; et al. The mucus and mucins of the goblet cells and enterocytes provide the first defense line of the gastrointestinal tract and interact with the immune system. Immunol. Rev. 2014, 260, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baurhoo, B.; Ferket, P.R.; Zhao, X. Effects of diets containing different concentrations of mannanoligosaccharide or antibiotics on growth performance, intestinal development, cecal and litter microbial populations, and carcass parameters of broilers. Poult. Sci. 2009, 88, 2262–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benites, V.; Gilharry, R.; Gernat, A.G.; Murillo, J.G. Effect of Dietary Mannan Oligosaccharide from Bio-Mos or SAF-Mannan on Live Performance of Broiler Chickens. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2008, 17, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žikić, D.; Perić, L.; Ušćebrka, G.; Stojanović, S.; Milić, D.; Nollet, L. Influence of Dietary Mannanoligosaccharides on Histological Parameters of the Jejunal Mucosa and Growth Performance of Broiler Chickens; Academic Journals: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2002; Volume 10, pp. 6172–6176. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Cappelletti, V.; Picotti, P. Quantitative proteomics of model organisms. Curr. Opin. Syst. Biol. 2017, 6, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendixen, E.; Danielsen, M.; Hollung, K.; Gianazza, E.; Miller, I. Farm animal proteomics—A review. J. Proteom. 2011, 74, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, A.M.; Bassols, A.; Bendixen, E.; Bhide, M.; Ceciliani, F.; Cristobal, S.; Eckersall, P.D.; Hollung, K.; Lisacek, F.; Mazzucchelli, G.; et al. Animal board invited review: Advances in proteomics for animal and food sciences. Anim. Int. J. Anim. Biosci. 2015, 9, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Girolamo, F.; D’Amato, A.; Lante, I.; Signore, F.; Muraca, M.; Putignani, L. Farm Animal Serum Proteomics and Impact on Human Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 15396–15411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horvatić, A.; Guillemin, N.; Kaab, H.; McKeegan, D.; O’Reilly, E.; Bain, M.; Kuleš, J.; Eckersall, P.D. Integrated dataset on acute phase protein response in chicken challenged with Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide endotoxin. Data Brief 2018, 21, 684–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvatić, A.; Guillemin, N.; Kaab, H.; McKeegan, D.; O’Reilly, E.; Bain, M.; Kuleš, J.; Eckersall, P.D. Quantitative proteomics using tandem mass tags in relation to the acute phase protein response in chicken challenged with Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide endotoxin. J. Proteom. 2019, 192, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packialakshmi, B.; Liyanage, R.; Lay, J.O.; Makkar, S.K.; Rath, N.C. Proteomic changes in chicken plasma induced by Salmonella typhimurium lipopolysaccharides. Proteom. Insights 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hawkridge, A.M.; Wysocky, R.B.; Petitte, J.N.; Anderson, K.E.; Mozdziak, P.E.; Fletcher, O.J.; Horowitz, J.M.; Muddiman, D.C. Measuring the intra-individual variability of the plasma proteome in the chicken model of spontaneous ovarian adenocarcinoma. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, S.-Y.; Lin, J.-H.; Chen, Y.-H.; Chuang, C.-K.; Chiu, Y.-F.; Chen, M.-Y.; Chen, H.-H.; Lee, W.-C. Analysis of chicken serum proteome and differential protein expression during development in single-comb White Leghorn hens. Proteomics 2006, 6, 2217–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, C.D.; Lichti, C.F.; Diekman, A.B.; Foley, S.L. Evaluation of Differentially Expressed Proteins Following Serum Exposure in Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Avian Dis. 2008, 52, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packialakshmi, B.; Liyanage, R.; Lay, J.O.; Okimoto, R.; Rath, N.C. Proteomic Changes in the Plasma of Broiler Chickens with Femoral Head Necrosis. Biomark. Insights 2016, 11, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desoubeaux, G.; Chauvin, D.; Del Carmen Piqueras, M.; Bronson, E.; Bhattacharya, S.K.; Sirpenski, G.; Bailly, E.; Cray, C. Translational proteomic study to address host protein changes during aspergillosis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Bai, X.; Luo, C.; Jiang, D.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Y.; Huang, Y. Quantitative proteomic analysis of chicken serum reveals key proteins affecting follicle development during reproductive phase transitions. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidiropoulos, K.; Viteri, G.; Sevilla, C.; Jupe, S.; Webber, M.; Orlic-Milacic, M.; Jassal, B.; May, B.; Shamovsky, V.; Duenas, C.; et al. Reactome enhanced pathway visualization. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3461–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cepelak, I.; Cvoriscec, D. Biochemical markers of bone remodeling—review. Biochem. Med. 2009, 19, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanotra, G.S.; Lund, J.D.; Ersbøll, A.K.; Petersen, J.S.; Vestergaard, K.S. Monitoring leg problems in broilers: A survey of commercial broiler production in Denmark. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 2001, 57, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, M.E. Skeletal Deformities and Their Causes: Introduction. Poult. Sci. 2000, 79, 982–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Yang, J.; Cai, J.; Luan, Y.; Sattar, H.; Liu, M.; Xu, S.; Zhang, Z. Analysis of the Interactions Between Thioredoxin and 20 Selenoproteins in Chicken. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2017, 179, 304–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menheniott, T.R.; O’Connor, L.; Chionh, Y.T.; Däbritz, J.; Scurr, M.; Rollo, B.N.; Ng, G.Z.; Jacobs, S.; Catubig, A.; Kurklu, B.; et al. Loss of gastrokine-2 drives premalignant gastric inflammation and tumor progression. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 1383–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brümmer, M.; Jansen van Rensburg, C.; Moran, C.A. Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Cell Wall Products: The Effects on Gut Morphology and Performance of Broiler Chickens; South African Society of Animal Production: Pietermaritzburg, South Africa, 2010; Volume 40. [Google Scholar]
