Contribution of Capillary Zone Electrophoresis Hyphenated with Drift Tube Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometry as a Complementary Tool to Microfluidic Reversed Phase Liquid Chromatography for Antigen Discovery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Optimization of CZE-MS/MS Method
2.1.1. Use of Neutral Coated Capillaries
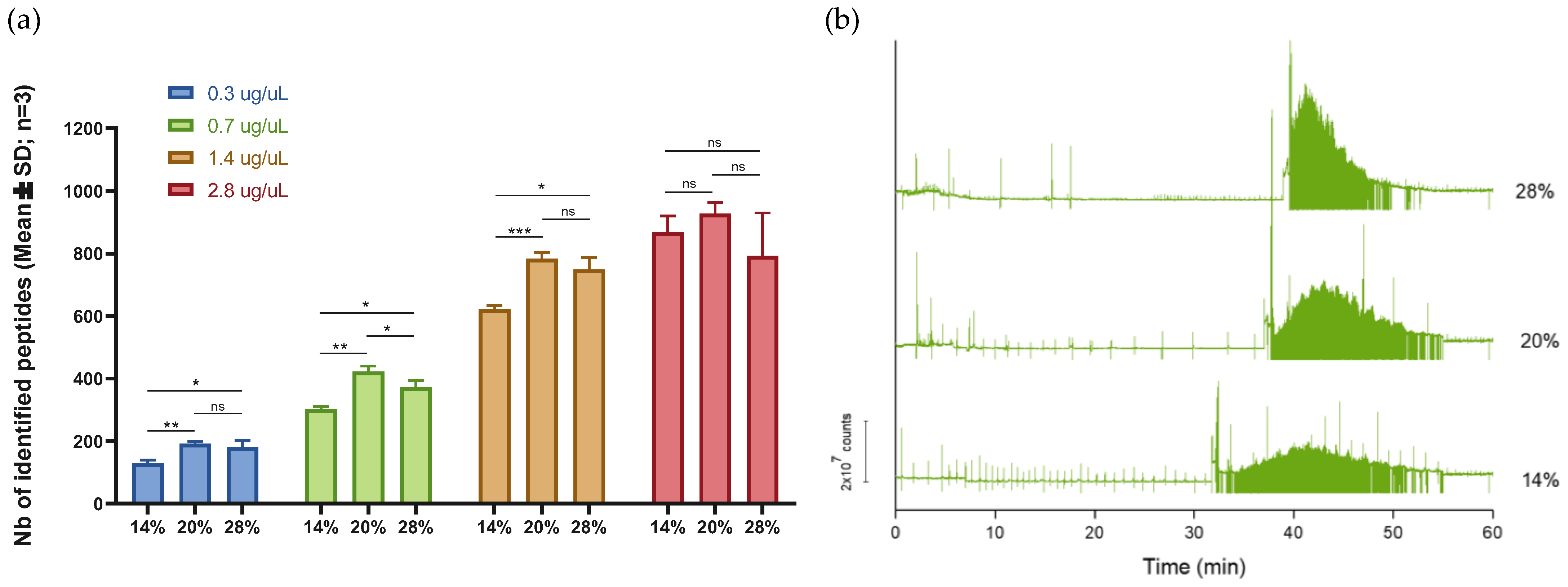
2.1.2. Sample Injection Volume
2.2. Analysis of MM Cell Line Surface Proteins Using CZE-DTIMS-QTOF
2.2.1. Uniqueness of Identifications between CZE-DTIMS-QTOF and RPLC-Chip-DTIMS-QTOF Methods
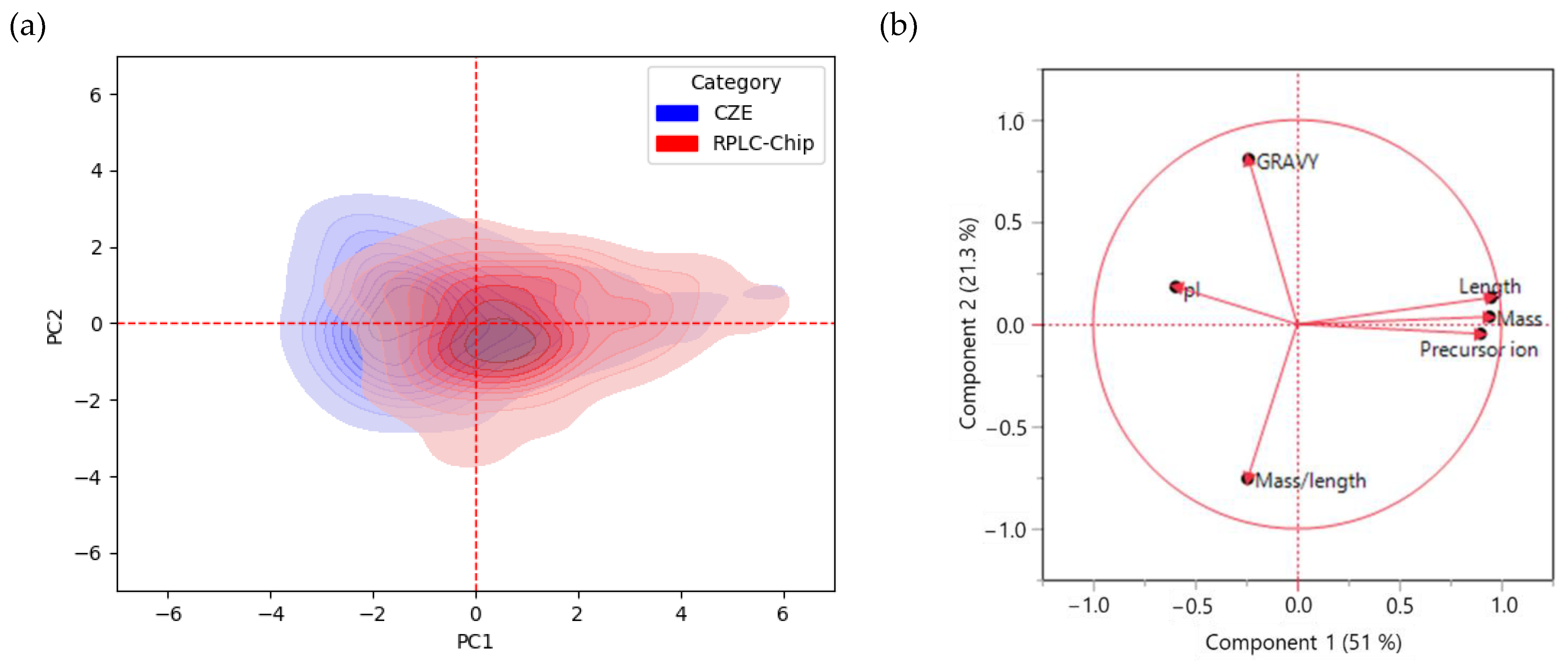
2.2.2. Orthogonality of RPLC-Chip and CZE
2.2.3. Physicochemical properties of identified peptides in RPLC-Chip and CZE
2.3. Contribution of DTIMS to CZE Analysis in Proteomics
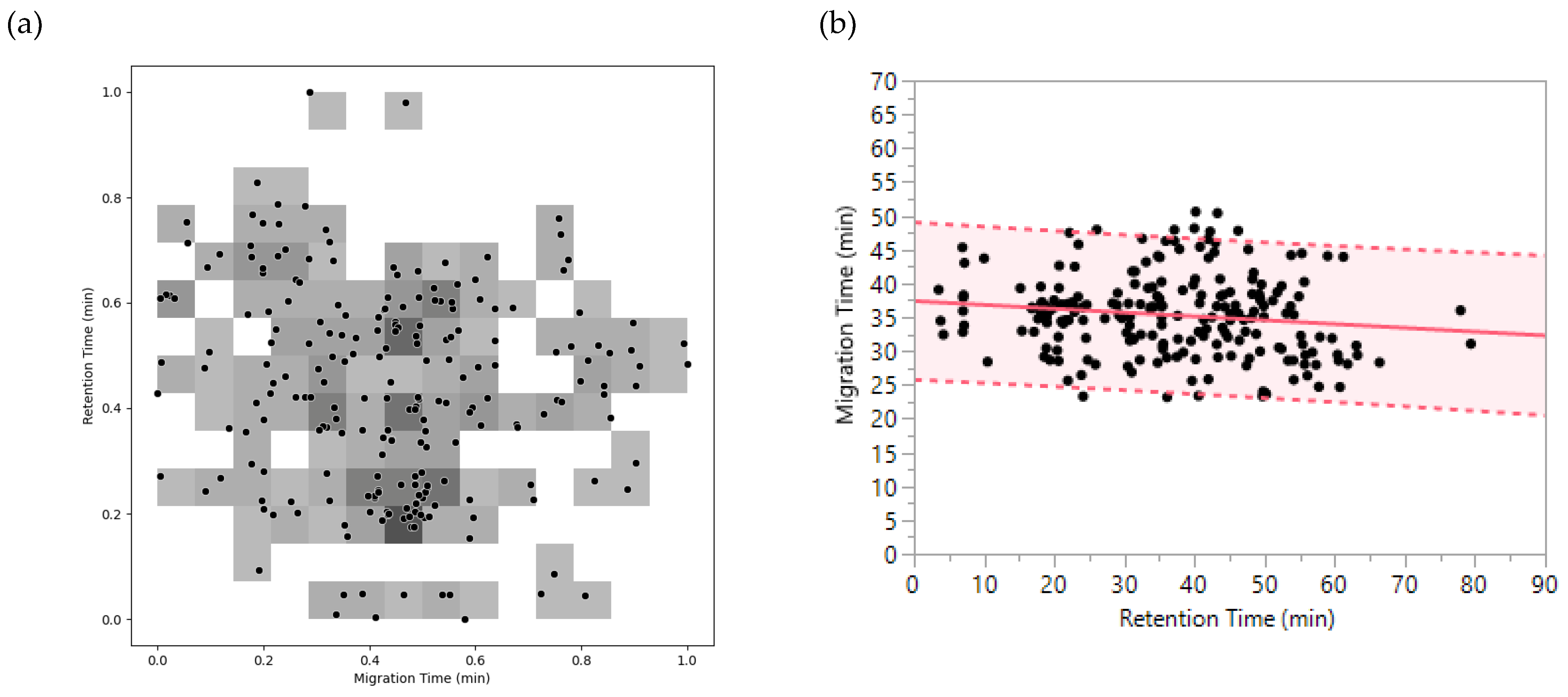
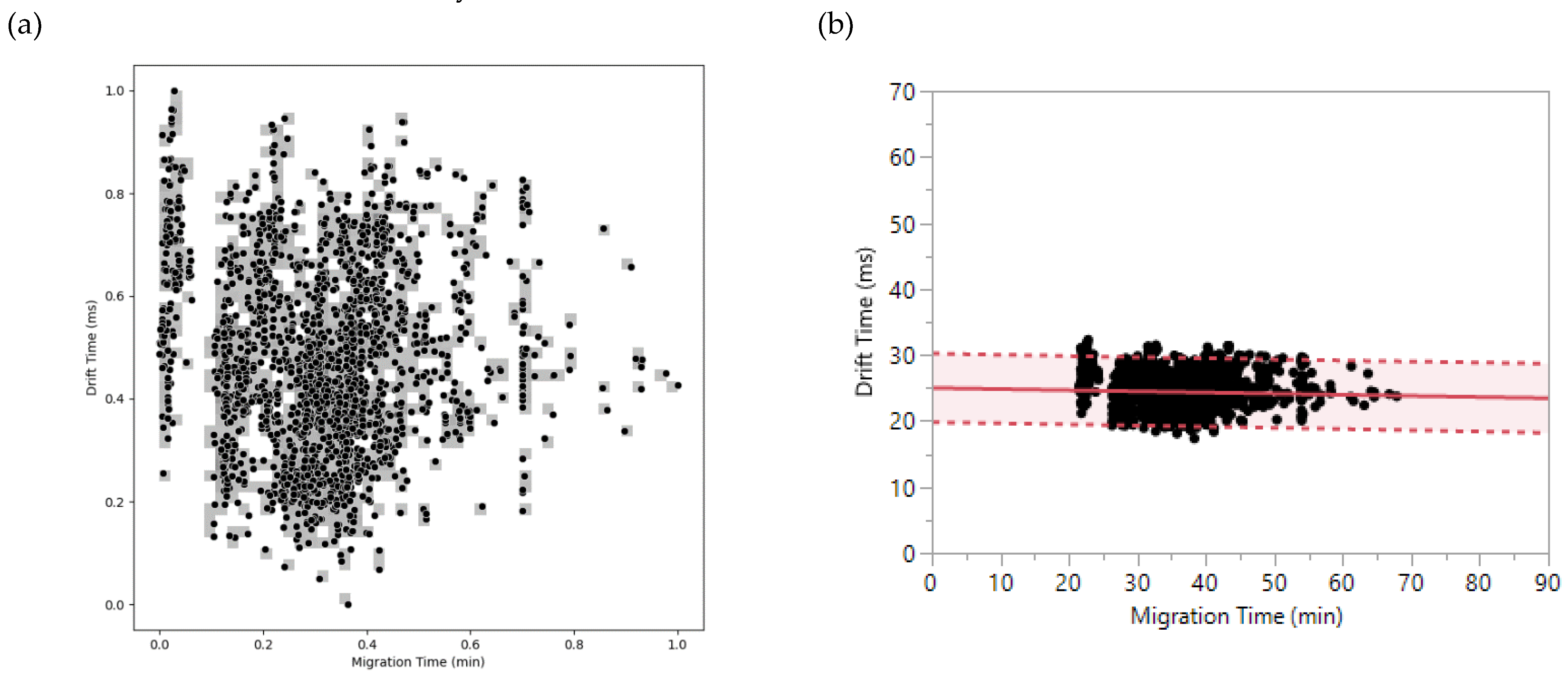
2.3.1. Orthogonality CZE x DTIMS
2.3.2. Co-migrating and Co-isolated Peptides
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Cell Culture
3.3. Sample Preparation
3.4. Instrumentation and Working Conditions
3.4.1. Instrumentation
3.4.2. Optimized CZE-DTIMS-QTOF Method for Cell Sample Analysis
3.5. Data Analysis
3.6. Protein Identification
3.7. Orthogonality Calculation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Graves, P.R.; Haystead, T.A.J. Molecular Biologist’s Guide to Proteomics. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2002, 66, 39–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupree, E.J.; Jayathirtha, M.; Yorkey, H.; Mihasan, M.; Petre, B.A.; Darie, C.C. A Critical Review of Bottom-up Proteomics: The Good, the Bad, and the Future of This Field. Proteomes 2020, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moseley, F.L.; Bicknell, K.A.; Marber, M.S.; Brooks, G. The Use of Proteomics to Identify Novel Therapeutic Targets for the Treatment of Disease. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 59, 609–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillet, L.C.; Leitner, A.; Aebersold, R. Mass Spectrometry Applied to Bottom-Up Proteomics: Entering the High-Throughput Era for Hypothesis Testing. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2016, 9, 449–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camerini, S.; Mauri, P. The Role of Protein and Peptide Separation before Mass Spectrometry Analysis in Clinical Proteomics. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1381, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, Y.; Zheng, R.; Bayer, F.P.; Wong, C.; Chang, Y.-C.; Meng, C.; Zolg, D.P.; Reinecke, M.; Zecha, J.; Wiechmann, S.; et al. Robust, Reproducible and Quantitative Analysis of Thousands of Proteomes by Micro-Flow LC–MS/MS. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nys, G.; Cobraiville, G.; Fillet, M. Multidimensional Performance Assessment of Micro Pillar Array Column Chromatography Combined to Ion Mobility-Mass Spectrometry for Proteome Research. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1086, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Shen, X.; Chen, D.; Sun, L. Improved Nanoflow RPLC-CZE-MS/MS System with High Peak Capacity and Sensitivity for Nanogram Bottom-up Proteomics. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 4046–4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Shen, X.; Sun, L. Strong Cation Exchange-Reversed Phase Liquid Chromatography-Capillary Zone Electrophoresis-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Platform with High Peak Capacity for Deep Bottom-up Proteomics. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1012, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Champion, M.M.; Sun, L.; Champion, P.A.D.; Wojcik, R.; Dovichi, N.J. Capillary Zone Electrophoresis-Electrospray Ionization-Tandem Mass Spectrometry as an Alternative Proteomics Platform to Ultraperformance Liquid Chromatography-Electrospray Ionization-Tandem Mass Spectrometry for Samples of Intermediate Complexity. