Basic Leucine Zipper Transcription Factors as Important Regulators of Leydig Cells’ Functions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Classification of bZIP Transcription Factors
3. Mechanisms of Gene Regulation by bZIP Transcription Factors
3.1. CREB-like Subfamily Members
3.2. AP-1 Members
3.3. CEBP Members
3.4. Maf-Related Members
3.5. XBP1-Related Members
3.6. CREB3-like Subfamily Members
3.7. ATF-4 Related Members
4. bZIP Transcription Factors and Leydig Cell Proliferation and Development
4.1. CREB-Related Members
4.2. AP-1 Members
4.3. CEBP-Related Members
4.4. Transmembrane bZIP Transcription Factors
5. bZIP Transcription Factors and Steroidogenesis
5.1. CREB-Related Members
5.2. AP-1 Members
NFE2 Subfamily Members
5.3. CEBP Members
5.4. Transmembrane bZIP Transcription Factors
6. bZIP Transcription Factors and INSL3
7. bZIP Transcription Factors and Leydig Cell Communication
7.1. CREB Members
7.2. AP-1 Members
7.2.1. NFE2 Subfamily Members
7.2.2. ATF3-like Subfamily Members
7.3. MAF-Related Members
7.4. CEBP Members
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wingender, E.; Schoeps, T.; Haubrock, M.; Krull, M.; Dönitz, J. TFClass: Expanding the Classification of Human Transcription Factors to Their Mammalian Orthologs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D343–D347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayr, B.; Montminy, M. Transcriptional Regulation by the Phosphorylation-Dependent Factor CREB. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hai, T.; Curran, T. Cross-Family Dimerization of Transcription Factors Fos/Jun and ATF/CREB Alters DNA Binding Specificity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 3720–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radhakrishnan, I.; Pérez-Alvarado, G.C.; Parker, D.; Dyson, H.J.; Montminy, M.R.; Wright, P.E. Solution Structure of the KIX Domain of CBP Bound to the Transactivation Domain of CREB: A Model for Activator:Coactivator Interactions. Cell 1997, 91, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clem, B.F.; Hudson, E.A.; Clark, B.J. Cyclic Adenosine 3′,5′-Monophosphate (CAMP) Enhances CAMP-Responsive Element Binding (CREB) Protein Phosphorylation and Phospho-CREB Interaction with the Mouse Steroidogenic Acute Regulatory Protein Gene Promoter. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 1348–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Inaoka, Y.; Yazawa, T.; Uesaka, M.; Mizutani, T.; Yamada, K.; Miyamoto, K. Regulation of NGFI-B/Nur77 Gene Expression in the Rat Ovary and in Leydig Tumor Cells MA-10. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2008, 75, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dash, P.K.; Karl, K.A.; Colicos, M.A.; Prywes, R.; Kandel, E.R. CAMP Response Element-Binding Protein Is Activated by Ca2+/Calmodulin- as Well as CAMP-Dependent Protein Kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 5061–5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, M.; Thompson, M.A.; Greenberg, M.E. CREB: A Ca(2+)-Regulated Transcription Factor Phosphorylated by Calmodulin-Dependent Kinases. Science 1991, 252, 1427–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, K.; Montminy, M. CREB Is a Regulatory Target for the Protein Kinase Akt/PKB. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 32377–32379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginty, D.D.; Bonni, A.; Greenberg, M.E. Nerve Growth Factor Activates a Ras-Dependent Protein Kinase That Stimulates c-Fos Transcription via Phosphorylation of CREB. Cell 1994, 77, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oury, F.; Sumara, G.; Sumara, O.; Ferron, M.; Chang, H.; Smith, C.E.; Hermo, L.; Suarez, S.; Roth, B.L.; Ducy, P.; et al. Endocrine Regulation of Male Fertility by the Skeleton. Cell 2011, 144, 796–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, Y.; King, S.R.; Khan, S.A.; Stocco, D.M. Involvement of Protein Kinase C and Cyclic Adenosine 3’,5’-Monophosphate-Dependent Kinase in Steroidogenic Acute Regulatory Protein Expression and Steroid Biosynthesis in Leydig Cells. Biol. Reprod. 2005, 73, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manna, P.R.; Chandrala, S.P.; Jo, Y.; Stocco, D.M. CAMP-Independent Signaling Regulates Steroidogenesis in Mouse Leydig Cells in the Absence of StAR Phosphorylation. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 37, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stocco, D.M.; Wang, X.; Jo, Y.; Manna, P.R. Multiple Signaling Pathways Regulating Steroidogenesis and Steroidogenic Acute Regulatory Protein Expression: More Complicated than We Thought. Mol. Endocrinol. 2005, 19, 2647–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manna, P.R.; Soh, J.-W.; Stocco, D.M. The Involvement of Specific PKC Isoenzymes in Phorbol Ester-Mediated Regulation of Steroidogenic Acute Regulatory Protein Expression and Steroid Synthesis in Mouse Leydig Cells. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manna, P.R.; Jo, Y.; Stocco, D.M. Regulation of Leydig Cell Steroidogenesis by Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase 1/2: Role of Protein Kinase A and Protein Kinase C Signaling. J. Endocrinol. 2007, 193, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sassone-Corsi, P. Coupling Gene Expression to CAMP Signalling: Role of CREB and CREM. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1998, 30, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassone-Corsi, P. Transcription Factors Responsive to CAMP. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1995, 11, 355–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, P.R.; Eubank, D.W.; Lalli, E.; Sassone-Corsi, P.; Stocco, D.M. Transcriptional Regulation of the Mouse Steroidogenic Acute Regulatory Protein Gene by the CAMP Response-Element Binding Protein and Steroidogenic Factor 1. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2003, 30, 381–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, C.A.; Foulkes, N.S.; Lalli, E.; Sassone-Corsi, P. Inducibility and Negative Autoregulation of CREM: An Alternative Promoter Directs the Expression of ICER, an Early Response Repressor. Cell 1993, 75, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laoide, B.M.; Foulkes, N.S.; Schlotter, F.; Sassone-Corsi, P. The Functional Versatility of CREM Is Determined by Its Modular Structure. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 1179–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurst, H.C.; Totty, N.F.; Jones, N.C. Identification and Functional Characterisation of the Cellular Activating Transcription Factor 43 (ATF-43) Protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991, 19, 4601–4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, T.W.; Liu, F.; Coukos, W.J.; Green, M.R. Transcription Factor ATF CDNA Clones: An Extensive Family of Leucine Zipper Proteins Able to Selectively Form DNA-Binding Heterodimers. Genes Dev. 1989, 3, 2083–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoeffler, J.P.; Lustbader, J.W.; Chen, C.Y. Identification of Multiple Nuclear Factors That Interact with Cyclic Adenosine 3’,5’-Monophosphate Response Element-Binding Protein and Activating Transcription Factor-2 by Protein-Protein Interactions. Mol. Endocrinol. 1991, 5, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ivashkiv, L.B.; Liou, H.C.; Kara, C.J.; Lamph, W.W.; Verma, I.M.; Glimcher, L.H. MXBP/CRE-BP2 and c-Jun Form a Complex Which Binds to the Cyclic AMP, but Not to the 12-O-Tetradecanoylphorbol-13-Acetate, Response Element. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1990, 10, 1609–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlén, M.; Fagerberg, L.; Hallström, B.M.; Lindskog, C.; Oksvold, P.; Mardinoglu, A.; Sivertsson, Å.; Kampf, C.; Sjöstedt, E.; Asplund, A.; et al. Proteomics. Tissue-Based Map of the Human Proteome. Science 2015, 347, 1260419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimomura, A.; Ogawa, Y.; Kitani, T.; Fujisawa, H.; Hagiwara, M. Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase II Potentiates Transcriptional Activation through Activating Transcription Factor 1 but Not CAMP Response Element-Binding Protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 17957–17960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Shea, E.K.; Rutkowski, R.; Kim, P.S. Mechanism of Specificity in the Fos-Jun Oncoprotein Heterodimer. Cell 1992, 68, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryseck, R.P.; Bravo, R. C-JUN, JUN B, and JUN D Differ in Their Binding Affinities to AP-1 and CRE Consensus Sequences: Effect of FOS Proteins. Oncogene 1991, 6, 533–542. [Google Scholar]