- Surai, P.F.; Earle-Payne, K. Antioxidant Defences and Redox Homeostasis in Animals. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, I.P.; Koziel, H.; Alan, R.; Ezekowitz, B. The serum mannose-binding protein and the macrophage mannose receptor are pattern recognition molecules that link innate and adaptive immunity. Semin. Immunol. 1998, 10, 363–372. [Google Scholar]
- Worthley, D.L.; Bardy, P.G.; Mullighan, C.G. Mannose-binding lectin: Biology and clinical implications. Intern. Med. J. 2005, 35, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich-Lynge, S.L.; Dalgaard, T.S.; Norup, L.R.; Song, X.; Sørensen, P.; Juul-Madsen, H.R. Chicken mannose-binding lectin function in relation to antibacterial activity towards Salmonella enterica. Immunobiology 2015, 220, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, A.E.; Cai, S.; Liu, D. The Biological Role of the C1 Inhibitor in Regulation of Vascular Permeability and Modulation of Inflammation. Adv. Immunol. 2004, 82, 331–363. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Turner, M.W. The role of mannose-binding lectin in health and disease. Mol. Immunol. 2003, 40, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slawinska, A.; Plowiec, A.; Siwek, M.; Jaroszewski, M.; Bednarczyk, M. Long-Term Transcriptomic Effects of Prebiotics and Synbiotics Delivered In Ovo in Broiler Chickens. PloS ONE 2016, 11, e0168899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mensink, M.A.; Frijlink, H.W.; van der Voort Maarschalk, K.; Hinrichs, W.L.J. Inulin, a flexible oligosaccharide. II: Review of its pharmaceutical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 134, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cerezuela, R.; Guardiola, F.A.; Meseguer, J.; Esteban, M.Á. Increases in immune parameters by inulin and Bacillus subtilis dietary administration to gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L.) did not correlate with disease resistance to Photobacterium damselae. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 32, 1032–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haagsman, H.P.; Hogenkamp, A.; van Eijk, M.; Veldhuizen, E.J.A. Surfactant Collectins and Innate Immunity. Neonatology 2008, 93, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rodacka, A. Properties and functional diversity of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Postep. Hig. I Med. Dosw. (Online) 2013, 67, 775–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, A. (Ed.) Chapter 7 - β-Hexosaminidase, Acetaldehyde–Protein Adducts, and Dolichol as Alcohol Biomarkers. In Alcohol and its Biomarkers; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015; pp. 163–180. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, E.A.; Schroeder, W.A. Microbial carotenoids. Adv. Biochem. Eng./Biotechnol. 1996, 53, 119–178. [Google Scholar]
- Clagett-Dame, M.; DeLuca, H.F. The role of vitamin A in mammalian reproduction and embryonic development. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2002, 22, 347–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, C.Y.; Sell, J.L. Effect of all-trans Retinol and Retinoic Acid Nutriture on the Immune System of Chicks. J. Nutr. 1983, 113, 1914–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sklan, D.; Melamed, D.; Friedman, A. The Effect of Varying Levels of Dietary Vitamin A on Immune Response in the Chick. Poult. Sci. 1994, 73, 843–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabetian-Targhi, F.; Mahmoudi, M.J.; Rezaei, N.; Mahmoudi, M. Retinol Binding Protein 4 in Relation to Diet, Inflammation, Immunity, and Cardiovascular Diseases. Adv. Nutr. 2015, 6, 748–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, C.; Keen, H.L.; Lu, K.-T.; Liu, X.; Wu, J.; Davis, D.R.; Ibeawuchi, S.-R.C.; Vogel, S.; Quelle, F.W.; Sigmund, C.D. Retinol-binding protein 7 is an endothelium-specific PPARγ cofactor mediating an antioxidant response through adiponectin. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e91738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Shen, J.; Sun, Z.; Li, J.; Li, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y. Discovery of Several Novel Targets that Enhance β-Carotene Production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamano, S.; Ishii, T.; Nakagawa, M.; Ikenaga, H.; Misawa, N. Metabolic engineering for production of beta-carotene and lycopene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1994, 58, 1112–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choct, M.; Naylor, A.J.; Reinke, N. Selenium supplementation affects broiler growth performance, meat yield and feather coverage. Br. Poult. Sci. 2004, 45, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surai, P.F. Selenium in poultry nutrition 1. Antioxidant properties, deficiency and toxicity. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 2002, 58, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surai, P.F.; Fisinin, V.I. Selenium in poultry breeder nutrition: An update. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2014, 191, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lönnerdal, B.; Vargas-Fernández, E.; Whitacre, M. Selenium fortification of infant formulas: Does selenium form matter? Food Funct. 2017, 8, 3856–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peric, L.; Milosevic, N.; Zikic, D.; Kanacki, Z.; Dzinic, N.; Nollet, L.; Spring, P. Effect of selenium sources on performance and meat characteristics of broiler chickens. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2009, 18, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayman, M.P. The use of high-selenium yeast to raise selenium status: How does it measure up? Br. J. Nutr. 2004, 92, 557–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.-B.; Xu, B.-H. Effect of different selenium source (sodium selenite and selenium yeast) on broiler chickens. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2008, 144, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; Zhan, X.A.; Yuan, D.; Zhang, X.W.; Wu, R.J. Effects of selenomethionine and sodium selenite supplementation on meat quality, selenium distribution and antioxidant status in broilers. Czech J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 56, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahan, D.C.; Cline, T.R.; Richert, B. Effects of dietary levels of selenium-enriched yeast and sodium selenite as selenium sources fed to growing-finishing pigs on performance, tissue selenium, serum glutathione peroxidase activity, carcass characteristics, and loin quality. J. Anim. Sci. 1999, 77, 2172–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beckett, G.J.; Hayes, J.D. Glutathione S-Transferases: Biomedical Applications. Adv. Clin. Chem. 1993, 30, 281–380. [Google Scholar]
- Kilty, C.; Doyle, S.; Hassett, B.; Manning, F. Glutathione S-transferases as biomarkers of organ damage: Applications of rodent and canine GST enzyme immunoassays. Chem. Biol. Interact. 1998, 111-112, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, G.W.; Trull, A.K.; Doyle, S. Evaluation of an enzyme-immunometric assay for serum alpha-glutathione S-transferase. Ann Clin. Biochem. 1995, 32 Pt 6, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Federico, A.; Tuccillo, C.; Crafa, E.; Loguercio, C. The significance of alpha-glutathione S-transferase determination in patients with chronic liver diseases. Minerva Gastroenterol. Dietol. 1999, 45, 181–185. [Google Scholar]
- Yukihiko, A.; Kazuomi, H.; Yoshiro, T.; Misuzu, T.; Yasuhiro, O.; Toshio, Y. Serum glutathione s-transferase activity in liver diseases. Clin. Chim. Acta 1980, 106, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrigan, A.; Fay, B.J.; Corcionivoschi, N.; Murphy, R.A. Effect of yeast mannan-rich fractions on reducing Campylobacter colonization in broiler chickens. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2017, 26, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolan, S.K.; Bock, T.; Hering, V.; Owens, R.A.; Jones, G.W.; Blankenfeldt, W.; Doyle, S. Structural, mechanistic and functional insight into gliotoxin bis-thiomethylation in Aspergillus fumigatus. Open Biol. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traynor, A.M.; Owens, R.A.; Coughlin, C.M.; Holton, M.C.; Jones, G.W.; Calera, J.A.; Doyle, S. At the metal-metabolite interface in Aspergillus fumigatus: Towards untangling the intersecting roles of zinc and gliotoxin. Microbiol. (Read.) 2021, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyanova, S.; Temu, T.; Carlson, A.; Sinitcyn, P.; Mann, M.; Cox, J. Visualization of LC-MS/MS proteomics data in MaxQuant. Proteomics 2015, 15, 1453–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tyanova, S.; Temu, T.; Sinitcyn, P.; Carlson, A.; Hein, M.Y.; Geiger, T.; Mann, M.; Cox, J. The Perseus computational platform for comprehensive analysis of (prote)omics data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
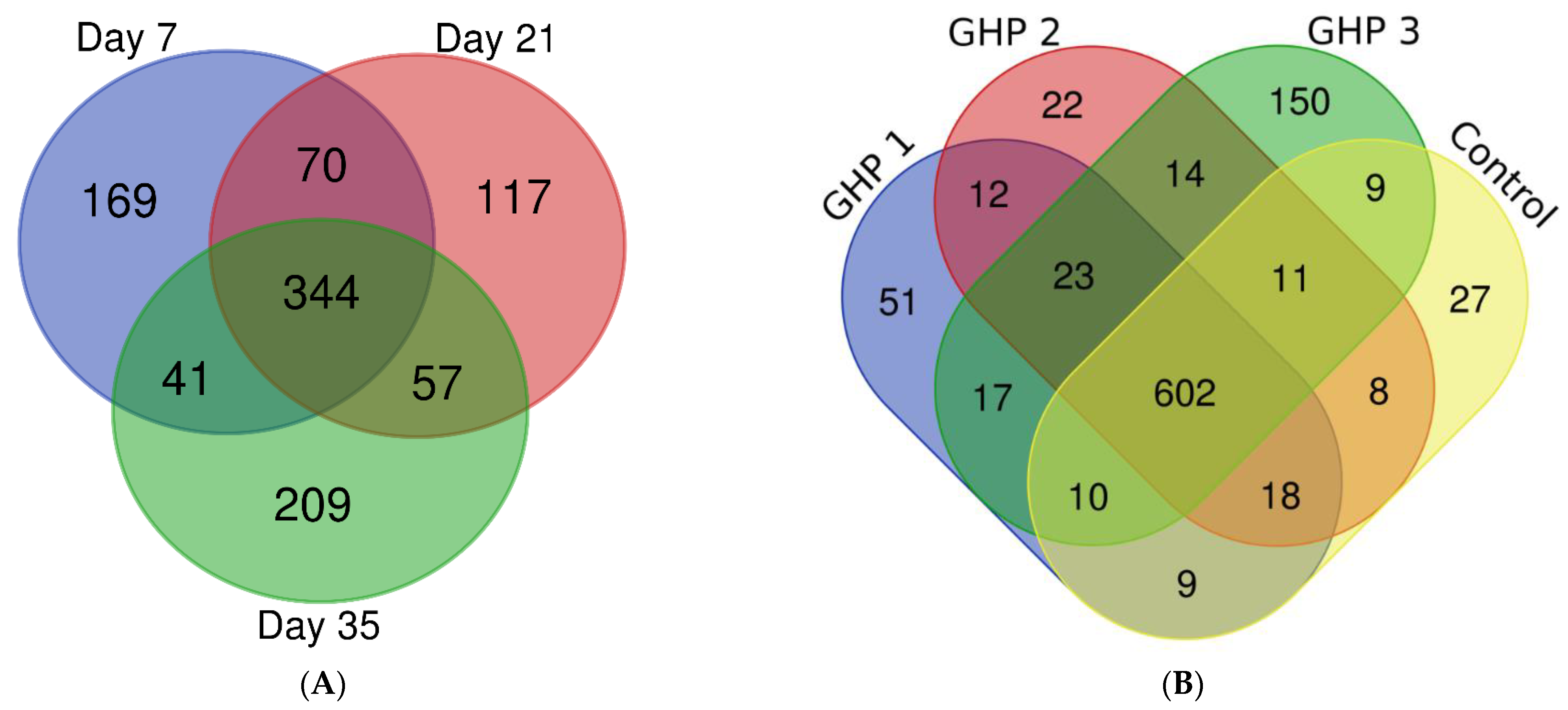

| Comparator Group | Total Identified Proteins | Significant changes * | Unique/Absent Changes ** | Total Changes | Total Changes (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D7 GHP1 vs. D7 control | 651 | 51 | 21 | 72 | 11.06 |
| D7 GHP2 vs. D7 control | 38 | 26 | 64 | 9.83 | |
| D7 GHP3 vs. D7 control | 14 | 28 | 42 | 6.45 | |
| D21 GHP1 vs. D21 control | 588 | 34 | 9 | 43 | 7.31 |
| D21 GHP2 vs. D21 control | 25 | 9 | 34 | 5.78 | |
| D21 GHP3 vs. D21 control | 23 | 10 | 33 | 5.61 | |
| D35 GHP1 vs. D35 control | 624 | 21 | 10 | 31 | 4.97 |
| D35 GHP2 vs. D35 control | 21 | 17 | 38 | 6.09 | |
| D35 GHP3 vs. D35 control | 29 | 14 | 43 | 6.89 |
| Protein Description | Fold Change 1 | Peptides | Coverage (%) 2 | Day 3 | Accession |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N-acetyl-alpha-glucosaminidase | Unique | 2 | 3.7 | Day 7 | A0A1D5NU78 |
| Uncharacterized protein | Unique | 2 | 1 | Day 7 | A0A1D5NZ61 |
| Dynactin subunit 2 | Unique | 6 | 22.1 | Day 7 | A0A1D5PGQ9 |
| Uncharacterized protein | Unique | 5 | 41.4 | Day 7 | A0A1D5PQ15 |
| Proteasome endopeptidase complex | Unique | 3 | 43.7 | Day 7 | A0A1L1RSU8 |
| Proteasome subunit beta 1 | Unique | 3 | 36.4 | Day 7 | A0A1L1RYR5 |
| Retinol binding protein 7 | Unique | 3 | 32.1 | Day 7 | E1C0M1 |
| Uncharacterized protein | Unique | 4 | 30.8 | Day 7 | F1N8Y3 |
| Elongation factor 1-alpha | Unique | 15 | 49.9 | Day 7 | F1N9H4 |
| Succinyl-CoA:3-ketoacid-coenzyme A transferase | Unique | 3 | 11 | Day 7 | F1N9Z7 |
| Endoplasmic reticulum lectin 1 | Unique | 3 | 12 | Day 7 | F1NCV8 |
| Small nuclear ribonucleoprotein 13 | Unique | 3 | 30.5 | Day 7 | F1NII6 |
| PDZ and LIM domain 5 | Unique | 4 | 8.2 | Day 7 | F1NTC8 |
