Proteomics of Aqueous Humor as a Source of Disease Biomarkers in Retinoblastoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
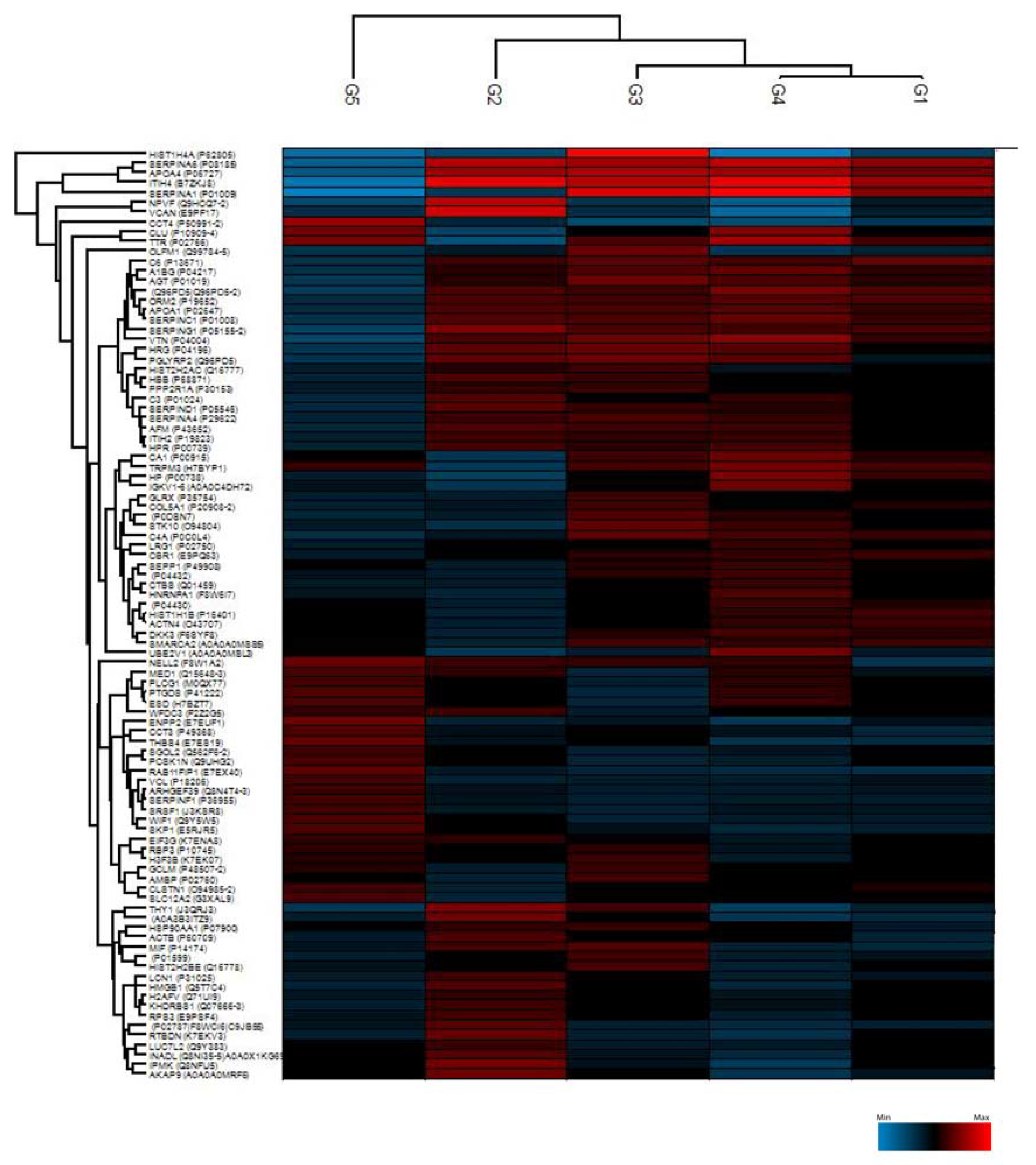
2.1. Proteomic Characterization of AH Samples
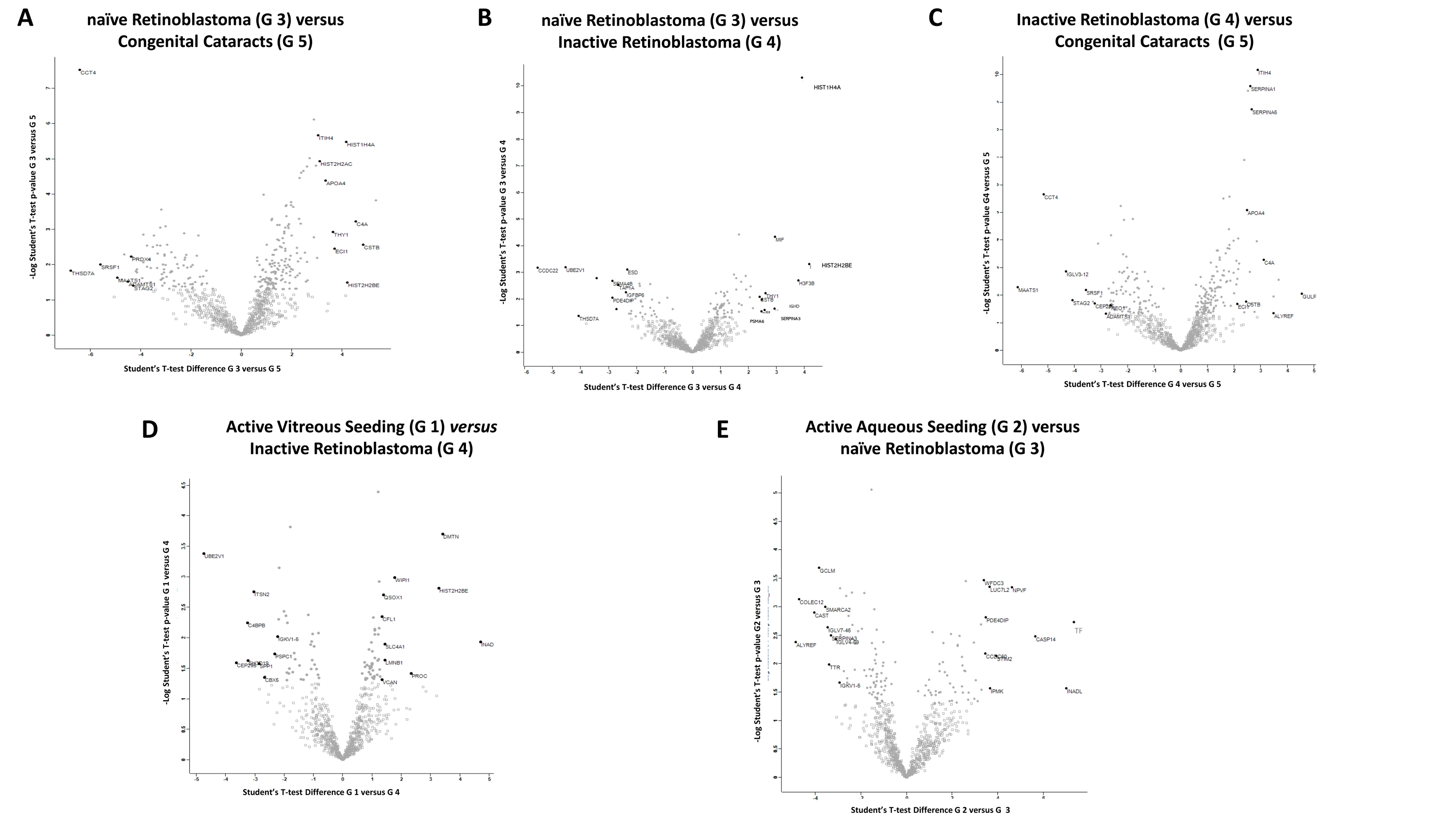
2.2. Student’s t-Test Analysis
2.2.1. Differentially Expressed Proteins in Group 3 (Naïve RB) Compared to Group 5 (Congenital Cataracts)
2.2.2. Differentially Expressed Proteins in Group 3 (Naïve RB) Compared to Group 4 (Inactive RB)
2.2.3. Differentially Expressed Proteins in Group 4 (Inactive RB) Compared to Group 5 (Congenital Cataracts)
2.2.4. Differentially Expressed Proteins in Group 1 (Active Vitreous Seeding) Compared to Group 4 (Inactive RB)
2.2.5. Differentially Expressed Proteins in Group 2 (Active Aqueous Seeding) Compared to Group 3 (Naïve RB)
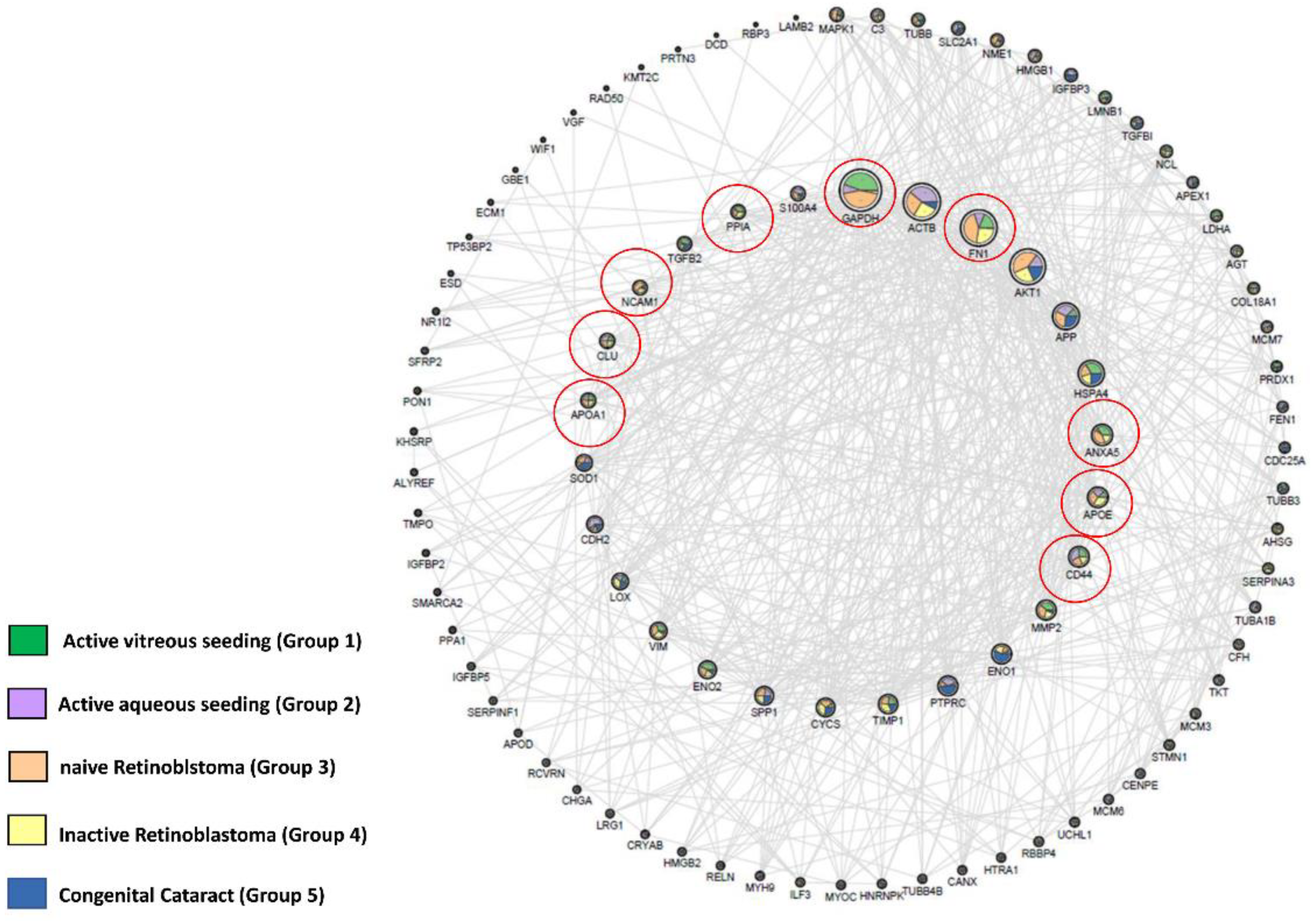
2.3. Identification of RB Related Genes in Our Experimental Matrix Using the OPENTARGET Tool
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
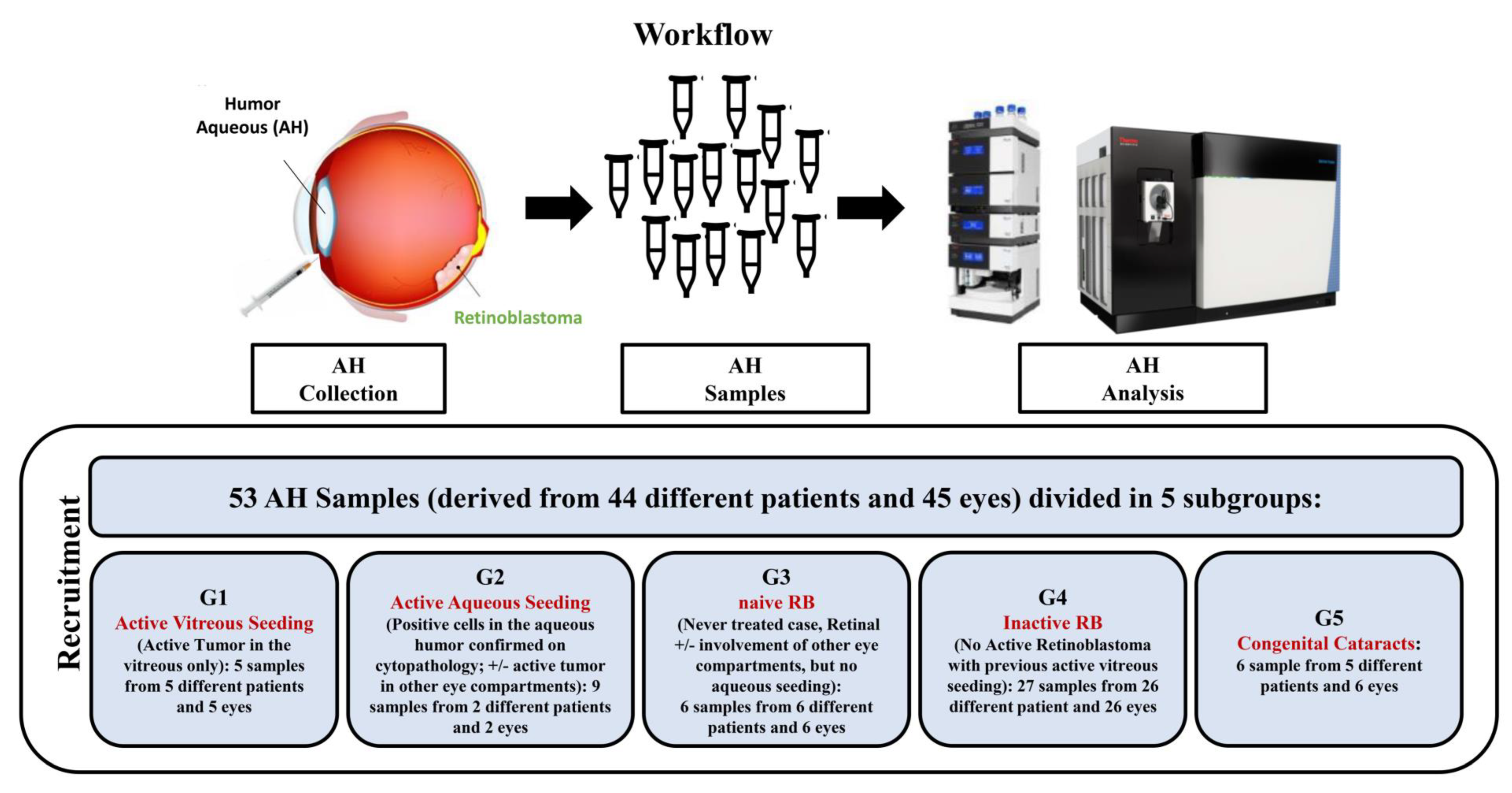
4.1. Subjects and Collection of AH
4.2. Proteomic Setup
4.2.1. Sample Preparation
4.2.2. NanoLC Setup
4.2.3. Mass Spectrometer Setup
4.2.4. Data Analysis
4.2.5. Bioinformatic Analysis
4.2.6. Open Target Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kivelä, T. The epidemiological challenge of the most frequent eye cancer: Retinoblastoma, an issue of birth and death. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2009, 9, 1129–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyson, N.J. RB1: A prototype tumor suppressor and an enigma. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 1492–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munier, F.L.; Soliman, S.; Moulin, A.P.; Gaillard, M.C.; Balmer, A.; Beck-Popovic, M. Profiling safety of intravitreal injections for retinoblastoma using an anti-reflux procedure and sterilisation of the needle track. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 8, 1084–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, J.L.; Xu, L.; Murphree, A.L.; Krishnan, S.; Stachelek, K.; Zolfaghari, E.; McGovern, K.; Lee, T.C.; Carlsson, A.; Kuhn, P.; et al. Potential of Aqueous Humor as a Surrogate Tumor Biopsy for Retinoblastoma. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2017, 135, 1221–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raval, V.; Racher, H.; Wrenn, J.; Singh, A.D. Aqueous humor as a surrogate biomarker for retinoblastoma tumor tissue. J. AAPOS. 2022, 13, 137.e1–137.