ppGpp, the General Stress Response Alarmone, Is Required for the Expression of the α-Hemolysin Toxin in the Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Isolate, J96
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
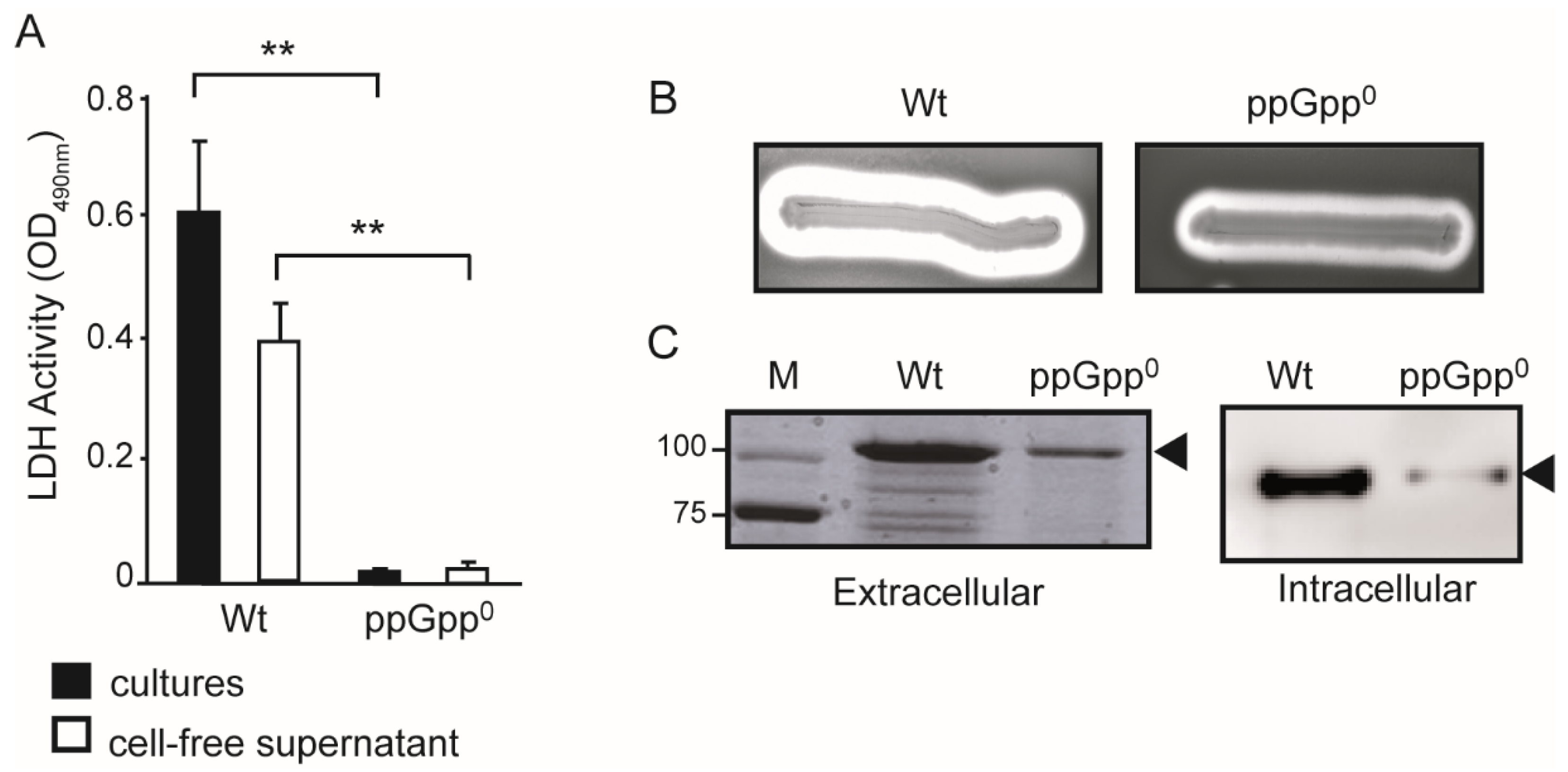
2.1. The Production of the α-Hemolysin Is Impaired in ppGpp-Deficient Strains
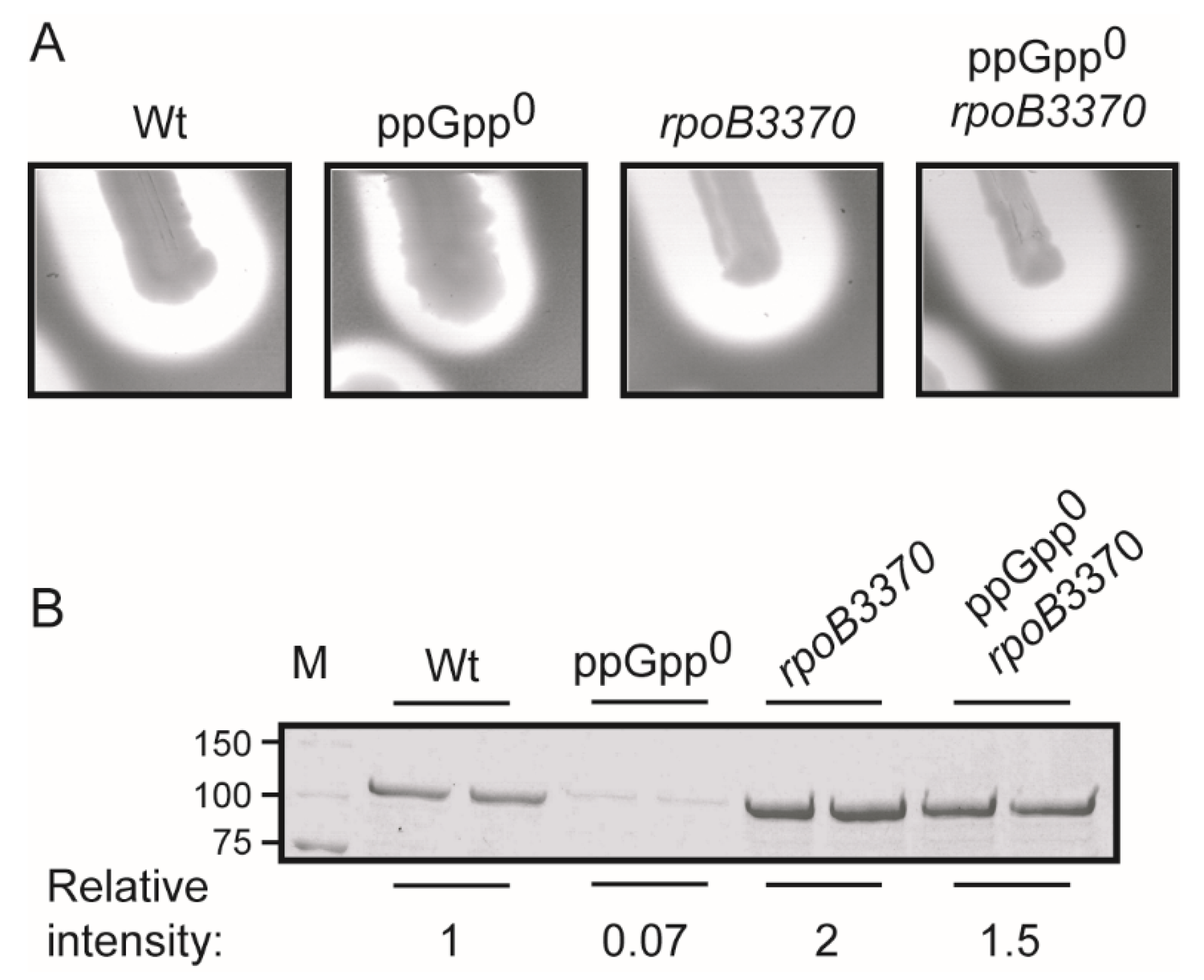
2.2. Suppressor Mutants of the Auxotrophic Phenotype Depicted by the ppGpp0 Restore α-Hemolysin Expression from the hlyCABDII Operon
2.3. ppGpp Stimulates the Transcriptional Expression of the hlyCABDII Operon
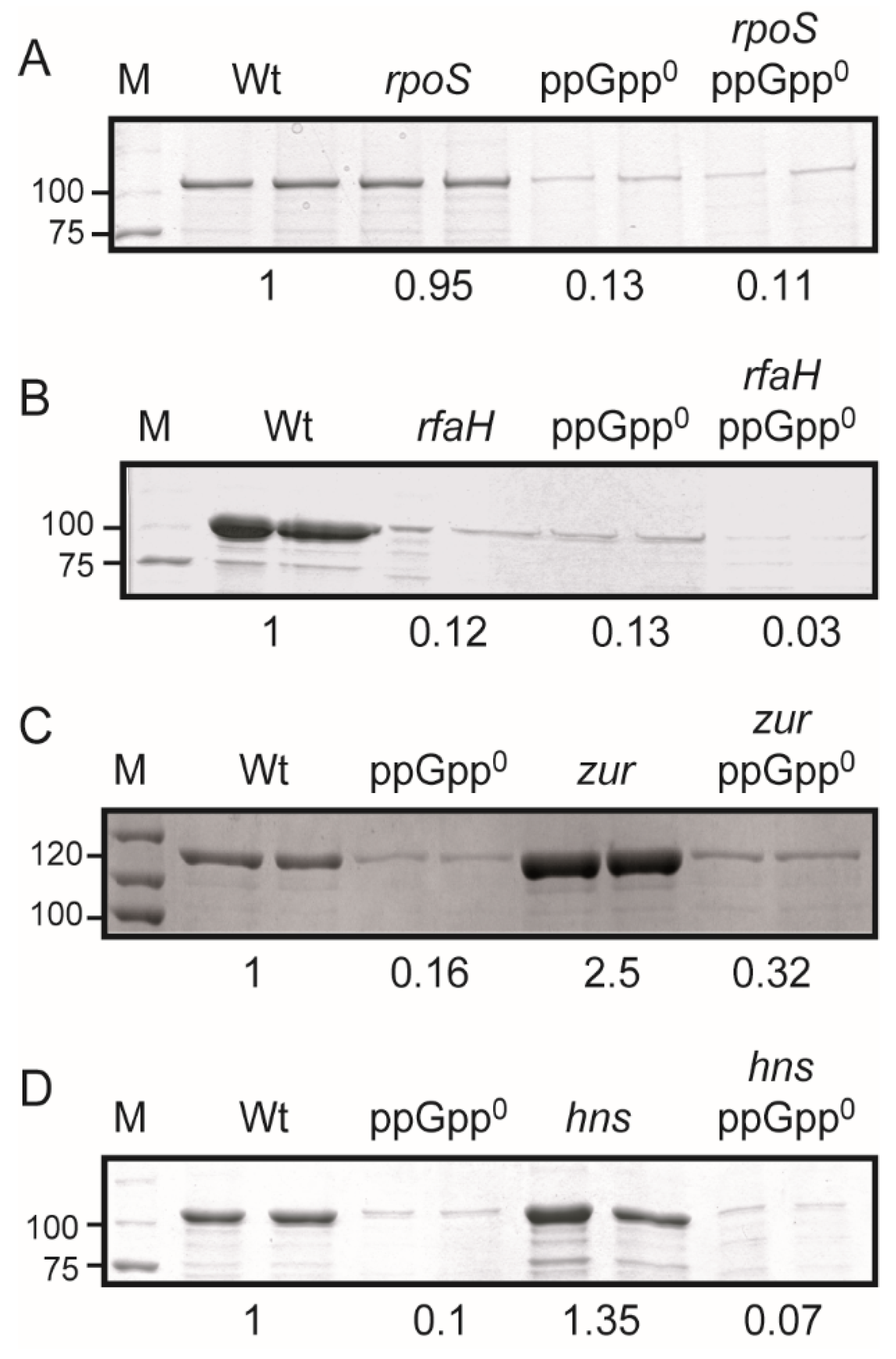
2.4. The ppGpp-Mediated Regulation of the hlyCABDII Operon Is Independent of RpoS, RfaH, Zur, and H-NS
2.5. ppGpp Is Required for the Thermoregulation but Not for the Osmoregulation of hlyCABDII Expression
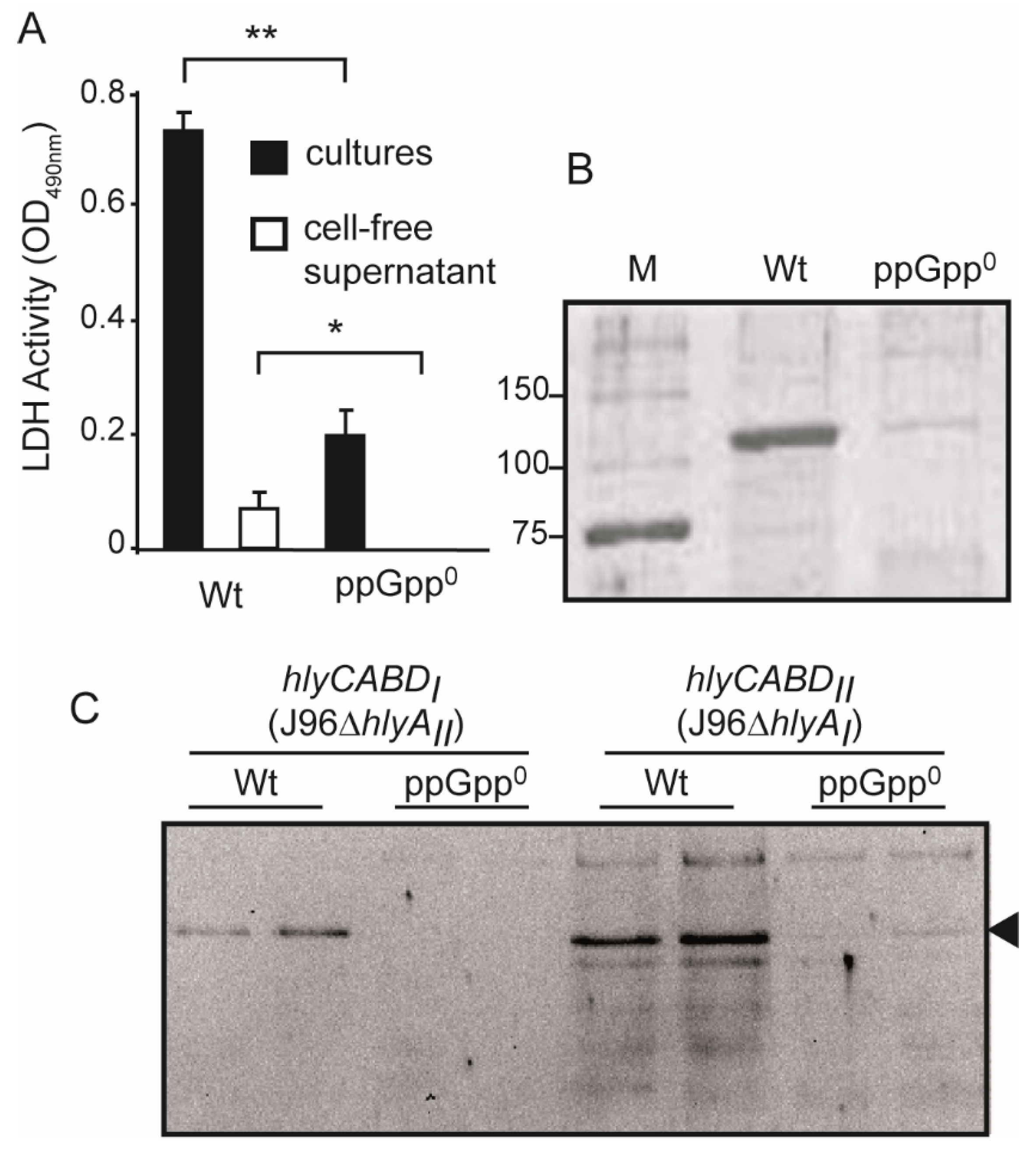
2.6. ppGpp-Deficiency Causes a Drastic Drop in the α-Hemolysin Production in the Uropathogenic Isolate J96
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains, Plasmids, and Growth Conditions
4.2. Genetic Techniques
| Strain | Relevant Characteristics | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| J96 | Pathogenic isolate | [37] |
| J96 relA spoT | J96 relA251::KmR, spoT207::CmR | [19] |
| JFV16 | J96 ΔhlyAII | [28] |
| JFV18 | JFV16 relA251::KmR, spoT207::CmR | This study |
| JFV21 | J96 ΔhlyAI | [28] |
| JFV22 | JFV21 relA251::KmR, spoT207::CmR | This study |
| AAG1 | MG1655 ΔlacZ | [38] |
| CF1693 | MG1655 relA251::KmR, spoT207::CmR | [39] |
| JFV2 | AAG1 ΔrelA ΔspoT | [20] |
| JFV23 | AAG16 spoT207::CmR | This study |
| EC3954 | MG1655 rpoB3370 thi::Tn10 | [19] |
| JFV19 | AAG1 rpoB3370 thi::Tn10 | This study |
| JFV20 | JFV2 rpoB3370 thi::Tn10 | This study |
| RH90 | MC4100 rpoS359::Tn10 | [40] |
| AAG18 | AAG1 rpoS359::Tn10 | This study |
| 5KC 1.8 | recAI hsdR hsdS rfaH::Tn5 1.8 | [41] |
| JFV14 | AAG1 rfaH::Tn5 1.8 | This study |
| JFV15 | JFV2 rfaH::Tn5 1.8 | This study |
| BSN27 | MC4100 Δhns-trp::Tn10 | [42] |
| JFV5 | AAG1 Δhns-trp::Tn10 | This study |
| JFV6 | JFV2 Δhns-trp::Tn10 | This study |
| MG1655Δzur | MG1655 Δzur::CmR | This study |
| CJM1 | AAG1 Δzur::CmR | This study |