| Proteasome 26S subunit, ATPase 5 | Unique | 3 | 12.7 | Day 7 | F1NU79 |
| Natriuretic peptides A (Prepronatriodilatin) | Unique | 3 | 17.9 | Day 7 | P18908 |
| Profilin | Unique | 2 | 27.9 | Day 7 | Q5ZL50 |
| Twisted gastrulation protein homolog 1 | Unique | 2 | 15.6 | Day 7 | Q98T89 |
| Cytidine/uridine monophosphate kinase 2 | Unique | 6 | 26.5 | Day 7 | R4GJC4 |
| Nucleoside diphosphate kinase | Unique | 2 | 20.3 | Day 21 | O57535 |
| Osteocalcin | Unique | 3 | 45.4 | Day 21 | P02822 |
| Tenascin | Unique | 8 | 8.7 | Day 21 | P10039 |
| Gastrokine 2 | Unique | 2 | 18.6 | Day 35 | A0A1D5PFM9 |
| N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphate transferase γ subunit | Unique | 2 | 16 | Day 35 | E1BS68 |
| N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphate transferase γ subunit | 0.34 | 5 | 27.2 | Day 7 | E1BS68 |
| Adhesion G protein-coupled receptor G6 | Unique | 2 | 2.5 | Day 35 | E1C8C2 |
| Alpha-1-anti-ase | Unique | 9 | 27.8 | Day 35 | F1NPN5 |
| Aggrecan core protein | Unique | 3 | 2.3 | Day 35 | F1NZX1 |
| Alpha-1-acid glycoprotein | 2.12 | 7 | 13.9 | Day 35 | Q8JIG5 |
| Transferrin receptor protein 1 | 1.7 | 10 | 10.5 | Day 35 | Q90997 |
| Heat shock protein beta-1 | 1.3 | 18 | 77.9 | Day 7 | F1P593 |
| Myosin light chain 1, skeletal muscle isoform | 1.23 | 9 | 54.9 | Day 7 | P02604 |
| Myosin regulatory light chain 2, skeletal muscle isoform | 1.22 | 9 | 57.7 | Day 7 | P02609 |
| Adenylate kinase isoenzyme 1 | 1.15 | 11 | 58.1 | Day 7 | P05081 |
| Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | 1.13 | 20 | 72.1 | Day 7 | P00356 |
| Proline and arginine rich end leucine rich repeat protein | 1.13 | 10 | 27.9 | Day 7 | A0A1D5PAN0 |
| Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | 1.11 | 9 | 24 | Day 7 | A0A1D5P1Y7 |
| Proteasome subunit alpha type | 1.08 | 7 | 36.2 | Day 7 | F1NC02 |
| Uncharacterized protein | 1.08 | 7 | 21.1 | Day 7 | F1NIP5 |
| N-Phosphoglycerate kinase | 0.94 | 17 | 51.9 | Day 7 | F1NU17 |
| Complement C5 | 0.93 | 82 | 54.8 | Day 35 | E1BRS7 |
| Dynactin subunit 3 | 0.89 | 6 | 32.9 | Day 7 | A0A1D6UPU1 |
| Glutaredoxin 3 | 0.88 | 8 | 29.8 | Day 7 | A0A1D5NW30 |
| Uncharacterized protein | 0.86 | 7 | 15.2 | Day 7 | A0A1L1RQM3 |
| Low mol. weight phosphotyrosine protein phosphatase | 0.84 | 10 | 58.5 | Day 7 | A0A1D5P9Z1 |
| Proteasome subunit alpha type | 0.84 | 9 | 46.3 | Day 7 | A0A1L1S0K9 |
| Protein/nucleic acid deglycase DJ-1 | 0.84 | 5 | 51.4 | Day 7 | A0A1D5PN39 |
| Complement C6 | 0.83 | 29 | 33.4 | Day 35 | B8ZX71 |
| Proteasome subunit beta type | 0.79 | 13 | 56.6 | Day 7 | A0A1L1RUE7 |
| Proteasome subunit alpha type | 0.79 | 5 | 36.1 | Day 7 | A0A1D5PHL0 |
| Periostin | 0.77 | 16 | 24.5 | Day 21 | F1P4N9 |
| Receptor of-activated protein C kinase 1 | 0.76 | 9 | 40.9 | Day 7 | A0A1I7Q3Y2 |
| Proteasome subunit alpha type | 0.76 | 6 | 23.9 | Day 7 | F1NEQ6 |
| Serpin H1 | 0.76 | 12 | 34.9 | Day 7 | P13731 |
| Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 | 0.75 | 6 | 13 | Day 21 | F1P201 |
| Ribosomal protein S14 | 0.69 | 4 | 34.9 | Day 7 | Q5ZHW8 |
| T-complex 1 | 0.68 | 9 | 17.6 | Day 7 | Q5ZMG9 |
| Uncharacterized protein | 0.67 | 8 | 38.3 | Day 7 | A0A1D5PAH2 |
| Complement C7 | 0.66 | 28 | 52.3 | Day 35 | E1C6U2 |
| T-complex protein 1 subunit zeta | 0.64 | 20 | 51.8 | Day 7 | Q5ZJ54 |
| Elongation factor 1-alpha 1 | 0.63 | 18 | 54 | Day 7 | Q90835 |
| Retinol-binding protein 4 | 0.61 | 11 | 68.9 | Day 7 | P41263 |
| Proteasome subunit alpha type | 0.6 | 6 | 41.5 | Day 7 | Q5ZJX9 |
| Nuclear transport factor 2 | 0.55 | 3 | 33.9 | Day 7 | F1NLL4 |
| Chaperonin containing TCP1 subunit 5 | 0.55 | 17 | 34.4 | Day 7 | Q5F411 |
| 40S ribosomal protein S12 | 0.54 | 7 | 61.4 | Day 7 | P84175 |
| Uncharacterized protein | 0.54 | 6 | 39.8 | Day 35 | A0A1D5PK48 |
| Peroxiredoxin-6 | 0.53 | 12 | 66.4 | Day 7 | F1NBV0 |
| Uncharacterized protein | 0.51 | 6 | 40.2 | Day 35 | A0A1D5PZU8 |
| Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A-1 | 0.5 | 6 | 56.6 | Day 7 | Q09121 |
| Glia maturation factor beta | 0.5 | 5 | 31.6 | Day 7 | A0A1D6UPR3 |
| Complement C4 precursor | 0.48 | 61 | 45.6 | Day 35 | A0A1D5P5V5 |
| Collagen type V alpha 1 chain | 0.46 | 6 | 4.8 | Day 21 | F1NI79 |
| Insulin-like growth factor binding protein acid labile subunit | 0.44 | 8 | 15.4 | Day 21 | F1NI07 |
| TRK-fused gene | 0.41 | 4 | 12.9 | Day 7 | A0A1L1RK44 |
| Complement factor B-like protease | 0.39 | 6 | 36.8 | Day 7 | P81475 |
| Nidogen 2 | 0.36 | 20 | 16.3 | Day 35 | F1NDL4 |
| Uncharacterized protein | 0.35 | 5 | 17.6 | Day 7 | Q5ZMC1 |
| Complement factor H | 0.32 | 93 | 71.5 | Day 7 | E1C7P4 |
| Glutathione peroxidase | 0.3 | 11 | 45.9 | Day 7 | F1NPJ8 |
| Interleukin 6 signal transducer | 0.29 | 3 | 5 | Day 7 | A0A1D5PMY8 |
| Sortilin | 0.28 | 14 | 21.3 | Day 7 | A0A1D5PNT8 |
| Glutaminyl-peptide cyclotransferase | 0.26 | 13 | 58.5 | Day 7 | A0A1D5PRR0 |
| Fibromodulin | 0.23 | 2 | 3.7 | Day 21 | P51887 |
| Mimecan | 0.15 | 9 | 32.7 | Day 35 | Q9W6H0 |
| Protein Description | Fold Change 1 | Peptides | Coverage (%) 2 | Day 3 | Accession |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Malate dehydrogenase | Absent | 3 | 23.3 | Day 7 | A0A1D5PZS3 |
| Junction plakoglobin | Absent | 6 | 10.4 | Day 7 | E1C1V3 |
| Uncharacterized protein | Absent | 2 | 19.1 | Day 7 | R4GIC2 |
| DEAD-box helicase 17 | Absent | 3 | 6.1 | Day 21 | A0A1D5PD32 |
| Uncharacterized protein | Absent | 3 | 9 | Day 21 | A0A1D5PF52 |
| V-type proton ATPase subunit B, brain isoform | Absent | 3 | 11.3 | Day 21 | A0A1D5PP57 |
| Splicing factor proline and glutamine rich | Absent | 3 | 18.4 | Day 21 | A0A1D5PPW4 |
| Glutathione S-transferase | Absent | 2 | 9.5 | Day 21 | Q08392 |
