Global Proteomic Profile of Aluminum-Induced Hippocampal Impairments in Rats: Are Low Doses of Aluminum Really Safe?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
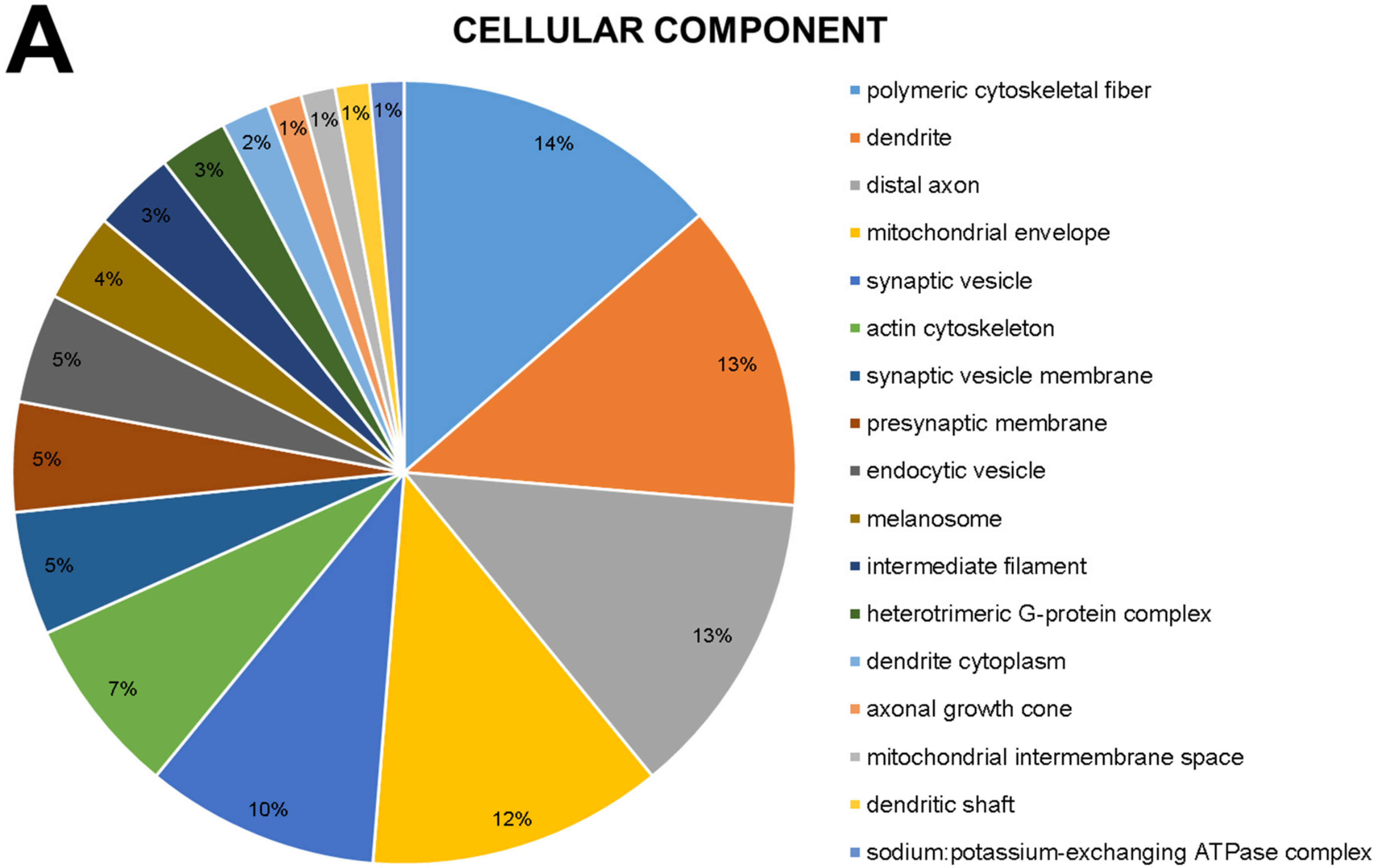
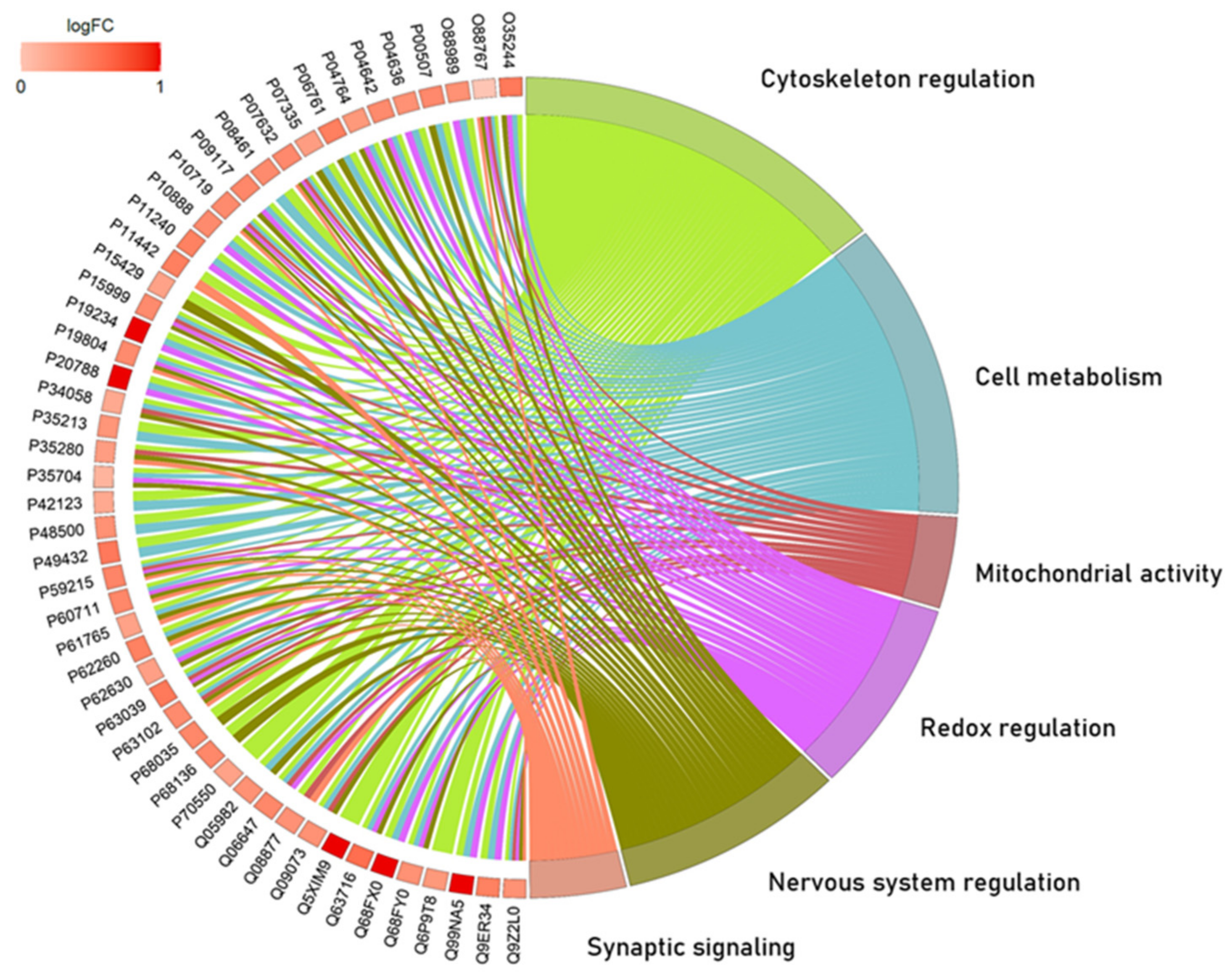
2.1. The Global Proteomic Profile of Rats’ Hippocampus Was Significantly Affected by Long-Term and Low-Dose Aluminum Exposure
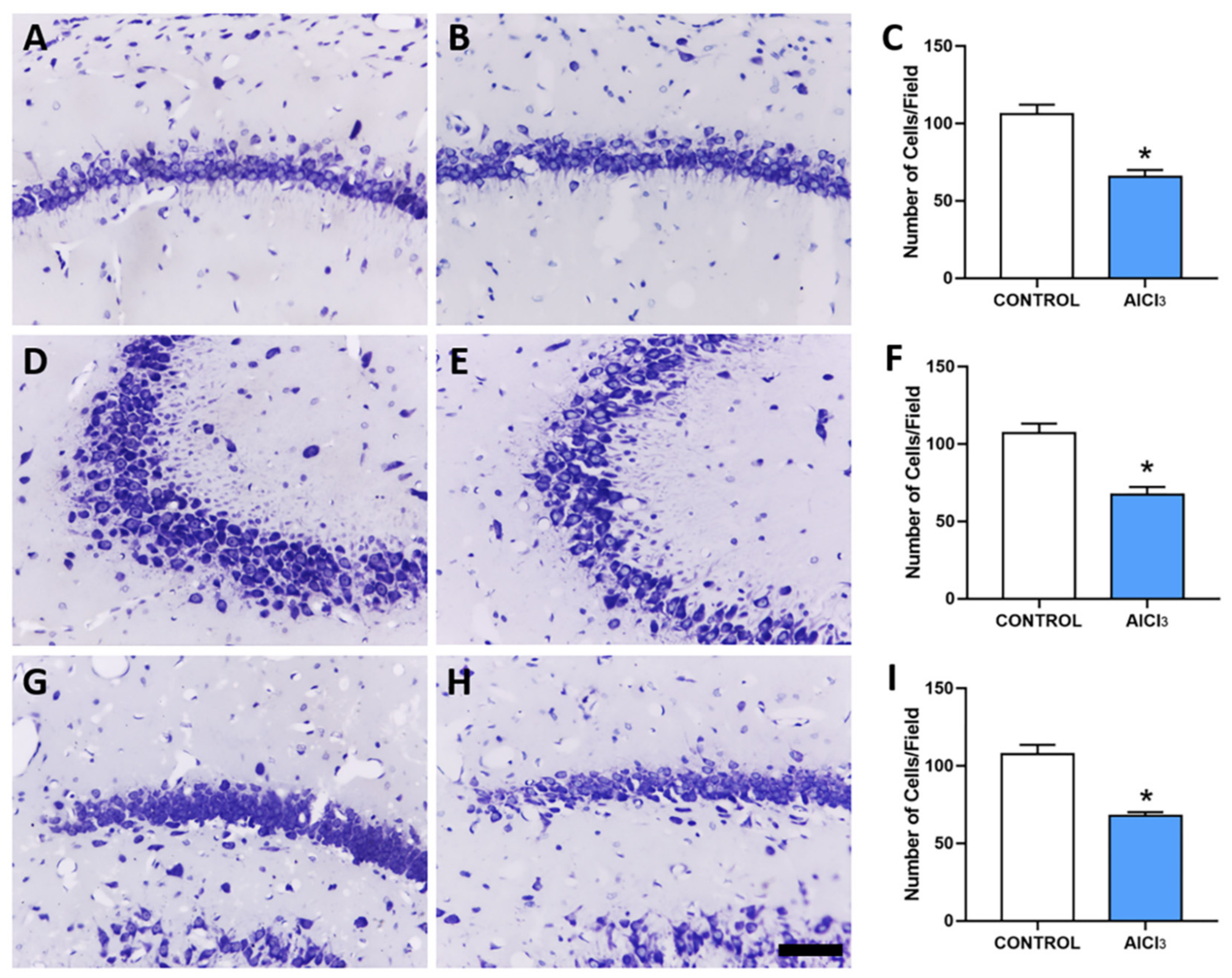
2.2. Aluminum-Exposed Rats Displayed Morphological Damages in the Hippocampus
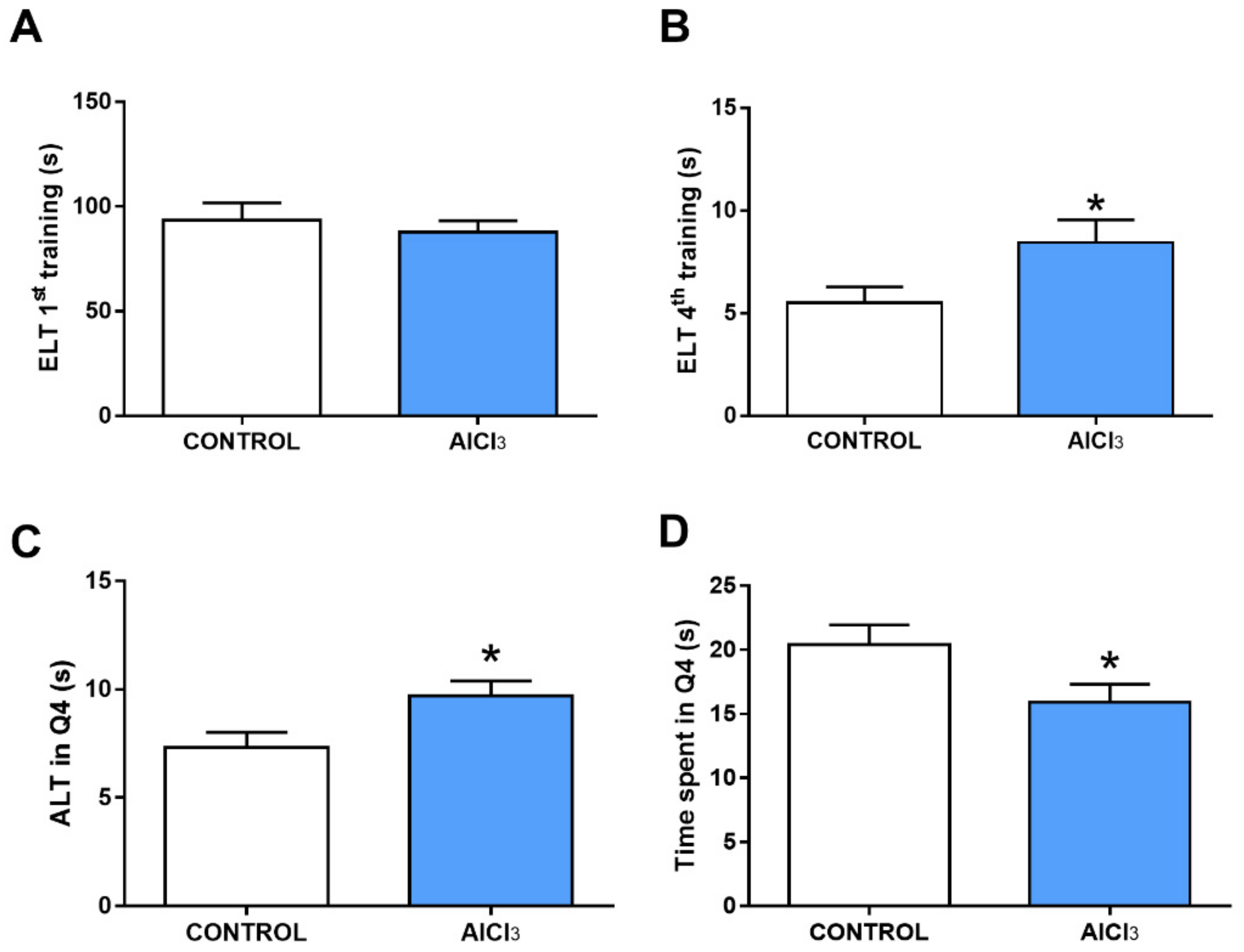
2.3. This Prolonged Exposure to Aluminum at Doses Equivalent to Urban Regions Was Associated with Cognitive Impairment in Rats
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethical Aspects and Experimental Design
4.2. Water Maze Test
4.3. Proteomic Analysis
4.4. Bioinformatic Analysis
4.5. Morphological Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Favero, G.; Jobstraibizer, P. The Distribution of Aluminium in the Earth: From Cosmogenesis to Sial Evolution. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1996, 149, 367–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabi, O.A.; Apata, S.A.; Adeoluwa, Y.M.; Sorungbe, A.A. Effect of the Duration of Use of Aluminum Cookware on Its Metal Leachability and Cytogenotoxicity in Allium Cepa Assay. Protoplasma 2020, 257, 1607–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ćirović, A.; Nikolić, D.; Ivanovski, A.; Ivanovski, P. The Adjuvant Aluminum Fate—Metabolic Tale Based on the Basics of Chemistry and Biochemistry. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2021, 68, 126822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, H.J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Li, D.; Ren, Y.; Kang, J.; Liu, D. Evaluation of Carboxymethylpullulan-AlCl 3 as a Coagulant for Water Treatment: A Case Study with Kaolin. Water Environ. Res. 2020, 92, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alasfar, R.H.; Isaifan, R.J. Aluminum Environmental Pollution: The Silent Killer. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 44587–44597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotz, K.; Weistenhöfer, W.; Neff, F.; Hartwig, A.; van Thriel, C.; Drexler, H. The Health Effects of Aluminum Exposure. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2017, 114, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, Y.K.; Meenu, M.; Peshin, S.S. Aluminium Utensils: Is It a Concern? Natl. Med. J. India 2019, 32, 38–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willhite, C.C.; Karyakina, N.A.; Yokel, R.A.; Yenugadhati, N.; Wisniewski, T.M.; Arnold, I.M.F.; Momoli, F.; Krewski, D. Systematic Review of Potential Health Risks Posed by Pharmaceutical, Occupational and Consumer Exposures to Metallic and Nanoscale Aluminum, Aluminum Oxides, Aluminum Hydroxide and Its Soluble Salts. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2014, 44 (Suppl. 4), 1–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, C.H.; Kwon, H.C.; Kim, D.H.; Cheng, W.N.; Kang, S.; Shin, D.M.; Yune, J.H.; Yoon, J.E.; Chang, Y.H.; Sohn, H.; et al. Effects of Aluminum on the Integrity of the Intestinal Epithelium: An in Vitro and in Vivo Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2020, 128, 017013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukiw, W.; Kruck, T.; Percy, M.; Pogue, A.; Alexandrov, P.; Walsh, W.; Sharfman, N.; Jaber, V.; Zhao, Y.; Li, W.; et al. Aluminum in Neurological Disease—A 36 Year Multicenter Study. