Adult-Onset Still’s Disease—A Complex Disease, a Challenging Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
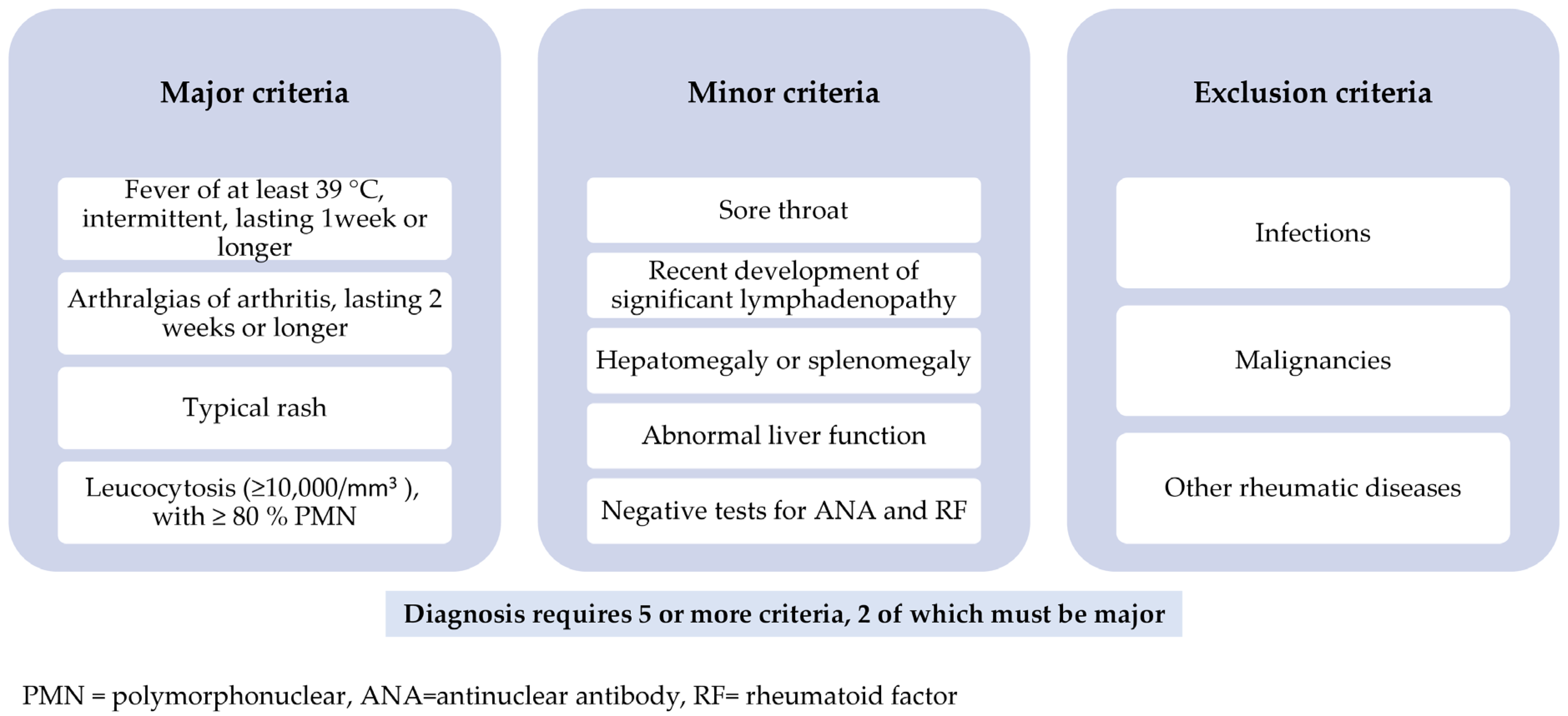
2. AOSD-Clinical Picture and Diagnostic Criteria
3. AOSD-Prognosis and Complications
4. AOSD-Pathogenesis
5. AOSD-Treatment
5.1. Goals and Categories of Therapy
5.2. NSAIDs, CS and csDMARDs Treatment
5.2.1. NSAIDs
5.2.2. CS
5.2.3. csDMARDs
5.3. IL-1 Inhibitors
5.3.1. Anakinra
5.3.2. Canakinumab
5.3.3. Rilonacept
5.4. IL-6 Inhibitors
5.4.1. Tocilizumab
5.4.2. Sarilumab
5.5. IL-18 Inhibitors
5.5.1. Tadekinig Alpha
5.5.2. AVTX 007
5.5.3. APB R3
5.6. IL-17 Inhibitors
Secukinumab
5.7. TNFα Inhibitors
5.7.1. Infliximab
5.7.2. Etanercept
5.7.3. Adalimumab
5.8. IFN- γ Inhibitors
Emapalumab
5.9. Janus Kinases Inhibitors
5.9.1. Baricitinib
5.9.2. Tofacitinib
5.9.3. Ruxolitinib
5.10. GM-CSF Inhibitors
Mavrilimumab and Otilimab
5.11. NLRP3 Inflammasome Inhibitors
Dapansutrile
5.12. Long Non-Coding RNAs
5.13. Other Therapeutical Approaches
5.13.1. Rituximab
5.13.2. Abatacept
5.13.3. IVIGs
5.14. MAS Treatment
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feist, E.; Mitrovic, S.; Fautrel, B. Mechanisms, Biomarkers and Targets for Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2018, 14, 603–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bywaters, E. Still’s Disease in the Adult. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1971, 30, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitrovic, S.; Fautrel, B. Clinical Phenotypes of Adult-Onset Still’s Disease: New Insights from Pathophysiology and Literature Findings. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galozzi, P.; Bindoli, S.; Doria, A.; Sfriso, P. Progress in Biological Therapies for Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Biologics 2022, 16, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, A.; Kokuzawa, A.; Yamauchi, Y.; Kirino, Y.; Nagai, H.; Inoue, Y.; Ota, T.; Chifu, Y.; Inokuchi, S.; Koarada, S.; et al. Clinical Features of Elderly-Onset Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Mod. Rheumatol. 2020, 31, 862–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerfaud-Valentin, M.; Maucort-Boulch, D.; Hot, A.; Iwaz, J.; Ninet, J.; Durieu, I.; Broussolle, C.; Sève, P. Adult-Onset Still Disease. Medicine 2014, 93, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGonagle, D.; McDermott, M. A Proposed Classification of the Immunological Diseases. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, Y. Interluekin-6 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Mod. Rheumatol. 2021, 32, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaux, C.; El-Jammal, T.; Neau, P.; Fournier, N.; Gerfaud-Valentin, M.; Perard, L.; Fouillet-Desjonqueres, M.; Le Scanff, J.; Vignot, E.; Durupt, S.; et al. Detection and Prediction of Macrophage Activation Syndrome in Still’s Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 11, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torigoe, M.; Maeshima, K.; Kuriyama, Y.; Abe, I.; Ozaki, T.; Omura, Y.; Umeki, T.; Imada, C.; Ishii, K.; Shibata, H. Effectiveness of Subcutaneous Tocilizumab in Refractory Adult Still’s Disease: Report of Three Cases and a Review of the Literature. Mod. Rheumatol. 2021, 5, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fautrel, B. Adult-Onset Still Disease. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2008, 22, 773–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomaras, S.; Goetzke, C.; Kallinich, T.; Feist, E. Adult-Onset Still’s Disease: Clinical Aspects and Therapeutic Approach. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poursac, N.; Odriozola, I.; Truchetet, M. Strategy and Challenges of Paraclinical Examinations in Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fautrel, B. Ferritin Levels in Adult Still’s Disease: Any Sugar? Jt. Bone Spine 2002, 69, 355–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shad, I.; Shafique, M.; Waris, S.; Shabbir, F.; Begum, A. Adult-Onset Still’s Disease: A Case Report. Cureus 2022, 14, e21033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebrun, D.; Mestrallet, S.; Dehoux, M.; Golmard, J.; Granger, B.; Georgin-Lavialle, S.; Arnaud, L.; Grateau, G.; Pouchot, J.; Fautrel, B. Validation of the Fautrel Classification Criteria for Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2018, 47, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, B.; Ibrahim, S.; Briggs, W.; Efthimiou, P. Racial/Ethnic Variations in Morbidity and Mortality in Adult Onset Still’s Disease: An Analysis of National Dataset. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2019, 49, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crayne, C.; Albeituni, S.; Nichols, K.; Cron, R. The Immunology of Macrophage Activation Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machaczka, M.; Klimkowska, M. Bone Marrow Assessment in the Diagnosis of Acquired Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Adults. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2015, 143, 308–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnari, V.; Colina, M.; Ciancio, G.; Govoni, M.; Trotta, F. Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Rheumatol. Int. 2009, 30, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efthimiou, P.; Kontzias, A.; Ward, C.; Ogden, N. Adult-Onset Still’s Disease: Can Recent Advances in Our understanding of Its Pathogenesis Lead to Targeted Therapy? Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2007, 3, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouchot, J.; Sampalis, J.; Beaudet, F.; Carette, S.; Decary, F.; Salusinky-Sternbach, M.; Hill, R.; Gutkowski, A.; Harth, M.; Myhal, D.; et al. Adult Still’s Disease. Medicine 1991, 70, 118–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colafrancesco, S.; Manara, M.; Bortoluzzi, A.; Serban, T.; Bianchi, G.; Cantarini, L.; Ciccia, F.; Dagna, L.; Govoni, M.; Montecucco, C.; et al. Correction to: Management of Adult-Onset Still’s Disease with Interleukin-1 Inhibitors: Evidence- and Consensus-Based Statements by a Panel of Italian Experts. