Zn-Catalyzed Regioselective and Chemoselective Reduction of Aldehydes, Ketones and Imines
Abstract
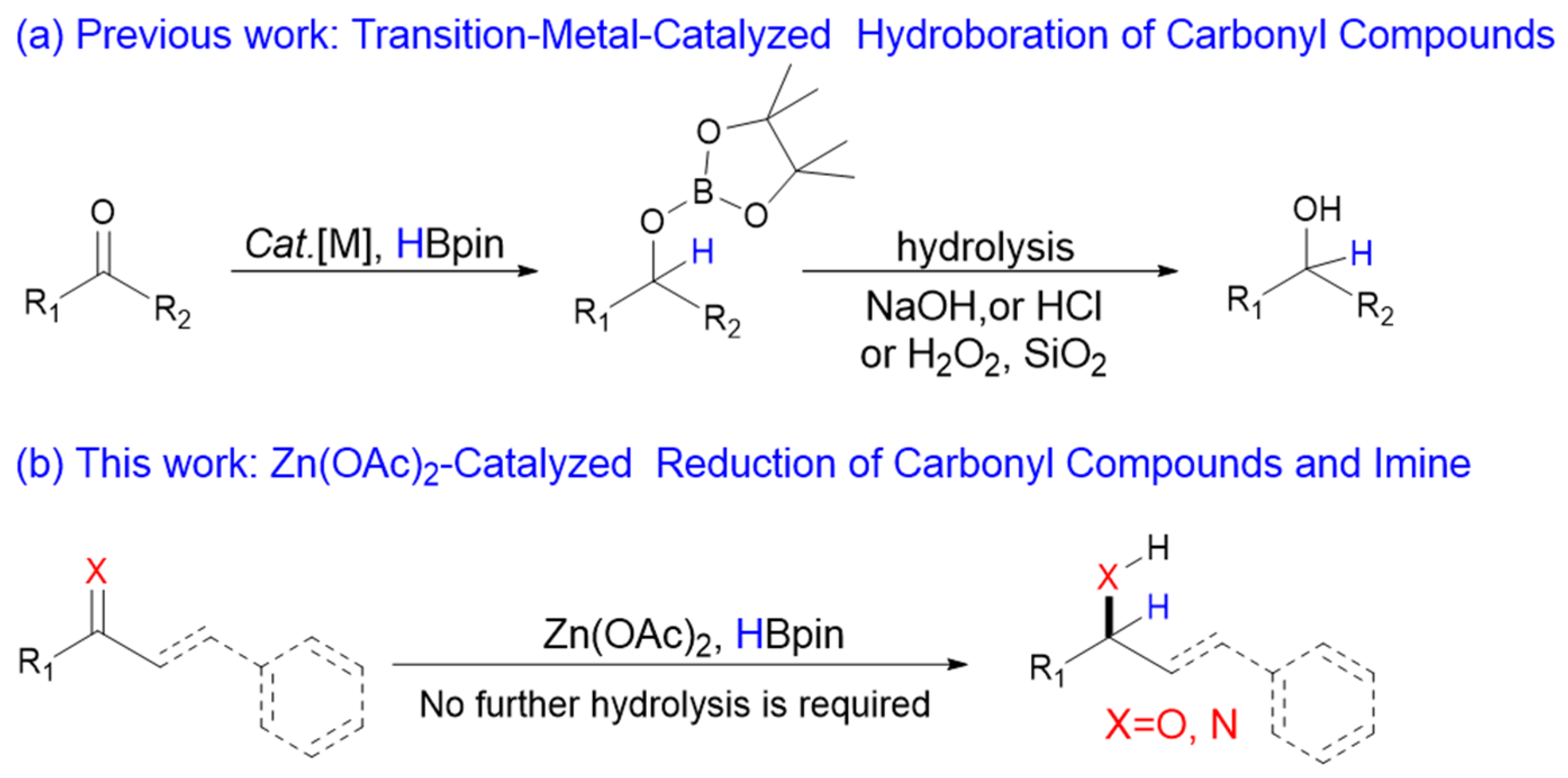
:1. Introduction
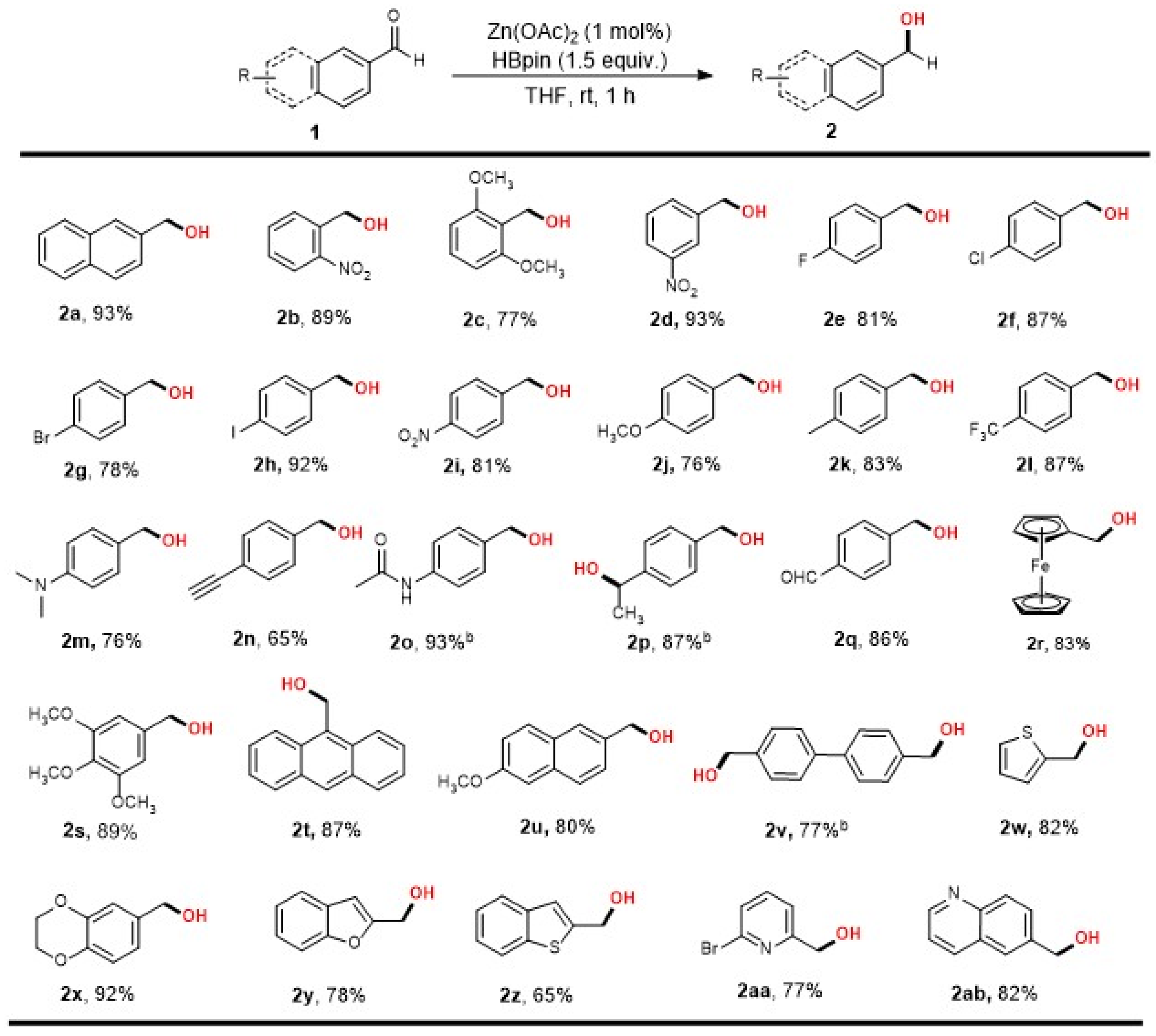
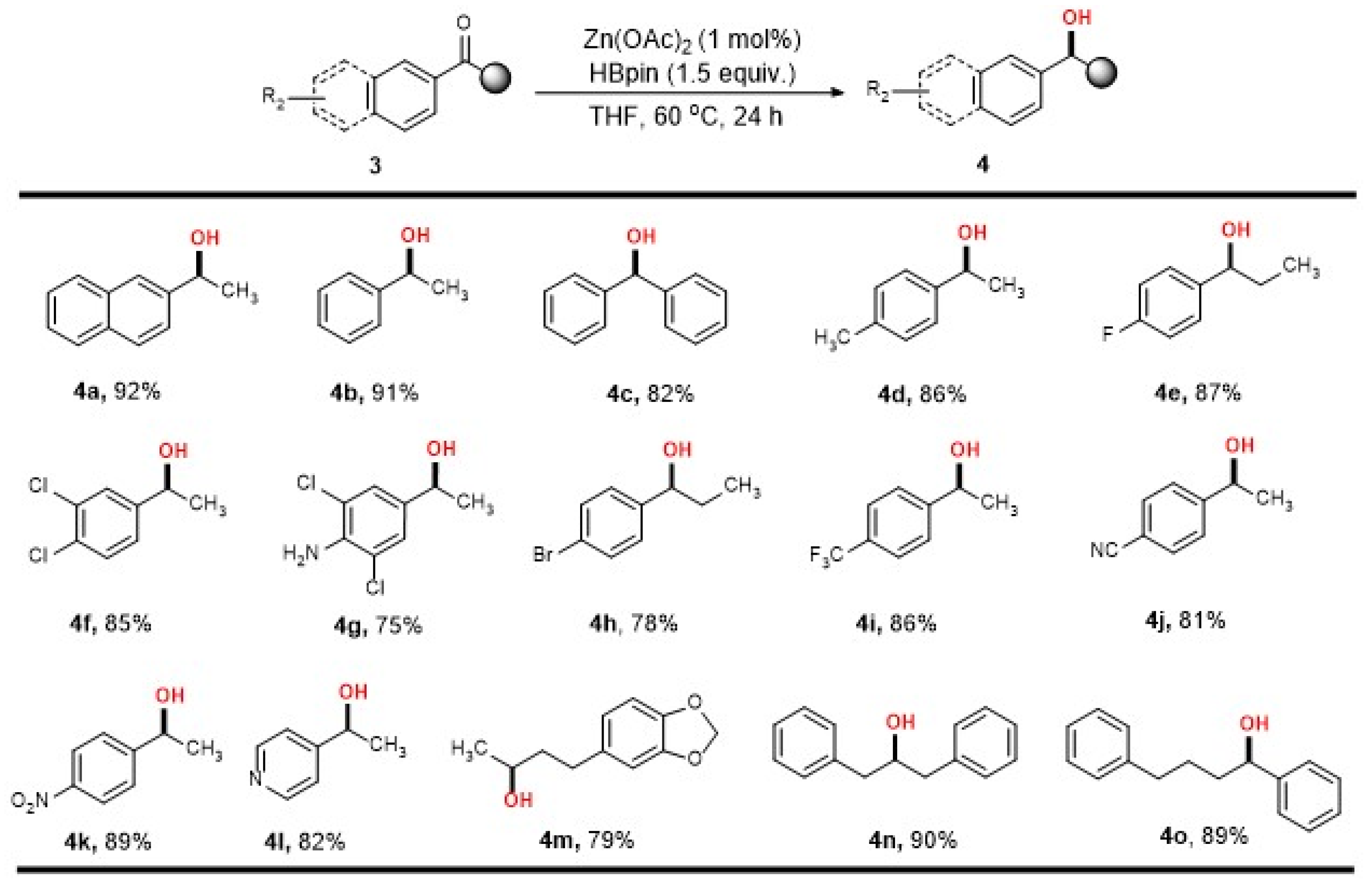
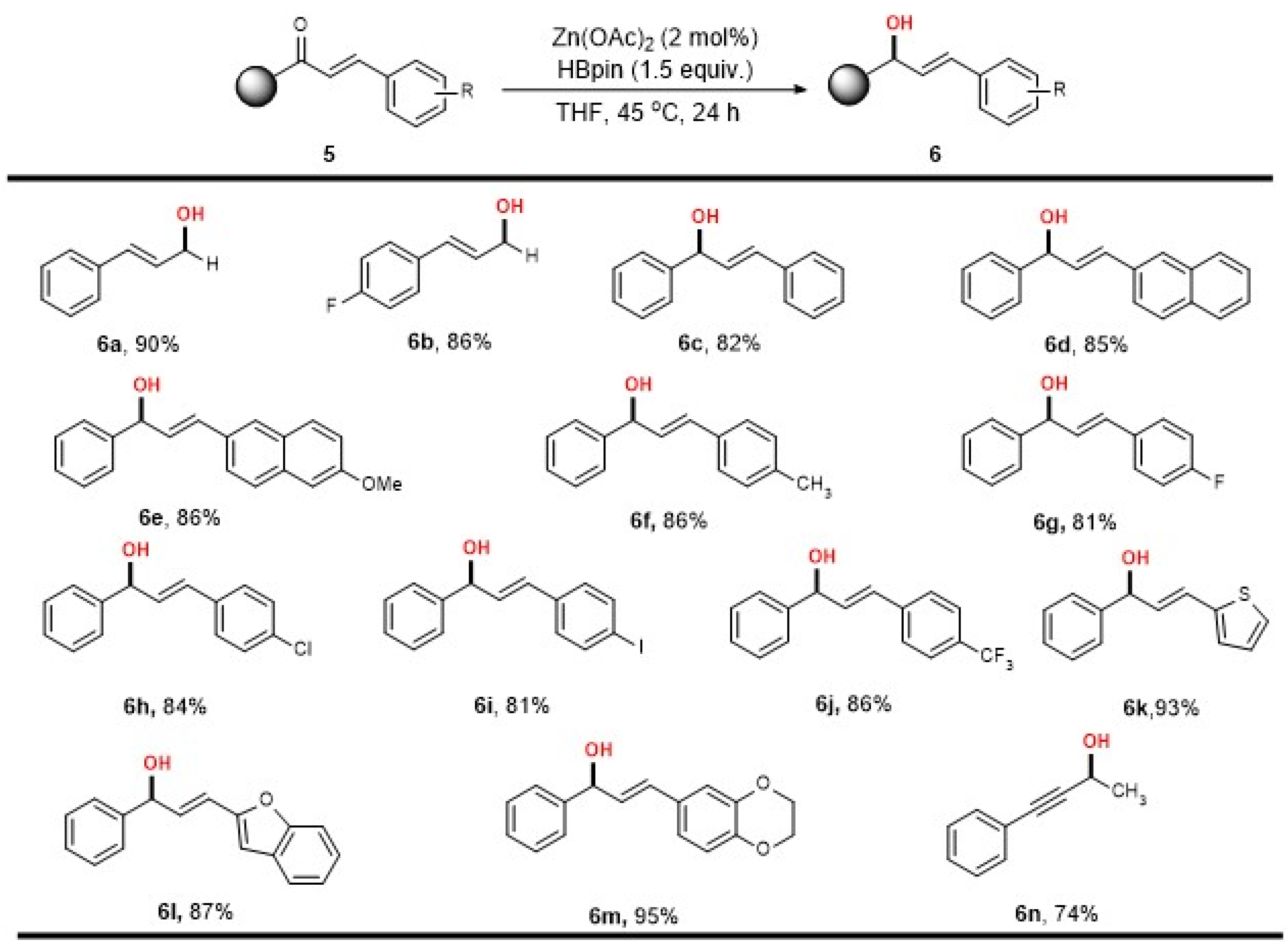
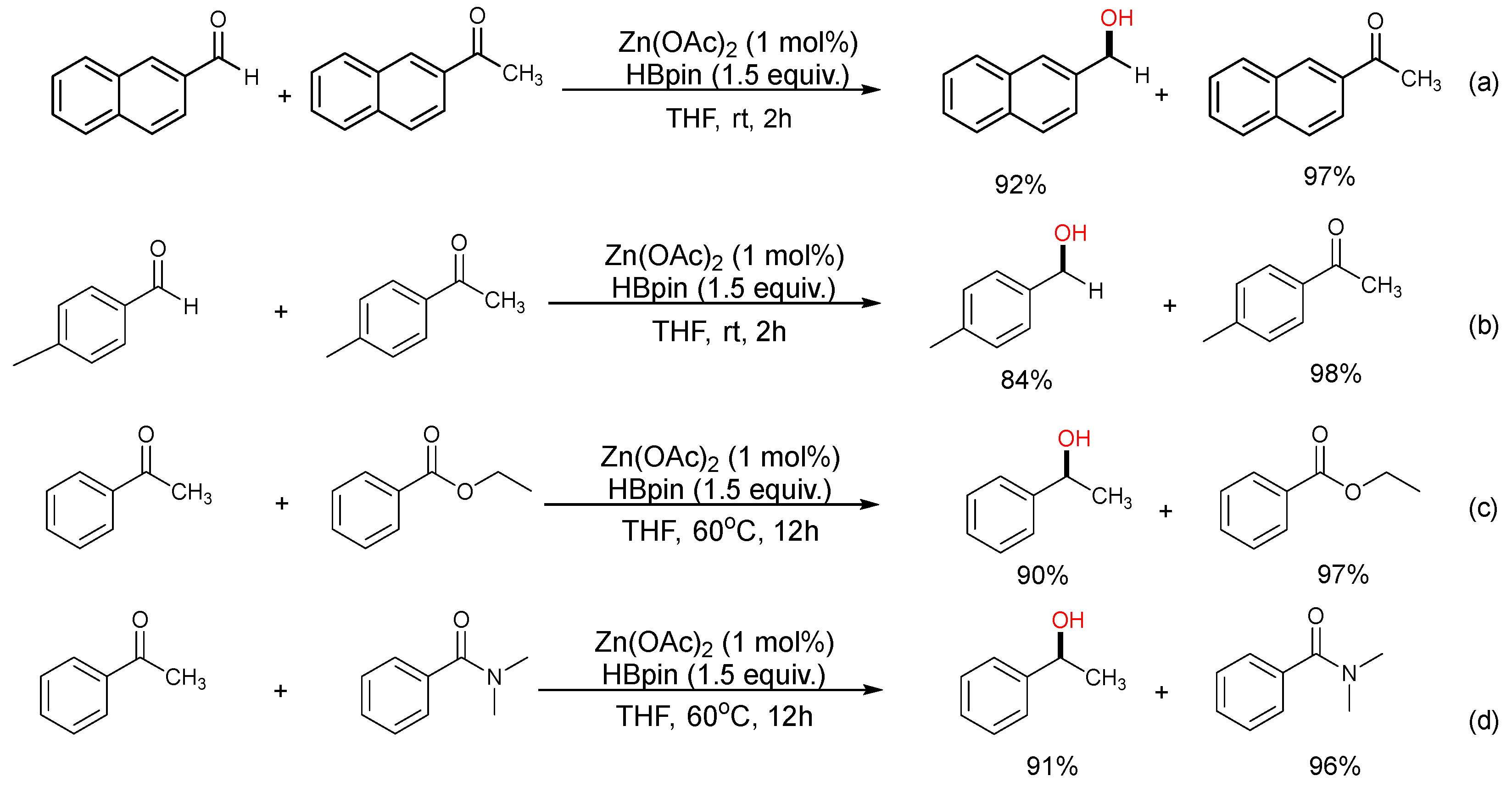
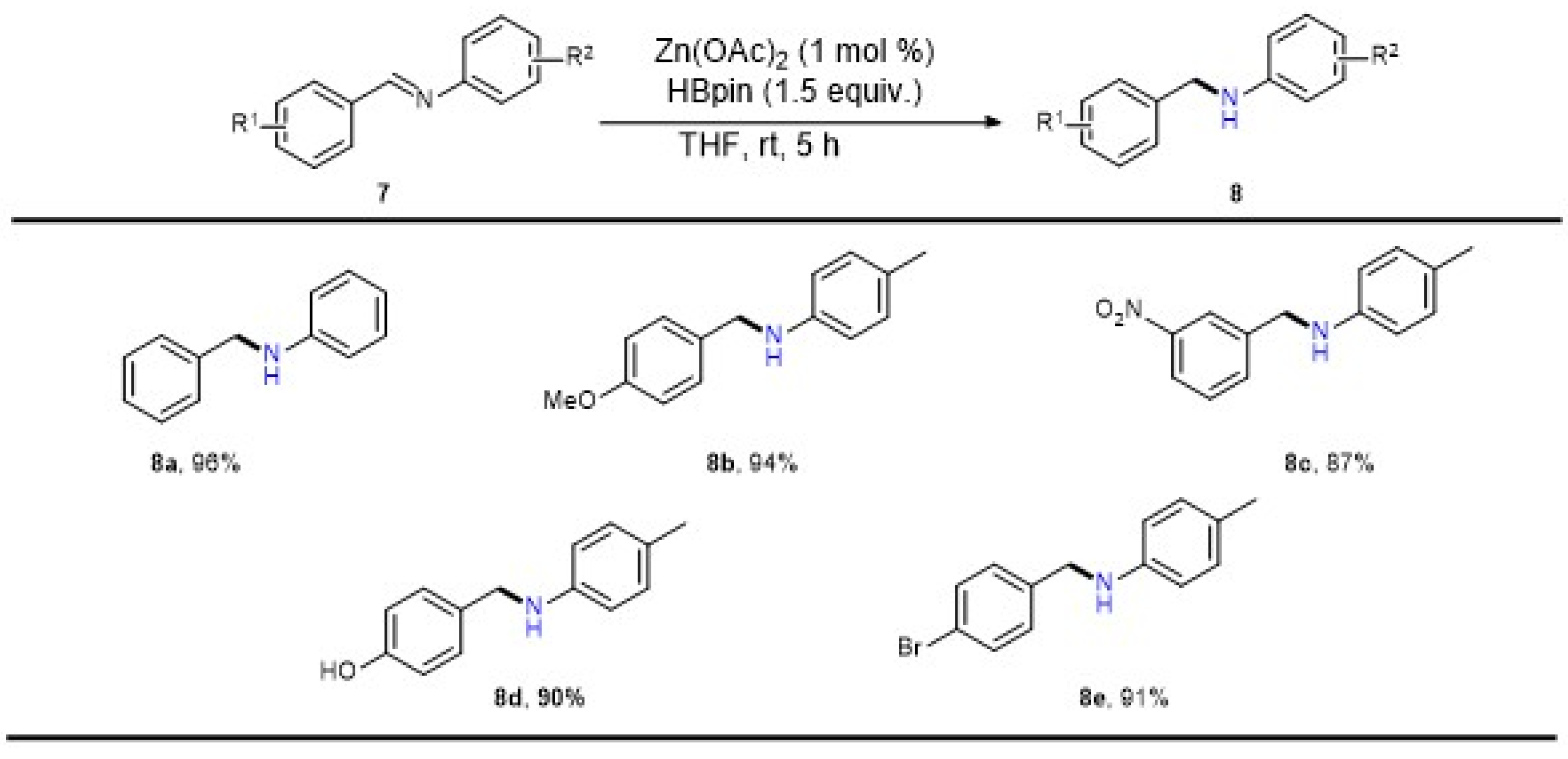
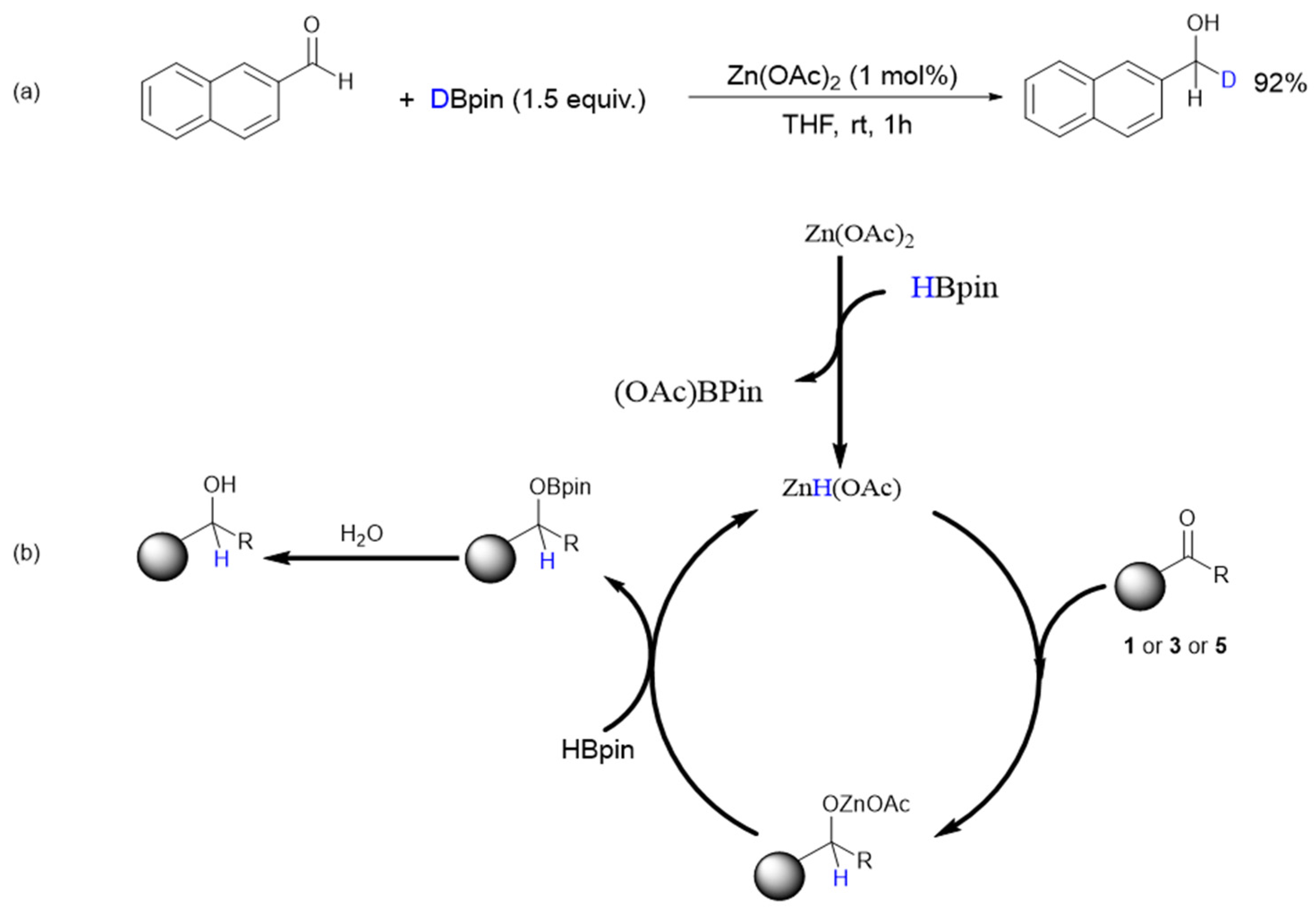
2. Results
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
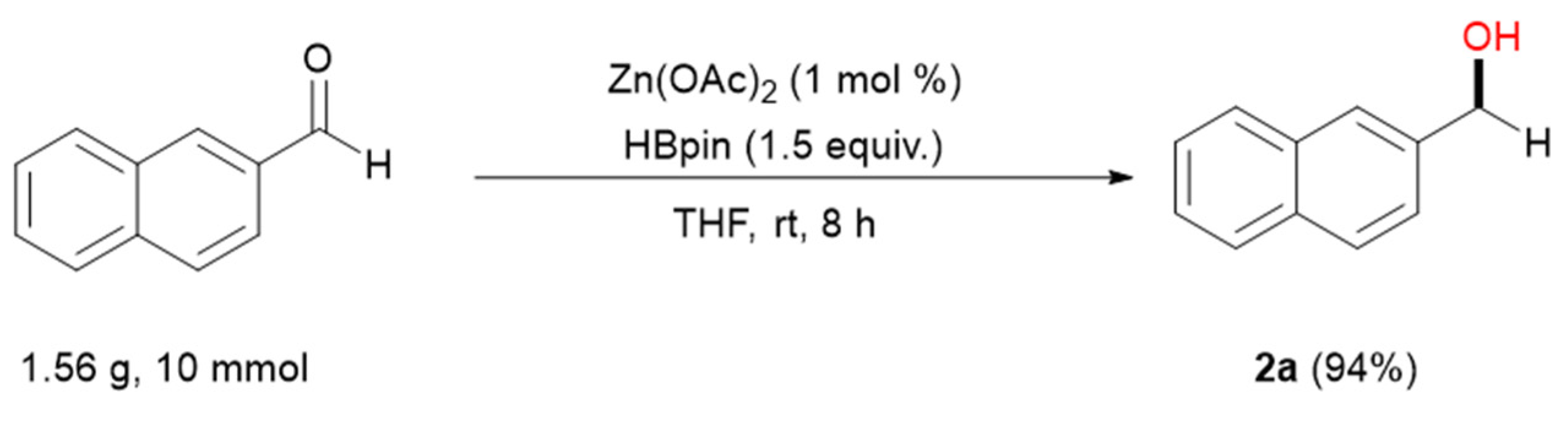
3.2. General Procedure for Zn-Catalyzed Reduction of Aldehydes
3.3. General Procedure for Zn-Catalyzed Reduction of Ketones
3.4. General Procedure for Zn-Catalyzed Reduction of Imines
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xie, J.-H.; Zhu, S.-F.; Zhou, Q.-L. Transition Metal-Catalyzed Enantioselective Hydrogenation of Enamines and Imines. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 1713–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.S.; Chen, Q.A.; Lu, S.M.; Zhou, Y.G. Asymmetric Hydrogenation of Heteroarenes and Arenes. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 2557–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.M.; Feng, Y.; Fan, Q.H. Asymmetric Hydrogenation in the Core of Dendrimers. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 2894–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.; Ma, P.; Cong, X.; Chen, H.; Zeng, X. Chromium- and Cobalt-Catalyzed, Regiocontrolled Hydrogenation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: A Combined Experimental and Theoretical Study. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 9018–9026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikariya, T.; Murata, K.; Noyori, R. Bifunctional transition metal-based molecular catalysts for asymmetric syntheses. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2006, 4, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gladiali, S.; Alberico, E. Asymmetric transfer hydrogenation: Chiral ligands and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2006, 35, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Roy, S.; Das, P.K. Efficient and Simple NaBH4 Reduction of Esters at Cationic Micellar Surface. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 4133–4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forkel, N.V.; Henderson, D.A.; Fuchter, M.J. Lanthanide replacement in organic synthesis: Luche-type reduction of α,β-unsaturated ketones in the presence of calcium triflate. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 2129–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.M.; He, L.; Liu, Y.M.; Cao, Y.; He, H.Y.; Fan, K.N. Gold supported on mesostructured ceria as an efficient catalyst for the chemoselective hydrogenation of carbonyl compounds in neat water. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merel, D.S.; Elie, M.; Lohier, J.-F.; Gaillard, S.; Renaud, J.-L. Bifunctional Iron Complexes: Efficient Catalysts for C=O and C=N Reduction in Water. ChemCatChem 2013, 5, 2939–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spasyuk, D.; Vicent, C.; Gusev, D.G. Chemoselective Hydrogenation of Carbonyl Compounds and Acceptorless Dehydrogenative Coupling of Alcohols. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 3743–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dub, P.A.; Scott, B.L.; Gordon, J.C. Why Does Alkylation of the N–H Functionality within M/NH Bifunctional Noyori-Type Catalysts Lead to Turnover? J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 1245–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, C.C.; Kinjo, R. Catalytic Hydroboration of Carbonyl Derivatives, Imines, and Carbon Dioxide. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 3238–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shegavi, M.L.; Bose, S.K. Recent advances in the catalytic hydroboration of carbonyl compounds. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 3307–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erik, A.R.; Jesse, L.P.; Rodolphe, J.; Bertrand, G. Catalyst Free Dehydrocoupling of Amines, Alcohols, and Thiols with Pinacol Borane and 9-Borabicyclononane (9-BBN). Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 10563–10565. [Google Scholar]