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. Parkinsonism. 2019, 8, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittencourt, L.O.; Chemelo, V.S.; Bragança Aragão, W.A.; Puty, B.; Dionizio, A.; Teixeira, F.B.; Fernandes, M.S.; Freitas Silva, M.C.; Pereira Fernandes, L.M.; Corrêa De Oliveira, E.H.; et al. From Molecules to Behavior in Long-Term Inorganic Mercury Intoxication: Unraveling Proteomic Features in Cerebellar Neurodegeneration of Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huat, T.J.; Camats-Perna, J.; Newcombe, E.A.; Valmas, N.; Kitazawa, M.; Medeiros, R. Metal Toxicity Links to Alzheimer’s Disease and Neuroinflammation. J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 1843–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Exley, C.; Clarkson, E. Aluminium in Human Brain Tissue from Donors without Neurodegenerative Disease: A Comparison with Alzheimer’s Disease, Multiple Sclerosis and Autism. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mold, M.J.; O’Farrell, A.; Morris, B.; Exley, C. Aluminum and Neurofibrillary Tangle Co-Localization in Familial Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Neurological Disorders. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2020, 78, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza-Monteiro, D.; Guerra, M.C.D.S.; Bittencourt, L.O.; Aragão, W.A.B.; Dionizio, A.; Silveira, F.M.; Buzalaf, M.A.R.; Martins, M.D.; Crespo-Lopez, M.E.; Lima, R.R. Salivary Glands after Prolonged Aluminum Exposure: Proteomic Approach Underlying Biochemical and Morphological Impairments in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, R.M.; Corrêa, M.G.; Aragão, W.A.B.; Nascimento, P.C.; Cartágenes, S.C.; Rodrigues, C.A.; Sarmiento, L.F.; Monteiro, M.C.; do Maia, C.S.F.; Crespo-López, M.E.; et al. Preclinical Evidences of Aluminum-Induced Neurotoxicity in Hippocampus and Pre-Frontal Cortex of Rats Exposed to Low Doses. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 206, 111139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maya, S.; Prakash, T.; das Madhu, K.; Goli, D. Multifaceted Effects of Aluminium in Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 83, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehpara Farhat, S.; Mahboob, A.; Ahmed, T. Oral Exposure to Aluminum Leads to Reduced Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Gene Expression, Severe Neurodegeneration and Impaired Hippocampus Dependent Learning in Mice. Drug. Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 44, 1587452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.C.A.; Dionizio, A.; Teixeira, F.B.; Bittencourt, L.O.; Miranda, G.H.N.; Lopes, G.O.; Varela, E.L.P.; Nabiça, M.; Ribera, P.; Dantas, K.; et al. Hippocampal Impairment Triggered by Long-Term Lead Exposure from Adolescence to Adulthood in Rats: Insights from Molecular to Functional Levels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.; Hwang, J.J.; Poston, K.L. Episodic Recognition Memory and the Hippocampus in Parkinson’s Disease: A Review. Cortex 2019, 113, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Martinez, Y.; Sánchez-Huerta, K.B.; Pacheco-Rosado, J. Quantitative Characterization of Proliferative Cells Subpopulations in the Hilus of the Hippocampus of Adult Wistar Rats: An Integrative Study. J. Mol. Histol. 