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Gall, J.; Dehainault, C.; Benoist, C.; Matet, A.; Lumbroso-Le Rouic, L.; Aerts, I.; Jiménez, I.; Schleiermacher, G.; Houdayer, C.; Radvanyi, F.; et al. Highly Sensitive Detection Method of Retinoblastoma Genetic Predisposition and Biomarkers. J. Mol. Diagn. 2021, 23, 1714–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.E.; Xu, L.; Prabakar, R.K.; Shen, L.; Peng, C.C.; Kuhn, P.; Gai, X.; Hicks, J.; Berry, J.L. Aqueous Humor as a Liquid Biopsy for Retinoblastoma: Clear Corneal Paracentesis and Genomic Analysis. J. Vis. Exp. 2021, 175, e62939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, E.Y.; Xu, L.; Shen, L.; Kim, M.E.; Polski, A.; Prabakar, R.K.; Shah, R.; Jubran, R.; Kim, J.W.; Biegel, J.A.; et al. Inter-eye genomic heterogeneity in bilateral retinoblastoma via aqueous humor liquid biopsy. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2021, 27, 51–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Kim, M.E.; Polski, A.; Prabakar, R.K.; Shen, L.; Peng, C.C.; Reid, M.W.; Chévez-Barrios, P.; Kim, J.W.; Shah, R.; et al. Establishing the Clinical Utility of ctDNA Analysis for Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Treatment Monitoring of Retinoblastoma: The Aqueous Humor Liquid Biopsy. Cancers 2021, 13, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Shen, L.; Polski, A.; Prabakar, R.K.; Shah, R.; Jubran, R.; Kim, J.W.; Biegel, J.; Kuhn, P.; Cobrinik, D.; et al. Simultaneous identification of clinically relevant RB1 mutations and copy number alterations in aqueous humor of retinoblastoma eyes. Ophthalmic Genet. 2020, 41, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polski, A.; Xu, L.; Prabakar, R.K.; Gai, X.; Kim, J.W.; Shah, R.; Jubran, R.; Kuhn, P.; Cobrinik, D.; Hicks, J.; et al. Variability in retinoblastoma genome stability is driven by age and not heritability. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2020, 59, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, J.L.; Xu, L.; Polski, A.; Jubran, R.; Kuhn, P.; Kim, J.W.; Hicks, J. Aqueous Humor Is Superior to Blood as a Liquid Biopsy for Retinoblastoma. Ophthalmology 2020, 127, 552–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerrish, A.; Stone, E.; Clokie, S.; Ainsworth, J.R.; Jenkinson, H.; McCalla, M.; Hitchcott, C.; Colmenero, I.; Allen, S.; Parulekar, M.; et al. Non-invasive diagnosis of retinoblastoma using cell-free DNA from aqueous humour. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 5, 721–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, J.L.; Xu, L.; Kooi, I.; Murphree, A.L.; Prabakar, R.K.; Reid, M.; Stachelek, K.; Le, B.H.A.; Welter, L.; Reiser, B.J.; et al. Genomic cfDNA Analysis of Aqueous Humor in Retinoblastoma Predicts Eye Salvage: The Surrogate Tumor Biopsy for Retinoblastoma. Mol. Cancer Res. 2018, 11, 1701–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polski, A.; Xu, L.; Prabakar, R.K.; Kim, J.W.; Shah, R.; Jubran, R.; Kuhn, P.; Cobrinik, D.; Hicks, J.; Berry, J.L. Cell-Free DNA Tumor Fraction in the Aqueous Humor Is Associated with Therapeutic Response in Retinoblastoma Patients. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 10–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Polski, A.; Prabakar, R.K.; Reid, M.W.; Chevez-Barrios, P.; Jubran, R.; Kim, J.W.; Kuhn, P.; Cobrinik, D.; Hicks, J.; et al. Chromosome 6p Amplification in Aqueous Humor Cell-Free DNA Is a Prognostic Biomarker for Retinoblastoma Ocular Survival. Mol. Cancer Res. 2020, 8, 1166–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, P.L. Correlation of aqueous humour lactic acid dehydrogenase activity with intraocular pathology. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1979, 8, 574–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naru, J.; Aggarwal, R.; Singh, U.; Mohanty, A.K.; Bansal, D.; Mangat, N.; Kakkar, N.; Agnihotri, N. Proteomic analysis of differentially expressed proteins in vitreous humor of patients with retinoblastoma using iTRAQ-coupled ESI-MS/MS approach. Tumour. Biol. 2016, 10, 13915–13926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Meng, Q.; Huang, L.; Shi, X.; Hou, J.; Li, X.; Liang, J. iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomic analysis and bioinformatics study of proteins in retinoblastoma. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 6, 8084–8091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, H.H.; Abou Ghalia, A.H.; Elsayed, E.K.; Ahmed Said, A.M.; Mahmoud, S.S. Clinical significance of high levels of survivin and transforming growth factor beta-1 proteins in aqueous humor and serum of retinoblastoma patients. J. AAPOS. 2016, 5, 444.e1–444.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, J.L.; Bechtold, M.; Shah, S.; Zolfaghari, E.; Reid, M.; Jubran, R.; Kim, J.W. Not All Seeds Are Created Equal: Seed Classification Is Predictive of Outcomes in Retinoblastoma. Ophthalmology 2017, 12, 1817–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, M.A.; Haase, A.; Miroschnikov, N.; Doege, A.; Biewald, E.; Bechrakis, N.E.; Beier, M.; Kanber, D.; Lohmann, D.; Metz, K.; et al. TFF1 in Aqueous Humor-A Potential New Biomarker for Retinoblastoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuadrado-Vilanova, M.; Liu, J.; Paco, S.; Aschero, R.; Burgueño, V.; Sirab, N.; Pascual-Pasto, G.; Correa, G.; Balaguer-Lluna, L.; Castillo-Ecija, H.; et al. Identification of immunosuppressive factors in retinoblastoma cell secretomes and aqueous humor from patients. J. Pathol. 