- Kucinski, K.; Hreczycho, G. Chemoselective and Catalyst-Free O-Borylation of Silanols: A Facile Access to Borasiloxanes. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 4695–4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazmierczak, J.; Kucinski, K.; Stachowiak, H.; Hreczycho, G. Introduction of Boron Functionalities into Silsesquioxanes: Novel Independent Methodologies. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 2509–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.H.; Jaladi, A.K.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, T.S.; Shin, W.K.; Hwang, H.; An, D.K. Catalytic Hydroboration of Aldehydes, Ketones, and Alkenes Using Potassium Carbonate: A Small Key to Big Transformation. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 15893–15903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Luo, M.; Zhu, D.; Yao, W.; Xu, L.; Ma, M. Green hydroboration of carboxylic acids and mechanism investigation. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2019, 17, 3604–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harinath, A.; Bhattacharjee, J.; Panda, T.K. Facile reduction of carboxylic acids to primary alcohols under catalyst-free and solvent-free conditions. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 1386–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Yan, D.; Zhu, Z.; Kang, Z.; Yao, Y.; Shen, Q.; Xue, M. Catalyst-Free Approach for Hydroboration of Carboxylic Acids under Mild Conditions. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 6775–6783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.J.; Davis Cheng, K.; Bonifacio, M.G.; Zajaczkowski, C. Practical and selective hydroboration of aldehydes and ketones in air catalysed by an iron(II) coordination polymer. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucin Ski, K.; Hreczycho, G. Lithium triethylborohydride as catalyst for solvent-free hydroboration of aldehydes and ketones. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 1912–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidner, V.L.; Barger, C.J.; Delferro, M.; Lohr, T.L.; Marks, T.J. Rapid, mild, and selective ketone and aldehyde hydroboration/reduction mediated by a simple lanthanide catalyst. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 1244–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamang, S.R.; Findlater, M. Iron catalyzed hydroboration of aldehydes and ketones. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 12857–12862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Zeng, H.; Wu, J.; Yin, Z.; Zheng, S.; Fettinger, J.C. Highly selective hydroboration of alkenes, ketones and aldehydes catalyzed by a well-defined manganese complex. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 14369–14372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, T.; Janes, T.; Song, D. Homoleptic iron(ii) and cobalt(ii) bis(phosphoranimide) complexes for the selective hydrofunctionalization of unsaturated molecules. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 12408–12412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaithal, A.; Chatterjee, B.; Gunanathan, C. Ruthenium Catalyzed Selective Hydroboration of Carbonyl Compounds. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 4790–4793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuciński, K.; Hreczycho, G. Potassium Fluoride-Catalyzed Hydroboration of Aldehydes and Ketones: Facile Reduction to Primary and Secondary Alcohols. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 5, 552–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, R.K.; Mahato, M.; Jana, A.; Nembenna, S. Zinc Hydride-Catalyzed Hydrofuntionalization of Ketones. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 85, 11200–11210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamang, S.R.; Bedi, D.; Shafifiei-Haghighi, S.; Smith, C.R.; Crawford, C.; Findlater, M. Cobalt-Catalyzed Hydroboration of Alkenes, Aldehydes, and Ketones. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 6695–6700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.H.; Zeng, J.; Cheng, S.; Zheng, J.A.; Golen, D.; Manke, R.; Zhang, G. Cobalt(II) Coordination Polymer as a Precatalyst for Selective Hydroboration of Aldehydes, Ketones, and Imines. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 9442–9448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.; Wu, J.; Li, S.; Hui, C.; Ta, A.; Cheng, S.-Y.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, G. Copper(II)-Catalyzed Selective Hydroboration of Ketones and Aldehydes. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Zheng, T.; Zhou, J.; Dong, Y.; Zuo, X.; Li, X.; Sun, H.; Fuhr, O.; Fenske, D. Synthesis and Catalytic Activity of Iron Hydride Ligated with Bidentate N-Heterocyclic Silylenes for Hydroboration of Carbonyl Compounds. Organometallics 2019, 38, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijjamarri, S.; O’Denius, T.M.; Yao, B.; Kubátová, A.; Du, G. Highly Selective Hydroboration of Carbonyls by a Manganese Catalyst: Insight into the Reaction Mechanism. Organometallics 2020, 39, 3375–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasius, C.K.; Vasilenkom, V.; Gade, L.H. Ultrafast Iron-Catalyzed Reduction of Functionalized Ketones: Highly Enantioselective Synthesis of Halohydrines, Oxaheterocycles, and Aminoalcohols. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 10231–10235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, Y.K.; Magre, M.; Rueping, M. Chemoselective Luche-Type Reduction of α,β-Unsaturated Ketones by Magnesium Catalysis. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 8349–8352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirik, P.J. Iron- and Cobalt-Catalyzed Alkene Hydrogenation: Catalysis with Both Redox-Active and Strong Field Ligands. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 1687–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryken, S.A.; Schafer, L.L. N,O-Chelating Four-Membered Metallacyclic Titanium(IV) Complexes for Atom-Economic Catalytic Reactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 2576–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.B.; Wu, F.P.; Wu, X.F. First-Row Transition-Metal-Catalyzed Carbonylative Transformations of Carbon Electrophiles. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 2090–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, R.; Cabrero-Antonino, J.R.; Spannenberg, A.; Junge, K.; Jackstell, R.; Beller, M. A General and Highly Selective Cobalt-Catalyzed Hydrogenation of N-Heteroarenes under Mild Reaction Conditions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 3216–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Hu, C.; Cong, X.; Geng, G.; Liu, L.L.; Luo, M.; Zeng, X. Cyclic (Alkyl)(amino)carbene Ligand-Promoted Nitro Deoxygenative Hydroboration with Chromium Catalysis: Scope, Mechanism, and Applications. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 1618–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Zhang, M.; Jiao, H.; Ma, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. Ligand-enabled and magnesium-activated hydrogenation with earth-abundant cobalt catalysts. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 39934–39939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkin, G. Synthetic Analogues Relevant to the Structure and Function of Zinc Enzymes. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 699–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psomas, G.; Kessissoglou, D.P. Quinolones and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs interacting with copper(ii), nickel(ii), cobalt(ii) and zinc(ii): Structural features, biological evaluation and perspectives. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 6252–6276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, T.J.; Bin Break, M.K.; Crouse, K.A.; Tahir, M.I.M.; Ali, A.M.; Cowley, A.R.; Watkin, D.J.; Tarafder, M.T.H. Synthesis, characterization and biological activity of two Schiff base ligands and their nickel(II), copper(II), zinc(II) and cadmium(II) complexes derived from S-4-picolyldithiocarbazate and X-ray crystal structure of cadmium(II) complex derived from pyridine-2-carboxaldehyde. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2014, 413, 68–76. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.-F.; Neumann, H. Zinc-Catalyzed Organic Synthesis: C-C, C-N, C-O Bond Formation Reactions. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2012, 354, 3141–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatano, M.H.; Suzuki, S.; Lshihara, K. Highly Efficient Alkylation to Ketones and Aldimines with Grignard Reagents Catalyzed by Zinc(II) Chloride. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 9998–9999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, T.; Jana, S.; Dash, J. Zinc-Mediated Efficient and Selective Reduction of Carbonyl Compounds. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 33, 4972–4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Rawal, P.; Banerjee, I.; Nayek, H.P.; Gupta, P.; Panda, T.K. Zinc-Mediated Efficient and Selective Reduction of Carbonyl Compounds. Chem. Asian. J. 2022, 17, 4972–4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.S.; Harinath, A.; Narvariya, R.; Panda, T.K. Homoleptic Zinc-Catalyzed Hydroboration of Aldehydes and Ketones in the Presence of HBpin. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 5, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezłada, A.; Szewczyk, M.; Mlynarski, J. Enantioselective Hydrosilylation of Imines Catalyzed by Chiral Zinc Acetate Complexes. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolla, E.L.; Tonguea, T.; Andrewsa, K.G.; Valetteb, D.; Hirstb, D.J.; Denton, R.M. A practical catalytic reductive amination of carboxylic acids. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 9494–9500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Procter, R.J.; Uzelac, M.; Cid, J.; Rushworth, P.J.; Ingleson, M.J. Low-Coordinate NHC–Zinc Hydride Complexes Catalyze Alkyne C–H Borylation and Hydroboration Using Pinacolborane. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 5760–5771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Metal Salt | Reductant | Solvent | Time/h | Yield of 2a/% |