2020, 51, 437–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Xue, X.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, T.; Wang, Y.; Meng, H.; Pan, B.; Niu, Q. Aluminum-Induced Synaptic Plasticity Impairment via PI3K-Akt-MTOR Signaling Pathway. Neurotox. Res. 2020, 37, 996–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, N.; Zhang, P.; Wang, S.; Chen, J.; Fan, R.; Chen, J.; Huang, T.; Wang, Y.; Duncan, J.; Zhang, L.; et al. Aluminum-Induced Cognitive Impairment and PI3K/Akt/MTOR Signaling Pathway Involvement in Occupational Aluminum Workers. Neurotox Res. 2020, 38, 344–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, W.; Xu, F.; Cao, Z.; Jia, F.; Li, Y. Iron Dyshomeostasis Participated in Rat Hippocampus Toxicity Caused by Aluminum Chloride. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 197, 580–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tietz, T.; Lenzner, A.; Kolbaum, A.E.; Zellmer, S.; Riebeling, C.; Gürtler, R.; Jung, C.; Kappenstein, O.; Tentschert, J.; Giulbudagian, M.; et al. Aggregated Aluminium Exposure: Risk Assessment for the General Population. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 3503–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietary Exposure to Aluminium-Containing Food Additives; EFSA Supporting Publication; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013.
- Aluminium in Drinking-Water: Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/75362 (accessed on 22 August 2022).
- Reagan-Shaw, S.; Nihal, M.; Ahmad, N. Dose Translation from Animal to Human Studies Revisited. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 659–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, R.M.; Nascimento, P.C.; Martins, M.K.; Aragão, W.A.B.; Rivera, L.F.S.; Bittencourt, L.O.; Cartágenes, S.C.; Crespo-Lopez, M.E.; do Socorro Ferraz Maia, C.; Lima, R.R. Evaluation of Cerebellar Function and Integrity of Adult Rats After Long-Term Exposure to Aluminum at Equivalent Urban Region Consumption Concentrations. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 199, 1425–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaoka, M.H.; Maitani, T. Binding Affinity of Aluminium to Human Serum Transferrin and Effects of Carbohydrate Chain Modification as Studied by HPLC/High-Resolution ICP-MS--Speciation of Aluminium in Human Serum. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2005, 99, 1887–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokel, R.A.; McNamara, P.J. Aluminium Toxicokinetics: An Updated Minireview. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2001, 88, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, Y.; Hosoya, A.; Yahagi, K.; Ferecskó, A.S.; Yahagi, K.; Sík, A.; Itakura, M.; Takahashi, M.; Hirase, H. Hippocampal CA3 and CA2 have distinct bilateral innervation patterns to CA1 in rodents. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2012, 35, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliday, G. Pathology and Hippocampal Atrophy in Alzheimer’s Disease. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 862–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.; Costafreda, S.G.; McGuffin, P.; Fu, C.H.Y. Hippocampal Atrophy in First Episode Depression: A Meta-Analysis of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies. J. Affect. Disord. 2011, 134, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawahara, M.; Kato-Negishi, M.; Hosoda, R.; Imamura, L.; Tsuda, M.; Kuroda, Y. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Protects Cultured Rat Hippocampal Neurons from Aluminum Maltolate Neurotoxicity. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2003, 97, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryavanshi, J.; Prakash, C.; Sharma, D. Asiatic Acid Attenuates Aluminium Chloride-Induced Behavioral Changes, Neuronal Loss and Astrocyte Activation in Rats. Metab. Brain. Dis. 2022, 37, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.F.; Aguiar, M.S.S.; Carvalho, O.S.; Santana, L.D.N.S.; Franco, E.C.S.; Lima, R.R.; de Siqueira, N.V.M.; Augusto Feio, R.; Faro, L.R.F.; Gomes-Leal, W. Hippocampal Neuronal Loss, Decreased GFAP Immunoreactivity and Cognitive Impairment Following Experimental Intoxication of Rats with Aluminum Citrate. Brain. Res. 2013, 1491, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oteiza, P.I.; Keen, C.L.; Han, B.; Golub, M.S. Aluminum Accumulation and Neurotoxicity in Swiss-Webster Mice after Long-Term Dietary Exposure to Aluminum and Citrate. Metabolism 1993, 42, 1296–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatta, P.; Favarato, M.; Nicolini, M. Deposition of Aluminum in Brain Tissues of Rats Exposed to Inhalation of Aluminum Acetylacetonate. Neuroreport 1993, 4, 1119–1122. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Snow, P.J. The Structural and Functional Organization of Cognition. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drew, M.R.; Huckleberry, K.A. Modulation of Aversive Memory by Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis. Neurotherapeutics 2017, 14, 646–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomari, M.A.; Alzoubi, K.H.; Khabour, O.F. Swimming exercise improves short- and long-term memories: Time-course changes. Physiol. Rep. 2021, 9, e14851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Hooge, R.; de Deyn, P.P. Applications of the Morris Water Maze in the Study of Learning and Memory. Brain. Res. Rev. 2001, 36, 60–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lissner, L.J.; Wartchow, K.M.; Toniazzo, A.P.; Gonçalves, C.A.; Rodrigues, L. Object Recognition and Morris Water Maze to Detect Cognitive Impairment from Mild Hippocampal Damage in Rats: A Reflection Based on the Literature and Experience. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2021, 210, 173273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.H.; Zheng, G.; Wang, T.; Du, K.J.; Han, X.; Luo, W.J.; Shen, X.F.; Chen, J.Y. Low-Level Gestational Lead Exposure Alters Dendritic Spine Plasticity in the Hippocampus and Reduces Learning and Memory in Rats. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crown, L.M.; Gray, D.T.; Schimanski, L.A.; Barnes, C.A.; Cowen, S.L. Aged Rats Exhibit Altered Behavior-Induced Oscillatory Activity, Place Cell Firing Rates, and Spatial Information Content in the CA1 Region of the Hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 2022, 42, 4505–4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moser, M.B.; Rowland, D.C.; Moser, E.I. Place Cells, Grid Cells, and Memory. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a021808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booker, S.A.; Vida, I. Morphological Diversity and Connectivity of Hippocampal Interneurons. Cell. Tissue Res. 2018, 373, 619–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharfman, H.E.; Myers, C.E. Hilar Mossy Cells of the Dentate Gyrus: A Historical Perspective. Front. Neural Circuits 2012, 6, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miu, A.C.; Andreescu, C.E.; Vasiu, R.; Olteanu, A.I. A behavioral and histological study of the effects of long-term exposure of adult rats to aluminum. Int. J. Neurosci. 2003, 113, 1197–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q. Aluminum-Induced Neural Cell Death. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1091, 129–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.K.M.; Aragão, W.A.B.; Bittencourt, L.O.; Puty, B.; Dionizio, A.; de Souza, M.P.C.; Buzalaf, M.A.R.; de Oliveira, E.H.; Crespo-Lopez, M.E.; Lima, R.R. Fluoride Exposure during Pregnancy and Lactation Triggers Oxidative Stress and Molecular Changes in Hippocampus of Offspring Rats. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittencourt, L.O.; Dionizio, A.; Nascimento, P.C.; Puty, B.; Leão, L.K.R.; Luz, D.A.; Silva, M.C.F.; Amado, L.L.; Leite, A.; Buzalaf, M.R.; et al. Proteomic Approach Underlying the Hippocampal Neurodegeneration Caused by Low Doses of Methylmercury after Long-Term Exposure in Adult Rats. Metallomics 2019, 11, 390–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madeira, C.; Costa, P.M. Proteomics in Systems Toxicology. Adv. Protein. Chem. Struct. Biol. 2021, 127, 55–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ye, J.; Shi, Z.; Bu, C.; Bao, F. Quantitative analyses of the global proteome and phosphoproteome reveal the different impacts of propofol and dexmedetomidine on HT22 cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Wen, D.-X.; Hang, Y.-N. Study on proteomic profiling of hippocampus tissues of spontaneously hypertensive rats after propofol anesthesia. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. (Med. Sci.) 2014, 34, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Zhang, W.; Nie, L.; Wang, L.; Guo, Z.; Yu, X.; Fan, Z.; Cao, D. Effect of ketamine anesthesia on proteome in hippocampus of aged rats. Chin. J. Anesthesiol. 2019, 12, 1194–1198. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, S.; Yue, Y.; Wu, A. Profiling of the soluble proteome in rat hippocampus post propofol anesthesia. Neurochem. Res. 2013, 38, 2661–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Shweiki, M.R.; Oeckl, P.; Steinacker, P.; Barschke, P.; Pryce, C.; Dorner-Ciossek, C.; Schönfeldt-Lecuona, C.; Hengerer, B.; Otto, M. S-ketamine induces acute changes in the proteome of the mouse amygdala. J. Proteom. 2020, 216, 103679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, M.J.; Mulia, G.E.; van Rijn, R.M. Commonly Used Anesthesia/Euthanasia Methods for Brain Collection Differentially Impact MAPK Activity in Male and Female C57BL/6 Mice. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Xue, Q.; Ding, H.; Qin, Z.; Xiao, J.; Lin, C.; Liu, Y.; Tao, T. Proteomic profiling of the phosphoproteins in the rat thalamus, hippocampus and frontal lobe after propofol anesthesia. BMC Anesthesiol. 2014, 14, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Ding, J.; Li, L.; Bai, H.; Li, X.; Lan, L.; Fan, H.; Gao, L. Effects of Ketamine on Learning and Memory in the Hippocampus of Rats through ERK, CREB, and Arc. Brain. Sci. 2021, 11, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, S.; Panetta, J.C.; Roberts, J.K.; Schuetz, E.G. Ketamine pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics are altered by P-glycoprotein and breast cancer resistance protein Efflux transporters in mice. Drug. Metab. Dispos. 