Deciphering Mechanisms of Action of Sortilin/Neurotensin Receptor-3 in the Proliferation Regulation of Colorectal and Other Cancers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Membrane-Bound Sortilin/NTSR3
2.1. The Role of Membrane Sortilin/NTSR3 in the Signaling and Trafficking of Neurotrophin Receptors
2.2. The Role of Membrane Sortilin/NTSR3 in the Signaling and Trafficking of Neurotensin Receptors
3. The Soluble Form of Sortilin/NTSR3
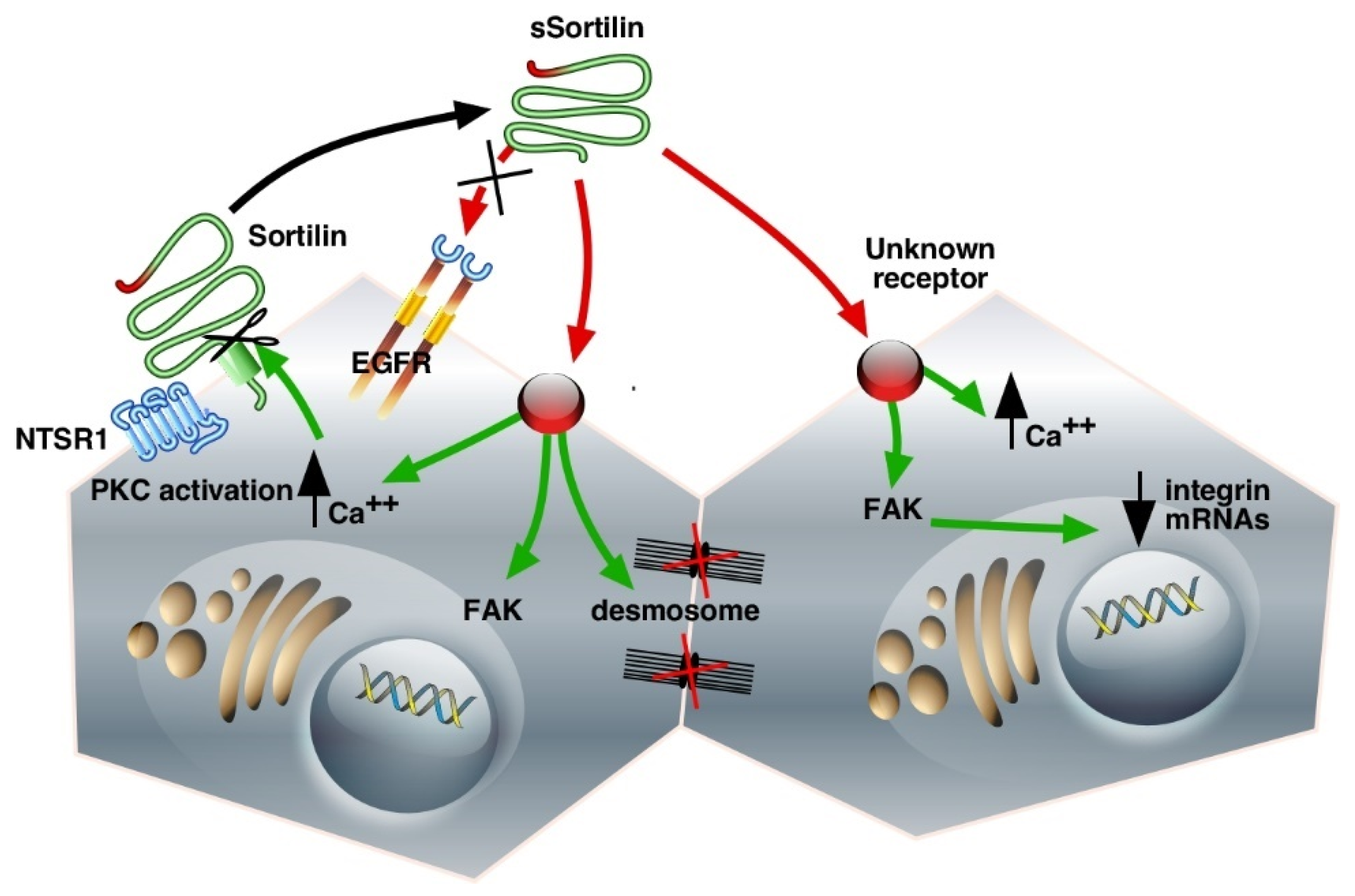
3.1. Shedding of the Cell Surface Sortilin/NTSR3
3.2. Binding and Internalization Properties of sSortilin/NTSR3
3.3. Cell Functions of sSortilin/NTSR3 in HT29 Cells
3.4. Morphological Changes of HT29 Cells Induced by sSortilin/NTSR3
4. Another Crucial Function of Sortilin/NTSR3: Possible Role in the Field of Cancer
Involvement of Sortilin/NTSR3 in the Membrane Expression of TREK-1OK
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thiery, J.P. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in tumour progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peralta, M.; Osmani, N.; Goetz, J.G. Circulating tumor cells: Towards mechanical phenotyping of metastasis. eScience 2022, 25, 103969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reubi, J.C. Peptide receptors as molecular targets for cancer diagnosis and therapy. Endocr. Rev. 2003, 24, 389–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Lei, W.I.; Lee, L.T.O. The Role of Neuropeptide-Stimulated cAMP-EPACs Signalling in Cancer Cells. Molecules 2022, 27, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.C.; Dharmasivam, M.; Richardson, D.R. The Role of Extracellular Proteases in Tumor Progression and the Development of Innovative Metal Ion Chelators that Inhibit their Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasina, S.; Scherle, P.A.; Hall, C.L.; Macoska, J.A. ADAM-mediated amphiregulin shedding and EGFR transactivation. Cell Prolif. 2009, 42, 799–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlenko, E.; Cabron, A.S.; Arnold, P.; Dobert, J.P.; Rose-John, S.; Zunke, F. Functional Characterization of Colon Cancer-Associated Mutations in ADAM17: Modifications in the Pro-Domain Interfere with Trafficking and Maturation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christou, N.; Blondy, S.; David, V.; Verdier, M.; Lalloué, F.; Jauberteau, M.O.; Mathonnet, M.; Perraud, A. Neurotensin pathway in digestive cancers and clinical applications: An overview. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Farra, C.; Sarret, P.; Navarro, V.; Botto, J.M.; Mazella, J.; Vincent, J.P. Involvement of the neurotensin receptor subtype NTR3 in the growth effect of neurotensin on cancer cell lines. Int. J. Cancer 2001, 92, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, M.L.; Coveñas, R. The Neurotensinergic System: A Target for Cancer Treatment. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 29, 3231–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, M.R.; Kunos, G. Therapeutic approaches targeting the neurotensin receptors. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2021, 31, 361–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazella, J.; Zsurger, N.; Navarro, V.; Chabry, J.; Kaghad, M.; Caput, D.; Ferrara, P.; Vita, N.; Gully, D.; Maffrand, J.P.; et al. The 100-kDa neurotensin receptor is gp95/sortilin, a non-G-protein-coupled receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 26273–26276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, C.M.; Nielsen, M.S.; Nykjaer, A.; Jacobsen, L.; Tommerup, N.; Rasmussen, H.H.; Roigaard, H.; Gliemann, J.; Madsen, P.; Moestrup, S.K. Molecular identification of a novel candidate sorting receptor purified from human brain by receptor-associated protein affinity chromatography. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 3599–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, V.; Vincent, J.P.; Mazella, J. Shedding of the luminal domain of the neurotensin receptor-3/sortilin in the HT29 cell line. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 298, 760–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.Z.; Pilch, P.F.; Kandror, K.V. Sortilin is a major protein component of Glut4-containing vesicles. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 24145–24147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willnow, T.E.; Petersen, C.M.; Nykjaer, A. VPS10P-domain receptors—Regulators of neuronal viability and function. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 899–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, S.; Jia, B.; Xie, W.; Yang, J.; Lv, Y. Mechanism underlying the regulation of sortilin expression and its trafficking function. J. Cell Physiol. 2020, 235, 8958–8971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefrancois, S.; Zeng, J.; Hassan, A.J.; Canuel, M.; Morales, C.R. The lysosomal trafficking of sphingolipid activator proteins (SAPs) is mediated by sortilin. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 6430–6437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, J.W.; Aarnio-Peterson, M.; Norris, J.; Haskins, M.; Flanagan-Steet, H.; Steet, R. Upregulation of Sortilin, a Lysosomal Sorting Receptor, Corresponds with Reduced Bioavailability of Latent TGFβ in Mucolipidosis II Cells. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.; Vincent, J.P.; Mazella, J. Involvement of the neurotensin receptor-3 in the neurotensin-induced migration of human microglia. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 1198–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, M.S.; Jacobsen, C.; Olivecrona, G.; Gliemann, J.; Petersen, C.M. Sortilin/neurotensin receptor-3 binds and mediates degradation of lipoprotein lipase. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 8832–8836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beraud-Dufour, S.; Coppola, T.; Massa, F.; Mazella, J. Neurotensin receptor-2 and -3 are crucial for the anti-apoptotic effect of neurotensin on pancreatic beta-TC3 cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2009, 41, 2398–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daziano, G.; Blondeau, N.; Béraud-Dufour, S.; Abderrahmani, A.; Rovère, C.; Heurteaux, C.; Mazella, J.; Lebrun, P.; Coppola, T. Sortilin-derived peptides promote pancreatic beta-cell survival through CREB signaling pathway. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 167, 105539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blondeau, N.; Béraud-Dufour, S.; Lebrun, P.; Hivelin, C.; Coppola, T. Sortilin in Glucose Homeostasis: From Accessory Protein to Key Player? Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, S.; Navarro, V.; Vincent, J.P.; Mazella, J. Neurotensin receptor-1 and -3 complex modulates the cellular signaling of neurotensin in the HT29 cell line. Gastroenterology 2002, 123, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.T.; Weiss, H.L.; Evers, B.M. Diverse expression patterns and tumorigenic role of neurotensin signaling components in colorectal cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 50, 2200–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nykjaer, A.; Lee, R.; Teng, K.K.; Jansen, P.; Madsen, P.; Nielsen, M.S.; Jacobsen, C.; Kliemannel, M.; Schwarz, E.; Willnow, T.E.; et al. Sortilin is essential for proNGF-induced neuronal cell death. Nature 2004, 427, 843–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dedoni, S.; Marras, L.; Olianas, M.C.; Ingianni, A.; Onali, P. Valproic acid upregulates the expression of the p75NTR/sortilin receptor complex to induce neuronal apoptosis. Apoptosis Int. J. Program. Cell Death 2020, 25, 697–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.K.; Teng, K.K.; Lee, R.; Wright, S.; Tevar, S.; Almeida, R.D.; Kermani, P.; Torkin, R.; Chen, Z.Y.; Lee, F.S.; et al. ProBDNF induces neuronal apoptosis via activation of a receptor complex of p75NTR and sortilin. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 5455–5463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggert, S.; Kins, S.; Endres, K.; Brigadski, T. Brothers in arms: ProBDNF/BDNF and sAPPα/Aβ-signaling and their common interplay with ADAM10, TrkB, p75NTR, sortilin, and sorLA in the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Biol. Chem. 2022, 403, 43–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asaro, A.; Sinha, R.; Bakun, M.; Kalnytska, O.; Carlo-Spiewok, A.S.; Rubel, T.; Rozeboom, A.; Dadlez, M.; Kaminska, B.; Aronica, E.; et al. ApoE4 disrupts interaction of sortilin with fatty acid-binding protein 7 essential to promote lipid signaling. J. Cell Sci. 2021, 134, jcs258894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Pietro, P.; Carrizzo, A.; Sommella, E.; Oliveti, M.; Iacoviello, L.; Di Castelnuovo, A.; Acernese, F.; Damato, A.; De Lucia, M.; Merciai, F.; et al. Targeting the ASMase/S1P pathway protects from sortilin-evoked vascular damage in hypertension. J. Clin. Invest. 2022, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, P.L.; Rohde, P.D.; Winther, S.; Breining, P.; Nissen, L.; Nykjaer, A.; Bøttcher, M.; Nyegaard, M.; Kjolby, M. Sortilin as a Biomarker for Cardiovascular Disease Revisited. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 652584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaemimanesh, F.; Mehravar, M.; Milani, S.; Poursani, E.M.; Saliminejad, K. The multifaceted role of sortilin/neurotensin receptor 3 in human cancer development. J. Cell Physiol. 2021, 236, 6271–6281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.T.; Napier, D.L.; Weiss, H.L.; Lee, E.Y.; Townsend, C.M., Jr.; Evers, B.M. Neurotensin Receptor 3/Sortilin Contributes to Tumorigenesis of Neuroendocrine Tumors Through Augmentation of Cell Adhesion and Migration. Neoplasia 2018, 20, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roselli, S.; Pundavela, J.; Demont, Y.; Faulkner, S.; Keene, S.; Attia, J.; Jiang, C.C.; Zhang, X.D.; Walker, M.M.; Hondermarck, H. Sortilin is associated with breast cancer aggressiveness and contributes to tumor cell adhesion and invasion. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 10473–10486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaemimanesh, F.; Ahmadian, G.; Talebi, S.; Zarnani, A.H.; Behmanesh, M.; Hemmati, S.; Hadavi, R.; Jeddi-Tehrani, M.; Farzi, M.; Akhondi, M.M.; et al. The effect of sortilin silencing on ovarian carcinoma cells. Avicenna J. Med. Biotechnol. 