| CJM2 | JFV2 Δzur::CmR | This study |
| Plasmid | ||
| pSF4000 | hlyCABDII J96 in pACYC184, CmR | [43] |
| pMGP-1 | hlyCABDII J96 in pBR322, ApR | This study |
4.3. Cytotoxicity Assay
4.4. SDS-PAGE and Western Immunobloting Analyses
4.5. Expression Analysis by qPCR
4.6. Isolation of Suppressor Mutants
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cashel, M.; Gentry, D.R.; Hernandez, V.J.; Vinella, D.M. The Stringent Response. In Escherichia coli and Salmonella: Cellular and Molecular Biology; Neidhardt, F.C., Curtiss, R., III, Ingraham, J.L., Lin, E.C.C., Low, K.B., Magasanik, B., Reznikoff, W.S., Riley, M., Schaechter, M., Umbarger, H.E., Eds.; American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 1996; pp. 1458–1496. [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson, L.U.; Farewell, A.; Nyström, T. ppGpp: A Global Regulator in Escherichia coli. Trends Microbiol. 2005, 13, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varik, V.; Oliveira, S.R.A.; Hauryliuk, V.; Tenson, T. HPLC quantification of bacterial housekeeping nucleotides and alarmone messengers ppGpp and pppGpp. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Coll, L.; Cashel, M. Possible Roles for Basal Levels of (p)ppGpp: Growth Efficiency vs. Surviving Stress. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanjee, U.; Ogata, K.; Houry, W.A. Direct Binding Targets of the Stringent Response Alarmone (p)ppGpp. Mol. Microbiol. 2012, 85, 1029–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaca, A.O.; Colomer-Winter, C.; Lemos, J.A. Many Means to a Common End: The Intricacies of (p)ppGpp Metabolism and Its Control of Bacterial Homeostasis. J. Bacteriol. 2015, 197, 1146–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhu, J.; Xu, J.; Shao, H.; Zhou, R. Regulation of (p)ppGpp and Its Homologs on Environmental Adaptation, Survival, and Pathogenicity of Streptococci. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalebroux, Z.D.; Svensson, S.L.; Gaynor, E.C.; Swanson, M.S. ppGpp Conjures Bacterial Virulence. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2010, 74, 171–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundra, S.; Colomer-Winter, C.; Lemos, J.A. Survival of the Fittest: The Relationship of (p)ppGpp with Bacterial Virulence. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, T.A.; Ventura, C.L.; Smith, M.A.; Merrell, D.S.; O’Brien, A.D. Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 and Hemolysin from Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Elicit Different Host Responses in the Murine Bladder. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, R.A.; Dellinger, E.P.; Minshew, B.; Falkow, S. Haemolysin Contributes to Virulence of Extra-Intestinal E. coli Infections. Nature 1981, 294, 665–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lally, E.T.; Hill, R.B.; Kieba, I.R.; Korostoff, J. The Interaction between RTX Toxins and Target Cells. Trends Microbiol. 1999, 7, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristow, L.C.; Welch, R.A. Hemolysin of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli: A Cloak or a Dagger? Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2016, 1858, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, R.A. Pore-Forming Cytolysins of Gram-Negative Bacteria. Mol. Microbiol. 1991, 5, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanley, P.; Koronakis, V.; Hughes, C. Acylation of Escherichia coli Hemolysin: A Unique Protein Lipidation Mechanism Underlying Toxin Function. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1998, 62, 309–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanabalu, T.; Koronakis, E.; Hughes, C.; Koronakis, V. Substrate-Induced Assembly of a Contiguous Channel for Protein Export from E. coli: Reversible Bridging of an Inner-Membrane Translocase to an Outer Membrane Exit Pore. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 6487–6496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, D.L.; Bukanov, N.O.; Berg, D.E.; Welch, R.A. Two pathogenicity islands in uropathogenic Escherichia coli J96: Cosmid cloning and sample sequencing. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 3736–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, G.; Altenhoefer, A.; Knapp, O.; Maier, E.; Dobrindt, U.; Blum-Oehler, G.; Benz, R.; Emody, L.; Hacker, J. Both alpha-haemolysin determinants contribute to full virulence of uropathogenic Escherichia coli strain 536. Microbes Infect. 