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franchini, S.; Dagna, L.; Salvo, F.; Aiello, P.; Baldissera, E.; Sabbadini, M. Efficacy of Traditional and Biologic Agents in Different Clinical Phenotypes of Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2010, 62, 2530–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamilloux, Y.; Gerfaud-Valentin, M.; Martinon, F.; Belot, A.; Henry, T.; Sève, P. Pathogenesis of Adult-Onset Still’s Disease: New Insights from the Juvenile Counterpart. Immunol. Res. 2014, 61, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Hsieh, T.; Chen, Y.; Hsieh, C.; Lan, J.; Lin, F. Proinflammatory Cytokine Profiles of Patients with Elderly-Onset Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Comparison with Younger-Onset Disease. Gerontology 2008, 55, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, M.; Nakagishi, Y.; Yachie, A. Distinct Subsets of Patients with Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Based on Their Cytokine Profiles. Cytokine 2013, 61, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfriso, P.; Bindoli, S.; Galozzi, P. Adult-Onset Still’s Disease: Molecular Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Advances. Drugs 2018, 78, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Meng, J.; Jia, J.; Wang, M.; Teng, J.; Zhu, D.; Yang, C.; Hu, Q. Current and Emerging Biological Therapy in Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 3986–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T. Cytokine and Immunogenetic Profiles in Japanese Patients with Adult Still’s Disease. Association with Chronic Articular Disease. Rheumatology 2001, 40, 1398–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavragani, C.; Spyridakis, E.; Koutsilieris, M. Adult-Onset Still’s Disease: From Pathophysiology to Targeted Therapies. Int. J. Inflam. 2012, 2012, 879020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Lan, J.; Lin, F.; Hsieh, T. Association of Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 with Clinical Manifestations and Interleukin-18 in Patients with Active, Untreated Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2005, 53, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Shi, H.; Zeng, T.; Liu, H.; Su, Y.; Cheng, X.; Ye, J.; Yin, Y.; Liu, M.; Zheng, H.; et al. Increased Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Activate NLRP3 and Inflammatory Macrophages in Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Ahn, M.; Jung, J.; Suh, C.; Kim, H. An Update on the Pathogenic Role of Neutrophils in Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis and Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Song, R.; Wang, Z.; Jing, Z.; Wang, S.; Ma, J. S100A8/A9 in Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Park, Y.; Ha, Y.; Lee, K.; Lee, S. Serum Calprotectin as a Marker for Disease Activity and Severity in Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. J. Rheumatol. 2010, 37, 1029–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Chen, D. An Update on the Pathogenic Role of Macrophages in Adult-Onset Still’s Disease and Its Implication in Clinical Manifestations and Novel Therapeutics. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 8998358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Park, W.; Kim, T.; Jun, J.; Yoo, D. Interleukin-18 as an Efficient Marker for Remission and Follow-Up in Patients with Inactive Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2013, 43, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplanski, G. Interleukin-18: Biological Properties and Role in Disease Pathogenesis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 281, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rau, M.; Schiller, M.; Krienke, S.; Heyder, P.; Lorenz, H.; Blank, N. Clinical Manifestations But Not Cytokine Profiles Differentiate Adult-Onset Still’s Disease and Sepsis. J. Rheumatol. 2010, 37, 2369–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, P.; Cron, R.; Hartwell, J.; Manson, J.; Tattersall, R. Silencing the Cytokine Storm: The Use of Intravenous Anakinra in Haemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis or Macrophage Activation Syndrome. Lancet 2020, 2, e358–e367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, G.; Farina, N.; Campochiaro, C.; Baldissera, E.; Dagna, L. Current Treatment Options and Safety Considerations When Treating Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2020, 19, 1549–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarello, C. Immunological and Inflammatory Functions of the Interleukin-1 Family. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 519–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarello, C. Interleukin-1 in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Inflammatory Diseases. Blood 2011, 117, 3720–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santarlasci, V.; Cosmi, L.; Maggi, L.; Liotta, F.; Annunziato, F. IL-1 and T Helper Immune Responses. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudela, H.; Drynda, S.; Lux, A.; Horneff, G.; Kekow, J. Comparative Study of Interleukin-18 (IL-18) Serum Levels in Adult Onset Still’s Disease (AOSD) and Systemic Onset Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (Sjia) and Its Use as a Biomarker for Diagnosis and Evaluation of Disease Activity. BMC Rheumatol. 2019, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priori, R.; Barone, F.; Alessandri, C.; Colafrancesco, S.; McInnes, I.; Pitzalis, C.; Valesini, G.; Bombardieri, M. Markedly Increased IL-18 Liver Expression in Adult-Onset Still’s Disease-Related Hepatitis. Rheumatology 2010, 50, 776–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, C.; Rech, J.; Brown, M.; Allali, D.; Roux-Lombard, P.; Spertini, F.; Schiffrin, E.; Schett, G.; Manger, B.; Bas, S.; et al. Elevated Serum Levels of Free Interleukin-18 in Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 2237–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, J.; Inokuma, S. Cytokine Profiles of Macrophage Activation Syndrome Associated with Rheumatic Diseases. J. Rheumatol. 