Adiponectin Suppresses Metastasis of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma through Blocking the Activation of NF-κB and STAT3 Signaling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Association of Serum Adiponectin Level with Clinicopathological Characteristics
2.2. Adiponectin Inhibits Migration and Invasion of NPC Cell
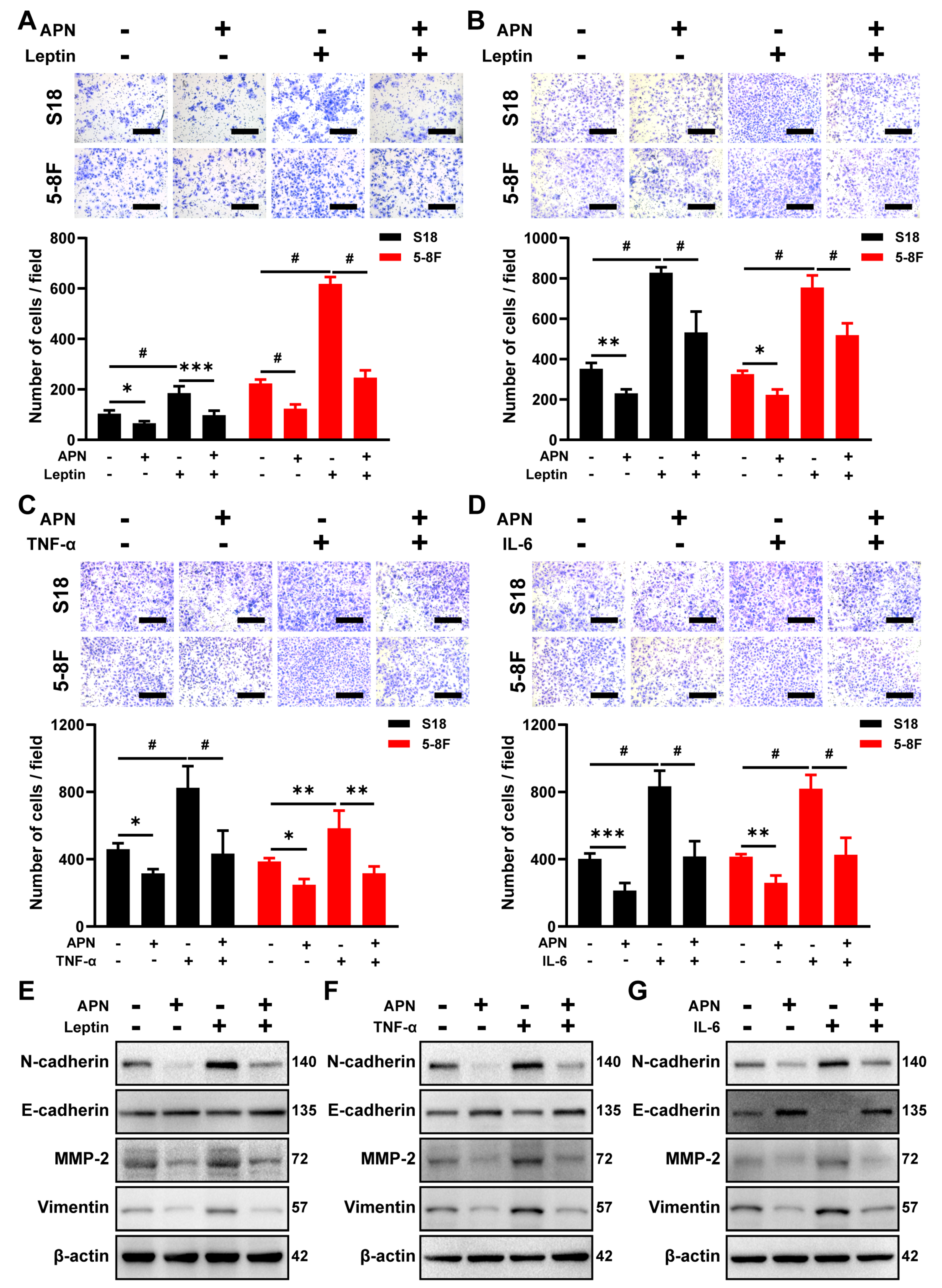
2.3. Adiponectin Blocks the Migration and Invasion Induced by IL-6, TNF-α, and Leptin Treatment
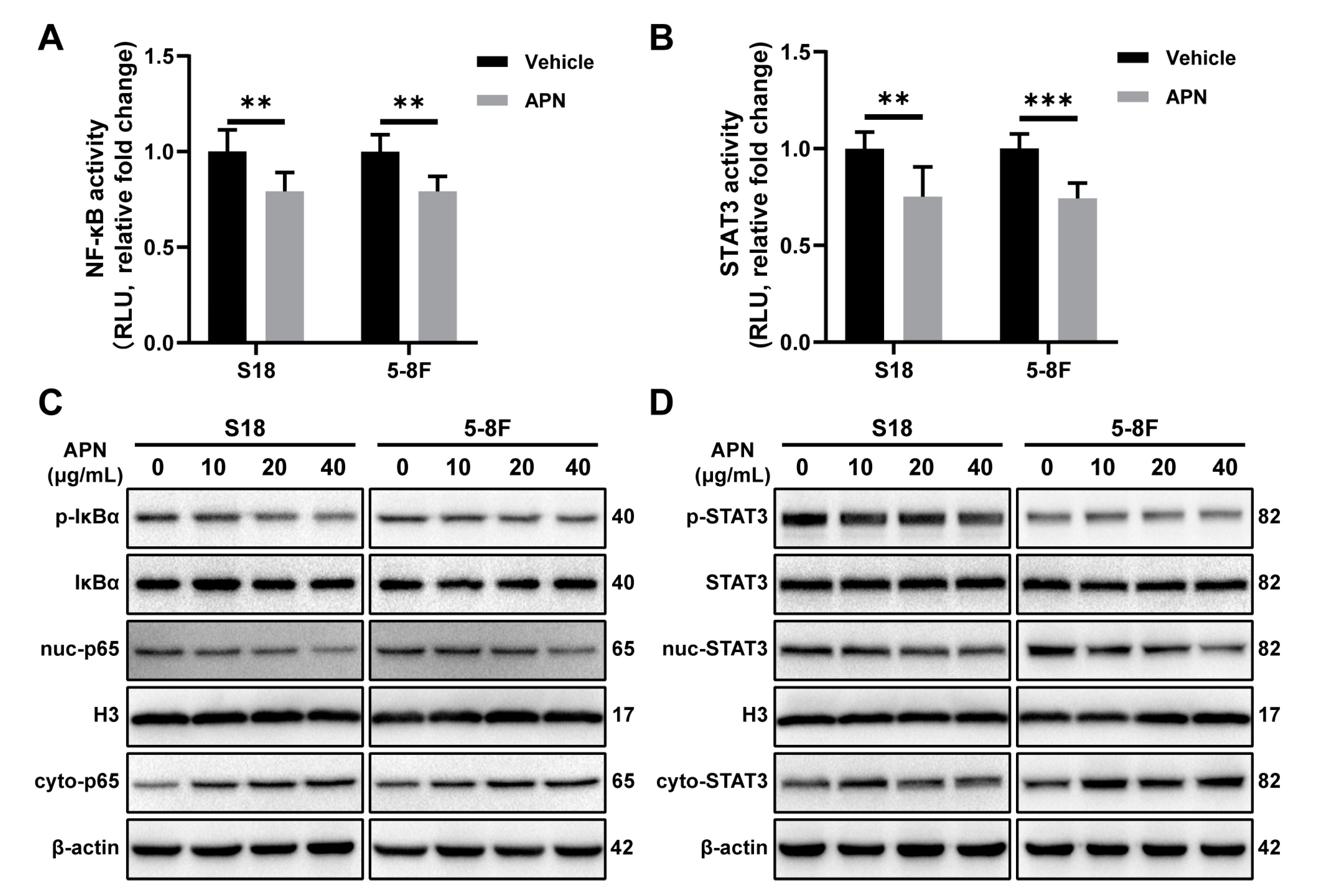
2.4. Adiponectin Inhibits the Activation of NF-κB and STAT3 Signaling Pathways
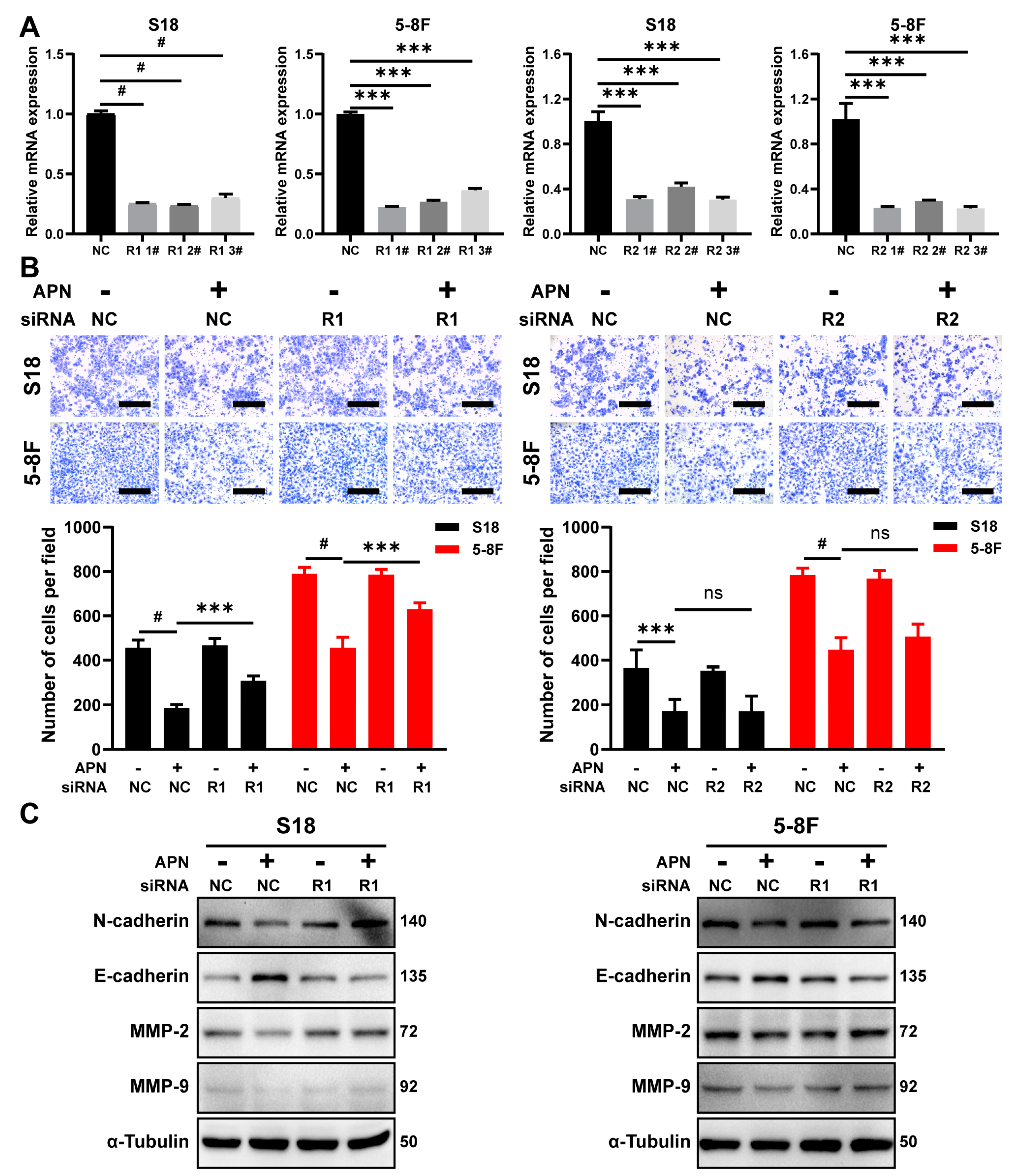
2.5. AdipoR1 Mediates the Inhibitory Effect of Adiponectin on Migration
2.6. AdipoRon Inhibits NPC Cell Invasion and Migration In Vitro
2.7. AdipoRon Inhibits Metastasis of NPC In Vivo
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Designs and Participants
4.2. Blood Collection, Detection, and Statistical Analysis
4.3. Animal Study
4.4. Cell Culture and Regents
4.5. Wound-Healing Assay
4.6. Migration and Invasion Assays
4.7. Transient Transfection with Small Interfering RNA (siRNA)
4.8. RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR
4.9. Immunoblotting Analysis
4.10. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.11. Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay
4.12. Immunohistochemistry Staining
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Y.P.; Chan, A.T.C.; Le, Q.T.; Blanchard, P.; Sun, Y.; Ma, J. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet 2019, 394, 64–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Sun, K.; Zheng, R.; Zeng, H.; Wang, S.; Chen, R.; Wei, W.; He, J. Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2015. J. Nat. Cancer Cent. 2021, 1, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.C.A.; Woo, J.K.S.; King, A.; Zee, B.C.Y.; Lam, W.K.J.; Chan, S.L.; Chu, S.W.I.; Mak, C.; Tse, I.O.L.; Leung, S.Y.M.; et al. Analysis of Plasma Epstein-Barr Virus DNA to Screen for Nasopharyngeal Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Chen, H.; Ji, M. Epstein-Barr virus-based nasopharyngeal carcinoma population screening. Ann. Nasopharynx Cancer 2021, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yang, D.; Liao, X.; Lu, Y.; Yu, B.; Xu, M.; Bin, Y.; Zhou, P.; Yang, Z.; Liu, K.; et al. Failure Patterns of Recurrence and Metastasis After Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy in Patients With Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Results of a Multicentric Clinical Study. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 693199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kholy, A.F.; Abdullah, O.A.; Abadier, M.Z.; Hassaan, M.M.; Shindy, M.F.; Nor El-Dien, D.M.; Hasaneen, A. Pre-treatment serum inflammatory cytokines as survival predictors of patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma receiving chemoradiotherapy. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 5, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.J.; Guo, J.; Ye, Y.F.; Chen, S.H.; Peng, L.X.; Lin, C.Y.; Hu, T.; Xie, S.H.; Xie, C.B.; Huang, Q.H.; et al. Decreased macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-1alpha and MIP-1beta increase the risk of developing nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Commun. 2018, 38, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadir, A.; Retnowati, K.; Amsyar Akil, M.; Usman, A. The Evaluation of Serum Il-6 Changes as Proliferative Cytokines in Patients with Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Before and After the Ionizing Radiotherapy. Glob. J. Health Sci. 2018, 10, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Ke, L.; Xia, W.X.; Xiang, Y.; Lv, X.; Bu, J. Elevated Levels of TNF-alpha and Decreased Levels of CD68-Positive Macrophages in Primary Tumor Tissues Are Unfavorable for the Survival of Patients With Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 18, 1533033819874807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landskron, G.; De la Fuente, M.; Thuwajit, P.; Thuwajit, C.; Hermoso, M.A. Chronic inflammation and cytokines in the tumor microenvironment. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 149185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, L.; Yan, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y. Inflammation and tumor progression: Signaling pathways and targeted intervention. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallegar, N.K.; Christian, S.L. Adipocytes in the Tumour Microenvironment. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1234, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.H.; Wang, P.J.; Hsieh, Y.C.; Lo, S.; Lee, Y.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Tsai, C.H.; Chiu, W.C.; Chu-Sung Hu, S.; Lu, C.W.; et al. Resistin facilitates breast cancer progression via TLR4-mediated induction of mesenchymal phenotypes and stemness properties. Oncogene 2018, 37, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Simone, N.; Di Nicuolo, F.; Sanguinetti, M.; Castellani, R.; D’Asta, M.; Caforio, L.; Caruso, A. Resistin regulates human choriocarcinoma cell invasive behaviour and endothelial cell angiogenic processes. J. Endocrinol. 