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 1617–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, K.A.; Clowers, B.H. Fundamentals and Applications of Incorporating Chromatographic Separations with Ion Mobility-Mass Spectrometry. Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 119, 115625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, J.N.; Baker, E.S. Ion Mobility Spectrometry: Fundamental Concepts, Instrumentation, Applications, and the Road Ahead. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2019, 30, 2185–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Atri, V.; Causon, T.; Hernandez-Alba, O.; Mutabazi, A.; Veuthey, J.L.; Cianferani, S.; Guillarme, D. Adding a New Separation Dimension to MS and LC–MS: What Is the Utility of Ion Mobility Spectrometry? J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 20–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Wojcik, R.; Zhang, X.; Ibrahim, Y.M.; Burnum-Johnson, K.E.; Orton, D.J.; Monroe, M.E.; Moore, R.J.; Smith, R.D.; Baker, E.S. Coupling Front-End Separations, Ion Mobility Spectrometry, and Mass Spectrometry for Enhanced Multidimensional Biological and Environmental Analyses. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2017, 10, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jooß, K.; Meckelmann, S.W.; Klein, J.; Schmitz, O.J.; Neusüß, C. Capillary Zone Electrophoresis Coupled to Drift Tube Ion Mobility-Mass Spectrometry for the Analysis of Native and APTS-Labeled N-Glycans. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 6255–6264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drouin, N.; Mielcarek, A.; Wenz, C.; Rudaz, S. Evaluation of Ion Mobility in Capillary Electrophoresis Coupled to Mass Spectrometry for the Identification in Metabolomics. Electrophoresis 2021, 42, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, M.