2010, 37, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Chen, Y.; Lan, J.; Lin, C.; Chen, H.; Hsieh, C. Potential Role of Th17 Cells in the Pathogenesis of Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Rheumatology 2010, 49, 2305–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Suh, C.; Jung, J.; Nam, J.; Kwon, J.; Yim, H.; Kim, H. Association of CXCL10 and CXCL13 Levels with Disease Activity and Cutaneous Manifestation in Active Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Suh, C.; Jung, J.; Ahn, M.; Han, M.; Kwon, J.; Yim, H.; Kim, H. Elevated Circulating Levels of the Interferon-Γ–Induced Chemokines Are Associated with Disease Activity and Cutaneous Manifestations in Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, N.; Shimizu, M.; Tsunoda, S.; Kawano, M.; Matsumura, M.; Yachie, A. Cytokine Profile in Adult-Onset Still’s Disease: Comparison with Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 169, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadavath, S.; Efthimiou, P. Adult-Onset Still’s Disease—Pathogenesis, Clinical Manifestations, and New Treatment Options. Ann. Med. 2015, 47, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Jia, J.; Yang, C.; Hu, Q. Pathogenesis, Disease Course, and Prognosis of Adult-Onset Still’s Disease: An Update and Review. Ann. Med. 2019, 132, 2856–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruscitti, P.; Berardicurti, O.; Barile, A.; Cipriani, P.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Iagnocco, A.; Giacomelli, R. Severe COVID-19 and Related Hyperferritinaemia: More Than an Innocent Bystander? Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 1515–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voskoboinik, I.; Smyth, M.; Trapani, J. Perforin-Mediated Target-Cell Death and Immune Homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 940–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vastert, S.; van Wijk, R.; D’Urbano, L.; de Vooght, K.; de Jager, W.; Ravelli, A.; Magni-Manzoni, S.; Insalaco, A.; Cortis, E.; van Solinge, W.; et al. Mutations in the Perforin Gene Can Be Linked to Macrophage Activation Syndrome in Patients with Systemic Onset Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. Rheumatology 2009, 49, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimojima, Y.; Kishida, D.; Ueno, K.; Ushiyama, S.; Ichikawa, T.; Sekijima, Y. Characteristics of Circulating Natural Killer Cells and Their Interferon-Γ Production in Active Adult-Onset Still Disease. J. Rheumatol. 2019, 46, 1268–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chi, H.; Hu, Q.; Ye, J.; Liu, H.; Cheng, X.; Shi, H.; Zhou, Z.; Teng, J.; et al. Elevated Serum Levels of Interleukin-10 in Adult-Onset Still’s Disease Are Associated with Disease Activity. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 38, 3205–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ip, W.; Hoshi, N.; Shouval, D.; Snapper, S.; Medzhitov, R. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of IL-10 Mediated by Metabolic Reprogramming of Macrophages. Science 2017, 356, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nold, M.; Nold-Petry, C.; Zepp, J.; Palmer, B.; Bufler, P.; Dinarello, C. IL-37 Is a Fundamental Inhibitor of Innate Immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, H.; Liu, D.; Sun, Y.; Hu, Q.; Liu, H.; Cheng, X.; Ye, J.; Shi, H.; Yin, Y.; Liu, M.; et al. Interleukin-37 Is Increased in Adult-Onset Still’s Disease and Associated with Disease Activity. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shouval, D.; Biswas, A.; Goettel, J.; McCann, K.; Conaway, E.; Redhu, N.; Mascanfroni, I.; Al Adham, Z.; Lavoie, S.; Ibourk, M.; et al. Interleukin-10 Receptor Signaling in Innate Immune Cells Regulates Mucosal Immune Tolerance and Anti-Inflammatory Macrophage Function. Immunity 2014, 40, 706–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, D. Treatment of Adult-Onset Still’s Disease: Up to Date. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 13, 849–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimura, T.; Kondo, Y.; Ohta, A.; Iwamoto, M.; Ota, A.; Okamoto, N.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Kono, H.; Takasaki, Y.; Takei, S.; et al. Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guideline for Adult Still’s Disease. Mod. Rheumatol. 2018, 28, 736–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efthimiou, P.; Kontzias, A.; Hur, P.; Rodha, K.; Ramakrishna, G.; Nakasato, P. Adult-Onset Still’s Disease in Focus: Clinical Manifestations, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Unmet Needs in the Era of Targeted Therapies. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2021, 51, 858–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda, S.; Blanco, R.; González-Gay, M. Adult-Onset Still’s Disease: Advances in the Treatment. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2016, 30, 222–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgers, L.; Raza, K.; van der Helm-van Mil, A. Window of Opportunity in Rheumatoid Arthritis—Definitions and Supporting Evidence: From Old to New Perspectives. RMD Open 2019, 5, e000870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, G.; Franchini, S.; Aiello, P.; Guglielmi, B.; Berti, A.; Campochiaro, C.; Sabbadini, M.; Baldissera, E.; Dagna, L. Efficacy and Safety of Biological Agents in Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2015, 44, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Yoo, S.; Ko, R.; Yoo, W. Adalimumab in the Treatment of Refractory Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 20, 1798–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahiri, M.; Teng, G. A Case of Refractory Adult-Onset Still’s Disease Treated with Anakinra. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 13, e36–e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aikawa, N.; de Medeiros Ribeiro, A.; Saad, C.; Pereira, R.; Levy, M.; Silva, C.; Bonfá, E.; de Carvalho, J. Is Anti-TNF Switching in Refractory Still’s Disease Safe and Effective? J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2011, 30, 1129–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias, J.; Sathiraju, S.; Marik, P. Severe Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome with Shock and ARDS Resulting from Still’s Disease. Chest 1999, 115, 1738–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henter, J. Treatment of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis with HLH-94 Immunochemotherapy and Bone Marrow Transplantation. Blood 2002, 100, 2367–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebrahtu, T.; Morgan, A.; West, R.; Stewart, P.; Pujades-Rodriguez, M. Oral Glucocorticoids and Incidence of Hypertension in People with Chronic Inflammatory Diseases: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2020, 192, E295–E301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trelle, S.; Reichenbach, S.; Wandel, S.; Hildebrand, P.; Tschannen, B.; Villiger, P.; Egger, M.; Juni, P. Cardiovascular Safety of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: Network Meta-Analysis. BMJ 2011, 342, c7086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomelli, R.; Ruscitti, P.; Shoenfeld, Y. A Comprehensive Review on Adult Onset Still’s Disease. J. Autoimmun. 2018, 93, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, E.; Clarke, S.; Ramanan, A. Macrophage Activation Syndrome. Indian J. Pediatr. 2015, 83, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhou, H.; Liu, L. Side Effects of Methotrexate Therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 158, 502–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramiro, S.; Gaujoux-Viala, C.; Nam, J.; Smolen, J.; Buch, M.; Gossec, L.; van der Heijde, D.; Winthrop, K.; Landewé, R. Safety of Synthetic and Biological Dmards: A Systematic Literature Review Informing the 2013 Update of the EULAR Recommendations for Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyoncu, U.; Solmaz, D.; Emmungil, H.; Yazici, A.; Kasifoglu, T.; Kimyon, G.; Balkarli, A.; Bes, C.; Ozmen, M.; Alibaz-Oner, F.; et al. Response Rate of Initial Conventional Treatments, Disease Course, and Related Factors of Patients with Adult-Onset Still’s Disease: Data from a Large Multicenter Cohort. J. Autoimmun. 2016, 69, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordström, D.; Knight, A.; Luukkainen, R.; van Vollenhoven, R.; Rantalaiho, V.; Kajalainen, A.; Brun, J.; Proven, A.; Ljung, L.; Kautiainen, H.; et al. Beneficial Effect of Interleukin 1 Inhibition with Anakinra in Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. An Open, Randomized, Multicenter Study. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 39, 2008–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lequerre, T.; Quartier, P.; Rosellini, D.; Alaoui, F.; De Bandt, M.; Mejjad, O.; Kone-Paut, I.; Michel, M.; Dernis, E.; Khellaf, M.; et al. Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist (Anakinra) Treatment in Patients with Systemic-Onset Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis or Adult Onset Still Disease: Preliminary Experience in France. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2007, 67, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedor, C.; Listing, J.; Zernicke, J.; Weiß, A.; Behrens, F.; Blank, N.; Henes, J.; Kekow, J.; Rubbert-Roth, A.; Schulze-Koops, H.; et al. Canakinumab for Treatment of Adult-Onset Still’s Disease to Achieve Reduction of Arthritic Manifestation (CONSIDER): Phase II, Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Multicentre, Investigator-Initiated Trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 1090–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, A.; LeClercq, S.; Yan, A.; Homik, J.; Dinarello, C. Rapid Responses to Anakinra in Patients with Refractory Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2005, 52, 1794–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kötter, I.; Wacker, A.; Koch, S.; Henes, J.; Richter, C.; Engel, A.; Günaydin, I.; Kanz, L. Anakinra in Patients with Treatment-Resistant Adult-Onset Still’s Disease: Four Case Reports with Serial Cytokine Measurements and a Review of the Literature. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 37, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junge, G.; Mason, J.; Feist, E. Adult Onset Still’s Disease—The Evidence That Anti-Interleukin-1 Treatment Is Effective and Well-Tolerated (a Comprehensive Literature Review). Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2017, 47, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Sanjuán, F.; Blanco, R.; Riancho-Zarrabeitia, L.; Castañeda, S.; Olivé, A.; Riveros, A.; Velloso-Feijoo, M.; Narváez, J.; Jiménez-Moleón, I.; Maiz-Alonso, O.; et al. Efficacy of Anakinra in Refractory Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Medicine 2015, 94, e1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Ara, F.; Frassi, M.; Tincani, A.; Airò, P. A Retrospective Study of Patients with Adult-Onset Still’s Disease: Is Pericarditis a Possible Predictor for Biological Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs Need? J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2016, 35, 2117–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercruysse, F.; Barnetche, T.; Lazaro, E.; Shipley, E.; Lifermann, F.; Balageas, A.; Delbrel, X.; Fautrel, B.; Richez, C.; Schaeverbeke, T.; et al. Adult-Onset Still’s Disease Biological Treatment Strategy May Depend on the Phenotypic Dichotomy. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schanberg, L.; Nigrovic, P.; Cooper, A.; Chatham, W.; Akoghlanian, S.; Singh, N.; Rabinovich, E.; Thatayatikom, A.; Taxter, A.; Hausmann, J.; et al. AB1059 a Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study of Anakinra in Patients with Still’s Disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis 2020, 79, 1819–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, A.; Berlengiero, V.; Sota, J.; Ciarcia, L.; Ricco, N.; Barneschi, S.; Mourabi, M.; Lopalco, G.; Marzo, C.; Bellisai, F.; et al. Real-Life Data on the Efficacy of Canakinumab in Patients with Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020, 2020, 8054961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruscitti, P.; Ursini, F.; Sota, J.; De Giorgio, R.; Cantarini, L.; Giacomelli, R. The Reduction of Concomitant Glucocorticoids Dosage Following Treatment with IL-1 Receptor Antagonist in Adult Onset Still’s Disease. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodard, Q.; Langlois, V.; Guilpain, P.; Le Quellec, A.; Vittecoq, O.; Noel, D.; Eble, V.; Josse, S.; Schmidt, J.; Aouba, A.; et al. Cardiac Involvement in Adult-Onset Still’s Disease: Manifestations, Treatments and Outcomes in a Retrospective Study of 28 Patients. J. Autoimmun. 2021, 116, 102541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campochiaro, C.; Farina, N.; Tomelleri, A.; De Luca, G.; Baldissera, E.; Cavalli, G.; Dagna, L. Drug Retention Rates of Biological Agents in Adult Onset Still’s Disease. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2021, 51, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, A.; Insalaco, A.; Sfriso, P.; Lopalco, G.; Emmi, G.; Cattalini, M.; Manna, R.; Cimaz, R.; Priori, R.; Talarico, R.; et al. A Snapshot on the On-Label and Off-Label Use of the Interleukin-1 Inhibitors in Italy Among Rheumatologists and Pediatric Rheumatologists: A Nationwide Multi-Center Retrospective Observational Study. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vastert, S.; de Jager, W.; Noordman, B.; Holzinger, D.; Kuis, W.; Prakken, B.; Wulffraat, N. Effectiveness of First-Line Treatment with Recombinant Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist in Steroid-Naive Patients with New-Onset Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: Results of a Prospective Cohort Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 1034–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, G.; Tomelleri, A.; De Luca, G.; Campochiaro, C.; Dinarello, C.; Baldissera, E.; Dagna, L. Efficacy of Canakinumab as First-Line Biologic Agent in Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedor, C.; Listing, J.; Zernicke, J.; Feist, E. Response to: ‘Changing the Outcome Measures, Changing the Results? The Urgent Need of a Specific Disease Activity Score to Adult-Onset Still’s Disease’ by Ruscitti et al. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 81, e104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomelleri, A.; Campochiaro, C.; De Luca, G.; Farina, N.; Baldissera, E.; Cavalli, G.; Dagna, L. FRI0506 Efficacy and Safety Of Canakinumab in Adult-Onset Still’s Disease: A Single-Center Real-Life Experience. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 851–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskari, K.; Tektonidou, M.; Katsiari, C.; Athanassiou, P.; Dimopoulou, D.; Gerodimos, C.; Salamaliki, C.; Papagoras, C.; Settas, L.; Vassilopoulos, D.; et al. Outcome of Refractory to Conventional And/or Biologic Treatment Adult Still’s Disease Following Canakinumab Treatment: Countrywide Data in 50 Patients. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2021, 51, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petryna, O.; Cush, J.; Efthimiou, P. IL-1 Trap Rilonacept in Refractory Adult Onset Still’s Disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 2056–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belfeki, N.; Smiti Khanfir, M.; Said, F.; Hamzaoui, A.; Ben Salem, T.; Ben Ghorbel, I.; Lamloum, M.; Houman, M. Successful Treatment of Refractory Adult Onset Still’s Disease with Rituximab. Reumatismo 2016, 68, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gao, X.; Petryna, O. Clinical Utility of MBDa Panel in the Management of Adult Onset Still’s Disease. J. Rheumatol. 2017, 28, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalarathinam, R.; Orlowsky, E.; Kesavalu, R.; Yelaminchili, S. Adult Onset Still’s Disease: A Review on Diagnostic Workup and Treatment Options. Case Rep. Rheumatol. 2016, 2016, 6502373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didion, S. Cellular and Oxidative Mechanisms Associated with Interleukin-6 Signaling in the Vasculature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheller, J.; Chalaris, A.; Schmidt-Arras, D.; Rose-John, S. The Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of the Cytokine Interleukin-6. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2011, 1813, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrovic, S.; Fautrel, B. New Markers for Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Jt. Bone Spine 2018, 85, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Sanjuán, F.; Blanco, R.; Calvo-Rio, V.; Narvaez, J.; Rubio Romero, E.; Olivé, A.; Castañeda, S.; Gallego Flores, A.; Hernández, M.; Mata, C.; et al. Efficacy of Tocilizumab in Conventional Treatment-Refractory Adult-Onset Still’s Disease: Multicenter Retrospective Open-Label Study of Thirty-Four Patients. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 1659–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, E.; Wazir, T.; Drake, M.; Cuthbert, R.; Wright, G. Fulminant Myocarditis and Macrophage Activation Syndrome Secondary to Adult-Onset Still’s Disease Successfully Treated with Tocilizumab. Rheumatology 2014, 53, 1352–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishina, N.; Kaneko, Y.; Kameda, H.; Takeuchi, T. The Effect of Tocilizumab on Preventing Relapses in Adult-Onset Still’s Disease: A Retrospective, Single-Center Study. Mod. Rheumatol. 