2006, 189, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.; Cleary, M.P. The potential role of leptin in tumor invasion and metastasis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2017, 38, 80–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Peng, X.L.; Deng, Q.H.; Sheng, L.M.; Liu, P.; Xu, S.H.; Su, D. Prognostic Role of Serum Cytokines in Patients with Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Onkologie 2012, 35, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Qian, C.N.; Mu, Y.G.; Li, N.W.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.B.; Li, S.W.; Wang, F.L.; Guo, X.; Xiang, Y.Q. Serum CCL2 and serum TNF-alpha--two new biomarkers predict bone invasion, post-treatment distant metastasis and poor overall survival in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2011, 47, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Y.; Liu, D.; Peng, P.; Liu, S.; Long, G.; Hu, G.; Sun, W. Induction of interleukin-6 by irradiation and its role in epithelial mesenchymal transition and radioresistance of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Head Neck 2021, 43, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyer, C.; Funahashi, T.; Tanaka, S.; Hotta, K.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Pratley, R.E.; Tataranni, P.A. Hypoadiponectinemia in obesity and type 2 diabetes: Close association with insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 1930–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, Y.; Kihara, S.; Ouchi, N.; Nishida, M.; Arita, Y.; Kumada, M.; Ohashi, K.; Sakai, N.; Shimomura, I.; Kobayashi, H.; et al. Adiponectin reduces atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Circulation 2002, 106, 2767–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, A.M.; Wolf, D.; Rumpold, H.; Enrich, B.; Tilg, H. Adiponectin induces the anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-10 and IL-1RA in human leukocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 323, 630–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadowaki, T.; Yamauchi, T. Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors. Endocr. Rev. 2005, 26, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, K.; Ng, K.T.; Xu, A.; Cheng, Q.; Lo, C.M.; Xiao, J.W.; Sun, B.S.; Lim, Z.X.; Cheung, J.S.; Wu, E.X.; et al. Suppression of liver tumor growth and metastasis by adiponectin in nude mice through inhibition of tumor angiogenesis and downregulation of Rho kinase/IFN-inducible protein 10/matrix metalloproteinase 9 signaling. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Lam, J.B.; Lam, K.S.; Liu, J.; Lam, M.C.; Hoo, R.L.; Wu, D.; Cooper, G.J.; Xu, A. Adiponectin modulates the glycogen synthase kinase-3beta/beta-catenin signaling pathway and attenuates mammary tumorigenesis of MDA-MB-231 cells in nude mice. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 11462–11470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalamaga, M.; Diakopoulos, K.N.; Mantzoros, C.S. The role of adiponectin in cancer: A review of current evidence. Endocr. Rev. 2012, 33, 547–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Wang, J.; Fu, P.P.; Sharma, S.; Nagalingam, A.; Mells, J.; Handy, J.; Page, A.J.; Cohen, C.; Anania, F.A.; et al. Adiponectin antagonizes the oncogenic actions of leptin in hepatocellular carcinogenesis. Hepatology 2010, 52, 1713–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Martino, M.; Leitner, C.V.; Hofbauer, S.L.; Lucca, I.; Haitel, A.; Shariat, S.F.; Klatte, T. Serum Adiponectin Predicts Cancer-specific Survival of Patients with Renal Cell Carcinoma. Eur. Urol. Focus 2016, 2, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.H.; Wang, J.Y.; Gao, Y.; Gao, M.; Yu, G.Y.; Xiang, R.L.; Li, L.; Yang, N.Y.; Cong, X.; Xu, X.Y.; et al. Decreased adiponectin level is associated with aggressive phenotype of tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2013, 104, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Stampfer, M.J.; Mucci, L.; Rifai, N.; Qiu, W.; Kurth, T.; Ma, J. A 25-year prospective study of plasma adiponectin and leptin concentrations and prostate cancer risk and survival. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, L.; Gasser, J.; Zhao, J.; Yang, B.; Li, F.; Zhao, A.Z. Human adiponectin inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis in human endometrial carcinoma cells, HEC-1-A and RL95 2. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2007, 14, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Shi, H.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhou, S.; Mu, Y.; Ding, N.; Lai, Y.; Zhao, A.Z.; Cheng, L.; et al. Adiponectin deficiency promotes endometrial carcinoma pathogenesis and development via activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase. J. Pathol. 2022, 257, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Du, J.; Shi, H.; Wang, S.; Yan, Y.; Xu, Q.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, Z.; Mu, Y.; Qian, C.; et al. Adiponectin suppresses tumor growth of nasopharyngeal carcinoma through activating AMPK signaling pathway. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, B.P. TNF-alpha/NF-kappaB/Snail pathway in cancer cell migration and invasion. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.E.; O’Keefe, R.A.; Grandis, J.R. Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling axis in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, R.C.; Jian, M.; Ma, O.K.; Bunting, M.; Kwan, J.S.; Zhou, G.J.; Senthilkumar, K.; Iyaswamy, A.; Chan, P.K.; Li, M.; et al. Chronic oral administration of adipoRon reverses cognitive impairments and ameliorates neuropathology in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 5669–5689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.G.; Liu, C.L.; Yan, H.J. AdipoRon improves cognitive dysfunction of Alzheimer’s disease and rescues impaired neural stem cell proliferation through AdipoR1/AMPK pathway. Exp. Neurol. 2020, 327, 113249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Liu, D.B.; Li, W.W.; Zhang, L.L.; Long, G.X.; Wang, J.F.; Mei, Q.; Hu, G.Q. Interleukin-6 promotes the migration and invasion of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell lines and upregulates the expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 44, 1551–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Wang, G.; Chu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Jiang, M.; He, Q.; Liu, M.; Qin, J.; Hu, J. TNF-alpha up-regulates cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein 2 (c-IAP2) via c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2013, 16, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lang, J.Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Feng, G.; Jiang, Y.; Deng, Y.L.; Wang, X.J.; Yang, Y.H.; Dai, T.Z.; et al. Association of nuclear factor kappaB expression with a poor outcome in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Med. Oncol. 2011, 28, 1338–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, R.; Liu, Y.P.; Lin, D.C.; Li, Q.; Yu, T.; Zou, X.; Lin, M.; Zhang, X.L.; He, G.P.; Yang, Q.; et al. Clonal Mutations Activate the NF-kappaB Pathway to Promote Recurrence of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 5930–5943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, M.; Ding, X.; Song, W.; Chen, H.; Guan, H.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, X. Correlation of IL-6 and JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway with prognosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Aging 2021, 13, 16667–16683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lui, V.W.; Wong, E.Y.; Ho, Y.; Hong, B.; Wong, S.C.; Tao, Q.; Choi, G.C.; Au, T.C.; Ho, K.; Yau, D.M.; et al. STAT3 activation contributes directly to Epstein-Barr virus-mediated invasiveness of nasopharyngeal cancer cells in vitro. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 1884–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Luo, F.; Li, L.; Yang, L.; Hu, D.; Ma, X.; Lu, Z.; Sun, L.; Cao, Y. STAT3 activation induced by Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein1 causes vascular endothelial growth factor expression and cellular invasiveness via JAK3 And ERK signaling. Eur. J. Cancer 2010, 46, 2996–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messaggio, F.; Mendonsa, A.M.; Castellanos, J.; Nagathihalli, N.S.; Gorden, L.; Merchant, N.B.; VanSaun, M.N. Adiponectin receptor agonists inhibit leptin induced pSTAT3 and in vivo pancreatic tumor growth. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 85378–85391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akimoto, M.; Maruyama, R.; Kawabata, Y.; Tajima, Y.; Takenaga, K. Antidiabetic adiponectin receptor agonist AdipoRon suppresses tumour growth of pancreatic cancer by inducing RIPK1/ERK-dependent necroptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brakenhielm, E.; Veitonmaki, N.; Cao, R.; Kihara, S.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Zhivotovsky, B.; Funahashi, T.; Cao, Y. Adiponectin-induced antiangiogenesis and antitumor activity involve caspase-mediated endothelial cell apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 2476–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Lodish, H.F. Adiponectin deficiency promotes tumor growth in mice by reducing macrophage infiltration. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Tsang, J.Y.; Ho, D.H.; Zhang, R.; Xiao, H.; Li, D.; Zhu, J.; Wang, F.; Bian, Z.; Lui, V.C.; et al. Modulatory effects of adiponectin on the polarization of tumor-associated macrophages. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 848–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Variable | n | Adiponectin (μg/mL) | Z/χ2 | pa | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | IQR | |||||
| Gender | Female | 15 | 2.17 | 7.84 | ||
| Male | 91 | 2.12 | 6.68 | −0.567 | 0.571 | |
| Age (years) | ≤45 | 56 | 2.10 | 6.14 | ||
| >45 | 50 | 2.38 | 6.68 | −0.516 | 0.606 | |
| Grade | I/II | 37 | 3.87 | 10.81 | ||
| III/IV | 69 | 2.06 | 5.86 | −2.343 | 0.019 | |
| VCA-IgA | ≤1:80 | 26 | 3.64 | 8.19 | ||
| >1:80 | 80 | 2.12 | 6.41 | −0.958 | 0.338 | |
| EBNA1/IgA | ≤20 | 66 | 2.32 | 6.80 | ||
| >20 | 40 | 2.13 | 6.28 | −0.404 | 0.686 | |
| Family history | Yes | 24 | 1.67 | 7.00 | ||
| No | 82 | 2.08 | 6.09 | −2.110 | 0.035 | |
| Recurrence | Yes | 5 | 1.05 | 4.30 | ||
| No | 101 | 2.28 | 6.67 | −2.161 | 0.031 | |
| Metastasis | Yes | 38 | 1.57 | 3.47 | ||
| No | 68 | 3.05 | 8.77 | −3.255 | 0.001 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | <25 | 78 | 2.59 | 6.52 | ||
| ≥25 | 28 | 1.41 | 3.31 | −2.297 | 0.022 | |
| Variable | Univariable | Multivariable b | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95%CI) | p | HR (95%CI) | p | |
| Gender | ||||
| Female | 1.000 (ref) | 1.000 (ref) | ||
| Male | 1.139 (0.444–2.922) | 0.787 | 0.794 (0.284–2.224) | 0.661 |
| Age (years) | ||||
| ≤45 | 1.000 (ref) | 1.000 (ref) | ||
| >45 | 0.886 (0.467–1.681) | 0.710 | 0.788 (0.378–1.643) | 0.525 |