2014, 6, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Charfi, C.; Demeule, M.; Currie, J.C.; Larocque, A.; Zgheib, A.; Danalache, B.A.; Ouanouki, A.; Béliveau, R.; Marsolais, C.; Annabi, B. New Peptide-Drug Conjugates for Precise Targeting of SORT1-Mediated Vasculogenic Mimicry in the Tumor Microenvironment of TNBC-Derived MDA-MB-231 Breast and Ovarian ES-2 Clear Cell Carcinoma Cells. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 760787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, J.; Zhou, L.; Yang, M.; Lim, Y.; Zhu, Y.H.; Fu, D.L.; Li, Z.W.; Zhong, J.H.; Xiao, Z.C.; Zhou, X.F. ProBDNF and its receptors are upregulated in glioma and inhibit the growth of glioma cells in vitro. Neuro Oncol. 2013, 15, 990–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinet, S.; Bessette, B.; Vedrenne, N.; Lacroix, A.; Richard, L.; Jauberteau, M.O.; Battu, S.; Lalloue, F. TrkB-containing exosomes promote the transfer of glioblastoma aggressiveness to YKL-40-inactivated glioblastoma cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 50349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Wu, P.F.; Ma, J.X.; Liao, M.J.; Wang, X.H.; Xu, L.S.; Xu, M.H.; Yi, L. Sortilin promotes glioblastoma invasion and mesenchymal transition through GSK-3β/β-catenin/twist pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faulkner, S.; Jobling, P.; Rowe, C.W.; Rodrigues Oliveira, S.M.; Roselli, S.; Thorne, R.F.; Oldmeadow, C.; Attia, J.; Jiang, C.C.; Zhang, X.D.; et al. Neurotrophin Receptors TrkA, p75(NTR), and Sortilin Are Increased and Targetable in Thyroid Cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2018, 188, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farahi, L.; Ghaemimanesh, F.; Milani, S.; Razavi, S.M.; Akhondi, M.M.; Rabbani, H. Sortilin as a Novel Diagnostic and Therapeutic Biomarker in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Avicenna J. Med. Biotechnol. 2019, 11, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hermey, G.; Sjogaard, S.S.; Petersen, C.M.; Nykjaer, A.; Gliemann, J. Tumour necrosis factor alpha-converting enzyme mediates ectodomain shedding of Vps10p-domain receptor family members. Biochem. J. 2006, 395, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.M.; Naves, T.; Vincent, F.; Melloni, B.; Bonnaud, F.; Lalloue, F.; Jauberteau, M.O. Sortilin mediates the release and transfer of exosomes in concert with two tyrosine kinase receptors. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127 Pt 18, 3983–3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartkowska, K.; Turlejski, K.; Djavadian, R.L. Neurotrophins and their receptors in early development of the mammalian nervous system. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2010, 70, 454–467. [Google Scholar]
- Blondy, S.; Christou, N.; David, V.; Verdier, M.; Jauberteau, M.O.; Mathonnet, M.; Perraud, A. Neurotrophins and their involvement in digestive cancers. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Ieraci, A.; Teng, H.; Dall, H.; Meng, C.X.; Herrera, D.G.; Nykjaer, A.; Hempstead, B.L.; Lee, F.S. Sortilin controls intracellular sorting of brain-derived neurotrophic factor to the regulated secretory pathway. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 6156–6166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akil, H.; Perraud, A.; Melin, C.; Jauberteau, M.O.; Mathonnet, M. Fine-tuning roles of endogenous brain-derived neurotrophic factor, TrkB and sortilin in colorectal cancer cell survival. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Nikolaou, S.; Zhu, J.; Jeffery, P.; Goldin, R.; Kinross, J.; Alexander, J.L.; Rasheed, S.; Tekkis, P.; Kontovounisios, C. Characterisation of the Expression of Neurotensin and Its Receptors in Human Colorectal Cancer and Its Clinical Implications. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morinville, A.; Martin, S.; Lavallee, M.; Vincent, J.P.; Beaudet, A.; Mazella, J. Internalization and trafficking of neurotensin via NTS3 receptors in HT29 cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 36, 2153–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, V.; Martin, S.; Mazella, J. Internalization-dependent regulation of HT29 cell proliferation by neurotensin. Peptides 2006, 27, 2502–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warhurst, G.; Fogg, K.E.; Higgs, N.B.; Tonge, A.; Grundy, J. Ca(2+)-mobilising agonists potentiate forskolin- and VIP-stimulated cAMP production in human colonic cell line, HT29-cl.19A: Role of [Ca2+]i and protein kinase C. Cell Calcium 1994, 15, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massa, F.; Devader, C.; Beraud-Dufour, S.; Brau, F.; Coppola, T.; Mazella, J. Focal adhesion kinase dependent activation of the PI3 kinase pathway by the functional soluble form of neurotensin receptor-3 in HT29 cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 952–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampe, W.; Riedel, I.B.; Lintzel, J.; Bader, C.O.; Franke, I.; Schaller, H.C. Ectodomain shedding, translocation and synthesis of SorLA are stimulated by its ligand head activator. J. Cell Sci. 2000, 113, 4475–4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Zhan, Y.; Zeng, H.; Koon, H.W.; Moyer, M.P.; Pothoulakis, C. Neurotensin stimulates expression of early growth response gene-1 and EGF receptor through MAP kinase activation in human colonic epithelial cells. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 120, 1652–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, T.W.; Nuche-Berenguer, B.; Nakamura, T.; Jensen, R.T. EGFR Transactivation by Peptide G Protein-Coupled Receptors in Cancer. Curr. Drug Targets 2016, 17, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumaresq-Doiron, K.; Jules, F.; Lefrancois, S. Sortilin turnover is mediated by ubiquitination. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 433, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evron, T.; Daigle, T.L.; Caron, M.G. GRK2: Multiple roles beyond G protein-coupled receptor desensitization. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 33, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.M. Structural, biochemical and signaling properties of the low-density lipoprotein receptor gene family. Front. Biosci. 2001, 6, D417–D428. [Google Scholar]