2006, 8, 2006–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åberg, A.; Shingler, V.; Balsalobre, C. (p)ppGpp Regulates Type 1 Fimbriation of Escherichia coli by Modulating the Expression of the Site-Specific Recombinase FimB. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 60, 1520–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Åberg, A.; Fernández-Vázquez, J.; Cabrer-Panes, J.D.; Sánchez, A.; Balsalobre, C. Similar and Divergent Effects of ppGpp and DksA Deficiencies on Transcription in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 3226–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrer-Panes, J.D.; Fernández-Coll, L.; Fernández-Vázquez, J.; Gaviria-Cantin, T.C.; El Mouali, Y.; Åberg, A.; Balsalobre, C. ppGpp Mediates the Growth Phase-Dependent Regulation of agn43, a Phase Variable Gene, by Stimulating Its Promoter Activity. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2020, 12, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobley, H.L.; Green, D.M.; Trifillis, A.L.; Johnson, D.E.; Chippendale, G.R.; Lockatell, C.V.; Jones, B.D.; Warren, J.W. Pyelonephritogenic Escherichia coli and Killing of Cultured Human Renal Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cells: Role of Hemolysin in Some Strains. Infect. Immun. 1990, 58, 1281–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, H.; Cashel, M. Isolation of RNA Polymerase Suppressors of a (p)ppGpp Deficiency. Methods Enzymol. 2003, 371, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.N.; Jin, D.J. The RpoB Mutants Destabilizing Initiation Complexes at Stringently Controlled Promoters Behave like “Stringent” RNA Polymerases in Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 2908–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koronakis, V.; Cross, M.; Hughes, C. Expression of the E. coli Hemolysin Secretion Gene hlyB Involves Transcript Anti-Termination within the hly Operon. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988, 16, 4789–4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leeds, J.A.; Welch, R.A. RfaH Enhances Elongation of Escherichia coli hlyCABD mRNA. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 1850–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leeds, J.A.; Welch, R.A. Enhancing Transcription through the Escherichia coli Hemolysin Operon, hlyCABD: RfaH and Upstream JUMPStart DNA Sequences Function Together via a Post initiation Mechanism. J. Bacteriol. 1997, 179, 3519–3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasco, E.; Wang, S.; Sanet, M.; Fernández-Vázquez, J.; Jové, D.; Glaría, E.; Valledor, A.F.; O’Halloran, T.V.; Balsalobre, C. A New Role for Zinc Limitation in Bacterial Pathogenicity: Modulation of α-Hemolysin from Uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto, J.M.; Madrid, C.; Prenafeta, A.; Miquelay, E.; Balsalobre, C.; Carrascal, M.; Juárez, A. Expression of the Hemolysin Operon in Escherichia coli Is Modulated by a Nucleoid-Protein Complex That Includes the Proteins Hha and H-NS. Mol. Gen. Genet. 2000, 263, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.M.; Dobrindt, U.; Nagy, G.; Emödy, L.; Uhlin, B.E.; Hacker, J. Role of Histone-like Proteins H-NS and StpA in Expression of Virulence Determinants of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 5428–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouriño, M.; Muñoa, F.; Balsalobre, C.; Diaz, P.; Madrid, C.; Juarez, A. Environmental Regulation of α-Haemolysin Expression in Escherichia coli. Microb. Pathog. 1994, 16, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhas, M. Horizontal Gene Transfer in Human Pathogens. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 41, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorman, C.J. H-NS: A Universal Regulator for a Dynamic Genome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizarro-Cerdá, J.; Tedin, K. The Bacterial Signal Molecule, ppGpp, Regulates Salmonella Virulence Gene Expression. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 52, 1827–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, A.; Rolfe, M.D.; Lucchini, S.; Schwerk, P.; Hinton, J.C.D.; Tedin, K. The Bacterial Signal Molecule, ppGpp, Mediates the Environmental Regulation of Both the Invasion and Intracellular Virulence Gene Programs of Salmonella. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 30112–30121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datsenko, K.A.; Wanner, B.L. One-Step Inactivation of Chromosomal Genes in Escherichia coli K-12 Using PCR Products. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 6640–6645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hull, R.A.; Gill, R.E.; Hsu, P.; Minshew, B.H.; Falkow, S. Construction and Expression of Recombinant Plasmids Encoding Type 1 or D-Mannose-Resistant Pili from a Urinary Tract Infection Escherichia coli Isolate. Infect. Immun. 1981, 33, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aberg, A.; Shingler, V.; Balsalobre, C. Regulation of the fimB Promoter: A Case of Differential Regulation by ppGpp and DksA in vivo. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 67, 1223–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Kalman, M.; Ikehara, K.; Zemel, S.; Glaser, G.; Cashel, M. Residual Guanosine 3’,5’-Bispyrophosphate Synthetic Activity of relA Null Mutants Can Be Eliminated by spoT Null Mutations. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 5980–5990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengge-Aronis, R.; Fischer, D. Identification and Molecular Analysis of glgS, a Novel Growth-Phase-Regulated and RpoS-Dependent Gene Involved in Glycogen Synthesis in Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 1992, 6, 1877–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, M.J.A.; Koronakis, V.; Schmoll, T.; Hughes, C. Escherichia coli HlyT Protein, a Transcriptional Activator of Haemolysin Synthesis and Secretion, Is Encoded by the rfaH (sfrB) Locus Required for Expression of Sex Factor and Lipopolysaccharide Genes. Mol. Microbiol. 1992, 6, 1003–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, J.; Dagberg, B.; Richet, E.; Uhlin, B.E. H-NS and StpA Proteins Stimulate Expression of the Maltose Regulon in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 6117–6125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, R.A.; Hull, R.; Falkow, S. Molecular Cloning and Physical Characterization of a Chromosomal Hemolysin from Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 1983, 42, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellett, S.; Boehm, D.F.; Snyder, I.S.; Rowe, G.; Welch, R.A. Characterization of Monoclonal Antibodies against the Escherichia coli Hemolysin. Infect. Immun. 