2022, 3, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochoa, D.; Hercules, A.; Carmona, M.; Suveges, D.; Gonzalez-Uriarte, A.; Malangone, C.; Miranda, A.; Fumis, L.; Carvalho-Silva, D.; Spitzer, M.; et al. Open Targets Platform: Supporting systematic drug-target identification and prioritisation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, D1, D1302–D1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Zhang, F.; Hong, C.Q.; Giuliano, A.E.; Cui, X.J.; Zhou, G.J.; Zhang, G.J.; Cui, Y.K. Critical protein GAPDH and its regulatory mechanisms in cancer cells. Cancer Biol. Med. 2015, 1, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, A.; Fujikawa, A.; Miyata, Y.; Kosano, H. Nuclear Translocation of GAPDH in Retinal Ganglion Cells is an Early Event in Diabetic Retinopathy. J. Endocrinol. Diabetes. 2014, 2, 1058. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, B.; Guo, C.; Guan, H.; Liu, S.; Sun, M.Z. Annexin A5 as a potential marker in tumors. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2014, 1, 427–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Muñoz, L.E.; Mallavarapu, M.; Herrmann, M.; Finnemann, S.C. Annexin A5 regulates surface αvβ5 integrin for retinal clearance phagocytosis. J. Cell Sci. 2019, 16, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Shen, W.; Peng, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, F.; Zheng, L.; Xu, J.; Jia, L. Fibronectin 1 promotes melanoma proliferation and metastasis by inhibiting apoptosis and regulating EMT. Onco Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 3207–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sradhanjali, S.; Rout, P.; Tripathy, D.; Kaliki, S.; Rath, S.; Modak, R.; Mittal, R.; Chowdary, T.K.; Reddy, M.M. The Oncogene MYCN Modulates Glycolytic and Invasive Genes to Enhance Cell Viability and Migration in Human Retinoblastoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 5248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Cheng, M.H.; Zhang, M.; Cheng, K. Identifying key genes in retinoblastoma by comparing classifications of several kinds of significant genes. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2018, 14, S22–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, L.; Yi, J.; Li, W.; Zheng, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Du, G. Apolipoproteins and cancer. Cancer Med. 2019, 16, 7032–7043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.A.; Lee, T.J.; Kodeboyina, S.K.; Jones, G.; Bollinger, K.; Ulrich, L.; Bogorad, D.; Estes, A.; Zhi, W.; Sharma, S.; et al. Intra-population differences