| T-complex protein 1 subunit theta | Absent | 3 | 6.8 | Day 21 | Q6EE31 |
| NSF attachment protein alpha | Absent | 2 | 8.2 | Day 35 | A0A1D5NUZ0 |
| Uncharacterized protein | Absent | 3 | 2.5 | Day 35 | A0A1D5NW21 |
| Glia maturation factor beta | Absent | 2 | 28 | Day 35 | A0A1D6UPR3 |
| Uncharacterized protein | Absent | 5 | 11.7 | Day 35 | E1BSP1 |
| Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2/B1 | Absent | 5 | 20.1 | Day 35 | Q5ZME1 |
| Serpin family F member 2 | −2.17 | 13 | 24.2 | Day 7 | F1NAR5 |
| Beta-enolase | −1.65 | 12 | 40.9 | Day 35 | P07322 |
| Receptor of-activated protein C kinase 1 | −1.33 | 6 | 21.9 | Day 21 | A0A1I7Q3Y2 |
| Serpin family G member 1 | −1.24 | 12 | 15.8 | Day 7 | F1NA58 |
| Uncharacterized protein | −1.18 | 2 | 0.7 | Day 7 | A0A1L1RLW1 |
| Tubulin beta-7 chain | −1.18 | 12 | 40.1 | Day 21 | P09244 |
| Uncharacterized protein | −1.11 | 11 | 8.6 | Day 21 | A0A1L1RJ91 |
| Phosphoglycerate kinase | −1.03 | 11 | 27.8 | Day 21 | A0A1D5NZW9 |
| Fibulin 5 | −0.85 | 7 | 17.2 | Day 35 | A0A1L1RQ98 |
| Elongation factor 1-alpha 1 | −0.84 | 16 | 49.7 | Day 21 | Q90835 |
| Pyruvate kinase PKM | −0.83 | 26 | 45.6 | Day 35 | P00548 |
| Adenosine deaminase | −0.8 | 17 | 60.4 | Day 35 | Q5ZKP6 |
| DAZ associated protein 1 | −0.79 | 4 | 15.4 | Day 21 | Q5ZM92 |
| Alpha-enolase | −0.74 | 14 | 34.3 | Day 21 | A0A1D5PSH6 |
| Chaperonin containing TCP1 subunit 5 | −0.73 | 9 | 22.25 | Day 21 | Q5F411 |
| Macrophage receptor with collagenous structure | −0.71 | 10 | 21.4 | Day 21 | A0A1D5PJZ3 |
| Adenosine deaminase | −0.7 | 20 | 69.8 | Day 21 | A0A1D5PDK4 |
| Tubulin alpha chain | −0.68 | 11 | 30.3 | Day 21 | A0A1D5PC38 |
| Uncharacterized protein | −0.68 | 10 | 30.3 | Day 21 | E1C477 |
| Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K | −0.68 | 3 | 8.4 | Day 21 | A0A1L1S010 |
| T-complex protein 1 subunit zeta | −0.67 | 14 | 31.2 | Day 21 | Q5ZJ54 |
| Phosphoglycerate mutase 1 | −0.62 | 9 | 25.4 | Day 35 | Q5ZLN1 |
| Tubulin beta-6 chain | −0.62 | 14 | 38.2 | Day 21 | P09207 |
| LSM8 homolog, U6 small nuclear RNA associated | −0.6 | 4 | 55.9 | Day 21 | E1BZ75 |
| Chaperonin containing TCP1 subunit 2 | −0.57 | 11 | 26.5 | Day 21 | Q5F424 |
| Alpha-actinin-1 | −0.56 | 4 | 4.8 | Day 21 | A0A1D5P9P3 |
| Uncharacterized protein | −0.54 | 7 | 18.5 | Day 21 | F1NIP5 |
| Complement C1q C chain | −0.52 | 5 | 24 | Day 21 | A0A1D5PGB2 |
| Kininogen 1 | −0.52 | 15 | 28.1 | Day 7 | A0A1L1RNR4 |
| Complement C1q B chain | −0.51 | 6 | 33.6 | Day 21 | F1NH19 |
| Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 | −0.5 | 3 | 19.3 | Day 35 | F1ND88 |
| Vitronectin | −0.48 | 15 | 39.5 | Day 7 | E1C7A7 |
| Fibulin-1 | −0.46 | 23 | 39.3 | Day 35 | O73775 |
| Ubiquilin 4 | −0.46 | 5 | 12.4 | Day 21 | A0A1D5P624 |
| Methylthioribose-1-phosphate isomerase 1 | −0.46 | 9 | 46.6 | Day 21 | A0A1D5PN97 |
| EGF containing fibulin like extracellular matrix protein 1 | −0.45 | 19 | 52.7 | Day 35 | A0A1D5P380 |
| Far upstream element binding protein 1 | −0.45 | 12 | 21.5 | Day 21 | A0A1D5P2H3 |
| Apolipoprotein H | −0.44 | 14 | 42.7 | Day 35 | A0A1L1RTQ4 |
| Epiphycan | −0.43 | 5 | 13.7 | Day 7 | Q90944 |
| Ig lambda chain C region | −0.42 | 9 | 53.3 | Day 35 | P20763 |
| Aggrecan core protein | −0.38 | 16 | 7.7 | Day 7 | F1NZX1 |
| Fibulin-1 | −0.38 | 18 | 31.8 | Day 21 | A0A1L1RU28 |
| Uncharacterized protein | −0.34 | 43 | 25.4 | Day 35 | F1NEQ4 |
| Far upstream element-binding protein 2 | −0.3 | 13 | 18.7 | Day 21 | Q8UVD9 |
| F-actin-capping protein subunit beta isoforms 1 and 2 | −0.29 | 11 | 36.2 | Day 21 | P14315 |
| Uncharacterized protein | −0.28 | 2 | 38.5 | Day 21 | F1NSC8 |
| Vimentin | −0.27 | 30 | 64.6 | Day 21 | A0A1L1RXL9 |
| Fibrinogen gamma chain | −0.18 | 9 | 33.7 | Day 7 | E1BV78 |
| Protein Description | Fold change 1 | Peptides | Coverage (%) 2 | Day 3 | Accession |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Barrier to autointegration factor 1 | Unique | 2 | 42.2 | Day 7 | A0A1D5NXY4 |
| Uncharacterized protein | Unique | 2 | 1.0 | Day 7 | A0A1D5NZ61 |
| Dynactin subunit 2 | Unique | 6 | 22.1 | Day 7 | A0A1D5PGQ9 |
| Legumain | Unique | 2 | 11.8 | Day 7 | A0A1L1RX51 |
| Proteasome subunit beta 1 | Unique | 3 | 36.4 | Day 7 | A0A1L1RYR5 |
| Retinol binding protein 7 | Unique | 3 | 32.1 | Day 7 | E1C0M1 |
| Ankyrin repeat domain 2 | Unique | 2 | 8.9 | Day 7 | E1C1Q6 |
| Mediator of cell motility 1 | Unique | 3 | 21.9 | Day 7 | E1C6C0 |
| 3’-phosphoadenosine 5’-phosphosulfate synthase 1 | Unique | 5 | 12.3 | Day 7 | E1C8P2 |
| Uncharacterized protein | Unique | 4 | 30.8 | Day 7 | F1N8Y3 |
| Elongation factor 1-alpha | Unique | 15 | 49.9 | Day 7 | F1N9H4 |
| Succinyl-CoA:3-ketoacid-coenzyme A transferase | Unique | 3 | 11.0 | Day 7 | F1N9Z7 |
| Four and a half LIM domains 1 | Unique | 4 | 18.5 | Day 7 | F1NED9 |
| Myeloid protein 1 | Unique | 6 | 30.1 | Day 7 | F1NEF7 |
| mall nuclear ribonucleoprotein 13 | Unique | 3 | 30.5 | Day 7 | F1NII6 |
| Chromogranin A | Unique | 2 | 10.7 | Day 7 | F1NLZ2 |
| PDZ and LIM domain 5 | Unique | 4 | 8.2 | Day 7 | F1NTC8 |
| Proteasome 26S subunit, ATPase 5 | Unique | 3 | 12.7 | Day 7 | F1NU79 |
| Cofilin-2 | Unique | 3 | 25.9 | Day 7 | P21566 |
| Uncharacterized protein | Unique | 2 | 3.7 | Day 7 | Q5F491 |
| Profilin | Unique | 2 | 27.9 | Day 7 | Q5ZL50 |
| Endophilin-A2 | Unique | 4 | 20.4 | Day 7 | Q8AXV0 |
| Surfactant protein A | Unique | 3 | 16.2 | Day 7 | Q90XB2 |
| Seryl-tRNA synthetase | Unique | 2 | 4.3 | Day 7 | R4GJ59 |
| Disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 33 precursor | Unique | 2 | 3.6 | Day 21 | A0A1D5NV10 |
| Calpastatin | Unique | 2 | 3.9 | Day 21 | A0A1D5PFJ2 |
| Tubulointerstitial nephritis antigen like 1 | Unique | 2 | 10 | Day 21 | F1N8G6 |