- Halazonetis, T.D.; Georgopoulos, K.; Greenberg, M.E.; Leder, P. C-Jun Dimerizes with Itself and with c-Fos, Forming Complexes of Different DNA Binding Affinities. Cell 1988, 55, 917–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angel, P.; Karin, M. The Role of Jun, Fos and the AP-1 Complex in Cell-Proliferation and Transformation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Rev. Cancer 1991, 1072, 129–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazon, H.; Barbeau, B.; Mesnard, J.-M.; Peloponese, J.-M.J. Hijacking of the AP-1 Signaling Pathway during Development of ATL. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karin, M. The Regulation of AP-1 Activity by Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 16483–16486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauscher, F.J.; Voulalas, P.J.; Franza, B.R.; Curran, T. Fos and Jun Bind Cooperatively to the AP-1 Site: Reconstitution in Vitro. Genes Dev. 1988, 2, 1687–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Okuno, H.; Yoshida, T.; Endo, T.; Nishina, H.; Iba, H. Difference in Transcriptional Regulatory Function between C-Fos and Fra-2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991, 19, 5537–5542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakabeppu, Y.; Nathans, D. The Basic Region of Fos Mediates Specific DNA Binding. EMBO J. 1989, 8, 3833–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jochum, W.; Passegué, E.; Wagner, E.F. AP-1 in Mouse Development and Tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2001, 20, 2401–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passegué, E.; Jochum, W.; Behrens, A.; Ricci, R.; Wagner, E.F. JunB Can Substitute for Jun in Mouse Development and Cell Proliferation. Nat. Genet. 2002, 30, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, W.J.; Smeal, T.; Defize, L.H.; Angel, P.; Woodgett, J.R.; Karin, M.; Hunter, T. Activation of Protein Kinase C Decreases Phosphorylation of C-Jun at Sites That Negatively Regulate Its DNA-Binding Activity. Cell 1991, 64, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abate, C.; Baker, S.J.; Lees-Miller, S.P.; Anderson, C.W.; Marshak, D.R.; Curran, T. Dimerization and DNA Binding Alter Phosphorylation of Fos and Jun. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 6766–6770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dam, H.; Duyndam, M.; Rottier, R.; Bosch, A.; de Vries-Smits, L.; Herrlich, P.; Zantema, A.; Angel, P.; van der Eb, A.J. Heterodimer Formation of CJun and ATF-2 Is Responsible for Induction of c-Jun by the 243 Amino Acid Adenovirus E1A Protein. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.C.; Richards, J.S. Regulation of AP1 (Jun/Fos) Factor Expression and Activation in Ovarian Granulosa Cells: Relation of JunD and Fra2 to terminal differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 33718–33728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, L.M.; Kerppola, T.K.; Vendrell, M.; Luk, D.; Smeyne, R.J.; Morgan, J.I.; Curran, T. Regulation of C-Los Expression in Transgenic Mice Requires Multiple Interdependent Transcription Control Elements. Neuron 1995, 14, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, M.; McFadden, G.; Greenberg, M.E. Membrane Depolarization and Calcium Induce C-Fos Transcription via Phosphorylation of Transcription Factor CREB. Neuron 1990, 4, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, B.J.; Hayes, T.E.; Hoban, C.J.; Cochran, B.H. The SIF Binding Element Confers Sis/PDGF Inducibility onto the c-Fos Promoter. EMBO J. 1990, 9, 4477–4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, M.; Dougan, S.T.; McFadden, G.; Greenberg, M.E. Calcium and Growth Factor Pathways of C-Fos Transcriptional Activation Require Distinct Upstream Regulatory Sequences. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1988, 8, 2787–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavigelli, M.; Dolfi, F.; Claret, F.X.; Karin, M. Induction of C-Fos Expression through JNK-Mediated TCF/Elk-1 Phosphorylation. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 5957–5964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowski, H.B.; Shuai, K.; Darnell, J.E.; Gilman, M.Z. A Common Nuclear Signal Transduction Pathway Activated by Growth Factor and Cytokine Receptors. Science 1993, 261, 1739–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoey, T.; Schindler, U. STAT Structure and Function in Signaling. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 1998, 8, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.; Nebert, D.W.; Ozato, K. The AP-1 Site and the CAMP- and Serum Response Elements of the c-Fos Gene Are Constitutively Occupied in Vivo. DNA Cell Biol. 1991, 10, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angel, P.; Hattori, K.; Smeal, T.; Karin, M. The Jun Proto-Oncogene Is Positively Autoregulated by Its Product, Jun/AP-1. Cell 1988, 55, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozek, D.; Pfeifer, G.P. In Vivo Protein-DNA Interactions at the c-Jun Promoter: Preformed Complexes Mediate the UV Response. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1993, 13, 5490–5499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sassone-Corsi, P.; Sisson, J.C.; Verma, I.M. Transcriptional Autoregulation of the Proto-Oncogene Fos. Nature 1988, 334, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, R.; Boyle, W.J.; Meek, J.; Smeal, T.; Hunter, T.; Karin, M. The C-Fos Protein Interacts with c-Jun/AP-1 to Stimulate Transcription of AP-1 Responsive Genes. Cell 1988, 54, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibi, M.; Lin, A.; Smeal, T.; Minden, A.; Karin, M. Identification of an Oncoprotein- and UV-Responsive Protein Kinase That Binds and Potentiates the c-Jun Activation Domain. Genes Dev. 1993, 7, 2135–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.; Frost, J.; Deng, T.; Smeal, T.; al-Alawi, N.; Kikkawa, U.; Hunter, T.; Brenner, D.; Karin, M. Casein Kinase II Is a Negative Regulator of C-Jun DNA Binding and AP-1 Activity. Cell 1992, 70, 777–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, S.; Davis, R.J.; McLaren, A.; Cohen, P. A Reinvestigation of the Multisite Phosphorylation of the Transcription Factor C-Jun. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 3876–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, J.; Alberts, A.S.; Brindle, P.; Claret, F.X.; Smeal, T.; Karin, M.; Feramisco, J.; Montminy, M. Activation of CAMP and Mitogen Responsive Genes Relies on a Common Nuclear Factor. Nature 1994, 370, 226–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelson, K.G.; Contois, L.R.; Tevosian, S.G.; Davis, R.J.; Paulson, K.E. Independent Regulation of JNK/P38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases by Metabolic Oxidative Stress in the Liver. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 12908–12913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dephoure, N.; Zhou, C.; Villén, J.; Beausoleil, S.A.; Bakalarski, C.E.; Elledge, S.J.; Gygi, S.P. A Quantitative Atlas of Mitotic Phosphorylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10762–10767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.; Karin, M. C-Fos Transcriptional Activity Stimulated by H-Ras-Activated Protein Kinase Distinct from JNK and ERK. Nature 1994, 371, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, L.O.; Smith, S.; Chen, R.-H.; Fingar, D.C.; Blenis, J. Molecular Interpretation of ERK Signal Duration by Immediate Early Gene Products. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002, 4, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, M.J.; Stork, P.J.S. Sustained Activation of Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase by Nerve Growth Factor Regulates c-Fos Protein Stabilization and Transactivation in PC12 Cells. J Neurochem 2006, 99, 1480–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tratner, I.; Ofir, R.; Verma, I.M. Alteration of a Cyclic AMP-Dependent Protein Kinase Phosphorylation Site in the c-Fos Protein Augments Its Transforming Potential. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1992, 12, 998–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallunki, T.; Deng, T.; Hibi, M.; Karin, M. C-Jun Can Recruit JNK to Phosphorylate Dimerization Partners via Specific Docking Interactions. Cell 1996, 87, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, S.H.; Berthelon, M.C.; Avallet, O.; Saez, J.M. Regulation of C-Fos, c-Jun, Jun-B, and c-Myc Messenger Ribonucleic Acids by Gonadotropin and Growth Factors in Cultured Pig Leydig Cell. Endocrinology 1991, 129, 1243–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vietor, I.; Schwenger, P.; Li, W.; Schlessinger, J.; Vilcek, J. Tumor Necrosis Factor-Induced Activation and Increased Tyrosine Phosphorylation of Mitogen-Activated Protein (MAP) Kinase in Human Fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 18994–18999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, I.; Hughes, R.T.; Mayer, B.J.; Yee, K.; Woodgett, J.R.; Avruch, J.; Kyriakis, J.M.; Zon, L.I. Role of SAPK/ERK Kinase-1 in the Stress-Activated Pathway Regulating Transcription Factor c-Jun. Nature 1994, 372, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hales, K.H.; Watanabe, G.; Lee, R.J.; Pestell, R.G.; Hales, D.B. The Effect of Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha and CAMP on Induction of AP-1 Activity in MA-10 Tumor Leydig Cells. Endocrine 1997, 6, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, K.Y.; Roby, K.F.; Terranova, P.F. Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF) Suppresses CAMP Response Element (CRE) Activity and Nuclear CRE Binding Protein in MA-10 Mouse Leydig Tumor Cells. Endocrine 2005, 27, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.J.; Tremblay, J.J. The Nuclear Receptors NUR77 and SF1 Play Additive Roles with C-JUN through Distinct Elements on the Mouse Star Promoter. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2009, 42, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roumaud, P.; Rwigemera, A.; Martin, L.J. Transcription Factors SF1 and CJUN Cooperate to Activate the Fdx1 Promoter in MA-10 Leydig Cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 171, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, S.; Nagaya, T.; Suganuma, N.; Tomoda, Y.; Seo, H. Inductions of Immediate Early Genes (IEGS) and Ref-1 by Human Chorionic Gonadotropin in Murine Leydig Cell Line (MA-10). Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int. 1998, 44, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegner, M.; Cao, Z.; Rosenfeld, M.G. Calcium-Regulated Phosphorylation within the Leucine Zipper of C/EBP Beta. Science 1992, 256, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Nie, L.; Kim, S.-H.; Sun, X.-H. STAT5-Induced Id-1 Transcription Involves Recruitment of HDAC1 and Deacetylation of C/EBPbeta. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 893–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramji, D.P.; Foka, P. CCAAT/Enhancer-Binding Proteins: Structure, Function and Regulation. Biochem. J. 2002, 365, 561–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalbant, D.; Williams, S.C.; Stocco, D.M.; Khan, S.A. Luteinizing Hormone-Dependent Gene Regulation in Leydig Cells May Be Mediated by CCAAT/Enhancer-Binding Protein-Beta. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Newman, J.R.S.; Keating, A.E. Comprehensive Identification of Human BZIP Interactions with Coiled-Coil Arrays. Science 2003, 300, 2097–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Kinoshita, S.; Sasagawa, T.; Sasaki, K.; Naruto, M.; Kishimoto, T.; Akira, S. Phosphorylation at Threonine-235 by a Ras-Dependent Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Cascade Is Essential for Transcription Factor NF-IL6. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 2207–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, E.M.; Sealy, L. Modification of CCAAT/Enhancer-Binding Protein-Beta by the Small Ubiquitin-like Modifier (SUMO) Family Members, SUMO-2 and SUMO-3. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 33416–33421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, K.; Noda, M.; Nishizawa, M. Maf Nuclear Oncoprotein Recognizes Sequences Related to an AP-1 Site and Forms Heterodimers with Both Fos and Jun. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1994, 14, 700–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFalco, T.; Takahashi, S.; Capel, B. Two Distinct Origins for Leydig Cell Progenitors in the Fetal Testis. Dev. Biol. 2011, 352, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawki, H.H.; Oishi, H.; Usui, T.; Kitadate, Y.; Basha, W.A.; Abdellatif, A.M.; Hasegawa, K.; Okada, R.; Mochida, K.; El-Shemy, H.A.; et al. MAFB Is Dispensable for the Fetal Testis Morphogenesis and the Maintenance of Spermatogenesis in Adult Mice. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, H.C.; Boothby, M.R.; Glimcher, L.H. Distinct Cloned Class II MHC DNA Binding Proteins Recognize the X Box Transcription Element. Science 1988, 242, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sriburi, R.; Jackowski, S.; Mori, K.; Brewer, J.W. XBP1: A Link between the Unfolded Protein Response, Lipid Biosynthesis, and Biogenesis of the Endoplasmic Reticulum. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 167, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.-H.; Heidtman, K.; Hotamisligil, G.S.; Glimcher, L.H. Dual and Opposing Roles of the Unfolded Protein Response Regulated by IRE1alpha and XBP1 in Proinsulin Processing and Insulin Secretion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 8885–8890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, H.; Yang, Z.; Yang, W.; Zhao, C.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Q. Melatonin Receptor Depletion Suppressed HCG-Induced Testosterone Expression in Mouse Leydig Cells. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2019, 24, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, F.-C.; Wang, S.-C.; Chang, M.-M.; Pan, B.-S.; Wong, K.-L.; Cheng, K.-S.; So, E.C.; Huang, B.-M. Midazolam Activates Caspase, MAPKs and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Pathways, and Inhibits Cell Cycle and Akt Pathway, to Induce Apoptosis in TM3 Mouse Leydig Progenitor Cells. Onco Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 1475–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-J.; Kim, T.-S.; Park, C.-K.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, J.-M.; Lee, K.-S.; Lee, I.-K.; Park, J.-W.; Lawson, M.A.; Lee, D.-S. HCG-Induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Triggers Apoptosis and Reduces Steroidogenic Enzyme Expression through Activating Transcription Factor 6 in Leydig Cells of the Testis. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2013, 50, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.; Matsui, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Okada, T.; Mori, K. XBP1 MRNA Is Induced by ATF6 and Spliced by IRE1 in Response to ER Stress to Produce a Highly Active Transcription Factor. Cell 2001, 107, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, S.J.; Liou, H.C.; Davidon, R.; Strominger, J.L.; Glimcher, L.H. Human X-Box-Binding Protein 1 Is Required for the Transcription of a Subset of Human Class II Major Histocompatibility Genes and Forms a Heterodimer with c-Fos. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 4309–4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Sato, T.; Matsui, T.; Sato, M.; Okada, T.; Yoshida, H.; Harada, A.; Mori, K. Transcriptional Induction of Mammalian ER Quality Control Proteins Is Mediated by Single or Combined Action of ATF6alpha and XBP1. Dev. Cell 2007, 13, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, T.; Saito, A.; Hino, S.; Kondo, S.; Kanemoto, S.; Chihara, K.; Sekiya, H.; Tsumagari, K.; Ochiai, K.; Yoshinaga, K.; et al. Signalling Mediated by the Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Transducer OASIS Is Involved in Bone Formation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Shen, X.; Wu, J.; Sakaki, K.; Saunders, T.; Rutkowski, D.T.; Back, S.H.; Kaufman, R.J. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Activates Cleavage of CREBH to Induce a Systemic Inflammatory Response. Cell 2006, 124, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podust, L.M.; Krezel, A.M.; Kim, Y. Crystal Structure of the CCAAT Box/Enhancer-Binding Protein Beta Activating Transcription Factor-4 Basic Leucine Zipper Heterodimer in the Absence of DNA. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, J.V.; Vermeulen, M.; Santamaria, A.; Kumar, C.; Miller, M.L.; Jensen, L.J.; Gnad, F.; Cox, J.; Jensen, T.S.; Nigg, E.A.; et al. Quantitative Phosphoproteomics Reveals Widespread Full Phosphorylation Site Occupancy during Mitosis. Sci. Signal. 2010, 3, ra3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Cesare, D.; Sassone-Corsi, P. Transcriptional Regulation by Cyclic AMP-Responsive Factors. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 2000, 64, 343–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hai, T.; Wolfgang, C.D.; Marsee, D.K.; Allen, A.E.; Sivaprasad, U. ATF3 and Stress Responses. Gene Expr. 1999, 7, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dluzen, D.; Li, G.; Tacelosky, D.; Moreau, M.; Liu, D.X. BCL-2 Is a Downstream Target of ATF5 That Mediates the Prosurvival Function of ATF5 in a Cell Type-Dependent Manner. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 7705–7713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, D.; O’Hare, P. Transmembrane BZIP Transcription Factors in ER Stress Signaling and the Unfolded Protein Response. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2007, 9, 2305–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Aviles, G.; Liu, Y.; Tian, R.; Unger, B.A.; Lin, Y.-H.T.; Wiita, A.P.; Xu, K.; Correia, M.A.; Kampmann, M. Mitochondrial Stress Is Relayed to the Cytosol by an OMA1-DELE1-HRI Pathway. Nature 2020, 579, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohoka, N.; Yoshii, S.; Hattori, T.; Onozaki, K.; Hayashi, H. TRB3, a Novel ER Stress-Inducible Gene, Is Induced via ATF4-CHOP Pathway and Is Involved in Cell Death. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 1243–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basque, A.; Nguyen, H.T.; Touaibia, M.; Martin, L.J. Gigantol Improves Cholesterol Metabolism and Progesterone Biosynthesis in MA-10 Leydig Cells. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Couture, R.; Touaibia, M.; Martin, L.J. Transcriptome Modulation Following Administration of Luteolin to Bleomycin-Etoposide-Cisplatin Chemotherapy on Rat LC540 Tumor Leydig Cells. Andrologia 2021, 53, e13960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauci, S.; Helbig, A.O.; Slijper, M.; Krijgsveld, J.; Heck, A.J.R.; Mohammed, S. Lys-N and Trypsin Cover Complementary Parts of the Phosphoproteome in a Refined SCX-Based Approach. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 4493–4501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Sun, M.; Jiang, J.; Shen, X.; Sun, Q.; Liu, W.; Shen, H.; Gu, J. Cyclin D3 Interacts with Human Activating Transcription Factor 5 and Potentiates Its Transcription Activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 321, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ge, R.-S.; Zirkin, B.R. Leydig Cells: From Stem Cells to Aging. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2009, 306, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teerds, K.J.; Rijntjes, E.; Veldhuizen-Tsoerkan, M.B.; Rommerts, F.F.G.; de Boer-Brouwer, M. The Development of Rat Leydig Cell Progenitors in Vitro: How Essential Is Luteinising Hormone? J. Endocrinol. 2007, 194, 579–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, R.S.; Hardy, D.O.; Catterall, J.F.; Hardy, M.P. Opposing Changes in 3alpha-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Oxidative and Reductive Activities in Rat Leydig Cells during Pubertal Development. Biol. Reprod. 1999, 60, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benton, L.; Shan, L.X.; Hardy, M.P. Differentiation of Adult Leydig Cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1995, 53, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaukua, J.; Pekkarinen, T.; Sane, T.; Mustajoki, P. Sex Hormones and Sexual Function in Obese Men Losing Weight. Obes. Res. 2003, 11, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, W.H. Molecular Mechanisms of Testosterone Action in Spermatogenesis. Steroids 2009, 74, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, D.; Cho, Y.-Y.; Lau, A.T.Y.; Zhang, J.; Ma, W.-Y.; Bode, A.M.; Dong, Z. Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 3-Mediated Activating Transcription Factor 1 Phosphorylation Enhances Cell Transformation. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 7650–7660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Meng, Q.; Yang, L.; Yang, D.; Guo, W.; Lin, P.; Chen, H.; Tang, K.; Wang, A.; Jin, Y. Luman/CREB3 Knock-down Inhibit HCG Induced MLTC-1 Apoptosis. Theriogenology 2021, 161, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisdom, R.; Johnson, R.S.; Moore, C. C-Jun Regulates Cell Cycle Progression and Apoptosis by Distinct Mechanisms. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakiri, L.; Lallemand, D.; Bossy-Wetzel, E.; Yaniv, M. Cell Cycle-Dependent Variations in c-Jun and JunB Phosphorylation: A Role in the Control of Cyclin D1 Expression. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 2056–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weitzman, J.B.; Fiette, L.; Matsuo, K.; Yaniv, M. JunD Protects Cells from P53-Dependent Senescence and Apoptosis. Mol Cell 2000, 6, 1109–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, F.; Wen, W.; Zykova, T.; Li, X.; Liu, K.; Peng, C.; Ma, W.; Shi, G.; et al. P21-Activated Protein Kinase (PAK2)-Mediated c-Jun Phosphorylation at 5 Threonine Sites Promotes Cell Transformation. Carcinogenesis 2011, 32, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eferl, R.; Wagner, E.F. AP-1: A Double-Edged Sword in Tumorigenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piechaczyk, M.; Farràs, R. Regulation and Function of JunB in Cell Proliferation. Biochem Soc Trans 2008, 36, 864–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karin, M.; Liu, Z.; Zandi, E. AP-1 Function and Regulation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1997, 9, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, R.-S.; Dong, Q.; Sottas, C.M.; Chen, H.; Zirkin, B.R.; Hardy, M.P. Gene Expression in Rat Leydig Cells during Development from the Progenitor to Adult Stage: A Cluster Analysis. Biol. Reprod. 2005, 72, 1405–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, X.; Chen, P.; Ji, M.; Wen, X.; Chen, D.; Zhao, X.; Huang, F.; Wang, J.; Shao, J.; Xie, J.; et al. Identification of Rat Testicular Leydig Precursor Cells by Single-Cell-RNA-Sequence Analysis. Front. Cell Dev Biol. 2022, 10, 805249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, L.X.; Hardy, M.P. Developmental Changes in Levels of Luteinizing Hormone Receptor and Androgen Receptor in Rat Leydig Cells. Endocrinology 1992, 131, 1107–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, L.; O’Shaughnessy, P.J. Testicular Steroidogenesis in the Testicular Feminized (Tfm) Mouse: Loss of 17 Alpha-Hydroxylase Activity. J. Endocrinol. 1991, 131, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, M.-Y.; Yeh, S.-D.; Wang, R.-S.; Yeh, S.; Zhang, C.; Lin, H.-Y.; Tzeng, C.-R.; Chang, C. Differential Effects of Spermatogenesis and Fertility in Mice Lacking Androgen Receptor in Individual Testis Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 18975–18980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Lin, H.