Bufalin Inhibits Tumorigenesis, Stemness, and Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition in Colorectal Cancer through a C-Kit/Slug Signaling Axis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Bufalin Inhibits the Proliferation and Viability of CRC Cells
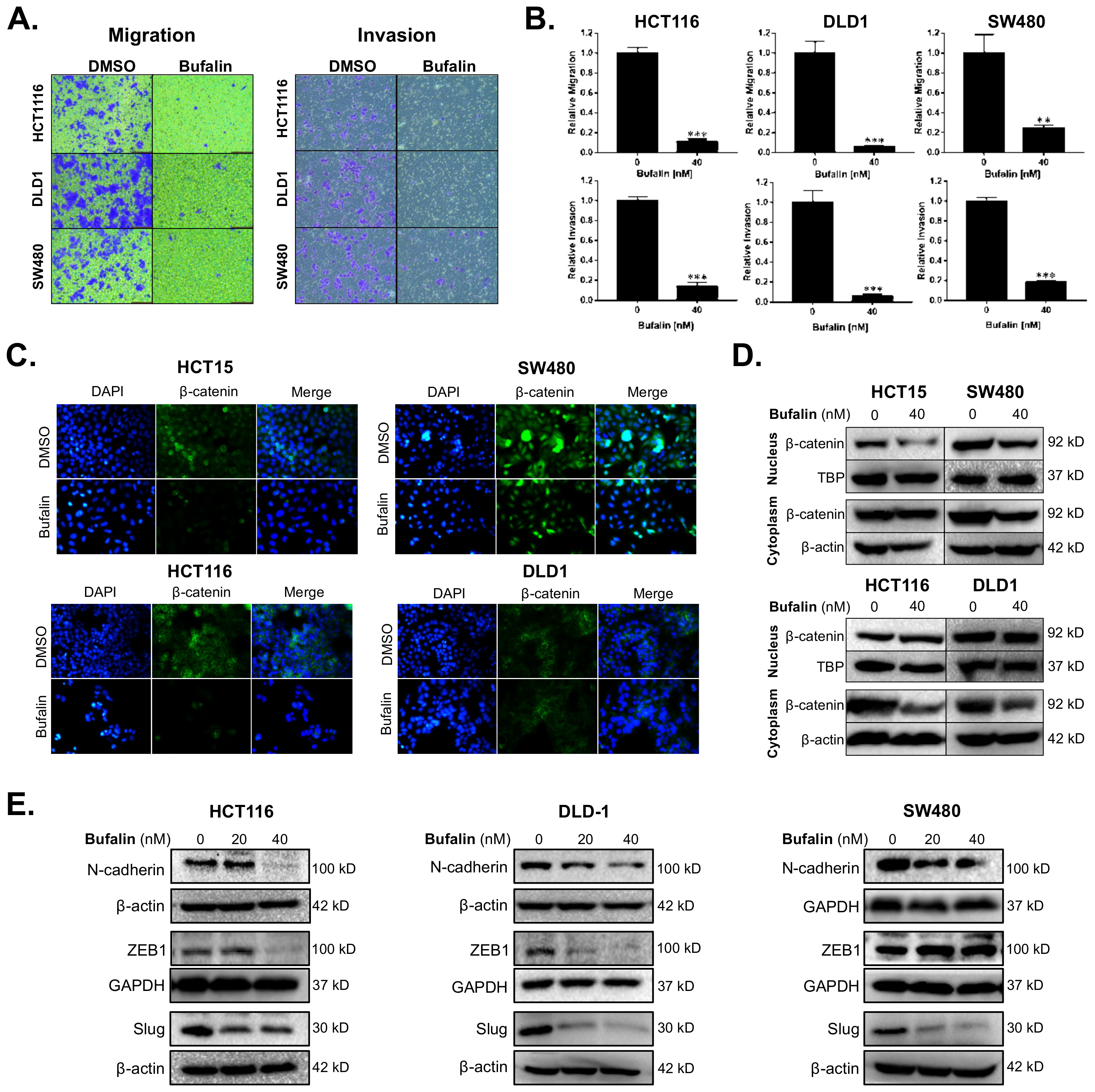
2.2. Bufalin Inhibits Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Invasiveness of CRC Cells
2.3. Bufalin Inhibits Stemness in CRC Cell Lines
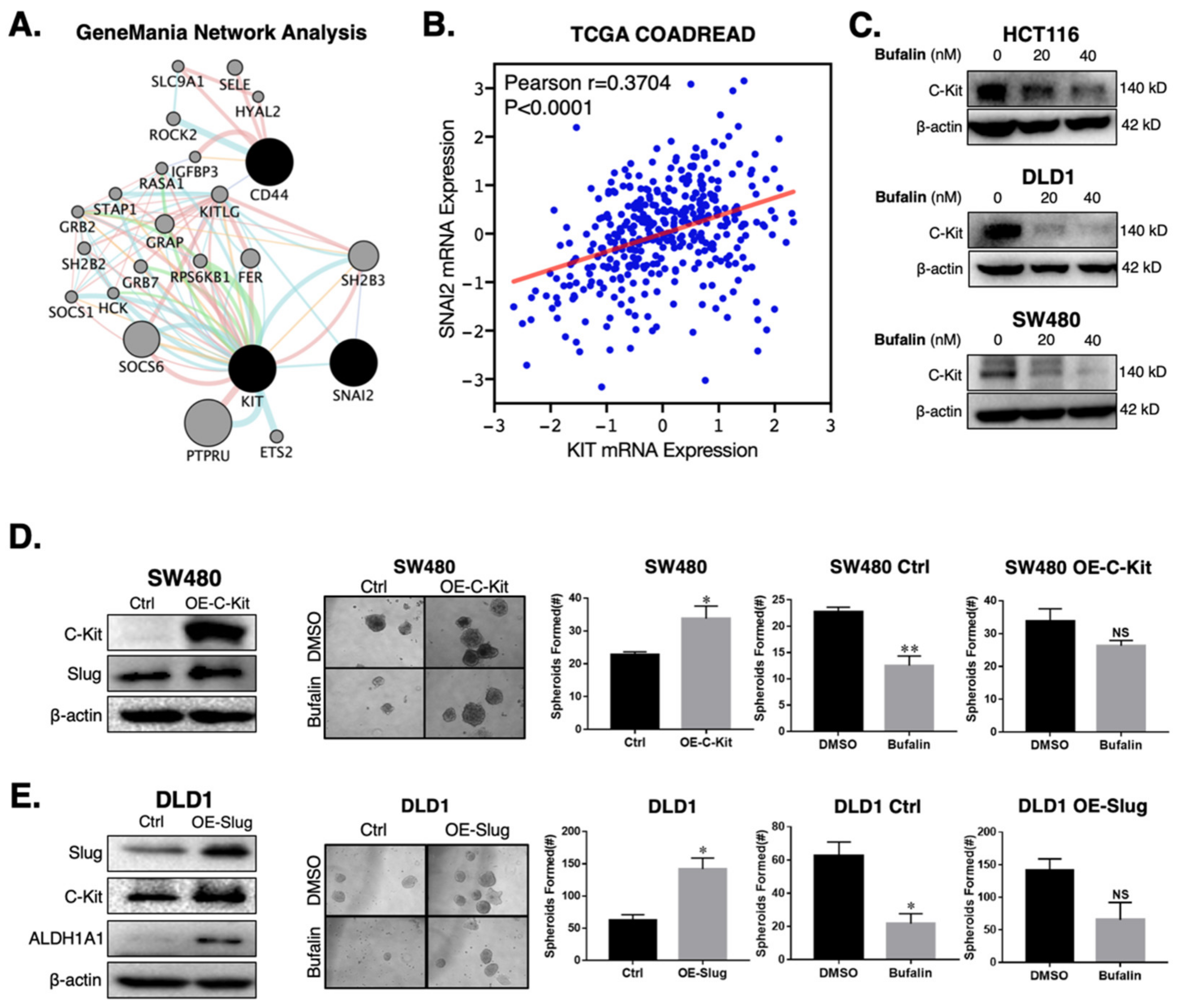
2.4. Bufalin’s Anti-CSC Activity Is Dependent on a C-Kit/Slug Signaling Axis
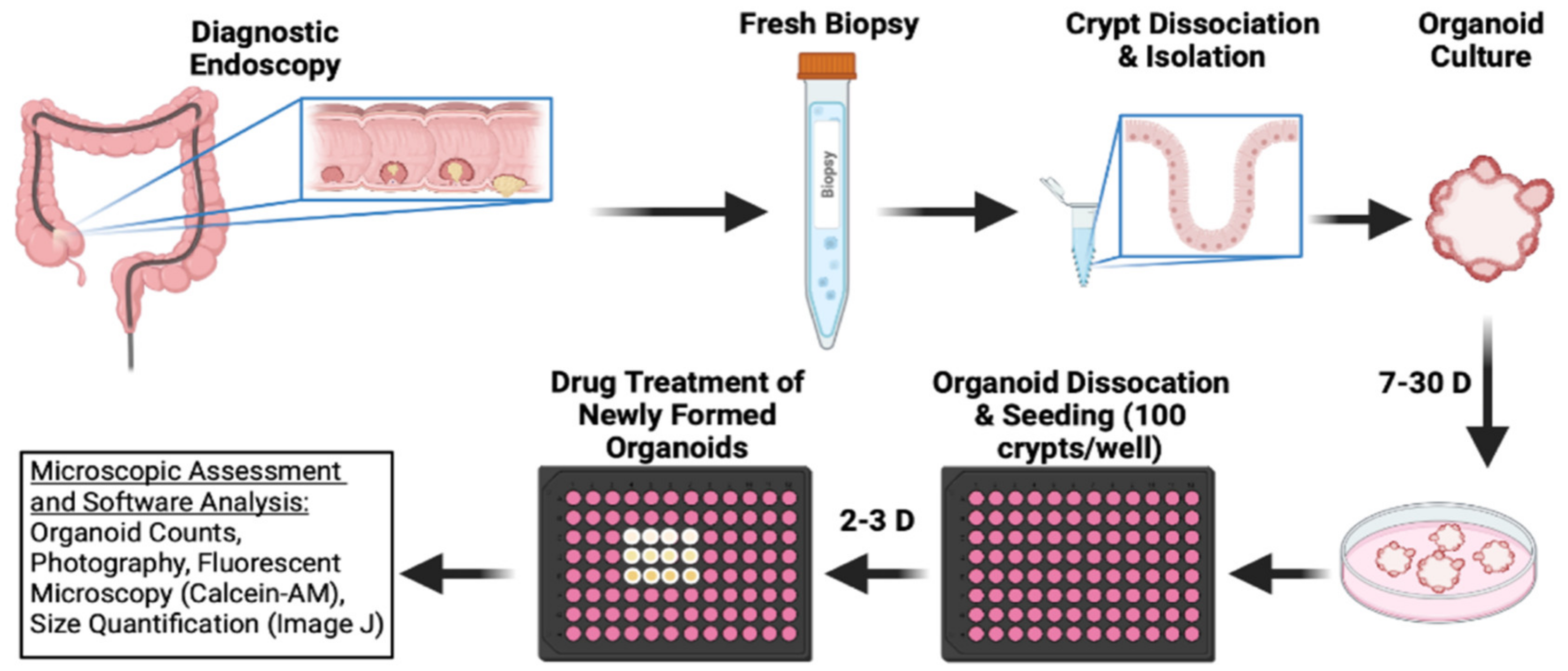
2.5. Bufalin Inhibits C-Kit/Slug Signaling and Tumorigenesis in CRC Patient-Derived Organoids
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Establishment and Cultivation of PDOs
4.2. PDO Western Blot Assay
4.3. PDO Growth Assay
4.4. Cell Lines and Culture
4.5. Cell Proliferation and LIVE/DEAD Assays
4.6. Matrigel Spheroid-Forming Assay
4.7. Transwell Migration and Invasion Assay
4.8. Plasmid Transfection
4.9. Lentivirus Infection
4.10. ALDEFLUOR Assay
4.11. Separation of Nuclear and Cytoplasmic Proteins
4.12. Immunofluorescence Microscopy
4.13. Western Blot
4.14. Bioinformatics and Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oliveira, L.; Predes, D.; Borges, H.; Abreu, J. Therapeutic Potential of Naturally Occurring Small Molecules to Target the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Coussens, L.M. Accessories to the crime: Functions of cells recruited to the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hirata, A.; Hatano, Y.; Niwa, M.; Hara, A.; Tomita, H. Heterogeneity in Colorectal Cancer Stem Cells. Cancer Prev. Res. 2019, 12, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T. Chemopreventive drugs: Mechanisms via inhibition of cancer stem cells in colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 3835–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Shi, P.; Zhao, G.; Xu, J.; Peng, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, X.; Dong, Z.; Chen, F.; et al. Targeting cancer stem cell pathways for cancer therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quail, D.; Taylor, M.; Postovit, L. Microenvironmental regulation of cancer stem cell phenotypes. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2012, 7, 197–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, L.; de Sousa E Melo, F.; van der Heijden, M.; Cameron, K.; de Jong, J.; Borovski, T.; Tuynman, J.; Todaro, M.; Merz, C.; Rodermond, H.; et al. Wnt activity defines colon cancer stem cells and is regulated by the microenvironment. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, M.; Huang, R.; Jackson, R.; Thiery, J. EMT: 2016. Cell 2016, 166, 21–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hatano, Y.; Fukuda, S.; Hisamatsu, K.; Hirata, A.; Hara, A.; Tomita, H. Multifaceted Interpretation of Colon Cancer Stem Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Robertis, M.; Poeta, M.; Signori, E.; Fazio, V. Current understanding and clinical utility of miRNAs regulation of colon cancer stem cells. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018, 53, 232–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, N.; van Es, J.; Kuipers, J.; Kujala, P.; van den Born, M.; Cozijnsen, M.; Haegebarth, A.; Korving, J.; Begthel, H.; Peters, P.; et al. Identification of stem cells in small intestine and colon by marker gene Lgr5. Nature 2007, 449, 1003–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Vries, R.; Snippert, H.; van de Wetering, M.; Barker, N.; Stange, D.; van Es, J.; Abo, A.; Kujala, P.; Peters, P.; et al. Single Lgr5 stem cells build crypt-villus structures in vitro without a mesenchymal niche. Nature 2009, 459, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Stange, D.; Ferrante, M.; Vries, R.; van Es, J.; van den Brink, S.; van Houdt, W.; Pronk, A.; van Gorp, J.; Siersema, P.; et al. Long-term expansion of epithelial organoids from human colon, adenoma, adenocarcinoma, and Barrett’s epithelium. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1762–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, J.; Mayhew, C.; Rankin, S.; Kuhar, M.; Vallance, J.; Tolle, K.; Hoskins, E.; Kalinichenko, V.; Wells, S.; Zorn, A.; et al. Directed differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into intestinal tissue in vitro. Nature 2011, 470, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huch, M.; Dorrell, C.; Boj, S.; van Es, J.; Li, V.; van de Wetering, M.; Sato, T.; Hamer, K.; Sasaki, N.; Finegold, M.; et al. In vitro expansion of single Lgr5+ liver stem cells induced by Wnt-driven regeneration. Nature 2013, 494, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Linnekamp, J.; Hooff, S.; Prasetyanti, P.; Kandimalla, R.; Buikhuisen, J.; Fessler, E.; Ramesh, P.; Lee, K.; Bochove, G.; de Jong, J.; et al. Consensus molecular subtypes of colorectal cancer are recapitulated in in vitro and in vivo models. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 616–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matano, M.; Date, S.; Shimokawa, M.; Takano, A.; Fujii, M.; Ohta, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Kanai, T.; Sato, T. Modeling colorectal cancer using CRISPR-Cas9-mediated engineering of human intestinal organoids. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Y. 2D- and 3D-Based Intestinal Stem Cell Cultures for Personalized Medicine. Cells 2018, 7, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stankov, K.; Popovic, S.; Mikov, M. C-KIT signaling in cancer treatment. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 2849–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakabe, T.; Azumi, J.; Haruki, T.; Umekita, Y.; Nakamura, H.; Shiota, G. CD117 expression is a predictive marker for poor prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 3703–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Zeng, J.; Liang, B.; Zhao, Z.; Sun, L.; Cao, D.; Yang, J.; Shen, K. Ovarian cancer cells with the CD117 phenotype are highly tumorigenic and are related to chemotherapy outcome. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2011, 91, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, K.; Shi, L.; Foster, B.; Mobley, M.; Elliott, P.; Song, C.; Watabe, K.; Langefeld, C.; Kerr, B. CD117/c-kit defines a prostate CSC-like subpopulation driving progression and TKI resistance. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothenberg, M.; Nusse, Y.; Kalisky, T.; Lee, J.; Dalerba, P.; Scheeren, F.; Lobo, N.; Kulkarni, S.; Sim, S.; Qian, D.; et al. Identification of a cKit+ colonic crypt base secretory cell that supports Lgr5+ stem cells in mice. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1195–1205.e1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Toiyama, Y.; Yasuda, H.; Saigusa, S.; Tanaka, K.; Inoue, Y.; Goel, A.; Kusunoki, M. Increased expression of Slug and Vimentin as novel predictive biomarkers for lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 2548–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Phillips, S.; Kuperwasser, C. SLUG: Critical regulator of epithelial cell identity in breast development and cancer. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2014, 8, 578–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X. Targeting c-kit inhibits gefitinib resistant NSCLC cell growth and invasion through attenuations of stemness, EMT and acquired resistance. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 4251–4265. [Google Scholar]
- Catalano, A.; Rodilossi, S.; Rippo, M.; Caprari, P.; Procopio, A. Induction of stem cell factor/c-Kit/slug signal transduction in multidrug-resistant malignant mesothelioma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 46706–46714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Chen, C.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, P.; Gao, Z.; Xu, J.; Feng, D.; Zuo, Q.; Zhao, R.; et al. Bufalin Inhibits HCT116 Colon Cancer Cells and Its Orthotopic Xenograft Tumor in Mice Model through Genes Related to Apoptotic and PTEN/AKT Pathways. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2015, 2015, 457193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, R.; Yu, F.; Wu, W.