| Osteocalcin | Unique | 3 | 45.4 | Day 21 | P02822 |
| Tenascin | Unique | 8 | 8.7 | Day 21 | P10039 |
| Tenascin | Unique | 10 | 10.8 | Day 35 | P10039 |
| Gastrokine-2 | Unique | 2 | 18.6 | Day 35 | A0A1D5PFM9 |
| N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphate transferase γ subunit | Unique | 2 | 16 | Day 35 | E1BS68 |
| Pantetheinase precursor | Unique | 10 | 27 | Day 35 | E1BUA6 |
| Adhesion G protein-coupled receptor G6 | Unique | 2 | 2.5 | Day 35 | E1C8C2 |
| Alpha-1-anti-ase | Unique | 9 | 27.8 | Day 35 | F1NPN5 |
| Nucleoside diphosphate kinase | Unique | 3 | 28.1 | Day 35 | O57535 |
| Apolipoprotein B (Fragment) | Unique | 7 | 24.7 | Day 35 | P11682 |
| Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | 1.55 | 9 | 37.5 | Day 7 | A0A1D5P1Y7 |
| Adenylate kinase isoenzyme 1 | 1.44 | 11 | 63.4 | Day 7 | P05081 |
| Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | 1.33 | 20 | 75.1 | Day 7 | P00356 |
| Myosin regulatory light chain 2, skeletal muscle isoform | 1.22 | 9 | 64.3 | Day 7 | P02609 |
| Heat shock protein beta-1 | 1.15 | 18 | 79.4 | Day 7 | F1P593 |
| Myosin light chain 1, skeletal muscle isoform | 1.08 | 9 | 60.9 | Day 7 | P02604 |
| Phosphoglycerate kinase | 1.07 | 17 | 60.9 | Day 7 | F1NU17 |
| Proline and arginine rich end leucine rich repeat protein | 1 | 10 | 32.9 | Day 7 | A0A1D5PAN0 |
| Uncharacterized protein | 0.97 | 7 | 25.5 | Day 7 | F1NIP5 |
| Protein/nucleic acid deglycase DJ-1 | 0.91 | 5 | 59 | Day 7 | A0A1D5PN39 |
| Actin, alpha skeletal muscle | 0.89 | 13 | 24.4 | Day 21 | A0A1I7Q414 |
| Uncharacterized protein | 0.84 | 2 | 3.7 | Day 21 | F1NMN2 |
| Carbonic anhydrase 2 | 0.83 | 7 | 44.6 | Day 35 | P07630 |
| Alpha-1,4 glucan phosphorylase | 0.81 | 5 | 7.8 | Day 35 | E1BSN7 |
| Uncharacterized protein | 0.8 | 54 | 24 | Day 21 | A0A1D5PW77 |
| Receptor of-activated protein C kinase 1 | 0.75 | 9 | 56.9 | Day 7 | A0A1I7Q3Y2 |
| Complement C7 | 0.73 | 28 | 54.3 | Day 35 | E1C6U2 |
| Low mol. weight phosphotyrosine protein phosphatase | 0.69 | 10 | 60.8 | Day 7 | A0A1D5P9Z1 |
| Uncharacterized protein | 0.69 | 7 | 24.1 | Day 7 | A0A1L1RQM3 |
| T-complex protein 1 subunit theta | 0.65 | 8 | 21 | Day 7 | F1NEF2 |
| Proteasome subunit beta type | 0.65 | 14 | 25.1 | Day 21 | A0A1L1RUE7 |
| Transthyretin | 0.64 | 9 | 72.7 | Day 35 | P27731 |
| Cystatin A | 0.62 | 4 | 18.3 | Day 21 | F1NHG8 |
| Tropomyosin alpha-1 chain | 0.61 | 16 | 57.2 | Day 7 | A0A1D5NVL7 |
| Serpin H1 | 0.58 | 12 | 44 | Day 7 | P13731 |
| 60 kDa heat shock protein | 0.57 | 12 | 34.4 | Day 7 | Q5ZL72 |
| Complement C6 | 0.56 | 29 | 40.3 | Day 35 | B8ZX71 |
| Elongation factor 1-alpha 1 | 0.53 | 18 | 58.9 | Day 7 | Q90835 |
| Ribosomal protein L23a | 0.53 | 3 | 24.5 | Day 7 | E1BS06 |
| Proteasome subunit alpha type | 0.53 | 15 | 27.9 | Day 21 | F1NEQ6 |
| Collagen type V alpha 1 chain | 0.49 | 11 | 57 | Day 21 | F1NI79 |
| Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A-1 | 0.47 | 6 | 63.9 | Day 7 | Q09121 |
| C-type lectin domain family 3-member B | 0.45 | 6 | 40.5 | Day 21 | Q9DDD4 |
| Metalloproteinase inhibitor 2 | 0.42 | 11 | 67.7 | Day 21 | R4GIL5 |
| F-actin-capping protein | 0.38 | 6 | 6.7 | Day 21 | P14315 |
| Uncharacterized protein | 0.37 | 5 | 41.1 | Day 21 | A0A1L1S0T3 |
| Cathepsin D | 0.37 | 5 | 87.6 | Day 21 | Q05744 |
| Sortilin | 0.35 | 13 | 67.7 | Day 21 | A0A1D5PNT8 |
| Sortilin | 0.28 | 14 | 25.6 | Day 7 | A0A1D5PNT8 |
| Uncharacterized protein | 0.33 | 5 | 52.9 | Day 7 | A0A1D5PH37 |
| Complement C4 precursor | 0.3 | 61 | 59.2 | Day 35 | A0A1D5P5V5 |
| Heparan sulfate proteoglycan 2 | 0.24 | 8 | 42.6 | Day 21 | A0A1L1RJ69 |
| Fibromodulin (FM) | 0.14 | 24 | 62.7 | Day 21 | P51887 |
| Far upstream element-binding protein 2 | 0.13 | 13 | 44.1 | Day 21 | Q8UVD9 |
| Protein Description | Fold Change 1 | Peptides | Coverage (%) 2 | Day 3 | Accession |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Growth differentiation factor 11 | Absent | 2 | 6.4 | Day 7 | A0A1D5P7V6 |
| Uncharacterized protein | Absent | 5 | 10.3 | Day 7 | F1NZV7 |
| Uncharacterized protein | Absent | 3 | 9 | Day 21 | A0A1D5PF52 |
| Glutathione S-transferase | Absent | 2 | 9.5 | Day 21 | Q08392 |
| Catalase | Absent | 2 | 8.9 | Day 21 | Q5ZL24 |
| T-complex protein 1 subunit theta | Absent | 3 | 6.8 | Day 21 | Q6EE31 |
| NSF attachment protein alpha | Absent | 2 | 8.2 | Day 35 | A0A1D5NUZ0 |
| Uncharacterized protein | Absent | 3 | 2.5 | Day 35 | A0A1D5NW21 |
| Fibulin-1 | Absent | 6 | 36.5 | Day 35 | A0A1L1RU28 |
| ERH, mRNA splicing and mitosis factor | Absent | 17 | 39.4 | Day 35 | A0A1L1RZP8 |
| Endoplasmic reticulum lectin 1 | Absent | 2 | 8.5 | Day 35 | F1NCV8 |
| Nuclear transport factor 2 | Absent | 2 | 63 | Day 35 | F1NLL4 |
| Nuclear transport factor 2 | −0.6 | 4 | 40.7 | Day 21 | F1NLL4 |
| TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) | Absent | 4 | 14.5 | Day 35 | Q5ZLN5 |
| Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2/B1 | Absent | 3 | 20.1 | Day 35 | Q5ZME1 |
| Junction plakoglobin | −1.45 | 33 | 7.1 | Day 7 | E1C1V3 |
| Uncharacterized protein | −1.23 | 12 | 0.7 | Day 7 | A0A1L1RLW1 |
| Insulin like growth factor binding protein 5 | −1.17 | 3 | 15.9 | Day 35 | F1ND88 |
| Fibromodulin | −1.08 | 4 | 6.3 | Day 35 | P51887 |
| Fibulin 5 | −1.02 | 7 | 16.7 | Day 35 | A0A1L1RQ98 |
| Serpin family D member 1 | −1.00 | 21 | 37.9 | Day 21 | A0A1D5PLZ2 |
| Uncharacterized protein | −0.93 | 2 | 37.5 | Day 7 | F1NSC7 |
| Uncharacterized protein | −0.33 | 3 | 37.5 | Day 21 | F1NSC7 |
| Olfactomedin-like protein 3 | −0.92 | 20 | 50.5 | Day 35 | Q25C36 |
| Ovoinhibitor | −0.82 | 9 | 60.6 | Day 7 | P10184 |
| EGF containing fibulin like extracellular matrix protein 1 | −0.78 | 19 | 53.7 | Day 35 | A0A1D5P380 |