| 1 b | Zn(OTf)2 | HBpin | THF | 24 | 44 |
| 2 b | ZnCl2 | HBpin | THF | 24 | 80 |
| 3 b | Zn(OAc)2 | HBpin | THF | 24 | 94 |
| 4 b | Zn(OAc)2 | PhSiH3 | THF | 24 | nd c |
| 5 | Zn(OAc)2 | HBpin | THF | 1 | 94 |
| 6 | Zn(OAc)2 | HBpin | THF | 1 | 93(88) d |
| 7 | Zn(OAc)2 | HBpin | EtOH | 1 | 16 |
| 8 | Zn(OAc)2 | HBpin | Toluene | 1 | 41 |
| 9 | Zn(OAc)2 | HBpin | DCM | 1 | 48 |
| 10 | Zn(OAc)2 | HBpin | CH3CN | 1 | trace |
| 11 | FeCl2 | HBpin | THF | 1 | 58 |
| 12 | CoBr2 | HBpin | THF | 1 | 71 |
| 13 | NiBr2 | HBpin | THF | 1 | 41 |
| 14 | MnBr(CO)5 | HBpin | THF | 1 | 80 |
| 15 | CrCl2 | HBpin | THF | 1 | nd c |
| 16 | CuCl2 | HBpin | THF | 1 | nd c |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, M.; Jiao, H.; Ma, H.; Li, R.; Han, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. Zn-Catalyzed Regioselective and Chemoselective Reduction of Aldehydes, Ketones and Imines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232012679
Zhang M, Jiao H, Ma H, Li R, Han B, Zhang Y, Wang J. Zn-Catalyzed Regioselective and Chemoselective Reduction of Aldehydes, Ketones and Imines. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(20):12679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232012679
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Miaomiao, Hongmei Jiao, Haojie Ma, Ran Li, Bo Han, Yuqi Zhang, and Jijiang Wang. 2022. "Zn-Catalyzed Regioselective and Chemoselective Reduction of Aldehydes, Ketones and Imines" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 20: 12679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232012679
APA StyleZhang, M., Jiao, H., Ma, H., Li, R., Han, B., Zhang, Y., & Wang, J. (2022). Zn-Catalyzed Regioselective and Chemoselective Reduction of Aldehydes, Ketones and Imines. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(20), 12679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232012679