- Toker, A. Phosphoinositide 3-kinases-a historical perspective. Subcell Biochem. 2012, 58, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Temraz, S.; Mukherji, D.; Shamseddine, A. Dual Inhibition of MEK and PI3K Pathway in KRAS and BRAF Mutated Colorectal Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 22976–22988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchheit, C.L.; Rayavarapu, R.R.; Schafer, Z.T. The regulation of cancer cell death and metabolism by extracellular matrix attachment. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012, 23, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, W.; Hall, J.E.; Schaller, M.D. Focal adhesion kinase-regulated signaling events in human cancer. Biomol. Concepts 2012, 3, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, J.T. Focal adhesion kinase: The first ten years. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116 Pt 8, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massa, F.; Devader, C.; Lacas-Gervais, S.; Beraud-Dufour, S.; Coppola, T.; Mazella, J. Impairement of HT29 Cancer Cells Cohesion by the Soluble Form of Neurotensin Receptor-3. Genes Cancer 2014, 5, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaji, R.; Wheeler, A.P.; Erasmus, J.C.; Lee, S.Y.; Endres, R.G.; Cramer, L.P.; Braga, V.M. ROCK1 and ROCK2 regulate epithelial polarisation and geometric cell shape. Biol. Cell 2012, 104, 435–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadifar, R.; Roper, J.C.; Aigouy, B.; Eaton, S.; Julicher, F. The influence of cell mechanics, cell-cell interactions, and proliferation on epithelial packing. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 2095–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutzmann, J.; Bellissent-Waydelich, A.; Fontao, L.; Launay, J.F.; Simon-Assmann, P. Adhesion complexes implicated in intestinal epithelial cell-matrix interactions. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2000, 51, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, K.J.; Gaudry, C.A. Are desmosomes more than tethers for intermediate filaments? Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000, 1, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusek, R.L.; Attardi, L.D. Desmosomes: New perpetrators in tumour suppression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooke, M.A.; Nitoiu, D.; Kelsell, D.P. Cell-cell connectivity: Desmosomes and disease. J. Pathol. 2012, 226, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeichi, M. Dynamic contacts: Rearranging adherens junctions to drive epithelial remodelling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koretz, K.; Schlag, P.; Boumsell, L.; Moller, P. Expression of VLA-alpha 2, VLA-alpha 6, and VLA-beta 1 chains in normal mucosa and adenomas of the colon, and in colon carcinomas and their liver metastases. Am. J. Pathol. 1991, 138, 741–750. [Google Scholar]
- Stallmach, A.; Riecken, E.O. Colorectal carcinoma—Current pathogenetic concepts. Significance of cell-matrix interaction for invasive growth and metastasis. Schweiz. Rundsch. Med. Prax. 1992, 81, 847–849. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mazella, J.; Petrault, O.; Lucas, G.; Deval, E.; Beraud-Dufour, S.; Gandin, C.; El-Yacoubi, M.; Widmann, C.; Guyon, A.; Chevet, E.; et al. Spadin, a sortilin-derived peptide, targeting rodent TREK-1 channels: A new concept in the antidepressant drug design. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsotto, M.; Veyssiere, J.; Moha Ou Maati, H.; Devader, C.; Mazella, J.; Heurteaux, C. Targeting two-pore domain K(+) channels TREK-1 and TASK-3 for the treatment of depression: A new therapeutic concept. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 771–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heurteaux, C.; Lucas, G.; Guy, N.; El Yacoubi, M.; Thummler, S.; Peng, X.D.; Noble, F.; Blondeau, N.; Widmann, C.; Borsotto, M.; et al. Deletion of the background potassium channel TREK-1 results in a depression-resistant phenotype. Nat. Neurosci. 