| Hemoglobin subunit alpha-D | −0.77 | 7 | 90.1 | Day 7 | P02001 |
| Fibrinogen beta chain | −0.65 | 8 | 26.9 | Day 7 | Q02020 |
| Carboxypeptidase | −0.62 | 7 | 16 | Day 21 | A0A1L1RXB2 |
| Fibrinogen gamma chain | −0.61 | 6 | 34.1 | Day 7 | E1BV78 |
| Insulin-like growth factor II | −0.59 | 2 | 11 | Day 35 | P33717 |
| Uncharacterized protein | −0.59 | 21 | 23.5 | Day 7 | A0A1D5PSJ4 |
| Histone H2B 8 | −0.58 | 11 | 19 | Day 7 | Q9PSW9 |
| Uncharacterized protein | −0.53 | 3 | 36.4 | Day 21 | F1NC22 |
| Chemerin | −0.52 | 7 | 43.3 | Day 35 | A0A0K0PUH6 |
| Uncharacterized protein | −0.52 | 2 | 38.5 | Day 21 | F1NSC8 |
| Matrilin-3 | −0.5 | 53 | 27.9 | Day 7 | O42401 |
| Matrilin-3 | −0.38 | 7 | 16.8 | Day 35 | O42401 |
| Uncharacterized protein | −0.48 | 25 | 52 | Day 7 | R9PXM5 |
| Hyaluronan binding protein 2 | −0.48 | 15 | 31.4 | Day 21 | F1NEB3 |
| Uncharacterized protein | −0.47 | 8 | 58.7 | Day 21 | A0A1D5PV72 |
| Ig lambda chain C region | −0.45 | 9 | 50.7 | Day 21 | P20763 |
| Protein-lysine 6-oxidase | −0.43 | 7 | 28 | Day 35 | A0A1D5P1U0 |
| Adenosine deaminase | −0.4 | 17 | 66 | Day 35 | A0A1D5PDK4 |
| HGF activator | −0.37 | 11 | 15.6 | Day 7 | E1BZN8 |
| Collagen alpha 1(VI) chain | −0.34 | 10 | 12.7 | Day 35 | A0A1D5PWN6 |
| Apolipoprotein A-I | −0.25 | 2 | 90.3 | Day 7 | P08250 |
| Transforming growth factor beta induced | −0.25 | 8 | 70.3 | Day 7 | A0A1D5NX81 |
| CD74 molecule | −0.21 | 4 | 20.8 | Day 35 | F1NYL5 |
| ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif 13 | −0.12 | 29 | 27.1 | Day 35 | A0A1D5PEF7 |
| Protein Description | Fold Change 1 | Peptides | Coverage (%) 2 | Day 3 | Accession |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Barrier to autointegration factor 1 | Unique | 2 | 42.2 | Day 7 | A0A1D5NXY4 |
| HSPA (Hsp70) binding protein 1 | Unique | 5 | 12.1 | Day 7 | A0A1D5P628 |
| Uncharacterized protein | Unique | 9 | 41.4 | Day 7 | A0A1D5PQ15 |
| Proteasome subunit beta 1 | Unique | 4 | 36.4 | Day 7 | A0A1L1RYR5 |
| Ankyrin repeat domain 2 | Unique | 5 | 8.9 | Day 7 | E1C1Q6 |
| Plexin domain containing 2 | Unique | 3 | 5.9 | Day 7 | E1C486 |
| Mediator of cell motility 1 | Unique | 2 | 21.9 | Day 7 | E1C6C0 |
| 3’-phosphoadenosine 5’-phosphosulfate synthase 1 | Unique | 3 | 12.3 | Day 7 | E1C8P2 |
| Elongation factor 1-alpha | Unique | 3 | 49.9 | Day 7 | F1N9H4 |
| Four and a half LIM domains 1 | Unique | 3 | 18.5 | Day 7 | F1NED9 |
| Small nuclear ribonucleoprotein 13 | Unique | 4 | 30.5 | Day 7 | F1NII6 |
| Chromogranin A | Unique | 3 | 10.7 | Day 7 | F1NLZ2 |
| PDZ and LIM domain 5 | Unique | 3 | 8.2 | Day 7 | F1NTC8 |
| Proteasome 26S subunit, ATPase 5 | Unique | 2 | 12.7 | Day 7 | F1NU79 |
| Uncharacterized protein | Unique | 2 | 14.1 | Day 7 | F1NWB2 |
| Natriuretic peptides A | Unique | 2 | 17.9 | Day 7 | P18908 |
| Cofilin-2 | Unique | 4 | 25.9 | Day 7 | P21566 |
| Stratifin | Unique | 15 | 28.5 | Day 7 | R4GF89 |
| Seryl-tRNA synthetase | Unique | 3 | 4.3 | Day 7 | R4GJ59 |
| Disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 33 precursor | Unique | 2 | 3.6 | Day 21 | A0A1D5NV10 |
| Gastrokine 2 | Unique | 3 | 18.6 | Day 35 | A0A1D5PFM9 |
| Dual specificity phosphatase 3 | Unique | 2 | 26.3 | Day 35 | A0A1L1S0I4 |
| Alpha-1-anti-ase | Unique | 2 | 27.8 | Day 35 | F1NPN5 |
| Aggrecan core protein | Unique | 2 | 2.3 | Day 35 | F1NZX1 |
| Insulin-like growth factor I | Unique | 3 | 19.0 | Day 35 | P18254 |
| Zyxin | Unique | 5 | 4.8 | Day 35 | Q04584 |
| Adenylate kinase isoenzyme 1 | 1.12 | 11 | 60.3 | Day 7 | P05081 |
| Transferrin receptor protein 1 | 1.07 | 10 | 9.7 | Day 35 | F1NTM6 |
| Myosin regulatory light chain 2, skeletal muscle isoform | 1.07 | 9 | 57.8 | Day 7 | P02609 |
| Uncharacterized protein | 1.04 | 2 | 19.2 | Day 35 | A0A1D5P1L5 |
| Complement C5 | 1.04 | 82 | 55.5 | Day 35 | E1BRS7 |
| Heat shock protein beta-1 | 1.03 | 18 | 77.9 | Day 7 | F1P593 |
| Transthyretin | 1.00 | 9 | 71.4 | Day 35 | P27731 |
| Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | 0.95 | 20 | 72.0 | Day 7 | P00356 |
| Uncharacterized protein | 0.94 | 4 | 37.9 | Day 21 | A0A1L1RQF3 |
| Myosin light chain 1, skeletal muscle isoform | 0.90 | 9 | 53.9 | Day 7 | P02604 |
| Alpha-1,4 glucan phosphorylase | 0.89 | 5 | 6.5 | Day 35 | E1BSN7 |
| Uncharacterized protein | 0.79 | 6 | 39.8 | Day 35 | A0A1D5PK48 |
| Actin, alpha skeletal muscle | 0.78 | 13 | 34.8 | Day 21 | A0A1I7Q414 |
| Low mol. weight phosphotyrosine protein phosphatase | 0.75 | 10 | 58.5 | Day 7 | A0A1D5P9Z1 |
| Uncharacterized protein | 0.70 | 7 | 21.5 | Day 7 | F1NIP5 |
| Complement C6 | 0.68 | 29 | 34.6 | Day 35 | B8ZX71 |
| Complement C7 | 0.68 | 28 | 52.0 | Day 35 | E1C6U2 |
| Uncharacterized protein | 0.67 | 4 | 37.1 | Day 35 | A0A1L1RQF3 |
| Uncharacterized protein | 0.63 | 18 | 22.3 | Day 35 | A0A1L1S0T3 |
| Uncharacterized protein | 0.60 | 2 | 23.0 | Day 21 | A0A1D5P058 |
| Uncharacterized protein | 0.56 | 5 | 42.3 | Day 35 | F1NSC7 |
| Complement C4 precursor | 0.55 | 61 | 48.1 | Day 35 | A0A1D5P5V5 |
| Mannose-binding protein | 0.50 | 8 | 27.5 | Day 35 | Q98TA4 |
| Proteasome subunit alpha type | 0.45 | 6 | 23.5 | Day 7 | F1NEQ6 |
| Beta-2-microglobulin | 0.45 | 5 | 60.5 | Day 21 | P21611 |
| Uncharacterized protein | 0.44 | 4 | 38.5 | Day 35 | F1NSC8 |
| Beta-hexosaminidase | 0.42 | 20 | 49.2 | Day 7 | F1NTQ2 |
| Sortilin | 0.41 | 14 | 20.9 | Day 7 | A0A1D5PNT8 |
| RAD23 homolog B, nucleotide excision repair protein | 0.41 | 28 | 9.0 | Day 7 | F1N9B7 |
| Complement C2 | 0.41 | 2 | 15.7 | Day 35 | A0A1D5P4P1 |
| Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 | 0.39 | 9 | 12.3 | Day 21 | F1P201 |
| Uncharacterized protein | 0.38 | 6 | 21.3 | Day 21 | A0A1L1S0T3 |