2014, 25, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Wu, M.; Zhang, X.; Xia, Q.; Yang, J.; Xu, S.; Pan, F. Efficacy and Safety of Tocilizumab with Inhibition of Interleukin-6 in Adult-Onset Still’s Disease: A Meta-Analysis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2018, 28, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Qiao, J.; Bai, J.; Wu, Y.; Fang, H. Biological Therapy of Traditional Therapy-Resistant Adult-Onset Still’s Disease: An Evidence-Based Review. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2018, 14, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puéchal, X.; DeBandt, M.; Berthelot, J.; Breban, M.; Dubost, J.; Fain, O.; Kahn, J.; Lequen, L.; Longy-Boursier, M.; Perdriger, A.; et al. Tocilizumab in Refractory Adult Still’s Disease. Arthritis Care Res. 2010, 63, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suematsu, R.; Ohta, A.; Matsuura, E.; Takahashi, H.; Fujii, T.; Horiuchi, T.; Minota, S.; Ishigatsubo, Y.; Ota, T.; Takei, S.; et al. Therapeutic Response of Patients with Adult Still’s Disease to Biologic Agents: Multicenter Results in Japan. Mod. Rheumatol. 2011, 22, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, Y.; Kameda, H.; Ikeda, K.; Ishii, T.; Murakami, K.; Takamatsu, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Abe, T.; Takeuchi, T. Tocilizumab in Patients with Adult-Onset Still’s Disease Refractory to Glucocorticoid Treatment: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase III Trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 1720–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamoto, M.; Nara, H.; Hirata, D.; Minota, S.; Nishimoto, N.; Yoshizaki, K. Humanized Monoclonal Anti-Interleukin-6 Receptor Antibody for Treatment of Intractable Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2002, 46, 3388–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Gu, L.; Wang, X.; Guo, L.; Shi, H.; Yang, C.; Chen, S. A Pilot Study on Tocilizumab for Treating Refractory Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, E.; Sugawara, H.; Yamashita, T.; Ishii, A.; Oda, A.; Terai, C. Successful Tocilizumab Therapy for Macrophage Activation Syndrome Associated with Adult-Onset Still’s Disease: A Case-Based Review. Case Rep. Med. 2016, 2016, 5656320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadavath, S.; Zapantis, E.; Zolty, R.; Efthimiou, P. A Novel Therapeutic Approach in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension as a Complication of Adult-Onset Still’s Disease: Targeting IL-6. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 17, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castañeda, S.; Martínez-Quintanilla, D.; Martín-Varillas, J.; García-Castañeda, N.; Atienza-Mateo, B.; González-Gay, M. Tocilizumab for the Treatment of Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2019, 19, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalli, G.; Favalli, E. Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Impact of Classic and Disease-Specific Risk Factors. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, S82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simeni Njonnou, S.; Soyfoo, M.; Vandergheynst, F. Efficacy of Sarilumab in Adult-Onset Still’s Disease as a Corticosteroid-Sparing Agent. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 1878–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamb, Y.; Deeks, E. Sarilumab: A Review in Moderate to Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis. Drugs 2018, 78, 929–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonina, I.; Müller, C.; Martin, S.; Beyaert, R. Proteolytic Processing of Interleukin-1 Family Cytokines: Variations on a Common Theme. Immunity 2015, 42, 991–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.; Novick, D.; Kim, S.; Kaplanski, G. Interleukin-18 and IL-18 Binding Protein. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabay, C.; Fautrel, B.; Rech, J.; Spertini, F.; Feist, E.; Kötter, I.; Hachulla, E.; Morel, J.; Schaeverbeke, T.; Hamidou, M.; et al. Open-Label, Multicentre, Dose-Escalating Phase II Clinical Trial on the Safety and Efficacy of Tadekinig Alfa (IL-18BP) in Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiltz, U.; Kiefer, D.; Braun, J.; Schiffrin, E.; Girard-Guyonvarc’h, C.; Gabay, C. Prolonged Treatment with Tadekinig Alfa in Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 79, e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cua, D.; Tato, C. Innate IL-17-Producing Cells: The Sentinels of the Immune System. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrovic, S.; Hassold, N.; Kamissoko, A.; Rosine, N.; Mathian, A.; Mercy, G.; Pertuiset, E.; Nocturne, G.; Fautrel, B.; Koné-Paut, I. Adult-Onset Still’s Disease or Systemic-Onset Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis and Spondyloarthritis: Overlapping Syndrome or Phenotype Shift? Rheumatology 2021, 61, 2535–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faustman, D.; Davis, M. TNF Receptor 2 Pathway: Drug Target for Autoimmune Diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 482–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldmann, M.; Brennan, F.; Maini, R. Role of Cytokines in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1996, 14, 397–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fautrel, B. Tumour Necrosis Factor Blocking Agents in Refractory Adult Still’s Disease: An Observational Study of 20 Cases. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2005, 64, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Homood, I. Biologic Treatments for Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Rheumatology 2013, 53, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechant, C.; Schauenberg, P.; Antoni, C.; Kraetsch, H.; Kalden, J.; Manger, B. Langzeitergebnisse Einer TNF-Blockade Beim Morbus Still im Erwachsenenalter. Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. 2004, 129, 1308–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husni, M.; Maier, A.; Mease, P.; Overman, S.; Fraser, P.; Gravallese, E.; Weinblatt, M. Etanercept in the Treatment of Adult Patients with Still’s Disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2002, 46, 1171–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rech, J.; Ronneberger, M.; Englbrecht, M.; Finzel, S.; Katzenbeisser, J.; Manger, K.; Manger, B.; Schett, G. Successful Treatment of Adult-Onset Still’s Disease Refractory to TNF and IL-1 Blockade by IL-6 Receptor Blockade. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 70, 390–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cola, I.; Ruscitti, P.; Giacomelli, R.; Cipriani, P. The Pathogenic Role of Interferons in the Hyperinflammatory Response on Adult-Onset Still’s Disease and Macrophage Activation Syndrome: Paving the Way towards New Therapeutic Targets. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatterer, E.; Richard, F.; Malinge, P.; Sergé, A.; Startchick, S.; Kosco-Vilbois, M.; Deehan, M.; Ferlin, W.; Guilhot, F. P156 Investigating the Novel Mechanism of Action for NI-0501, a Human Interferon Gamma Monoclonal Antibody. Cytokine 2012, 59, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabr, J.; Liu, E.; Mian, S.; Pillittere, J.; Bonilla, E.; Banki, K.; Perl, A. Successful Treatment of Secondary Macrophage Activation Syndrome with Emapalumab in a Patient with Newly Diagnosed Adult-Onset Still’s Disease: Case Report and Review of the Literature. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, W.; O’Shea, J. JAKS AND STATS: Biological Implications. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1998, 16, 293–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, D.; Kanno, Y.; Villarino, A.; Ward, M.; Gadina, M.; O’Shea, J. JAK Inhibition as a Therapeutic Strategy for Immune and Inflammatory Diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 843–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillard, L.; Mitrovic, S.; Reumaux, H.; Michaud, M.; Cohen, F.; Pouchot, J.; Fautrel, B. AB0772 JAK Inhibitors in Refractory Adult and Childhood Onset Still’s Disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 1412–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacar, M.; Fitton, J.; Gough, A.; Buch, M.; McGonagle, D.; Savic, S. Mixed Results with Baricitinib in Biological-Resistant Adult-Onset Still’s Disease and Undifferentiated Systemic Autoinflammatory Disease. RMD Open 2020, 6, e001246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Wang, M.; Jia, J.; Teng, J.; Chi, H.; Liu, T.; Liu, H.; Cheng, X.; Ye, J.; Su, Y.; et al. Tofacitinib in Refractory Adult-Onset Still’s Disease: 14 Cases from a Single Centre in China. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 842–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoff, P.; Walther, M.; Wesselmann, H.; Weinerth, J.; Feist, E.; Ohrndorf, S. Erfolgreiche Behandlung Eines Adulten Morbus Still Mit Tofacitinib Bei Einer HIV-2-Positiven Patientin. Z. Rheumatol. 2020, 79, 1046–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, R.; Guan, P.; Sprague, L.; Verbist, K.; Tedrick, P.; An, Q.; Cheng, C.; Kurachi, M.; Levine, R.; Wherry, E.; et al. Janus Kinase Inhibition Lessens Inflammation and Ameliorates Disease in Murine Models of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Blood 2016, 127, 1666–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Wei, A.; Ma, H.H.; Zhang, L.; Lian, H.Y.; Wang, D.; Zhao, Y.Z.; Cui, L.; Li, W.J.; Yang, Y.; et al. A Pilot Study of Ruxolitinib as a Front-Line Therapy for 12 Children with Secondary Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Haematologica 2020, 106, 1892–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greven, D.; Cohen, E.; Gerlag, D.; Campbell, J.; Woods, J.; Davis, N.; van Nieuwenhuijze, A.; Lewis, A.; Heasmen, S.; McCourt, M.; et al. Preclinical Characterisation of the GM-CSF Receptor as a Therapeutic Target in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 74, 1924–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, A.; Louis, C.; Robinson, M.; Saleh, R.; Sleeman, M.; Hamilton, J. Granulocyte Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor Receptor α Expression and Its Targeting in Antigen-Induced Arthritis and Inflammation. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, J. GM-CSF in Inflammation. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 217, e20190945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, G.; Cavalli, G.; Campochiaro, C.; Della-Torre, E.; Angelillo, P.; Tomelleri, A.; Boffini, N.; Tentori, S.; Mette, F.; Farina, N.; et al. GM-CSF Blockade with Mavrilimumab in Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia and Systemic Hyperinflammation: A Single-Centre, Prospective Cohort Study. Lancet 2020, 2, e465–e473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliviero, F.; Bindoli, S.; Scanu, A.; Feist, E.; Doria, A.; Galozzi, P.; Sfriso, P. Autoinflammatory Mechanisms in Crystal-Induced Arthritis. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klück, V.; Jansen, T.; Janssen, M.; Comarniceanu, A.; Efdé, M.; Tengesdal, I.; Schraa, K.; Cleophas, M.; Scribner, C.; Skouras, D.; et al. Dapansutrile, an Oral Selective NLRP3 Inflammasome Inhibitor, for Treatment of Gout Flares: An Open-Label, Dose-Adaptive, Proof-Of-Concept, Phase 2a Trial. Lancet 2020, 2, e270–e280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.; Aiello, D.; Atianand, M.; Ricci, E.; Gandhi, P.; Hall, L.; Byron, M.; Monks, B.; Henry-Bezy, M.; Lawrence, J.; et al. A Long Noncoding RNA Mediates Both Activation and Repression of Immune Response Genes. Science 2013, 341, 789–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathy, N.; Chen, X. Long Non-Coding RNAs (LncRNAs) and Their Transcriptional Control of Inflammatory Responses. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 12375–12382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atianand, M.; Fitzgerald, K. Long Non-Coding RNAs and Control of Gene Expression in the Immune System. Trends Mol. Med. 2014, 20, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjicharalambous, M.R.; Lindsay, M.A. Long Non-Coding RNAs and the Innate Immune Response. Non-Coding RNA 2019, 5, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Chen, P.; Lan, J.; Chang, C.; Chang, J.; Chang, S.; Lin, C.; Chen, D. Expression Signature of Inflammation-Associated Long Non-Coding RNAs in Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2021, 39, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörner, T.; Burmester, G. The Role of B Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2003, 15, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi-Simab, K. Successful Treatment of Refractory Adult Onset Still’s Disease with Rituximab. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2006, 65, 1117–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babacan, T.; Onat, A.; Pehlivan, Y.; Comez, G.; Karakök, M. Successful Treatment of Refractory Adult Still’s Disease and Membranous Glomerulonephritis with Infliximab. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2010, 29, 423–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrowski, R.; Tehrani, R.; Kadanoff, R. Refractory Adult-Onset Still Disease Successfully Treated with Abatacept. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2011, 17, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Permal, S.; Wechsler, B.; Cabane, J.; Perrot, S.; Blum, L.; Imbert, J. Traitement de la Maladie de Still de L’adulte par Immunoglobulines Intraveineuses. Rev. Med. Interne 1995, 16, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruscitti, P.; Cipriani, P.; Ciccia, F.; Masedu, F.; Liakouli, V.; Carubbi, F.; Berardicurti, O.; Guggino, G.; Di Benedetto, P.; Di Bartolomeo, S.; et al. Prognostic Factors of Macrophage Activation Syndrome, At the Time of Diagnosis, in Adult Patients Affected by Autoimmune Disease: Analysis of 41 Cases Collected in 2 Rheumatologic Centers. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janka, G. Familial and Acquired Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2006, 166, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grom, A.; Mellins, E. Macrophage Activation Syndrome: Advances towards Understanding Pathogenesis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2010, 22, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grom, A.; Horne, A.; De Benedetti, F. Macrophage Activation Syndrome in the Era of Biologic Therapy. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 12, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravelli, A.; Grom, A.; Behrens, E.; Cron, R. Macrophage Activation Syndrome as Part of Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: Diagnosis, Genetics, Pathophysiology and Treatment. Genes Immun. 2012, 13, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sönmez, H.; Demir, S.; Bilginer, Y.; Özen, S. Anakinra Treatment in Macrophage Activation Syndrome: A Single Center Experience and Systemic Review of Literature. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 3329–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Yamashita, H.; Kaneko, H.; Mimori, A. Benefit and a Possible Risk of Tocilizumab Therapy for Adult-Onset Still’s Disease Accompanied by Macrophage-Activation Syndrome. Mod. Rheumatol. 2011, 21, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokota, S.; Itoh, Y.; Morio, T.; Sumitomo, N.; Daimaru, K.; Minota, S. Macrophage Activation Syndrome in Patients with Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis under Treatment with Tocilizumab. J. Rheumatol. 2015, 42, 712–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, M.; Mizuta, M.; Okamoto, N.; Yasumi, T.; Iwata, N.; Umebayashi, H.; Okura, Y.; Kinjo, N.; Kubota, T.; Nakagishi, Y.; et al. Tocilizumab Modifies Clinical and Laboratory Features of Macrophage Activation Syndrome Complicating Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. Pediatr. Rheumatol. 2020, 18, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naniwa, T.; Uehara, K.; Yamabe, T.; Ohmura, S. Reintroduction of Tocilizumab Elicited Macrophage Activation Syndrome in a Patient with Adult-Onset Still’s Disease with a Previous Successful Tocilizumab Treatment. Mod. Rheumatol. 2021, 5, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Macovei, L.A.; Burlui, A.; Bratoiu, I.; Rezus, C.; Cardoneanu, A.; Richter, P.; Szalontay, A.; Rezus, E. Adult-Onset Still’s Disease—A Complex Disease, a Challenging Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12810. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232112810
Macovei LA, Burlui A, Bratoiu I, Rezus C, Cardoneanu A, Richter P, Szalontay A, Rezus E. Adult-Onset Still’s Disease—A Complex Disease, a Challenging Treatment. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(21):12810. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232112810
Chicago/Turabian StyleMacovei, Luana Andreea, Alexandra Burlui, Ioana Bratoiu, Ciprian Rezus, Anca Cardoneanu, Patricia Richter, Andreea Szalontay, and Elena Rezus. 2022. "Adult-Onset Still’s Disease—A Complex Disease, a Challenging Treatment" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 21: 12810. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232112810
APA StyleMacovei, L. A., Burlui, A., Bratoiu, I., Rezus, C., Cardoneanu, A., Richter, P., Szalontay, A., & Rezus, E. (2022). Adult-Onset Still’s Disease—A Complex Disease, a Challenging Treatment. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(21), 12810. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232112810






