The Intestinal Barrier and Its Dysfunction in Patients with Metabolic Diseases and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Abstract
:1. Background
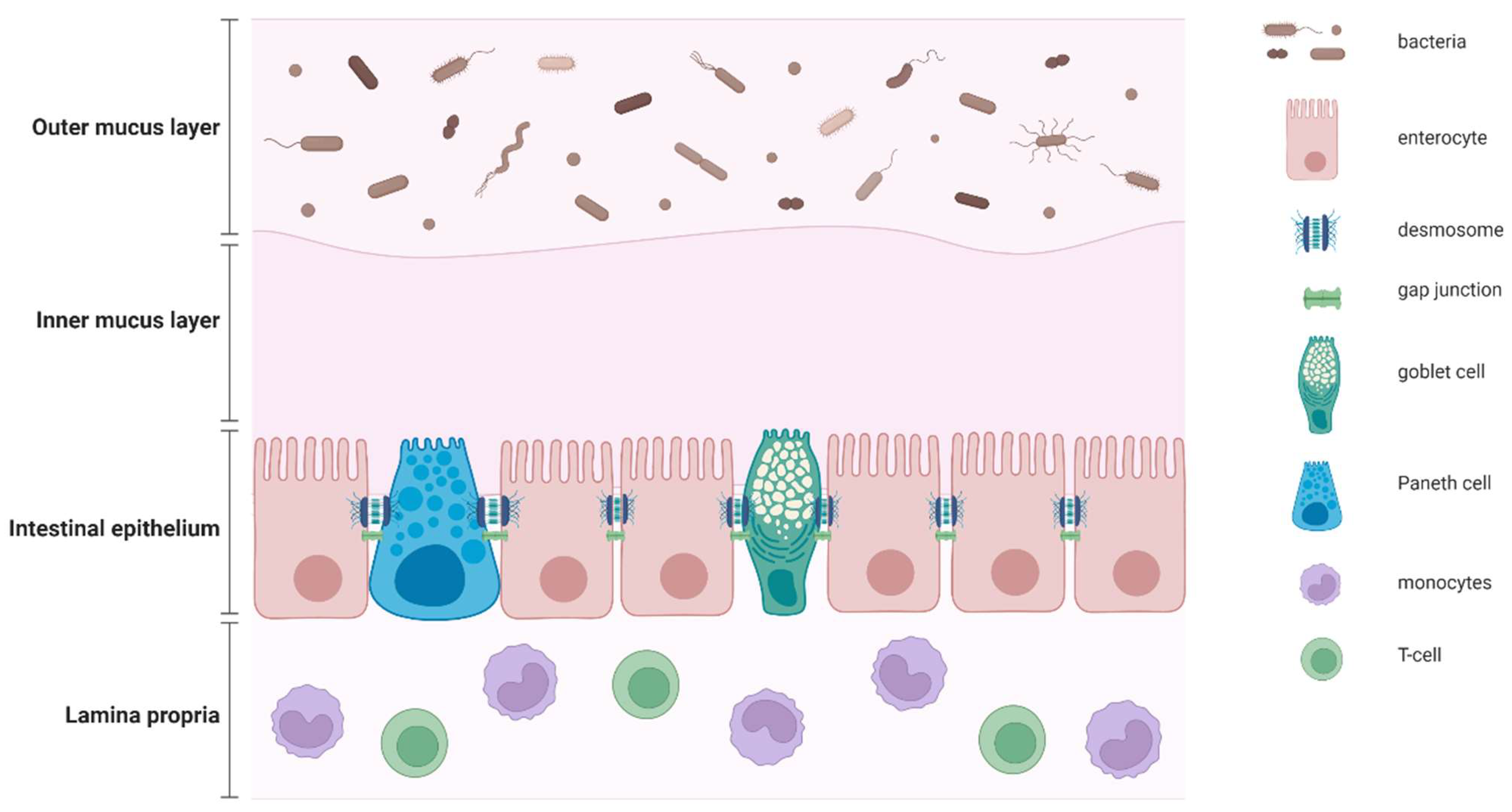
2. Definition of Gut Barrier and Gut Permeability
3. Methods for Assessing the Gut Permeability
4. Translocation of Intestinal Bacterial Products and Hepatic Inflammation
5. Gut Permeability in Patients with T2DM
6. Gut Permeability in Patients with Obesity
7. Gut Permeability in Patients with NAFLD
8. Manipulation of the Gut Permeability as Potential Therapeutical Target in Patients with NAFLD
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NAFLD | non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| NAFL | non-alcoholic fatty liver |
| NASH | non-alcoholic steato-hepatitis |
| T2DM | type-2 diabetes mellitus |
| GI | gastro-intestinal |
| TJ | tight-junctions |
| kDa | kiloDalton |
| TEER | transepithelial electric resistance |
| EVOM | epithelial volt/ohm meter |
| FABP | fatty acid binding protein |
| i-FABP | intestinal FABP |
| CHB | chronic hepatitis B |
| CHC | chronic hepatitis C |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| PAMPs | pathogen-associated molecular patterns |
| DAMPs | damage-associated molecular patterns |
| TFG-β | transforming growth factor-beta |
| IL-1 | interleukin-1 |
| IL-6 | interleukin-6 |
| TNF-α | tumour necrosis factor-alpha |
| TLR-4 | toll-like receptor 4 |
| GLP-2 | glucagon-like peptide 2 |
| GLUT-2 | glucose transporter-2 |
| BMI | body mass index |
| IL-1β | interleukin-1 beta |
| SCFA | short chain fatty acid |
| FMT | faecal microbiota transplant |
References
- Younossi, Z.; Stepanova, M.; Ong, J.P.; Jacobson, I.M.; Bugianesi, E.; Duseja, A.; Eguchi, Y.; Wong, V.W.; Negro, F.; Yilmaz, Y.; et al. Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Is the Fastest Growing Cause of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Liver Transplant Candidates. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.M.; Van Natta, M.; Behling, C.; Contos, M.J.; Cummings, O.W.; Ferrell, L.D.; Liu, Y.-C.; Torbenson, M.S.; Unalp-Arida, A.; et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunt, E.M.; Kleiner, D.E.; Carpenter, D.H.; Rinella, M.; Harrison, S.A.; Loomba, R.; Younossi, Z.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Sanyal, A.J. NAFLD: Reporting Histologic Findings in Clinical Practice. Hepatology 2021, 73, 2028–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.; Tacke, F.; Arrese, M.; Sharma, B.C.; Mostafa, I.; Bugianesi, E.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Yilmaz, Y.; George, J.; Fan, J.; et al. Global Perspectives on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2019, 69, 2672–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bergheim, I.; Weber, S.; Vos, M.; Krämer, S.; Volynets, V.; Kaserouni, S.; McClain, C.J.; Bischoff, S.C. Antibiotics protect against fructose-induced hepatic lipid accumulation in mice: Role of endotoxin. J. Hepatol. 2008, 48, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Fox, C.S.; Jacques, P.F.; Speliotes, E.K.; Hoffmann, U.; Smith, C.E.; Saltzman, E.; McKeown, N.M. Sugar-sweetened beverage, diet soda, and fatty liver disease in the Framingham Heart Study cohorts. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zelber-Sagi, S.; Ivancovsky-Wajcman, D.; Isakov, N.F.; Webb, M.; Orenstein, D.; Shibolet, O.; Kariv, R. High red and processed meat consumption is associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and insulin resistance. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Lin, A.; Kong, M.; Yao, X.; Yin, M.; Xia, H.; Ma, J.; Liu, H. Intestinal microbiome and NAFLD: Molecular insights and therapeutic perspectives. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 55, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caturano, A.; Acierno, C.; Nevola, R.; Pafundi, P.C.; Galiero, R.; Rinaldi, L.; Salvatore, T.; Adinolfi, L.E.; Sasso, F.C. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: From Pathogenesis to Clinical Impact. Processes 2021, 9, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, L.; Pafundi, P.C.; Galiero, R.; Caturano, A.; Morone, M.V.; Silvestri, C.F.; Giordano, M.; Salvatore, T.; Sasso, F.C. Mechanisms of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in the Metabolic Syndrome. A Narrative Review. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirpich, I.A.; Marsano, L.S.; McClain, C.J. Gut-liver axis, nutrition, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Biochem. 2015, 48, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Odenwald, M.A.; Turner, J.R. Intestinal permeability defects: Is it time to treat? Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 11, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johansson, M.E.V.; Phillipson, M.; Petersson, J.; Velcich, A.; Holm, L.; Hansson, G.C. The inner of the two Muc2 mucin-dependent mucus layers in colon is devoid of bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 15064–15069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crosnier, C.; Stamataki, D.; Lewis, J. Organizing cell renewal in the intestine: Stem cells, signals and combinatorial control. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006, 7, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farquhar, M.G.; Palade, G.E. Junctional Complexes in Various Epithelia. J. Cell Biol. 1963, 17, 375–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srinivasan, B.; Kolli, A.R.; Esch, M.B.; Abaci, H.E.; Shuler, M.L.; Hickman, J.J. TEER Measurement Techniques for In Vitro Barrier Model Systems. J. Lab. Autom. 2015, 20, 107–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schoultz, I.; Keita, A.V. The Intestinal Barrier and Current Techniques for the Assessment of Gut Permeability. Cells 2020, 9, 1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, M.; Vella, A. What to do about the leaky gut. Gut 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meddings, J.B.; Gibbons, I. Discrimination of site-specific alterations in gastrointestinal permeability in the rat. Gastroenterology 1998, 114, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjarnason, I.; MacPherson, A.; Hollander, D. Intestinal permeability: An overview. Gastroenterology 1995, 108, 1566–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niewold, T.A.; Meinen, M.; van der Meulen, J. Plasma intestinal fatty acid binding protein (I-FABP) concentrations increase following intestinal ischemia in pigs. Res. Vet. Sci. 2004, 77, 89–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, T.; Nakatomi, Y.; Ishikawa, H.; Hitomi, M.; Matsubara, Y.; Ono, T.; Muto, T. Intestinal fatty acid-binding protein as a sensitive marker of intestinal ischemia. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1992, 37, 1362–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gollin, G.; Marks, C.; Marks, W.H. Intestinal fatty acid binding protein in serum and urine reflects early ischemic injury to the small bowel. Surgery 1993, 113, 545–551. [Google Scholar]
- Kanda, T.; Fujii, H.; Tani, T.; Murakami, H.; Suda, T.; Sakai, Y.; Ono, T.; Hatakeyama, K. Intestinal fatty acid-binding protein is a useful diagnostic marker for mesenteric infarction in humans. Gastroenterology 1996, 110, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, N.G.; Koh, C.; Roque, A.; Eccleston, J.L.; Siegel, R.B.; Demino, M.; Kleiner, D.; Deeks, S.G.; Liang, T.J.; Heller, T.; et al. Host Response to Translocated Microbial Products Predicts Outcomes of Patients with HBV or HCV Infection. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1220–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fasano, A. Leaky gut and autoimmune diseases. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2012, 42, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasano, A. Zonulin, regulation of tight junctions, and autoimmune diseases. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1258, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fasano, A. Intestinal Permeability and Its Regulation by Zonulin: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Implications. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 1096–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schoepfer, A.M.; Beglinger, C.; Straumann, A.; Trummler, M.; Vavricka, S.R.; Bruegger, L.E.; Seibold, F. Fecal calprotectin correlates more closely with the Simple Endoscopic Score for Crohn’s disease (SES-CD) than CRP, blood leukocytes, and the CDAI. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Konikoff, M.R.; Denson, L.A. Role of fecal calprotectin as a biomarker of intestinal inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2006, 12, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurice, J.; Lett, A.M.; Skinner, C.; Lim, A.; Richardson, M.; Thomas, A.P.; Summers, P.A.; Vyas, K.; Tadbier, A.W.; Vilar, R.; et al. Transcutaneous fluorescence spectroscopy as a tool for non-invasive monitoring of gut function: First clinical experiences. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, R.D.; Owens, W.E. Inhibition of translocation of viable Escherichia coli from the gastrointestinal tract of mice by bacterial antagonism. Infect. Immun. 1979, 25, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keita, A.V.; Söderholm, J.D. The intestinal barrier and its regulation by neuroimmune factors. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2010, 22, 718–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlugosz, A.; Nowak, P.; D’Amato, M.; Kermani, G.M.; Nyström, J.; Abdurahman, S.; Lindberg, G. Increased serum levels of lipopolysaccharide and antiflagellin antibodies in patients with diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2015, 27, 1747–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du Plessis, J.; Vanheel, H.; Janssen, C.E.; Roos, L.; Slavik, T.; Stivaktas, P.I.; Nieuwoudt, M.; Beukes, M.; Tack, J.; Van der Merwe, S.W.; et al. Activated intestinal macrophages in patients with cirrhosis release NO and IL-6 that may disrupt intestinal barrier function. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luci, C.; Bourinet, M.; Leclère, P.S.; Anty, R.; Gual, P. Chronic Inflammation in Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 597648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Zhang, X.-J.; Li, H. The Role of Innate Immune Cells in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2019, 70, 1026–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammoutene, A.; Rautou, P.-E. Role of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 1278–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baratta, F.; Pastori, D.; Bartimoccia, S.; Cammisotto, V.; Cocomello, N.; Colantoni, A.; Nocella, C.; Carnevale, R.; Ferro, D.; Angelico, F.; et al. Poor Adherence to Mediterranean Diet and Serum Lipopolysaccharide Are Associated with Oxidative Stress in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, K.-L.; Su, W.-W.; Chang, C.-C.; Kor, C.-T.; Chou, C.-T.; Chen, T.-Y.; Wu, H.-M. Comparisons of parallel potential biomarkers of 1H-MRS-measured hepatic lipid content in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zelber-Sagi, S.; Ivancovsky-Wajcman, D.; Fliss-Isakov, N.; Hahn, M.; Webb, M.; Shibolet, O.; Kariv, R.; Tirosh, O. Serum Malondialdehyde is Associated with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver and Related Liver Damage Differentially in Men and Women. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D.; Bibiloni, R.; Knauf, C.; Waget, A.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Delzenne, N.M.; Burcelin, R. Changes in Gut Microbiota Control Metabolic Endotoxemia-Induced Inflammation in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity and Diabetes in Mice. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1470–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cani, P.D.; Possemiers, S.; Van De Wiele, T.; Guiot, Y.; Everard, A.; Rottier, O.; Geurts, L.; Naslain, D.; Neyrinck, A.; Lambert, D.M.; et al. Changes in gut microbiota control inflammation in obese mice through a mechanism involving GLP-2-driven improvement of gut permeability. Gut 2009, 58, 1091–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harte, A.L.; Varma, M.C.; Tripathi, G.; McGee, K.C.; Al-Daghri, N.M.; Al-Attas, O.S.; Sabico, S.; O’Hare, J.P.; Ceriello, A.; Saravanan, P.; et al. High Fat Intake Leads to Acute Postprandial Exposure to Circulating Endotoxin in Type 2 Diabetic Subjects. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pussinen, P.J.; Havulinna, A.S.; Lehto, M.; Sundvall, J.; Salomaa, V. Endotoxemia Is Associated with an Increased Risk of Incident Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gomes, J.M.G.; Costa, J.A.; Alfenas, R.C.G. Metabolic endotoxemia and diabetes mellitus: A systematic review. Metabolis 2017, 68, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabke, K.; Hendrick, G.; Devkota, S. The gut microbiome and metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 4050–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.J.; Sears, D.D. TLR4 and Insulin Resistance. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2010, 2010, 212563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, C.; Jia, G.; Deng, Q.; Zhao, H.; Chen, X.; Liu, G.; Wang, K. The Effects of Glucagon-like Peptide-2 on the Tight Junction and Barrier Function in IPEC-J2 Cells through Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase–Protein Kinase B–Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Signaling Pathway. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 29, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, R.; Rah, B.; Bastola, D.; Dhawan, P.; Singh, A.B. Obesity-induces Organ and Tissue Specific Tight Junction Restructuring and Barrier Deregulation by Claudin Switching. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gruzdeva, O.; Borodkina, D.; Uchasova, E.; Dyleva, Y.; Barbarash, O. Leptin resistance: Underlying mechanisms and diagnosis. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Desai, M.S.; Seekatz, A.M.; Koropatkin, N.M.; Kamada, N.; Hickey, C.A.; Wolter, M.; Pudlo, N.A.; Kitamoto, S.; Terrapon, N.; Muller, A.; et al. A Dietary Fiber-Deprived Gut Microbiota Degrades the Colonic Mucus Barrier and Enhances Pathogen Susceptibility. Cell 2016, 167, 1339–1353.e1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thaiss, C.A.; Levy, M.; Grosheva, I.; Zheng, D.; Soffer, E.; Blacher, E.; Braverman, S.; Tengeler, A.C.; Barak, O.; Elazar, M.; et al. Hyperglycemia drives intestinal barrier dysfunction and risk for enteric infection. Science 2018, 359, 1376–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruel, L.; Sulzenbacher, G.; Tison, M.C.; Pujol, A.; Nicoletti, C.; Perrier, J.; Galinier, A.; Ropartz, D.; Fons, M.; Pompeo, F.; et al. α-Galactosidase/Sucrose Kinase (AgaSK), a Novel Bifunctional Enzyme from the Human Microbiome Coupling Galactosidase and Kinase Activities. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 40814–40823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mkumbuzi, L.; Mfengu, M.M.; Engwa, G.A.; Sewani-Rusike, C.R. Insulin Resistance is Associated with Gut Permeability Without the Direct Influence of Obesity in Young Adults. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 2997–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Sabater-Masdeu, M.; Ortega, F.J.; Ricart, W.; Fernández-Real, J.M. Circulating Zonulin, a Marker of Intestinal Permeability, Is Increased in Association with Obesity-Associated Insulin Resistance. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Henao-Mejia, J.; Elinav, E.; Jin, C.; Hao, L.; Mehal, W.Z.; Strowig, T.; Thaiss, C.A.; Kau, A.L.; Eisenbarth, S.C.; Jurczak, M.J.; et al. Inflammasome-mediated dysbiosis regulates progression of NAFLD and obesity. Nature 2012, 482, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Sadi, R.; Guo, S.; Ye, D.; Dokladny, K.; Alhmoud, T.; Ereifej, L.; Ma, T.Y. Mechanism of IL-1beta modulation of intestinal epithelial barrier involves p38 kinase and activating transcription factor-2 activation. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 6596–6606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ott, B.; Skurk, T.; Hastreiter, L.; Lagkouvardos, I.; Fischer, S.; Büttner, J.; Kellerer, T.; Clavel, T.; Rychlik, M.; Haller, D.; et al. Effect of caloric restriction on gut permeability, inflammation markers, and fecal microbiota in obese women. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nier, A.; Engstler, A.J.; Maier, I.B.; Bergheim, I. Markers of intestinal permeability are already altered in early stages of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Studies in children. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giorgio, V.; Miele, L.; Principessa, L.; Ferretti, F.; Villa, M.P.; Negro, V.; Grieco, A.; Alisi, A.; Nobili, V. Intestinal permeability is increased in children with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and correlates with liver disease severity. Dig. Liver Dis. 2014, 46, 556–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luther, J.; Garber, J.J.; Khalili, H.; Dave, M.; Bale, S.S.; Jindal, R.; Motola, D.L.; Luther, S.; Bohr, S.; Jeoung, S.W.; et al. Hepatic Injury in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Contributes to Altered Intestinal Permeability. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 1, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miele, L.; Valenza, V.; La Torre, G.; Montalto, M.; Cammarota, G.; Ricci, R.; Mascianà, R.; Forgione, A.; Gabrieli, M.L.; Perotti, G.; et al. Increased intestinal permeability and tight junction alterations in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1877–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assimakopoulos, S.F.; Tsamandas, A.C.; Tsiaoussis, G.I.; Karatza, E.; Triantos, C.; Vagianos, C.E.; Spiliopoulou, I.; Kaltezioti, V.; Charonis, A.; Nikolopoulou, V.N.; et al. Altered intestinal tight junctions’ expression in patients with liver cirrhosis: A pathogenetic mechanism of intestinal hyperpermeability. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 42, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoletti, A.; Ponziani, F.R.; Biolato, M.; Valenza, V.; Marrone, G.; Sganga, G.; Gasbarrini, A.; Miele, L.; Grieco, A. Intestinal permeability in the pathogenesis of liver damage: From non-alcoholic fatty liver disease to liver transplantation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 4814–4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailing, L.J.; Allen, J.M.; Buford, T.W.; Fields, C.J.; Woods, J.A. Exercise and the Gut Microbiome: A Review of the Evidence, Potential Mechanisms, and Implications for Human Health. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2019, 47, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keirns, B.H.; Koemel, N.A.; Sciarrillo, C.M.; Anderson, K.L.; Emerson, S.R. Exercise and intestinal permeability: Another form of exercise-induced hormesis? Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2020, 319, G512–G518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva, A.; Gray, E.H.; Azarian, S.; Zamalloa, A.; McPhail, M.J.W.; Vincent, R.P.; Williams, R.; Chokshi, S.; Patel, V.C.; Edwards, L.A. Faecal cytokine profiling as a marker of intestinal inflammation in acutely decompensated cirrhosis. JHEP Rep. 2020, 2, 100151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Munck, T.J.; Xu, P.; Verwijs, H.J.; Masclee, A.A.; Jonkers, D.; Verbeek, J.; Koek, G.H. Intestinal permeability in human nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 2906–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosso, C.; Caviglia, G.P.; Younes, R.; Foglia, B.; Blanco, M.J.G.; Ribaldone, D.G.; Bugianesi, E. Circulating Zonulin is Related to Hepatic Necroinflammation in Patients with Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Clin. Lab. 2020, 66, 705–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Mercado, A.I.; Navarro-Oliveros, M.; Robles-Sánchez, C.; Plaza-Díaz, J.; Sáez-Lara, M.J.; Muñoz-Quezada, S.; Fontana, L.; Abadía-Molina, F. Microbial Population Changes and Their Relationship with Human Health and Disease. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thuy, S.; Ladurner, R.; Volynets, V.; Wagner, S.; Strahl, S.; Königsrainer, A.; Maier, K.-P.; Bischoff, S.C.; Bergheim, I. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Humans Is Associated with Increased Plasma Endotoxin and Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor 1 Concentrations and with Fructose Intake. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 1452–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biolato, M.; Manca, F.; Marrone, G.; Cefalo, C.; Racco, S.; Miggiano, G.A.; Valenza, V.; Gasbarrini, A.; Miele, L.; Grieco, A. Intestinal permeability after Mediterranean diet and low-fat diet in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Rodriguez, E.; Egea-Zorrilla, A.; Plaza-Díaz, J.; Aragón-Vela, J.; Muñoz-Quezada, S.; Tercedor-Sánchez, L.; Abadia-Molina, F. The Gut Microbiota and Its Implication in the Development of Atherosclerosis and Related Cardiovascular Diseases. Nutrients 2020, 12, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferolla, S.M.; Couto, C.A.; Costa-Silva, L.; Armiliato, G.N.A.; Pereira, C.A.S.; Martins, F.S.; Ferrari, M.D.; Vilela, E.G.; Torres, H.O.G.; Cunha, A.S.; et al. Beneficial Effect of Synbiotic Supplementation on Hepatic Steatosis and Anthropometric Parameters, But Not on Gut Permeability in a Population with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Nutrients 2016, 8, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Damms-Machado, A.; Louis, S.; Schnitzer, A.; Volynets, V.; Rings, A.; Basrai, M.; Bischoff, S.C. Gut permeability is related to body weight, fatty liver disease, and insulin resistance in obese individuals undergoing weight reduction. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krawczyk, M.; Maciejewska, D.; Ryterska, K.; Czerwińka-Rogowska, M.; Jamioł-Milc, D.; Skonieczna-Żydecka, K.; Milkiewicz, P.; Raszeja-Wyszomirska, J.; Stachowska, E. Gut Permeability Might be Improved by Dietary Fiber in Individuals with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Undergoing Weight Reduction. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kessoku, T.; Imajo, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Ozaki, A.; Iwaki, M.; Honda, Y.; Kato, T.; Ogawa, Y.; Tomeno, W.; Kato, S.; et al. Lubiprostone in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2a trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 996–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craven, L.; Rahman, A.; Nair Parvathy, S.; Beaton, M.; Silverman, J.; Qumosani, K.; Hramiak, I.; Hegele, R.; Joy, T.; Meddings, J.; et al. Allogenic Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Improves Abnormal Small Intestinal Permeability: A Randomized Control Trial. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 115, 1055–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, N.; Emoto, T.; Yamashita, T.; Watanabe, H.; Hayashi, T.; Tabata, T.; Hirata, K.I. Bacteroides vulgatus and Bacteroides dorei Reduce Gut Microbial Lipopolysaccharide Production and Inhibit Atherosclerosis. Circulation 2018, 138, 2486–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plovier, H.; Everard, A.; Druart, C.; Depommier, C.; Van Hul, M.; Geurts, L.; Chilloux, J.; Ottman, N.; Duparc, T.; Lichtenstein, L.; et al. A purified membrane protein from Akkermansia muciniphila or the pasteurized bacterium improves metabolism in obese and diabetic mice. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belzer, C.; Chia, L.W.; Aalvink, S.; Chamlagain, B.; Piironen, V.; Knol, J.; de Vos, W.M. Microbial Metabolic Networks at the Mucus Layer Lead to Diet-Independent Butyrate and Vitamin B 12 Production by Intestinal Symbionts. mBio 2017, 8, e00770-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munukka, E.; Rintala, A.; Toivonen, R.; Nylund, M.; Yang, B.; Takanen, A.; Hänninen, A.; Vuopio, J.; Huovinen, P.; Jalkanen, S.; et al. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii treatment improves hepatic health and reduces adipose tissue inflammation in high-fat fed mice. ISME J. 2017, 11, 1667–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Technique | Sample Tested | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Orally indigested probes (lactulose to mannitol ratio, sucralose) | Urine | Informative on damage of intestinal mucosa Specific timing of urinary excretion for regional analysis of the intestine Non-invasive | Preparation required (diet/fasting) Time-consuming procedure Not informative on TJs Influenced by kidney function |
| FABP-2 | Serum | Highly specific for small intestine enterocytes Informative on damage of intestinal mucosa Non-invasive and rapid measurement Rapid sample collection | Not informative on TJs False positives (ischemia-reperfusion injury) |
| Zonulin | Serum | Informative on TJs Non-invasive Rapid sample collection | Lack of standardisation between commercial kits |
| Calprotectin | Stool | Informative on damage of intestinal mucosa Non-invasive Rapid sample collection | Not informative on TJs False positives (inflammatory bowel disease) |
| Fluorescence spectroscopy | Transcutaneous assessment | Non-invasive Informative on intestinal permeability and motility Automated analysis | Skin colour and BMI impact on fluorescent measurement Requires specialised equipment Limited evidence in healthy individuals |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Forlano, R.; Mullish, B.H.; Roberts, L.A.; Thursz, M.R.; Manousou, P. The Intestinal Barrier and Its Dysfunction in Patients with Metabolic Diseases and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23020662
Forlano R, Mullish BH, Roberts LA, Thursz MR, Manousou P. The Intestinal Barrier and Its Dysfunction in Patients with Metabolic Diseases and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(2):662. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23020662
Chicago/Turabian StyleForlano, Roberta, Benjamin H. Mullish, Lauren A. Roberts, Mark R. Thursz, and Pinelopi Manousou. 2022. "The Intestinal Barrier and Its Dysfunction in Patients with Metabolic Diseases and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 2: 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23020662
APA StyleForlano, R., Mullish, B. H., Roberts, L. A., Thursz, M. R., & Manousou, P. (2022). The Intestinal Barrier and Its Dysfunction in Patients with Metabolic Diseases and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(2), 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23020662