2018, 46, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Lin, D.; Wu, B.; Zhou, W. Ketamine abuse potential and use disorder. Brain. Res. Bull. 2016, 126, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widman, A.J.; McMahon, L.L. Effects of ketamine and other rapidly acting antidepressants on hippocampal excitatory and inhibitory transmission. Adv. Pharmacol. 2020, 89, 3–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leão, L.K.R.; Bittencourt, L.O.; Oliveira, A.C.A.; Nascimento, P.C.; Ferreira, M.K.M.; Miranda, G.H.N.; Ferreira, R.D.O.; Eiró-Quirino, L.; Puty, B.; Dionizio, A.; et al. Lead-Induced Motor Dysfunction Is Associated with Oxidative Stress, Proteome Modulation, and Neurodegeneration in Motor Cortex of Rats. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 5595047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leão, L.K.R.; Bittencourt, L.O.; Oliveira, A.C.; Nascimento, P.C.; Miranda, G.H.N.; Ferreira, R.O.; Nabiça, M.; Dantas, K.; Dionizio, A.; Cartágenes, S.; et al. Long-Term Lead Exposure Since Adolescence Causes Proteomic and Morphological Alterations in the Cerebellum Associated with Motor Deficits in Adult Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankowska, N.; Lisowska, K.; Witkowski, J.M. Proteolysis Dysfunction in the Process of Aging and Age-Related Diseases. Front. Aging 2022, 3, 927630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szyller, J.; Bil-Lula, I. Heat Shock Proteins in Oxidative Stress and Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury and Benefits from Physical Exercises: A Review to the Current Knowledge. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 6678457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackie, R.E.; Maciejewski, A.; Ostapchenko, V.G.; Marques-Lopes, J.; Choy, W.Y.; Duennwald, M.L.; Prado, V.F.; Prado, M.A.M. The Hsp70/Hsp90 Chaperone Machinery in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruipérez, F.; Mujika, J.I.; Ugalde, J.M.; Exley, C.; Lopez, X. Pro-Oxidant Activity of Aluminum: Promoting the Fenton Reaction by Reducing Fe(III) to Fe(II). J. Inorg. Biochem. 2012, 117, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Jiang, X.; Lin, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, D.; Zhou, L.; Liu, J.; Yang, X. Hippocampal Subcellular Organelle Proteomic Alteration of Copper-Treated Mice. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 164, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wang, D.; Zou, L.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, H.; Zhu, F.; Ren, X.; Xu, B.; Yuan, J.; Liu, J.; et al. Proteomic Alterations of Brain Subcellular Organelles Caused by Low-Dose Copper Exposure: Implication for Alzheimer’s Disease. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 1363–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, P.Y.; Niu, Q.; Zhang, Q.L.; Wang, L.P.; He, S.E.; Wu, T.C.; Conti, P.; di Gioacchino, M.; Boscolo, P. Aluminum Impairs Rat Neural Cell Mitochondria in Vitro. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2005, 18, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tönnies, E.; Trushina, E. Oxidative Stress, Synaptic Dysfunction, and Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 57, 1105–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.J.; Lin, C.H.; Lane, H.Y. Involvement of Cholinergic, Adrenergic, and Glutamatergic Network Modulation with Cognitive Dysfunction in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yin, G.; Zhang, W.; Song, K.; Zhang, L.; Guo, Z. Prostaglandin Reductase 1 as a Potential Therapeutic Target for Cancer Therapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crews, L.; Tsigelny, I.; Hashimoto, M.; Masliah, E. Role of Synucleins in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurotox. Res. 2009, 16, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twohig, D.; Nielsen, H.M. α-Synuclein in the Pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2019, 14, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skalny, A.; Aschner, M.; Jiang, Y.; Gluhcheva, Y.G.; Tizabi, Y.; Lobinski, R.; Tinkov, A.A. Molecular Mechanisms of Aluminum Neurotoxicity: Update on Adverse Effects and Therapeutic Strategies. Adv. Neurotoxicol. 2021, 5, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza-Monteiro, D.; de Oliveira Nunes, P.B.; de Oliveira Ferreira, R.; Eiró, L.G.; Bittencourt, L.O.; dos Santos Chemelo, V.; dos Santos, S.M.; de Souza-Rodrigues, R.D.; Monteiro, M.C.; Lima, R.R. Aluminum-Induced Toxicity in Salivary Glands of Mice After Long-Term Exposure: Insights into the Redox State and Morphological Analyses. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 198, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza-Monteiro, D.; Ferreira, R.O.; Eiró, L.G.; de Oliveira Lima, L.A.; Balbinot, G.S.; da Paz, S.P.A.; Albuquerque, A.R.L.; Collares, F.M.; Angélica, R.S.; Pessanha, S.; et al. Long-Term Exposure to Low Doses of Aluminum Affects Mineral Content and Microarchitecture of Rats Alveolar Bone. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 45879–45890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, C.S.; Alterman, C.D.C.; Peçanha, F.M.; Vassallo, D.; Mello-Carpes, P.B.; Miguel, M.; Wiggers, G.A. Aluminum Exposure at Human Dietary Levels for 60 Days Reaches a Threshold Sufficient to Promote Memory Impairment in Rats. Neurotox. Res. 2017, 31, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.L.; Luz, D.A.; da Paixão, T.P.; Silva, J.P.B.; Belém-Filho, I.J.A.; Fernandes, L.M.P.; Gonçalves, A.C.B.; Fontes-Júnior, E.A.; de Andrade, M.A.; Maia, C.S.F. Petiveria Alliacea Exerts Mnemonic and Learning Effects on Rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 169, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, R. Developments of a Water-Maze Procedure for Studying Spatial Learning in the Rat. J. Neurosci. Methods 1984, 11, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dionizio, A.; Melo, C.G.S.; Sabino-Arias, I.T.; Araujo, T.T.; Ventura, T.M.O.; Leite, A.L.; Souza, S.R.G.; Santos, E.X.; Heubel, A.D.; Souza, J.G.; et al. Effects of Acute Fluoride Exposure on the Jejunum and Ileum of Rats: Insights from Proteomic and Enteric Innervation Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A Software Environment for Integrated Models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiró, L.G.; Ferreira, M.K.M.; Bittencourt, L.O.; Aragão, W.A.B.; de Souza, M.P.C.; Silva, M.C.F.; Dionizio, A.; Buzalaf, M.A.R.; Crespo-López, M.E.; Lima, R.R. Chronic Methylmercury Exposure Causes Spinal Cord Impairment: Proteomic Modulation and Oxidative Stress. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 146, 111772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, M.A.M.; Faber, J.; Picanço-Diniz, C.W.; Franca, J.G.; Pereira, A. Morphometric variability of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate diaphorase neurons in the primary sensory areas of the rat. Neuroscience 2012, 205, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.C.A.; Pereira, M.C.S.; Santana, L.N.D.S.; Fernandes, R.M.; Teixeira, F.B.; Oliveira, G.B.; Fernandes, L.M.P.; Fontes-Júnior, E.A.; Prediger, R.D.; Crespo-López, M.E.; et al. Chronic Ethanol Exposure during Adolescence through Early Adulthood in Female Rats Induces Emotional and Memory Deficits Associated with Morphological and Molecular Alterations in Hippocampus. J. Psychopharmacol. 2015, 29, 712–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, F.; Zou, X.; Torbey, M. Comparison of Unbiased Estimation of Neuronal Number in the Rat Hippocampus with Different Staining Methods. J. Neurosci. Methods 2015, 254, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A., Jr.; Freire, M.A.M.; Franca, J.G.; Picanco-Diniz, C.W. The barrel field of the adult mouse SmI cortex as revealed by NADPH-diaphorase histochemistry. Neuroreport 2000, 11, 1889–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza-Rodrigues, R.D.; Costa, A.M.; Lima, R.R.; Dos Santos, C.D.; Picanço-Diniz, C.W.; Gomes-Leal, W. Inflammatory response and white matter damage after microinjections of endothelin-1 into the rat striatum. Brain Res. 2008, 1200, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bittencourt, L.O.; Damasceno-Silva, R.D.; Aragão, W.A.B.; Eiró-Quirino, L.; Oliveira, A.C.A.; Fernandes, R.M.; Freire, M.A.M.; Cartágenes, S.C.; Dionizio, A.; Buzalaf, M.A.R.; et al. Global Proteomic Profile of Aluminum-Induced Hippocampal Impairments in Rats: Are Low Doses of Aluminum Really Safe? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232012523
Bittencourt LO, Damasceno-Silva RD, Aragão WAB, Eiró-Quirino L, Oliveira ACA, Fernandes RM, Freire MAM, Cartágenes SC, Dionizio A, Buzalaf MAR, et al. Global Proteomic Profile of Aluminum-Induced Hippocampal Impairments in Rats: Are Low Doses of Aluminum Really Safe? International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(20):12523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232012523
Chicago/Turabian StyleBittencourt, Leonardo Oliveira, Rakhel Dayanne Damasceno-Silva, Walessa Alana Bragança Aragão, Luciana Eiró-Quirino, Ana Carolina Alves Oliveira, Rafael Monteiro Fernandes, Marco Aurelio M. Freire, Sabrina Carvalho Cartágenes, Aline Dionizio, Marília Afonso Rabelo Buzalaf, and et al. 2022. "Global Proteomic Profile of Aluminum-Induced Hippocampal Impairments in Rats: Are Low Doses of Aluminum Really Safe?" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 20: 12523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232012523
APA StyleBittencourt, L. O., Damasceno-Silva, R. D., Aragão, W. A. B., Eiró-Quirino, L., Oliveira, A. C. A., Fernandes, R. M., Freire, M. A. M., Cartágenes, S. C., Dionizio, A., Buzalaf, M. A. R., Cassoli, J. S., Cirovic, A., Cirovic, A., Maia, C. d. S. F., & Lima, R. R. (2022). Global Proteomic Profile of Aluminum-Induced Hippocampal Impairments in Rats: Are Low Doses of Aluminum Really Safe? International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(20), 12523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232012523