-Y.; Yeh, S.-D.; Yu, I.-C.; Wang, R.-S.; Chen, Y.-T.; Zhang, C.; Altuwaijri, S.; Chen, L.-M.; Chuang, K.-H.; et al. Infertility with Defective Spermatogenesis and Steroidogenesis in Male Mice Lacking Androgen Receptor in Leydig Cells. Endocrine 2007, 32, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arango, N.A.; Kobayashi, A.; Wang, Y.; Jamin, S.P.; Lee, H.-H.; Orvis, G.D.; Behringer, R.R. A Mesenchymal Perspective of Müllerian Duct Differentiation and Regression in Amhr2-LacZ Mice. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2008, 75, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shemshedini, L.; Knauthe, R.; Sassone-Corsi, P.; Pornon, A.; Gronemeyer, H. Cell-Specific Inhibitory and Stimulatory Effects of Fos and Jun on Transcription Activation by Nuclear Receptors. EMBO J. 1991, 10, 3839–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bubulya, A.; Wise, S.C.; Shen, X.Q.; Burmeister, L.A.; Shemshedini, L. C-Jun Can Mediate Androgen Receptor-Induced Transactivation. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 24583–24589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faid, I.; Al-Hussaini, H.; Kilarkaje, N. Resveratrol Alleviates Diabetes-Induced Testicular Dysfunction by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase Signaling in Rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2015, 289, 482–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngan, E.S.W.; Hashimoto, Y.; Ma, Z.-Q.; Tsai, M.-J.; Tsai, S.Y. Overexpression of Cdc25B, an Androgen Receptor Coactivator, in Prostate Cancer. Oncogene 2003, 22, 734–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moilanen, A.M.; Karvonen, U.; Poukka, H.; Jänne, O.A.; Palvimo, J.J. Activation of Androgen Receptor Function by a Novel Nuclear Protein Kinase. Mol. Biol. Cell 1998, 9, 2527–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, D.; Xiang, Z.; Ding, J.; Yang, X.; Li, D.; Han, X. M6A MRNA Methylation Regulates Testosterone Synthesis through Modulating Autophagy in Leydig Cells. Autophagy 2021, 17, 457–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazawa, T.; Imamichi, Y.; Yuhki, K.-I.; Uwada, J.; Mikami, D.; Shimada, M.; Miyamoto, K.; Kitano, T.; Takahashi, S.; Sekiguchi, T.; et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 Is Acutely Induced by CCAAT/Enhancer-Binding Protein β to Produce Prostaglandin E 2 and F 2α Following Gonadotropin Stimulation in Leydig Cells. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2019, 86, 786–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ron, D.; Habener, J.F. CHOP, a Novel Developmentally Regulated Nuclear Protein That Dimerizes with Transcription Factors C/EBP and LAP and Functions as a Dominant-Negative Inhibitor of Gene Transcription. Genes Dev. 1992, 6, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, H.; Wang, H.-G. CHOP Is Involved in Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Induced Apoptosis by Enhancing DR5 Expression in Human Carcinoma Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 45495–45502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaman-Pillet, N.; Roduit, R.; Oberson, A.; Abdelli, S.; Ruiz, J.; Beckmann, J.S.; Schorderet, D.F.; Bonny, C. Circadian Regulation of Islet Genes Involved in Insulin Production and Secretion. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2004, 226, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Xiao, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, M.; Ma, T.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Jiang, H.; et al. Zearalenone Perturbs the Circadian Clock and Inhibits Testosterone Synthesis in Mouse Leydig Cells. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2021, 84, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logue, S.E.; Cleary, P.; Saveljeva, S.; Samali, A. New Directions in ER Stress-Induced Cell Death. Apoptosis 2013, 18, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kania, E.; Pająk, B.; Orzechowski, A. Calcium Homeostasis and ER Stress in Control of Autophagy in Cancer Cells. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 352794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, B.J.; Wells, J.; King, S.R.; Stocco, D.M. The Purification, Cloning, and Expression of a Novel Luteinizing Hormone-Induced Mitochondrial Protein in MA-10 Mouse Leydig Tumor Cells. Characterization of the Steroidogenic Acute Regulatory Protein (StAR). J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 28314–28322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, P.R.; Dyson, M.T.; Eubank, D.W.; Clark, B.J.; Lalli, E.; Sassone-Corsi, P.; Zeleznik, A.J.; Stocco, D.M. Regulation of Steroidogenesis and the Steroidogenic Acute Regulatory Protein by a Member of the CAMP Response-Element Binding Protein Family. Mol. Endocrinol. 2002, 16, 184–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, P.R.; Stocco, D.M. Crosstalk of CREB and Fos/Jun on a Single Cis-Element: Transcriptional Repression of the Steroidogenic Acute Regulatory Protein Gene. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2007, 39, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Wang, H.; Dong, T.; Huang, J.; Li, T.; Ren, H.; Wang, X.; Qu, J.; Wang, S. Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) Disrupts Testosterone Biosynthesis via CREB/CRTC2/StAR Signaling Pathway in Leydig Cells. Toxicology 2021, 449, 152663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altarejos, J.Y.; Montminy, M. CREB and the CRTC Co-Activators: Sensors for Hormonal and Metabolic Signals. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, P.R.; Huhtaniemi, I.T.; Stocco, D.M. Mechanisms of Protein Kinase C Signaling in the Modulation of 3’,5’-Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate-Mediated Steroidogenesis in Mouse Gonadal Cells. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 3308–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdou, H.S.; Robert, N.M.; Tremblay, J.J. Calcium-Dependent Nr4a1 Expression in Mouse Leydig Cells Requires Distinct AP1/CRE and MEF2 Elements. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2016, 56, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.J.; Boucher, N.; Brousseau, C.; Tremblay, J.J. The Orphan Nuclear Receptor NUR77 Regulates Hormone-Induced StAR Transcription in Leydig Cells through Cooperation with Ca2+/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase I. Mol. Endocrinol. 2008, 22, 2021–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdou, H.S.; Villeneuve, G.; Tremblay, J.J. The Calcium Signaling Pathway Regulates Leydig Cell Steroidogenesis through a Transcriptional Cascade Involving the Nuclear Receptor NR4A1 and the Steroidogenic Acute Regulatory Protein. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.J.; Tremblay, J.J. The Human 3beta-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase/Delta5-Delta4 Isomerase Type 2 Promoter Is a Novel Target for the Immediate Early Orphan Nuclear Receptor Nur77 in Steroidogenic Cells. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Mellon, S.H. Multiple Orphan Nuclear Receptors Converge to Regulate Rat P450c17 Gene Transcription: Novel Mechanisms for Orphan Nuclear Receptor Action. Mol. Endocrinol. 1997, 11, 891–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassett, M.H.; Suzuki, T.; Sasano, H.; De Vries, C.J.M.; Jimenez, P.T.; Carr, B.R.; Rainey, W.E. The Orphan Nuclear Receptor NGFIB Regulates Transcription of 3beta-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase. Implications for the Control of Adrenal Functional Zonation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 37622–37630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlando, U.; Cooke, M.; Cornejo Maciel, F.; Papadopoulos, V.; Podestá, E.J.; Maloberti, P. Characterization of the Mouse Promoter Region of the Acyl-CoA Synthetase 4 Gene: Role of Sp1 and CREB. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2013, 369, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinero, M.J.; Colas, B.; Prieto, J.C.; López-Ruiz, M.P. Different Sites of Action of Arachidonic Acid on Steroidogenesis in Rat Leydig Cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1996, 118, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abayasekara, D.R.; Band, A.M.; Cooke, B.A. Evidence for the Involvement of Phospholipase A2 in the Regulation of Luteinizing Hormone-Stimulated Steroidogenesis in Rat Testis Leydig Cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1990, 70, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronco, A.M.; Moraga, P.F.; Llanos, M.N. Arachidonic Acid Release from Rat Leydig Cells: The Involvement of G Protein, Phospholipase A2 and Regulation of CAMP Production. J. Endocrinol. 2002, 172, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, B.A.; Dirami, G.; Chaudry, L.; Choi, M.S.; Abayasekara, D.R.; Phipp, L. Release of Arachidonic Acid and the Effects of Corticosteroids on Steroidogenesis in Rat Testis Leydig Cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1991, 40, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, M.-C.; Wu, L.-S.; Jong, D.-S.; Chiu, C.-H. KISS1R Signaling Modulates Gonadotropin Sensitivity in Mouse Leydig Cell. Reproduction 2020, 160, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lu, M.; Zhang, R.; Guo, W.; Lin, P.; Yang, D.; Chen, H.; Tang, K.; Zhou, D.; Wang, A.; et al. Inhibition of Luman/CREB3 Expression Leads to the Upregulation of Testosterone Synthesis in Mouse Leydig Cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.K.; Wills, K.N.; Husmann, M.; Hermann, T.; Pfahl, M. Novel Pathway for Thyroid Hormone Receptor Action through Interaction with Jun and Fos Oncogene Activities. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1991, 11, 6016–6025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schüle, R.; Rangarajan, P.; Yang, N.; Kliewer, S.; Ransone, L.J.; Bolado, J.; Verma, I.M.; Evans, R.M. Retinoic Acid Is a Negative Regulator of AP-1-Responsive Genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 6092–6096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Zhang, R.; Yu, T.; Wang, L.; Liu, S.; Cai, R.; Guo, X.; Jia, Y.; Wang, A.; Jin, Y.; et al. CREBZF Regulates Testosterone Production in Mouse Leydig Cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 22819–22832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogan, M.R.; Cockram, G.P.; Lu, R. Cooperative Interaction of Zhangfei and ATF4 in Transactivation of the Cyclic AMP Response Element. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Rapin, N.; Ying, Z.; Shklanka, E.; Bodnarchuk, T.W.; Verge, V.M.K.; Misra, V. Zhangfei/CREB-ZF - a Potential Regulator of the Unfolded Protein Response. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batarseh, A.; Li, J.; Papadopoulos, V. Protein Kinase C Epsilon Regulation of Translocator Protein (18 KDa) Tspo Gene Expression Is Mediated through a MAPK Pathway Targeting STAT3 and c-Jun Transcription Factors. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 4766–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.J.; Boucher, N.; El-Asmar, B.; Tremblay, J.J. CAMP-Induced Expression of the Orphan Nuclear Receptor Nur77 in MA-10 Leydig Cells Involves a CaMKI Pathway. J. Androl. 2009, 30, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, I.-C.; Huang, C.-Y.; Wang, C.-K.L.; Chung, B. Activating Protein-1 Cooperates with Steroidogenic Factor-1 to Regulate 3′,5′-Cyclic Adenosine 5’-Monophosphate-Dependent Human CYP11A1 Transcription in Vitro and in Vivo. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 1804–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Gong, E.-Y.; Hong, C.Y.; Kim, K.-H.; Han, J.-S.; Ryu, J.C.; Chae, H.Z.; Yun, C.-H.; Lee, K. ROS Inhibit the Expression of Testicular Steroidogenic Enzyme Genes via the Suppression of Nur77 Transactivation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 47, 1591–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göttlicher, M.; Heck, S.; Doucas, V.; Wade, E.; Kullmann, M.; Cato, A.C.; Evans, R.M.; Herrlich, P. Interaction of the Ubc9 Human Homologue with C-Jun and with the Glucocorticoid Receptor. Steroids 1996, 61, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teyssier, C.; Belguise, K.; Galtier, F.; Chalbos, D. Characterization of the Physical Interaction between Estrogen Receptor Alpha and JUN Proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 36361–36369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang-Yen, H.F.; Zhang, X.K.; Graupner, G.; Tzukerman, M.; Sakamoto, B.; Karin, M.; Pfahl, M. Antagonism between Retinoic Acid Receptors and AP-1: Implications for Tumor Promotion and Inflammation. New Biol. 1991, 3, 1206–1219. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martin, L.J.; Bergeron, F.; Viger, R.S.; Tremblay, J.J. Functional Cooperation between GATA Factors and CJUN on the Star Promoter in MA-10 Leydig Cells. J. Androl. 2012, 33, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manna, P.R.; Eubank, D.W.; Stocco, D.M. Assessment of the Role of Activator Protein-1 on Transcription of the Mouse Steroidogenic Acute Regulatory Protein Gene. Mol. Endocrinol. 2004, 18, 558–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea-Eaton, W.; Sandhoff, T.W.; Lopez, D.; Hales, D.B.; McLean, M.P. Transcriptional Repression of the Rat Steroidogenic Acute Regulatory (StAR) Protein Gene by the AP-1 Family Member c-Fos. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2002, 188, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdou, H.S.; Bergeron, F.; Tremblay, J.J. A Cell-Autonomous Molecular Cascade Initiated by AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Represses Steroidogenesis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2014, 34, 4257–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardassis, D.; Papakosta, P.; Pardali, K.; Moustakas, A. C-Jun Transactivates the Promoter of the Human P21(WAF1/Cip1) Gene by Acting as a Superactivator of the Ubiquitous Transcription Factor Sp1. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 29572–29581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sher, N.; Yivgi-Ohana, N.; Orly, J. Transcriptional Regulation of the Cholesterol Side Chain Cleavage Cytochrome P450 Gene (CYP11A1) Revisited: Binding of GATA, Cyclic Adenosine 3’,5’-Monophosphate Response Element-Binding Protein and Activating Protein (AP)-1 Proteins to a Distal Novel Cluster of Cis-Regulatory Elements Potentiates AP-2 and Steroidogenic Factor-1-Dependent Gene Expression in the Rodent Placenta and Ovary. Mol. Endocrinol. 2007, 21, 948–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, D.A.; Kirkman, M.S.; Aitken, L.D.; Mouw, A.R.; Schimmer, B.P.; Parker, K.L. Analysis of the Promoter Region of the Gene Encoding Mouse Cholesterol Side-Chain Cleavage Enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 11713–11720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, V.; Stocco, D.M.; Clark, B.J. Current Knowledge on the Acute Regulation of Steroidogenesis. Biol. Reprod. 2018, 99, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morohaku, K.; Pelton, S.H.; Daugherty, D.J.; Butler, W.R.; Deng, W.; Selvaraj, V. Translocator Protein/Peripheral Benzodiazepine Receptor Is Not Required for Steroid Hormone Biosynthesis. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Wang, K.; Zirkin, B.; Papadopoulos, V. CRISPR/Cas9–Mediated Tspo Gene Mutations Lead to Reduced Mitochondrial Membrane Potential and Steroid Formation in MA-10 Mouse Tumor Leydig Cells. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 1130–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batarseh, A.; Giatzakis, C.; Papadopoulos, V. Phorbol-12-Myristate 13-Acetate Acting through Protein Kinase Cepsilon Induces Translocator Protein (18-KDa) TSPO Gene Expression. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 12886–12899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.; Haskell, J.; Vinson, N.; Terracio, L. Characterization of Insulin and Insulin-like Growth Factor I Receptors of Purified Leydig Cells and Their Role in Steroidogenesis in Primary Culture: A Comparative Study. Endocrinology 1986, 119, 1641–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Blaisdell, J.; Haskell, J.F. Transforming Growth Factor-Beta Inhibits Leydig Cell Steroidogenesis in Primary Culture. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1987, 146, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sordoillet, C.; Chauvin, M.A.; Revol, A.; Morera, A.M.; Benahmed, M. Fibroblast Growth Factor Is a Regulator of Testosterone Secretion in Cultured Immature Leydig Cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1988, 58, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millena, A.C.; Reddy, S.C.; Bowling, G.H.; Khan, S.A. Autocrine Regulation of Steroidogenic Function of Leydig Cells by Transforming Growth Factor-Alpha. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2004, 224, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saez, J.M.; Avallet, O.; Naville, D.; Perrard-Sapori, M.H.; Chatelain, P.G. Sertoli-Leydig Cell Communications. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1989, 564, 210–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, P.R.; Chandrala, S.P.; King, S.R.; Jo, Y.; Counis, R.; Huhtaniemi, I.T.; Stocco, D.M. Molecular Mechanisms of Insulin-like Growth Factor-I Mediated Regulation of the Steroidogenic Acute Regulatory Protein in Mouse Leydig Cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 20, 362–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weekes, D.; Kashima, T.G.; Zandueta, C.; Perurena, N.; Thomas, D.P.; Sunters, A.; Vuillier, C.; Bozec, A.; El-Emir, E.; Miletich, I.; et al. Regulation of Osteosarcoma Cell Lung Metastasis by the C-Fos/AP-1 Target FGFR1. Oncogene 2016, 35, 2852–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, G.; Hu, Q.; Xiao, X.; Chen, S. AML1/ETO Trans-Activates c-KIT Expression through the Long Range Interaction between Promoter and Intronic Enhancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 3706–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hébert-Mercier, P.-O.; Bergeron, F.; Robert, N.M.; Mehanovic, S.; Pierre, K.J.; Mendoza-Villarroel, R.E.; de Mattos, K.; Brousseau, C.; Tremblay, J.J. Growth Hormone-Induced STAT5B Regulates Star Gene Expression Through a Cooperation With CJUN in Mouse MA-10 Leydig Cells. Endocrinology 2022, 163, bqab267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simard, J.; Ricketts, M.-L.; Gingras, S.; Soucy, P.; Feltus, F.A.; Melner, M.H. Molecular Biology of the 3beta-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase/Delta5-Delta4 Isomerase Gene Family. Endocr. Rev 2005, 26, 525–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, S.; Heinrich, R.; Aronheim, A. The AP-1 Repressor, JDP2, Is a Bona Fide Substrate for the c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase. FEBS Lett. 2001, 506, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Ugai, H.; Song, J.; Murata, T.; Nili, F.; Sun, K.; Horikoshi, M.; Yokoyama, K.K. Identification of Mouse Jun Dimerization Protein 2 as a Novel Repressor of ATF-2. FEBS Lett. 2001, 489, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Jin, S.; Guo, J.; Kombairaju, P.; Biswal, S.; Zirkin, B.R. Knockout of the Transcription Factor Nrf2: Effects on Testosterone Production by Aging Mouse Leydig Cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2015, 409, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beattie, M.C.; Adekola, L.; Papadopoulos, V.; Chen, H.; Zirkin, B.R. Leydig Cell Aging and Hypogonadism. Exp. Gerontol. 2015, 68, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Kong, A.-N. Molecular Mechanisms of Nrf2-Mediated Antioxidant Response. Mol. Carcinog. 2009, 48, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.-Y.; Liu, Z.; Johnson, P.F.; Richards, J.S. CCAAT/Enhancer-Binding Proteins (C/EBP)-α and -β Are Essential for Ovulation, Luteinization, and the Expression of Key Target Genes. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 25, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinhart, A.J.; Williams, S.C.; Clark, B.J.; Stocco, D.M. SF-1 (Steroidogenic Factor-1) and C/EBP Beta (CCAAT/Enhancer Binding Protein-Beta) Cooperate to Regulate the Murine StAR (Steroidogenic Acute Regulatory) Promoter. Mol. Endocrinol. 1999, 13, 729–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, J.J.; Hamel, F.; Viger, R.S. Protein Kinase A-Dependent Cooperation between GATA and CCAAT/Enhancer-Binding Protein Transcription Factors Regulates Steroidogenic Acute Regulatory Protein Promoter Activity. Endocrinology 2002, 143, 3935–3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiroi, H.; Christenson, L.K.; Chang, L.; Sammel, M.D.; Berger, S.L.; Strauss, J.F. Temporal and Spatial Changes in Transcription Factor Binding and Histone Modifications at the Steroidogenic Acute Regulatory Protein (StAR) Locus Associated with StAR Transcription. Mol. Endocrinol. 2004, 18, 791–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhl, A.J.; Ross, S.M.; Gaido, K.W. CCAAT/Enhancer Binding Protein Beta, but Not Steroidogenic Factor-1, Modulates the Phthalate-Induced Dysregulation of Rat Fetal Testicular Steroidogenesis. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 5851–5864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Dong, C.; Chen, M.; Lu, J.; Han, X.; Qiu, L.; Chen, Y.; Qin, J.; Li, X.; Gu, A.; et al. Low-Dose Monobutyl Phthalate Stimulates Steroidogenesis through Steroidogenic Acute Regulatory Protein Regulated by SF-1, GATA-4 and C/EBP-Beta in Mouse Leydig Tumor Cells. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2013, 11, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manna, P.R.; Wang, X.-J.; Stocco, D.M. Involvement of Multiple Transcription Factors in the Regulation of Steroidogenic Acute Regulatory Protein Gene Expression. Steroids 2003, 68, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christenson, L.K.; Strauss, J.F. Steroidogenic Acute Regulatory Protein (StAR) and the Intramitochondrial Translocation of Cholesterol. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1529, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Asmar, B.; Giner, X.C.; Tremblay, J.J. Transcriptional Cooperation between NF-KappaB P50 and CCAAT/Enhancer Binding Protein Beta Regulates Nur77 Transcription in Leydig Cells. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2009, 42, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frungieri, M.B.; Calandra, R.S.; Mayerhofer, A.; Matzkin, M.E. Cyclooxygenase and Prostaglandins in Somatic Cell Populations of the Testis. Reproduction 2015, 149, R169–R180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Luo, L.; Liu, J.; Zirkin, B.R. Cyclooxygenases in Rat Leydig Cells: Effects of Luteinizing Hormone and Aging. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kondo, S.; Saito, A.; Asada, R.; Kanemoto, S.; Imaizumi, K. Physiological Unfolded Protein Response Regulated by OASIS Family Members, Transmembrane BZIP Transcription Factors. IUBMB Life 2011, 63, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adham, I.M.; Eck, T.J.; Mierau, K.; Müller, N.; Sallam, M.A.; Paprotta, I.; Schubert, S.; Hoyer-Fender, S.; Engel, W. Reduction of Spermatogenesis but Not Fertility in Creb3l4-Deficient Mice. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 7657–7664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamori, I.; Yomogida, K.; Ikawa, M.; Okabe, M.; Yabuta, N.; Nojima, H. The Testes-Specific BZip Type Transcription Factor Tisp40 Plays a Role in ER Stress Responses and Chromatin Packaging during Spermiogenesis. Genes Cells 2006, 11, 1161–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivell, R.; Anand-Ivell, R. Biology of Insulin-like Factor 3 in Human Reproduction. Hum. Reprod. Update 2009, 15, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Rivas, B.; Agoulnik, A.I. Insulin-like 3 Signaling Is Important for Testicular Descent but Dispensable for Spermatogenesis and Germ Cell Survival in Adult Mice. Biol. Reprod. 2012, 87, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, S.; Schöttler, P.; Engel, W.; Adham, I.M. Mouse Leydig Insulin-like (Ley I-L) Gene: Structure and Expression during Testis and Ovary Development. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 1997, 47, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivell, R.; Balvers, M.; Domagalski, R.; Ungefroren, H.; Hunt, N.; Schulze, W. Relaxin-like Factor: A Highly Specific and Constitutive New Marker for Leydig Cells in the Human Testis. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 1997, 3, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Balvers, M.; Spiess, A.N.; Domagalski, R.; Hunt, N.; Kilic, E.; Mukhopadhyay, A.K.; Hanks, E.; Charlton, H.M.; Ivell, R. Relaxin-like Factor Expression as a Marker of Differentiation in the Mouse Testis and Ovary. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 2960–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bay, K.; Andersson, A.-M. Human Testicular Insulin-like Factor 3: In Relation to Development, Reproductive Hormones and Andrological Disorders. Int. J. Androl. 2011, 34, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Anderson, H.; Buo, A.M.; Moorer, M.C.; Ren, M.; Stains, J.P. Communication of CAMP by Connexin43 Gap Junctions Regulates Osteoblast Signaling and Gene Expression. Cell Signal 2016, 28, 1048–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, P.A.; Kumar, N.M. Differences in Expression Patterns between Mouse Connexin-30.2 (Cx30.2) and Its Putative Human Orthologue, Connexin-31.9. FEBS Lett. 2003, 540, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risley, M.S.; Tan, I.P.; Roy, C.; Sáez, J.C. Cell-, Age- and Stage-Dependent Distribution of Connexin43 Gap Junctions in Testes. J. Cell. Sci. 1992, 103 Pt 1, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Sekhon, P.; Barr, K.J.; Márquez-Rosado, L.; Lampe, P.D.; Kidder, G.M. Connexins and Steroidogenesis in Mouse Leydig Cells. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2013, 91, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najih, M.; Nguyen, H.T.; Martin, L.J. Involvement of Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase I in the Regulation of the Expression of Connexin 43 in MA-10 Tumor Leydig Cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roscoe, W.A.; Barr, K.J.; Mhawi, A.A.; Pomerantz, D.K.; Kidder, G.M. Failure of Spermatogenesis in Mice Lacking Connexin43. Biol. Reprod. 2001, 65, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahiri, C.N.; Khalil, M.W.; Tekpetey, F.; Kidder, G.M. Leydig Cell Function in Mice Lacking Connexin43. Reproduction 2006, 132, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridharan, S.; Simon, L.; Meling, D.D.; Cyr, D.G.; Gutstein, D.E.; Fishman, G.I.; Guillou, F.; Cooke, P.S. Proliferation of Adult Sertoli Cells Following Conditional Knockout of the Gap Junctional Protein GJA1 (Connexin 43) in Mice. Biol. Reprod. 2007, 76, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brehm, R.; Zeiler, M.; Rüttinger, C.; Herde, K.; Kibschull, M.; Winterhager, E.; Willecke, K.; Guillou, F.; Lécureuil, C.; Steger, K.; et al. A Sertoli Cell-Specific Knockout of Connexin43 Prevents Initiation of Spermatogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 171, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noelke, J.; Wistuba, J.; Damm, O.S.; Fietz, D.; Gerber, J.; Gaehle, M.; Brehm, R. A Sertoli Cell-Specific Connexin43 Knockout Leads to Altered Interstitial Connexin Expression and Increased Leydig Cell Numbers. Cell Tissue Res. 2015, 361, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salameh, A.; Krautblatter, S.; Karl, S.; Blanke, K.; Gomez, D.R.; Dhein, S.; Pfeiffer, D.; Janousek, J. The Signal Transduction Cascade Regulating the Expression of the Gap Junction Protein Connexin43 by Beta-Adrenoceptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 158, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, S.P.; Park, S.S.; Ryu, J.M.; Park, J.H.; Kim, M.O.; Lee, J.-H.; Han, H.J. Mechanism of PKA-Dependent and Lipid-Raft Independent Stimulation of Connexin43 Expression by Oxytoxin in Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 2012, 26, 1144–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- You, S.; Li, W.; Lin, T. Expression and Regulation of Connexin43 in Rat Leydig Cells. J. Endocrinol. 2000, 166, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Armendariz, E.M.; Luna, J.; Miranda, C.; Talavera, D.; Romano, M.C. Luteinizing and Human Chorionic Gonadotropin Hormones Increase Intercellular Communication and Gap Junctions in Cultured Mouse Leydig Cells. Endocrine 1996, 4, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo-Moreno, J.F.; Díaz-Sánchez, V.; Montoya-Flores, J.G.; Lamoyi, E.; Saéz, J.C.; Pérez-Armendariz, E.M. Expression of Connexin43 in Mouse Leydig, Sertoli, and Germinal Cells at Different Stages of Postnatal Development. Anat. Rec. 2001, 264, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
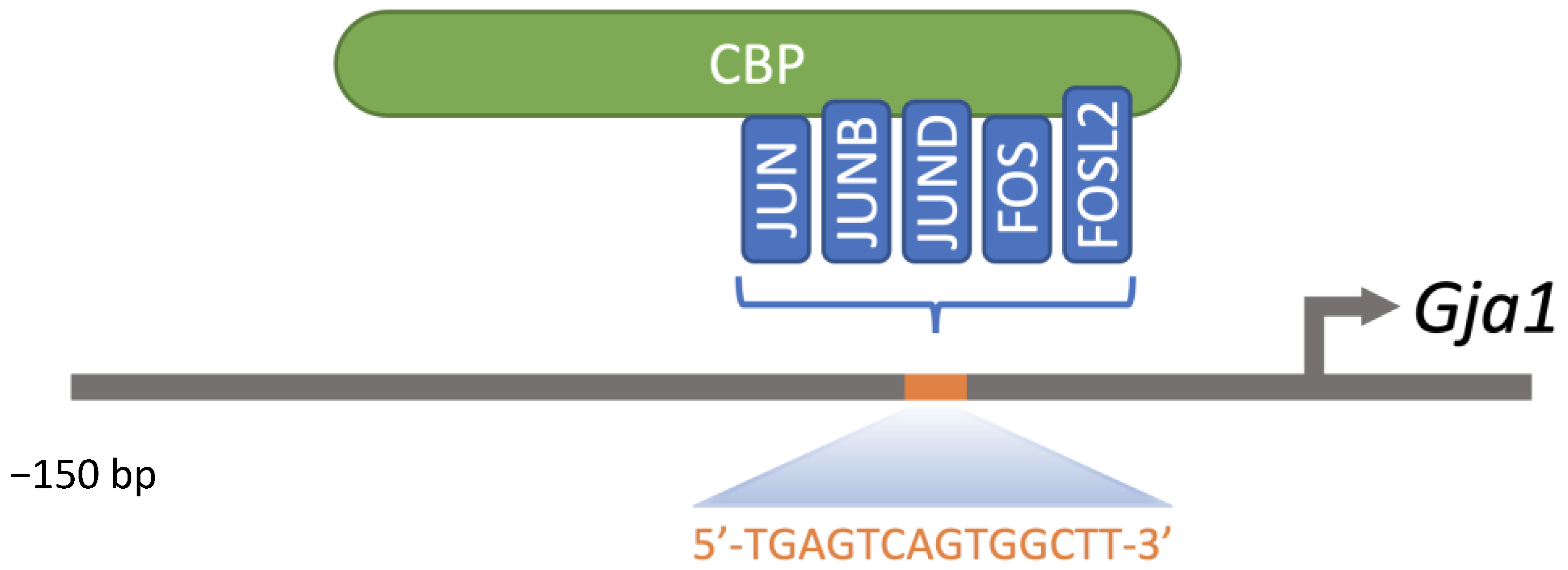
- Ghouili, F.; Martin, L.J. Cooperative Regulation of Gja1 Expression by Members of the AP-1 Family CJun and CFos in TM3 Leydig and TM4 Sertoli Cells. Gene 2017, 635, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landry, D.A.; Sormany, F.; Haché, J.; Roumaud, P.; Martin, L.J. Steroidogenic Genes Expressions Are Repressed by High Levels of Leptin and the JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway in MA-10 Leydig Cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 433, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zhao, A.; Zhou, Y.; Ying, H.; Zhang, Q. Luteolin Ameliorates Testis Injury and Blood-Testis Barrier Disruption through the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway and by Upregulating Cx43. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1800843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehat, I.; Hasin, T.; Aronheim, A. The Role of Basic Leucine Zipper Protein-Mediated Transcription in Physiological and Pathological Myocardial Hypertrophy. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1080, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, H.M.; Urano, A.; Shimada, N.; Yasuda, K. Sequential and Combinatorial Roles of Maf Family Genes Define Proper Lens Development. Mol. Vis. 2007, 13, 18–30. [Google Scholar]
- Ming, J.; Zhou, Y.; Du, J.; Fan, S.; Pan, B.; Wang, Y.; Fan, L.; Jiang, J. MiR-381 Suppresses C/EBPα-Dependent Cx43 Expression in Breast Cancer Cells. Biosci. Rep. 2015, 35, e00266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Family | Subfamily | Transcription Factors |
|---|---|---|
| JUN-related | JUN | JUN, JUNB, JUND |
| NFE2 | NFE2, NFE2L1, NFE2L2, NFE2L3, BACH1, BACH2 | |
| ATF2 | ATF2, ATF7, CREB5 | |
| FOS-related | FOS | FOS, FOSB, FOSL1, FOSL2 |
| ATF3-like | ATF3, JDP2 | |
| MAF-related | Large MAF | MAF, MAFA, MAFB, NRL |
| Small MAF | MAFF, MAFG, MAFK | |
| B-ATF-related | BATF, BATF2, BATF3 | |
| XBP1-related | XBP1 | |
| ATF4-related | ATF4, ATF5 | |
| CREB-related | CREB-like | CREB1, ATF1, CREM |
| CREB3-like | CREB3, CREB3L1, CREB3L2, CREB3L3, CREB3L4 | |
| ATF6 | ATF6, ATF6B | |
| CREBZF-like | CREBZF | |
| CREBL2-like | CREBL2 | |
| CEBP-related | CEBP | CEBPA, CEBPB, CEBPG, CEBPD, CEBPE, DDIT3 |
| PAR | DBP, HLF, NFIL3, TEF |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martin, L.J.; Nguyen, H.T. Basic Leucine Zipper Transcription Factors as Important Regulators of Leydig Cells’ Functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12887. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232112887
Martin LJ, Nguyen HT. Basic Leucine Zipper Transcription Factors as Important Regulators of Leydig Cells’ Functions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(21):12887. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232112887
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartin, Luc J., and Ha Tuyen Nguyen. 2022. "Basic Leucine Zipper Transcription Factors as Important Regulators of Leydig Cells’ Functions" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 21: 12887. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232112887
APA StyleMartin, L. J., & Nguyen, H. T. (2022). Basic Leucine Zipper Transcription Factors as Important Regulators of Leydig Cells’ Functions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(21), 12887. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232112887