| Complement factor H | 0.28 | 15 | 71.9 | Day 21 | E1C7P4 |
| Plasminogen | 0.23 | 94 | 69.7 | Day 21 | R4GMH5 |
| Apolipoprotein A-I | 0.20 | 57 | 92.8 | Day 21 | P08250 |
| Uncharacterized protein | 0.19 | 55 | 17.3 | Day 7 | Q5ZMC1 |
| Lumican | 0.17 | 5 | 39.2 | Day 35 | P51890 |
| Prolyl 4-hydroxylase subunit alpha-1 | 0.13 | 11 | 21.5 | Day 7 | P16924 |
| Protein Description | Fold Change 1 | Peptides | Coverage (%) 2 | Day 3 | Accession |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glutamate dehydrogenase 1, mitochondrial | Absent | 4 | 9.9 | Day 7 | A0A1D5NT61 |
| Growth differentiation factor 11 | Absent | 2 | 6.4 | Day 7 | A0A1D5P7V6 |
| Catalase | Absent | 3 | 5.3 | Day 7 | A0A1D5PPU9 |
| Malate dehydrogenase | Absent | 3 | 23.3 | Day 7 | A0A1D5PZS3 |
| Integral membrane protein 2B | Absent | 2 | 46.2 | Day 7 | A0A1L1RIU5 |
| Uncharacterized protein | Absent | 2 | 0.9 | Day 7 | A0A1L1RLW1 |
| Beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase 4 | Absent | 2 | 8.5 | Day 7 | E1C9B0 |
| Carbamoyl-phosphate synthase 1 | Absent | 4 | 3.3 | Day 7 | F1N9N8 |
| Glutathione S-transferase | Absent | 2 | 9.5 | Day 7 | Q08392 |
| NSF attachment protein alpha | Absent | 2 | 8.2 | Day 21 | A0A1D5NUZ0 |
| Uncharacterized protein | Absent | 3 | 9 | Day 21 | A0A1D5PF52 |
| Deoxythymidylate kinase | Absent | 3 | 22.6 | Day 21 | A0A1D5PKC2 |
| Lysophospholipase II | Absent | 2 | 19 | Day 21 | E1BRI5 |
| Small nuclear ribonucleoprotein 13 | Absent | 3 | 36.7 | Day 21 | F1NII6 |
| Proteasome 26S subunit, ATPase 5 | Absent | 3 | 12.7 | Day 21 | F1NU79 |
| Glutathione S-transferase | Absent | 2 | 9.5 | Day 21 | Q08392 |
| Catalase | Absent | 2 | 8.9 | Day 21 | Q5ZL24 |
| Carbohydrate sulfotransferase 3 | Absent | 4 | 13.3 | Day 21 | Q92179 |
| NSF attachment protein alpha | Absent | 2 | 8.2 | Day 35 | A0A1D5NUZ0 |
| Uncharacterized protein | Absent | 3 | 2.5 | Day 35 | A0A1D5NW21 |
| Reversion inducing cysteine rich protein with kazal motifs | Absent | 6 | 8.9 | Day 35 | A0A1D5PTW4 |
| Uncharacterized protein | Absent | 3 | 29.6 | Day 35 | A0A1D5PZ95 |
| Glutathione S-transferase | Absent | 2 | 9.5 | Day 35 | Q08392 |
| TAR DNA-binding protein 43 | Absent | 3 | 14.5 | Day 35 | Q5ZLN5 |
| Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2/B1 | Absent | 5 | 20.1 | Day 35 | Q5ZME1 |
| Cytidine/uridine monophosphate kinase 2 | Absent | 5 | 25.7 | Day 35 | R4GJC4 |
| Gastrin-releasing peptide | −1.30 | 3 | 19.7 | Day 35 | A0A1D5PXC4 |
| Fibromodulin | −1.20 | 4 | 7.7 | Day 35 | P51887 |
| Tubulin beta-7 chain | −1.20 | 12 | 39.7 | Day 21 | P09244 |
| Beta-tropomyosin | −1.18 | 27 | 62.2 | Day 35 | Q05705 |
| Integrin-linked kinase | −1.11 | 4 | 10.3 | Day 35 | Q9DF58 |
| cAMP-dependent protein kinase type I-alpha regulatory subunit | −1.02 | 11 | 27.4 | Day 35 | Q5ZM91 |
| Fibulin 5 | −0.90 | 7 | 16.8 | Day 35 | A0A1L1RQ98 |
| cAMP-dependent protein kinase type I-alpha regulatory subunit | −0.89 | 6 | 20.3 | Day 21 | Q5ZM91 |
| Tropomyosin alpha-1 chain | −0.84 | 12 | 47.6 | Day 21 | A0A1D5P342 |
| MHC class II beta chain 2 | −0.82 | 3 | 14.8 | Day 21 | A5HUL4 |
| Elongation factor 1-alpha 1 | −0.77 | 16 | 50.0 | Day 21 | Q90835 |
| Beta-tropomyosin | −0.71 | 22 | 61.3 | Day 21 | Q05705 |
| Hyaluronan binding protein 2 | −0.70 | 15 | 32.5 | Day 21 | F1NEB3 |
| Phosphatidylcholine-sterol acyltransferase | −0.68 | 13 | 37.4 | Day 21 | P53760 |
| Heat shock protein beta-1 | −0.67 | 17 | 79.4 | Day 35 | F1P593 |
| Collagen alpha-2(I) chain | −0.65 | 11 | 10.1 | Day 35 | P02467 |
| Complement C7 | −0.61 | 21 | 43.8 | Day 7 | E1C6U2 |
| Alpha-actinin-1 | −0.48 | 4 | 4.37 | Day 21 | A0A1D5P9P3 |
| DAZ associated protein 1 | −0.47 | 4 | 14.0 | Day 21 | Q5ZM92 |
| Adenosine deaminase | −0.41 | 17 | 65.6 | Day 35 | A0A1D5PDK4 |
| Alpha-actinin-1 | −0.41 | 15 | 12.7 | Day 35 | A0A1D5P9P3 |
| Chemerin | −0.41 | 7 | 46.2 | Day 35 | A0A0K0PUH6 |
| Collagen type XVIII alpha 1 chain | −0.40 | 5 | 4.7 | Day 35 | A0A1D5P5M7 |
| Guanine deaminase | −0.38 | 8 | 23.5 | Day 21 | F1NJD6 |
| Macrophage receptor with collagenous structure | −0.33 | 10 | 21.4 | Day 21 | A0A1D5PJZ3 |
| Peroxiredoxin-1 | −0.30 | 8 | 45.5 | Day 35 | P0CB50 |
| Fibulin-1 | −0.16 | 18 | 31.1 | Day 21 | A0A1L1RU28 |
| Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein M | −0.15 | 6 | 7.7 | Day 21 | F7B5K7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Conlon, N.; Murphy, R.A.; Corrigan, A.; Doyle, S.; Owens, R.A.; Fagan, S. Quantitative Proteomic Analysis Reveals Yeast Cell Wall Products Influence the Serum Proteome Composition of Broiler Chickens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911844
Conlon N, Murphy RA, Corrigan A, Doyle S, Owens RA, Fagan S. Quantitative Proteomic Analysis Reveals Yeast Cell Wall Products Influence the Serum Proteome Composition of Broiler Chickens. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(19):11844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911844
Chicago/Turabian StyleConlon, Niall, Richard A. Murphy, Aoife Corrigan, Sean Doyle, Rebecca A. Owens, and Sheena Fagan. 2022. "Quantitative Proteomic Analysis Reveals Yeast Cell Wall Products Influence the Serum Proteome Composition of Broiler Chickens" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 19: 11844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911844
APA StyleConlon, N., Murphy, R. A., Corrigan, A., Doyle, S., Owens, R. A., & Fagan, S. (2022). Quantitative Proteomic Analysis Reveals Yeast Cell Wall Products Influence the Serum Proteome Composition of Broiler Chickens. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(19), 11844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911844