1990, 58, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernández-Vázquez, J.; Cabrer-Panes, J.D.; Åberg, A.; Juárez, A.; Madrid, C.; Gaviria-Cantin, T.; Fernández-Coll, L.; Vargas-Sinisterra, A.F.; Jiménez, C.J.; Balsalobre, C. ppGpp, the General Stress Response Alarmone, Is Required for the Expression of the α-Hemolysin Toxin in the Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Isolate, J96. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12256. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232012256
Fernández-Vázquez J, Cabrer-Panes JD, Åberg A, Juárez A, Madrid C, Gaviria-Cantin T, Fernández-Coll L, Vargas-Sinisterra AF, Jiménez CJ, Balsalobre C. ppGpp, the General Stress Response Alarmone, Is Required for the Expression of the α-Hemolysin Toxin in the Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Isolate, J96. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(20):12256. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232012256
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernández-Vázquez, Jorge, Juan David Cabrer-Panes, Anna Åberg, Antonio Juárez, Cristina Madrid, Tania Gaviria-Cantin, Llorenç Fernández-Coll, Andrés Felipe Vargas-Sinisterra, Carlos Jonay Jiménez, and Carlos Balsalobre. 2022. "ppGpp, the General Stress Response Alarmone, Is Required for the Expression of the α-Hemolysin Toxin in the Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Isolate, J96" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 20: 12256. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232012256
APA StyleFernández-Vázquez, J., Cabrer-Panes, J. D., Åberg, A., Juárez, A., Madrid, C., Gaviria-Cantin, T., Fernández-Coll, L., Vargas-Sinisterra, A. F., Jiménez, C. J., & Balsalobre, C. (2022). ppGpp, the General Stress Response Alarmone, Is Required for the Expression of the α-Hemolysin Toxin in the Uropathogenic Escherichia coli Isolate, J96. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(20), 12256. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232012256