of apolipoproteins in the aqueous humor. Lipids Health Dis. 2021, 20, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallikarjuna, K.; Sundaram, C.S.; Sharma, Y.; Deepa, P.R.; Khetan, V.; Gopal, L.; Biswas, J.; Sharma, T.; Krishnakumar, S. Comparative proteomic analysis of differentially expressed proteins in primary retinoblastoma tumors. Proteomics Clin. Appl. 2010, 4, 449–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, S.; Karnad, A.; Freeman, J.W. The biology and role of CD44 in cancer progression: Therapeutic implications. J. Hematol Oncol. 2018, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balla, M.M.; Vemuganti, G.K.; Kannabiran, C.; Honavar, S.G.; Murthy, R. Phenotypic characterization of retinoblastoma for the presence of putative cancer stem-like cell markers by flow cytometry. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 4, 1506–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djeu, J.Y.; Wei, S. Clusterin and chemoresistance. Adv. Cancer Res. 2009, 105, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.B.; Jun, H.O.; Kim, J.H.; Yu, Y.S.; Kim, K.W.; Min, B.H.; Kim, J.H. Anti-apoptotic effect of clusterin on cisplatin-induced cell death of retinoblastoma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 6, 2713–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Guan, G.; Niu, X.; Qiao, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhong, M. Upregulation of Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule 1 (NCAM1) by hsa-miR-141-3p Suppresses Ameloblastoma Cell Migration. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 26, e923491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madigan, M.C.; Penfold, P.L.; King, N.J.; Billson, F.A.; Conway, R.M. Immunoglobulin superfamily expression in primary retinoblastoma and retinoblastoma cell lines. Oncol. Res. 2002, 2, 103–111. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Zuo, L.; Yang, J.; Xin, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, J.; Li, G.; Tang, J.; Lu, J. Exosomal cyclophilin A as a novel noninvasive biomarker for Epstein-Barr virus associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2019, 6, 3142–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, D.J.; Liu, C.Y.; Lee, W.H. Mutation of N-terminal regions render the retinoblastoma protein insufficient for functions in development and tumor suppression. Mol. Cell Biol. 1997, 17, 7342–7352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Kohan, A.B.; Lo, C.M.; Liu, M.; Howles, P.; Tso, P. Apolipoprotein A-IV: A protein intimately involved in metabolism. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 8, 1403–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pihl, R.; Jensen, R.K.; Poulsen, E.C.; Jensen, L.; Hansen, A.G.; Thøgersen, I.B.; Dobó, J.; Gál, P.; Andersen, G.R.; Enghild, J.J.; et al. ITIH4 acts as a protease inhibitor by a novel inhibitory mechanism. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Bollinger, K.E.; Kodeboyina, S.K.; Zhi, W.; Patton, J.; Bai, S.; Edwards, B.; Ulrich, L.; Bogorad, D.; Sharma, A. Proteomic Alterations in Aqueous Humor From Patients With Primary Open Angle Glaucoma. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2018, 6, 2635–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaal, E.A.; Berkers, C.R. The Influence of Metabolism on Drug Response in Cancer. Front Oncol. 2018, 8, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzi, L.; Garg, A.D. Immunology of Cell Death in Cancer Immunotherapy. Cells 2021, 5, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Zhao, F.; Thompson, C.B. The molecular determinants of de novo nucleotide biosynthesis in cancer cells. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2009, 1, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Davey, C.A. Nucleosome structural studies. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2011, 21, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albig, W.; Kioschis, P.; Poustka, A.; Meergans, K.; Doenecke, D. Human histone gene organization: Nonregular arrangement within a large cluster. Genomics 1997, 40, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swartzentruber, J.; Korshunov, A.; Liu, X.Y.; Jones, D.T.; Pfaff, E.; Jacob, K.; Sturm, D.; Fontebasso, A.M.; Quang, D.A.; Tönjes, M.; et al. Driver mutations in histone H3.3 and chromatin remodelling genes in paediatric glioblastoma. Nature 2012, 482, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.R.; Harrington, E.; Boone, D.; Hartmaier, R.; Chen, J.; Pathiraja, T.N.; Cooper, K.L.; Fine, J.L.; Sanfilippo, J.; Davidson, N.E.; et al. A role for histone H2B variants in endocrine-resistant breast cancer. Horm. Cancer 2015, 5–6, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Bassett, E.; Chakravarti, A.; Parthun, M.R. Replication-dependent histone isoforms: A new source of complexity in chromatin structure and function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 17, 8665–8678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, W.F.; Shen, D.F.; Yang, X.F.; Zhao, S.; Liu, Y.P.; Sun, H.Z.; Su, R.J.; Luo, J.S.; Zheng, H.C. ING5 suppresses proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion, and induces autophagy and differentiation of gastric cancer cells: A good marker for carcinogenesis and subsequent