2006, 9, 1134–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Huang, L.; Liao, P.; Jiang, R. Contribution of Neuronal and Glial Two-Pore-Domain Potassium Channels in Health and Neurological Disorders. Neural Plast. 2021, 2021, 8643129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.Y.; Jiang, J.; Pan, A.; Yan, C.; Yan, X.X. Sortilin: A new player in dementia and Alzheimer-type neuropathology. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 96, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, S.; Devader, C.M.; Pietri, M.; Borsotto, M.; Heurteaux, C.; Mazella, J. Altered Trek-1 Function in Sortilin Deficient Mice Results in Decreased Depressive-Like Behavior. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voloshyna, I.; Besana, A.; Castillo, M.; Matos, T.; Weinstein, I.B.; Mansukhani, M.; Robinson, R.B.; Cordon-Cardo, C.; Feinmark, S.J. TREK-1 is a novel molecular target in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 1197–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.M.; Wan, F.N.; Qin, X.J.; Cao, D.L.; Zhang, H.L.; Zhu, Y.; Dai, B.; Shi, G.H.; Ye, D.W. Prognostic significance of the TREK-1 K2P potassium channels in prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 18460–18468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Patel, S.K.; Jackson, L.; Warren, A.Y.; Arya, P.; Shaw, R.W.; Khan, R.N. A role for two-pore potassium (K2P) channels in endometrial epithelial function. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2013, 17, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondy, S.; Talbot, H.; Saada, S.; Christou, N.; Battu, S.; Pannequin, J.; Jauberteau, M.O.; Lalloué, F.; Verdier, M.; Mathonnet, M.; et al. Overexpression of sortilin is associated with 5-FU resistance and poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomellini, E.; Lagadec, C.; Polakowska, R.; Le Bourhis, X. Role of p75 neurotrophin receptor in stem cell biology: More than just a marker. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 2467–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meldolesi, J. Neurotrophin receptors in the pathogenesis, diagnosis and therapy of neurodegenerative diseases. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 121, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demeule, M.; Charfi, C.; Currie, J.C.; Larocque, A.; Zgheib, A.; Kozelko, S.; Béliveau, R.; Marsolais, C.; Annabi, B. TH1902, a new docetaxel-peptide conjugate for the treatment of sortilin-positive triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 4317–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, N.; Hosain, S.; Zhao, J.; Shen, Y.; Luo, X.; Jiang, J.; Endo, Y.; Wu, W.J. Atezolizumab potentiates Tcell-mediated cytotoxicity and coordinates with FAK to suppress cell invasion and motility in PD-L1(+) triple negative breast cancer cells. Oncoimmunology 2019, 8, e1624128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjannet, S.; Rhainds, D.; Essalmani, R.; Mayne, J.; Wickham, L.; Jin, W.; Asselin, M.C.; Hamelin, J.; Varret, M.; Allard, D.; et al. NARC-1/PCSK9 and its natural mutants: Zymogen cleavage and effects on the low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor and LDL cholesterol. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 48865–48875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nozue, T.; Hattori, H.; Ogawa, K.; Kujiraoka, T.; Iwasaki, T.; Michishita, I. Effects of Statin Therapy on Plasma Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/kexin Type 9 and Sortilin Levels in Statin-Naive Patients with Coronary Artery Disease. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2016, 23, 848–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molgaard, S.; Demontis, D.; Nicholson, A.M.; Finch, N.A.; Petersen, R.C.; Petersen, C.M.; Rademakers, R.; Nykjaer, A.; Glerup, S. Soluble sortilin is present in excess and positively correlates with progranulin in CSF of aging individuals. Exp. Gerontol. 2016, 84, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.; Padukkavidana, T.; Vaegter, C.B.; Brady, O.A.; Zheng, Y.; Mackenzie, I.R.; Feldman, H.H.; Nykjaer, A.; Strittmatter, S.M. Sortilin-mediated endocytosis determines levels of the frontotemporal dementia protein, progranulin. Neuron 2010, 68, 654–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanimoto, R.; Palladino, C.; Xu, S.Q.; Buraschi, S.; Neill, T.; Gomella, L.G.; Peiper, S.C.; Belfiore, A.; Iozzo, R.V.; Morrione, A. The perlecan-interacting growth factor progranulin regulates ubiquitination, sorting, and lysosomal degradation of sortilin. Matrix Biol. J. Int. Soc. Matrix Biol. 2017, 64, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Zhou, X.; Feng, T.; Hu, F. Regulation of lysosomal trafficking of progranulin by sortilin and prosaposin. Brain Commun. 2022, 4, fcab310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernegger, S.; Jarzab, M.; Wessler, S.; Posselt, G. Proteolytic Landscapes in Gastric Pathology and Cancerogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
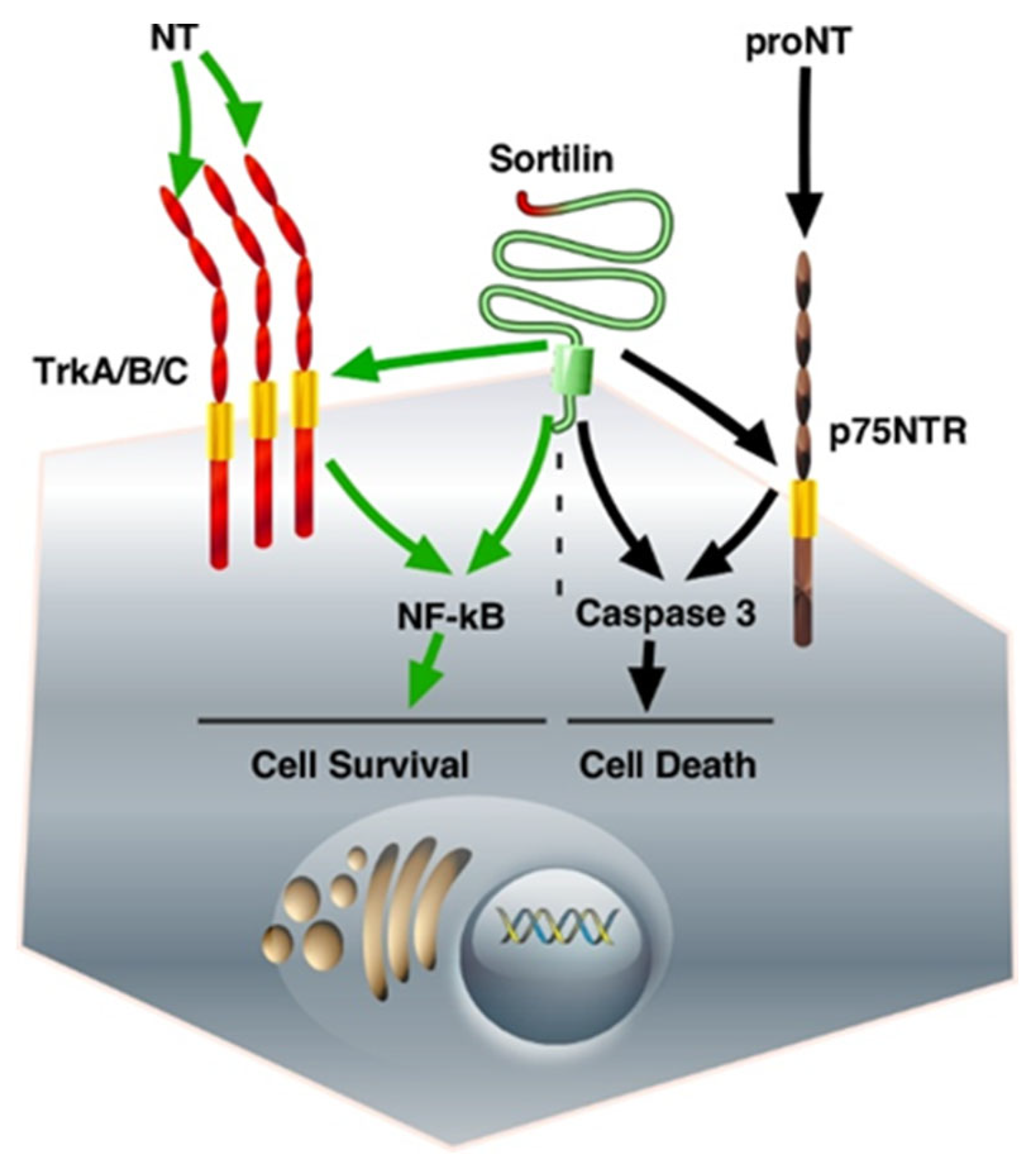
| Membrane-Bound Sortilin as a Co-Receptor | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ligand and receptor | Function | Pathways |
| NTS, NTSR1 BDNF, TrkB Pro-BDNF, p75NTR | Cell proliferation Cell proliferation, anti-apoptotic Cell apoptosis | PKC, ERK1/2, PI3K/Akt PI3K/Akt |
| Soluble Sortilin as a Ligand | ||
| Receptor | Function | Pathways |
| Unknown Unknown Unknown, EGFR- independent | Cell-cell disruption Cell morphological changes Cytoskeleton redistribution Cell proliferation | FAK/Src, PI3K/Akt Integrins expression changes ERK1/2, PKCα |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mazella, J. Deciphering Mechanisms of Action of Sortilin/Neurotensin Receptor-3 in the Proliferation Regulation of Colorectal and Other Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11888. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911888
Mazella J. Deciphering Mechanisms of Action of Sortilin/Neurotensin Receptor-3 in the Proliferation Regulation of Colorectal and Other Cancers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(19):11888. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911888
Chicago/Turabian StyleMazella, Jean. 2022. "Deciphering Mechanisms of Action of Sortilin/Neurotensin Receptor-3 in the Proliferation Regulation of Colorectal and Other Cancers" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 19: 11888. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911888
APA StyleMazella, J. (2022). Deciphering Mechanisms of Action of Sortilin/Neurotensin Receptor-3 in the Proliferation Regulation of Colorectal and Other Cancers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(19), 11888. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911888