| Grade | ||||
| I/II | 1.000 (ref) | 1.000 (ref) | ||
| III/IV | 22.789 (3.122–166.353) | 0.002 | 23.445 (3.105–177.040) | 0.002 |
| VCA-IgA | ||||
| ≤1:80 | 1.000 (ref) | 1.000 (ref) | ||
| >1:80 | 1.114 (0.511–2.431) | 0.786 | 0.600 (0.218–1.652) | 0.323 |
| EBNA1/IgA | ||||
| ≤20 | 1.000 (ref) | 1.000 (ref) | ||
| >20 | 1.518 (0.802–2.871) | 0.200 | 0.934 (0.426–2.050) | 0.865 |
| Family history | ||||
| No | 1.000 (ref) | 1.000 (ref) | ||
| Yes | 0.912 (0.418–1.991) | 0.817 | 1.074 (0.435–2.653) | 0.876 |
| Recurrence | ||||
| No | 1.000 (ref) | 1.000 (ref) | ||
| Yes | 3.165 (1.117–8.968) | 0.030 | 1.500 (0.481–4.680) | 0.485 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | ||||
| <25 | 1.000 (ref) | 1.000 (ref) | ||
| ≥25 | 0.727 (0.341–1.547) | 0.408 | 0.507 (0.207–1.241) | 0.137 |
| Adiponectin c | 0.883 (0.798–0.976) | 0.015 | 0.890 (0.796–0.996) | 0.043 |
| Low | 1.000 (reference) | 1.000 (reference) | ||
| High | 0.282 (0.100–0.796) | 0.005 | 0.245 (0.080–0.745) | 0.013 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Du, J.; Xu, Q.; Xing, C.; Li, Y.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, Z.; Mu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Cao, S.; et al. Adiponectin Suppresses Metastasis of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma through Blocking the Activation of NF-κB and STAT3 Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12729. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232112729
Zhang Z, Du J, Xu Q, Xing C, Li Y, Zhou S, Zhao Z, Mu Y, Zhao Z, Cao S, et al. Adiponectin Suppresses Metastasis of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma through Blocking the Activation of NF-κB and STAT3 Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(21):12729. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232112729
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zongmeng, Jinlin Du, Qihua Xu, Chaofeng Xing, Yuyu Li, Sujin Zhou, Zhenggang Zhao, Yunping Mu, Zijian (Allan) Zhao, Sumei Cao, and et al. 2022. "Adiponectin Suppresses Metastasis of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma through Blocking the Activation of NF-κB and STAT3 Signaling" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 21: 12729. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232112729
APA StyleZhang, Z., Du, J., Xu, Q., Xing, C., Li, Y., Zhou, S., Zhao, Z., Mu, Y., Zhao, Z., Cao, S., & Li, F. (2022). Adiponectin Suppresses Metastasis of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma through Blocking the Activation of NF-κB and STAT3 Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(21), 12729. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232112729