progression. Oncotarget 2015, 23, 19552–19579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenguer-Daize, C.; Astorgues-Xerri, L.; Odore, E.; Cayol, M.; Cvitkovic, E.; Noel, K.; Bekradda, M.; MacKenzie, S.; Rezai, K.; Lokiec, F.; et al. OTX015 (MK-8628), a novel BET inhibitor, displays in vitro and in vivo antitumor effects alone and in combination with conventional therapies in glioblastoma models. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 139, 2047–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Song, J.Y.; Karnam, S.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, J.J.; Kim, S.; Cho, S.H. Common and distinctive localization patterns of Crumbs polarity complex proteins in the mammalian eye. Gene Expr. Patterns. 2015, 1, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wells, C.D.; Fawcett, J.P.; Traweger, A.; Yamanaka, Y.; Goudreault, M.; Elder, K.; Kulkarni, S.; Gish, G.; Virag, C.; Lim, C.; et al. A Rich1/Amot complex regulates the Cdc42 GTPase and apical-polarity proteins in epithelial cells. Cell 2006, 3, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandalovičová, A.; Vomastek, T.; Rosel, D.; Brábek, J. Cell polarity signaling in the plasticity of cancer cell invasiveness. Oncotarget 2016, 18, 25022–25049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halaoui, R.; McCaffrey, L. Rewiring cell polarity signaling in cancer. Oncogene 2015, 34, 939–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Cai, L.D.; Liu, Y.H.; Li, S.; Gan, W.J.; Li, X.M.; Wang, J.R.; Guo, P.D.; Zhou, Q.; Lu, X.X.; et al. Ube2v1-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of Sirt1 promotes metastasis of colorectal cancer by epigenetically suppressing autophagy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 17, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munier, F.L.; Gaillard, M.C.; Decembrini, S.; Bongiovanni, M.; Beck-Popovic, M. Intracameral Chemotherapy (Melphalan) for Aqueous Seeding in Retinoblastoma: Bicameral Injection Technique and Related Toxicity in a Pilot Case Study. Ocul. Oncol. Pathol. 2017, 2, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munier, F.; Gaillard, M.C.; Balmer, A.; Beck-Popovic, M. Intravitreal chemotherapy for vitreous seeding in retinoblastoma: Recent advances and perspectives. Saudi J. Ophthalmol. 2013, 3, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulak, N.A.; Pichler, G.; Paron, I.; Nagaraj, N.; Mann, M. Minimal, encapsulated proteomic-sample processing applied to copy-number estimation in eukaryotic cells. Nat. Methods 2014, 3, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruschi, M.; Petretto, A.; Santucci, L.; Vaglio, A.; Pratesi, F.; Migliorini, P.; Bertelli, R.; Lavarello, C.; Bartolucci, M.; Candiano, G.; et al. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps protein composition is specific for patients with Lupus nephritis and includes methyl-oxidized αenolase (methionine sulfoxide 93). Sci. Rep. 2019, 1, 7934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizcaíno, J.A.; Csordas, A.; del-Toro, N.; Dianes, J.A.; Griss, J.; Lavidas, I.; Mayer, G.; Perez-Riverol, Y.; Reisinger, F.; Ternent, T.; et al. 2016 update of the PRIDE database and its related tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, D1, D447–D456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyanova, S.; Temu, T.; Sinitcyn, P.; Carlson, A.; Hein, M.Y.; Geiger, T.; Mann, M.; Cox, J. The Perseus computational platform for comprehensive analysis of (prote)omics data. Nat. Methods 2016, 9, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardou, P.; Mariette, J.; Escudié, F.; Djemiel, C.; Klopp, C. jvenn: An interactive Venn diagram viewer. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 1, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galardi, A.; Stathopoulos, C.; Colletti, M.; Lavarello, C.; Russo, I.; Cozza, R.; Romanzo, A.; Carcaboso, A.M.; Locatelli, F.; Petretto, A.; et al. Proteomics of Aqueous Humor as a Source of Disease Biomarkers in Retinoblastoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13458. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113458
Galardi A, Stathopoulos C, Colletti M, Lavarello C, Russo I, Cozza R, Romanzo A, Carcaboso AM, Locatelli F, Petretto A, et al. Proteomics of Aqueous Humor as a Source of Disease Biomarkers in Retinoblastoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(21):13458. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113458
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalardi, Angela, Christina Stathopoulos, Marta Colletti, Chiara Lavarello, Ida Russo, Raffaele Cozza, Antonino Romanzo, Angel M. Carcaboso, Franco Locatelli, Andrea Petretto, and et al. 2022. "Proteomics of Aqueous Humor as a Source of Disease Biomarkers in Retinoblastoma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 21: 13458. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113458
APA StyleGalardi, A., Stathopoulos, C., Colletti, M., Lavarello, C., Russo, I., Cozza, R., Romanzo, A., Carcaboso, A. M., Locatelli, F., Petretto, A., Munier, F. L., & Di Giannatale, A. (2022). Proteomics of Aqueous Humor as a Source of Disease Biomarkers in Retinoblastoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(21), 13458. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113458