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Guo, F.; Xu, L.; Wang, F.; Cui, X. Bufalin enhances the killing efficacy of NK cells against hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting MICA shedding. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 101, 108195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Zhan, Y.; Zhu, R.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Sun, M.; Qiu, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Liang, X.; Yin, P.; et al. Bufalin suppresses tumour microenvironment-mediated angiogenesis by inhibiting the STAT3 signalling pathway. J. Transl. Med. 2021, 19, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Shih, Y.; Lee, M.; Au, M.; Chen, Y.; Lu, H.; Chung, J. Bufalin Induces Apoptosis of Human Osteosarcoma U-2 OS Cells through Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, Caspase- and Mitochondria-Dependent Signaling Pathways. Molecules 2017, 22, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Yao, Z.; Qin, H.; Wang, K.; Xin, X. Bufalin inhibits the malignant development of non-small cell lung cancer by mediating the circ_0046264/miR-522-3p axis. Biotechnol. Lett. 2021, 43, 1229–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Ng, T.; Sham, K.; Zhang, L.; Chan, M.; Wu, W.; Cheng, C. Bufalin, a Traditional Chinese Medicine Compound, Prevents Tumor Formation in Two Murine Models of Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Prev. Res. 2019, 12, 653–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, D.; Zhou, W.; Lin, X.; Fang, L.; Xie, C. Bufalin induces apoptosis via mitochondrial ROS-mediated caspase-3 activation in HCT-116 and SW620 human colon cancer cells. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 42, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Chaudhuri, O. Beyond proteases: Basement membrane mechanics and cancer invasion. J. Cell Biol. 2019, 218, 2456–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, K.; Xie, K.; Lan, T.; Xu, L.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Liao, M.; Li, J.; Huang, J.; Zeng, Y.; et al. TXNDC12 promotes EMT and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via activation of β-catenin. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 1355–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielecka, Z.; Maliszewska-Olejniczak, K.; Safir, I.; Szczylik, C.; Czarnecka, A. Three-dimensional cell culture model utilization in cancer stem cell research. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2017, 92, 1505–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Liu, Y.; Bian, X.; Zhou, F.; Liu, Y. ALDH1A3 affects colon cancer in vitro proliferation and invasion depending on CXCR4 status. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 118, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhan, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Xu, J.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Li, W.; Cao, Y.; Le, V.; et al. Bufalin reverses multidrug resistance by regulating stemness through the CD133/nuclear factor-κB/MDR1 pathway in colorectal cancer. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 1619–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhan, H.; Wei, X.; Liu, T.; Zheng, B. Bufalin inhibits the differentiation and proliferation of human osteosarcoma cell line hMG63-derived cancer stem cells. Tumor Biol. 2013, 35, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Su, H.; Wang, G.; Li, B.; Shen, G.; Gao, Q. Anti-tumor Activity of Bufalin by Inhibiting c-MET Mediated MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathways in Gallbladder Cancer. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 3114–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munro, M.; Peng, L.; Wickremesekera, S.; Tan, S. Colon adenocarcinoma-derived cells that express induced-pluripotent stem cell markers possess stem cell function. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Dong, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, K.; Qin, J.; Zhao, J.; Sun, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wartmann, T.; Jauch, K.; et al. Targeting cancer stem cells and their niche: Perspectives for future therapeutic targets and strategies. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018, 53, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, A.; Weinberg, R. Linking EMT programmes to normal and neoplastic epithelial stem cells. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dongre, A.; Weinberg, R. New insights into the mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and implications for cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, K.C.G.; Eide, P.W.; Eilertsen, I.A.; Johannessen, B.; Bruun, J.; Danielsen, S.A.; Bjørnslett, M.; Meza-Zepeda, L.A.; Eknæs, M.; Lind, G.E.; et al. Multi-omics of 34 colorectal cancer cell lines—A resource for biomedical studies. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Xu, K.; Qiu, Y.; Gao, H.; Xu, J.; Tang, Q.; Yin, P. Bufalin reverses acquired drug resistance by inhibiting stemness in colorectal cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 1420–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leng, Z.; Tao, K.; Xia, Q.; Tan, J.; Yue, Z.; Chen, J.; Xi, H.; Li, J.; Zheng, H. Krüppel-like factor 4 acts as an oncogene in colon cancer stem cell-enriched spheroid cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomizawa, F.; Jang, M.; Mashima, T.; Seimiya, H. c-KIT regulates stability of cancer stemness in CD44-positive colorectal cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 527, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.; Karl, T.; Kalisky, T.; Gupta, S.; O’Brien, C.; Longacre, T.; van de Rijn, M.; Quake, S.; Clarke, M.; Rothenberg, M. KIT Signaling Promotes Growth of Colon Xenograft Tumors in Mice and Is Up-Regulated in a Subset of Human Colon Cancers. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 705–717.e702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, W.; Ji, J.; Shu, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, S.; Wu, L.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Z.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, X.; et al. Downregulation of DAPK1 promotes the stemness of cancer stem cells and EMT process by activating ZEB1 in colorectal cancer. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 97, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, G.; Zhuang, J.; Wei, L.; Wang, Z.; Sun, M.; Wang, J. siRNA-induced CD44 knockdown suppresses the proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer stem cells through inhibiting epithelial–mesenchymal transition. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 1969–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boesch, M.; Spizzo, G.; Seeber, A. Concise Review: Aggressive Colorectal Cancer: Role of Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule in Cancer Stem Cells and Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2018, 7, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhu, P.; Zhou, Y.; Sheng, Y.; Hong, Y.; Xiang, D.; Qian, Z.; Mosenson, J.; Wu, W. A novel slug-containing negative-feedback loop regulates SCF/c-Kit-mediated hematopoietic stem cell self-renewal. Leukemia 2017, 31, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Dai, W.; Xia, X.; Wang, R.; Zhao, J.; Han, L.; Mo, S.; Xiang, W.; Du, L.; Zhu, G.; et al. Modeling tumor development and metastasis using paired organoids derived from patients with colorectal cancer liver metastases. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooft, S.; Weeber, F.; Dijkstra, K.; McLean, C.; Kaing, S.; van Werkhoven, E.; Schipper, L.; Hoes, L.; Vis, D.; van de Haar, J.; et al. Patient-derived organoids can predict response to chemotherapy in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaay2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toshimitsu, K.; Takano, A.; Fujii, M.; Togasaki, K.; Matano, M.; Takahashi, S.; Kanai, T.; Sato, T. Organoid screening reveals epigenetic vulnerabilities in human colorectal cancer. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2022, 18, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnalzger, T.; de Groot, M.; Zhang, C.; Mosa, M.; Michels, B.; Röder, J.; Darvishi, T.; Wels, W.; Farin, H. 3D model for CAR-mediated cytotoxicity using patient-derived colorectal cancer organoids. EMBO J. 2019, 38, e100928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warde-Farley, D.; Donaldson, S.L.; Comes, O.; Zuberi, K.; Badrawi, R.; Chao, P.; Franz, M.; Grouios, C.; Kazi, F.; Lopes, C.T.; et al. The GeneMANIA prediction server: Biological network integration for gene prioritization and predicting gene function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, W214–W220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Sample | T0519 | T0528 | T0714 | T1208 | T1101 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | M | M | M | F | M |
| Age | 80 | 84 | 73 | 72 | 81 |
| Pathology | Villous tubular adenoma | Adenocarcinoma | Adenocarcinoma | Adenocarcinoma | Adenocarcinoma |
| Anatomic site | Rectum | Sigmoid Colon | Rectum | Rectum | Rectum |
| AFP (ng/mL) | 1.6 | 1.34 | N/A | 2.37 | 2.82 |
| CA-125 (U/mL) | 10.8 | 6 | N/A | 12.74 | N/A |
| CEA (ng/mL) | 2.56 | 1.77 | N/A | 1.58 | 7.71 |
| CA19-9 (U/mL) | <2 | 2.1 | N/A | 6.5 | 18.31 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, L.; Yang, Y.; Lu, Q.; Qu, D.; Chandrakesan, P.; Feng, H.; Chen, H.; Chen, X.; Liao, Z.; Du, J.; et al. Bufalin Inhibits Tumorigenesis, Stemness, and Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition in Colorectal Cancer through a C-Kit/Slug Signaling Axis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113354
Ding L, Yang Y, Lu Q, Qu D, Chandrakesan P, Feng H, Chen H, Chen X, Liao Z, Du J, et al. Bufalin Inhibits Tumorigenesis, Stemness, and Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition in Colorectal Cancer through a C-Kit/Slug Signaling Axis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(21):13354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113354
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Ling, Yuning Yang, Qin Lu, Dongfeng Qu, Parthasarathy Chandrakesan, Hailan Feng, Hong Chen, Xuzheng Chen, Zhuhui Liao, Jian Du, and et al. 2022. "Bufalin Inhibits Tumorigenesis, Stemness, and Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition in Colorectal Cancer through a C-Kit/Slug Signaling Axis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 21: 13354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113354
APA StyleDing, L., Yang, Y., Lu, Q., Qu, D., Chandrakesan, P., Feng, H., Chen, H., Chen, X., Liao, Z., Du, J., Cao, Z., & Weygant, N. (2022). Bufalin Inhibits Tumorigenesis, Stemness, and Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition in Colorectal Cancer through a C-Kit/Slug Signaling Axis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(21), 13354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113354






