The Bottlenecks of Preparing Virus Particles by Size Exclusion for Antibody Generation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Analysis of Chicken IgY Antibodies after Immunization
2.2. Construction and Selection of Phage Displaying scFv Antibodies
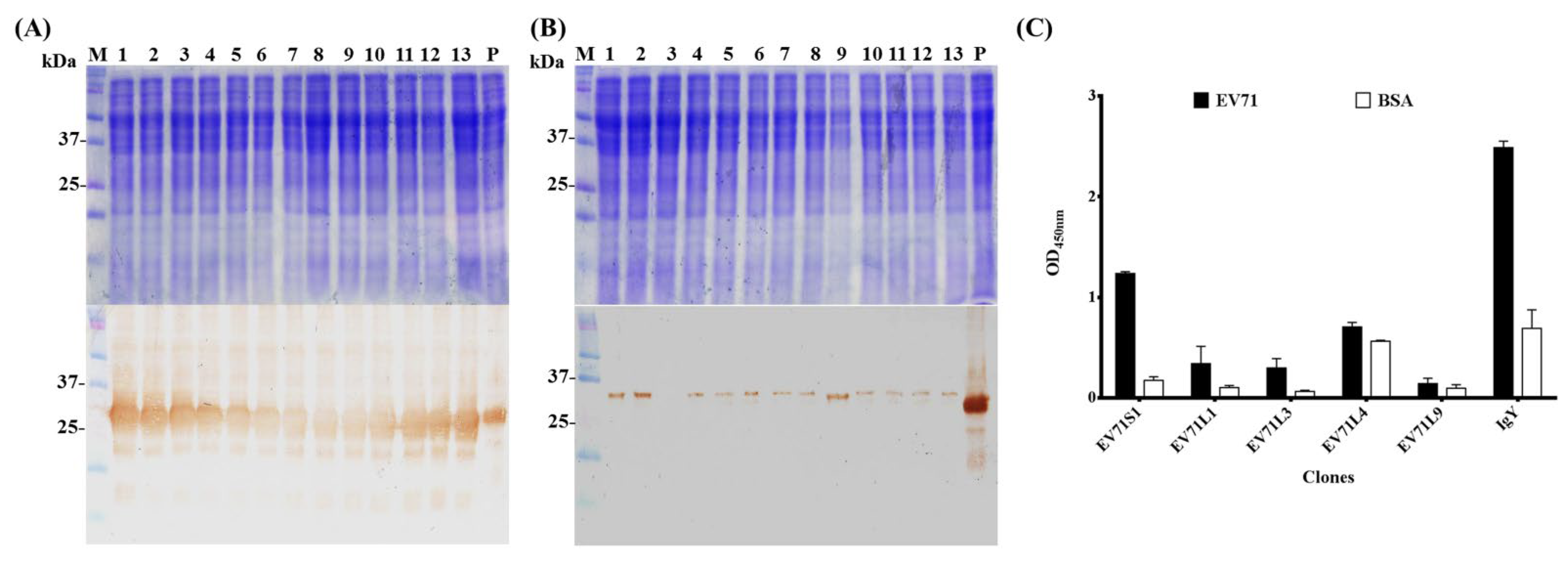
2.3. Expression, Sequence Analysis, Classification, Binding Test, and Purification of scFv Antibodies
2.4. Cross-Reactivity of Chicken Derived IgY and scFv Antibodies
2.5. Neutralization Analysis of Chicken-Derived IgY and scFv Antibodies
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Ethics Declaration
4.2. Preparation of Virus-Infected Cell Lysate and Viral Particles
4.3. Immunization of Chicken with EV71 Viral Particles
4.4. Construction of scFv Antibody Libraries
4.5. Bio-Panning of scFv Antibodies
4.6. Protein Expression and Purification of scFv Antibody
4.7. Sequencing and Analysis of scFv Genes
4.8. SDS-PAGE and Western Blot
4.9. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.10. In Vitro Antibodies Neutralization Assay
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EV71 | Enterovirus 71 |
| CA16 | Coxsackievirus 16 |
| CFU | colony-forming units |
| HFMD | hand, foot, and mouth disease |
| IgY | yolk-immunoglobulin |
| PFU | plaque-forming units |
| VP | viral protein |
| VH | heavy variable |
| VL | light variable |
| FR | framework region |
| CDR | complementarity determining region |
| IC50 | half maximal inhibitory concentration |
| RD | rhabdomyosarcoma |
| Amp | ampicillin |
| DAB | 3,3ʹ-diaminobenzidine |
| TMB | 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine |
| scFv | single-chain variable fragment |
| h | hour |
| sec | second |
| min | minute |
References
- Picornaviridae. Available online: https://www.picornaviridae.com/ (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- Gaaloul, I.; Riabi, S.; Evans, M.; Hunter, T.; Huber, S.; Aouni, M. Coxsackievirus B heart infections and their putative contribution to sudden unexpected death: An 8-year review of patients and victims in the coastal region of Tunisia. Forensic. Sci. Int. 2016, 268, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royston, L.; Tapparel, C. Rhinoviruses and Respiratory Enteroviruses: Not as Simple as ABC. Viruses 2016, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brouwer, L.; van der Sanden, S.M.G.; Calis, J.C.J.; Bruning, A.H.L.; Wang, S.; Wildenbeest, J.G.; Rebers, S.P.H.; Phiri, K.S.; Westerhuis, B.M.; van Hensbroek, M.B.; et al. High frequency of Polio-like Enterovirus C strains with differential clustering of CVA-13 and EV-C99 subgenotypes in a cohort of Malawian children. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 2645–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Knowles, N.; Hovi, T.; Hyypiä, T.; King, A.; Lindberg, A.; Pallansch, M.; Palmenberg, A.; Simmonds, P.; Skern, T.; Stanway, G. Virus Taxonomy: Classification and Nomenclature of Viruses; Ninth Report of The International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses; King, A., Adams, M.J., Carstens, E.B., Lefkowitz, E.J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 855–880. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Shukla, D.; Kumar, R.; Idris, M.Z.; Jauhari, P.; Srivastava, S.; Dhole, T.N. Molecular identification of enteroviruses associated with aseptic meningitis in children from India. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.D.; Yang, M.-Y.; Li, C.-C.; Lin, S.-F.; Chong, M.-C.; Wang, C.-L.; Chen, R.-F.; Lin, T.-Y. Altered cellular but not humoral reactions in children with complicated enterovirus 71 infections in Taiwan. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 183, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosoya, M.; Kawasaki, Y.; Sato, M.; Honzumi, K.; Kato, A.; Hiroshima, T.; Ishiko, H.; Suzuki, H. Genetic diversity of enterovirus 71 associated with hand, foot and mouth disease epidemics in Japan from 1983 to 2003. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2006, 25, 691–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chumakov, M.; Voroshilova, M.; Shindarov, L.; Lavrova, I.; Gracheva, L.; Koroleva, G.; Vasilenko, S.; Brodvarova, I.; Nikolova, M.; Gyurova, S.; et al. Enterovirus 71 isolated from cases of epidemic poliomyelitis-like disease in Bulgaria. Arch. Virol. 1979, 60, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, G.; Takatsy, S.; Kukan, E.; Mihaly, I.; Domok, I. Virological diagnosis of enterovirus type 71 infections: Experiences gained during an epidemic of acute CNS diseases in Hungary in 1978. Arch. Virol. 1982, 71, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, S.R.; Ho, M.S.; Lin, K.H.; Wu, S.L.; Chen, Y.T.; Wu, C.N.; Lin, T.Y.; Chang, L.Y.; Tsao, K.C.; Ning, H.C.; et al. Genetic analysis of enterovirus 71 isolated from fatal and non-fatal cases of hand, foot and mouth disease during an epidemic in Taiwan, 1998. Virus Res. 2000, 68, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, M.; Chen, E.R.; Hsu, K.H.; Twu, S.J.; Chen, K.T.; Tsai, S.F.; Wang, J.R.; Shih, S.R. An epidemic of enterovirus 71 infection in Taiwan. Taiwan Enterovirus Epidemic Working Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Peng, W.; Ren, J.; Hu, Z.; Xu, J.; Lou, Z.; Li, X.; Yin, W.; Shen, X.; Porta, C. A sensor-adaptor mechanism for enterovirus uncoating from structures of EV71. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012, 19, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Yeo, A.; Phoon, M.C.; Tan, E.L.; Poh, C.L.; Quak, S.H.; Chow, V.T. The largest outbreak of hand; foot and mouth disease in Singapore in 2008: The role of enterovirus 71 and coxsackievirus A strains. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 14, e1076–e1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thoa le, P.K.; Chiang, P.S.; Khanh, T.H.; Luo, S.T.; Dan, T.N.; Wang, Y.F.; Thuong, T.C.; Chung, W.Y.; Hung, N.T.; Wang, J.R.; et al. Genetic and antigenic characterization of enterovirus 71 in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 2011. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qiu, J. Enterovirus 71 infection: A new threat to global public health? Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 868–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Xu, W.; Xia, J.; Liang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tan, X.; Wang, L.; Mao, Q.; Wu, J.; et al. Efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity of an enterovirus 71 vaccine in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 818–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y. Enterovirus 71 infection and neurological complications. Korean J. Pediatr. 2016, 59, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.-C.; Guo, M.-S.; Lin, F.H.-Y.; Hsiao, K.-N.; Chang, K.H.-W.; Chou, A.-H.; Wang, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.-C.; Yang, C.-S.; Chong, P.C.-S. Purification and characterization of enterovirus 71 viral particles produced from vero cells grown in a serum-free microcarrier bioreactor system. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, Y. Recent progress on functional genomics research of enterovirus 71. Virol. Sin. 2019, 34, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curry, S.; Fry, E.; Blakemore, W.; Abu-Ghazaleh, R.; Jackson, T.; King, A.; Lea, S.; Newman, J.; Stuart, D. Dissecting the roles of VP0 cleavage and RNA packaging in picornavirus capsid stabilization: The structure of empty capsids of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 9743–9752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weiner, L.M.; Surana, R.; Wang, S. Monoclonal antibodies: Versatile platforms for cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias da Silva, W.; Tambourgi, D.V. IgY: A promising antibody for use in immunodiagnostic and in immunotherapy. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2010, 135, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schade, R.; Burger, W.; Schoneberg, T.; Schniering, A.; Schwarzkopf, C.; Hlinak, A.; Kobilke, H. Avian egg yolk antibodies. The egg laying capacity of hens following immunisation with antigens of different kind and origin and the efficiency of egg yolk antibodies in comparison to mammalian antibodies. Altex 1994, 11, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kovacs-Nolan, J.; Mine, Y. Egg yolk antibodies for passive immunity. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 3, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andris-Widhopf, J.; Rader, C.; Steinberger, P.; Fuller, R.; Barbas Iii, C.F. Methods for the generation of chicken monoclonal antibody fragments by phage display. J. Immunol. Methods 2000, 242, 159–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-H.; Liu, I.-J.; Lu, R.-M.; Wu, H.-C. Advancement and applications of peptide phage display technology in biomedical science. J. Biomed. Sci. 2016, 23, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Petrus, M.L.; Kiefer, L.A.; Puri, P.; Heemskerk, E.; Seaman, M.S.; Barouch, D.H.; Arias, S.; van Wezel, G.P.; Havenga, M. A microbial expression system for high-level production of scFv HIV-neutralizing antibody fragments in Escherichia coli. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 8875–8888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.-H.; Lee, Y.-C.; Lee, Y.-L.; Leu, S.-J.; Lin, L.-T.; Chen, C.-C.; Chiang, J.-R.; Mwale, P.F.; Tsai, B.-Y.; Hung, C.-S. Single chain antibody fragment against venom from the snake daboia russelii formosensis. Toxins 2017, 9, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leu, S.J.; Lee, Y.C.; Lee, C.H.; Liao, P.Y.; Chiang, C.W.; Yang, C.M.; Su, C.H.; Ou, T.Y.; Liu, K.J.; Lo, H.J.; et al. Generation and Characterization of Single Chain Variable Fragment against Alpha-Enolase of Candida albicans. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mwale, P.F.; Lee, C.H.; Huang, P.N.; Tseng, S.N.; Shih, S.R.; Huang, H.Y.; Leu, S.J.; Huang, Y.J.; Chiang, L.C.; Mao, Y.C.; et al. In Vitro Characterization of Neutralizing Hen Antibodies to Coxsackievirus A16. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-N.; Lin, Y.-C.; Fann, C.; Liao, N.-S.; Shih, S.-R.; Ho, M.-S. Protection against lethal enterovirus 71 infection in newborn mice by passive immunization with subunit VP1 vaccines and inactivated virus. Vaccine 2001, 20, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, L.; Moreni, G.; Wolthers, K.C.; Pajkrt, D. World-Wide Prevalence and Genotype Distribution of Enteroviruses. Viruses 2021, 13, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Civardi, E.; Tzialla, C.; Baldanti, F.; Strocchio, L.; Manzoni, P.; Stronati, M. Viral outbreaks in neonatal intensive care units: What we do not know. Am. J. Infect. Control 2013, 41, 854–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.; Samardzic, K.; Wallach, M.; Frumkin, L.R.; Mochly-Rosen, D. Immunoglobulin Y for Potential Diagnostic and Therapeutic Applications in Infectious Diseases. Front Immunol. 2021, 12, 696003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gassmann, M.; Thommes, P.; Weiser, T.; Hubscher, U. Efficient production of chicken egg yolk antibodies against a conserved mammalian protein. FASEB J. 1990, 4, 2528–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nilsson, E.; Larsson, A.; Olesen, H.V.; Wejaker, P.E.; Kollberg, H. Good effect of IgY against Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections in cystic fibrosis patients. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2008, 43, 892–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huse, W.D.; Sastry, L.; Iverson, S.A.; Kang, A.S.; Alting-Mees, M.; Burton, D.R.; Benkovic, S.J.; Lerner, R.A. Generation of a large combinatorial library of the immunoglobulin repertoire in phage lambda. Science 1989, 246, 1275–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Mao, S.; Kaufmann, G.; Wirsching, P.; Lerner, R.A.; Janda, K.D. A method for the generation of combinatorial antibody libraries using pIX phage display. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 12612–12616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maynard, J.; Georgiou, G. Antibody engineering. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2000, 2, 339–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S. Hybridoma technology for production of monoclonal antibodies. Hybridoma 2010, 1, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Hammers, C.M.; Stanley, J.R. Antibody phage display: Technique and applications. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vashist, S.K.; Luong, J.H. Handbook of Immunoassay Technologies: Approaches, Performances, and Applications; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.H.; Lee, Y.C.; Liang, M.H.; Leu, S.J.; Lin, L.T.; Chiang, J.R.; Yang, Y.Y. Antibodies against Venom of the Snake Deinagkistrodon acutus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvari, R.; Ziv, E.; Lantner, F.; Heller, D.; Schechter, I. Somatic diversification of chicken immunoglobulin light chains by point mutations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 3072–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reynaud, C.A.; Dahan, A.; Anquez, V.; Weill, J.C. Somatic hyperconversion diversifies the single Vh gene of the chicken with a high incidence in the D region. Cell 1989, 59, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.L.; Davis, M.M. Diversity in the CDR3 region of V(H) is sufficient for most antibody specificities. Immunity 2000, 13, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Isaacs, S.R.; Kim, K.W.; Cheng, J.X.; Bull, R.A.; Stelzer-Braid, S.; Luciani, F.; Rawlinson, W.D.; Craig, M.E. Amplification and next generation sequencing of near full-length human enteroviruses for identification and characterisation from clinical samples. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saarinen, N.V.; Stone, V.M.; Hankaniemi, M.M.; Mazur, M.A.; Vuorinen, T.; Flodström-Tullberg, M.; Hyöty, H.; Hytönen, V.P.; Laitinen, O.H. Antibody Responses against Enterovirus Proteases are Potential Markers for an Acute Infection. Viruses 2020, 12, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.Y.; Yu, S.L.; Chen, Y.T.; Chen, Y.H.; Hsiao, P.W.; Chow, Y.H.; Chen, J.R. The mature EV71 virion induced a broadly cross-neutralizing VP1 antibody against subtypes of the EV71 virus. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phanthong, S.; Densumite, J.; Seesuay, W.; Thanongsaksrikul, J.; Teimoori, S.; Sookrung, N.; Poovorawan, Y.; Onvimala, N.; Guntapong, R.; Pattanapanyasat, K.; et al. Human Antibodies to VP4 Inhibit Replication of Enteroviruses Across Subgenotypes and Serotypes, and Enhance Host Innate Immunity. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 562768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo-Nguyen, H.V.; Nguyen, T.T.; Vu, H.T.; Nguyen, T.T.; Hoang, Q.C.; Tran, T.L.; Tran-Van, H. Recombinant Human SCARB2 Expressed in Escherichia coli and its Potential in Enterovirus 71 Blockage. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. A Sci. 2021, 45, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Koike, S. Cellular receptors for enterovirus A71. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.L.; Shih, S.R.; Tolbert, B.S.; Brewer, G. Enterovirus A71 Vaccines. Vaccines 2021, 9, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.Y.; Kung, Y.A.; Shih, S.R. Antivirals and vaccines for Enterovirus A71. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 26, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bek, E.J.; Hussain, K.M.; Phuektes, P.; Kok, C.C.; Gao, Q.; Cai, F.; Gao, Z.; McMinn, P.C. Formalin-inactivated vaccine provokes cross-protective immunity in a mouse model of human enterovirus 71 infection. Vaccine 2011, 29, 4829–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ElHadidy, A.M.; Peldszus, S.; Van Dyke, M.I. An evaluation of virus removal mechanisms by ultrafiltration membranes using MS2 and φX174 bacteriophage. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 120, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Young, T.A.; Schwab, K.J.; Jacangelo, J.G. Mechanisms of virus removal from secondary wastewater effluent by low pressure membrane filtration. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 409, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akita, E.; Nakai, S. Production and purification of Fab′ fragments from chicken egg yolk immunoglobulin Y (IgY). J. Immunol. Methods 1993, 162, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akita, E.M.; Nakai, S. Comparison of four purification methods for the production of immunoglobulins from eggs laid by hens immunized with an enterotoxigenic E. coli strain. J. Immunol. Methods 1993, 160, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukra, A.M.; Sridevi, N.V.; Dev, C.; Kapil, M. Production of recombinant antibodies using bacteriophages. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2014, 4, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, P.N.; Wang, H.C.; Hung, H.C.; Tseng, S.N.; Chang, T.Y.; Chou, M.Y.; Chen, Y.J.; Wang, Y.M.; Shih, S.R.; Hsu, J.T. Antiviral Activity of a Llama-Derived Single-Domain Antibody against Enterovirus A71. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e01922–e02019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Group | Short Linker | Long Linker | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VL | VH | Percentage | VL | VH | Percentage | |
| Group 1 | S1, S2, S3, S4 S5, S6, S7, S8, S9, S10, S11, S12, S13 | S1, S2, S3, S4 S5, S6, S7, S8, S9, S10, S11, S12, S13 | 100% | L1, L2 | L1, L2 | 15.38% |
| Group 2 | L3 | L3 * | 7.69% | |||
| Group 3 | L4, L5, L6, L7, L8, L10, L11, L12, L13 | L4, L5, L6, L7, L8, L10, L11, L12, L13 | 69.23% | |||
| Group 4 | L9 | L9 | 7.69% | |||
| Clones | Region | FR1 | FR2 | FR3 | FR4 | Total FR | CDR1 | CDR2 | CDR3 | Total CDR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EV71S1 | VL | 5% | 6% | 13% | 0% | 8% | 22% | 0% | 45% | 19% |
| VH | 7% | 7% | 16% | 0% | 9% | 40% | 47% | 67% | 52% | |
| EV71L1 | VL | 5% | 6% | 9% | 0% | 6% | 29% | 14% | 89% | 48% |
| VH | 7% | 21% | 16% | 0% | 11% | 60% | 47% | 71% | 55% | |
| EN71L4 | VL | 5% | 13% | 16% | 0% | 10% | 38% | 43% | 63% | 48% |
| VH | 7% | 21% | 16% | 0% | 11% | 60% | 47% | 71% | 55% | |
| EN71L9 | VL | 5% | 25% | 9% | 0% | 10% | 60% | 43% | 88% | 64% |
| VH | 7% | 21% | 22% | 9% | 15% | 60% | 47% | 71% | 55% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, C.-H.; Huang, P.-N.; Mwale, P.F.; Wang, W.-C.; Leu, S.-J.; Tseng, S.-N.; Shih, S.-R.; Chiang, L.-C.; Mao, Y.-C.; Tsai, B.-Y.; et al. The Bottlenecks of Preparing Virus Particles by Size Exclusion for Antibody Generation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12967. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232112967
Lee C-H, Huang P-N, Mwale PF, Wang W-C, Leu S-J, Tseng S-N, Shih S-R, Chiang L-C, Mao Y-C, Tsai B-Y, et al. The Bottlenecks of Preparing Virus Particles by Size Exclusion for Antibody Generation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(21):12967. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232112967
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Chi-Hsin, Peng-Nien Huang, Pharaoh Fellow Mwale, Wei-Chu Wang, Sy-Jye Leu, Sung-Nien Tseng, Shin-Ru Shih, Liao-Chun Chiang, Yan-Chiao Mao, Bor-Yu Tsai, and et al. 2022. "The Bottlenecks of Preparing Virus Particles by Size Exclusion for Antibody Generation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 21: 12967. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232112967
APA StyleLee, C.-H., Huang, P.-N., Mwale, P. F., Wang, W.-C., Leu, S.-J., Tseng, S.-N., Shih, S.-R., Chiang, L.-C., Mao, Y.-C., Tsai, B.-Y., Dlamini, N. B., Nguyen, T.-C., Tsai, C.-H., & Yang, Y.-Y. (2022). The Bottlenecks of Preparing Virus Particles by Size Exclusion for Antibody Generation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(21), 12967. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232112967