-J.; Nys, G.; Cobraiville, G.; Demelenne, A.; Servais, A.-C.; Fillet, M. Hyphenation of Capillary Zone Electrophoresis with Mass Spectrometry for Proteomic Analysis: Optimization and Comparison of Two Coupling Interfaces. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1618, 460873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mast, D.H.; Liao, H.W.; Romanova, E.V.; Sweedler, J.V. Analysis of Peptide Stereochemistry in Single Cells by Capillary Electrophoresis-Trapped Ion Mobility Spectrometry Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 6205–6213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Shen, X.; Sun, L. Capillary Zone Electrophoresis-Mass Spectrometry with Microliter-Scale Loading Capacity, 140 Min Separation Window and High Peak Capacity for Bottom-up Proteomics. Analyst 2017, 142, 2118–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, Z.; Mou, S.; Dovichi, N.J. Third-Generation Electrokinetically Pumped Sheath-Flow Nanospray Interface with Improved Stability and Sensitivity for Automated Capillary Zone Electrophoresis-Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Complex Proteome Digests. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 2312–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nys, G.; Nix, C.; Cobraiville, G.; Servais, A.C.; Fillet, M. Enhancing Protein Discoverability by Data Independent Acquisition Assisted by Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometry. Talanta 2020, 213, 120812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, D.; Mizero, B.; Gussakovsky, D.; Klaassen, N.; Lao, Y.; Spicer, V.; Krokhin, O.V. Separation Orthogonality in Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry for Proteomic Applications: Comparison of 16 Different Two-Dimensional Combinations. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 3904–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.; Pursch, M.; Eeltink, S.; Desmet, G. Maximizing Two-Dimensional Liquid Chromatography Peak Capacity for the Separation of Complex Industrial Samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1609, 460457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilar, M.; Fridrich, J.; Schure, M.R.; Jaworski, A. Comparison of Orthogonality Estimation Methods for the Two-Dimensional Separations of Peptides. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 8722–8732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilar, M.; Olivova, P.; Daly, A.E.; Gebler, J.C. Orthogonality of Separation in Two-Dimensional Liquid Chromatography. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 6426–6434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schure, M.R.; Davis, J.M. Orthogonal Separations: Comparison of Orthogonality Metrics by Statistical Analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1414, 60–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruotolo, B.T.; Gillig, K.J.; Stone, E.G.; Russell, D.H. Peak Capacity of Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometry: Separation of Peptides in Helium Buffer Gas. J. Chromatogr. B 2002, 782, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Shah, R.L.; Rathore, A.S. Harnessing the Power of Electrophoresis and Chromatography: Offline Coupling of Reverse Phase Liquid Chromatography-Capillary Zone Electrophoresis-Tandem Mass Spectrometry for Peptide Mapping for Monoclonal Antibodies. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1620, 460954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalobos Solis, M.I.; Giannone, R.J.; Hettich, R.L.; Abraham, P.E. Exploiting the Dynamic Relationship between Peptide Separation Quality and Peptide Coisolation in a Multiple-Peptide Matches-per-Spectrum Approach Offers a Strategy to Optimize Bottom-Up Proteomics Throughput and Depth. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 7273–7279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gou, M.-J.; Kose, M.C.; Crommen, J.; Nix, C.; Cobraiville, G.; Caers, J.; Fillet, M. Contribution of Capillary Zone Electrophoresis Hyphenated with Drift Tube Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometry as a Complementary Tool to Microfluidic Reversed Phase Liquid Chromatography for Antigen Discovery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13350. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113350
Gou M-J, Kose MC, Crommen J, Nix C, Cobraiville G, Caers J, Fillet M. Contribution of Capillary Zone Electrophoresis Hyphenated with Drift Tube Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometry as a Complementary Tool to Microfluidic Reversed Phase Liquid Chromatography for Antigen Discovery. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(21):13350. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113350
Chicago/Turabian StyleGou, Marie-Jia, Murat Cem Kose, Jacques Crommen, Cindy Nix, Gael Cobraiville, Jo Caers, and Marianne Fillet. 2022. "Contribution of Capillary Zone Electrophoresis Hyphenated with Drift Tube Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometry as a Complementary Tool to Microfluidic Reversed Phase Liquid Chromatography for Antigen Discovery" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 21: 13350. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113350
APA StyleGou, M.-J., Kose, M. C., Crommen, J., Nix, C., Cobraiville, G., Caers, J., & Fillet, M. (2022). Contribution of Capillary Zone Electrophoresis Hyphenated with Drift Tube Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometry as a Complementary Tool to Microfluidic Reversed Phase Liquid Chromatography for Antigen Discovery. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(21), 13350. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113350





